Lesson 13. Moon and its phases 2022.pptx
Download as PPTX, PDF0 likes27 views
Grade 5 Science
1 of 29
Download to read offline




























Recommended
Our moon 



Our moon garlicandwater
╠²
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite, located approximately 384,000 km away. It has no atmosphere and extreme surface temperatures, ranging from 130┬░C during the day to -190┬░C at night. The Moon's surface is marked by impact craters formed by meteorites, and it revolves around Earth every 27 days while rotating on its axis at the same rate, so the same side always faces Earth. The Moon has different illuminated phases that change as it orbits Earth, from new to waxing crescent to first quarter to waxing gibbous to full and then waning phases back to new. Humans first explored the Moon in the 1960s and 1970s through a series of Apollo missions that walked 12Earth's moon



Earth's moonMichael Maggiar
╠²
This is a presentation about our Earth's moon. It is extremely extensive and is wonderful for academic purposes. It's extremely easy to edit, and this is sure to get you that A+ you've been wanting. Our moon



Our moonDurant Road Middle
╠²
The document provides information about the Moon. It discusses that the Moon is Earth's only natural satellite, located about 384,000 km away. The Moon has no atmosphere or liquid water and experiences extreme temperatures. It has various features like mountains, trenches, craters formed by impacts, and dark maria areas filled with ancient lava. The Moon orbits Earth every 27 days while rotating on its axis at the same rate, so the same side always faces Earth. Lunar phases and eclipses are explained by the relative positions of the Moon, Earth and Sun. Tides on Earth are caused by the gravitational pull of the Moon.Moon Characteristics and Motion



Moon Characteristics and Motiondwinter1
╠²
The moon is tidally locked to Earth, meaning the same side always faces Earth. This is why there is a big difference between the appearance of the near side, which faces Earth, and the far side. The near side has many visible maria (dark plains) while the far side has fewer maria and a thicker crust with more craters. Additionally, the Earth and moon orbit a common center of gravity called the barycenter, located about 900 miles from Earth's surface. Both bodies revolve around this point, which itself revolves around the sun.Our moon



Our moonDurant Road Middle
╠²
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite, located about 384,000 km away. It was formed 4-5 billion years ago from debris after a collision between Earth and a Mars-sized object. The Moon has no atmosphere and extreme temperature variations, and its features include mountains, rills, large impact craters, and dark basaltic plains called maria. It always keeps the same face towards Earth due to synchronous rotation as it revolves around our planet every 27 days.our_moon.ppt



our_moon.pptKeenlearner4
╠²
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite and orbits our planet about every 27 days. It has no atmosphere and experiences extreme temperature ranges. The lunar surface features highlands, craters, and low-lying maria plains filled with hardened lava. The side facing Earth always appears the same while the far side has more craters and few maria. Phases and eclipses occur due to the relative positions of the Moon, Earth, and Sun. Twelve American astronauts walked on the Moon between 1969-1972, with future lunar bases potentially allowing long-term human habitation.Our moon



Our moonNeilfieOrit2
╠²
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite and orbits our planet about every 27 days. It has no atmosphere and experiences extreme temperature ranges. The lunar surface features highlands, craters, and low-lying maria plains filled with hardened lava. The side facing Earth always appears the same while the far side has more craters and few maria. The Moon's phases and eclipses are caused by its orbit around Earth. Humans first explored the Moon in 1969 and collected rocks and data, but future missions may establish lunar bases.Earth's Moon



Earth's MoonSimple ABbieC
╠²
The document provides information about the Moon and its exploration history. It describes the Moon's size and distance from Earth. Key events in lunar exploration included Soviet missions in 1959 and US missions in the 1960s including Rangers, Lunar Orbiters, and Surveyors. The Apollo 11 mission in 1969 was the first to land humans on the Moon. The document discusses lunar geology, noting differences from Earth like the lack of an atmosphere, water, or plate tectonics. It describes lunar features such as maria, highlands, craters, and rilles. The formation of the Moon is also summarized.earth's moon (1).ppt



earth's moon (1).pptNikhilNag5
╠²
The document provides information about the Moon through a series of slides. It discusses the Moon's location in our solar system, its physical features such as craters and maria, phases of the Moon, lunar eclipses and solar eclipses. The document also covers tides caused by the Moon's gravity, past exploration of the Moon including Apollo missions, and possibilities for future lunar bases. Photos and diagrams accompany the text to illustrate different phases of the Moon, lunar terrain, and other concepts. Additional online photo resources are also listed.Moon



MoonOyster River HS
╠²
This document provides an overview of the Moon including its location, physical characteristics, surface features, phases and movements. Key details include that the Moon is Earth's only natural satellite, has no atmosphere or liquid water, and its surface contains craters, highlands, and low-lying volcanic plains called maria. The Moon revolves around Earth every 27 days while rotating on its axis in the same time, keeping the same hemisphere facing Earth. Its phases are caused by the varying illumination of its surface from Earth's perspective over the course of its revolution.New astronomy presentation



New astronomy presentationkshukla
╠²
The document provides information about astronomy and the universe. It discusses the three main theories of the origin of the universe: the Big Bang theory, Steady State theory, and Creation theory. It then describes the lifecycles of stars and their different stages from yellow star to black dwarf. Additional details include facts about the sun such as its size, temperature, and distance from Earth. Information is also provided about the moon, its phases and effects of low gravity, as well as details about solar and lunar eclipses.The earth in the solar system



The earth in the solar systemKabitha madhu
╠²
The document provides information about the Earth and its place in the solar system and universe. It discusses that the Earth is a planet that orbits the Sun. It receives light and heat from the Sun and has one moon. It also describes that the solar system includes the Sun and eight planets that orbit it, as well as asteroids and other smaller objects. Finally, it notes that the solar system is located within the Milky Way galaxy, and the galaxy is part of the wider universe.Is moon



Is moonSidMarnnyLopena
╠²
Gathered from many sources of ║▌║▌▀Żshare users, some of the pictures are not ours, we give credits to the owners. Our purpose of creating this slideshare are to pass our project and to inform others as well.Astonishing Astronomy 101 - Chapter 1



Astonishing Astronomy 101 - Chapter 1Don R. Mueller, Ph.D.
╠²
This document provides an overview of astronomy topics including:
- The basic properties of Earth, Moon, Sun and other planets in our solar system.
- How the tilt of Earth's axis causes the seasons and the celestial sphere model used to understand sky motions.
- Key events like solstices, equinoxes, and lunar phases that occur as Earth orbits the Sun and the Moon orbits Earth.
- The causes and viewing locations of solar and lunar eclipses when the Sun, Earth and Moon are directly aligned.
- Concepts like sidereal time, precession and time zones used to measure and communicate about time and sky positions.Star and the solar system 1



Star and the solar system 1Poonam Singh
╠²
This document provides information about various celestial bodies including stars, planets, moons, asteroids, comets, and more. It discusses their characteristics and compositions. The solar system consists of the sun and eight planets that revolve around it, including Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. It also describes features of the moon, stars, and constellations like Ursa Major.Sun, moon, and earth



Sun, moon, and earthharvey09
╠²
The document summarizes key concepts about the Earth, moon, sun, and universe. It describes how the Earth rotates daily and revolves yearly around the sun, causing day/night and seasons. It also discusses the moon's phases, tides, and eclipses due to the positions of the Earth, moon and sun. Finally, it briefly outlines historic models of our solar system and discoveries about gravity and our sun.Stars and the solar system/ class8 / science / physics / ncert



Stars and the solar system/ class8 / science / physics / ncertTaufiqOMG
╠²
The document provides information about celestial objects in our solar system. It begins by describing objects visible in the night sky like stars, planets and the moon. It then discusses the moon's phases and that it does not produce its own light. It notes that astronauts found the moon's surface to be dusty and barren with many craters. The document outlines that stars produce their own light and are much farther than planets. It defines constellations and provides examples. It describes the makeup of our solar system including planets, dwarf planets, asteroids, comets, meteors, and artificial satellites.Kamini ppt



Kamini pptSaad Ali
╠²
The presentation provides an overview of our solar system and its components. It was presented by Kamini Sharma, a first year B.Ed student at V.D Institute of Technology, Indraprastha University. The presentation describes the sun and nine planets of our solar system, categorizing them as either inner rocky planets like Earth and Mars or outer gas giants like Jupiter and Saturn. It provides details on the characteristics and properties of each planet.Solar system and the constituents in Solar system



Solar system and the constituents in Solar systemsubashini kumari
╠²
The Solar System consists of the Sun and everything that orbits it, including 8 planets, over 100 moons, asteroids, comets, and other objects. The 4 inner planets are small and rocky, while the 4 outer planets are large gas giants. The document describes each planet's characteristics such as composition, size, orbital period, and presence of moons and rings. It explains that the Sun is much larger than the planets and provides their light and heat through nuclear fusion in its core.Solar system



Solar systemsubashini kumari
╠²
The Solar System consists of the Sun and everything that orbits it, including 8 planets, Pluto, moons, asteroids, comets and other objects. The 4 inner planets are small and rocky, while the 4 outer planets are large gas giants. The document describes each planet's characteristics such as composition, size, orbital period, moons, temperature and other features. It explains that the Sun is at the center and provides energy through nuclear fusion, while planets reflect sunlight.Space Facts for Kids Infographic



Space Facts for Kids InfographicSearch Frog Local Directory
╠²
We're off to space! Let your kids explore the wonders of the great vast universe and launch their ideas to space. Here are some fascinating facts about space to kick off your child's dreams.Astronomy



Astronomymiller4075
╠²
The document provides an overview of the solar system, including the sun, eight planets, dwarf planets, asteroids, comets, and meteoroids. It describes the characteristics of asteroids as mostly lying between Mars and Jupiter and having irregular shapes. Comets are described as large "dirty snowballs" that produce a glowing head and tail when approaching the sun. Meteoroids are small solid particles that can become meteors when entering Earth's atmosphere or meteorites if reaching the surface. The document also discusses the resolution that established three categories for objects in the solar system: planets, dwarf planets like Pluto, and small solar system bodies.Universe 1



Universe 1Soumya Jain
╠²
The document provides information about various celestial bodies in our solar system including:
- The sun is a star that is approximately 150 million kilometers from Earth and it takes light about 8 minutes to reach us.
- Mercury is the closest planet to the sun and has extreme temperature variations.
- Venus is similar in size to Earth but has a toxic atmosphere and rotates backwards.
- Earth is the only known planet capable of supporting life.Solar System



Solar Systemrebelbrindley
╠²
The document provides information about the solar system, including:
- The solar nebula hypothesis which explains how the sun and planets formed from a cloud of gas and dust.
- Distances in space are measured in light years or astronomical units.
- The eight major planets consist of four inner terrestrial planets and four outer gas giants, along with the dwarf planet Pluto.
- Key facts are provided about each of the planets, such as their composition, moons, temperatures, densities and more.Solar system



Solar systemSAMANVITHAG
╠²
The solar system consists of the Sun and everything that orbits it, including 8 planets that orbit the Sun. The inner planets are Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars. The outer planets are Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. The planets can be categorized as either small, rocky terrestrial planets or large gas giants. Other objects in the solar system include asteroids located in the asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter, comets that have elongated orbits, and meteoroids that burn up as meteors upon entering Earth's atmosphere.Solar system



Solar systemSAMANVITHAG
╠²
The solar system consists of the Sun and everything that orbits it, including 8 planets that orbit the Sun. The inner planets are Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars. The outer planets are Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. The planets can be categorized as either small, rocky terrestrial planets or large gas giants. Other objects in the solar system include asteroids located in the asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter, comets made of ice and dust, and meteoroids that burn up as meteors upon entering Earth's atmosphere.Solar system



Solar systemRishab garg
╠²
The Solar System consists of the Sun and everything that orbits it, including 8 planets. The inner planets are rocky and include Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars. The outer planets are gas giants - Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. The planets vary in size, composition, atmospheric conditions, and number of moons. The Earth stands alone in its ability to support life.Solar system and eclipse



Solar system and eclipseLOURDU ANTHONI
╠²
The document provides an overview of the solar system, including:
- The solar system consists of the Sun and eight planets that orbit it, along with moons, asteroids, comets, and other objects.
- The planets can be divided into inner planets like Earth and Mars that are rocky, and outer gas giants like Jupiter and Saturn.
- Each planet has unique characteristics like Mercury's extreme temperatures or Jupiter's large moons. The document also discusses features of the Sun, Earth's moon, and other bodies in our solar system.CBSE Arabic Grammar - Class 10 ppt.pptx



CBSE Arabic Grammar - Class 10 ppt.pptxsuhail849886
╠²
cbse arabic grammar
grade 10 cbse arabic grammar
cbse class 10 arabic grammar
arabic marathon cbse arabic 10
nominal sentences
Kaun TALHA quiz Finals -- El Dorado 2025



Kaun TALHA quiz Finals -- El Dorado 2025Conquiztadors- the Quiz Society of Sri Venkateswara College
╠²
Finals of Kaun TALHA : a Travel, Architecture, Lifestyle, Heritage and Activism quiz, organized by Conquiztadors, the Quiz society of Sri Venkateswara College under their annual quizzing fest El Dorado 2025. More Related Content
Similar to Lesson 13. Moon and its phases 2022.pptx (20)
earth's moon (1).ppt



earth's moon (1).pptNikhilNag5
╠²
The document provides information about the Moon through a series of slides. It discusses the Moon's location in our solar system, its physical features such as craters and maria, phases of the Moon, lunar eclipses and solar eclipses. The document also covers tides caused by the Moon's gravity, past exploration of the Moon including Apollo missions, and possibilities for future lunar bases. Photos and diagrams accompany the text to illustrate different phases of the Moon, lunar terrain, and other concepts. Additional online photo resources are also listed.Moon



MoonOyster River HS
╠²
This document provides an overview of the Moon including its location, physical characteristics, surface features, phases and movements. Key details include that the Moon is Earth's only natural satellite, has no atmosphere or liquid water, and its surface contains craters, highlands, and low-lying volcanic plains called maria. The Moon revolves around Earth every 27 days while rotating on its axis in the same time, keeping the same hemisphere facing Earth. Its phases are caused by the varying illumination of its surface from Earth's perspective over the course of its revolution.New astronomy presentation



New astronomy presentationkshukla
╠²
The document provides information about astronomy and the universe. It discusses the three main theories of the origin of the universe: the Big Bang theory, Steady State theory, and Creation theory. It then describes the lifecycles of stars and their different stages from yellow star to black dwarf. Additional details include facts about the sun such as its size, temperature, and distance from Earth. Information is also provided about the moon, its phases and effects of low gravity, as well as details about solar and lunar eclipses.The earth in the solar system



The earth in the solar systemKabitha madhu
╠²
The document provides information about the Earth and its place in the solar system and universe. It discusses that the Earth is a planet that orbits the Sun. It receives light and heat from the Sun and has one moon. It also describes that the solar system includes the Sun and eight planets that orbit it, as well as asteroids and other smaller objects. Finally, it notes that the solar system is located within the Milky Way galaxy, and the galaxy is part of the wider universe.Is moon



Is moonSidMarnnyLopena
╠²
Gathered from many sources of ║▌║▌▀Żshare users, some of the pictures are not ours, we give credits to the owners. Our purpose of creating this slideshare are to pass our project and to inform others as well.Astonishing Astronomy 101 - Chapter 1



Astonishing Astronomy 101 - Chapter 1Don R. Mueller, Ph.D.
╠²
This document provides an overview of astronomy topics including:
- The basic properties of Earth, Moon, Sun and other planets in our solar system.
- How the tilt of Earth's axis causes the seasons and the celestial sphere model used to understand sky motions.
- Key events like solstices, equinoxes, and lunar phases that occur as Earth orbits the Sun and the Moon orbits Earth.
- The causes and viewing locations of solar and lunar eclipses when the Sun, Earth and Moon are directly aligned.
- Concepts like sidereal time, precession and time zones used to measure and communicate about time and sky positions.Star and the solar system 1



Star and the solar system 1Poonam Singh
╠²
This document provides information about various celestial bodies including stars, planets, moons, asteroids, comets, and more. It discusses their characteristics and compositions. The solar system consists of the sun and eight planets that revolve around it, including Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. It also describes features of the moon, stars, and constellations like Ursa Major.Sun, moon, and earth



Sun, moon, and earthharvey09
╠²
The document summarizes key concepts about the Earth, moon, sun, and universe. It describes how the Earth rotates daily and revolves yearly around the sun, causing day/night and seasons. It also discusses the moon's phases, tides, and eclipses due to the positions of the Earth, moon and sun. Finally, it briefly outlines historic models of our solar system and discoveries about gravity and our sun.Stars and the solar system/ class8 / science / physics / ncert



Stars and the solar system/ class8 / science / physics / ncertTaufiqOMG
╠²
The document provides information about celestial objects in our solar system. It begins by describing objects visible in the night sky like stars, planets and the moon. It then discusses the moon's phases and that it does not produce its own light. It notes that astronauts found the moon's surface to be dusty and barren with many craters. The document outlines that stars produce their own light and are much farther than planets. It defines constellations and provides examples. It describes the makeup of our solar system including planets, dwarf planets, asteroids, comets, meteors, and artificial satellites.Kamini ppt



Kamini pptSaad Ali
╠²
The presentation provides an overview of our solar system and its components. It was presented by Kamini Sharma, a first year B.Ed student at V.D Institute of Technology, Indraprastha University. The presentation describes the sun and nine planets of our solar system, categorizing them as either inner rocky planets like Earth and Mars or outer gas giants like Jupiter and Saturn. It provides details on the characteristics and properties of each planet.Solar system and the constituents in Solar system



Solar system and the constituents in Solar systemsubashini kumari
╠²
The Solar System consists of the Sun and everything that orbits it, including 8 planets, over 100 moons, asteroids, comets, and other objects. The 4 inner planets are small and rocky, while the 4 outer planets are large gas giants. The document describes each planet's characteristics such as composition, size, orbital period, and presence of moons and rings. It explains that the Sun is much larger than the planets and provides their light and heat through nuclear fusion in its core.Solar system



Solar systemsubashini kumari
╠²
The Solar System consists of the Sun and everything that orbits it, including 8 planets, Pluto, moons, asteroids, comets and other objects. The 4 inner planets are small and rocky, while the 4 outer planets are large gas giants. The document describes each planet's characteristics such as composition, size, orbital period, moons, temperature and other features. It explains that the Sun is at the center and provides energy through nuclear fusion, while planets reflect sunlight.Space Facts for Kids Infographic



Space Facts for Kids InfographicSearch Frog Local Directory
╠²
We're off to space! Let your kids explore the wonders of the great vast universe and launch their ideas to space. Here are some fascinating facts about space to kick off your child's dreams.Astronomy



Astronomymiller4075
╠²
The document provides an overview of the solar system, including the sun, eight planets, dwarf planets, asteroids, comets, and meteoroids. It describes the characteristics of asteroids as mostly lying between Mars and Jupiter and having irregular shapes. Comets are described as large "dirty snowballs" that produce a glowing head and tail when approaching the sun. Meteoroids are small solid particles that can become meteors when entering Earth's atmosphere or meteorites if reaching the surface. The document also discusses the resolution that established three categories for objects in the solar system: planets, dwarf planets like Pluto, and small solar system bodies.Universe 1



Universe 1Soumya Jain
╠²
The document provides information about various celestial bodies in our solar system including:
- The sun is a star that is approximately 150 million kilometers from Earth and it takes light about 8 minutes to reach us.
- Mercury is the closest planet to the sun and has extreme temperature variations.
- Venus is similar in size to Earth but has a toxic atmosphere and rotates backwards.
- Earth is the only known planet capable of supporting life.Solar System



Solar Systemrebelbrindley
╠²
The document provides information about the solar system, including:
- The solar nebula hypothesis which explains how the sun and planets formed from a cloud of gas and dust.
- Distances in space are measured in light years or astronomical units.
- The eight major planets consist of four inner terrestrial planets and four outer gas giants, along with the dwarf planet Pluto.
- Key facts are provided about each of the planets, such as their composition, moons, temperatures, densities and more.Solar system



Solar systemSAMANVITHAG
╠²
The solar system consists of the Sun and everything that orbits it, including 8 planets that orbit the Sun. The inner planets are Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars. The outer planets are Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. The planets can be categorized as either small, rocky terrestrial planets or large gas giants. Other objects in the solar system include asteroids located in the asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter, comets that have elongated orbits, and meteoroids that burn up as meteors upon entering Earth's atmosphere.Solar system



Solar systemSAMANVITHAG
╠²
The solar system consists of the Sun and everything that orbits it, including 8 planets that orbit the Sun. The inner planets are Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars. The outer planets are Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. The planets can be categorized as either small, rocky terrestrial planets or large gas giants. Other objects in the solar system include asteroids located in the asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter, comets made of ice and dust, and meteoroids that burn up as meteors upon entering Earth's atmosphere.Solar system



Solar systemRishab garg
╠²
The Solar System consists of the Sun and everything that orbits it, including 8 planets. The inner planets are rocky and include Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars. The outer planets are gas giants - Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. The planets vary in size, composition, atmospheric conditions, and number of moons. The Earth stands alone in its ability to support life.Solar system and eclipse



Solar system and eclipseLOURDU ANTHONI
╠²
The document provides an overview of the solar system, including:
- The solar system consists of the Sun and eight planets that orbit it, along with moons, asteroids, comets, and other objects.
- The planets can be divided into inner planets like Earth and Mars that are rocky, and outer gas giants like Jupiter and Saturn.
- Each planet has unique characteristics like Mercury's extreme temperatures or Jupiter's large moons. The document also discusses features of the Sun, Earth's moon, and other bodies in our solar system.Recently uploaded (20)
CBSE Arabic Grammar - Class 10 ppt.pptx



CBSE Arabic Grammar - Class 10 ppt.pptxsuhail849886
╠²
cbse arabic grammar
grade 10 cbse arabic grammar
cbse class 10 arabic grammar
arabic marathon cbse arabic 10
nominal sentences
Kaun TALHA quiz Finals -- El Dorado 2025



Kaun TALHA quiz Finals -- El Dorado 2025Conquiztadors- the Quiz Society of Sri Venkateswara College
╠²
Finals of Kaun TALHA : a Travel, Architecture, Lifestyle, Heritage and Activism quiz, organized by Conquiztadors, the Quiz society of Sri Venkateswara College under their annual quizzing fest El Dorado 2025. Year 10 The Senior Phase Session 3 Term 1.pptx



Year 10 The Senior Phase Session 3 Term 1.pptxmansk2
╠²
Year 10 The Senior Phase Session 3 Term 1.pptxPrinciple and Practices of Animal Breeding || Boby Basnet



Principle and Practices of Animal Breeding || Boby BasnetBoby Basnet
╠²
Principle and Practices of Animal Breeding Full Note
|| Assistant Professor Boby Basnet ||IAAS || AFU || PU || FUComputer Network Unit IV - Lecture Notes - Network Layer



Computer Network Unit IV - Lecture Notes - Network LayerMurugan146644
╠²
Title:
Lecture Notes - Unit IV - The Network Layer
Description:
Welcome to the comprehensive guide on Computer Network concepts, tailored for final year B.Sc. Computer Science students affiliated with Alagappa University. This document covers fundamental principles and advanced topics in Computer Network. PDF content is prepared from the text book Computer Network by Andrew S. Tenanbaum
Key Topics Covered:
Main Topic : The Network Layer
Sub-Topic : Network Layer Design Issues (Store and forward packet switching , service provided to the transport layer, implementation of connection less service, implementation of connection oriented service, Comparision of virtual circuit and datagram subnet), Routing algorithms (Shortest path routing, Flooding , Distance Vector routing algorithm, Link state routing algorithm , hierarchical routing algorithm, broadcast routing, multicast routing algorithm)
Other Link :
1.Introduction to computer network - /slideshow/lecture-notes-introduction-to-computer-network/274183454
2. Physical Layer - /slideshow/lecture-notes-unit-ii-the-physical-layer/274747125
3. Data Link Layer Part 1 : /slideshow/lecture-notes-unit-iii-the-datalink-layer/275288798
Target Audience:
Final year B.Sc. Computer Science students at Alagappa University seeking a solid foundation in Computer Network principles for academic.
About the Author:
Dr. S. Murugan is Associate Professor at Alagappa Government Arts College, Karaikudi. With 23 years of teaching experience in the field of Computer Science, Dr. S. Murugan has a passion for simplifying complex concepts in Computer Network
Disclaimer:
This document is intended for educational purposes only. The content presented here reflects the authorŌĆÖs understanding in the field of Computer NetworkThe Story Behind the Abney Park Restoration Project by Tom Walker



The Story Behind the Abney Park Restoration Project by Tom WalkerHistory of Stoke Newington
╠²
Presented at the 24th Stoke Newington History Talks event on 27th Feb 2025
https://stokenewingtonhistory.com/stoke-newington-history-talks/TLE 7 - 3rd Topic - Hand Tools, Power Tools, Instruments, and Equipment Used ...



TLE 7 - 3rd Topic - Hand Tools, Power Tools, Instruments, and Equipment Used ...RizaBedayo
╠²
Hand Tools, Power Tools, and Equipment in Industrial ArtsEDL 290F Week 3 - Mountaintop Views (2025).pdf



EDL 290F Week 3 - Mountaintop Views (2025).pdfLiz Walsh-Trevino
╠²
EDL 290F Week 3 - Mountaintop Views (2025).pdfResearch & Research Methods: Basic Concepts and Types.pptx



Research & Research Methods: Basic Concepts and Types.pptxDr. Sarita Anand
╠²
This ppt has been made for the students pursuing PG in social science and humanities like M.Ed., M.A. (Education), Ph.D. Scholars. It will be also beneficial for the teachers and other faculty members interested in research and teaching research concepts.A PPT Presentation on The Princess and the God: A tale of ancient India by A...



A PPT Presentation on The Princess and the God: A tale of ancient India by A...Beena E S
╠²
A PPT Presentation on The Princess and the God: A tale of ancient India by Aaron ShepardDatabase population in Odoo 18 - Odoo slides



Database population in Odoo 18 - Odoo slidesCeline George
╠²
In this slide, weŌĆÖll discuss the database population in Odoo 18. In Odoo, performance analysis of the source code is more important. Database population is one of the methods used to analyze the performance of our code. APM People Interest Network Conference - Oliver Randall & David Bovis - Own Y...



APM People Interest Network Conference - Oliver Randall & David Bovis - Own Y...Association for Project Management
╠²
APM People Interest Network Conference 2025
- Autonomy, Teams and Tension
- Oliver Randall & David Bovis
- Own Your Autonomy
Oliver Randall
Consultant, Tribe365
Oliver is a career project professional since 2011 and started volunteering with APM in 2016 and has since chaired the People Interest Network and the North East Regional Network. Oliver has been consulting in culture, leadership and behaviours since 2019 and co-developed HPTM┬«ŌĆ»an off the shelf high performance framework for teams and organisations and is currently working with SAS (Stellenbosch Academy for Sport) developing the culture, leadership and behaviours framework for future elite sportspeople whilst also holding down work as a project manager in the NHS at North Tees and Hartlepool Foundation Trust.
David Bovis
Consultant, Duxinaroe
A Leadership and Culture Change expert, David is the originator of BTFAŌäó and The Dux Model.
With a Masters in Applied Neuroscience from the Institute of Organisational Neuroscience, he is widely regarded as the ŌĆśGo-ToŌĆÖ expert in the field, recognised as an inspiring keynote speaker and change strategist.
He has an industrial engineering background, majoring in TPS / Lean. David worked his way up from his apprenticeship to earn his seat at the C-suite table. His career spans several industries, including Automotive, Aerospace, Defence, Space, Heavy Industries and Elec-Mech / polymer contract manufacture.
Published in LondonŌĆÖs Evening Standard quarterly business supplement, James CaanŌĆÖs ŌĆśYour businessŌĆÖ Magazine, ŌĆśQuality WorldŌĆÖ, the Lean Management Journal and Cambridge Universities ŌĆśPMAŌĆÖ, he works as comfortably with leaders from FTSE and Fortune 100 companies as he does owner-managers in SMEŌĆÖs. He is passionate about helping leaders understand the neurological root cause of a high-performance culture and sustainable change, in business.
Session | Own Your Autonomy ŌĆō The Importance of Autonomy in Project Management
#OwnYourAutonomy is aiming to be a global APM initiative to position everyone to take a more conscious role in their decision making process leading to increased outcomes for everyone and contribute to ŌĆ£a world in which all projects succeedŌĆØ.
We want everyone to join the journey.
#OwnYourAutonomy is the culmination of 3 years of collaborative exploration within the Leadership Focus Group which is part of the APM People Interest Network. The work has been pulled together using the 5 HPTM® Systems and the BTFA neuroscience leadership programme.
https://www.linkedin.com/showcase/apm-people-network/about/The Battle of Belgrade Road: A WW1 Street Renaming Saga by Amir Dotan



The Battle of Belgrade Road: A WW1 Street Renaming Saga by Amir DotanHistory of Stoke Newington
╠²
Presented at the 24th Stoke Newington History Talks event on 27th Feb 2025
https://stokenewingtonhistory.com/stoke-newington-history-talks/How to attach file using upload button Odoo 18



How to attach file using upload button Odoo 18Celine George
╠²
In this slide, weŌĆÖll discuss on how to attach file using upload button Odoo 18. Odoo features a dedicated model, 'ir.attachments,' designed for storing attachments submitted by end users. We can see the process of utilizing the 'ir.attachments' model to enable file uploads through web forms in this slide.How to Manage Putaway Rule in Odoo 17 Inventory



How to Manage Putaway Rule in Odoo 17 InventoryCeline George
╠²
Inventory management is a critical aspect of any business involved in manufacturing or selling products.
Odoo 17 offers a robust inventory management system that can handle complex operations and optimize warehouse efficiency. APM People Interest Network Conference - Tim Lyons - The neurological levels ...



APM People Interest Network Conference - Tim Lyons - The neurological levels ...Association for Project Management
╠²
APM People Interest Network Conference 2025
-Autonomy, Teams and Tension: Projects under stress
-Tim Lyons
-The neurological levels of
team-working: Harmony and tensions
With a background in projects spanning more than 40 years, Tim Lyons specialised in the delivery of large, complex, multi-disciplinary programmes for clients including Crossrail, Network Rail, ExxonMobil, Siemens and in patent development. His first career was in broadcasting, where he designed and built commercial radio station studios in Manchester, Cardiff and Bristol, also working as a presenter and programme producer. Tim now writes and presents extensively on matters relating to the human and neurological aspects of projects, including communication, ethics and coaching. He holds a MasterŌĆÖs degree in NLP, is an NLP Master Practitioner and International Coach. He is the Deputy Lead for APMŌĆÖs People Interest Network.
Session | The Neurological Levels of Team-working: Harmony and Tensions
Understanding how teams really work at conscious and unconscious levels is critical to a harmonious workplace. This session uncovers what those levels are, how to use them to detect and avoid tensions and how to smooth the management of change by checking you have considered all of them.Kaun TALHA quiz Finals -- El Dorado 2025



Kaun TALHA quiz Finals -- El Dorado 2025Conquiztadors- the Quiz Society of Sri Venkateswara College
╠²
APM People Interest Network Conference - Oliver Randall & David Bovis - Own Y...



APM People Interest Network Conference - Oliver Randall & David Bovis - Own Y...Association for Project Management
╠²
APM People Interest Network Conference - Tim Lyons - The neurological levels ...



APM People Interest Network Conference - Tim Lyons - The neurological levels ...Association for Project Management
╠²
Lesson 13. Moon and its phases 2022.pptx
- 1. SCIENCE
- 2. The Moon L e s s o n 1 3
- 3. The Lunar Surfaces L e s s o n 1 3 . 1
- 4. Our Moon has been admired for thousands of years, and because of this is one of the most familiar astronomical objects to children of all ages.
- 5. What is the Moon? ŌĆó A natural satellite ŌĆó One of more than 96 moons in our Solar System ŌĆó The only moon of the planet Earth
- 6. Location, location, location! ŌĆóAbout 384,000 km (240,000 miles) from Earth ŌĆó3,468 km (2,155 miles) in diameter (about ┬╝ the size of Earth)
- 7. Major divisions of the Lunar interior ŌĆóCrust - average thickness of about 70 kilometers ŌĆóMantle ŌĆóCore - radius is between 300 and 425 kilometers
- 8. The MoonŌĆÖs Surface ŌĆóNo atmosphere ŌĆóNo liquid water ŌĆóExtreme temperatures ŌĆó Daytime = 130’é░C (265┬░F) ŌĆó Nighttime = -190’é░C (-310 ’é░F) ŌĆó1/6 EarthŌĆÖs gravity
- 9. Lunar Features - Highlands ŌĆóMountains up to 7500 m (25,000 ft) tall ŌĆóRille (trenchlike valleys) ŌĆóAlso known as the lunar terrae, which is Latin for ŌĆ£landŌĆØ)
- 10. Lunar Features - Craters ŌĆóMost formed by meteorite impact on the Moon
- 11. Lunar Features - Maria ŌĆóOriginally thought to be ŌĆ£seasŌĆØ by early astronomers ŌĆóDarkest parts of lunar landscape
- 12. Far Side of the Moon ŌĆó First seen by Luna 3 Russian space probe in 1959 ŌĆó Surface features different from near side ŌĆó More craters ŌĆó Very few maria ŌĆó Thicker crust
- 13. Movements of the Moon ŌĆó Revolution ŌĆō Moon orbits the Earth every 271/3 days ŌĆó The moon rises in the east and sets in the west ŌĆó The moon rises and sets 50 minutes later each day ŌĆó Rotation ŌĆō Moon turns on its axis every 27 days ŌĆó Same side of Moon always faces Earth
- 14. The Tides ŌĆó Tides caused by pull of MoonŌĆÖs gravity on Earth ŌĆó High tide ŌĆō ŌĆó Side facing Moon and side away from Moon ŌĆó Every 12 hours, 25 ┬Į minutes ŌĆó Low tide ŌĆō ŌĆó On sides of Earth
- 15. Exploring the Moon ŌĆó1950s to 1960s - probes ŌĆóNeil Armstrong First man on the Moon ŌĆō July 20, 1969 ŌĆóSix Apollo missions (1969-1972) ŌĆó382 kg (842 lbs) rocks ŌĆó12 Americans have
- 16. SCIENCE
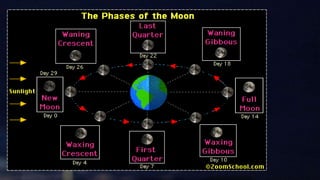
- 17. Phases of the Moon L e s s o n 1 3 . 2
- 18. ItŌĆÖs Just a Phase ŌĆó Moonlight is reflected sunlight ŌĆó Half the moonŌĆÖs surface is always reflecting light ŌĆó From Earth we see different amounts of the MoonŌĆÖs lit surface ŌĆó The amount seen is called a ŌĆ£phaseŌĆØ
- 21. new moon The moon is not visible in the sky. waxing crescent The lighted side of the moon slowly becomes visible.
- 22. first quarter The lighted area appears as half moon. waxing gibbous The lighted side is shaped like an egg.
- 23. full moon ŌĆó The complete lighted side of the moon visible in the sky. ŌĆó Earth is then somewhere between the moon and the sun.
- 24. Earth during the new moon phase and the full moon phase
- 25. waning gibbous ŌĆó More than half of the moon is visible. ŌĆó The lighted area appears to grow smaller. last quarter ŌĆó Half of the moon is lighted.
- 26. waning crescent ŌĆó Small portion of the moon is lit but most of the surface is dark.
- 28. Lunar Eclipses ŌĆó Moon moves into EarthŌĆÖs shadow ŌĆō this shadow darkens the Moon ŌĆó Umbra ŌĆó Penumbra ŌĆó About 2-3 per year ŌĆó Last up to 4 hours
- 29. Solar Eclipses ŌĆó Moon moves between Earth and Sun ŌĆó Moon casts a shadow on part of the Earth ŌĆó Total eclipses rare ŌĆō only once every 360 years from one location!



