Land forms sakeena saidou
?Download as PPTX, PDF?
1 like?172 views
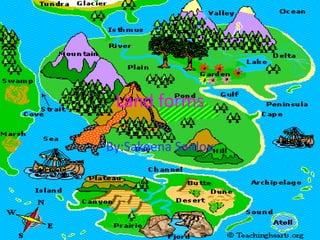
Bodies of water include lakes, oceans, ponds, rivers, and lagoons. Volcanoes can create or destroy land and are dangerous. Caves provide habitat for bears and bats. Glaciers are moving ice and canons are deep valleys carved by erosion.
1 of 6
Download to read offline





Recommended
Water bodies 



Water bodies Akanksha
?
This document summarizes the major water bodies of Earth. It explains that 3/4 of the Earth's surface is covered by water in various forms called water bodies. The largest water bodies are the five oceans: Pacific, Atlantic, Indian, Arctic, and Antarctic oceans. It also describes seas as large water bodies smaller than oceans, which can be marginal seas partly enclosed by land or inland seas covering central land areas. Minor water bodies include bays, lakes, gulfs, lagoons, straits, and rivers.Landforms and bodies of water



Landforms and bodies of waterJoGono
?
Topography refers to the physical features of a place or region, which can be natural or man-made. Topography is caused by volcanic eruptions, soil erosion from water and wind, and the flow of water from high to low elevations. The document defines and describes various landforms like mountains, hills, islands, deserts, plains, valleys, canyons, and plateaus. It also defines bodies of water like oceans, seas, rivers, lakes, waterfalls, and coasts. Major oceans, deepest ocean trenches, historically important rivers, and examples of large lakes are identified.Bodies of water



Bodies of waterLyric Treco-Hanna
?
The document discusses the five main oceans of the world - the Pacific, Atlantic, Indian, Southern, and Arctic oceans. It provides data on the size and depths of each ocean, with the Pacific being the largest and the Mariana Trench in the Pacific being the deepest location at over 36,000 feet deep. Rivers are described as large bodies of fresh water that flow across land into seas or oceans, while lakes are bodies of fresh water surrounded by land.Major bodies of water



Major bodies of waterfernando_bruaj
?
The document discusses the major bodies of water on Earth. It notes that there are four oceans - Pacific, Atlantic, Indian, and Arctic. The Pacific is the largest and deepest. It also describes that there are five oceans with the addition of the Southern Ocean north of Antarctica in 2000. Coral reefs form in shallow, warm seas and are made of coral polyps' skeletons. The oceans are divided into three zones - the sunlit zone down to 650 feet, the twilight zone down to 3,300 feet, and the sunless zone down to 13,100 feet with different types of life in each zone.Landforms powerpoint



Landforms powerpointmisteralpert
?
This document defines and describes various landforms and bodies of water. It explains that a bay is an area of water bordered by land on three sides, a gulf is a larger body of water partly surrounded by land, and a peninsula is a piece of land surrounded by water on three sides. It also defines deltas, isthmuses, straits, lakes, mountains, hills, plains, plateaus, rivers, waterfalls, fjords, valleys, glaciers, archipelagos, seas, and oceans.Quiz about landforms



Quiz about landformsElena Garc¨Şa
?
Landforms are natural shapes on the Earth's surface and include plains, plateaus, hills, mountains, valleys, depressions, canyons, peninsulas, islands, archipelagos, coasts, lakes, rivers, capes, gulfs, bays, and straits or channels. Plains are flat areas, plateaus are flat, high areas, hills are small elevations, and mountains are high areas surrounded by lower land. Valleys are low areas between high lands, depressions are lower areas, and canyons are deep, steep valleys.Oceans continents



Oceans continentsRebecca Newton
?
There are five major oceans - Arctic, Indian, Atlantic, Pacific, and Southern - that together cover almost three-quarters of the Earth's surface. Salt in the oceans comes from rocks that have been worn down by water over time, releasing salt. Sand is formed from rocks that have broken apart into tiny grains, and tides are caused by the gravitational pull of the moon, causing water levels to rise and fall daily. Waves are mostly produced by wind blowing over the surface of the water.Bodies Of Water



Bodies Of Waterdhelm
?
Oceans, rivers, and lakes are the three main types of bodies of water on Earth. Oceans are large bodies of salt water surrounding continents, with the Pacific being the largest. Rivers are flowing bodies of fresh water that cross land and empty into seas or oceans. Lakes are large bodies of fresh water surrounded by land on all sides, such as Lake Kaweah in Tulare County.Bodies of water. adriana, leire and ainara



Bodies of water. adriana, leire and ainaraandare2
?
Most of Earth is covered in water, including five major oceans - Pacific, Atlantic, Indian, Southern, and Arctic. There are also smaller seas and lakes surrounded by land. Rivers are bodies of moving water that flow into oceans, seas, lakes or other rivers, with examples given of the Camarmilla, Henares, and Tajo rivers ultimately draining into the Atlantic Ocean. The document provides a basic overview of the different types of bodies of water on Earth.Land forms



Land formsChristineFreier
?
This document defines and provides brief descriptions of different types of landforms. It explains that mountains are the highest kind of land with peaks, hills rise above surrounding land with rounded tops, islands are surrounded by water, deserts are dry with few plants due to lack of rain, rivers are long bodies of flowing water through land, lakes are bodies of water surrounded by land, oceans are large bodies of salty water covering large areas, plains are flat land, valleys are low land between hills or mountains, and plateaus are large elevated areas rising steeply above surrounding land.Landforms diva jamaria



Landforms diva jamariapeggy Williams
?
Canyons are deep, narrow valleys that sometimes contain streams, while caves are dark, cool, and wet places that require specialized adaptations for the creatures living there. Mountains have snow at their peaks and rise sharply from the land, as volcanoes explode lava and eruptions form hard rock. Gulfs are portions of sea almost surrounded by land with a narrow opening, whereas islands are smaller than continents and completely encircled by water. Bays connect to oceans or lakes, and harbors shelter ships from storms in connected bodies of water. Cliffs are tall, steep slopes of rock or soil, and hills form from erosion and are part of raised areas of earth's crust. Glaciers contain ice and have pointedRead about landforms 2014 (1)



Read about landforms 2014 (1)Teach6
?
This document provides information about various types of landforms. It includes definitions and facts about volcanoes, canyons, waterfalls, plains, mountains, rivers, caves, oceans, valleys, islands, deltas, peninsulas, lakes, hills, and continents. For each landform, it gives a brief description of its characteristics and formation and often links to additional online resources for learning more.ocean and man



ocean and manranjithkumarbs
?
The document discusses the formation of oceans on Earth. As the molten surface cooled over time, volcanic gases formed an atmosphere and water condensed from the atmosphere to form oceans. Life then emerged in the oceans. The three major oceans - Pacific, Atlantic, and Indian - formed as the supercontinent Pangaea broke apart. These oceans have varying depths, islands, currents, and features such as coral reefs and mid-ocean ridges. The document also describes how salinity and temperature vary in ocean waters due to factors like evaporation, rainfall, and ocean currents.Bodies of Water



Bodies of WaterCrystal Dunn
?
The document describes four major bodies of water: oceans, gulfs, rivers, and lakes. Oceans are the largest body of water and have salty water. Gulfs are bodies of ocean water surrounded by land on three sides. Rivers are streams of water that flow across land. Lakes are bodies of fresh water surrounded by land.EarthˇŻs water forms



EarthˇŻs water formsval_p
?
The document provides information about various bodies of water on Earth. It discusses that 3/4 of the Earth's surface is covered by water, most of which is found in the oceans. The four main oceans - Pacific, Atlantic, Indian, and Arctic - contain salt water and cover about half of the Earth's surface. Smaller bodies of water like seas, bays, lakes, rivers, and springs are also described. The document also lists and provides details about many bays found within the Philippines.Landforms



Landformssbartleson1989
?
This document describes different types of landforms including rivers, lakes, oceans, waterfalls, islands, canyons, mountains, volcanoes, and plains. Rivers run downhill and can power mills. Lakes are large bodies of water surrounded by land that are good for fishing. Oceans take up most of the Earth and are salty. Waterfalls occur when there is a sharp drop off from a river. Islands can be reached by boat as they are surrounded by water. Canyons have very steep sides carved out over time by erosion. Mountains are the tallest landforms with snowy peaks. Volcanoes have vents that spew lava, steam, and rocks. Plains are broad and flat areas that were once underBodies of water



Bodies of watershawntelford
?
The document discusses different types of bodies of water on Earth. It states that about 3/4 of Earth's surface is covered by water, but only 1/2 cup out of a gallon jug represents the amount of fresh water. The largest oceans are the Pacific, Atlantic, Indian, and Arctic. Lakes are bodies of water surrounded by land, and the Great Lakes are located in Michigan. Rivers contain fresh water and flow into larger bodies of water. Ponds and streams are smaller than lakes and rivers.Water forms of the philippines



Water forms of the philippinesjhonric Lugtu
?
This document describes the various water forms found in the Philippines, including oceans, seas, lakes, channels, waterfalls, bays, straits, gulfs, rivers, streams, creeks, and springs. It provides examples of each water form type in the Philippines and notes key characteristics, such as oceans being the largest bodies of water, seas being salty, lakes containing fresh water, and rivers flowing toward the sea.Bodies of water



Bodies of waterEster Corell Calatayud
?
Power Point done and used to teach 2nd and 3rd Graders in Sciences. (Bodies of water- seas-oceans...)Geography Vocabulary



Geography VocabularyAmy LC
?
This presentation was prepared for Deaf and hard of hearing students in Ms. Amy LC's social studies classes.Seas, Lakes and Rivers (Project in Science)



Seas, Lakes and Rivers (Project in Science)Luna Nightmare
?
This powerpoint presentation is for the study of some waterforms that are found in our beautiful and blessed planet, Earth. Please enjoy and comment what kind of powerpoint do you want next :).Landformppt quiz



Landformppt quizinscores
?
This document is a quiz about landforms that provides descriptions of 24 different landforms and asks the reader to identify each one out of 3 multiple choice options. It tests knowledge of common geographic features including glaciers, valleys, loess, deserts, plateaus, peninsulas, cliffs, canyons, plains, swamps, waterfalls, archipelagos, isthmuses, capes, mesas, dunes, deltas, faults, mountains, valleys, prairies, and volcanoes. major water bodies



major water bodiesAadrika Kaleru
?
This document provides an overview of major water bodies on Earth. It introduces the hydrosphere, which includes oceans, seas, ice sheets, underground water, and atmospheric water vapor. There are five major oceans: the Pacific, Atlantic, Indian, Southern, and Arctic Oceans. The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest ocean, containing the Mariana Trench. The Atlantic Ocean is the second largest and saltiest ocean. The Indian Ocean is triangular in shape and contains the Arabian Sea and Bay of Bengal. The Southern Ocean surrounds Antarctica, while the Arctic Ocean is the smallest and shallowest ocean located around the North Pole. Oceans are important as they help regulate temperature and provide food, oil/gas resources, andLand and Water forms



Land and Water formseboreman
?
This document provides an introduction to common land and water forms for second graders. It defines the ocean, continent, river, island, lake, hill, plain, mountain, peninsula, and bay. It then instructs students to choose a land or water form to research with a buddy, find three interesting facts about it using a provided search engine, and create a PowerPoint to share with the class.Landforms review



Landforms reviewevancil
?
This document defines and provides examples of different types of landforms and physical regions. It discusses 8 major regions: 1) mountain, 2) valley, 3) river basin, 4) desert, 5) plains, 6) coastal plain, 7) island, and provides information on key landforms within each region, such as mountains, plateaus, valleys, deltas, mesas, buttes, peninsulas, bays, gulfs, seas, islands, straits, and isthmuses. Examples are given for many of the landforms.Bodies of water



Bodies of waterubiquinone
?
The water cycle describes the continuous movement of water on, above, and below the surface of the Earth. Water can change between liquid, solid, and gas states in this cycle. In its purest form, water is a chemical compound made up of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom. Bodies of flowing water include rivers, creeks, brooks, and canals, which vary in size and flow. Bodies of non-flowing water include oceans, lakes, ponds, reservoirs, sloughs, marshes, and estuaries, and also vary in size and salinity.The philippine landforms



The philippine landformsElma Camion
?
The document describes various landforms found in the Philippines. It discusses mountains, volcanoes, plains, hills, plateaus, mountain ranges, peninsulas, and valleys. Mountains rise high above the surrounding land and can be steep and difficult to climb. Volcanoes have openings that erupt hot rocks and lava. Plains are large, flat, low-lying areas where many towns and cities are located. Hills are smaller and lower than mountains. Plateaus are flat areas at the top of mountains. Mountain ranges are chains of mountains separated by passes or valleys. Peninsulas jut out from land into water on three sides. Valleys are low-lying areas between hills or mountains. Examples of each landform type inBodies of water



Bodies of waterDaralynneMay
?
There are many bodies of water in the United States including lakes, rivers, and oceans. Some important rivers discussed include the Mississippi River, which is the largest river system in North America, the Colorado River, and the Arkansas River. The Great Lakes along the US-Canada border were also covered, including Lake Erie being the southernmost, shallowest, and smallest by volume of the five lakes. Finally, the three oceans bordering the US were mentioned with the Pacific Ocean identified as the largest oceanic division.Yokohama ČËżÚÓčËăĂć·e



Yokohama ČËżÚÓčËăĂć·e¤Ż¤µ¤Ţ¸ŐŁ¨şáäşĘĐ»áŇéÔ±Ł©
?
¶ĽÖţ¤Î¤Ż¤Ţ¤ÎĄÇ©`ĄżŃĐľżËů¤Çˇ˘şáäşĘФÎČËżÚ?ÓčËă?Ăć»ý¤ňĄąĄéĄ¤ĄÉ¤Ë¤·¤Ć¤ď¤«¤ę¤ä¤ą¤ŻŐhĂ÷¤·¤ż¤â¤Î¤Ç¤ąˇŁˇˇMore Related Content
What's hot (20)
Bodies of water. adriana, leire and ainara



Bodies of water. adriana, leire and ainaraandare2
?
Most of Earth is covered in water, including five major oceans - Pacific, Atlantic, Indian, Southern, and Arctic. There are also smaller seas and lakes surrounded by land. Rivers are bodies of moving water that flow into oceans, seas, lakes or other rivers, with examples given of the Camarmilla, Henares, and Tajo rivers ultimately draining into the Atlantic Ocean. The document provides a basic overview of the different types of bodies of water on Earth.Land forms



Land formsChristineFreier
?
This document defines and provides brief descriptions of different types of landforms. It explains that mountains are the highest kind of land with peaks, hills rise above surrounding land with rounded tops, islands are surrounded by water, deserts are dry with few plants due to lack of rain, rivers are long bodies of flowing water through land, lakes are bodies of water surrounded by land, oceans are large bodies of salty water covering large areas, plains are flat land, valleys are low land between hills or mountains, and plateaus are large elevated areas rising steeply above surrounding land.Landforms diva jamaria



Landforms diva jamariapeggy Williams
?
Canyons are deep, narrow valleys that sometimes contain streams, while caves are dark, cool, and wet places that require specialized adaptations for the creatures living there. Mountains have snow at their peaks and rise sharply from the land, as volcanoes explode lava and eruptions form hard rock. Gulfs are portions of sea almost surrounded by land with a narrow opening, whereas islands are smaller than continents and completely encircled by water. Bays connect to oceans or lakes, and harbors shelter ships from storms in connected bodies of water. Cliffs are tall, steep slopes of rock or soil, and hills form from erosion and are part of raised areas of earth's crust. Glaciers contain ice and have pointedRead about landforms 2014 (1)



Read about landforms 2014 (1)Teach6
?
This document provides information about various types of landforms. It includes definitions and facts about volcanoes, canyons, waterfalls, plains, mountains, rivers, caves, oceans, valleys, islands, deltas, peninsulas, lakes, hills, and continents. For each landform, it gives a brief description of its characteristics and formation and often links to additional online resources for learning more.ocean and man



ocean and manranjithkumarbs
?
The document discusses the formation of oceans on Earth. As the molten surface cooled over time, volcanic gases formed an atmosphere and water condensed from the atmosphere to form oceans. Life then emerged in the oceans. The three major oceans - Pacific, Atlantic, and Indian - formed as the supercontinent Pangaea broke apart. These oceans have varying depths, islands, currents, and features such as coral reefs and mid-ocean ridges. The document also describes how salinity and temperature vary in ocean waters due to factors like evaporation, rainfall, and ocean currents.Bodies of Water



Bodies of WaterCrystal Dunn
?
The document describes four major bodies of water: oceans, gulfs, rivers, and lakes. Oceans are the largest body of water and have salty water. Gulfs are bodies of ocean water surrounded by land on three sides. Rivers are streams of water that flow across land. Lakes are bodies of fresh water surrounded by land.EarthˇŻs water forms



EarthˇŻs water formsval_p
?
The document provides information about various bodies of water on Earth. It discusses that 3/4 of the Earth's surface is covered by water, most of which is found in the oceans. The four main oceans - Pacific, Atlantic, Indian, and Arctic - contain salt water and cover about half of the Earth's surface. Smaller bodies of water like seas, bays, lakes, rivers, and springs are also described. The document also lists and provides details about many bays found within the Philippines.Landforms



Landformssbartleson1989
?
This document describes different types of landforms including rivers, lakes, oceans, waterfalls, islands, canyons, mountains, volcanoes, and plains. Rivers run downhill and can power mills. Lakes are large bodies of water surrounded by land that are good for fishing. Oceans take up most of the Earth and are salty. Waterfalls occur when there is a sharp drop off from a river. Islands can be reached by boat as they are surrounded by water. Canyons have very steep sides carved out over time by erosion. Mountains are the tallest landforms with snowy peaks. Volcanoes have vents that spew lava, steam, and rocks. Plains are broad and flat areas that were once underBodies of water



Bodies of watershawntelford
?
The document discusses different types of bodies of water on Earth. It states that about 3/4 of Earth's surface is covered by water, but only 1/2 cup out of a gallon jug represents the amount of fresh water. The largest oceans are the Pacific, Atlantic, Indian, and Arctic. Lakes are bodies of water surrounded by land, and the Great Lakes are located in Michigan. Rivers contain fresh water and flow into larger bodies of water. Ponds and streams are smaller than lakes and rivers.Water forms of the philippines



Water forms of the philippinesjhonric Lugtu
?
This document describes the various water forms found in the Philippines, including oceans, seas, lakes, channels, waterfalls, bays, straits, gulfs, rivers, streams, creeks, and springs. It provides examples of each water form type in the Philippines and notes key characteristics, such as oceans being the largest bodies of water, seas being salty, lakes containing fresh water, and rivers flowing toward the sea.Bodies of water



Bodies of waterEster Corell Calatayud
?
Power Point done and used to teach 2nd and 3rd Graders in Sciences. (Bodies of water- seas-oceans...)Geography Vocabulary



Geography VocabularyAmy LC
?
This presentation was prepared for Deaf and hard of hearing students in Ms. Amy LC's social studies classes.Seas, Lakes and Rivers (Project in Science)



Seas, Lakes and Rivers (Project in Science)Luna Nightmare
?
This powerpoint presentation is for the study of some waterforms that are found in our beautiful and blessed planet, Earth. Please enjoy and comment what kind of powerpoint do you want next :).Landformppt quiz



Landformppt quizinscores
?
This document is a quiz about landforms that provides descriptions of 24 different landforms and asks the reader to identify each one out of 3 multiple choice options. It tests knowledge of common geographic features including glaciers, valleys, loess, deserts, plateaus, peninsulas, cliffs, canyons, plains, swamps, waterfalls, archipelagos, isthmuses, capes, mesas, dunes, deltas, faults, mountains, valleys, prairies, and volcanoes. major water bodies



major water bodiesAadrika Kaleru
?
This document provides an overview of major water bodies on Earth. It introduces the hydrosphere, which includes oceans, seas, ice sheets, underground water, and atmospheric water vapor. There are five major oceans: the Pacific, Atlantic, Indian, Southern, and Arctic Oceans. The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest ocean, containing the Mariana Trench. The Atlantic Ocean is the second largest and saltiest ocean. The Indian Ocean is triangular in shape and contains the Arabian Sea and Bay of Bengal. The Southern Ocean surrounds Antarctica, while the Arctic Ocean is the smallest and shallowest ocean located around the North Pole. Oceans are important as they help regulate temperature and provide food, oil/gas resources, andLand and Water forms



Land and Water formseboreman
?
This document provides an introduction to common land and water forms for second graders. It defines the ocean, continent, river, island, lake, hill, plain, mountain, peninsula, and bay. It then instructs students to choose a land or water form to research with a buddy, find three interesting facts about it using a provided search engine, and create a PowerPoint to share with the class.Landforms review



Landforms reviewevancil
?
This document defines and provides examples of different types of landforms and physical regions. It discusses 8 major regions: 1) mountain, 2) valley, 3) river basin, 4) desert, 5) plains, 6) coastal plain, 7) island, and provides information on key landforms within each region, such as mountains, plateaus, valleys, deltas, mesas, buttes, peninsulas, bays, gulfs, seas, islands, straits, and isthmuses. Examples are given for many of the landforms.Bodies of water



Bodies of waterubiquinone
?
The water cycle describes the continuous movement of water on, above, and below the surface of the Earth. Water can change between liquid, solid, and gas states in this cycle. In its purest form, water is a chemical compound made up of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom. Bodies of flowing water include rivers, creeks, brooks, and canals, which vary in size and flow. Bodies of non-flowing water include oceans, lakes, ponds, reservoirs, sloughs, marshes, and estuaries, and also vary in size and salinity.The philippine landforms



The philippine landformsElma Camion
?
The document describes various landforms found in the Philippines. It discusses mountains, volcanoes, plains, hills, plateaus, mountain ranges, peninsulas, and valleys. Mountains rise high above the surrounding land and can be steep and difficult to climb. Volcanoes have openings that erupt hot rocks and lava. Plains are large, flat, low-lying areas where many towns and cities are located. Hills are smaller and lower than mountains. Plateaus are flat areas at the top of mountains. Mountain ranges are chains of mountains separated by passes or valleys. Peninsulas jut out from land into water on three sides. Valleys are low-lying areas between hills or mountains. Examples of each landform type inBodies of water



Bodies of waterDaralynneMay
?
There are many bodies of water in the United States including lakes, rivers, and oceans. Some important rivers discussed include the Mississippi River, which is the largest river system in North America, the Colorado River, and the Arkansas River. The Great Lakes along the US-Canada border were also covered, including Lake Erie being the southernmost, shallowest, and smallest by volume of the five lakes. Finally, the three oceans bordering the US were mentioned with the Pacific Ocean identified as the largest oceanic division.Viewers also liked (17)
Yokohama ČËżÚÓčËăĂć·e



Yokohama ČËżÚÓčËăĂć·e¤Ż¤µ¤Ţ¸ŐŁ¨şáäşĘĐ»áŇéÔ±Ł©
?
¶ĽÖţ¤Î¤Ż¤Ţ¤ÎĄÇ©`ĄżŃĐľżËů¤Çˇ˘şáäşĘФÎČËżÚ?ÓčËă?Ăć»ý¤ňĄąĄéĄ¤ĄÉ¤Ë¤·¤Ć¤ď¤«¤ę¤ä¤ą¤ŻŐhĂ÷¤·¤ż¤â¤Î¤Ç¤ąˇŁˇˇ

Partes del teclado vianneyvianney carrera espinoza
?
El documento trata sobre las partes del teclado. Fue elaborado por Vianney Carrera Espinoza para su grupo 202 de la carrera de P.T.B en Inform¨˘tica en el CONALEP Estado de M¨¦xico en Tlalneplantla 1 y fue entregado al profesor Hugo Acosta Serna.Ad Infinitum: The Remediation of the Postcard in PostSecret.com



Ad Infinitum: The Remediation of the Postcard in PostSecret.comDawn Armfield
?
presentation at CCCC 2013

Doc1 (2)juanapaolagarciapinzon
?
El documento habla sobre el recaudo anticipado del impuesto de industria y comercio en Colombia. Se practica la retenci¨®n en la fuente a proveedores con sede en el mismo municipio del agente retenedor. Los agentes de retenci¨®n incluyen entidades p¨˛blicas y grandes contribuyentes. La tarifa de retenci¨®n depende de la actividad del sujeto o una tarifa m¨˘xima si no se conoce la actividad.CHIAPAS



CHIAPASivettguadalupe
?
This document lists the names of several photographers who have contributed photos to Haiku Deck presentations on şÝşÝߣShare, including Ted's photos, Mr. Theklan, Catedrales e Iglesias, nathangibbs, vicos, and Carlos Adampol. It encourages the reader to get started creating their own Haiku Deck presentation.plac



placLyn Anthony-Calhoun
?
Lyn Anthony-Calhoun is a human resources professional with over 10 years of experience in office management and human resources for private sector organizations. She has a background in meeting facilitation, OSHA compliance, expense management, event planning, performance reviews, policies and procedures, technology, and vendor relationships. Currently, she works as a Business Manager for Promise Dental in Nashville, TN where her responsibilities include updating HR policies and manuals, employee relations, analyzing practice performance, meeting planning, and ensuring regulatory compliance.

Presentaci¨®n 1Nayeli Thu Real Mami
?
Este documento describe tres tipos de mantenimiento de computadoras: mantenimiento correctivo, que ocurre despu¨¦s de una falla; mantenimiento preventivo, que se realiza peri¨®dicamente antes de una falla; y mantenimiento del PC, que incluye rutinas como diagn¨®stico, limpieza y desfragmentaci¨®n para mantener un rendimiento ¨®ptimo.

Mantenimiento de computadorasMariielys Moliina
?
El documento describe diferentes tipos de mantenimiento de computadoras, incluyendo mantenimiento preventivo de nivel 1 y 2, que involucran limpieza f¨Şsica y de software para prevenir fallas. Tambi¨¦n describe mantenimiento preventivo pasivo para proteger equipos de factores ambientales, y mantenimiento correctivo que incluye limpieza y reemplazo de partes con fallas. Se recomienda mantenimiento cada mes para equipos usados 8 horas diarias, cada 6 meses para equipos dom¨¦sticos, y anual para equipos de uso espor¨˘dico.

Los virus y vacunas informaticasVivianayara91
?
Los virus son programas que infectan computadores sin el conocimiento del usuario, alterando o destruyendo archivos. Los dispositivos se pueden infectar a trav¨¦s de mensajes, archivos adjuntos, sitios web sospechosos, USBs, descargas o anuncios. Las vacunas act¨˛an como filtros para detectar y desinfectar virus, comparando firmas de archivos de manera heur¨Şstica e invoc¨˘ndose ante actividad del sistema o usuario.

Fenomenos detransporteIsrael Flores
?
1) El documento describe el an¨˘lisis matem¨˘tico del flujo de agua sobre una superficie esf¨¦rica como una fuente ornamental. 2) Se establecen las ecuaciones de movimiento en coordenadas esf¨¦ricas para un fluido newtoniano y se asumen condiciones de estado estacionario y sin desplazamiento. 3) Luego de analizar cada componente y establecer condiciones de frontera, se obtiene una ecuaci¨®n que describe la velocidad del fluido en funci¨®n de la posici¨®n.

Conflicto laboralMiguel Guerrero
?
Este documento describe los tipos de conflictos que pueden ocurrir en entornos laborales, incluyendo entre trabajadores y patrones, solo entre trabajadores, y entre patrones. Tambi¨¦n discute los efectos negativos como problemas de salud y baja productividad, pero tambi¨¦n efectos positivos como mejor comunicaci¨®n. Finalmente, propone mecanismos para resolver conflictos como negociaci¨®n, mediaci¨®n, y acudir a un tercero.Comic strip



Comic stripWikimedia Italia
?
Comic strip
Max Olla per "SGRUNT! Carta e bit al servizio dell'open culture", Festival delle Libert¨¤ Digitali 2010Corridors of Power: Constitutional Power and Architecture



Corridors of Power: Constitutional Power and ArchitectureSanjana Hattotuwa
?
Overview of the 'Corridors of Power' exhibition, delivered to Friedrich Naumann Foundation for Freedom in Colombo, Sri Lanka. 

La Web 2.0 en el proceso de ense?anza - aprendizaje AlejandraGarduno
?
Este documento describe las herramientas digitales de la Web 2.0 y su aplicaci¨®n en la educaci¨®n. Explica conceptos clave como la Web 2.0, sus principios y ventajas, as¨Ş como ejemplos de herramientas como redes sociales, blogs y wikis que pueden apoyar los procesos de ense?anza y aprendizaje. Tambi¨¦n presenta algunas actividades did¨˘cticas dise?adas para ense?ar conceptos b¨˘sicos de tecnolog¨Şas de informaci¨®n a estudiantes y evaluar sus conocimientos sobre el uso de estas herramientas.More from peggy Williams (6)
Landformskrish



Landformskrishpeggy Williams
?
The document discusses different landforms such as volcanoes, rivers, caves, caverns, islands, and waterfalls. Volcanoes create new land while rivers are flowing bodies of water. Caves are holes in the ground that can contain inner caverns, and islands are landmasses surrounded by water. Waterfalls are where water cascades over rocks from a height.Landform jeremiah clark



Landform jeremiah clarkpeggy Williams
?
Mountains are formed when two landmasses collide, caves are often made of limestone and erode out of rock over time. Rivers carry water from higher elevations down to the ocean, creating features like waterfalls where the moving water experiences a dramatic drop in elevation due to gravity. Plains are wide open flat lands while valleys are lower areas of land situated between mountains.Landform emilio



Landform emiliopeggy Williams
?
students created a powerpoint identifying the major landforms we discussed in class.Landforms emmanual



Landforms emmanualpeggy Williams
?
This document defines and describes various landforms including oceans, islands, valleys, mountains, caves, glaciers, streams, rivers, plains, and isthmus. It notes that oceans include the Pacific, Indian, and Southern Oceans. Islands are land surrounded by water, valleys are areas between hills, and mountains may form from volcanoes. Caves are formed from limestone and rock, and some glaciers contain caves. Streams flow like paths of water and rivers lead to the sea. Plains are very flat land, while an isthmus connects two land areas surrounded by water.Land forms cayden



Land forms caydenpeggy Williams
?
students created a powerpoint identifying the major landforms we discussed in class.Landforms hollykostecki



Landforms hollykosteckipeggy Williams
?
Volcanoes form at tectonic plate boundaries and can erupt with lava that travels for miles, destroying everything in its path. Caverns contain stalagmites and stalactites and people visit and modify them for tourism. Bodies of water like oceans, lakes and rivers cover 75% of the Earth and are important for sustaining life. Glaciers are found in cold places and are melting due to rising ocean temperatures, which can cause them to crack and calve large icebergs. Mountains are formed by earthquakes pushing the ground upward and are made of solid rock rather than hollow magma chambers like volcanoes.Recently uploaded (20)
RRB ALP CBT 2 Mechanic Motor Vehicle Question Paper (MMV Exam MCQ)



RRB ALP CBT 2 Mechanic Motor Vehicle Question Paper (MMV Exam MCQ)SONU HEETSON
?
RRB ALP CBT 2 Mechanic Motor Vehicle Question Paper. MMV MCQ PDF Free Download for Railway Assistant Loco Pilot Exam.Azure Administrator Interview Questions By ScholarHat



Azure Administrator Interview Questions By ScholarHatScholarhat
?
Azure Administrator Interview Questions By ScholarHatEffective Product Variant Management in Odoo 18



Effective Product Variant Management in Odoo 18Celine George
?
In this slide weˇŻll discuss on the effective product variant management in Odoo 18. Odoo concentrates on managing product variations and offers a distinct area for doing so. Product variants provide unique characteristics like size and color to single products, which can be managed at the product template level for all attributes and variants or at the variant level for individual variants.Intellectual Honesty & Research Integrity.pptx



Intellectual Honesty & Research Integrity.pptxNidhiSharma495177
?
Research Publication & Ethics contains a chapter on Intellectual Honesty and Research Integrity.
Different case studies of intellectual dishonesty and integrity were discussed.One Click RFQ Cancellation in Odoo 18 - Odoo şÝşÝߣs



One Click RFQ Cancellation in Odoo 18 - Odoo şÝşÝߣsCeline George
?
In this slide, weˇŻll discuss the one click RFQ Cancellation in odoo 18. One-Click RFQ Cancellation in Odoo 18 is a feature that allows users to quickly and easily cancel Request for Quotations (RFQs) with a single click.Interim Guidelines for PMES-DM-17-2025-PPT.pptx



Interim Guidelines for PMES-DM-17-2025-PPT.pptxsirjeromemanansala
?
This is the latest issuance on PMES as replacement of RPMS. Kindly message me to gain full access of the presentation. Full-Stack .NET Developer Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHat



Full-Stack .NET Developer Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHatScholarhat
?
Full-Stack .NET Developer Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHatHow to Configure Recurring Revenue in Odoo 17 CRM



How to Configure Recurring Revenue in Odoo 17 CRMCeline George
?
This slide will represent how to configure Recurring revenue. Recurring revenue are the income generated at a particular interval. Typically, the interval can be monthly, yearly, or we can customize the intervals for a product or service based on its subscription or contract. BISNIS BERKAH BERANGKAT KE MEKKAH ISTIKMAL SYARIAH



BISNIS BERKAH BERANGKAT KE MEKKAH ISTIKMAL SYARIAHcoacharyasetiyaki
?
BISNIS BERKAH BERANGKAT KE MEKKAH ISTIKMAL SYARIAHMeeting the needs of modern students?, Selina McCoy



Meeting the needs of modern students?, Selina McCoyEconomic and Social Research Institute
?
NAPD Annual Symposium
ˇ°Equity in our Schools: Does the system deliver for all young people?ˇ±Entity Framework Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHat



Entity Framework Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHatScholarhat
?
Entity Framework Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHatDot NET Core Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHat



Dot NET Core Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHatScholarhat
?
Dot NET Core Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHatDr. Ansari Khurshid Ahmed- Factors affecting Validity of a Test.pptx



Dr. Ansari Khurshid Ahmed- Factors affecting Validity of a Test.pptxKhurshid Ahmed Ansari
?
Validity is an important characteristic of a test. A test having low validity is of little use. Validity is the accuracy with which a test measures whatever it is supposed to measure. Validity can be low, moderate or high. There are many factors which affect the validity of a test. If these factors are controlled, then the validity of the test can be maintained to a high level. In the power point presentation, factors affecting validity are discussed with the help of concrete examples.Azure Data Engineer Interview Questions By ScholarHat



Azure Data Engineer Interview Questions By ScholarHatScholarhat
?
Azure Data Engineer Interview Questions By ScholarHatLand forms sakeena saidou
- 2. Bodies of Waters ? Lakes, lakes are very large. They trail down really long. ? Oceans, Arctic, Atlantic, Pacific, Southern, and Indian ? Ponds, ponds are smaller then lakes. ? Rivers, rivers are like lakes. They are long and trail down. ? Coast, coast is when there is a part of land near the sea ? Lagoon, lagoon is a small fresh lake near a larger lake. ? Waterfalls, water that falls from a land. ? Peninsula, a piece of land almost surrounded by water
- 3. Volcano! Volcanoes can create new lands. It can also destroy lands. Volcanoes are very dangerous.
- 4. Caves Caves can be were bears and bats hide or live.
- 5. Glaciers Glaciers are moving ice on water.
- 6. Canyon








