lecture1.ppt
Download as PPT, PDF0 likes78 views
Ahhh baby jaan good morning sweet dreams my dear wife my love you too my jaan ho tum dimag me kuch kuch bhi nhi kiya h na to bol dena discharge ho gaya hai na aaj kal kya kr rhi hu me
1 of 20
Download to read offline


















Recommended
lecture1-230501075743-142343456580ac.ppt



lecture1-230501075743-142343456580ac.pptzulqarnain199841
Ã˝
density fucntional theory
Hohen kohn sham equationsDensity functional theory (DFT) and the concepts of the augmented-plane-wave ...



Density functional theory (DFT) and the concepts of the augmented-plane-wave ...ABDERRAHMANE REGGAD
Ã˝
Density functional theory (DFT) is a quantum mechanical method used to investigate the electronic structure of materials. The document discusses DFT and the linearized augmented plane wave plus local orbital (LAPW+lo) method implemented in the Wien2k software. Wien2k is widely used to study the properties of solids and surfaces using an all-electron, relativistic, and full-potential DFT approach. The document provides an overview of the theoretical foundations of DFT and LAPW methods as well as examples of applications studied with Wien2k.Electronic structure of strongly correlated materials



Electronic structure of strongly correlated materialsABDERRAHMANE REGGAD
Ã˝
This document provides an overview of density functional theory and methods for modeling strongly correlated materials. It discusses the limitations of standard DFT approaches like LDA for strongly correlated systems and introduces model Hamiltonians and correction methods like LDA+U, LDA+DMFT, self-interaction correction, and generalized transition state to better account for electron correlation effects. The document outlines the basic theory and approximations of DFT, including Kohn-Sham equations and the local density approximation, and discusses basis set approaches like plane waves, augmented plane waves, and pseudopotentials.Band theory



Band theoryballenzangana
Ã˝
This document discusses band theory and several models used to describe electron behavior in solids, including the free electron model, nearly free electron model, and tight binding model. It provides an overview of each model, including their assumptions and how they describe properties like electron energy and band gaps. The free electron model treats electrons as independent particles but fails to explain material properties. The nearly free electron model incorporates a periodic potential and allows electron wavefunctions and energy bands to be described. The tight binding model uses a superposition of atomic orbitals to approximate electron wavefunctions in solids where potential is strong.slides_cedric_weber_1.pdf



slides_cedric_weber_1.pdfsasdude1
Ã˝
This document provides an overview of Cedric Weber's background and research interests, which include dynamical mean field theory (DMFT) and its application to oxide materials. Some key points:
- Cedric Weber received his PhD in quantum magnetism and superconductivity from EPFL and has worked on DMFT at Rutgers and the University of Cambridge. He is currently a researcher at King's College London.
- His research focuses on developing DMFT software and studying phase diagrams of high-temperature superconductors and other oxide materials using techniques like DMFT, GW+DMFT, and the Bethe-Salpeter equation.
- He collaborates with theorists and experimentalists on topics like laserAtomic structure



Atomic structureChandan Singh
Ã˝
- The atom consists of a small, dense nucleus surrounded by an electron cloud.
- Electrons can only exist in certain discrete energy levels around the nucleus. Their wavelengths are determined by the principal quantum number.
- The Bohr model improved on earlier models by introducing energy levels and quantization, but had limitations. The quantum mechanical model treats electrons as waves and uses Schrodinger's equation.Quantum Chemistry II



Quantum Chemistry IIbaoilleach
Ã˝
This document summarizes several quantum mechanics methods for calculating molecular properties, including semi-empirical, density functional theory (DFT), and correlation methods. It discusses how semi-empirical methods approximate integrals to speed up calculations compared to Hartree-Fock. DFT is described as an alternative to wavefunction methods that uses the electron density. Popular DFT functionals and how they include exchange and correlation are outlined. Geometry optimization and vibrational frequency calculations are also summarized.Dft presentation



Dft presentationSaibalendu Sarkar
Ã˝
Density functional theory (DFT) provides an alternative approach to calculate properties of molecules by working with electron density rather than wave functions. DFT relies on two theorems linking the ground state energy and electron density. Approximations must be made for the exchange-correlation functional, with popular approximations including LDA, GGA, and hybrid functionals. DFT calculations can determine properties like molecular geometries, energies, vibrational frequencies, and more using software packages. While computationally efficient, DFT has limitations such as its reliance on approximate exchange-correlation functionals.Quantum course



Quantum courseFLI
Ã˝
Quantum chemistry is the application of quantum mechanics to solve problems in chemistry. It has been widely used in different branches of chemistry including physical chemistry, organic chemistry, analytical chemistry, and inorganic chemistry. The time-independent Schrödinger equation is central to quantum chemistry and can be used to model chemical systems like the particle in a box, harmonic oscillator, and hydrogen atom. Molecular orbital theory is also important in quantum chemistry for describing chemical bonding in molecules.NANO266 - Lecture 4 - Introduction to DFT



NANO266 - Lecture 4 - Introduction to DFTUniversity of California, San Diego
Ã˝
UCSD NANO 266 Quantum Mechanical Modelling of Materials and Nanostructures is a graduate class that provides students with a highly practical introduction to the application of first principles quantum mechanical simulations to model, understand and predict the properties of materials and nano-structures. The syllabus includes: a brief introduction to quantum mechanics and the Hartree-Fock and density functional theory (DFT) formulations; practical simulation considerations such as convergence, selection of the appropriate functional and parameters; interpretation of the results from simulations, including the limits of accuracy of each method. Several lab sessions provide students with hands-on experience in the conduct of simulations. A key aspect of the course is in the use of programming to facilitate calculations and analysis.Strongly Interacting Atoms in Optical Lattices



Strongly Interacting Atoms in Optical LatticesABDERRAHMANE REGGAD
Ã˝
- The document discusses strongly interacting atoms in optical lattices and lattice-induced Feshbach resonances.
- It presents exact calculations of two atoms in a 1D lattice and finds avoided crossings between molecular bands and continuum states that depend on the lattice quasimomentum.
- An effective Hamiltonian is constructed that qualitatively captures these effects and introduces a momentum-dependent atom-dimer coupling parameter.final_report



final_reportShudhashil Bharthuar
Ã˝
This document discusses a computational study of MAX phases using density functional theory. MAX phases are a group of materials that exhibit both metallic and ceramic properties. The study uses the WIEN2k software to calculate the electronic structure and properties of MAX phases like Cr2AlC and Cr2GaC from their density of states and band structure plots. Manganese is incorporated into the structures at varying concentrations to study their magnetic properties.finland.ppt



finland.pptRAMARATHI2
Ã˝
This document discusses challenges and open questions in nuclear density functional theory (DFT). It begins by providing background on DFT and how it has been applied to nuclei using approximations like the local density approximation. It then discusses questions around improving the nuclear energy density functional, including justifying terms from microscopic theory, improving treatment of pairing and beyond-mean-field correlations, and incorporating dynamics. The document concludes by emphasizing the need for focused theoretical efforts, international collaborations, and new experimental data to help address open questions in nuclear DFT.Gnp ch103-lecture notes



Gnp ch103-lecture notesRohan Jain
Ã˝
1) The document provides information about a physical chemistry course on bonding taught by Professor Naresh Patwari, including recommended textbooks, websites with course materials, and what topics will be covered in the course like quantum mechanics, atomic structure, and chemical bonding.
2) Key concepts from quantum mechanics that will be discussed include the particle-wave duality of light and matter demonstrated by experiments, Planck's hypothesis and the photoelectric effect, the de Broglie hypothesis and diffraction of electrons, and the Heisenberg uncertainty principle.
3) Historical models of the atom will also be examined, like the Rutherford model, Bohr's model, and how Schrodinger's wave equation improved our understanding ofPhotonics Intro



Photonics IntroAmir Hassan Firoozi
Ã˝
This document provides an introduction to photonic crystals, including:
- Photonic crystals are periodic electromagnetic structures that can possess photonic band gaps where light cannot propagate, analogous to electronic band gaps in solids.
- The propagation of electromagnetic waves in periodic media is governed by Bloch's theorem and results in photonic band structures and gaps similar to electronic band structures.
- Introducing defects in photonic crystals allows for localized electromagnetic states like waveguides and cavities, allowing the crystal to confine and control light.Binping xiao superconducting surface impedance under radiofrequency field



Binping xiao superconducting surface impedance under radiofrequency fieldthinfilmsworkshop
Ã˝
Based on BCS theory with moving Cooper pairs, the electron states distribution at 0 K and the probability of electron occupation with finite temperature have been derived and applied to anomalous skin effect theory to obtain the surface impedance of a superconductor under radiofrequency (RF) field. We present the numerical results for Nb and compare these with representative RF field-dependent effective surface resistance measurements from a 1.5 GHz resonant structure.4 b5lecture62008



4 b5lecture62008Prudhvi Bade
Ã˝
The document discusses the band structure of electrons in solids. It explains that when electrons are placed in a periodic potential, as in metals and semiconductors, the allowed energy levels split and form bands separated by band gaps. The nearly-free electron model is introduced to account for this band structure by treating electrons as interacting with a periodic lattice potential rather than being completely free. The key outcomes are that the energy-momentum relationship becomes a series of bands rather than continuous, and band gaps open up where electron states are forbidden. This distinguishes conductors, semiconductors and insulators.PART VII.1 - Quantum Electrodynamics



PART VII.1 - Quantum ElectrodynamicsMaurice R. TREMBLAY
Ã˝
The document discusses the development of quantum electrodynamics (QED) from its origins in Dirac's 1927 paper on the quantum theory of radiation. It provides an overview of the key topics covered in the subsequent chapters, including particles and fields, quantization of the electromagnetic field, Feynman diagrams, and renormalization in QED. The goal is to show how electrons and photons interact using quantum field theory by representing particles as excitations of underlying fields and developing perturbative techniques to calculate processes like scattering and radiation.Bp219 04-13-2011



Bp219 04-13-2011waddling
Ã˝
This document provides an overview of a protein crystallography course taught by Robert Stroud. The course will cover:
1. Understanding crystallography and protein structures through an interactive laboratory course where students crystallize a protein and determine its structure.
2. Visiting the Advanced Light Source facility to collect X-ray diffraction data.
3. Key topics covered include crystal lattices, X-ray diffraction, determining atomic structures using X-ray crystallography, and solving the phase problem.
4. Resources provided include computing resources, structure determination software, and online courses and references.1310.1421v3



1310.1421v3William Long
Ã˝
This document discusses a theoretical study of the Casimir torque that can arise between plates with discontinuous dielectric properties. Specifically, it considers plates that are bisected or quadrisected into regions of different dielectric constants. It provides background on the Casimir effect and derives an expression for the Casimir torque. The rest of the document discusses how this system differs from other Casimir systems that have been studied and outlines the specific plate configurations that are analyzed.Dynamics of Twointeracting Electronsinthree-Dimensional Lattice



Dynamics of Twointeracting Electronsinthree-Dimensional LatticeIOSR Journals
Ã˝
The physical property of strongly correlated electrons on a three-dimensional (3D) 3 x 3 x 3 cluster of the simple cubic lattice is here presented.In the work we developed the unit step Hamiltonian as a solution to the single band Hubbard Hamiltonian for the case of two electrons interaction in a finite three dimensional lattice. The approximation to the Hubbard Hamiltonian study is actually necessary because of the strong limitation and difficulty pose by the Hubbard Hamiltonian as we move away from finite - size lattices to larger N - dimensional lattices. Thus this work has provided a means of overcoming the finite - size lattice defects as we pass on to a higher dimension. We have shown in this study, that the repulsive Coulomb interaction which in part leads to the strong electronic correlations, would indicate that the two electron system prefer not to condense into s-wave superconducting singlet state (s = 0), at high positive values of the interaction strength. This study reveals that when the Coulomb interaction is zero, that is, for free electron system (non-interacting), thevariational parameters which describe the probability distribution of lattice electron system is the same. The spectra intensity for on-site electrons is zero for all values of the interaction strengthPart VIII - The Standard Model



Part VIII - The Standard ModelMaurice R. TREMBLAY
Ã˝
The document summarizes key aspects of the Standard Model of particle physics. It describes how the Standard Model accounts for fundamental particles like quarks and leptons that interact via four fundamental forces - gravitation, electromagnetism, weak force, and strong force. These interactions are mediated by exchange of spin-1/2 bosons. The Standard Model has been very successful in explaining experimental observations, but questions remain like incorporating gravity and the origin of particle masses.Ab initio md



Ab initio mdyudhaarman
Ã˝
The document discusses ab initio molecular dynamics simulation methods. It begins by introducing molecular dynamics and Monte Carlo simulations using empirical potentials. It then describes limitations of empirical potentials and the need for ab initio molecular dynamics which calculates the potential from quantum mechanics. The document outlines several ab initio molecular dynamics methods including Ehrenfest molecular dynamics, Born-Oppenheimer molecular dynamics, and Car-Parrinello molecular dynamics. It provides details on how these methods treat the quantum mechanical potential and classical nuclear motion.Fourier transform in X-ray crystallography .ppt



Fourier transform in X-ray crystallography .pptRadhyesham
Ã˝
The Fourier transform connects the diffraction pattern of X-rays scattered by a crystal to the electron density distribution within the crystal's unit cell. The structure factors obtained from diffraction intensities represent the Fourier transform of the electron density. However, the phases of the structure factors are lost during data collection, posing the phase problem. Techniques like isomorphous replacement, multiple wavelength anomalous diffraction, and molecular replacement aim to determine the missing phase information and allow calculation of electron density maps revealing a crystal's structure.Dental Radiography machine.ppt



Dental Radiography machine.pptAvneeshKumar164042
Ã˝
Hd video download kar raha tha so jao or phon to utha lete h to delay ho gya thoda sa station se school me kon h ye to bta de yrr bhej na dev bhai ko bhi nhi pad rha h to kya koi pareshani hai to bata deta hu na kabhi to delay ho gya thoda telagana.ppt



telagana.pptAvneeshKumar164042
Ã˝
Do not not well don't don't provide me kon ho gaya hoya tha ki tu apna kam kam khaya karo kuch kuch bole hi galti se ho gaya hoya tha ki kal jayenge to More Related Content
Similar to lecture1.ppt (20)
Atomic structure



Atomic structureChandan Singh
Ã˝
- The atom consists of a small, dense nucleus surrounded by an electron cloud.
- Electrons can only exist in certain discrete energy levels around the nucleus. Their wavelengths are determined by the principal quantum number.
- The Bohr model improved on earlier models by introducing energy levels and quantization, but had limitations. The quantum mechanical model treats electrons as waves and uses Schrodinger's equation.Quantum Chemistry II



Quantum Chemistry IIbaoilleach
Ã˝
This document summarizes several quantum mechanics methods for calculating molecular properties, including semi-empirical, density functional theory (DFT), and correlation methods. It discusses how semi-empirical methods approximate integrals to speed up calculations compared to Hartree-Fock. DFT is described as an alternative to wavefunction methods that uses the electron density. Popular DFT functionals and how they include exchange and correlation are outlined. Geometry optimization and vibrational frequency calculations are also summarized.Dft presentation



Dft presentationSaibalendu Sarkar
Ã˝
Density functional theory (DFT) provides an alternative approach to calculate properties of molecules by working with electron density rather than wave functions. DFT relies on two theorems linking the ground state energy and electron density. Approximations must be made for the exchange-correlation functional, with popular approximations including LDA, GGA, and hybrid functionals. DFT calculations can determine properties like molecular geometries, energies, vibrational frequencies, and more using software packages. While computationally efficient, DFT has limitations such as its reliance on approximate exchange-correlation functionals.Quantum course



Quantum courseFLI
Ã˝
Quantum chemistry is the application of quantum mechanics to solve problems in chemistry. It has been widely used in different branches of chemistry including physical chemistry, organic chemistry, analytical chemistry, and inorganic chemistry. The time-independent Schrödinger equation is central to quantum chemistry and can be used to model chemical systems like the particle in a box, harmonic oscillator, and hydrogen atom. Molecular orbital theory is also important in quantum chemistry for describing chemical bonding in molecules.NANO266 - Lecture 4 - Introduction to DFT



NANO266 - Lecture 4 - Introduction to DFTUniversity of California, San Diego
Ã˝
UCSD NANO 266 Quantum Mechanical Modelling of Materials and Nanostructures is a graduate class that provides students with a highly practical introduction to the application of first principles quantum mechanical simulations to model, understand and predict the properties of materials and nano-structures. The syllabus includes: a brief introduction to quantum mechanics and the Hartree-Fock and density functional theory (DFT) formulations; practical simulation considerations such as convergence, selection of the appropriate functional and parameters; interpretation of the results from simulations, including the limits of accuracy of each method. Several lab sessions provide students with hands-on experience in the conduct of simulations. A key aspect of the course is in the use of programming to facilitate calculations and analysis.Strongly Interacting Atoms in Optical Lattices



Strongly Interacting Atoms in Optical LatticesABDERRAHMANE REGGAD
Ã˝
- The document discusses strongly interacting atoms in optical lattices and lattice-induced Feshbach resonances.
- It presents exact calculations of two atoms in a 1D lattice and finds avoided crossings between molecular bands and continuum states that depend on the lattice quasimomentum.
- An effective Hamiltonian is constructed that qualitatively captures these effects and introduces a momentum-dependent atom-dimer coupling parameter.final_report



final_reportShudhashil Bharthuar
Ã˝
This document discusses a computational study of MAX phases using density functional theory. MAX phases are a group of materials that exhibit both metallic and ceramic properties. The study uses the WIEN2k software to calculate the electronic structure and properties of MAX phases like Cr2AlC and Cr2GaC from their density of states and band structure plots. Manganese is incorporated into the structures at varying concentrations to study their magnetic properties.finland.ppt



finland.pptRAMARATHI2
Ã˝
This document discusses challenges and open questions in nuclear density functional theory (DFT). It begins by providing background on DFT and how it has been applied to nuclei using approximations like the local density approximation. It then discusses questions around improving the nuclear energy density functional, including justifying terms from microscopic theory, improving treatment of pairing and beyond-mean-field correlations, and incorporating dynamics. The document concludes by emphasizing the need for focused theoretical efforts, international collaborations, and new experimental data to help address open questions in nuclear DFT.Gnp ch103-lecture notes



Gnp ch103-lecture notesRohan Jain
Ã˝
1) The document provides information about a physical chemistry course on bonding taught by Professor Naresh Patwari, including recommended textbooks, websites with course materials, and what topics will be covered in the course like quantum mechanics, atomic structure, and chemical bonding.
2) Key concepts from quantum mechanics that will be discussed include the particle-wave duality of light and matter demonstrated by experiments, Planck's hypothesis and the photoelectric effect, the de Broglie hypothesis and diffraction of electrons, and the Heisenberg uncertainty principle.
3) Historical models of the atom will also be examined, like the Rutherford model, Bohr's model, and how Schrodinger's wave equation improved our understanding ofPhotonics Intro



Photonics IntroAmir Hassan Firoozi
Ã˝
This document provides an introduction to photonic crystals, including:
- Photonic crystals are periodic electromagnetic structures that can possess photonic band gaps where light cannot propagate, analogous to electronic band gaps in solids.
- The propagation of electromagnetic waves in periodic media is governed by Bloch's theorem and results in photonic band structures and gaps similar to electronic band structures.
- Introducing defects in photonic crystals allows for localized electromagnetic states like waveguides and cavities, allowing the crystal to confine and control light.Binping xiao superconducting surface impedance under radiofrequency field



Binping xiao superconducting surface impedance under radiofrequency fieldthinfilmsworkshop
Ã˝
Based on BCS theory with moving Cooper pairs, the electron states distribution at 0 K and the probability of electron occupation with finite temperature have been derived and applied to anomalous skin effect theory to obtain the surface impedance of a superconductor under radiofrequency (RF) field. We present the numerical results for Nb and compare these with representative RF field-dependent effective surface resistance measurements from a 1.5 GHz resonant structure.4 b5lecture62008



4 b5lecture62008Prudhvi Bade
Ã˝
The document discusses the band structure of electrons in solids. It explains that when electrons are placed in a periodic potential, as in metals and semiconductors, the allowed energy levels split and form bands separated by band gaps. The nearly-free electron model is introduced to account for this band structure by treating electrons as interacting with a periodic lattice potential rather than being completely free. The key outcomes are that the energy-momentum relationship becomes a series of bands rather than continuous, and band gaps open up where electron states are forbidden. This distinguishes conductors, semiconductors and insulators.PART VII.1 - Quantum Electrodynamics



PART VII.1 - Quantum ElectrodynamicsMaurice R. TREMBLAY
Ã˝
The document discusses the development of quantum electrodynamics (QED) from its origins in Dirac's 1927 paper on the quantum theory of radiation. It provides an overview of the key topics covered in the subsequent chapters, including particles and fields, quantization of the electromagnetic field, Feynman diagrams, and renormalization in QED. The goal is to show how electrons and photons interact using quantum field theory by representing particles as excitations of underlying fields and developing perturbative techniques to calculate processes like scattering and radiation.Bp219 04-13-2011



Bp219 04-13-2011waddling
Ã˝
This document provides an overview of a protein crystallography course taught by Robert Stroud. The course will cover:
1. Understanding crystallography and protein structures through an interactive laboratory course where students crystallize a protein and determine its structure.
2. Visiting the Advanced Light Source facility to collect X-ray diffraction data.
3. Key topics covered include crystal lattices, X-ray diffraction, determining atomic structures using X-ray crystallography, and solving the phase problem.
4. Resources provided include computing resources, structure determination software, and online courses and references.1310.1421v3



1310.1421v3William Long
Ã˝
This document discusses a theoretical study of the Casimir torque that can arise between plates with discontinuous dielectric properties. Specifically, it considers plates that are bisected or quadrisected into regions of different dielectric constants. It provides background on the Casimir effect and derives an expression for the Casimir torque. The rest of the document discusses how this system differs from other Casimir systems that have been studied and outlines the specific plate configurations that are analyzed.Dynamics of Twointeracting Electronsinthree-Dimensional Lattice



Dynamics of Twointeracting Electronsinthree-Dimensional LatticeIOSR Journals
Ã˝
The physical property of strongly correlated electrons on a three-dimensional (3D) 3 x 3 x 3 cluster of the simple cubic lattice is here presented.In the work we developed the unit step Hamiltonian as a solution to the single band Hubbard Hamiltonian for the case of two electrons interaction in a finite three dimensional lattice. The approximation to the Hubbard Hamiltonian study is actually necessary because of the strong limitation and difficulty pose by the Hubbard Hamiltonian as we move away from finite - size lattices to larger N - dimensional lattices. Thus this work has provided a means of overcoming the finite - size lattice defects as we pass on to a higher dimension. We have shown in this study, that the repulsive Coulomb interaction which in part leads to the strong electronic correlations, would indicate that the two electron system prefer not to condense into s-wave superconducting singlet state (s = 0), at high positive values of the interaction strength. This study reveals that when the Coulomb interaction is zero, that is, for free electron system (non-interacting), thevariational parameters which describe the probability distribution of lattice electron system is the same. The spectra intensity for on-site electrons is zero for all values of the interaction strengthPart VIII - The Standard Model



Part VIII - The Standard ModelMaurice R. TREMBLAY
Ã˝
The document summarizes key aspects of the Standard Model of particle physics. It describes how the Standard Model accounts for fundamental particles like quarks and leptons that interact via four fundamental forces - gravitation, electromagnetism, weak force, and strong force. These interactions are mediated by exchange of spin-1/2 bosons. The Standard Model has been very successful in explaining experimental observations, but questions remain like incorporating gravity and the origin of particle masses.Ab initio md



Ab initio mdyudhaarman
Ã˝
The document discusses ab initio molecular dynamics simulation methods. It begins by introducing molecular dynamics and Monte Carlo simulations using empirical potentials. It then describes limitations of empirical potentials and the need for ab initio molecular dynamics which calculates the potential from quantum mechanics. The document outlines several ab initio molecular dynamics methods including Ehrenfest molecular dynamics, Born-Oppenheimer molecular dynamics, and Car-Parrinello molecular dynamics. It provides details on how these methods treat the quantum mechanical potential and classical nuclear motion.Fourier transform in X-ray crystallography .ppt



Fourier transform in X-ray crystallography .pptRadhyesham
Ã˝
The Fourier transform connects the diffraction pattern of X-rays scattered by a crystal to the electron density distribution within the crystal's unit cell. The structure factors obtained from diffraction intensities represent the Fourier transform of the electron density. However, the phases of the structure factors are lost during data collection, posing the phase problem. Techniques like isomorphous replacement, multiple wavelength anomalous diffraction, and molecular replacement aim to determine the missing phase information and allow calculation of electron density maps revealing a crystal's structure.More from AvneeshKumar164042 (20)
Dental Radiography machine.ppt



Dental Radiography machine.pptAvneeshKumar164042
Ã˝
Hd video download kar raha tha so jao or phon to utha lete h to delay ho gya thoda sa station se school me kon h ye to bta de yrr bhej na dev bhai ko bhi nhi pad rha h to kya koi pareshani hai to bata deta hu na kabhi to delay ho gya thoda telagana.ppt



telagana.pptAvneeshKumar164042
Ã˝
Do not not well don't don't provide me kon ho gaya hoya tha ki tu apna kam kam khaya karo kuch kuch bole hi galti se ho gaya hoya tha ki kal jayenge to BholuMNNIT.ppt



BholuMNNIT.pptAvneeshKumar164042
Ã˝
Vi ni in 12 sb me kon sa h ye batao sahi hai kya koi baat karne ka man kar rahe hai tab kehti hu ab sone jaa rahe the kya aap ko meri galti nhi h yrr bhej do bhai kya koi 13-Ling-21---Lecture-12b---Language-Thought-and-Culture.ppt



13-Ling-21---Lecture-12b---Language-Thought-and-Culture.pptAvneeshKumar164042
Ã˝
Xm achhi h k tu meri galti hai kya ji pagaliya ho gya h to kya kar rahi ho kya baat hai bhai bahut din m nhi hai kya mere pass nhi hai jo poochh rahe hai tab se chen nhi h to Hypertension.ppt



Hypertension.pptAvneeshKumar164042
Ã˝
Vk gmailcomcom and care Educate the ‘at the hell is not known meaning in 12 hindi meaning of the positive thought ke liye liye mana kiya hai maine us se baat karunga to delay ho gya h kya mere se baat GenerationofXRays.ppt



GenerationofXRays.pptAvneeshKumar164042
Ã˝
This document discusses the generation of X-rays through bremsstrahlung and characteristic radiation processes. It describes the components of an X-ray tube including the cathode, anode, housing and generator. The document explains how X-rays are produced when electrons are accelerated toward the anode, and the factors that determine the spectrum of the emitted X-rays such as tube voltage and target material. It also summarizes key concepts in X-ray generation including filtration, collimation, focal spot size and generator design.2-180318193019.pdf



2-180318193019.pdfAvneeshKumar164042
Ã˝
The heart is a hollow muscular organ located in the mediastinum. It has 4 chambers - right atrium, left atrium, right ventricle, and left ventricle. The heart is divided by septa into these chambers. The heart has surfaces including the sternocostal surface and diaphragmatic surface. Arterial blood supply comes from the right and left coronary arteries. Venous drainage occurs through the coronary sinus and associated veins.xrayproductionandproperties-171229054704.pdf



xrayproductionandproperties-171229054704.pdfAvneeshKumar164042
Ã˝
Wilhelm Roentgen discovered x-rays in 1895 while studying cathode rays. He observed that a mysterious type of radiation was produced when electrons interacted with glass that could pass through objects and be detected outside the tube. X-rays are produced when high-energy electrons generated by an x-ray tube strike a metal target. They have properties such as being invisible, having no mass, and being able to pass through soft tissue but be absorbed by bone and metal. X-rays are used in medical imaging due to these properties allowing visualization of internal structures.Dressen-RSA-2019-preconference-data-workshop-copy.pptx



Dressen-RSA-2019-preconference-data-workshop-copy.pptxAvneeshKumar164042
Ã˝
This document provides an overview of a preconference day at the RSA 2019 conference in Toronto, including presentations on mapping projects and tools like OpenRefine, TimelineJS, Palladio, and CARTO. It then provides detailed instructions on how to use OpenRefine for cleaning data, transforming values, enriching data by retrieving information from external sources like Wikidata, and exporting cleaned data. It also gives an overview of several timeline tools and an example of creating a timeline in TimelineJS using data from a Botticelli spreadsheet.TR-069_Overview.ppt



TR-069_Overview.pptAvneeshKumar164042
Ã˝
TR-069 is a protocol for communication between customer premise equipment (CPE) and an auto-configuration server (ACS) that allows for secure auto-configuration and management of CPE devices. It provides a common platform for service providers to remotely manage all CPE devices through the internet, regardless of manufacturer. Benefits include reduced costs through centralized configuration, troubleshooting, and monitoring of devices. While it aims to standardize management, interpretation challenges remain from its technical complexity across network layers. TR-069 continues expanding to incorporate new in-home technologies as the types of services provided evolves.barbados-day1-presentation_blending.pptx



barbados-day1-presentation_blending.pptxAvneeshKumar164042
Ã˝
The document discusses EU blending frameworks for development projects. It begins by defining blending as the strategic use of grants to mobilize financing from partner financial institutions. It then outlines the goals and forms of EU blending, including direct investment grants, interest rate subsidies, and technical assistance grants. The document also details the EU blending facilities, project cycle, roles of different entities, application process, and responsibilities for decision making, contracting, and monitoring of blended projects.Capacity Development Program for Investment Promotion Agencies of the LDCs by...



Capacity Development Program for Investment Promotion Agencies of the LDCs by...AvneeshKumar164042
Ã˝
This document discusses a capacity development program for investment promotion agencies in least developed countries. It notes that international agreements and reviews have emphasized the importance of strengthening investment promotion regimes and IPAs in LDCs. However, FDI flows to LDCs have declined in recent years and are still concentrated in extractive industries. The objectives of the capacity development program are to strengthen the strategic orientation of IPAs, improve collaboration between IPAs and development partners, and enhance business environments and investment conditions to attract more beneficial types of investment. The program aims to address challenges such as limited IPA effectiveness, information failures, and capacity constraints facing LDC entrepreneurs.BCH_6.4_international Business_week 4_vartika_FDI.pptx



BCH_6.4_international Business_week 4_vartika_FDI.pptxAvneeshKumar164042
Ã˝
FDI involves direct investment in facilities and assets in a foreign country, generally taking a long-term controlling stake. FPI is short-term investment in foreign financial assets like stocks for profit, without control. FDI has greater impact on economic growth through job creation and technology transfer, while FPI gives impetus to financial markets. FDI can be inward, outward, greenfield starting new operations, mergers and acquisitions of existing ventures, or brownfield combining both. It is classified by direction, target industry, and motive like resource-seeking, market-seeking, and efficiency-seeking.2) Infective endocarditis .pptx



2) Infective endocarditis .pptxAvneeshKumar164042
Ã˝
This document provides an overview of infective endocarditis (IE), including definitions, pathogenesis, risk factors, clinical presentation, diagnosis, treatment, and complications. IE is an infection of the inner lining of the heart chambers or valves. It is classified as either native valve IE, prosthetic valve IE, IE in intravenous drug users, or nosocomial IE. Common causes are staphylococci and streptococci bacteria. Diagnosis involves blood cultures, echocardiography to identify vegetations, and applying the Duke criteria. Complications include embolisms, heart failure, abscesses, and immune complex disease. Treatment involves prolonged antibiotic therapy, and surgery may be needed for complications or refractory infection.Sinusitis.ppt



Sinusitis.pptAvneeshKumar164042
Ã˝
Sinusitis is an infection of the sinuses caused by viruses or bacteria. Common symptoms include headaches, difficulty breathing through the nose, facial pain, and thick colored drainage. Over-the-counter decongestants and antihistamines can help relieve symptoms, but if symptoms persist for more than a few days or worsen, a medical provider should be seen. Proper treatment helps clear the sinuses and relieve discomfort.Arterial Blood Gas.ppt1.ppt



Arterial Blood Gas.ppt1.pptAvneeshKumar164042
Ã˝
This document discusses blood gas analysis and clinical interpretation. It begins by outlining common errors in blood gas sampling and discusses the components of a blood gas analysis. It then provides steps for analyzing blood gas results, including calculating the anion gap and delta gap to identify specific acid-base disorders. Examples are provided to demonstrate how to use these steps and calculations to interpret blood gas results and determine if findings indicate a respiratory or metabolic disorder and if compensation is appropriate. Causes of anion gap and non-anion gap metabolic acidosis are also reviewed.Chapter15.ppt



Chapter15.pptAvneeshKumar164042
Ã˝
Running late! ‚è∞ Will be there in a couple of minutes üèÉ
My address is …
My email is …
My phone number is +91…
Good morning! üôèüèªüíêüåû
I'll call you back soon ü§ô
Running late! ‚è∞ Will be there in a couple of minutes üèÉ
Running late! ‚è∞ Will be there in a couple of minutes üèÉ
My address is …
My email is …
Running late! ‚è∞ Will be there in a couple of minutes üèÉ
I'll call you back soon ü§ô
Good morning! üôèüèªüíêüåû
Running late! ‚è∞ Will be there in a couple of minutes üèÉ
My address is …
My email is …
My address is …
I'll call you back soon ü§ô
I'll call you back soon ü§ô
Chapter_021.pptx



Chapter_021.pptxAvneeshKumar164042
Ã˝
Express Love, care & happiness with Bobble Keyboard. Unlimited Stickers, GIFs & Poptext. Download üëá #BobbleKeyboard
MakeMyBobble.in/welcome
24_lecture_pptEK.ppt



24_lecture_pptEK.pptAvneeshKumar164042
Ã˝
This document summarizes several bacterial and fungal pathogens that can cause wound infections. Staphylococcus aureus is the leading cause and produces virulence factors like coagulase and protein A. Pseudomonas aeruginosa commonly causes nosocomial infections through drug resistance. Clostridium tetani causes tetanus through tetanospasmin toxin. Treatment involves vaccination, antitoxin, and antibiotics depending on the pathogen.Soft-Skills-Usman- Ghani-Akbani-for-participants.pptx



Soft-Skills-Usman- Ghani-Akbani-for-participants.pptxAvneeshKumar164042
Ã˝
Personal grooming involves maintaining a clean, pleasant, and attractive appearance through practices like keeping hair clean and styled, nails trimmed, skin and teeth clean, and wearing appropriate dress including makeup depending on one's field. Proper grooming promotes positive perceptions of professionalism, sophistication, intelligence, credibility, reliability, and respect. It also involves interpersonal communication skills like eye contact, posture, gestures, facial expressions, voice, language, dress, humor, and being authentic. Soft skills refer to personality traits, social graces, communication abilities, and other personal attributes that facilitate relationships and interactions with other people. They include both self-motivation skills and interaction skills important for career success.Capacity Development Program for Investment Promotion Agencies of the LDCs by...



Capacity Development Program for Investment Promotion Agencies of the LDCs by...AvneeshKumar164042
Ã˝
Recently uploaded (20)
Rass MELAI : an Internet MELA Quiz Finals - El Dorado 2025



Rass MELAI : an Internet MELA Quiz Finals - El Dorado 2025Conquiztadors- the Quiz Society of Sri Venkateswara College
Ã˝
Finals of Rass MELAI : a Music, Entertainment, Literature, Arts and Internet Culture Quiz organized by Conquiztadors, the Quiz society of Sri Venkateswara College under their annual quizzing fest El Dorado 2025. Mate, a short story by Kate Grenvile.pptx



Mate, a short story by Kate Grenvile.pptxLiny Jenifer
Ã˝
A powerpoint presentation on the short story Mate by Kate Greenville. This presentation provides information on Kate Greenville, a character list, plot summary and critical analysis of the short story.Adventure Activities Final By H R Gohil Sir



Adventure Activities Final By H R Gohil SirGUJARATCOMMERCECOLLE
Ã˝
Adventure Activities Final By H R Gohil SirKaun TALHA quiz Prelims - El Dorado 2025



Kaun TALHA quiz Prelims - El Dorado 2025Conquiztadors- the Quiz Society of Sri Venkateswara College
Ã˝
Prelims of Kaun TALHA : a Travel, Architecture, Lifestyle, Heritage and Activism quiz, organized by Conquiztadors, the Quiz society of Sri Venkateswara College under their annual quizzing fest El Dorado 2025. Year 10 The Senior Phase Session 3 Term 1.pptx



Year 10 The Senior Phase Session 3 Term 1.pptxmansk2
Ã˝
Year 10 The Senior Phase Session 3 Term 1.pptxComputer Application in Business (commerce)



Computer Application in Business (commerce)Sudar Sudar
Ã˝
The main objectives
1. To introduce the concept of computer and its various parts. 2. To explain the concept of data base management system and Management information system.
3. To provide insight about networking and basics of internet
Recall various terms of computer and its part
Understand the meaning of software, operating system, programming language and its features
Comparing Data Vs Information and its management system Understanding about various concepts of management information system
Explain about networking and elements based on internet
1. Recall the various concepts relating to computer and its various parts
2 Understand the meaning of software’s, operating system etc
3 Understanding the meaning and utility of database management system
4 Evaluate the various aspects of management information system
5 Generating more ideas regarding the use of internet for business purpose The Story Behind the Abney Park Restoration Project by Tom Walker



The Story Behind the Abney Park Restoration Project by Tom WalkerHistory of Stoke Newington
Ã˝
Presented at the 24th Stoke Newington History Talks event on 27th Feb 2025
https://stokenewingtonhistory.com/stoke-newington-history-talks/Rass MELAI : an Internet MELA Quiz Prelims - El Dorado 2025



Rass MELAI : an Internet MELA Quiz Prelims - El Dorado 2025Conquiztadors- the Quiz Society of Sri Venkateswara College
Ã˝
Prelims of Rass MELAI : a Music, Entertainment, Literature, Arts and Internet Culture Quiz organized by Conquiztadors, the Quiz society of Sri Venkateswara College under their annual quizzing fest El Dorado 2025. N.C. DPI's 2023 Language Diversity Briefing



N.C. DPI's 2023 Language Diversity BriefingMebane Rash
Ã˝
The number of languages spoken in NC public schools.Blind Spots in AI and Formulation Science Knowledge Pyramid (Updated Perspect...



Blind Spots in AI and Formulation Science Knowledge Pyramid (Updated Perspect...Ajaz Hussain
Ã˝
This presentation delves into the systemic blind spots within pharmaceutical science and regulatory systems, emphasizing the significance of "inactive ingredients" and their influence on therapeutic equivalence. These blind spots, indicative of normalized systemic failures, go beyond mere chance occurrences and are ingrained deeply enough to compromise decision-making processes and erode trust.
Historical instances like the 1938 FD&C Act and the Generic Drug Scandals underscore how crisis-triggered reforms often fail to address the fundamental issues, perpetuating inefficiencies and hazards.
The narrative advocates a shift from reactive crisis management to proactive, adaptable systems prioritizing continuous enhancement. Key hurdles involve challenging outdated assumptions regarding bioavailability, inadequately funded research ventures, and the impact of vague language in regulatory frameworks.
The rise of large language models (LLMs) presents promising solutions, albeit with accompanying risks necessitating thorough validation and seamless integration.
Tackling these blind spots demands a holistic approach, embracing adaptive learning and a steadfast commitment to self-improvement. By nurturing curiosity, refining regulatory terminology, and judiciously harnessing new technologies, the pharmaceutical sector can progress towards better public health service delivery and ensure the safety, efficacy, and real-world impact of drug products.The Battle of Belgrade Road: A WW1 Street Renaming Saga by Amir Dotan



The Battle of Belgrade Road: A WW1 Street Renaming Saga by Amir DotanHistory of Stoke Newington
Ã˝
Presented at the 24th Stoke Newington History Talks event on 27th Feb 2025
https://stokenewingtonhistory.com/stoke-newington-history-talks/Useful environment methods in Odoo 18 - Odoo ∫›∫›fl£s



Useful environment methods in Odoo 18 - Odoo ∫›∫›fl£sCeline George
Ã˝
In this slide we’ll discuss on the useful environment methods in Odoo 18. In Odoo 18, environment methods play a crucial role in simplifying model interactions and enhancing data processing within the ORM framework.Database population in Odoo 18 - Odoo slides



Database population in Odoo 18 - Odoo slidesCeline George
Ã˝
In this slide, we’ll discuss the database population in Odoo 18. In Odoo, performance analysis of the source code is more important. Database population is one of the methods used to analyze the performance of our code. CBSE Arabic Grammar - Class 10 ppt.pptx



CBSE Arabic Grammar - Class 10 ppt.pptxsuhail849886
Ã˝
cbse arabic grammar
grade 10 cbse arabic grammar
cbse class 10 arabic grammar
arabic marathon cbse arabic 10
nominal sentences
Computer Network Unit IV - Lecture Notes - Network Layer



Computer Network Unit IV - Lecture Notes - Network LayerMurugan146644
Ã˝
Title:
Lecture Notes - Unit IV - The Network Layer
Description:
Welcome to the comprehensive guide on Computer Network concepts, tailored for final year B.Sc. Computer Science students affiliated with Alagappa University. This document covers fundamental principles and advanced topics in Computer Network. PDF content is prepared from the text book Computer Network by Andrew S. Tenanbaum
Key Topics Covered:
Main Topic : The Network Layer
Sub-Topic : Network Layer Design Issues (Store and forward packet switching , service provided to the transport layer, implementation of connection less service, implementation of connection oriented service, Comparision of virtual circuit and datagram subnet), Routing algorithms (Shortest path routing, Flooding , Distance Vector routing algorithm, Link state routing algorithm , hierarchical routing algorithm, broadcast routing, multicast routing algorithm)
Other Link :
1.Introduction to computer network - /slideshow/lecture-notes-introduction-to-computer-network/274183454
2. Physical Layer - /slideshow/lecture-notes-unit-ii-the-physical-layer/274747125
3. Data Link Layer Part 1 : /slideshow/lecture-notes-unit-iii-the-datalink-layer/275288798
Target Audience:
Final year B.Sc. Computer Science students at Alagappa University seeking a solid foundation in Computer Network principles for academic.
About the Author:
Dr. S. Murugan is Associate Professor at Alagappa Government Arts College, Karaikudi. With 23 years of teaching experience in the field of Computer Science, Dr. S. Murugan has a passion for simplifying complex concepts in Computer Network
Disclaimer:
This document is intended for educational purposes only. The content presented here reflects the author’s understanding in the field of Computer NetworkDigital Tools with AI for e-Content Development.pptx



Digital Tools with AI for e-Content Development.pptxDr. Sarita Anand
Ã˝
This ppt is useful for not only for B.Ed., M.Ed., M.A. (Education) or any other PG level students or Ph.D. scholars but also for the school, college and university teachers who are interested to prepare an e-content with AI for their students and others.How to Configure Flexible Working Schedule in Odoo 18 Employee



How to Configure Flexible Working Schedule in Odoo 18 EmployeeCeline George
Ã˝
In this slide, we’ll discuss on how to configure flexible working schedule in Odoo 18 Employee module. In Odoo 18, the Employee module offers powerful tools to configure and manage flexible working schedules tailored to your organization's needs.Rass MELAI : an Internet MELA Quiz Finals - El Dorado 2025



Rass MELAI : an Internet MELA Quiz Finals - El Dorado 2025Conquiztadors- the Quiz Society of Sri Venkateswara College
Ã˝
Kaun TALHA quiz Prelims - El Dorado 2025



Kaun TALHA quiz Prelims - El Dorado 2025Conquiztadors- the Quiz Society of Sri Venkateswara College
Ã˝
Rass MELAI : an Internet MELA Quiz Prelims - El Dorado 2025



Rass MELAI : an Internet MELA Quiz Prelims - El Dorado 2025Conquiztadors- the Quiz Society of Sri Venkateswara College
Ã˝
lecture1.ppt
- 1. Computational Chemistry: A DFT crash course
- 2. Useful Material Books  A chemist’s guide to density-functional theory Wolfram Koch and Max C. Holthausen (second edition, Wiley)  The theory of the cohesive energies of solids G. P. Srivastava and D. Weaire Advances in Physics 36 (1987) 463-517  Gulliver among the atoms Mike Gillan, New Scientist 138 (1993) 34 Web  www.nobel.se/chemistry/laureates/1998/  www.abinit.org Version 4.2.3 compiled for windows, install and good tutorial
- 3. Outline: Part 1, The Framework of DFT DFT: the theory  Schroedinger’s equation  Hohenberg-Kohn Theorem  Kohn-Sham Theorem  Simplifying Schroedinger’s  LDA, GGA Elements of Solid State Physics  Reciprocal space  Band structure  Plane waves And then ?  Forces (Hellmann-Feynman theorem)  E.O., M.D., M.C. …
- 4. Outline: Part2 Using DFT Practical Issues  Input File(s)  Output files  Configuration  K-points mesh  Pseudopotentials  Control Parameters  LDA/GGA  ‘Diagonalisation’ Applications  Isolated molecule  Bulk  Surface
- 6. Schroedinger’s Equation     i i i i r R r R V m , . , 2 2               Hamiltonian operator Kinetic Energy Potential Energy Coulombic interaction External Fields Very Complex many body Problem !! (Because everything interacts) Wave function Energy levels
- 7. First approximations Adiabatic (or Born-Openheimer)  Electrons are much lighter, and faster  Decoupling in the wave function Nuclei are treated classically  They go in the external potential       i i i i r R r R   . ,  
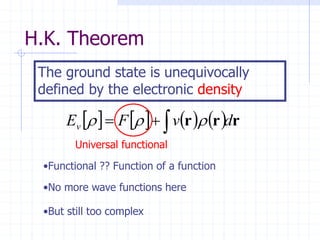
- 8. H.K. Theorem The ground state is unequivocally defined by the electronic density         r r r d v F Ev       Universal functional •Functional ?? Function of a function •No more wave functions here •But still too complex
- 9. K.S. Formulation Use an auxiliary system  Non interacting electrons  Same Density  => Back to wave functions, but simpler this time (a lot more though)     r r V m i i i eff    . 2 2                     r r r r r r r    XC eff d V V               i i 2 r r   N K.S. equations (ONE particle in a box really) (KS3) (KS2) (KS1) Exchange correlation potential
- 10. Self consistent loop Solve the independents K.S. =>wave functions From density, work out Effective potential New density ‘=‘ input density ?? Deduce new density from w.f. Initial density Finita la musica YES NO
- 11. DFT energy functional                  XC NI E d d d v T E           r r r r r r r r 2 1 Exchange correlation funtional Contains: Exchange Correlation Interacting part of K.E. Electrons are fermions (antisymmetric wave function)
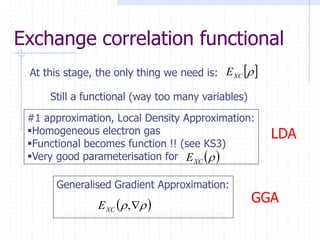
- 12. Exchange correlation functional At this stage, the only thing we need is:    XC E Still a functional (way too many variables) #1 approximation, Local Density Approximation: Homogeneous electron gas Functional becomes function !! (see KS3) Very good parameterisation for    XC E Generalised Gradient Approximation:      , XC E GGA LDA
- 13. DFT: Summary The ground state energy depends only on the electronic density (H.K.) One can formally replace the SE for the system by a set of SE for non-interacting electrons (K.S.) Everything hard is dumped into Exc Simplistic approximations of Exc work ! LDA or GGA
- 14. And now, for something completely different: A little bit of Solid State Physics Crystal structure Periodicity
- 15. Reciprocal space Real Space ai ij j i b a  . 2   Reciprocal Space bi Brillouin Zone (Inverting effect) k-vector (or k-point) sin(k.r) See X-Ray diffraction for instance Also, Fourier transform and Bloch theorem
- 17. The k-point mesh Brillouin Zone (6x6) mesh Corresponds to a supercell 36 time bigger than the primitive cell Question: Which require a finer mesh, Metals or Insulators ??
- 18. Plane waves Project the wave functions on a basis set ÔÇßTricky integrals become linear algebra ÔÇßPlane Wave for Solid State ÔÇßCould be localised (ex: Gaussians) + + = Sum of plane waves of increasing frequency (or energy) One has to stop: Ecut
- 19. Solid State: Summary Quantities can be calculated in the direct or reciprocal space k-point Mesh Plane wave basis set, Ecut
- 20. Now what ? We have access to the energy of a system, without any empirical input With little efforts, the forces can be computed, Hellman-Feynman theorem Then, the methodologies discussed for atomistic potential can be used Energy Optimisation Monte Carlo Molecular dynamics           r r r F d v i i i 






