material Science 7.pptx
0 likes31 views
This document discusses diffusion and Fick's laws of diffusion. It defines diffusion as the net flux of particles down a concentration gradient, with flux depending on concentration gradient and temperature. Diffusion processes like carburization can increase surface hardness by introducing carbon atoms. Diffusing atoms require activation energy to move into new sites. The Arrhenius equation relates diffusion rate to temperature and activation energy. The document also defines Fick's first law of diffusion, relating flux to the diffusion coefficient and concentration gradient. It provides examples calculating diffusion rates, activation energies, and concentration gradients.
1 of 16















Recommended
Material 8



Material 8Kareem Hossam
Ėý
This document discusses diffusion and its applications. It provides three key points:
1) Diffusion refers to the net flux of particles driven by a concentration gradient and temperature. The carburization process uses diffusion to increase surface hardness by introducing carbon into steel components.
2) Fick's First Law states that the flux of diffusing particles is proportional to the concentration gradient. The rate of diffusion depends on factors like concentration, temperature, and activation energy according to the Arrhenius equation.
3) Diffusion is applied in manufacturing transistors, where impurity atoms are diffused into silicon wafers to dope the semiconductor material. Concentration gradients provide the driving force for diffusion.Material science.pptx



Material science.pptxpostdocganesh
Ėý
The document discusses diffusion in materials, including:
1) Diffusion occurs via atomic mechanisms like vacancy and interstitial diffusion, moving atoms from high to low concentration areas.
2) Examples of diffusion applications are case hardening of gears and doping of semiconductors.
3) Fick's first law describes steady-state diffusion as flux proportional to the concentration gradient, via the diffusion coefficient D.material 9.pptx



material 9.pptxkareemhamad3
Ėý
This document discusses diffusion and Fick's first law of diffusion. It provides the Arrhenius equation for modeling diffusion rate as an exponential function of temperature. It also presents Fick's first law, which defines flux as the rate of diffusion. The document then provides an example problem calculating the number of nickel ions diffusing through magnesium oxide per second given the diffusion coefficient and concentrations. Another example calculates the thickness of an iron membrane needed to limit nitrogen and hydrogen diffusion rates. Finally, it presents a bonus problem using experimental diffusion rates to calculate activation energy.Material Science and Metallurgy



Material Science and Metallurgytaruian
Ėý
undamentals of Crystal Structure: BCC, FCC and HCP Structures, coordination number and atomic packing factors, crystal imperfections -point line and surface imperfections. Atomic Diffusion: Phenomenon, Fickâs laws of diffusion, factors affecting diffusion.Ch05



Ch05Ibrahim Abuawwad
Ėý
Diffusion is the mass transport of atoms in solids by atomic motion. There are two main mechanisms: vacancy diffusion, where atoms exchange with vacancies in the lattice, and interstitial diffusion, where smaller atoms diffuse between lattice sites. The rate of diffusion depends on factors like temperature, activation energy, and the concentration gradient. Fick's laws can be used to calculate the flux of diffusing atoms and model diffusion processes. Controlling diffusion is important for applications like alloy processing and semiconductor doping.Diffusion in Solids.pptx



Diffusion in Solids.pptxMARYADELADELACRUZ
Ėý
This document discusses diffusion in solids. It defines diffusion as the process of molecules moving from one area of a solid to another due to concentration differences. There are three main types of diffusion: self-diffusion, inter-diffusion/impurity diffusion, and surface diffusion. For an atom to diffuse, it must have an empty adjacent site available and enough energy to move into that site. Diffusion occurs via vacancies or interstitial spaces in the crystal lattice. Fick's laws provide a way to quantify the rate of diffusion based on flux, concentration gradients, and diffusion coefficients.Material 9



Material 9Kareem Hossam
Ėý
This document discusses diffusion through a membrane and solving related problems. It contains:
1) Information on Fick's first law of diffusion and the Arrhenius equation for calculating diffusion rates.
2) A sample problem calculating the number of nickel ions diffusing through MgO per second given parameters like thickness, temperature, and diffusion coefficient.
3) A multi-part problem designing an iron membrane thickness to allow less than 1% nitrogen loss per hour and 90% hydrogen passage per hour given gas concentrations and diffusion rates at 700C.Partcle dynamics for flow of particles in fluid



Partcle dynamics for flow of particles in fluidAABIDSHAIK3
Ėý
Partcle dynamics for flow of particles in fluidPhase Transformation Lecture 3 



Phase Transformation Lecture 3 NED University of Engineering and Technology
Ėý
1. Diffusion is the transport of atoms or molecules in solids, liquids, or gases due to a gradient in concentration or pressure. In solids, atoms constantly vibrate but bonds prevent long-range motion except through defects like vacancies.
2. There are two main diffusion mechanisms in solids - vacancy diffusion, where an atom hops into an adjacent vacant lattice site, and interstitial diffusion, where a small atom squeezes through spaces in the host lattice. Diffusion requires thermal energy to break bonds and depends strongly on temperature.
3. Fick's laws describe diffusion - the flux is proportional to the concentration gradient according to Fick's first law, and the rate of change of concentrationch05_.pdf.pdf



ch05_.pdf.pdfMuhammadMirwazi
Ėý
This summary provides the key information from the document in 3 sentences:
The document discusses diffusion, including how it occurs, why it is an important process, how the rate of diffusion can be predicted, and how it depends on structure and temperature. Different diffusion mechanisms like vacancy diffusion, interstitial diffusion, and self-diffusion are described. Examples of diffusion applications in areas like case hardening, semiconductor doping, and chemical protective clothing are presented to illustrate how diffusion is used in processing.Wave properties



Wave propertieswww.fixURscore.com
Ėý
Waves can be categorized as mechanical or electromagnetic. Mechanical waves require a medium to travel through, while electromagnetic waves do not. Waves can also be transverse or longitudinal depending on the direction of particle oscillation relative to wave propagation. Important wave properties include amplitude, wavelength, frequency, and speed. Reflection, refraction, diffraction, interference, and polarization are key wave phenomena. Reflection follows the laws of reflection, while refraction follows Snell's law. Diffraction and interference result in constructive and destructive patterns. Polarization occurs when waves vibrate in a single plane. Waves have many applications including ultrasound imaging, fiber optics, and 3D displays.7. dopant diffusion 1,2 2013 microtech



7. dopant diffusion 1,2 2013 microtechBhargav Veepuri
Ėý
This document discusses dopant diffusion, which is the process of introducing controlled amounts of chemical impurities into a semiconductor lattice. Dopant diffusion is used to form source, drain, base, and emitter regions in semiconductor devices. The document covers various diffusion techniques and parameters, including diffusion sources, solid solubility limits, Fick's laws of diffusion, analytical solutions to the diffusion equations, design of diffused layers, and an example design calculation for a boron diffusion process.CHEE_220_Lecture_Fluidization_2021[1].pptx![CHEE_220_Lecture_Fluidization_2021[1].pptx](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/chee220lecturefluidization20211-230329153950-84712558-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![CHEE_220_Lecture_Fluidization_2021[1].pptx](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/chee220lecturefluidization20211-230329153950-84712558-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![CHEE_220_Lecture_Fluidization_2021[1].pptx](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/chee220lecturefluidization20211-230329153950-84712558-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![CHEE_220_Lecture_Fluidization_2021[1].pptx](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/chee220lecturefluidization20211-230329153950-84712558-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
CHEE_220_Lecture_Fluidization_2021[1].pptxthokomelomoloi
Ėý
This document discusses unit operations and fluidization. It defines a unit operation as a basic step in a process involving a physical change. Some common unit operations are listed, including fluid flow processes, heat transfer processes, mass transfer processes, thermodynamic processes, and mechanical processes. The document then focuses on fluidization, explaining that it is a process where a granular material is converted from a static to dynamic fluid-like state by passing a fluid up through the material. The components, mechanics, and types (particulate and aggregate) of fluidization are described. Applications and characteristics of fluidized beds are also summarized.Fluid mechanics for chermical engineering students



Fluid mechanics for chermical engineering studentsZin Eddine Dadach
Ėý
This document outlines the goals and topics covered in a fluid mechanics course. The course covers fluid statics, fluid flow concepts, flow of incompressible and compressible fluids, pumping systems, fluid mixing, and fluidization. Key concepts discussed include fluid properties like density, viscosity, compressibility, and pressure. Laminar and turbulent flow regimes are defined. The continuity, Bernoulli, and Reynolds equations are introduced. Example problems are provided to help understand concepts like pressure, viscosity, flow rate calculations, and fluid flow analysis.Dimensional Effect on Engineering Systems & Clean Room & Classification



Dimensional Effect on Engineering Systems & Clean Room & ClassificationSamiran Tripathi
Ėý
The Presentation is divided in two halves: the first half is dimensional effect on engineering systems and the second half deals with the basics of clean room and its classification
diffusion final PPT.ppt



diffusion final PPT.pptSpartan1173
Ėý
Diffusion is the mass transport of atoms through a solid by atomic motion. There are two main mechanisms: vacancy diffusion, where atoms exchange with vacancies in the lattice, and interstitial diffusion, where smaller atoms diffuse through spaces in the lattice. The rate of diffusion increases exponentially with temperature according to an Arrhenius relationship and is quantified by Fick's laws of diffusion. Diffusion plays an important role in many materials processes and semiconductor device fabrication.Diffusion in Materials



Diffusion in MaterialsLuis Linde
Ėý
This document discusses the process of diffusion in materials. It defines diffusion as the movement of atoms within a material driven by concentration gradients. There are four main mechanisms of diffusion: self-diffusion, interchange diffusion, vacancy diffusion, and interstitial diffusion. Diffusion is thermally activated and follows the Arrhenius equation, requiring atoms to overcome an activation energy barrier. Fick's first law describes the flux of atoms down a concentration gradient, while Fick's second law models the change in concentration over time. Diffusion plays a key role in processes like grain growth, diffusion bonding, and sintering of materials.Fuels and Combustion



Fuels and CombustionYuri Melliza
Ėý
This document provides an overview of heat transfer topics covered in a module, including objectives, topics, and introductions. The key topics are the three modes of heat transfer - conduction, convection, and radiation. Equations for calculating heat transfer via these three modes are presented, including Fourier's law of conduction, Newton's law of cooling for convection, and the Stefan-Boltzmann law for radiation. Examples of combined radiation and convection heat transfer are also discussed.Ch05 diffusion-updated sept2016-sent fall2016



Ch05 diffusion-updated sept2016-sent fall2016Savanna Holt
Ėý
This document discusses diffusion in solids, including key concepts such as diffusion coefficients, flux, Fick's laws of diffusion, and factors that influence diffusion rates. It provides examples of steady-state and non-steady state diffusion, and how diffusion is used in processes like carburizing steel and doping semiconductors. Temperature is identified as having the most profound effect on diffusion rates, with an exponential relationship between diffusivity and temperature. Higher temperatures and lower activation energies result in faster diffusion.Rate of absorption of moisture



Rate of absorption of moistureINDIAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY DELHI (IIT-DELHI)
Ėý
This document discusses the absorption of moisture by different fibers. It explains that the rate of moisture absorption depends on factors like temperature, humidity, thickness, and fiber type. The absorption process involves the slow diffusion of water molecules through the fiber over time until equilibrium is reached. This diffusion is modeled using Fick's laws of diffusion. Fick's first law states that the rate of diffusion is proportional to the concentration gradient, while Fick's second law accounts for how concentration changes over time as moisture penetrates the fiber. The document provides examples of using these laws to analyze moisture absorption in fibers and other materials.HMT-Conduction1.pptx



HMT-Conduction1.pptxMohanraj385614
Ėý
The document provides an overview of key concepts in heat transfer including conduction, convection, and radiation. It defines heat transfer as the transfer of energy from one system to another due to a temperature difference. The three modes of heat transfer - conduction, convection, and radiation - are described. Conduction occurs via molecular interactions within a material. Convection involves the transfer of energy between a surface and adjacent moving fluid. Radiation transfers energy electromagnetically without a medium. Key equations for each mode are also presented, such as Fourier's law of conduction and Newton's law of cooling for convection.Diffusion v2



Diffusion v2Mirza Salman Baig
Ėý
- Diffusion is the spontaneous movement of molecules from a region of higher concentration to lower concentration driven by the concentration gradient until equilibrium is reached.
- It plays an important role in processes like drug release from dosage forms, absorption of drugs from the gastrointestinal tract, distribution of drugs in tissues, and excretion of drugs through organs like the kidneys.
- Fick's first law quantifies diffusion as being directly proportional to the concentration gradient, while Fick's second law describes how the concentration changes over time at different locations during diffusion.
- Steady state diffusion refers to a constant rate of diffusion over time when the concentration gradient remains unchanged, such as in a diffusion cell experiment.M6TeacheršÝšÝßĢs.pdf



M6TeacheršÝšÝßĢs.pdfssusercf6d0e
Ėý
- Convection involves heat transfer between a solid surface and a fluid in motion. It depends on parameters like fluid properties, geometry, nature of flow, and phases.
- The key parameters governing convection are classified by non-dimensional numbers like Reynolds number, Prandtl number, and Nusselt number.
- Solving convection problems requires determining the flow field, temperature field in the fluid, and the heat transfer coefficient using the governing equations of mass, momentum, and energy conservation.5460be7c0cf27487b4525bb0



5460be7c0cf27487b4525bb0emreyz
Ėý
- The document discusses numerical simulations of the electrostatic spray painting process using high-speed rotary bell atomizers.
- Experiments were conducted to validate the sensitivity of the simulations to variations in operating conditions like paint flow rate and bell speed, as well as different target geometries.
- The simulations demonstrated good agreement with experimental measurements of film thickness and were able to accurately predict changes based on different operating conditions and target shapes.Cyclones



Cyclonesahkiaen
Ėý
This document summarizes gaseous emission control technologies and cyclone separators. It discusses two approaches to controlling air pollution: pollution prevention at the source and treatment of fumes as they form. Cyclone separators are described as inexpensive devices with no moving parts that are widely used to remove particles from air streams. The document provides details on cyclone design, operation, advantages, disadvantages, and equations for calculating collection efficiency based on factors like particle size, gas velocity, and cyclone dimensions. An example calculation is included to demonstrate determining the collection efficiency of a conventional cyclone for a given particle size distribution.Chromatography



ChromatographyKamruzzaman Khan
Ėý
Gas chromatography and high performance liquid chromatography are analytical techniques used to separate mixtures. Mikhail Tswett invented chromatography in 1901 to separate plant pigments using a glass column packed with calcium carbonate. Liquid chromatography was later refined using smaller packing materials and pumps to deliver solvents at high pressures, allowing for faster separations and the development of high performance liquid chromatography. Chromatography works by separating components in a mixture based on how they interact differently with a stationary and mobile phase as they flow through a column.section 7 modified-2.pdf



section 7 modified-2.pdfkareemhamad3
Ėý
1. The document discusses four methods of calculating depreciation: straight line, use or production, double declining balance, and sum of years digits.
2. It provides the formulas for calculating depreciation under each method and works through an example problem to calculate the depreciation each year for a car purchased for $200,000 and sold for $100,000 over 10 years.
3. Using the straight line method, depreciation is $10,000 per year. Using the use or production method, depreciation ranges from $882 to $33,921 over the 10 years. Using the double declining balance method, depreciation declines from $40,000 to $7,272section 5.pptx



section 5.pptxkareemhamad3
Ėý
This document provides examples of calculating economics metrics for chemical plants, including:
1) Estimating total capital investment (TCI) and fixed capital investment (FCI) given purchased equipment costs.
2) Calculating turnover ratio given FCI, sales, production details.
3) Finding breakeven point and production costs considering raw materials, utilities, labor, capital investment, production levels.
Step-by-step workings are shown for various examples, covering definitions of key terms, factors to consider, and formulas used to determine costs, investments, turnover ratios and breakeven analysis.More Related Content
Similar to material Science 7.pptx (20)
Partcle dynamics for flow of particles in fluid



Partcle dynamics for flow of particles in fluidAABIDSHAIK3
Ėý
Partcle dynamics for flow of particles in fluidPhase Transformation Lecture 3 



Phase Transformation Lecture 3 NED University of Engineering and Technology
Ėý
1. Diffusion is the transport of atoms or molecules in solids, liquids, or gases due to a gradient in concentration or pressure. In solids, atoms constantly vibrate but bonds prevent long-range motion except through defects like vacancies.
2. There are two main diffusion mechanisms in solids - vacancy diffusion, where an atom hops into an adjacent vacant lattice site, and interstitial diffusion, where a small atom squeezes through spaces in the host lattice. Diffusion requires thermal energy to break bonds and depends strongly on temperature.
3. Fick's laws describe diffusion - the flux is proportional to the concentration gradient according to Fick's first law, and the rate of change of concentrationch05_.pdf.pdf



ch05_.pdf.pdfMuhammadMirwazi
Ėý
This summary provides the key information from the document in 3 sentences:
The document discusses diffusion, including how it occurs, why it is an important process, how the rate of diffusion can be predicted, and how it depends on structure and temperature. Different diffusion mechanisms like vacancy diffusion, interstitial diffusion, and self-diffusion are described. Examples of diffusion applications in areas like case hardening, semiconductor doping, and chemical protective clothing are presented to illustrate how diffusion is used in processing.Wave properties



Wave propertieswww.fixURscore.com
Ėý
Waves can be categorized as mechanical or electromagnetic. Mechanical waves require a medium to travel through, while electromagnetic waves do not. Waves can also be transverse or longitudinal depending on the direction of particle oscillation relative to wave propagation. Important wave properties include amplitude, wavelength, frequency, and speed. Reflection, refraction, diffraction, interference, and polarization are key wave phenomena. Reflection follows the laws of reflection, while refraction follows Snell's law. Diffraction and interference result in constructive and destructive patterns. Polarization occurs when waves vibrate in a single plane. Waves have many applications including ultrasound imaging, fiber optics, and 3D displays.7. dopant diffusion 1,2 2013 microtech



7. dopant diffusion 1,2 2013 microtechBhargav Veepuri
Ėý
This document discusses dopant diffusion, which is the process of introducing controlled amounts of chemical impurities into a semiconductor lattice. Dopant diffusion is used to form source, drain, base, and emitter regions in semiconductor devices. The document covers various diffusion techniques and parameters, including diffusion sources, solid solubility limits, Fick's laws of diffusion, analytical solutions to the diffusion equations, design of diffused layers, and an example design calculation for a boron diffusion process.CHEE_220_Lecture_Fluidization_2021[1].pptx![CHEE_220_Lecture_Fluidization_2021[1].pptx](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/chee220lecturefluidization20211-230329153950-84712558-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![CHEE_220_Lecture_Fluidization_2021[1].pptx](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/chee220lecturefluidization20211-230329153950-84712558-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![CHEE_220_Lecture_Fluidization_2021[1].pptx](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/chee220lecturefluidization20211-230329153950-84712558-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![CHEE_220_Lecture_Fluidization_2021[1].pptx](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/chee220lecturefluidization20211-230329153950-84712558-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
CHEE_220_Lecture_Fluidization_2021[1].pptxthokomelomoloi
Ėý
This document discusses unit operations and fluidization. It defines a unit operation as a basic step in a process involving a physical change. Some common unit operations are listed, including fluid flow processes, heat transfer processes, mass transfer processes, thermodynamic processes, and mechanical processes. The document then focuses on fluidization, explaining that it is a process where a granular material is converted from a static to dynamic fluid-like state by passing a fluid up through the material. The components, mechanics, and types (particulate and aggregate) of fluidization are described. Applications and characteristics of fluidized beds are also summarized.Fluid mechanics for chermical engineering students



Fluid mechanics for chermical engineering studentsZin Eddine Dadach
Ėý
This document outlines the goals and topics covered in a fluid mechanics course. The course covers fluid statics, fluid flow concepts, flow of incompressible and compressible fluids, pumping systems, fluid mixing, and fluidization. Key concepts discussed include fluid properties like density, viscosity, compressibility, and pressure. Laminar and turbulent flow regimes are defined. The continuity, Bernoulli, and Reynolds equations are introduced. Example problems are provided to help understand concepts like pressure, viscosity, flow rate calculations, and fluid flow analysis.Dimensional Effect on Engineering Systems & Clean Room & Classification



Dimensional Effect on Engineering Systems & Clean Room & ClassificationSamiran Tripathi
Ėý
The Presentation is divided in two halves: the first half is dimensional effect on engineering systems and the second half deals with the basics of clean room and its classification
diffusion final PPT.ppt



diffusion final PPT.pptSpartan1173
Ėý
Diffusion is the mass transport of atoms through a solid by atomic motion. There are two main mechanisms: vacancy diffusion, where atoms exchange with vacancies in the lattice, and interstitial diffusion, where smaller atoms diffuse through spaces in the lattice. The rate of diffusion increases exponentially with temperature according to an Arrhenius relationship and is quantified by Fick's laws of diffusion. Diffusion plays an important role in many materials processes and semiconductor device fabrication.Diffusion in Materials



Diffusion in MaterialsLuis Linde
Ėý
This document discusses the process of diffusion in materials. It defines diffusion as the movement of atoms within a material driven by concentration gradients. There are four main mechanisms of diffusion: self-diffusion, interchange diffusion, vacancy diffusion, and interstitial diffusion. Diffusion is thermally activated and follows the Arrhenius equation, requiring atoms to overcome an activation energy barrier. Fick's first law describes the flux of atoms down a concentration gradient, while Fick's second law models the change in concentration over time. Diffusion plays a key role in processes like grain growth, diffusion bonding, and sintering of materials.Fuels and Combustion



Fuels and CombustionYuri Melliza
Ėý
This document provides an overview of heat transfer topics covered in a module, including objectives, topics, and introductions. The key topics are the three modes of heat transfer - conduction, convection, and radiation. Equations for calculating heat transfer via these three modes are presented, including Fourier's law of conduction, Newton's law of cooling for convection, and the Stefan-Boltzmann law for radiation. Examples of combined radiation and convection heat transfer are also discussed.Ch05 diffusion-updated sept2016-sent fall2016



Ch05 diffusion-updated sept2016-sent fall2016Savanna Holt
Ėý
This document discusses diffusion in solids, including key concepts such as diffusion coefficients, flux, Fick's laws of diffusion, and factors that influence diffusion rates. It provides examples of steady-state and non-steady state diffusion, and how diffusion is used in processes like carburizing steel and doping semiconductors. Temperature is identified as having the most profound effect on diffusion rates, with an exponential relationship between diffusivity and temperature. Higher temperatures and lower activation energies result in faster diffusion.Rate of absorption of moisture



Rate of absorption of moistureINDIAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY DELHI (IIT-DELHI)
Ėý
This document discusses the absorption of moisture by different fibers. It explains that the rate of moisture absorption depends on factors like temperature, humidity, thickness, and fiber type. The absorption process involves the slow diffusion of water molecules through the fiber over time until equilibrium is reached. This diffusion is modeled using Fick's laws of diffusion. Fick's first law states that the rate of diffusion is proportional to the concentration gradient, while Fick's second law accounts for how concentration changes over time as moisture penetrates the fiber. The document provides examples of using these laws to analyze moisture absorption in fibers and other materials.HMT-Conduction1.pptx



HMT-Conduction1.pptxMohanraj385614
Ėý
The document provides an overview of key concepts in heat transfer including conduction, convection, and radiation. It defines heat transfer as the transfer of energy from one system to another due to a temperature difference. The three modes of heat transfer - conduction, convection, and radiation - are described. Conduction occurs via molecular interactions within a material. Convection involves the transfer of energy between a surface and adjacent moving fluid. Radiation transfers energy electromagnetically without a medium. Key equations for each mode are also presented, such as Fourier's law of conduction and Newton's law of cooling for convection.Diffusion v2



Diffusion v2Mirza Salman Baig
Ėý
- Diffusion is the spontaneous movement of molecules from a region of higher concentration to lower concentration driven by the concentration gradient until equilibrium is reached.
- It plays an important role in processes like drug release from dosage forms, absorption of drugs from the gastrointestinal tract, distribution of drugs in tissues, and excretion of drugs through organs like the kidneys.
- Fick's first law quantifies diffusion as being directly proportional to the concentration gradient, while Fick's second law describes how the concentration changes over time at different locations during diffusion.
- Steady state diffusion refers to a constant rate of diffusion over time when the concentration gradient remains unchanged, such as in a diffusion cell experiment.M6TeacheršÝšÝßĢs.pdf



M6TeacheršÝšÝßĢs.pdfssusercf6d0e
Ėý
- Convection involves heat transfer between a solid surface and a fluid in motion. It depends on parameters like fluid properties, geometry, nature of flow, and phases.
- The key parameters governing convection are classified by non-dimensional numbers like Reynolds number, Prandtl number, and Nusselt number.
- Solving convection problems requires determining the flow field, temperature field in the fluid, and the heat transfer coefficient using the governing equations of mass, momentum, and energy conservation.5460be7c0cf27487b4525bb0



5460be7c0cf27487b4525bb0emreyz
Ėý
- The document discusses numerical simulations of the electrostatic spray painting process using high-speed rotary bell atomizers.
- Experiments were conducted to validate the sensitivity of the simulations to variations in operating conditions like paint flow rate and bell speed, as well as different target geometries.
- The simulations demonstrated good agreement with experimental measurements of film thickness and were able to accurately predict changes based on different operating conditions and target shapes.Cyclones



Cyclonesahkiaen
Ėý
This document summarizes gaseous emission control technologies and cyclone separators. It discusses two approaches to controlling air pollution: pollution prevention at the source and treatment of fumes as they form. Cyclone separators are described as inexpensive devices with no moving parts that are widely used to remove particles from air streams. The document provides details on cyclone design, operation, advantages, disadvantages, and equations for calculating collection efficiency based on factors like particle size, gas velocity, and cyclone dimensions. An example calculation is included to demonstrate determining the collection efficiency of a conventional cyclone for a given particle size distribution.Chromatography



ChromatographyKamruzzaman Khan
Ėý
Gas chromatography and high performance liquid chromatography are analytical techniques used to separate mixtures. Mikhail Tswett invented chromatography in 1901 to separate plant pigments using a glass column packed with calcium carbonate. Liquid chromatography was later refined using smaller packing materials and pumps to deliver solvents at high pressures, allowing for faster separations and the development of high performance liquid chromatography. Chromatography works by separating components in a mixture based on how they interact differently with a stationary and mobile phase as they flow through a column.More from kareemhamad3 (20)
section 7 modified-2.pdf



section 7 modified-2.pdfkareemhamad3
Ėý
1. The document discusses four methods of calculating depreciation: straight line, use or production, double declining balance, and sum of years digits.
2. It provides the formulas for calculating depreciation under each method and works through an example problem to calculate the depreciation each year for a car purchased for $200,000 and sold for $100,000 over 10 years.
3. Using the straight line method, depreciation is $10,000 per year. Using the use or production method, depreciation ranges from $882 to $33,921 over the 10 years. Using the double declining balance method, depreciation declines from $40,000 to $7,272section 5.pptx



section 5.pptxkareemhamad3
Ėý
This document provides examples of calculating economics metrics for chemical plants, including:
1) Estimating total capital investment (TCI) and fixed capital investment (FCI) given purchased equipment costs.
2) Calculating turnover ratio given FCI, sales, production details.
3) Finding breakeven point and production costs considering raw materials, utilities, labor, capital investment, production levels.
Step-by-step workings are shown for various examples, covering definitions of key terms, factors to consider, and formulas used to determine costs, investments, turnover ratios and breakeven analysis.Section 4.pptx



Section 4.pptxkareemhamad3
Ėý
- The document discusses methods for estimating the costs of major chemical plant equipment such as condensers, columns, heat exchangers, and reactors. It provides examples of calculating equipment costs based on size, material, pressure, and cost constants from tables.
- Total capital investment is estimated considering equipment purchase costs, physical plant costs, fixed capital investment, working capital, and indirect costs. Examples are provided to estimate total costs for process plants and expansion projects.
- Cost indices can be used to adjust older cost estimates to current year dollar values.Section 3-2.pptx



Section 3-2.pptxkareemhamad3
Ėý
This document discusses methods for estimating capital costs for chemical plants. Quick rough estimates are needed early in the design process to evaluate alternative designs. More accurate estimates require more design detail. Capital costs include fixed costs for equipment, construction, and facilities, as well as working capital for start-up. Historical cost data can be escalated using cost indices. The factorial method estimates capital cost as factors applied to the total equipment cost. Detailed factorial estimates consider individual cost factors rather than a single overall factor.Section 9.pptx



Section 9.pptxkareemhamad3
Ėý
The document discusses optimum design parameters and provides examples of determining optimum values that minimize costs. Question 1 finds the optimum insulation thickness. Question 2 determines optimum temperature and pressure values that minimize total cost. Question 3 calculates the daily profit at the production rate giving minimum cost per unit and maximum daily profit. Question 4 involves determining the batch cycle time that gives the minimum total annual cost of producing 1 million kg of chemical product.Section 8.pptx



Section 8.pptxkareemhamad3
Ėý
The document discusses several questions related to evaluating investment options for chemical plants based on their economics.
For the first question, four heat exchanger designs to recover lost heat from waste gases are evaluated based on their initial cost, operating costs, heat savings value, and annual savings. Design 4 is determined to have the highest return on incremental investment.
The second question evaluates two investment alternatives based on their rate of return, minimum payback period, and capitalized cost to determine which meets the company's investment criteria.
The third question analyzes two reactor options based on their initial cost, maintenance costs, salvage value, service time, yield, and profit to determine which meets the ROI condition and maximum 3 year paySection 2.pptx



Section 2.pptxkareemhamad3
Ėý
1) The document discusses rules for calculating simple interest, compound interest, effective interest rates, and continuous compounding. It provides examples of calculating total amounts, interest rates, and present worth for various scenarios involving loans, bonds, and investments with different interest rates and time periods.
2) Questions are worked through calculating total amounts, interest rates, and present worth for investments with monthly, daily, semiannual compounding and continuous compounding over periods of 2, 4, 10, and 12 years.
3) Formulas used include simple interest, compound interest, effective interest rates, continuous compounding, and present worth. Results are calculated and explained for each question.Section 1.pptx



Section 1.pptxkareemhamad3
Ėý
This document discusses the importance of economics in chemical engineering and provides examples to illustrate key concepts. It notes that economics involves dealing with scarce resources efficiently to achieve optimal results at lowest cost. A case study compares the economics of an old versus new refrigerator design over time, factoring in capital costs, operating costs, and interest earnings. The document emphasizes choosing the optimum option by evaluating how variable factors like pipe diameter and insulation thickness impact both capital and operating costs. The overall goal is selecting designs that minimize total lifetime costs.section 6 .pptx



section 6 .pptxkareemhamad3
Ėý
The document discusses break even analysis for chemical plants. It provides examples of calculating the break even point in units and sales revenue for different unit retail prices and variable costs. It also contains examples of determining profit given production levels. Questions include calculating break even points, drawing break even charts, and determining if a plant is profitable based on supply and demand curves and fixed and variable costs.section 1.pptx



section 1.pptxkareemhamad3
Ėý
The document discusses common mechanical operations involving particulate matter including calculating the shape factor of different particle shapes, performing a sieve analysis to determine properties like specific surface area and average particle diameter, and using a correlation equation between cumulative fraction and particle size to calculate constants and the average surface volume diameter. Sieve analysis data is provided for a problem involving calculating values like specific surface area, average particle diameter, median diameter, and average surface volume particle diameter. section 4.pptx



section 4.pptxkareemhamad3
Ėý
This document discusses belt conveyor design and calculations. It provides guidelines for belt thickness and idler spacing based on material density being conveyed. It also outlines the equations needed to calculate the mass of the belt, idlers, and material per unit length, which are required for power calculations. These include factors like the number of idlers per side, mass of individual idlers, belt thickness and density, and flow rate and velocity of the material being conveyed. An example problem is provided to demonstrate how to apply these calculations.section 2.pptx



section 2.pptxkareemhamad3
Ėý
The document provides information on calculating mass storage in stockpiles and storage facilities using bulk density, angle of repose, and dimensional measurements. It includes examples of:
1) Calculating the mass of gravel that can be stored in a 6x6m area using the given bulk density of 1700kg/m3 and angle of repose of 45°, finding the answer is 48 tons.
2) Finding the minimum dimension H of 8.5m for a storage compartment with a 5x5m base to store 360 tons of bauxite ore over 3 days at a furnace rate of 5 tons/hr, using the given bulk density of 2000kg/m3 and angle of repose ofsection 5.pptx



section 5.pptxkareemhamad3
Ėý
This document provides rules and examples for calculating mechanical operations related to bulk solids storage and transport. It includes formulas for calculating volume and mass flow rate of cones, as well as vertical and lateral pressures at the bottom of a bin. An example calculates these pressures for a given bin geometry. It also discusses belt conveyor design, including belt and idler specifications and formulas for power calculations. The final example uses these formulas to calculate the motor power and storage bin dimensions needed for a given solid transportation rate and production period.section7.pptx



section7.pptxkareemhamad3
Ėý
1. The document discusses various rules and equations related to mechanical operations like crushing, grinding and milling including Rittinger's law, Kick's law, and equations for calculating ball mill dimensions, rotation speeds, and charge volumes.
2. It provides an example calculation for estimating the theoretical power required to grind a one ton batch in a roller mill over 30 minutes given the feed and product screen analyses.
3. Questions and examples are given for calculating reasonable ball mill speeds, ball charges, and rock feed charges given mill dimensions and properties of the balls and feed material.section 9.pptx



section 9.pptxkareemhamad3
Ėý
This document discusses three questions related to mechanical operations and flow through porous media:
1. It calculates the pressure drop across a catalyst bed packed with cylindrical pellets for an air stream, and how this would change with larger pellet size.
2. It estimates the inlet pressure of a catalyst tower given the outlet pressure, dimensions, flow properties, and contact time.
3. It calculates the porosity of a bed packed with Raschig rings given the pressure drop and flow properties of an air stream.section 8.pptx



section 8.pptxkareemhamad3
Ėý
This document provides information on mechanical operations like crushing and grinding. It includes:
- Rules for operations like Rittinger's law, Kick's law, and Bond work index.
- Parameters for equipment like ball mill rotation speed, ball size, and charge mass.
- Worked examples calculating time required to achieve a specific surface increase in crushing and grinding, based on parameters like feed size, product size, power, and work index.
- An example calculating the time required to grind one ton of material in a batch rod mill, given the motor power, grinding efficiency, feed and product sizes, and work index.section 6.pptx



section 6.pptxkareemhamad3
Ėý
This document discusses common mechanical operations used to transport materials, including bucket elevators, screw conveyors, and pneumatic transportation. It provides examples of how to calculate the power required for a bucket elevator to lift crushed alumina, the design of a screw conveyor to transport fly ash horizontally, and the conveying capacity of a pneumatic transportation system moving ground rock vertically and horizontally through pipes and elbows. Key parameters discussed include bulk density, spacing, pitch, filling ratio, pressure change, flow rate, and power.section 3-2.pptx



section 3-2.pptxkareemhamad3
Ėý
The document provides information to design a cylindrical storage bin for 450 tons of soda ash. It includes the material properties and design requirements. The summary is:
The dimensions of the bin are estimated as a diameter of 5m, conical bottom height of 6.5m, and cylindrical height of 11.5m. The minimum bottom opening diameter is 141.5mm. With a bottom diameter twice the minimum, the solid flow rate out of the bin would be 146 kg/s. The vertical pressure on the bottom is 29.3 kPa and equivalent liquid pressure is 211 kPa.material science 1 .pptx



material science 1 .pptxkareemhamad3
Ėý
This document provides notes on material science concepts. It discusses key points about assignments, quizzes, reports and presentations. It also covers classifications of materials, basic concepts like deformation, stress, strain and mechanical properties including elasticity, ductility, brittleness, hardness and toughness. Graphs of stress-strain curves are presented and terms like elastic limit, yield point and ultimate tensile strength are defined. Students are instructed to submit assignments on time and follow the instructor's directions.material science 2 .pptx



material science 2 .pptxkareemhamad3
Ėý
This document discusses material science concepts including stress, strain, Young's modulus, shear modulus, and bulk modulus. It provides definitions and formulas for these terms and includes examples of calculating stress, strain, elongation, shear stress, and changes in volume using given material properties and applied forces. Several practice problems are worked through applying these concepts to situations like stretching a cylinder, cutting a sheet, and determining changes to a bowling ball underwater.Recently uploaded (20)
AI-Powered Power Converter Design Workflow.pdf



AI-Powered Power Converter Design Workflow.pdfAleksandr Terlo
Ėý
Blending human expertise with AI-driven optimization for efficient power converter design.Turbocor Product and Technology Review.pdf



Turbocor Product and Technology Review.pdfTotok Sulistiyanto
Ėý
High Efficiency Chiller System in HVACAI ppt on water jug problem by shivam sharma



AI ppt on water jug problem by shivam sharmaShivamSharma588604
Ėý
this ppt is made on the topic of water jug problem.Sppu engineering artificial intelligence and data science semester 6th Artif...



Sppu engineering artificial intelligence and data science semester 6th Artif...pawaletrupti434
Ėý
Sppu University Third year AI&DS Artificial Neural Network unit 1Defining the Future of Biophilic Design in Crete.pdf



Defining the Future of Biophilic Design in Crete.pdfARENCOS
Ėý
Biophilic design is emerging as a key approach to enhancing well-being by integrating natural elements into residential architecture. In Crete, where the landscape is rich with breathtaking sea views, lush olive groves, and dramatic mountains, biophilic design principles can be seamlessly incorporated to create healthier, more harmonious living environments.
Environmental Product Declaration - Uni Bell



Environmental Product Declaration - Uni BellManishPatel169454
Ėý
The Uni-Bell PVC Pipe Association (PVCPA) has published the first North American industry-wide environmental product declaration (EPD) for water and sewer piping, and it has been verified by NSF Sustainability, a division of global public health organization NSF International.Taykon-Kalite belgeleri



Taykon-Kalite belgeleriTAYKON
Ėý
Kalite PolitikamÄąz
Taykon Ãelik için kalite, hayallerinizi bizlerle paylaÅtÄąÄÄąnÄąz an baÅlar. Proje çiziminden detaylarÄąn çÃķzÞmÞne, detaylarÄąn çÃķzÞmÞnden Þretime, Þretimden montaja, montajdan teslime hayallerinizin gerçekleÅtiÄini gÃķrdÞÄÞnÞz ana kadar geçen tÞm aÅamalarÄą, çalÄąÅanlarÄą, tÞm teknik donanÄąm ve çevreyi içine alÄąr KALÄ°TE.TASK-DECOMPOSITION BASED ANOMALY DETECTION OF MASSIVE AND HIGH-VOLATILITY SES...



TASK-DECOMPOSITION BASED ANOMALY DETECTION OF MASSIVE AND HIGH-VOLATILITY SES...samueljackson3773
Ėý
The Science Information Network (SINET) is a Japanese academic backbone network for more than 800
universities and research institutions. The characteristic of SINET traffic is that it is enormous and highly
variableHow to Build a Speed Sensor using Arduino?



How to Build a Speed Sensor using Arduino?CircuitDigest
Ėý
Learn how to measure speed using IR sensors in this simple DIY project. This tutorial cover circuit diagram, Sensor calibration and speed calculations and optimized Arduino code for real time speed measurements.Helium Boosting & Decanting With Hydro Test Machine



Helium Boosting & Decanting With Hydro Test MachinePaskals Fluid Systems Pvt. Ltd.
Ėý
About:
A helium boosting and decanting system is typically used in various industrial applications, particularly in the production and handling of gases, including helium including leak test of reciprocating cylinder. Hereâs a brief overview of its components and functions:
Components
1. Helium Storage Tanks: High-pressure tanks that store helium@ 150 bars.
2. Boosting Pumps: Designed to boost helium pressure up to 150 bar, ensuring efficient flow throughout the system.
3. Decanting Unit: Separates liquid helium from gas, facilitating decanting at pressures of up to 2 bars.
4. Pressure Regulators: Maintain and control the pressure of helium during transport.
5. Control Valves: automatic control valve is provided for the flow and direction of helium through the system.
6. Piping and Fittings: High-quality, corrosion-resistant materials for safe transport.
Functions
âĒ Boosting Pressure: The system boosts helium pressure up to 150 bar for various applications.
âĒ Decanting: Safely decants helium, separating liquid from gas at pressures of up to 2 bar.
âĒ Safety Measures: Equipped with relief valves and emergency shut-off systems to handle high pressures safely.
âĒ Monitoring and Control: Sensors and automated controls monitor pressure and flow rates.
Application:
âĒ Cryogenics: Cooling superconducting magnets in MRI machines and particle accelerators.
âĒ Welding: Used as a shielding gas in welding processes.
âĒ Research: Crucial for various scientific applications, including laboratories and space exploration.
Key Features:
âĒ Helium Storage & Boosting System
âĒ Decanting System
âĒ Pressure Regulation & Monitoring
âĒ Valves & Flow Control
âĒ Filtration & Safety Components
âĒ Structural & Material Specifications
âĒ Automation & Electrical Components
Failover System in Cloud Computing System



Failover System in Cloud Computing SystemHitesh Mohapatra
Ėý
Uses established clustering technologies for redundancy
Boosts availability and reliability of IT resources
Automatically transitions to standby instances when active resources become unavailable
Protects mission-critical software and reusable services from single points of failure
Can cover multiple geographical areas
Hosts redundant implementations of the same IT resource at each location
Relies on resource replication for monitoring defects and unavailability conditionsIndian Soil Classification System in Geotechnical Engineering



Indian Soil Classification System in Geotechnical EngineeringRajani Vyawahare
Ėý
This PowerPoint presentation provides a comprehensive overview of the Indian Soil Classification System, widely used in geotechnical engineering for identifying and categorizing soils based on their properties. It covers essential aspects such as particle size distribution, sieve analysis, and Atterberg consistency limits, which play a crucial role in determining soil behavior for construction and foundation design. The presentation explains the classification of soil based on particle size, including gravel, sand, silt, and clay, and details the sieve analysis experiment used to determine grain size distribution. Additionally, it explores the Atterberg consistency limits, such as the liquid limit, plastic limit, and shrinkage limit, along with a plasticity chart to assess soil plasticity and its impact on engineering applications. Furthermore, it discusses the Indian Standard Soil Classification (IS 1498:1970) and its significance in construction, along with a comparison to the Unified Soil Classification System (USCS). With detailed explanations, graphs, charts, and practical applications, this presentation serves as a valuable resource for students, civil engineers, and researchers in the field of geotechnical engineering. A Star Algorithm in Artificial intelligence



A Star Algorithm in Artificial intelligencevipulkondekar
Ėý
A Star Algorithm in Artificial intelligenceVon karman Equation full derivation .pdf



Von karman Equation full derivation .pdfEr. Gurmeet Singh
Ėý
Von karman Equation full derivation
By Er. GURMEET SINGH
G.C.E.T JAMMU
Contact: gurmeet.b.tech@gmail.com
M.tech Transportation Engineering Common Network Architecture:X.25 Networks, Ethernet (Standard and Fast): fram...



Common Network Architecture:X.25 Networks, Ethernet (Standard and Fast): fram...SnehPrasad2
Ėý
X.25 Networks, Ethernet (Standard and Fast): frame format and specifications, Wireless LANâs â 802.11x, 802.3 Bluetooth etc.
material Science 7.pptx
- 1. APPLICATION OF DIFFUSION ENG. KAREEM. H. MOKHTAR
- 2. DIFFUSION âĒ Diffusion refers to the net flux of any species âĒ The magnitude of this flux depends upon the concentration gradient and temperature.
- 3. APPLICATION âĒ The carburization process can be used to increase surface hardness. In carburization, a source of carbon, such as a graphite powder or gaseous phase containing carbon, is diffused into steel components
- 4. ACTIVATION ENERGY âĒ A diffusing atom must squeeze past the surrounding atoms to reach its new site. In order for this to happen, energy must be supplied to allow the atom to move to its new position
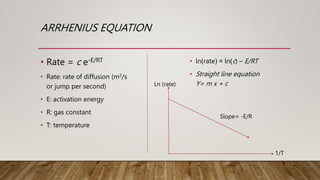
- 5. ARRHENIUS EQUATION âĒ Rate = c e-E/RT âĒ Rate: rate of diffusion (m2/s or jump per second) âĒ E: activation energy âĒ R: gas constant âĒ T: temperature âĒ ln(rate) = ln(c) â E/RT âĒ Straight line equation Y= m x + c Ln (rate) 1/T Slope= -E/R
- 6. SHEET 4 âĒ Q1) Suppose that atoms are found to move from one site to another at a rate of 109 jumps per second at 400 oC and the C0 is equal to 3.8 x 1016, calculate the activation energy (Calory) needed. âĒ Answer âĒ Rate = c e-E/RT âĒ 109 = 3.8 x 1016 x e-E/1.98*673 âĒ E= 23257 cal/mol
- 7. SHEET 4 âĒ Q2) Suppose that atoms are found to move from one site to another at a rate of 5x108 jumps/ second at 500 oC and 8x 1010 jumps/s at 800 oC, calculate the activation energy needed for the process âĒ Answer âĒ Q= 27,800 cal/mol
- 8. SHEET 4 âĒ Q3) At 300šC the diffusion and activation energy for Cu in Si are D(300šC) = 7.8 x 10-11 m2/s E = 41.5 kJ/mol What is the diffusion at 350šC? âĒ Answer âĒ Rate1 = c e-E/RT ï 7.8 x 10-11 = C e-41500/8.314* 573 âĒ Rate2 = c e-E/RT ï D= C e-41500/8.314* 623 âĒ Get D = 15.7 x 10-11 m2/s
- 9. DIFFUSION
- 10. FICKâS FIRST LAW âĒ The rate at which atoms, ions, particles or other species diffuse in a material can be measured by the flux J. Here we are mainly concerned with diffusion of ions or atoms. The flux J is defined as the number of atoms passing through a plane of unit area per unit time
- 11. FICKâS FIRST LAW âĒ J: flux âĒ D: diffusivity , cm2/s âĒ dc/dx : concentration gradient atoms / (cm3. cm) OR atomic % / cm
- 12. SHEET 4 âĒ Q4) Methylene chloride is a common ingredient of paint removers. Besides being an irritant, it also may be absorbed through skin. When using this paint remover, protective gloves should be worn. If butyl rubber gloves (0.04 cm thick) are used, what is the diffusive flux of methylene chloride through the glove? âĒ diffusion coefficient in butyl rubber: D = 110 x10-8 cm2/s âĒ surface concentrations: âĒ C1 = 0.44 g/cm3 âĒ C2 = 0.02 g/cm3
- 13. ANSWER
- 14. SHEET4 âĒ Q5) One step in manufacturing transistors, which function as electronic switches in integrated circuits, involves diffusing impurity atoms into a semiconductor material such as silicon (Si). Suppose a silicon wafer 0.1 cm thick, which originally contains one phosphorus atom for every 10 million Si atom, is treated so that there are 400 phosphorus atoms for every 10 million Si atoms at the surface. âĒ calculate the concentration gradient (at % / cm)
- 15. ANSWER âĒ Initial concentration in atom % âĒ Ci= 1ð ððĄðð 107 ððĄððð x 100 = 0.00001 at %P âĒ Cs= 400ð ððĄðð 107 ððĄððð x 100 = 0.004 at%P âĒ ððððĄð ðķ ð·ðððĄð ðĨ = 0.00001â0.004 0.1 = - 0.04 at% P /cm






