MATHematics 8 second quarter first module.pptx
- 2. DIFFERENTIATING LINEAR INEQUALITIES AND LINEAR EQUATIONS IN TWO VARIABLES OBJECTIVES WHATŌĆÖS IN WHATŌĆÖS NEW ACTIVITY DISCUSSION QUARTER 2 WEEK 1 MARC JOSHUA C. CLARETE, LPT SUBJECT TEACHER
- 3. PRAYER OBJECTIVES WHATŌĆÖS IN WHATŌĆÖS NEW DISCUSSION ACTIVITY After going through this lesson, you are expected to: 1.distinguish the linear inequalities in two variables from linear equations in two variables; 2.translate mathematical phrases into mathematical statements of linear equations and inequalities in two variables; and 3.cite real life situations that can be represented by linear equations and inequalities in two variables.
- 4. PRAYER OBJECTIVES WHATŌĆÖS IN WHATŌĆÖS NEW DISCUSSION ACTIVITY ACTIVITY: EXPRESS ME Directions: Express the following linear equations in two variables into its standard form + = . ØÉ┤Øæź ØÉĄØæ” ØÉČ 1. 2x = y ŌĆō 3 2. y = -4x + 7 3. 2y = 8x ŌĆō 9 4. x = 2y + 4 5. x ŌĆō 3y ŌĆō 7 = 0 2x ŌĆō y = -3 4x + y = 7 8x ŌĆō 2y = 9 x ŌĆō 2y = 4 x ŌĆō 3y = 7
- 5. PRAYER OBJECTIVES WHATŌĆÖS IN WHATŌĆÖS NEW DISCUSSION ACTIVITY ACTIVITY: BE MY PARTNER Directions: Match the verbal statement in column A to the mathematical statement in Column B.
- 6. PRAYER OBJECTIVES WHATŌĆÖS IN WHATŌĆÖS NEW DISCUSSION ACTIVITY Differentiating Linear Inequalities and Linear Equations in Two Variables Equations and inequalities are two significant concepts in mathematics that are related but are different in some ways. Inequality is a mathematical statement where one expression is not equal to another. It uses the symbols , Ōēż , Ōēź, ŌēĀ. While Øæ£Øæ¤ equation uses the symbol ŌĆ£=ŌĆØ indicating that the value of the expressions from both sides are equal.
- 7. PRAYER OBJECTIVES WHATŌĆÖS IN WHATŌĆÖS NEW DISCUSSION ACTIVITY Differentiating Linear Inequalities and Linear Equations in Two Variables LINEAR EQUATION Definition: A linear equation in two variables is written in the standard form of + + = 0, ØÉ┤Øæź ØÉĄØæ” ØÉČ where , , and ØÉ┤ ØÉĄ ØÉČ are real numbers and the coefficients of Øæź and , represented Øæ” by and ØÉ┤ ØÉĄ respectively, are not equal to zero. LINEAR INEQUALITY Definition: A linear inequality in two variables is formed when symbols other than equal to, such as greater than or less than are used to relate two expressions, and two variables are involved.
- 8. PRAYER OBJECTIVES WHATŌĆÖS IN WHATŌĆÖS NEW DISCUSSION ACTIVITY Differentiating Linear Inequalities and Linear Equations in Two Variables LINEAR EQUATION Standard Form: ØÉ┤Øæź + = C ØÉĄØæ” LINEAR INEQUALITY Standard Form: ØÉ┤Øæź + < ØÉĄØæ” ØÉČ ØÉ┤Øæź + > ØÉĄØæ” ØÉČ ØÉ┤Øæź + Ōēź ØÉĄØæ” ØÉČ ØÉ┤Øæź + ŌēĀ ØÉĄØæ” ØÉČ ØÉ┤Øæź + Ōēż C ØÉĄØæ”
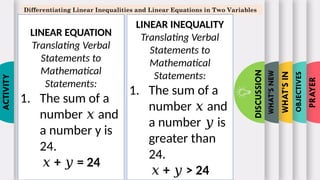
- 9. PRAYER OBJECTIVES WHATŌĆÖS IN WHATŌĆÖS NEW DISCUSSION ACTIVITY Differentiating Linear Inequalities and Linear Equations in Two Variables LINEAR EQUATION Translating Verbal Statements to Mathematical Statements: 1. The sum of a number and Øæź a number y is 24. Øæź + = 24 Øæ” LINEAR INEQUALITY Translating Verbal Statements to Mathematical Statements: 1. The sum of a number and Øæź a number is Øæ” greater than 24. Øæź + > 24 Øæ”
- 10. PRAYER OBJECTIVES WHATŌĆÖS IN WHATŌĆÖS NEW DISCUSSION ACTIVITY Differentiating Linear Inequalities and Linear Equations in Two Variables LINEAR EQUATION Translating Verbal Statements to Mathematical Statements: 2. A number x decreased by is Øæ” 24. ŌĆō Øæź Øæ” = 24 LINEAR INEQUALITY Translating Verbal Statements to Mathematical Statements: 2. A number Øæź decreased by a number is less Øæ” than 24. ŌĆō Øæź Øæ” < 24
- 11. PRAYER OBJECTIVES WHATŌĆÖS IN WHATŌĆÖS NEW DISCUSSION ACTIVITY Differentiating Linear Inequalities and Linear Equations in Two Variables LINEAR EQUATION Translating Verbal Statements to Mathematical Statements: 3. The sum of twice a number Øæź and thrice a number is 30. Øæ” 2 + 3 = 3 Øæź Øæ” 0 LINEAR INEQUALITY Translating Verbal Statements to Mathematical Statements: 3. The sum of twice a number Øæź and thrice a number is at Øæ” least 30. 2 + 3 Ōēź 30 Øæź Øæ”
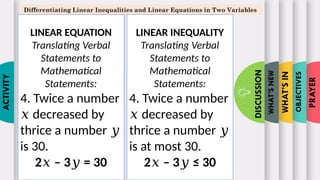
- 12. PRAYER OBJECTIVES WHATŌĆÖS IN WHATŌĆÖS NEW DISCUSSION ACTIVITY Differentiating Linear Inequalities and Linear Equations in Two Variables LINEAR EQUATION Translating Verbal Statements to Mathematical Statements: 4. Twice a number decreased by Øæź thrice a number Øæ” is 30. 2 ŌĆō 3 = 30 Øæź Øæ” LINEAR INEQUALITY Translating Verbal Statements to Mathematical Statements: 4. Twice a number decreased by Øæź thrice a number Øæ” is at most 30. 2 ŌĆō 3 Ōēż 30 Øæź Øæ”
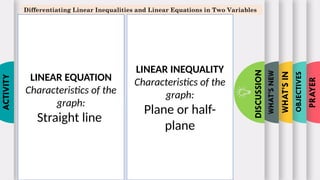
- 13. PRAYER OBJECTIVES WHATŌĆÖS IN WHATŌĆÖS NEW DISCUSSION ACTIVITY Differentiating Linear Inequalities and Linear Equations in Two Variables LINEAR EQUATION Characteristics of the graph: Straight line LINEAR INEQUALITY Characteristics of the graph: Plane or half- plane
- 14. PRAYER OBJECTIVES WHATŌĆÖS IN WHATŌĆÖS NEW DISCUSSION ACTIVITY Differentiating Linear Inequalities and Linear Equations in Two Variables LINEAR EQUATION Sample Graphs: LINEAR INEQUALITY Sample Graphs:
- 15. PRAYER OBJECTIVES WHATŌĆÖS IN WHATŌĆÖS NEW DISCUSSION ACTIVITY Differentiating Linear Inequalities and Linear Equations in Two Variables LINEAR EQUATION Graphical Solutions: set of points on the line LINEAR INEQUALITY Graphical Solutions: region of points bounded by a line
- 16. PRAYER OBJECTIVES WHATŌĆÖS IN WHATŌĆÖS NEW DISCUSSION ACTIVITY Differentiating Linear Inequalities and Linear Equations in Two Variables LINEAR EQUATION Effects when multiplied or divided by a negative integer: Equality symbol is not changed For example: 3 ŌĆō 2 = 6 Øæź Øæ” LINEAR INEQUALITY Effects when multiplied or divided by a negative integer: Direction of the inequality symbol is reversed For example: 3 ŌłÆ 2 > 6 Øæź Øæ”
- 17. PRAYER OBJECTIVES WHATŌĆÖS IN WHATŌĆÖS NEW DISCUSSION ACTIVITY ACTIVITY: DORA DŌĆÖ EXPLORER The class will be divided into four groups. Each group will begin at a different station simultaneously. Each station will have a unique activity that the group must complete before moving on to the next. After completing a station, the group will proceed to the next one in a clockwise direction. Each group will rotate until they complete all four stations. You have 20minutes to finish all the station. The first group to complete all four stations in the given time will receive 10 points, 2nd (8pts.), 3rd is 7pts, and 4th is (5pts.). The scores from all stations will be added, along with the bonus points based on the groupŌĆÖs finishing position.
- 18. PRAYER OBJECTIVES WHATŌĆÖS IN WHATŌĆÖS NEW DISCUSSION ACTIVITY ACTIVITY: DORA DŌĆÖ EXPLORER The class will be divided into four groups. Each group will begin at a different station simultaneously. Each station will have a unique activity that the group must complete before moving on to the next. After completing a station, the group will proceed to the next one in a clockwise direction. Each group will rotate until they complete all four stations. You have 20minutes to finish all the station. The first group to complete all four stations in the given time will receive 10 points, 2nd (8pts.), 3rd is 7pts, and 4th is (5pts.). The scores from all stations will be added, along with the bonus points based on the groupŌĆÖs finishing position. Station 1: Sort me well! Station 2: Name Me! Station 3: What am I? Station 4: Shall I Stay or Be the Other Way?
Editor's Notes
- #4: How did you find the activity? How did you transform the given equation into its standard form?
- #5: How did you find the activity? What did you observe with the symbols used in each mathematical statement? What is the difference between symbol ŌĆ£=ŌĆØ from the symbol ŌĆ£ŌēźŌĆØ? When shall you use the symbols Ōēź and Ōēż? How about symbols ŌĆ£>ŌĆØ and ŌĆ£<ŌĆ£? When do you use symbol ŌĆ£=ŌĆØ? What do you call mathematical statements a and d? How about b, c, e?
- #16: In multiplying, multiply both side by -1/2 ( -1/2 because the numerical value of y is -2)