Monobactam
5 likes7,730 views
Monobactams are Îē-lactam compounds that contain an isolated Îē-lactam ring not fused to another ring, making them effective only against aerobic Gram-negative bacteria like Neisseria and Pseudomonas. Examples include aztreonam, tigemonam, nocardicin A, and tabtoxin. Potential adverse effects are skin rash, abnormal liver functions, and risk of seizures in susceptible individuals.
1 of 5



Recommended
Broad spectrum antibiotics chloramphenicol



Broad spectrum antibiotics chloramphenicolSnehalChakorkar
Ėý
Chloramphenicol is a broad-spectrum antibiotic produced by Streptomyces venezuelae bacteria. It works by inhibiting bacterial protein synthesis at the ribosome. It has activity against both gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria as well as some protozoa. Chloramphenicol can cause serious and potentially fatal bone marrow suppression. As a result, it is now rarely used except for certain severe infections like meningitis and anaerobic infections. It is also used topically for eye and ear infections.Penicillins by Dr. Panchumarthy Ravisankar M.Pharm., Ph.D.



Penicillins by Dr. Panchumarthy Ravisankar M.Pharm., Ph.D.Dr. Ravi Sankar
Ėý
The document discusses penicillins, including their:
1) Historical background of discovery by Alexander Fleming in 1928 from Penicillium notatum.
2) Classification based on structure, spectrum, source and pharmacological activity, with penicillins classified under the beta-lactam class.
3) Structures of different penicillins such as penicillin G, penicillin V, methicillin, and isoxazolyl penicillins.Aminoglycosides



AminoglycosidesNarasimha Kumar G V
Ėý
Aminoglycosides are a class of antibiotics that bind to the 30S ribosomal subunit of bacteria, preventing proper initiation complex formation and causing misreading of the genetic code, which leads to bacterial death. They are administered parenterally due to poor oral absorption and distributed poorly outside of extracellular fluid. While effective against many gram-negative bacteria, aminoglycosides can cause nephrotoxicity, ototoxicity, and neuromuscular blockade as side effects if not properly dosed based on renal function.Monobactam antibiotics



Monobactam antibioticsRyma Chohan
Ėý
Monobactam Antibiotics
Introduction
Spectrum of activity
Pharmacokinetics
Pharmacodynamics
Clinical Uses
Adverse EffectTetracyclines



Tetracyclineskencha swathi
Ėý
- Tetracyclines are a class of broad spectrum antibiotic drugs derived from bacteria. They work by binding to the bacterial ribosome to inhibit protein synthesis and show bacteriostatic activity.
- Structurally, they contain four cyclic rings. Modifications to the structure can impact their activity. They are classified based on their duration of action as long, intermediate, or short acting.
- Common examples include tetracycline, doxycycline, and minocycline. They are used to treat various bacterial infections but have side effects like nausea, vomiting, and tooth staining when taken.Penicillins



PenicillinsNaser Tadvi
Ėý
Pharmacology of Penicllins (Beta lactam antibiotics), description of their mechanism of action, mechanism of resistance, classification, indications and adverse effectsSulfonamide



SulfonamideRasel Mahbub JNU
Ėý
This document discusses sulfonamides, which were the first effective chemotherapeutic agents used to treat bacterial infections. Sulfonamides work by inhibiting the bacterial synthesis of folic acid, which is essential for bacterial growth. They do this by competing with para-amino benzoic acid (PABA) for the folic acid synthetase enzyme. Common side effects include bone marrow suppression, allergic reactions, and crystalluria. Sulfonamides are often used in combination with other drugs to treat infections like typhoid, UTIs, and meningococcal meningitis.Tetracyclines- Ravisankar- Medicinal chemistry, Definition,classification,S...



Tetracyclines- Ravisankar- Medicinal chemistry, Definition,classification,S...Dr. Ravi Sankar
Ėý
Tetracyclines- Medicinal chemistry, Definition,classification,SAR,Mechanism of action, Side effects, uses.
By-Ravisankar.P,Vignan Pharmacy College, Vadlamudi Medicinal chemistry of Anti viral agents 



Medicinal chemistry of Anti viral agents Soujanya Pharm.D
Ėý
The document discusses the structure, life cycle, and classification of viruses as obligate intracellular parasites. It then summarizes the medicinal chemistry of various classes of anti-viral agents, including their synthesis and mechanisms of action. The main classes covered are adamantane derivatives like amantadine, purine nucleotides like acyclovir, pyrimidine nucleotides like trifluridine, and phosphorus derivatives like foscarnet. The anti-viral agents work by inhibiting viral DNA polymerase, incorporating into viral DNA, or substituting for thymidine in viral DNA synthesis.Medicinal chemistry-beta lactam antibiotics



Medicinal chemistry-beta lactam antibioticsDHARMENDRA BARIA
Ėý
- Îē-Lactam antibiotics include penicillins, cephalosporins, carbapenems, and monobactams. They contain a Îē-lactam ring structure and inhibit bacterial cell wall synthesis.
- Penicillins were the first discovered from the mold Penicillium and include natural penicillin G as well as semi-synthetic derivatives like ampicillin. Cephalosporins were later derived from the fungus Cephalosporium and have greater gram-negative spectrum.
- Carbapenems like imipenem and meropenem have a very broad spectrum including Pseudomonas aeruginosa resistance to most Îē-lactamases. Monobactams such as aztreBeta lactamase inhibitors and Monobactam



Beta lactamase inhibitors and MonobactamGauravBadwaik2
Ėý
This document discusses beta lactamase inhibitors and monobactams. It describes clavulanic acid, sulbactam, and tazobactam, which are beta lactamase inhibitors used to enhance the antibiotic properties of other antibiotics by preventing microbial resistance. It also discusses the monobactams aztreonam and tigemonam, which have activity against gram-negative bacteria by binding to penicillin binding proteins, but no activity against gram-positive bacteria or anaerobes. These monobactams are used to treat various infections when patients cannot tolerate penicillins or cephalosporins.Monobactams



MonobactamsDr. Ajmer Singh Grewal
Ėý
Monobactams are a class of Îē-lactam antibiotics that contain a single Îē-lactam ring, unlike penicillins and cephalosporins which have the ring fused to another. Aztreonam was the first to be approved in 1986. Monobactams are effective against gram-negative bacteria and show promise in treating multi-drug resistant pathogens. They work by inhibiting cell wall synthesis through binding to penicillin-binding proteins. Side effects are generally mild but can include rashes, liver problems, and seizures in susceptible individuals.Sulfonamides and cotrimoxazole - drdhriti



Sulfonamides and cotrimoxazole - drdhritihttp://neigrihms.gov.in/
Ėý
A Power point presentation on "Sulfonamides and cotrimoxazole" suitable for undergraduate level medical student and othersQuinolones & Fluoroquinolones



Quinolones & FluoroquinolonesDr Resu Neha Reddy
Ėý
Quinolones & Fluoroquinolones
Introduction
History
Anti microbial spectrum
Classification
Mechanism of Action
Resistance
Pharmacokinetics
Therapeutic uses
Adverse Effects
Interactions
Cephalosporins



CephalosporinsDr. Pooja
Ėý
This document discusses cephalosporins, a class of beta-lactam antibiotics. It describes their history, mechanism of action, classification, uses, and adverse effects. Cephalosporins are derived from the fungus Cephalosporium and work by inhibiting bacterial cell wall synthesis. They are divided into generations based on spectrum of activity, with later generations covering more resistant organisms. Common uses include skin, respiratory, and urinary tract infections. Adverse effects can include hypersensitivity reactions and antibiotic-associated colitis. Newer agents have been developed with activity against multidrug-resistant bacteria.Penicillin



PenicillinShilpa Harak
Ėý
Penicillin Classification, Mechanism of Action, Structure Activity Relationship, Structure of Penicillins, penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs) functional propertiesCross-linking of the peptidoglycan by transpeptidases, Cross-linking of the peptidoglycan by transpeptidases, Shape of penicillin G Penicillin SAR AcylSide Chain Modifications Instability of Îē-lactams to nucleophiles
Penicillinase-Resistant Penicillins Protein Binding of PenicillinsAminoglycosides.pptx



Aminoglycosides.pptxSubramani Parasuraman
Ėý
Aminoglycosides are a class of antibiotics that are produced by soil bacteria. They are primarily used to treat infections caused by aerobic gram-negative bacteria and some are used for mycobacterial infections. Aminoglycosides work by binding to bacterial ribosomes which interferes with protein synthesis. They have concentration-dependent bactericidal activity against many gram-negative organisms but limited activity against gram-positive bacteria. Common adverse effects include ototoxicity and nephrotoxicity. Therapeutic drug monitoring is important when using aminoglycosides to minimize toxicity risks.Macrolides



MacrolidesDr. Md Yaqub
Ėý
- Macrolides are a class of antibiotics that are produced by Streptomyces bacteria and contain a macrocyclic lactone ring. Erythromycin was the first macrolide discovered in 1952.
- Macrolides work by attaching to the 50S subunit of bacterial ribosomes and inhibiting protein synthesis. They are bacteriostatic and have selectivity for bacterial over mammalian cells.
- Common macrolides include erythromycin, clarithromycin, roxithromycin, and azithromycin. They are effective against many gram-positive bacteria and some gram-negatives. Azithromycin has the broadest spectrum of activity.Cephalosporin- Beta lactam Antibiotic 



Cephalosporin- Beta lactam Antibiotic DrVishalMore1
Ėý
This presentation highlights on the Introduction, chemistry, classification, structures, SAR and Mechanism of Action (MOA) of cephalosporins Anthelmintics (antihelminthics) drugs



Anthelmintics (antihelminthics) drugsRavish Yadav
Ėý
The all the content in this profile is completed by the teachers, students as well as other health care peoples.
thank you, all the respected peoples, for giving the information to complete this presentation.
this information is free to use by anyone.
Beta lactamase inhibitors



Beta lactamase inhibitorsJagirPatel3
Ėý
Beta lactamase inhibitors such as clavulanic acid, sulbactam, tazobactam, and avibactam work to inhibit beta-lactamase enzymes produced by bacteria that provide resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics like penicillins. They bind to and inactivate the beta-lactamase enzymes. When combined with beta-lactam antibiotics, the inhibitors can help the antibiotics overcome resistance and be effective against infections. Common combinations include amoxicillin-clavulanic acid, piperacillin-tazobactam, and ceftazidime-avibactam which are used to treat a variety of bacterial infections.Chemotherapy of Sexually Transmitted Diseases



Chemotherapy of Sexually Transmitted DiseasesSHUBHAM MANTRI
Ėý
This document provides information about sexually transmitted diseases (STDs), including their causes, symptoms, and treatments. It discusses several common STDs - Chlamydia, Epididymitis, Gonorrhea, HIV/AIDS, and Syphilis. For each STD, it describes the causative microorganism (e.g. bacteria, viruses), symptoms for men and women, methods of diagnosis (e.g. urine tests, swab tests), and recommended antibiotic or antiviral treatments. The document emphasizes that STDs are commonly transmitted through unprotected sex and can cause serious health issues if left untreated.Chemotherapy 



Chemotherapy AKHIL SHAIKH
Ėý
1. The document discusses various antimicrobial drugs including their classification, mechanisms of action, and pharmacological profiles. It covers sulfonamides, cotrimoxazole, penicillins, cephalosporins, chloramphenicol, and erythromycin.
2. The general principles of chemotherapy are outlined including identifying microorganisms, antimicrobial susceptibility testing, and factors affecting drug selection and administration.
3. Various antimicrobial drugs are classified based on their chemical structure, types of organisms they act on, spectrum of activity, and mechanism of action. Adverse effects and uses of different drugs are also mentioned.Aminoglycosides(medicinal chemistry by p.ravisankar)



Aminoglycosides(medicinal chemistry by p.ravisankar)Dr. Ravi Sankar
Ėý
Aminoglycosides,Aminocyclitols,Source,Structures of streptomycin,Dihydrostreptomycin,A mention of other aminoglycoside antibiotics,Acid hydrolysis,Mechanism of action,SAR,Dihydrostreptomycin and its importance,therapeutic uses, toxicity.
Sulfonamides and trimethoprim



Sulfonamides and trimethoprimSubramani Parasuraman
Ėý
Sulfonamides and trimethoprim are antibacterial drugs that work by inhibiting bacterial folic acid synthesis. Sulfonamides were the first antibacterial sulfone drugs discovered in the 1930s. Trimethoprim inhibits a different enzyme in the folic acid pathway. The combination of sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim is highly synergistic and known as cotrimoxazole. It is used to treat urinary tract, respiratory, and other infections. Both drugs can cause side effects like rash, nausea, and bone marrow suppression if not used carefully, especially in pregnancy, renal impairment, or the elderly.Antiulcer drugs 



Antiulcer drugs yogeeta Goyat
Ėý
this will give brief about the peptic ulcer and give information about the drug used for peptic ulcer and classification of drugs including drugs and there use adverse effect.Beta Lactam Antibiotics 



Beta Lactam Antibiotics Saurav Ch. Sarma
Ėý
This document provides an overview of beta lactam antibiotics, including their structure, mode of action, examples, and mechanisms of resistance. It begins by discussing the bacterial cell wall structure and how beta lactams work by inhibiting cell wall synthesis. Major classes of beta lactams covered include penicillins, cephalosporins, carbapenems, and monobactams. Examples such as methicillin, amoxicillin, and imipenem are described. The document also discusses beta lactamase resistance and concludes with a brief overview of classification.Cephalosporins - Pharmacology 



Cephalosporins - Pharmacology Areej Abu Hanieh
Ėý
Cephalosporins are a class of beta-lactam antibiotics that inhibit bacterial cell wall synthesis. They include first, second, third, fourth, and fifth generation drugs with varying spectra of coverage. They have concentration-dependent bactericidal activity and are excreted renally. Common side effects include diarrhea, rash, and nephrotoxicity. Vancomycin and polymyxins have activity against gram-positive and highly resistant gram-negative bacteria, respectively. Tetracyclines have broad-spectrum coverage including MRSA and are bacteriostatic.Cellular and molecular pharmacology



Cellular and molecular pharmacologySANDEEP MEWADA
Ėý
This document provides information about the cell cycle and its regulation. It discusses the key phases of the cell cycle including interphase, mitosis, and meiosis. Interphase consists of G1, S, and G2 phases where the cell grows and DNA is replicated. Mitosis involves nuclear division into two daughter cells with identical chromosomes. Meiosis involves two cell divisions resulting in four daughter cells each with half the original chromosome number, allowing for genetic variation. The document defines important cell cycle concepts and compares the processes of mitosis and meiosis.PHARMACOVIGILANCE (PV)



PHARMACOVIGILANCE (PV)SANDEEP MEWADA
Ėý
Thank YouâĻ ClinoSol Research Mujeebuddin Shaik (Founder & CEO)#Sir uma priya(Director) #Mem at ClinoSol Research Pvt. Ltd & Kabya Pratap (ClinoSol) at ï#Business #Development #Intern for giving me a great #opportunity in #internship at #ClinoSol Your all Best Efforts & Support helps me alot #šÝšÝßĢshare #innovation #pharmacovigilance #pv #linkedin #thankyou again ïââïļïĨģMore Related Content
What's hot (20)
Medicinal chemistry of Anti viral agents 



Medicinal chemistry of Anti viral agents Soujanya Pharm.D
Ėý
The document discusses the structure, life cycle, and classification of viruses as obligate intracellular parasites. It then summarizes the medicinal chemistry of various classes of anti-viral agents, including their synthesis and mechanisms of action. The main classes covered are adamantane derivatives like amantadine, purine nucleotides like acyclovir, pyrimidine nucleotides like trifluridine, and phosphorus derivatives like foscarnet. The anti-viral agents work by inhibiting viral DNA polymerase, incorporating into viral DNA, or substituting for thymidine in viral DNA synthesis.Medicinal chemistry-beta lactam antibiotics



Medicinal chemistry-beta lactam antibioticsDHARMENDRA BARIA
Ėý
- Îē-Lactam antibiotics include penicillins, cephalosporins, carbapenems, and monobactams. They contain a Îē-lactam ring structure and inhibit bacterial cell wall synthesis.
- Penicillins were the first discovered from the mold Penicillium and include natural penicillin G as well as semi-synthetic derivatives like ampicillin. Cephalosporins were later derived from the fungus Cephalosporium and have greater gram-negative spectrum.
- Carbapenems like imipenem and meropenem have a very broad spectrum including Pseudomonas aeruginosa resistance to most Îē-lactamases. Monobactams such as aztreBeta lactamase inhibitors and Monobactam



Beta lactamase inhibitors and MonobactamGauravBadwaik2
Ėý
This document discusses beta lactamase inhibitors and monobactams. It describes clavulanic acid, sulbactam, and tazobactam, which are beta lactamase inhibitors used to enhance the antibiotic properties of other antibiotics by preventing microbial resistance. It also discusses the monobactams aztreonam and tigemonam, which have activity against gram-negative bacteria by binding to penicillin binding proteins, but no activity against gram-positive bacteria or anaerobes. These monobactams are used to treat various infections when patients cannot tolerate penicillins or cephalosporins.Monobactams



MonobactamsDr. Ajmer Singh Grewal
Ėý
Monobactams are a class of Îē-lactam antibiotics that contain a single Îē-lactam ring, unlike penicillins and cephalosporins which have the ring fused to another. Aztreonam was the first to be approved in 1986. Monobactams are effective against gram-negative bacteria and show promise in treating multi-drug resistant pathogens. They work by inhibiting cell wall synthesis through binding to penicillin-binding proteins. Side effects are generally mild but can include rashes, liver problems, and seizures in susceptible individuals.Sulfonamides and cotrimoxazole - drdhriti



Sulfonamides and cotrimoxazole - drdhritihttp://neigrihms.gov.in/
Ėý
A Power point presentation on "Sulfonamides and cotrimoxazole" suitable for undergraduate level medical student and othersQuinolones & Fluoroquinolones



Quinolones & FluoroquinolonesDr Resu Neha Reddy
Ėý
Quinolones & Fluoroquinolones
Introduction
History
Anti microbial spectrum
Classification
Mechanism of Action
Resistance
Pharmacokinetics
Therapeutic uses
Adverse Effects
Interactions
Cephalosporins



CephalosporinsDr. Pooja
Ėý
This document discusses cephalosporins, a class of beta-lactam antibiotics. It describes their history, mechanism of action, classification, uses, and adverse effects. Cephalosporins are derived from the fungus Cephalosporium and work by inhibiting bacterial cell wall synthesis. They are divided into generations based on spectrum of activity, with later generations covering more resistant organisms. Common uses include skin, respiratory, and urinary tract infections. Adverse effects can include hypersensitivity reactions and antibiotic-associated colitis. Newer agents have been developed with activity against multidrug-resistant bacteria.Penicillin



PenicillinShilpa Harak
Ėý
Penicillin Classification, Mechanism of Action, Structure Activity Relationship, Structure of Penicillins, penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs) functional propertiesCross-linking of the peptidoglycan by transpeptidases, Cross-linking of the peptidoglycan by transpeptidases, Shape of penicillin G Penicillin SAR AcylSide Chain Modifications Instability of Îē-lactams to nucleophiles
Penicillinase-Resistant Penicillins Protein Binding of PenicillinsAminoglycosides.pptx



Aminoglycosides.pptxSubramani Parasuraman
Ėý
Aminoglycosides are a class of antibiotics that are produced by soil bacteria. They are primarily used to treat infections caused by aerobic gram-negative bacteria and some are used for mycobacterial infections. Aminoglycosides work by binding to bacterial ribosomes which interferes with protein synthesis. They have concentration-dependent bactericidal activity against many gram-negative organisms but limited activity against gram-positive bacteria. Common adverse effects include ototoxicity and nephrotoxicity. Therapeutic drug monitoring is important when using aminoglycosides to minimize toxicity risks.Macrolides



MacrolidesDr. Md Yaqub
Ėý
- Macrolides are a class of antibiotics that are produced by Streptomyces bacteria and contain a macrocyclic lactone ring. Erythromycin was the first macrolide discovered in 1952.
- Macrolides work by attaching to the 50S subunit of bacterial ribosomes and inhibiting protein synthesis. They are bacteriostatic and have selectivity for bacterial over mammalian cells.
- Common macrolides include erythromycin, clarithromycin, roxithromycin, and azithromycin. They are effective against many gram-positive bacteria and some gram-negatives. Azithromycin has the broadest spectrum of activity.Cephalosporin- Beta lactam Antibiotic 



Cephalosporin- Beta lactam Antibiotic DrVishalMore1
Ėý
This presentation highlights on the Introduction, chemistry, classification, structures, SAR and Mechanism of Action (MOA) of cephalosporins Anthelmintics (antihelminthics) drugs



Anthelmintics (antihelminthics) drugsRavish Yadav
Ėý
The all the content in this profile is completed by the teachers, students as well as other health care peoples.
thank you, all the respected peoples, for giving the information to complete this presentation.
this information is free to use by anyone.
Beta lactamase inhibitors



Beta lactamase inhibitorsJagirPatel3
Ėý
Beta lactamase inhibitors such as clavulanic acid, sulbactam, tazobactam, and avibactam work to inhibit beta-lactamase enzymes produced by bacteria that provide resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics like penicillins. They bind to and inactivate the beta-lactamase enzymes. When combined with beta-lactam antibiotics, the inhibitors can help the antibiotics overcome resistance and be effective against infections. Common combinations include amoxicillin-clavulanic acid, piperacillin-tazobactam, and ceftazidime-avibactam which are used to treat a variety of bacterial infections.Chemotherapy of Sexually Transmitted Diseases



Chemotherapy of Sexually Transmitted DiseasesSHUBHAM MANTRI
Ėý
This document provides information about sexually transmitted diseases (STDs), including their causes, symptoms, and treatments. It discusses several common STDs - Chlamydia, Epididymitis, Gonorrhea, HIV/AIDS, and Syphilis. For each STD, it describes the causative microorganism (e.g. bacteria, viruses), symptoms for men and women, methods of diagnosis (e.g. urine tests, swab tests), and recommended antibiotic or antiviral treatments. The document emphasizes that STDs are commonly transmitted through unprotected sex and can cause serious health issues if left untreated.Chemotherapy 



Chemotherapy AKHIL SHAIKH
Ėý
1. The document discusses various antimicrobial drugs including their classification, mechanisms of action, and pharmacological profiles. It covers sulfonamides, cotrimoxazole, penicillins, cephalosporins, chloramphenicol, and erythromycin.
2. The general principles of chemotherapy are outlined including identifying microorganisms, antimicrobial susceptibility testing, and factors affecting drug selection and administration.
3. Various antimicrobial drugs are classified based on their chemical structure, types of organisms they act on, spectrum of activity, and mechanism of action. Adverse effects and uses of different drugs are also mentioned.Aminoglycosides(medicinal chemistry by p.ravisankar)



Aminoglycosides(medicinal chemistry by p.ravisankar)Dr. Ravi Sankar
Ėý
Aminoglycosides,Aminocyclitols,Source,Structures of streptomycin,Dihydrostreptomycin,A mention of other aminoglycoside antibiotics,Acid hydrolysis,Mechanism of action,SAR,Dihydrostreptomycin and its importance,therapeutic uses, toxicity.
Sulfonamides and trimethoprim



Sulfonamides and trimethoprimSubramani Parasuraman
Ėý
Sulfonamides and trimethoprim are antibacterial drugs that work by inhibiting bacterial folic acid synthesis. Sulfonamides were the first antibacterial sulfone drugs discovered in the 1930s. Trimethoprim inhibits a different enzyme in the folic acid pathway. The combination of sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim is highly synergistic and known as cotrimoxazole. It is used to treat urinary tract, respiratory, and other infections. Both drugs can cause side effects like rash, nausea, and bone marrow suppression if not used carefully, especially in pregnancy, renal impairment, or the elderly.Antiulcer drugs 



Antiulcer drugs yogeeta Goyat
Ėý
this will give brief about the peptic ulcer and give information about the drug used for peptic ulcer and classification of drugs including drugs and there use adverse effect.Beta Lactam Antibiotics 



Beta Lactam Antibiotics Saurav Ch. Sarma
Ėý
This document provides an overview of beta lactam antibiotics, including their structure, mode of action, examples, and mechanisms of resistance. It begins by discussing the bacterial cell wall structure and how beta lactams work by inhibiting cell wall synthesis. Major classes of beta lactams covered include penicillins, cephalosporins, carbapenems, and monobactams. Examples such as methicillin, amoxicillin, and imipenem are described. The document also discusses beta lactamase resistance and concludes with a brief overview of classification.Cephalosporins - Pharmacology 



Cephalosporins - Pharmacology Areej Abu Hanieh
Ėý
Cephalosporins are a class of beta-lactam antibiotics that inhibit bacterial cell wall synthesis. They include first, second, third, fourth, and fifth generation drugs with varying spectra of coverage. They have concentration-dependent bactericidal activity and are excreted renally. Common side effects include diarrhea, rash, and nephrotoxicity. Vancomycin and polymyxins have activity against gram-positive and highly resistant gram-negative bacteria, respectively. Tetracyclines have broad-spectrum coverage including MRSA and are bacteriostatic.More from SANDEEP MEWADA (20)
Cellular and molecular pharmacology



Cellular and molecular pharmacologySANDEEP MEWADA
Ėý
This document provides information about the cell cycle and its regulation. It discusses the key phases of the cell cycle including interphase, mitosis, and meiosis. Interphase consists of G1, S, and G2 phases where the cell grows and DNA is replicated. Mitosis involves nuclear division into two daughter cells with identical chromosomes. Meiosis involves two cell divisions resulting in four daughter cells each with half the original chromosome number, allowing for genetic variation. The document defines important cell cycle concepts and compares the processes of mitosis and meiosis.PHARMACOVIGILANCE (PV)



PHARMACOVIGILANCE (PV)SANDEEP MEWADA
Ėý
Thank YouâĻ ClinoSol Research Mujeebuddin Shaik (Founder & CEO)#Sir uma priya(Director) #Mem at ClinoSol Research Pvt. Ltd & Kabya Pratap (ClinoSol) at ï#Business #Development #Intern for giving me a great #opportunity in #internship at #ClinoSol Your all Best Efforts & Support helps me alot #šÝšÝßĢshare #innovation #pharmacovigilance #pv #linkedin #thankyou again ïââïļïĨģPharmacovigilance (PV)



Pharmacovigilance (PV)SANDEEP MEWADA
Ėý
Pharmacovigilance is defined by the WHO as the science and activities related to detecting, assessing, understanding, and preventing adverse effects from medicines. Its main purpose is to reduce the risk of harm to patients from drug use. Pharmacovigilance involves post-marketing surveillance methods like voluntary reporting of adverse drug reactions, as well as disseminating data on ADRs to educate doctors and regulatory bodies.Vaginal route of administration



Vaginal route of administrationSANDEEP MEWADA
Ėý
This document discusses the vaginal route of drug administration. It notes that novel vaginal drug delivery systems (NVDDS) are designed with desirable distribution, bioadhesive, retention, and release characteristics. Some advantages of the vaginal route include ease of administration, reduced side effects, avoidance of first-pass metabolism, and effectiveness for orally inactive drugs. However, there are also disadvantages like local irritation, influence of sexual intercourse, and cultural sensitivity. Recent advances involve bioadhesive and other novel delivery systems. Applications of intravaginal drug delivery systems include vaginal immunization, treatment of HIV/fungal infections, hormone delivery, and contraceptive rings.Urethral route of administration



Urethral route of administrationSANDEEP MEWADA
Ėý
The document discusses the urethral route of drug administration and novel drug delivery systems. Specifically, it describes:
1) The urethral route involves inserting drugs like solutions or suppositories into the urethra to treat conditions like incontinence or impotence, but it can cause inconvenience or pain.
2) Alprostadil urethral microsuppositories are self-inserted drug delivery devices that are 1.4mm in diameter and release medication over 4-7 days.
3) Novel drug delivery systems aim to improve drug potency, provide sustained release, increase safety, and target specific tissues through formulation approaches and medical devices.Transdermal route



Transdermal routeSANDEEP MEWADA
Ėý
Transdermal drug delivery methods provide an alternative to oral administration and injections. Various technologies have been developed to bypass or modulate the skin's barrier function, including iontophoresis using electrical current, electroporation using intense electric charges to create small pores, phonophoresis using ultrasound, and microneedles coated with microscopic needles to deliver drugs through the skin. These methods provide effective and painless ways to deliver medication through the skin and into the bloodstream.Opthalmic route of administration



Opthalmic route of administrationSANDEEP MEWADA
Ėý
This document discusses various ophthalmic drug delivery routes and formulations. It describes common ophthalmic dosage forms like solutions, suspensions, and ointments. It also discusses newer forms like gel-forming solutions, ocular inserts, and contact lenses coated with drugs. Ocular inserts are solid or semisolid forms that can remain in the eye for longer periods with fewer disadvantages than traditional forms. Examples provided are Ocusert and Lacrisert inserts. Gel-forming solutions undergo sol-gel transitions when exposed to factors like pH or temperature to slow drug drainage and increase bioavailability. Timoptic-XE uses gellan gum to form a gel upon contact with tears. Contact lenses can absorb and slowly release drugs like timNovel drug delivery system



Novel drug delivery systemSANDEEP MEWADA
Ėý
Novel drug delivery systems aim to optimize drug delivery to achieve the desired therapeutic effects. They can provide precise dosing, improve drug efficacy through more efficient absorption, and enhance patient comfort. Rapidly dissolving tablets are one type of novel delivery system that can dissolve quickly in the mouth for rapid drug release. They are commonly prepared through direct compression of the drug with superdisintegrants or by freeze drying drug solutions in blister packs. Excipients like croscarmellose sodium, crospovidone, and sodium starch glycolate are often used as superdisintegrants in these systems to promote rapid tablet disintegration. Lollipops have also been used to deliver drugs through the oral mucosa for rapid absorption, such asCardiac Assessment Test



Cardiac Assessment TestSANDEEP MEWADA
Ėý
The document provides reference ranges and normal values for various cardiac tests and assessments including:
- Blood gas analysis values such as pH, pCO2, and pO2.
- Complete blood count components like hemoglobin, RBC count, WBC count and differentials.
- Electrolytes including sodium, potassium, calcium and their normal ranges.
- Kidney and liver function tests including creatinine, BUN, bilirubin and liver enzymes.
- Lipid profiles like cholesterol, triglycerides, and lipoproteins.
- Cardiac markers like CK-MB, troponin and their significance in diagnosing heart attacks.
- Coagulation tests like PTMedication errors



Medication errorsSANDEEP MEWADA
Ėý
This document discusses medication errors, including definitions of medication errors, adverse drug events, and adverse drug reactions. It notes that medication errors are preventable and a common cause of negative health outcomes. It provides examples of medication classes often involved in serious errors and recommendations for preventing errors, such as minimizing verbal orders, specifying indications for medications, avoiding abbreviations, questioning unclear orders, using leading rather than trailing zeros, and checking for allergies and patient identification before administering medications. Nurses are responsible for documenting medications before administration. If a medication order is unclear, nurses should contact the prescribing physician to verify the order.Medication administration



Medication administrationSANDEEP MEWADA
Ėý
This document discusses proper medication administration, including preparing for drug administration, different drug routes like oral and parenteral, and techniques for injections and intravenous medications. It covers topics such as enteral drugs, parenteral drugs, injection techniques, preparing intravenous medications, and topical drugs.Life span considerations



Life span considerationsSANDEEP MEWADA
Ėý
Pediatric patients have distinct pharmacokinetic considerations due to physiological differences compared to adults. These include more acidic gastric pH, slower gastric emptying, faster skin absorption and irregular intramuscular absorption. Children also have higher total body water percentages, a more immature blood-brain barrier, liver and kidneys. Dosages for pediatric patients must account for their smaller sizes and developing organ systems. Geriatric patients also have altered pharmacokinetics such as slower gastric emptying and GI transit, decreased liver and kidney function, and lower total body water percentages. Their medications require special monitoring due to increased risks.Legal, ethical, and cultural



Legal, ethical, and culturalSANDEEP MEWADA
Ėý
This document summarizes key pieces of U.S. drug legislation from 1906 to 1991, including the Federal Food and Drug Act, Harrison Narcotic Act, and Orphan Drug Act. It also outlines the FDA drug approval process including preclinical studies, clinical trial phases, and post-approval research. Finally, it discusses considerations for ethical nursing practice according to the ANA Code of Ethics and the importance of assessing cultural factors that may influence a patient's health beliefs, treatment compliance, and response to medications.Introduction to pharmacology in nursing



Introduction to pharmacology in nursingSANDEEP MEWADA
Ėý
Introduction to pharmacology in nursing Pharmacologic Principles
Parenteral Route Mechanism of Action Receptor Interaction
Enzyme Interaction
Non-Specific Interaction
Parenteral administration



Parenteral administrationSANDEEP MEWADA
Ėý
This document discusses various parenteral routes of drug administration including intravenous, intramuscular, intradermal, and subcutaneous. It outlines the advantages as the fastest onset of action and ability to administer drugs when the oral route is not possible. Disadvantages include potential for infection, tissue damage, and short duration of action for intravenous specifically. Proper administration techniques are important to ensure safety and efficacy.Dairy project



Dairy projectSANDEEP MEWADA
Ėý
Manoj Mewada Dairy project of JNS College from Shujalpur Ujjain Vikram University lives in kalapipal Mandi source collection and data village near dendi satendi gerkhedi jodâAN OVERVIEW OF PTEROSPERMUM ACERIFOLIUMâ



âAN OVERVIEW OF PTEROSPERMUM ACERIFOLIUMâSANDEEP MEWADA
Ėý
âAN OVERVIEW OF PTEROSPERMUM ACERIFOLIUMâ
RAJIV GANDHI PROUDYOGIKI VISHWAVIDYALAYA
BHOPAL (M.P.)
In partial fulfillment of requirement for
award of degree of
Bachelor of Pharmacy
SESSION:-2018-19
Under the guidance of: Submitted By: Dr. Om Prakash Agrawal Sandeep Mewada (Associate Professor) B.Pharm-VII Semester Patel College of Pharmacy, Enrollment No. 0146PY151074 Bhopal
Presentation of plasmalyte by ashvin sharma



Presentation of plasmalyte by ashvin sharmaSANDEEP MEWADA
Ėý
The document discusses cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) and the use of different intravenous fluids for priming the CPB circuit. It notes that CPB is used to temporarily take over the function of the heart and lungs during open-heart surgery. The ideal priming solution maintains electrolyte and acid-base balance. While Ringer's lactate is commonly used, studies have shown it can cause lactic acidosis. Plasmalyte-A is comparable to plasma and may avoid issues seen with Ringer's lactate. The study aims to compare Ringer's lactate and Plasmalyte-A as priming fluids to see which better prevents bypass-associated acidosis in patients undergoing valve replacementGPAT INSULIN,ORAL HYPOGLYCEMIC AGENTS



GPAT INSULIN,ORAL HYPOGLYCEMIC AGENTSSANDEEP MEWADA
Ėý
The document discusses various drugs used to treat diabetes, including their mechanisms of action, side effects, and classifications. It notes that lactic acidosis is common with phenformin, rosiglitazone acts as a PPAR gamma agonist but not by increasing insulin secretion, hypokalemia can occur if insulin is given rapidly for diabetic ketoacidosis, and metformin can cause vitamin B12 deficiency. Common side effects of thiazolidinadiones include water retention and weight gain.Recently uploaded (20)
N.C. DPI's 2023 Language Diversity Briefing



N.C. DPI's 2023 Language Diversity BriefingMebane Rash
Ėý
The number of languages spoken in NC public schools.How to use Init Hooks in Odoo 18 - Odoo šÝšÝßĢs



How to use Init Hooks in Odoo 18 - Odoo šÝšÝßĢsCeline George
Ėý
In this slide, weâll discuss on how to use Init Hooks in Odoo 18. In Odoo, Init Hooks are essential functions specified as strings in the __init__ file of a module.Database population in Odoo 18 - Odoo slides



Database population in Odoo 18 - Odoo slidesCeline George
Ėý
In this slide, weâll discuss the database population in Odoo 18. In Odoo, performance analysis of the source code is more important. Database population is one of the methods used to analyze the performance of our code. Research & Research Methods: Basic Concepts and Types.pptx



Research & Research Methods: Basic Concepts and Types.pptxDr. Sarita Anand
Ėý
This ppt has been made for the students pursuing PG in social science and humanities like M.Ed., M.A. (Education), Ph.D. Scholars. It will be also beneficial for the teachers and other faculty members interested in research and teaching research concepts.Reordering Rules in Odoo 17 Inventory - Odoo šÝšÝßĢs



Reordering Rules in Odoo 17 Inventory - Odoo šÝšÝßĢsCeline George
Ėý
In Odoo 17, the Inventory module allows us to set up reordering rules to ensure that our stock levels are maintained, preventing stockouts. Let's explore how this feature works.APM People Interest Network Conference - Tim Lyons - The neurological levels ...



APM People Interest Network Conference - Tim Lyons - The neurological levels ...Association for Project Management
Ėý
APM People Interest Network Conference 2025
-Autonomy, Teams and Tension: Projects under stress
-Tim Lyons
-The neurological levels of
team-working: Harmony and tensions
With a background in projects spanning more than 40 years, Tim Lyons specialised in the delivery of large, complex, multi-disciplinary programmes for clients including Crossrail, Network Rail, ExxonMobil, Siemens and in patent development. His first career was in broadcasting, where he designed and built commercial radio station studios in Manchester, Cardiff and Bristol, also working as a presenter and programme producer. Tim now writes and presents extensively on matters relating to the human and neurological aspects of projects, including communication, ethics and coaching. He holds a Masterâs degree in NLP, is an NLP Master Practitioner and International Coach. He is the Deputy Lead for APMâs People Interest Network.
Session | The Neurological Levels of Team-working: Harmony and Tensions
Understanding how teams really work at conscious and unconscious levels is critical to a harmonious workplace. This session uncovers what those levels are, how to use them to detect and avoid tensions and how to smooth the management of change by checking you have considered all of them.The Constitution, Government and Law making bodies .



The Constitution, Government and Law making bodies .saanidhyapatel09
Ėý
This PowerPoint presentation provides an insightful overview of the Constitution, covering its key principles, features, and significance. It explains the fundamental rights, duties, structure of government, and the importance of constitutional law in governance. Ideal for students, educators, and anyone interested in understanding the foundation of a nationâs legal framework.
Kaun TALHA quiz Prelims - El Dorado 2025



Kaun TALHA quiz Prelims - El Dorado 2025Conquiztadors- the Quiz Society of Sri Venkateswara College
Ėý
Prelims of Kaun TALHA : a Travel, Architecture, Lifestyle, Heritage and Activism quiz, organized by Conquiztadors, the Quiz society of Sri Venkateswara College under their annual quizzing fest El Dorado 2025. TLE 7 - 3rd Topic - Hand Tools, Power Tools, Instruments, and Equipment Used ...



TLE 7 - 3rd Topic - Hand Tools, Power Tools, Instruments, and Equipment Used ...RizaBedayo
Ėý
Hand Tools, Power Tools, and Equipment in Industrial ArtsThe Battle of Belgrade Road: A WW1 Street Renaming Saga by Amir Dotan



The Battle of Belgrade Road: A WW1 Street Renaming Saga by Amir DotanHistory of Stoke Newington
Ėý
Presented at the 24th Stoke Newington History Talks event on 27th Feb 2025
https://stokenewingtonhistory.com/stoke-newington-history-talks/Blind Spots in AI and Formulation Science Knowledge Pyramid (Updated Perspect...



Blind Spots in AI and Formulation Science Knowledge Pyramid (Updated Perspect...Ajaz Hussain
Ėý
This presentation delves into the systemic blind spots within pharmaceutical science and regulatory systems, emphasizing the significance of "inactive ingredients" and their influence on therapeutic equivalence. These blind spots, indicative of normalized systemic failures, go beyond mere chance occurrences and are ingrained deeply enough to compromise decision-making processes and erode trust.
Historical instances like the 1938 FD&C Act and the Generic Drug Scandals underscore how crisis-triggered reforms often fail to address the fundamental issues, perpetuating inefficiencies and hazards.
The narrative advocates a shift from reactive crisis management to proactive, adaptable systems prioritizing continuous enhancement. Key hurdles involve challenging outdated assumptions regarding bioavailability, inadequately funded research ventures, and the impact of vague language in regulatory frameworks.
The rise of large language models (LLMs) presents promising solutions, albeit with accompanying risks necessitating thorough validation and seamless integration.
Tackling these blind spots demands a holistic approach, embracing adaptive learning and a steadfast commitment to self-improvement. By nurturing curiosity, refining regulatory terminology, and judiciously harnessing new technologies, the pharmaceutical sector can progress towards better public health service delivery and ensure the safety, efficacy, and real-world impact of drug products.Principle and Practices of Animal Breeding || Boby Basnet



Principle and Practices of Animal Breeding || Boby BasnetBoby Basnet
Ėý
Principle and Practices of Animal Breeding Full Note
|| Assistant Professor Boby Basnet ||IAAS || AFU || PU || FUCBSE Arabic Grammar - Class 10 ppt.pptx



CBSE Arabic Grammar - Class 10 ppt.pptxsuhail849886
Ėý
cbse arabic grammar
grade 10 cbse arabic grammar
cbse class 10 arabic grammar
arabic marathon cbse arabic 10
nominal sentences
How to Modify Existing Web Pages in Odoo 18



How to Modify Existing Web Pages in Odoo 18Celine George
Ėý
In this slide, weâll discuss on how to modify existing web pages in Odoo 18. Web pages in Odoo 18 can also gather user data through user-friendly forms, encourage interaction through engaging features. How to Setup WhatsApp in Odoo 17 - Odoo šÝšÝßĢs



How to Setup WhatsApp in Odoo 17 - Odoo šÝšÝßĢsCeline George
Ėý
Integrate WhatsApp into Odoo using the WhatsApp Business API or third-party modules to enhance communication. This integration enables automated messaging and customer interaction management within Odoo 17.Year 10 The Senior Phase Session 3 Term 1.pptx



Year 10 The Senior Phase Session 3 Term 1.pptxmansk2
Ėý
Year 10 The Senior Phase Session 3 Term 1.pptxAPM People Interest Network Conference - Tim Lyons - The neurological levels ...



APM People Interest Network Conference - Tim Lyons - The neurological levels ...Association for Project Management
Ėý
Kaun TALHA quiz Prelims - El Dorado 2025



Kaun TALHA quiz Prelims - El Dorado 2025Conquiztadors- the Quiz Society of Sri Venkateswara College
Ėý
Monobactam
- 1. Monobactam âĒ Monobactams are Îē-lactam compounds wherein the Îē-lactam ring is alone and not fused to another ring, in contrast to most other Îē-lactams. âĒ They are effective only against aerobic Gram-negative bacteria. âĒ (e.g., Neisseria, Pseudomonas).
- 2. Other examples of monobactams are âĒaztreonam. âĒtigemonam, âĒnocardicin A, âĒand tabtoxin.
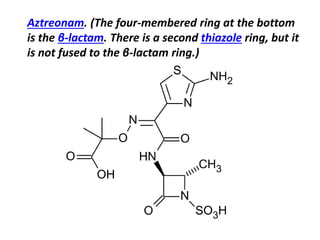
- 3. Aztreonam. (The four-membered ring at the bottom is the Îē-lactam. There is a second thiazole ring, but it is not fused to the Îē-lactam ring.)
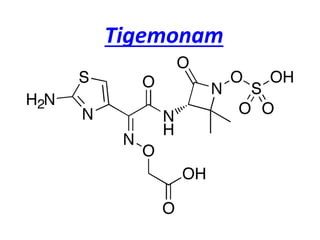
- 4. Tigemonam
- 5. Adverse effects to monobactams can include âĒ skin rash âĒ and occasional abnormal liver functions. âĒ They have no cross-hypersensitivity reactions with penicillin but like penicillins can trigger seizures in patients with history of seizures.





