object oriented programming language.pptx
- 1. Defining Member Functions • The member function must be declared inside the class. • They can be defined in a) private or public section b) inside or outside the class. • The member functions defined inside the class are treated as inline function. • If the member function is small then it should be defined inside the classotherwise it should be defined outside the class
- 2. Member function inside the class • Member function inside the class can be declared in public or private section public member functions WAP to define member function in public section. #include<iostream.h> class product { private: int pno; float p; public: void getdata() { cout<< "enter the product no and price"; cin>>pno>>p; } void show() { cout<<"product no="<<pno<<endl<<"price="<<p; }}; void main() { product x; x.getdata(); x.show(); }
- 3. Private member functions WAP to declare private member function and access it by using public member functions #include<iostream.h> class product { private: int pno; float p; void getdata() { cout<< "enter the product no and price"; cin>>pno>>p; } public: void show() { getdata(); cout<<"product no="<<pno<<endl<<"price="<<p; } }; void main() { product x; x.show(); }
- 4. Member function outside the class To define a function outside the class the following care must be taken: 1. The prototype of function must be declared inside the class. 2. The function name must be preceded by class name and its return type separated by scope resolution operator denoted by ::
- 5. Continue…. WAP to define member function of class outside the class. #include<iostream.h> class product { private: int pno; float p; public: void getdata() { cout<< "enter the product no and price"; cin>>pno>>p; } void show(); }; void product:: show() { cout<<"product no="<<pno<<endl<<"price="<<p; } void main() { product x; x.getdata(); x.show(); }
- 6. Characteristics of member functions 1. The difference between member and normal function is that the normal function can be invoked freely where as the member function only by using an object of the same class. 2. The private data or private function can be accessed by public member function . Other functions have no access permission. 3. The member function can invoke one another without using any object or dot operator.
- 7. Inline Functions • When a function is declared as inline, the compiler copies the code of the function in the calling function i.e. function body is inserted in place of function call during compilation. • Passing of control between caller and callee functions is avoided. • If the function is very large, in such a case inline function is not used because compiler copies the contents in the called function that reduces the program execution speed. • It is advisable to use inline function for only small function.
- 8. Continue… Following are some situations where inline function may not work: 1. The function should not be recursive. 2. Function should not contain static variables. 3. Functions containing control structure statements such as switch ,if, for loop etc. 4. The function main() cannot work as inline.
- 9. Function Overloading It is possible in c++ to use the same function name for a number of times for different intentions. Defining multiple functions with same name is known as function overloading. The overloaded function must be different in its argument list and with different data types
- 10. Example WAP to find the area of rectangle, square, triangle .use function overloading.
- 11. Static member variables Once a data member variable is declared as static, only one copy of that member is created for the whole class. For ex: static int a; int A::a=0; where A is the class name The class and scope of the static variable is defined outside the class declaration. The reason are: • The static data members are associated with the class and not with any object. • The static data member variable are stored individually rather than an element of an object. • It must be initialized otherwise the linker will generate an error. • The memory for static data is allocated only once. • Only one copy of static member variable is created for the whole class for any number of objects.
- 12. Static member functions When a function is defined as static , it can access only static member variables and functions of the same class. The static keyword makes the function free form the individual object of the class and its scope is global in the class without creating any side effect for other part of the program. The programmer must follow the following points while declaring static function: 1. Just one copy of static member is created in the memory for entire class. 2. Static member functions can access only static data members or functions. 3. Static member functions can be invoked using class name. 4. It is also possible to invoke static member functions using objects. 5. When one of the objects changes the value of data member variables, the effect is visible to all the objects of the class.
- 13. Continue.. WAP to declare static member functions. Class A { static int c; public: static void count(){ c++;} static void display() { cout<<“n value of c:”<<c; } }; int A::c=0; void main() { A::count(); A:: count(); A::display(); }
- 14. Friend Functions C++ allows a mechanism, in which a non-member function has access permission to the private members of the class. This can be done by declaring a non-member function friend to the class whose private data is to be accessed. Here friend is a keyword. The friend functions have the following properties: 1. There is no scope restriction for the friend function hence they can be called directly without using objects. 2. Unlike member functions of class, friend function cannot access the member directly. 3. Use of friend functions is rarely done , because it violates the rule of encapsulation and data hiding. 4. The function can be declared in public or private sections without changing its meaning.
- 15. Continue.. For example: Class A { friend void display( A); }; void display(A a) { } Where a is an object name
- 16. WAP to access private data using non-member function. Use friend function.
- 17. Constructor • Constructor is a special member function that has the same name as that of the class it belongs. • Constructor is executed when an object is declared. • It have neither return value nor void. • The main function of constructor is to initialize objects and allocate appropriate memory space to objects. • Though constructors are executed implicitly , they can be invoked explicitly. • Constructors can have default and can be overloaded
- 18. An example of constructor: class A { private: int a, b, c; public: A(); } A::A() { a=0 ; b=0;c=0;} void main() { A x; }
- 19. Types of Constructor • Default Constructor • Parametrized constructor • Copy Constructor • Overloaded Constructor
- 20. Default Constructor Constructors without arguments is known as default constructor. WAP to read values through the keyboard. Use default Constructor
- 21. Parametrized Constructor It is also possible to create constructor with arguments and such constructors are called as parameterized constructors. For such constructor ,it is necessary to pass values to the constructor when object is create
- 22. Continue.. WAP to create constructor with arguments and pass the arguments to the constructor. #include<iostream.h> class A { int a,b,c; public: A(int i,int j,int k) { a=i ;b=j;c=k; } void show() { cout<<“a=“<<a<<“b=“<<b<<“c=“<<c; } }; void main() { A x=A(4,5,7) //explicit call A y(1,2,8); x.show(); y.show(); }
- 23. Copy Constructors When we pass an object by value into a function, a temporary copy of that object is created. All copy constructors requires one argument with reference to an object of that class. Using copy constructors, it is possible for the programmers to declare and initialize one object using reference of another object.
- 24. Continue… WAP to demonstrate copy constructors. #include<iostream.h> class A { int n; public: A(){} A(int k) { n=k; } A(A &j) { n=j.n; } void show(){ cout<<“n=“<<n;} }; void main() { A x(50); A y(x); x.show(); y.show(); }
- 25. Overloaded constructors • Like functions, it is also possible to overload constructors. • A class can contain more than one constructor. This is known as constructor overloading. • All the constructors contain different no of arguments.
- 26. Destructors • It is also a special member function like constructor. • Destructors destroy the class objects created by constructors. • The destructors have the same name as their class, preceded by a tilde(~). • It is not possible to define more than one destructor. • The destructor is only way to destroy the object. Hence, they cannot be overloaded. • A destructor neither requires any argument nor returns any value. • It is automatically called when object goes out of space. Destructor release memory space occupied by the objects.
- 27. Continue… WAP to demonstrate execution of constructor and destructor. class A { public: A() { cout<<“n constructor executed”; } ~A() { cout<<“n destructor executed”; } }; void main() { A x; }
- 28. Continue… WAP to create an object and release them using destructors. int c=0; Class A { public: A() { c++; cout<<“n object created: object(“<<c<<“)”; } ~A() { cout<<“n object realeased: object(“<<c<<“)”; } }; void main() { A x,y,z; }
- 29. Inheritance It is the process by which one class acquire or inherit the properties of another class. In other words, the mechanism of deriving a new class from an old one is called inheritance. The old class is referred as base class and the new one is called the derived class. where A is a base class and b is a derived class A B
- 30. Types of Inheritance 1. Single Inheritance 2. Multiple Inheritance 3. Multilevel Inheritance 4. Hierarchical Inheritance 5. Hybrid Inheritance 6. Multipath Inheritance
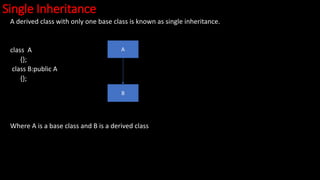
- 31. Single Inheritance A derived class with only one base class is known as single inheritance. class A {}; class B:public A {}; Where A is a base class and B is a derived class A B
- 32. Multiple Inheritance A derived class with several base classes is known as multiple inheritance. class A {}; class B {}; class C: public A, public B {}; Where A and B are base classes and C is derived class A C B
- 33. Multilevel Inheritance • The mechanism of deriving a class from another derived class i.e derived class act as a base class is known as Multilevel inheritance. Class A {}; Class B: public A {}; Class C :public B {}; Where A is base class and B is derived class B is base class and C is derived class( derived class B act as a base class ) A B C
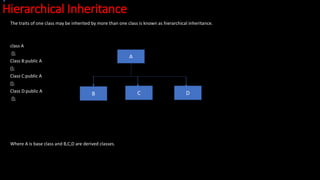
- 34. Hierarchical Inheritance The traits of one class may be inherited by more than one class is known as hierarchical inheritance. class A {}; Class B:public A {}; Class C:public A {}; Class D:public A {}; Where A is base class and B,C,D are derived classes. A B D C
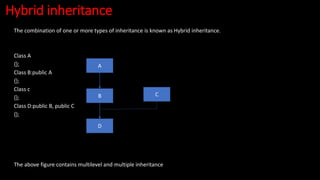
- 35. Hybrid inheritance The combination of one or more types of inheritance is known as Hybrid inheritance. Class A {}; Class B:public A {}; Class c {}; Class D:public B, public C {}; The above figure contains multilevel and multiple inheritance A C D B
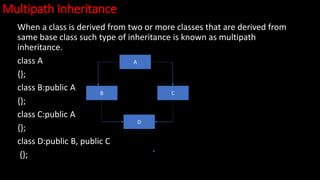
- 36. Multipath Inheritance When a class is derived from two or more classes that are derived from same base class such type of inheritance is known as multipath inheritance. class A {}; class B:public A {}; class C:public A {}; class D:public B, public C {}; A C B D
- 37. Defining derived classes A derived class is defined by specifying its relationship with the base class in addition to its own details. The general form of defining a derived class is: class derived class name: visibility mode base class name { members of derived class } The colon indicates that the derived class name is derived from the base class name. The visibility mode is optional and if present may be either private or public. The default visibility mode is private.
- 38. Continue.. class A: private B {}; When a base class is privately inherited by a derived class, public members of the base class become private members of the derived class and therefore the public members of the base class can only be accessed by the member functions of the derived class. They are inaccessible to the objects of the derived class.
- 39. Continue.. Class A: public B {}; When the base class is publicly inherited, public members of the base class become public members of the derived class and therefore they are accessible to the objects of the derived class
- 40. Protected C++ provides a third visibility modifier, protected, which serve a limited purpose in inheritance. A member declared as protected is accessible by the member functions within its class and any class immediately derived from it. It cannot be accessed by the functions outside these two classes. Syntax: class class name { private: //optional // visible to member functions within its class protected: //visible to member functions of its own // and derived class public: // visible to all functions in the program };