Physical sim vs smartnumbers
0 likes145 views
Why restrict your organisation to a single mobile network operator when all the clever stuff can be delivered from the cloud to any SIM?
1 of 2
Download to read offline

Recommended
Foundation fo e-commerec(final)



Foundation fo e-commerec(final)Anirban Mondal
╠²
This document provides an overview of electronic commerce. It defines electronic commerce and distinguishes between electronic markets and inter-organizational systems. The benefits of electronic commerce are described for organizations, consumers, and society, while also noting some technical and non-technical limitations. Driving forces behind the widespread adoption of electronic commerce are discussed, including business pressures from competition and new technologies. Major changes to organizations and business models expected due to electronic commerce are also outlined.Introduction to Electronic Business



Introduction to Electronic BusinessKAJAK E-business and E-marketing projects
╠²
Brief introduction to the issues of electronic business and information technology impact on business - suitable for activating first year business students.Feature Of Mobile Commerce



Feature Of Mobile CommerceSaumen Ray
╠²
This document discusses the future of mobile commerce (m-commerce). It describes how m-commerce allows users to access business services anytime and anywhere using mobile networks. The key advantages of m-commerce include providing context-specific, time-critical, and spontaneous services. Example m-commerce applications are mobile banking, shopping, entertainment, marketing, and information services. Challenges to the growth of m-commerce include security, developing profitable business models, and bandwidth limitations on mobile networks.Electronic Business



Electronic BusinessMayank Kashyap
╠²
The document provides information on e-commerce and e-business models. It defines e-commerce as buying and selling of goods and services over electronic systems like the internet. E-business is broader and includes using technology to improve business processes internally and externally. Some common e-commerce models discussed are the storefront model, marketplace model, information model, and community model. The storefront model involves companies selling directly through an online storefront, while the marketplace model involves retailers selling through larger marketplaces like Amazon.ž¬žĘ┘ł┘Ŗž▒ ┘łž©ž▒┘ģž¼┘ć ┘ģ┘ł┘éž╣ ž¦┘䞬ž¼ž¦ž▒ž® ž¦┘äžź┘ä┘āž¬ž▒┘ł┘å┘Ŗž® ž©ž¦ž│ž¬ž«ž»ž¦┘ģ ž¦┘䞦┘łž©┘å ┘āž¦ž▒ž¬ OpenCart



ž¬žĘ┘ł┘Ŗž▒ ┘łž©ž▒┘ģž¼┘ć ┘ģ┘ł┘éž╣ ž¦┘䞬ž¼ž¦ž▒ž® ž¦┘äžź┘ä┘āž¬ž▒┘ł┘å┘Ŗž® ž©ž¦ž│ž¬ž«ž»ž¦┘ģ ž¦┘䞦┘łž©┘å ┘āž¦ž▒ž¬ OpenCartMohamed Hanafy
╠²
┘ģ┘éž»┘ģž® ž╣┘å ┘łž¦┘éž╣ ž¦┘䞬ž¼ž¦ž▒ž® ž¦┘䞦┘ä┘āž¬ž▒┘ł┘å┘Ŗž® ┘ü┘ē ž¦┘ä┘łžĘ┘å ž¦┘äž╣ž▒ž©┘ē ┘łžĘž▒┘Ŗ┘éž® žź┘åž┤ž¦žĪ ┘ģ┘ł┘éž╣ ┘ä┘䞬ž¼ž¦ž▒ž® ž¦┘äžź┘ä┘āž¬ž▒┘ł┘å┘Ŗž® ┘ä┘䞬ž│┘ł┘é ž╣ž©ž▒ ž¦┘äžź┘垬ž▒┘垬žī ž©ž¦ž│ž¬ž«ž»ž¦┘ģ ž¦┘äž©ž▒┘ģž¼┘Ŗž¦ž¬ ┘ģ┘üž¬┘łžŁž® ž¦┘ä┘ģžĄž»ž▒ žī ┘łž┤ž▒žŁ ž¬┘åžĄ┘Ŗž© ┘łž¦ž»ž¦ž▒ž® ž¦┘łž©┘å ┘āž¦ž▒ž¬ OpenCartžī ┘ł ž©┘łž¦ž©ž¦ž¬ ž¦┘äž»┘üž╣ ž¦┘äžź┘ä┘āž¬ž▒┘ł┘å┘ē ž¦┘ä┘ģž¬ž¦žŁž® ┘ü┘ē ┘ģžĄž▒žī┘łžĘž▒┘é ž¦┘äž┤žŁ┘å ž¦┘ä┘ģž«ž¬┘ä┘üž®.E commerce 



E commerce Alvin Cabeli├▒o
╠²
This video is presented by USEP's BSCS student Alvin Mark U. Cabeli├▒o under Mr. ND Arquillano as a partial fulfilment for Elective 4 -E-Commerce It talks about E-Commerce Infrastructure. Finpro market opportunity virtual mobile networks china



Finpro market opportunity virtual mobile networks chinaBusiness Finland
╠²
The virtual mobile network sector is opening up in China and providing opportunities for Finnish companies. China has issued licenses to private companies allowing them to lease access to China's state-owned mobile networks. License holders come from various backgrounds like e-commerce, software, and media. They need business solutions to differentiate their services. Finnish mobile network expertise is valued in China and Finnish companies can take advantage of the growing Chinese virtual mobile network market.m-commerce Applications



m-commerce ApplicationsHimanshu Arya
╠²
This is the presentation on m-Commerce applications and its use in information system.
Outline of presentation:
Introduction
History
Overview
Services and Applications
CLOs(Class Learning Objective of Managing Information of Business)
Advantages
Disadvantages
Electronic commerce



Electronic commerceHarshit Gupta
╠²
Electronic commerce, or e-commerce, involves buying and selling of products or services over electronic systems like the Internet. It was invented in 1979 and is based on technologies like mobile commerce, electronic funds transfer, and supply chain management. There are several types of e-commerce including business-to-business, business-to-consumer, consumer-to-consumer, and mobile commerce. E-commerce provides advantages like overcoming geographical limitations and allowing comparison shopping but also has disadvantages such as lacking personal touch and potential security issues. It has many applications in areas like online shopping, banking, and ticketing.M-Commerce



M-CommerceBOSS Webtech
╠²
M-Commerce is the ability to conduct commerce using a mobile device, such as a smartphone, a Personal Digital Assistant (PDA), or other emerging mobile equipment such as dashtop mobile devices.Introduction to-ebusiness



Introduction to-ebusinessCyri Jones
╠²
E-business refers to conducting business electronically and integrating technology like the internet to streamline processes. In the late 1990s, many companies rushed to adopt e-business due to hype, but costs were high and customers were still uncomfortable using the internet. This led to the dot-com crash. Now, internet penetration is higher, costs are lower, and companies have refined their e-business models. E-business allows for speed, convenience, customization and new ways of defining product value compared to traditional business. The key benefits are cost reduction, increased sales, improved customer service and expanded markets.E commerce ppt



E commerce pptihedce
╠²
Commerce is the exchange of goods and services, and e-commerce refers specifically to electronic commerce over the internet. The history of e-commerce began in the 1960s with businesses sharing documents electronically, growing in the 1980s-90s with the rise of eBay and Amazon allowing consumers to shop online. There are various types of e-commerce relationships including business-to-business, business-to-consumer, and consumer-to-consumer. The e-commerce process involves a consumer browsing a merchant's website, adding items to a shopping cart, providing payment and shipping details, receiving order confirmation, and having the order fulfilled.Legal and regulatory environment e commerce



Legal and regulatory environment e commerceDr Vijay Vishwakarma
╠²
The document discusses cyber laws and hacking. It defines cyber law as laws related to the internet and defines different types of hacking (e.g. website, network, password). It also discusses advantages and disadvantages of hacking, and different types of hackers (e.g. white hat, black hat, grey hat) based on their intent when hacking systems. The document emphasizes that cyber laws are needed to prevent illegal activities online and establish a safe cyber environment as internet usage increases globally.Electronic data interchange



Electronic data interchangeRohit Kumar
╠²
EDI involves the electronic exchange of business documents like purchase orders and invoices between supply chain partners over networks like the internet. Standard message formats are used to automatically exchange documents between computer systems using EDI software. While the idea of EDI originated in the 1960s with railroads in the US, it grew in the 1970s with the development of national EDI standards to reduce costs and increase efficiency compared to paper-based document exchange. EDI allows organizations to streamline processes and improve trading relationships.What Is E Commerce



What Is E CommerceEd Dickinson
╠²
E-commerce relates to buying and selling goods and services electronically over the internet or intranets. It includes processes like e-sourcing, e-tendering, e-evaluation, and e-auctions. E-commerce reduces distances, encourages competition by allowing thorough research, and has led to new job opportunities and companies being established or expanding their business models. It also increases convenience for consumers and dependence on the internet for everyday tasks. However, privacy and security are ongoing issues as websites may collect and sell personal information, and theft of financial and identity information is still possible without proper authentication of transactions. Initiatives are underway to provide more government services electronically as well.Mobile commerce ppt



Mobile commerce pptTapesh Chalisgaonkar
╠²
M-commerce involves using mobile devices to transact, communicate, and entertain through wireless networks. It combines e-commerce and wireless web capabilities. Key features of m-commerce include cash deposits/withdrawals, third party deposits, retail purchases, prepaid top-ups, cash transfers, and bill payments. Mobile devices must support barcode scanning, display, and data transmission for point-of-sale transactions. Technologies used include GSM, 3G, Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, SMS, and MMS. Information is provided by global electronic parties and data synchronization networks. Transactions are facilitated through infrastructure involving multiple steps. Applications include advertising, in-store navigation, comparisons, payments, publications, ticketing, and catalogs. AdvThe business value of e invoicing



The business value of e invoicingFriso de Jong
╠²
This document discusses the business value of e-invoicing and the results of a study on the costs and benefits of automating invoice processes. Some key points:
- Automating invoice processes through e-invoicing can reduce costs by 90% for accounts payable and 44% for accounts receivable departments. It can also reduce errors by 37% and storage costs by up to 67% for accounts payable and 32% for accounts receivable invoices.
- A survey of 169 companies found the average costs to process invoices manually were $30 for accounts payable and $4 for accounts receivable, compared to $3.50 and $2.25 respectively for automated invoices.
- Moving to e-Electronic Communications Act (2000)



Electronic Communications Act (2000)Ed Dickinson
╠²
The Electronic Communications Act 2000 aims to build confidence in electronic commerce in the UK by creating a legal framework to ensure security and trust in online transactions. It does this by addressing cryptography, facilitating e-commerce, and regulating telecommunications licenses. The act was needed because electronic commerce had grown rapidly, with over 90% of UK businesses having internet access and many engaging in online ordering and payments, requiring certainty that digital communications are secure and unaltered.M commerce 1



M commerce 1Shiven Vashisht
╠²
This document discusses mobile commerce (m-commerce), which involves using mobile devices like phones and PDAs to conduct e-commerce transactions. The objectives are to understand m-commerce basics, benefits for small businesses, related technologies, and how to apply them. M-commerce allows buying and selling goods and services or paying for them using mobile devices over wireless networks. It offers businesses flexibility and reduced costs. While it provides advantages like various payment options and push advertising, disadvantages include expenses, small screens, slow speeds, and security issues. Examples include mobile banking, ticketing, marketing and micro-payments. Relevant technologies are SMS, WAP, Bluetooth and GPRS.E commerce and m-commerce



E commerce and m-commerceNaman Kothari
╠²
This document discusses e-commerce and m-commerce. It defines e-commerce as digital transactions within and between organizations, categorizing it into types like B2B, B2C, etc. Challenges to e-commerce in India include a preference for cash on delivery, high payment gateway failure rates, low internet penetration, and logistical issues. M-commerce refers to transactions initiated and completed on mobile devices and can involve technology, products, or services. Challenges to m-commerce are that it is mainly relevant for urban users, lacks awareness and has security concerns, payment issues, and an imbalanced relationship between service providers and networks.E business┌®ž│ž© ┘ł ┌®ž¦ž▒ ž¦┘ä┌®ž¬ž▒┘ł┘å█ī┌®█ī



E business┌®ž│ž© ┘ł ┌®ž¦ž▒ ž¦┘ä┌®ž¬ž▒┘ł┘å█ī┌®█īHanieh Ghofrani
╠²
This document defines key terms related to e-business and e-commerce such as electronic business, electronic commerce, and computer-mediated networks. It discusses how e-business can benefit organizations through increased productivity, selection, and information availability. Examples are given of how companies like Cisco, Nike, and Dell utilize e-business applications. The document also addresses how automobile manufacturers and other industries can apply e-business and considers the potential supply chain members involved in e-commerce.MIS 11 M-Commerce



MIS 11 M-CommerceTushar B Kute
╠²
The series of presentations contains the information about "Management Information System" subject of SEIT for University of Pune.
Subject Teacher: Tushar B Kute (Sandip Institute of Technology and Research Centre, Nashik)
http://www.tusharkute.comTraditional vs e business



Traditional vs e businessClean Agent Sdn Bhd
╠²
The document discusses trends, challenges and opportunities in e-commerce. It provides definitions and explanations of key terms like e-commerce and e-business. E-commerce enables businesses to reach global markets at low costs, facilitate online transactions, and increase competitiveness through timely delivery. The document outlines tools, mechanisms, incentives and statistics on the growth of e-commerce in Malaysia and globally. It also discusses relevant issues for businesses and provides resources for online research.Introduction to e commerce



Introduction to e commerceUtomo Prawiro
╠²
This document provides an introduction to e-commerce, including definitions, types, and frameworks. It defines commerce and e-commerce, discusses different definitions of e-commerce, and outlines the scopes and benefits. It also describes types of e-commerce like B2C, B2B, C2C, and frameworks like Kalakota and Whinston's four building blocks and two supporting pillars. Overall, the document serves as a comprehensive overview of the key concepts and models relating to e-commerce.E comerce i-ii soft copy 1



E comerce i-ii soft copy 1naaaaz
╠²
This document provides the syllabus for the course "E-Commerce and Governance (IT-721)" taught at Technocrats Institute of Technology in Bhopal, India. The syllabus covers 5 units: (1) Introduction to e-commerce including models, history and legal environment, (2) Electronic payment systems, (3) E-government and models, (4) E-readiness and applications, and (5) E-government security. The course aims to provide students an understanding of e-commerce and e-governance concepts, applications, benefits and issues.M commerce ppt



M commerce pptSantosh Kumar
╠²
This document discusses e-commerce in mobile computing. It begins with an introduction that defines commerce, e-commerce, and mobile commerce. It then provides a brief history of mobile commerce beginning in 1997. The bulk of the document covers various aspects of mobile commerce such as services and applications like mobile ticketing, payments methods including mobile wallets, and advantages and disadvantages. It concludes with references for further information.GSMA-Mobile-Identity_Case-Study_Dialog-Connect_May2013



GSMA-Mobile-Identity_Case-Study_Dialog-Connect_May2013Alix Murphy
╠²
Dialog Connect is a mobile identity service launched by Dialog, Sri Lanka's leading mobile operator. It allows subscribers to create a secure digital identity by presenting identity documents during registration at a Dialog store. This digital identity can then be used to access multiple third party services through single sign-on. It benefits both subscribers by reducing login fatigue and improving security, and third party services by providing access to a large user base through a single integrated platform. By establishing digital identity management on mobile networks, Dialog Connect positions the SIM card and mobile operators as important providers of identity solutions beyond traditional telecom services.Mobile commerce



Mobile commercesarah hamed
╠²
M-commerce refers to commercial transactions conducted on wireless devices such as phones and laptops. It utilizes wireless technologies like cellular networks as well as application layer technologies including micro-browsers and messaging. M-commerce provides benefits to both enterprises and users by improving market reach, reducing costs, and offering convenience. Popular methods of mobile payment include near field communication (NFC), QR codes, and mobile wallet apps, though adoption varies globally.smart guide to compliant call recording



smart guide to compliant call recordingmParticle
╠²
1) Mobile call recording is becoming increasingly important for compliance and risk management purposes, especially in regulated industries like banking where communications must be recorded.
2) However, recording mobile calls is challenging as most users have a single device for both personal and work use. Existing app-based or SIM-based recording methods are limited.
3) Smartnumbers Mobile Plus is a new cloud-based service that assigns a business phone number to an employee's personal mobile device. Any calls made on the business number are recorded, while personal calls remain private. This allows for easy, effective mobile call recording without hardware.BT's guide to MiFIDII for financial advisers and brokers



BT's guide to MiFIDII for financial advisers and brokersmParticle
╠²
The document discusses the implications of the upcoming Markets in Financial Instruments Directive (MiFID II) which aims to provide stronger investor protection and transparency. One key change is a new mandatory requirement for investment firms to record telephone conversations and electronic communications relating to transactions, including those made via mobile phones. While mobile call recording is not new, establishing a compliant system can be complex. The document examines different options for mobile call recording solutions under MiFID II such as app-based, network-based, and a new hybrid approach that combines the benefits of both while allowing firms to consider bring your own device policies without risk of non-compliance.More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Electronic commerce



Electronic commerceHarshit Gupta
╠²
Electronic commerce, or e-commerce, involves buying and selling of products or services over electronic systems like the Internet. It was invented in 1979 and is based on technologies like mobile commerce, electronic funds transfer, and supply chain management. There are several types of e-commerce including business-to-business, business-to-consumer, consumer-to-consumer, and mobile commerce. E-commerce provides advantages like overcoming geographical limitations and allowing comparison shopping but also has disadvantages such as lacking personal touch and potential security issues. It has many applications in areas like online shopping, banking, and ticketing.M-Commerce



M-CommerceBOSS Webtech
╠²
M-Commerce is the ability to conduct commerce using a mobile device, such as a smartphone, a Personal Digital Assistant (PDA), or other emerging mobile equipment such as dashtop mobile devices.Introduction to-ebusiness



Introduction to-ebusinessCyri Jones
╠²
E-business refers to conducting business electronically and integrating technology like the internet to streamline processes. In the late 1990s, many companies rushed to adopt e-business due to hype, but costs were high and customers were still uncomfortable using the internet. This led to the dot-com crash. Now, internet penetration is higher, costs are lower, and companies have refined their e-business models. E-business allows for speed, convenience, customization and new ways of defining product value compared to traditional business. The key benefits are cost reduction, increased sales, improved customer service and expanded markets.E commerce ppt



E commerce pptihedce
╠²
Commerce is the exchange of goods and services, and e-commerce refers specifically to electronic commerce over the internet. The history of e-commerce began in the 1960s with businesses sharing documents electronically, growing in the 1980s-90s with the rise of eBay and Amazon allowing consumers to shop online. There are various types of e-commerce relationships including business-to-business, business-to-consumer, and consumer-to-consumer. The e-commerce process involves a consumer browsing a merchant's website, adding items to a shopping cart, providing payment and shipping details, receiving order confirmation, and having the order fulfilled.Legal and regulatory environment e commerce



Legal and regulatory environment e commerceDr Vijay Vishwakarma
╠²
The document discusses cyber laws and hacking. It defines cyber law as laws related to the internet and defines different types of hacking (e.g. website, network, password). It also discusses advantages and disadvantages of hacking, and different types of hackers (e.g. white hat, black hat, grey hat) based on their intent when hacking systems. The document emphasizes that cyber laws are needed to prevent illegal activities online and establish a safe cyber environment as internet usage increases globally.Electronic data interchange



Electronic data interchangeRohit Kumar
╠²
EDI involves the electronic exchange of business documents like purchase orders and invoices between supply chain partners over networks like the internet. Standard message formats are used to automatically exchange documents between computer systems using EDI software. While the idea of EDI originated in the 1960s with railroads in the US, it grew in the 1970s with the development of national EDI standards to reduce costs and increase efficiency compared to paper-based document exchange. EDI allows organizations to streamline processes and improve trading relationships.What Is E Commerce



What Is E CommerceEd Dickinson
╠²
E-commerce relates to buying and selling goods and services electronically over the internet or intranets. It includes processes like e-sourcing, e-tendering, e-evaluation, and e-auctions. E-commerce reduces distances, encourages competition by allowing thorough research, and has led to new job opportunities and companies being established or expanding their business models. It also increases convenience for consumers and dependence on the internet for everyday tasks. However, privacy and security are ongoing issues as websites may collect and sell personal information, and theft of financial and identity information is still possible without proper authentication of transactions. Initiatives are underway to provide more government services electronically as well.Mobile commerce ppt



Mobile commerce pptTapesh Chalisgaonkar
╠²
M-commerce involves using mobile devices to transact, communicate, and entertain through wireless networks. It combines e-commerce and wireless web capabilities. Key features of m-commerce include cash deposits/withdrawals, third party deposits, retail purchases, prepaid top-ups, cash transfers, and bill payments. Mobile devices must support barcode scanning, display, and data transmission for point-of-sale transactions. Technologies used include GSM, 3G, Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, SMS, and MMS. Information is provided by global electronic parties and data synchronization networks. Transactions are facilitated through infrastructure involving multiple steps. Applications include advertising, in-store navigation, comparisons, payments, publications, ticketing, and catalogs. AdvThe business value of e invoicing



The business value of e invoicingFriso de Jong
╠²
This document discusses the business value of e-invoicing and the results of a study on the costs and benefits of automating invoice processes. Some key points:
- Automating invoice processes through e-invoicing can reduce costs by 90% for accounts payable and 44% for accounts receivable departments. It can also reduce errors by 37% and storage costs by up to 67% for accounts payable and 32% for accounts receivable invoices.
- A survey of 169 companies found the average costs to process invoices manually were $30 for accounts payable and $4 for accounts receivable, compared to $3.50 and $2.25 respectively for automated invoices.
- Moving to e-Electronic Communications Act (2000)



Electronic Communications Act (2000)Ed Dickinson
╠²
The Electronic Communications Act 2000 aims to build confidence in electronic commerce in the UK by creating a legal framework to ensure security and trust in online transactions. It does this by addressing cryptography, facilitating e-commerce, and regulating telecommunications licenses. The act was needed because electronic commerce had grown rapidly, with over 90% of UK businesses having internet access and many engaging in online ordering and payments, requiring certainty that digital communications are secure and unaltered.M commerce 1



M commerce 1Shiven Vashisht
╠²
This document discusses mobile commerce (m-commerce), which involves using mobile devices like phones and PDAs to conduct e-commerce transactions. The objectives are to understand m-commerce basics, benefits for small businesses, related technologies, and how to apply them. M-commerce allows buying and selling goods and services or paying for them using mobile devices over wireless networks. It offers businesses flexibility and reduced costs. While it provides advantages like various payment options and push advertising, disadvantages include expenses, small screens, slow speeds, and security issues. Examples include mobile banking, ticketing, marketing and micro-payments. Relevant technologies are SMS, WAP, Bluetooth and GPRS.E commerce and m-commerce



E commerce and m-commerceNaman Kothari
╠²
This document discusses e-commerce and m-commerce. It defines e-commerce as digital transactions within and between organizations, categorizing it into types like B2B, B2C, etc. Challenges to e-commerce in India include a preference for cash on delivery, high payment gateway failure rates, low internet penetration, and logistical issues. M-commerce refers to transactions initiated and completed on mobile devices and can involve technology, products, or services. Challenges to m-commerce are that it is mainly relevant for urban users, lacks awareness and has security concerns, payment issues, and an imbalanced relationship between service providers and networks.E business┌®ž│ž© ┘ł ┌®ž¦ž▒ ž¦┘ä┌®ž¬ž▒┘ł┘å█ī┌®█ī



E business┌®ž│ž© ┘ł ┌®ž¦ž▒ ž¦┘ä┌®ž¬ž▒┘ł┘å█ī┌®█īHanieh Ghofrani
╠²
This document defines key terms related to e-business and e-commerce such as electronic business, electronic commerce, and computer-mediated networks. It discusses how e-business can benefit organizations through increased productivity, selection, and information availability. Examples are given of how companies like Cisco, Nike, and Dell utilize e-business applications. The document also addresses how automobile manufacturers and other industries can apply e-business and considers the potential supply chain members involved in e-commerce.MIS 11 M-Commerce



MIS 11 M-CommerceTushar B Kute
╠²
The series of presentations contains the information about "Management Information System" subject of SEIT for University of Pune.
Subject Teacher: Tushar B Kute (Sandip Institute of Technology and Research Centre, Nashik)
http://www.tusharkute.comTraditional vs e business



Traditional vs e businessClean Agent Sdn Bhd
╠²
The document discusses trends, challenges and opportunities in e-commerce. It provides definitions and explanations of key terms like e-commerce and e-business. E-commerce enables businesses to reach global markets at low costs, facilitate online transactions, and increase competitiveness through timely delivery. The document outlines tools, mechanisms, incentives and statistics on the growth of e-commerce in Malaysia and globally. It also discusses relevant issues for businesses and provides resources for online research.Introduction to e commerce



Introduction to e commerceUtomo Prawiro
╠²
This document provides an introduction to e-commerce, including definitions, types, and frameworks. It defines commerce and e-commerce, discusses different definitions of e-commerce, and outlines the scopes and benefits. It also describes types of e-commerce like B2C, B2B, C2C, and frameworks like Kalakota and Whinston's four building blocks and two supporting pillars. Overall, the document serves as a comprehensive overview of the key concepts and models relating to e-commerce.E comerce i-ii soft copy 1



E comerce i-ii soft copy 1naaaaz
╠²
This document provides the syllabus for the course "E-Commerce and Governance (IT-721)" taught at Technocrats Institute of Technology in Bhopal, India. The syllabus covers 5 units: (1) Introduction to e-commerce including models, history and legal environment, (2) Electronic payment systems, (3) E-government and models, (4) E-readiness and applications, and (5) E-government security. The course aims to provide students an understanding of e-commerce and e-governance concepts, applications, benefits and issues.M commerce ppt



M commerce pptSantosh Kumar
╠²
This document discusses e-commerce in mobile computing. It begins with an introduction that defines commerce, e-commerce, and mobile commerce. It then provides a brief history of mobile commerce beginning in 1997. The bulk of the document covers various aspects of mobile commerce such as services and applications like mobile ticketing, payments methods including mobile wallets, and advantages and disadvantages. It concludes with references for further information.GSMA-Mobile-Identity_Case-Study_Dialog-Connect_May2013



GSMA-Mobile-Identity_Case-Study_Dialog-Connect_May2013Alix Murphy
╠²
Dialog Connect is a mobile identity service launched by Dialog, Sri Lanka's leading mobile operator. It allows subscribers to create a secure digital identity by presenting identity documents during registration at a Dialog store. This digital identity can then be used to access multiple third party services through single sign-on. It benefits both subscribers by reducing login fatigue and improving security, and third party services by providing access to a large user base through a single integrated platform. By establishing digital identity management on mobile networks, Dialog Connect positions the SIM card and mobile operators as important providers of identity solutions beyond traditional telecom services.Mobile commerce



Mobile commercesarah hamed
╠²
M-commerce refers to commercial transactions conducted on wireless devices such as phones and laptops. It utilizes wireless technologies like cellular networks as well as application layer technologies including micro-browsers and messaging. M-commerce provides benefits to both enterprises and users by improving market reach, reducing costs, and offering convenience. Popular methods of mobile payment include near field communication (NFC), QR codes, and mobile wallet apps, though adoption varies globally.Similar to Physical sim vs smartnumbers (20)
smart guide to compliant call recording



smart guide to compliant call recordingmParticle
╠²
1) Mobile call recording is becoming increasingly important for compliance and risk management purposes, especially in regulated industries like banking where communications must be recorded.
2) However, recording mobile calls is challenging as most users have a single device for both personal and work use. Existing app-based or SIM-based recording methods are limited.
3) Smartnumbers Mobile Plus is a new cloud-based service that assigns a business phone number to an employee's personal mobile device. Any calls made on the business number are recorded, while personal calls remain private. This allows for easy, effective mobile call recording without hardware.BT's guide to MiFIDII for financial advisers and brokers



BT's guide to MiFIDII for financial advisers and brokersmParticle
╠²
The document discusses the implications of the upcoming Markets in Financial Instruments Directive (MiFID II) which aims to provide stronger investor protection and transparency. One key change is a new mandatory requirement for investment firms to record telephone conversations and electronic communications relating to transactions, including those made via mobile phones. While mobile call recording is not new, establishing a compliant system can be complex. The document examines different options for mobile call recording solutions under MiFID II such as app-based, network-based, and a new hybrid approach that combines the benefits of both while allowing firms to consider bring your own device policies without risk of non-compliance.HeathWallace_Mobile_Whitepaper_2015



HeathWallace_Mobile_Whitepaper_2015Rory Yates
╠²
This document discusses emerging mobile themes that could impact financial services. It covers key themes like the internet of things (IoT), smart watches, and mobile payments. For IoT, it describes how connected devices are growing rapidly and could allow new types of personal insurance policies and banking services. Smart watches are presented as another connected device that could enable quick access to financial account information. Mobile payments are also growing significantly through mobile applications, with mobile expected to surpass cash usage globally. Financial institutions will need to ensure optimal mobile checkout experiences and maintain customer relationships as new players like Apple and Google enable payments.BT smartnumbers helps you deliver mobile innovation and reduce costs



BT smartnumbers helps you deliver mobile innovation and reduce costsmParticle
╠²
The client wants to reduce the cost of the mobile estate and deliver improvements to business processes. This is what we came up with.An analysis of the distribution channel of vodafone



An analysis of the distribution channel of vodafoneTirthankar Sutradhar
╠²
For a business to grow and respond to the threats and opportunities, VodafoneŌĆÖs flexible infrastructure helps to innovate and implement new communication technologies by reducing the cost and complexity of managing global communications. The mobile, fixed and machine-to-machine technology helps in creating new products, revenue streams and routes to market. Various powerful tools and flexible approach makes the people happier, more engaged and more productive at the same time.
Apart from Wireline solutions, Enterprise mobility, Machine to machine solutions and Business value added services Vodafone provides conferencing and collaboration facilities for the large corporates.The Hybrid Mobile Landscape



The Hybrid Mobile LandscapeVisage Mobile
╠²
Company paid? BYOD? Congratulations- you're both! Whether you know it or not, your company exists in a hybrid landscape of both corporate-paid and individually-paid (BYOD) wireless devices. That's the reality. The question is, what are you going to do about it?The 5 Biggest Financial Services Tech Trends In 2022



The 5 Biggest Financial Services Tech Trends In 2022Bernard Marr
╠²
Financial services firms have undergone some tumultuous few years while digitization and the adoption of technology innovations have been accelerated. Here we look at the five biggest tech trends in the financial services sector.The Amazing Ways Telecom Companies Use Artificial Intelligence And Machine Le...



The Amazing Ways Telecom Companies Use Artificial Intelligence And Machine Le...Bernard Marr
╠²
Telecom companies are increasingly using artificial intelligence and machine learning in many aspects of their business. They use these technologies to improve customer service through virtual assistants and chatbots, enable predictive maintenance to prevent network outages, and perform fraud detection and predictive analytics on large amounts of customer data to make better business decisions. Telecoms are among the industries that have most embraced and benefited from artificial intelligence and machine learning.Great Wireless Way, Best's Review, November 2000



Great Wireless Way, Best's Review, November 2000Gates Ouimette
╠²
Mobile commerce has the potential to impact insurers' distribution channels and increase market valuation by enabling business transactions anytime and anywhere through the convergence of the internet, enterprise applications, and wireless technologies. It allows claims adjusters and medical practitioners to capture customer data on-site using mobile devices and complete transactions in real-time. The biggest benefit of mobile commerce may be new opportunities for cross-selling through remote custom product development with customers. Speech recognition and associated technologies will further drive mobile commerce adoption by enabling input and retrieval of customer data through wireless devices.GDPR for Call Center Industry



GDPR for Call Center Industryjincy joy
╠²
General Data Protection Regulation has been implemented from 25th May,2018.
Get to know from this power-point what is GDPR and what all necessary changes needs to be done in the call center industry.BYOD- A Productivity Catalyst



BYOD- A Productivity CatalystPacket One
╠²
The document discusses Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) policies that allow employees to use their personal devices for work purposes. It notes that BYOD can improve employee productivity and satisfaction by giving them flexibility. However, it also presents challenges for ensuring corporate security and privacy protocols are followed. The document provides criteria organizations should consider for BYOD implementation, such as defining liability, supporting user experience and choice of devices, and developing internal marketing and sustainability of the program over time. It argues that with proper planning and policies, BYOD can balance employee freedom with corporate security and control over technology use.Bring Your Own Device is a disruptive phenomenon that is a significant IT trend



Bring Your Own Device is a disruptive phenomenon that is a significant IT trendMartin Perry
╠²
BYOD is the concept that employees (or students) will bring and use their own mobile devices (such as laptops, tablets, and smart phones) to their workplace (or college). These devices are used to access privileged company information and applications on the company's (or academic institute's) IT infrastructure; there is a challenge to balance the demand to be connected to everything with proper accountability or oversight to protect the company's (academic institute's) IT assets.
This webinar will analyse the demand for BYOD, driven by factors such as:
ŌĆó Pervasive connectivity
ŌĆó Globalisation
ŌĆó Workforce Age profile and expectations
ŌĆó Employee work life integration
ŌĆó The growth in personal devices connected to web [consumerisation of IT]
ŌĆó Change in our relationships with the outside world
ŌĆó Impact on the porosity of the border between private life and work.
And how the balance can be struck between this demand for BYOD, and the need to protect IT assets.
This webinar was first hosted with the Warwick Technology Professional Network of the Warwick Business School wbs.ac.uk
Part of the University of Warwick, we have an international reputation for top quality education and research in management and business.
Why the telecom industry needs conversational chatbots ?



Why the telecom industry needs conversational chatbots ?venkatvajradhar1
╠²
Companies from all industries are constantly trying to expand their business value to accommodate new changes in their field. The telecommunication industry is a clear reflection of this.
Knowing about the future of IoT services with Telecom billing software



Knowing about the future of IoT services with Telecom billing softwareVcare Corporation
╠²
The telecoms sector, though, stands to gain the most because IoT is so dependent on telecommunications providers. New mobile IoT apps and services provide excellent development potential for mobile operators. IoT is expected to bring approximately $1.8 trillion in revenue for mobile network operators by 2026. This will be a significant boost because telecom billing software income has been increasing recently.
https://www.vcarecorporation.com/blog/how-telecom-billing-software-can-lead-the-future-of-iot-servicesThe Internet of Things Drives Business Transformation



The Internet of Things Drives Business TransformationJAX Chamber IT Council
╠²
The document discusses how the Internet of Things is driving business transformation by blurring the digital and physical worlds. It provides examples of how connecting physical objects to the Internet and to each other can create new digital businesses and business models. For instance, it describes a scenario where a car crash automatically notifies emergency responders, assesses damage through vehicle sensors, and initiates insurance claims using data from the crash. The document advocates that combining current business models with digital technologies like the IoT, smart machines, and analytics can create new digital businesses and opportunities. However, it also notes risks both in transforming to digital business models and in failing to do so.Data-driven Banking: Managing the Digital Transformation



Data-driven Banking: Managing the Digital TransformationLindaWatson19
╠²
The digital revolution has arrived in banking. Evolving customer expectations, increasing cyber threats and growing volumes of data are just a few of the challenges faced by traditional financial institutions.How do financial institutions leverage Dell Boomi platform



How do financial institutions leverage Dell Boomi platformRay Business Technologies
╠²
A financial institution will be in an advantageous position to handle market conditions, pressures from competitors, and shift in buyer trends.
https://www.raybiztech.com/blog/dell-boomi/financial-institutions-leverage-boomi-platformThe 7 Biggest Technology Trends To Disrupt Banking & Financial Services In 2020



The 7 Biggest Technology Trends To Disrupt Banking & Financial Services In 2020Bernard Marr
╠²
New technology changes the operations and realities of organizations in all industries when it is widely adopted. It's no different with the latest innovation introduced by artificial intelligence, blockchain, and other technology. Here we look at the 7 biggest technology trends that will disrupt banking and financial services in 2020.Creating value through innovation: Opportunities for micro and small business...



Creating value through innovation: Opportunities for micro and small business...Monica Ioannidou Polemitis
╠²
This document discusses opportunities for micro businesses in the digital age. It outlines how technology has evolved from mainframes in the 1970s to exponential changes expected in areas like artificial intelligence by 2020. The digital age has transformed businesses through increased engagement, facilitation, visibility and immediacy. While this presents challenges in meeting changing customer expectations, opportunities exist for businesses that listen to customers and embrace digital tools to gain insights, reach new markets, and build customer loyalty. The document advocates starting small with digital initiatives and prioritizing data management to help businesses adapt and get ahead.Creating value through innovation: Opportunities for micro and small business...



Creating value through innovation: Opportunities for micro and small business...Monica Ioannidou Polemitis
╠²
More from mParticle (16)
Helping brands to foster deeper customer relationships 



Helping brands to foster deeper customer relationships mParticle
╠²
A brief introduction to the mParticle Customer Data Platform. In 5 mins learn how mParticle's API-powered consumer data platform is used by customer-centric organizations to fuel amazing Customer Experiences and improve Customer Lifetime Value.
Alex Kesaris
akesaris@mparticle.com
+447400999957Hogan Lovells - MiFIDII record keeping



Hogan Lovells - MiFIDII record keepingmParticle
╠²
Useful article published by Hogan Lovells - MiFID II requires firms to keep records of transactions and will require firms to retain additional information on transactions,
based on a list of the minimum records to be retained by firms
MiFID I allowed member states discretion as to whether they required firms to record telephone calls and electronic communications that resulted or might result in transactions
Under MiFID II, it will become a mandatory obligation for firms to record telephone calls and electronic communications.BT smartnumbers face to face recording



BT smartnumbers face to face recordingmParticle
╠²
WeŌĆÖve released a new product which records face to face conversations and stores them alongside mobile voice recordings and SMS.BT smartnumbers innovative cloud communications platform



BT smartnumbers innovative cloud communications platformmParticle
╠²
Brief introduction to the smartnumbers fixed and mobile cloud platform for business continuity, agility and mobility.The third generation of mobile voice recording smart guide



The third generation of mobile voice recording smart guidemParticle
╠²
If you're looking for a network independent mobile voice recording service that works everywhere, please read our eBook which highlights what a 3rd generation solution needs to look like.Comms business feb 2016



Comms business feb 2016mParticle
╠²
3rd generation mobile voice recording service from smartnumbers positioned for mainstream adoptionUnified business mailbox



Unified business mailboxmParticle
╠²
Unified Business Mailbox allows businesses to receive SMS, voicemails and recordings in one email inbox to improve collaboration. It simplifies user experience by distributing messages to groups or a central repository. Incoming SMS are automatically stored in salesforce under the relevant account, contact and case for audit purposes.The best ever mobile service for business use



The best ever mobile service for business usemParticle
╠²
smartnumbers completes the enterprise mobility story by joining together compliance, productivity and security applications and business mobile number in a single, easy to use service.Financial services Sales - A smart guide to exceptional service



Financial services Sales - A smart guide to exceptional servicemParticle
╠²
smartnumbers mobile provides a second mobile number on any smartphone for business use. This allows salespeople to use their personal device for both personal and business calls. The second number has business features like call delegation, recording, and integration with CRM platforms. Calls are charged to the business. When an employee leaves, the business number can be passed to their replacement. Mobile numbers have come of age for BYOD strategies and sales teams who need mobile access to information.MiFIDII - Timeline



MiFIDII - TimelinemParticle
╠²
The document outlines key milestones in the implementation of MiFID II regulations, including feedback from the FCA in early 2015, adoption of EU legislation on implementing measures in the summer of 2015, consultation on requirements in late 2015, finalization of implementing measures in early 2016, publication of FCA rules on implementation in mid-2016, and the rules coming into effect for all investment firms on January 3rd, 2017.smartnumbers management console datasheet



smartnumbers management console datasheetmParticle
╠²
The smartnumbers management console allows organizations to easily manage their mobile numbers and users. It provides secure web access to view all mobile numbers, order new numbers, and assign them to employees. The console also supports quickly reassigning mobile numbers or rerouting calls in response to organizational changes. Key benefits include simple acquisition and onboarding of mobile numbers and users, managing the entire mobile user base in one place, and generating reports to monitor spending.Gartner - The real economics of byod



Gartner - The real economics of byodmParticle
╠²
This document summarizes key points from a Gartner webinar on analyzing the costs of BYOD (bring your own device) programs. It discusses the various direct and indirect costs that should be considered in a BYOD cost analysis, such as hardware, software, support and administration. It also provides examples of total cost of ownership comparisons between enterprise-owned vs. BYOD options for smartphones and tablets. Lastly, it offers lessons learned on optimizing BYOD programs, subsidies, support models and managing liabilities.Data sheet - BT smartnumbers mobile for good



Data sheet - BT smartnumbers mobile for goodmParticle
╠²
The document describes the smartnumbers mobile for Good service which enables businesses to port mobile numbers directly into the Good for Work container. This masks private mobile numbers to address employee privacy concerns while helping businesses streamline expense processes. Some key benefits include accelerating BYOD adoption without compromising privacy, complying with regulations cost effectively, retaining business mobile numbers when employees leave, and improving client relationship management. The joint solution with Good provides features like granting secure access by user and device and encrypting and protecting enterprise content on remote devices.Sustainability - The corporate mobile device is redundant



Sustainability - The corporate mobile device is redundantmParticle
╠²
This document discusses the environmental impact of providing employees with separate work and personal mobile phones. It notes that around 30% of adults carry two phones, which is expensive for organizations and bad for the environment due to the resources required to produce the phones. The document recommends using a single smartphone for both work and personal use through a solution called smartnumbers mobile, which allows for separate work and personal phone numbers on one device. This reduces waste and costs while providing the benefits of separate work and personal lines on a single phone.BT smartnumbers for relationship management



BT smartnumbers for relationship managementmParticle
╠²
BT smartnumbers is a virtual phone number service that allows financial institutions to enhance customer service for high-income clients. It virtualizes mobile and landline numbers so that calls are routed according to defined rules to ensure the client's needs are met. This includes routing calls to the relationship manager's current location, notifying staff of missed calls via SMS, and overflowing calls to support teams if unanswered. The service provides a single point of contact for clients, allows "VIP" clients to receive elevated service, and gives staff tools to track and improve the client experience.Smartnumbers mobile plus



Smartnumbers mobile plusmParticle
╠²
Smartnumbers mobile plus enables regulated firms to affordably record calls made on mobile phones, bringing them into compliance with regulations. Previously, recording mobile calls was prohibitively expensive, so staff would return to the office to record transactions instead of breaking the rules. The service is affordable even for small organizations, is easy to implement on any mobile network, and can route calls to landlines or VoIP services when abroad to always record mobile calls and avoid roaming charges.Physical sim vs smartnumbers
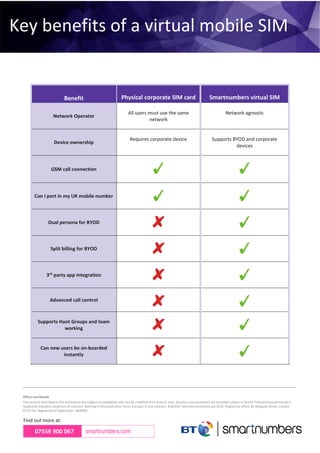
- 1. Enterprise BYOD. Without compromise. If you are considering, or implementing, a bring-your own-device (BYOD) strategy then the chances are youŌĆÖre already well aware of the benefits. BYOD gives your people simplicity and freedom to choose how they communicate. Naturally there have been security and compliance concerns around BYOD, but these appear to have been ironed out by the likes of enterprise software vendors MobileIron and Good Technology. BYOD is taking a hold even in data security conscious sectors such as healthcare, legal and banking. Thus itŌĆÖs natural for your organisation to consider BYOD as well. On the surface, the scheme seems to have a lot to offer. But there is still one piece of the puzzle that is missing: voice. Not everyone likes to use their personal mobile for Business calls because presenting personal mobile numbers on work related calls raises privacy issues. And splitting out work-related and personal calls is a pain for workers who need to file expenses claims. Whoever the job falls to, the administrative burden is significant. ItŌĆÖs a real problem if youŌĆÖve just made a decision to adopt BYOD across your business. Ideally, you would want to have a way to easily run work and personal voice calls off a single device, yet keep the services separate. Until recently, the available options were less than ideal. Thankfully, though, the situation has now changed. Enabling services on a virtual SIM. By enabling the business mobile identity on a virtual SIM rather than a physical SIM, financial enterprises are able to exceed business objectives around cost control, compliance, collaboration and customer experience in a way that was not previously possible. On the second page, we have outlined key differences between a physical and virtual SIM. Enterprise telephony services enabled on a virtual SIM card
- 2. Offices worldwide The services described in this publication are subject to availability and may be modified from time to time. Services and equipment are provided subject to British Telecommunications plcŌĆÖs respective standard conditions of contract. Nothing in this publication forms any part of any contract. ┬® British Telecommunications plc 2015. Registered office: 81 Newgate Street, London EC1A 7AJ. Registered in England No: 1800000 07559 900 067 smartnumbers.com Find out more at: Key benefits of a virtual mobile SIM card Benefit Physical corporate SIM card Smartnumbers virtual SIM Network Operator All users must use the same network Network agnostic Device ownership Requires corporate device Supports BYOD and corporate devices GSM call connection Can I port in my UK mobile number Dual persona for BYOD Split billing for BYOD 3rd party app integration Advanced call control Supports Hunt Groups and team working Can new users be on-boarded instantly

