Revekka Goldberg, "The FMEA as the Risk-Management Tool for the Hazardous Wastes Control in the Context of the Oil-Refining Industry"
- 1. The FMEA as the Risk-Management Tool for the Hazardous Wastes Control in the Context of the Oil-Refining Industry Revekka Goldberg Quality Management Department
- 2. Why it is needed to manage risks? risk assessment and risk management ŌĆō mandatory requirements of OHSAS 1800 0 & ISO 14000 ; new version of ISO 9004:2009 ; new series of standards ISO 31000 inadequacy of the dominating management tools ; special significance in the period of crisis .
- 3. Risk and risk-management Risk is: the quantifiable likelihood of loss or less-than-expected returns. (The InvestorWords Glossary) the probable frequency and probable magnitude of future loss. (ŌĆ£An Introduction to Factor Analysis of Information Risk (FAIR)ŌĆØ) a combination of the likelihood of an occurrence of a hazardous event or exposure and the severity of injury or ill health that can be caused by the event or exposure. (OHSAS 18001) Risk management is: the identification, assessment, and prioritization of followed by coordinated and economical application of resources to minimize, monitor, and control the probability and/or impact of unfortunate events or to maximize the realization of opportunities. (ISO 31000)
- 4. Qualitative risk analysis 1. Analysis of available information review and analysis of accounting and management documents; the analysis of periodic reports. 2. Collecting new information a standardized questionnaire; personalized inspection of production units; expert consultation (internal & external). 3. Modelling the organizationŌĆÖs activity the compilation and analysis of the organizational structure; the analysis of stream-maps. 4. Heuristic methods
- 5. Quantitative risk analysis 1. Analytical methods the sensitivity analysis; the scenario analysis. 2. Probability-theoretical methods the statistical methods; the simulation; the fault-three analysis; the logical and probabilistic methods. 3. Heuristic methods of quantitative analysis 4. Unconventional methods the artificial intelligence (neural networks); modeling based on fuzzy logic.
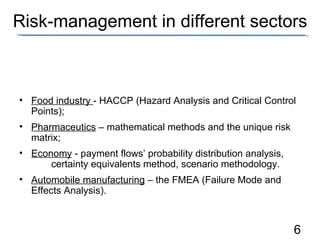
- 6. Risk-management in different sectors Food industry - HACCP ( Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points ); Pharmaceutics ŌĆō mathematical methods and the unique risk matrix ; Economy - payment flowsŌĆÖ probability distribution analysis, certainty equivalents method, scenario methodology. Automobile manufacturing ŌĆō the FMEA (Failure Mode and Effects Analysis).
- 7. Examples of the Oil-refining hazardous wastes oil-containing pulps; processed pulpsŌĆÖ water runoff ; demineralized pulps ; oil desulphatisation fragments ; elemental sulphur ; residual asphalt ; pulps containing hydrargyrum ; acid tar .
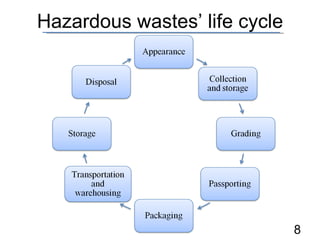
- 8. Hazardous wastesŌĆÖ life cycle
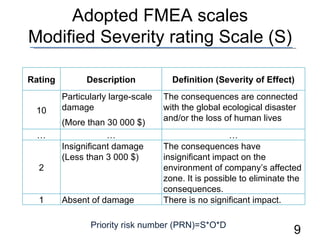
- 9. Adopted FMEA scales Modified Severity rating Scale (S) Priority risk number (PRN)=S*O*D Rating Description Definition (Severity of Effect) 10 Particularly large-scale damage (More than 30╠²000 $) The consequences are connected with the global ecological disaster and/or the loss of human lives ŌĆ” ŌĆ” ŌĆ” 2 Insignificant damage ( Less than 3 ╠²000 $) The consequences have insignificant impact on the environment of companyŌĆÖs affected zone. It is possible to eliminate the consequences. 1 Absent of damage There is no significant impact.
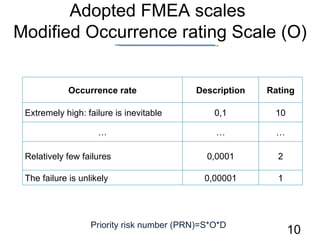
- 10. Adopted FMEA scales Modified Occurrence rating Scale (O) Priority risk number (PRN)=S*O*D Occurrence rate Description Rating Extremely high: failure is inevitable 0,1 10 ŌĆ” ŌĆ” ŌĆ” Relatively few failures 0,0001 2 The failure is unlikely 0,00 0 01 1
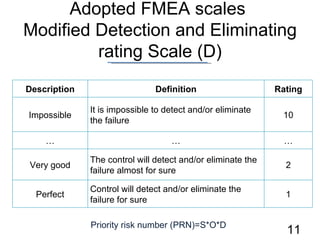
- 11. Adopted FMEA scales Modified Detection and Eliminating rating Scale (D) Priority risk number (PRN)=S*O*D Description Definition Rating Impossible It is impossible to detect and/or eliminate the failure 10 ŌĆ” ŌĆ” ŌĆ” Very good The control will detect and/or eliminate the failure almost for sure 2 Perfect Control will detect and/or eliminate the failure for sure 1
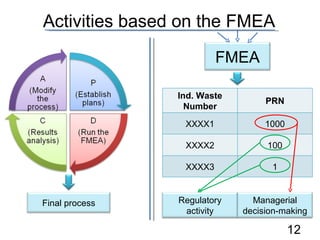
- 12. Activities based on the FMEA Ind. Waste Number PRN XXXX1 1000 XXXX2 100 XXXX3 1 FMEA Final process Regulatory activity Managerial decision-making