Data Driven Strategies for Communication Success
- 1. Data Driven Strategies for Successful Communication February 27, 2013
- 2. Communication is Essential to All
- 5. We Can Generalize Generation Y (18-28) I want to make a differenceŌĆötech entitled Generation X (29-40) I want to strike a balanceŌĆöflexibility matters Trailing Boomers (41-50) I donŌĆÖt trust institutionsŌĆöit may get worse Leading Boomers (51-59) I respect experienceŌĆönot authority Matures (60-69) I respect authorityŌĆömoney is recognition
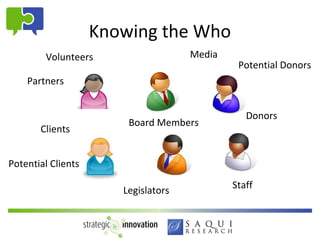
- 6. Knowing the Who Volunteers Media Potential Donors Partners Donors Board Members Clients Potential Clients Staff Legislators
- 7. What Do You Know ?
- 8. What Should You Know? Volunteer Work History of Giving Age Values Gender Educational Level Address Interests Use of Technology Email Occupation Activities Household Income
- 9. Research Process Profiles Donors Volunteers Partners Clients Others
- 10. How Do You Find It? ŌĆó Secondary research ŌĆō Census ŌĆó American Community Survey ŌĆō Bureau of Labor Statistics ŌĆō Pew Research ŌĆō Other non-profit associations related to your area of service or population, e.g., The Annie E. Casey Foundation Kids Count data center, Robert Wood Johnson Foundation ŌĆó Primary research
- 11. Types of Primary Research Quantitative Qualitative ŌĆó Surveys ŌĆó Interviews ŌĆó Assessments/Evaluations ŌĆó Focus Groups ŌĆó Historical Documents ŌĆó Historical Documents
- 12. Surveys ŌĆó Types of Surveys ŌĆō Telephone ŌĆō Mail ŌĆō Online ŌĆó Cautions! ŌĆō Ability to connect ŌĆō Extent of engagement ŌĆō Length of questionnaire ŌĆō Quality of questionnaire
- 13. Common Survey Question Mistakes BAD BETTER ŌĆó Double-barreled question ŌĆó Focus on one issue ŌĆō How often do you prefer email ŌĆō How often do you prefer email and/or mail communications communications from us? from us? ŌĆó Give time frames that make sense. ŌĆó Inability to recall ŌĆō How many times in the past 30 ŌĆō How many times in the past year days have you visited a medical have you visited a medical professional? professional? ŌĆó DonŌĆÖt ask for sensitive information. ŌĆó Requesting sensitive information ŌĆō If you or someone you know ŌĆō Have you or someone close to would like to confidentially share you ever required social services their experience with social service before? providers, please let us know.
- 14. Qualitative Research Why did you decide to volunteer with our organization? How do you decide which charitable organizations you will financially support? What was your experience like when you called our office for services?
- 15. Results Quantitative Examples Qualitative Examples ŌĆó Frequencies, Percentages ŌĆó Themes, Patterns ŌĆó Crosstabs, Averages ŌĆó Quotes, Case Studies ŌĆó Comparisons, Predictions ŌĆó Conceptual Relationships
- 16. Collaborative Interpretation 1. Preview draft of findings with task force/project team. 2. Present/discuss with Leadership/Board 3. Resolve any questions 4. Share with internal stakeholders 5. Share externally
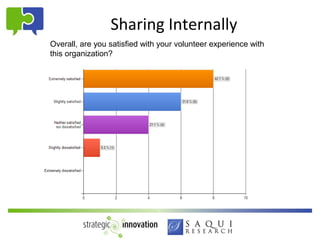
- 17. Sharing Internally Overall, are you satisfied with your volunteer experience with this organization?
- 19. Communicating About Research ŌĆó Invitation ŌĆó From your organizations leadership ŌĆó Providing the rationale ŌĆó Assuring confidentiality/introducing the researcher ŌĆó Asking for the action ŌĆó A Reminder ŌĆó From the researcher ŌĆó Offering overview of results (after shared internally)
- 20. Communicating About Research ŌĆó Results ŌĆó Reporting to the committee/director ŌĆó Reporting to the Board ŌĆó Reporting to Staff ŌĆó Sharing with Key Donors, Volunteers, Etc.
- 21. Turning Research into Strategy
- 22. Staying on Course Scorecard for Board Reporting Communication Target Last Month Today Clean up e-mail lists 20 days Identified On target to resources and lists complete xx/xx/xx Conduct Research to 30 days Research partner Survey launch determine current selected scheduled for perceptions xx/xx/xx Refresh Brand 120 days Pending research No progress to data report
- 23. Questions?
Editor's Notes
- #9: What should you know depends on your particular question and need for information. For example, for giving, income (higher income, increased capital gains), educational level (post-grad = higher giving), age (U shaped; lower for baby boomers), volunteer work, significantly affect charitable giving. For recruiting volunteers, here are some results: women were more likely to volunteer than men, married than other marital statuses, more educated, ages 35-54. For developing partnerships, understanding values and interests and maybe occupation would be helpful.
- #10: General research: trends and stats related to the economy, demographics (immigration trends), technology, social --kids count data center reported that the % of children living in poverty in Indiana increased from 17.1% in 2007 to 22.6% in 2011 Nonprofit research: research in the nonprofit sector (giving and volunteering trends) and in your specific area -report from National & Community Service reported that longer commuting time to work limit volunteer opportunities; strong relationship in metro areas between homeownership rates and volunteering -an update from Harvard Family Research Project reported that high-performing after-school programs typically offered a broad array of activities, opportunities for skill building and mastery; intentional relationship building; a strong experienced leader supported by staff, and support of sponsoring organization. Your research: research on your particular audiences -who are you serving? And how well are you serving them? -who is connecting to and engaging with your organization in terms of donors, volunteers, and partners? -is the community aware of your existence and services? Do they understand what you do? Result = very detailed profiles of ideal audiences set within a larger context of national/international & nonprofit trends
- #11: Coffee example to explain secondary vs. primary research Census: demographic data plus computer/internet use, commuting, health insurance, and well-being American Community Survey: subset of the Census data updated every year vs. every 10 years BLS: Info on things such as on what consumers are spending their money and how they spend their time from eldercare to household activities. Pew Research example: This report on those who gave to the ŌĆ£Text for HaitiŌĆØ campaign is based on telephone surveys with 863 individuals who contributed money to the Haiti earthquake efforts using the text messaging feature on their cell phones. One main result: The ability to send small donations using mobile phones facilitates ŌĆ£impulse givingŌĆØ in response to moving images or events for a sample who was tech advanced Jane to give her own personal example. Just posted a blog on website about social media demographics for those of you who want to know the best social media tools to use. Kids Count: hundreds of measures of child well-being RWJF: health and health care in the U.S. Checklist exercise
- #12: Coffee example to explain difference between quant & qual
- #13: Cautions: Survey method needs to match the audience: do they have access to internet? Do they have a landline? Example of Hispanic population: need to survey both landlines & cell phone to get representative coverage. Need to have way to contact: email, mailing address, phone #ŌĆÖs More likely to answer survey if they have a relationship with you or are interested in what you are asking about: might want to start with those you have a longer relationship with first, also look at how you frame your request for information Gather only the information you need to know to keep questionnaire short Well-written questionnaires with a clear stated purpose will increase response rate Online survey tools: SurveyMonkey, SurveyGizmo, GoogleForms Sampling: Asking everyone (census) or taking a sample: depends on what you are asking
- #14: Exercise: Survey question rewrite exercise
- #15: The qualitative method investigates the╠² why ╠²and╠² how ╠²of╠²decision making, not just╠² what ,╠² where ,╠² when . Smaller but focused╠²samples╠²are more often needed than large samples. Can be used alone, before and/or after quantitative research
- #16: Coffee example to explain difference between quant & qual