The Mathematical Epidemiology of Human Babesiosis in the North-Eastern United States - Jessica Dunn, QUT
- 1. The Mathematical Epidemiology of Human Babesiosis in the North-Eastern United States Jessica Margaret Dunn, Dr. Stephen Davis (RMIT), Dr. Andrew Stacey (RMIT), Assoc. Prof. Maria Diuk-Wasser (Yale/Columbia) J. M. Dunn (QUT) QUT Seminar 08.08.2014 1 / 41
- 2. J. M. Dunn (QUT) QUT Seminar 08.08.2014 2 / 41
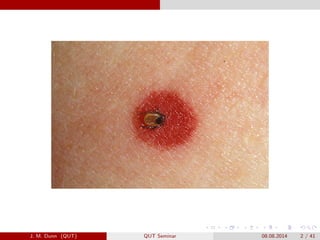
- 3. Tick-borne disease in the USA The geographical range of tick-borne diseases are expanding. There are seven emerging tick diseases: Lyme disease Human babesiosis Human anaplasmosis Powassan Deer tick encephalitis B. miyamotoi borreliosis Deer tick ehrlichiosis J. M. Dunn (QUT) QUT Seminar 08.08.2014 3 / 41
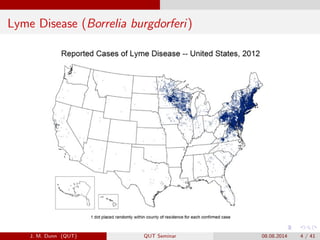
- 4. Lyme Disease (Borrelia burgdorferi) J. M. Dunn (QUT) QUT Seminar 08.08.2014 4 / 41
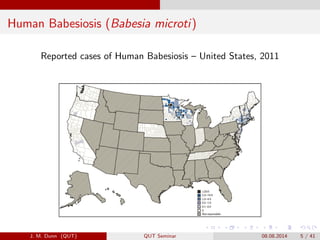
- 5. Human Babesiosis (Babesia microti) Reported cases of Human Babesiosis ¿C United States, 2011 J. M. Dunn (QUT) QUT Seminar 08.08.2014 5 / 41
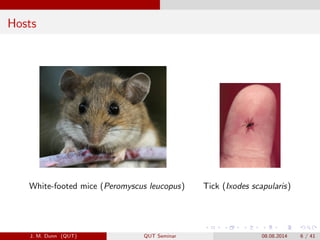
- 6. Hosts White-footed mice (Peromyscus leucopus) Tick (Ixodes scapularis) J. M. Dunn (QUT) QUT Seminar 08.08.2014 6 / 41
- 7. Research Objective To identify the key factors driving human babesiosis (B. microti) and Lyme disease (B. burgdorferi) in endemic sites, and their expansion into new areas in the north-eastern United States. J. M. Dunn (QUT) QUT Seminar 08.08.2014 7 / 41
- 8. Mathematical Modelling Challenges Deriving mathematical models of tick-borne disease transmission is notoriously di?cult! Multiple hosts (competent and non-competent) Tick life-cycle (biting rate) Multiple tranmission routes Multiple pathogens J. M. Dunn (QUT) QUT Seminar 08.08.2014 8 / 41
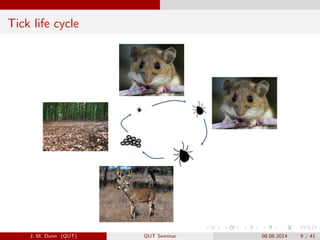
- 9. Tick life cycle J. M. Dunn (QUT) QUT Seminar 08.08.2014 9 / 41
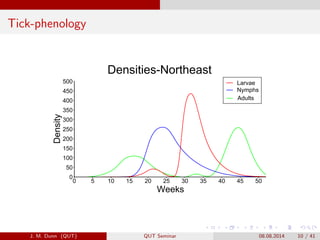
- 10. Tick-phenology Densities-Northeast Weeks Density 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 0 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450 500 Larvae Nymphs Adults J. M. Dunn (QUT) QUT Seminar 08.08.2014 10 / 41
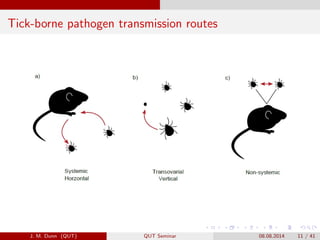
- 11. Tick-borne pathogen transmission routes J. M. Dunn (QUT) QUT Seminar 08.08.2014 11 / 41
- 12. Modelling challenges The modelling challenge then becomes to one of incorporating these complexities whilst maintaining a model that: 1 is representative of the transmission cycle 2 can be used with ?eld data which will provide meaningful estimates of the parameters 3 has a minimal number of parameters to ensure the model can be adequately analysed J. M. Dunn (QUT) QUT Seminar 08.08.2014 12 / 41
- 13. Overview Model emergence - Identify the factors driving emergence - Identify control measures Model the risk to humans - Incorporate the identi?ed factors - Analyse changes in risk J. M. Dunn (QUT) QUT Seminar 08.08.2014 13 / 41
- 14. Modelling emergence Modelling emergence The basic Reproduction number, R0 In single host systems, R0 is the expected number of secondary cases produced by one infectious individual in a fully susceptible population. R0 = 1 provides a threshold condition: pathogen will spread R0 > 1 pathogen will fade out R0 < 1 J. M. Dunn (QUT) QUT Seminar 08.08.2014 14 / 41
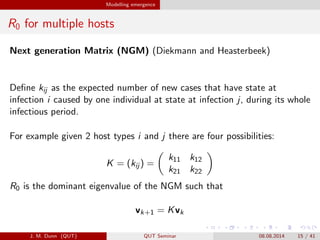
- 15. Modelling emergence R0 for multiple hosts Next generation Matrix (NGM) (Diekmann and Heasterbeek) De?ne kij as the expected number of new cases that have state at infection i caused by one individual at state at infection j, during its whole infectious period. For example given 2 host types i and j there are four possibilities: K = (kij ) = k11 k12 k21 k22 R0 is the dominant eigenvalue of the NGM such that vk+1 = Kvk J. M. Dunn (QUT) QUT Seminar 08.08.2014 15 / 41
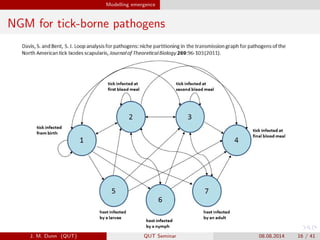
- 16. Modelling emergence NGM for tick-borne pathogens J. M. Dunn (QUT) QUT Seminar 08.08.2014 16 / 41
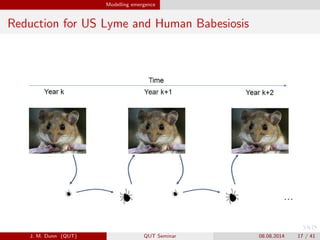
- 17. Modelling emergence Reduction for US Lyme and Human Babesiosis J. M. Dunn (QUT) QUT Seminar 08.08.2014 17 / 41
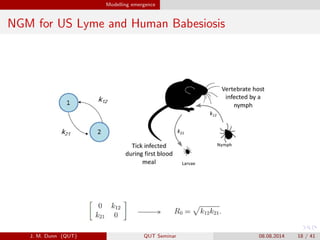
- 18. Modelling emergence NGM for US Lyme and Human Babesiosis J. M. Dunn (QUT) QUT Seminar 08.08.2014 18 / 41
- 19. Modelling emergence Quantifying R0 J. M. Dunn (QUT) QUT Seminar 08.08.2014 19 / 41
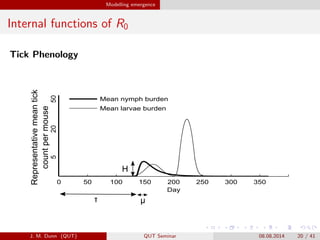
- 20. Modelling emergence Internal functions of R0 Tick Phenology 0 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 Day Mean nymph burden Mean larvae burden Representativemeantick countpermouse 52050 ª╠ H ªË J. M. Dunn (QUT) QUT Seminar 08.08.2014 20 / 41
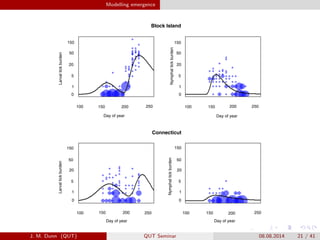
- 21. Modelling emergence Block Island Connecticut 100 250150 200 100 150 200 250 100 150 200 250100 150 200 250 0 1 5 20 50 150 0 1 5 20 50 150150 50 20 5 1 0 150 50 20 5 1 0 Day of year Day of year Day of year Day of year LarvaltickburdenLarvaltickburden NymphaltickburdenNymphaltickburden J. M. Dunn (QUT) QUT Seminar 08.08.2014 21 / 41
- 22. Modelling emergence Brunner and Ostfeld (2008) ?ZN(t) = HNe ?1 2 ln (t?ªËN ) ?N /ªÊN 2 if t í¦ ªËN; 0 otherwise ?ZL(t) = ? ? ? HE e ?1 2 t?ªËE ?E 2 if t í▄ ªËL; HLe ?1 2 ln (t?ªËL) ?L 2 + HE e ?1 2 t?ªËE ?E 2 otherwise J. M. Dunn (QUT) QUT Seminar 08.08.2014 22 / 41
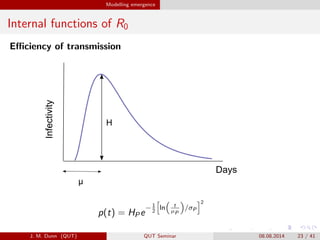
- 23. Modelling emergence Internal functions of R0 E?ciency of transmissionInfectivity Days H ª╠ p(t) = HPe ?1 2 ln t ?P /ªÊP 2 J. M. Dunn (QUT) QUT Seminar 08.08.2014 23 / 41
- 24. Modelling emergence Global Sensitivity Analysis of R0 Ranks the parameters by their contribution to the variation of R0 using Sobolí»s indices: Main e?ect: calculates the e?ect of parameter xi on R0 ?xing all other variables Total e?ect: includes the main e?ect for xi plus all other interaction involving xi . J. M. Dunn (QUT) QUT Seminar 08.08.2014 24 / 41
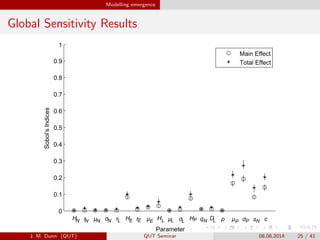
- 25. Modelling emergence Global Sensitivity Results 0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 1 Parameter Sobolí»sfIndices MainfEffect TotalfEffect H ªË ª╠ ªÊ ªË H ªË ª╠ H ª╠ ªÊ H Dq ªÐ ªÊª╠ s cN N N N L L L L P P PLE E E NN J. M. Dunn (QUT) QUT Seminar 08.08.2014 25 / 41
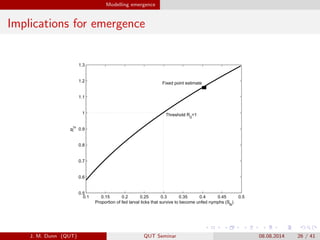
- 26. Modelling emergence Implications for emergence 0.1 0.15 0.2 0.25 0.3 0.35 0.4 0.45 0.5 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 1 1.1 1.2 1.3 Proportion of fed larval ticks that survive to become unfed nymphs (S N ) R 0 Threshold R 0 =1 Fixed point estimate J. M. Dunn (QUT) QUT Seminar 08.08.2014 26 / 41
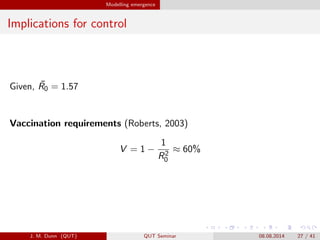
- 27. Modelling emergence Implications for control Given, ?R0 = 1.57 Vaccination requirements (Roberts, 2003) V = 1 ? 1 R2 0 íÍ 60% J. M. Dunn (QUT) QUT Seminar 08.08.2014 27 / 41
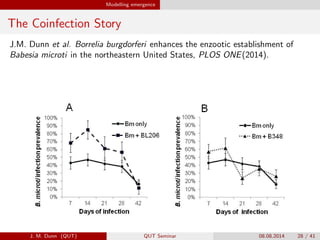
- 28. Modelling emergence The Coinfection Story J.M. Dunn et al. Borrelia burgdorferi enhances the enzootic establishment of Babesia microti in the northeastern United States, PLOS ONE(2014). J. M. Dunn (QUT) QUT Seminar 08.08.2014 28 / 41
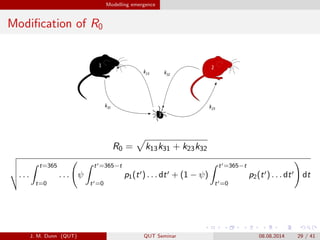
- 29. Modelling emergence Modi?cation of R0 k13 k31 k13 k31 k32 k23 k32 k23 White-footedm1: White-footedm2: Tickainfectedaw3: Ka= 0 0 0 0 0 1 2 3 R0 = k13k31 + k23k32 . . . t=365 t=0 . . . ªÎ t =365?t t =0 p1(t ) . . . dt + (1 ? ªÎ) t =365?t t =0 p2(t ) . . . dt dt J. M. Dunn (QUT) QUT Seminar 08.08.2014 29 / 41
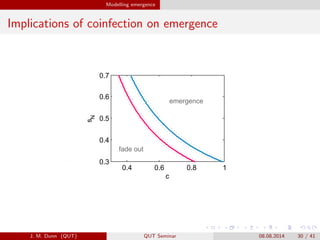
- 30. Modelling emergence Implications of coinfection on emergence 0.6 0.8 1 c 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 0.3 0.4 0.5 c 0.6 0.8 1 c 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 c sN B. microti B. microti C8B. Burgdorferi BL2068 fade8out fade8out emergence emergence 80w8B. burgdorferi8BL2068prevalence in8mice J. M. Dunn (QUT) QUT Seminar 08.08.2014 30 / 41
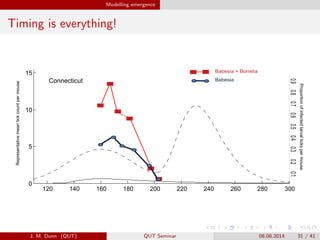
- 31. Modelling emergence Timing is everything!120 140 160 180 200 220 240 260 280 300 0 5 120 140 160 180 200 220 240 260 280 300 0 5 10 15 Re ouseProportion3of3infected3larval3ticks3per3mouse Representative3mean3tick3count3per3mouse Connecticut 3330.233333330.1 Mean nymph burden Mean larvae burden Babesia3+3Borrelia Babesia 3333333333333333333333333333330.93333330.83333330.73333330.63333330.53333330.43333330.333333330.233333330.1 J. M. Dunn (QUT) QUT Seminar 08.08.2014 31 / 41
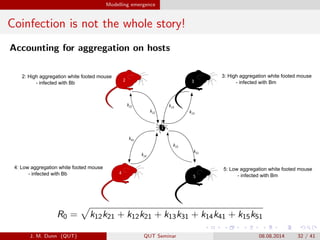
- 32. Modelling emergence Coinfection is not the whole story! Accounting for aggregation on hosts k13 k13 32 1 5 4 2 k51 k15 k12 k21 k14 k41 2: High aggregation white footed mouse - infected with Bb 4: Low aggregation white footed mouse - infected with Bb 3: High aggregation white footed mouse - infected with Bm 5: Low aggregation white footed mouse - infected with Bm R0 = k12k21 + k12k21 + k13k31 + k14k41 + k15k51 J. M. Dunn (QUT) QUT Seminar 08.08.2014 32 / 41
- 33. Modelling emergence Scenario Estimated R0 No co-aggregation; no coinfection 0.70 (0.62,0.78) Low co-aggregation; no coinfection 0.80 (0.71,0.86) Moderate co-aggregation; no coinfection 0.97 (0.81,1.04) High co-aggregation; no coinfection 1.13 (1.00, 1.21) High co-aggregation; coinfection 1.78 (1.64, 1.91) J. M. Dunn (QUT) QUT Seminar 08.08.2014 33 / 41
- 34. Modelling emergence Conclusions Epidemiological: Values of R0 are consistently low 1 < R0 < 3 Transmission e?ciency drives emergence Timing is everything! Mathematical: Models are mechanistic, transparent, linked directly with ?eld data Step towards a model for more complicated tick-borne pathogens First such model that that assesses the importance of (i) coinfection and (ii) aggregation J. M. Dunn (QUT) QUT Seminar 08.08.2014 34 / 41
- 35. Modelling emergence Questions? J. M. Dunn (QUT) QUT Seminar 08.08.2014 35 / 41
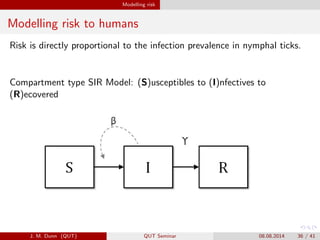
- 36. Modelling risk Modelling risk to humans Risk is directly proportional to the infection prevalence in nymphal ticks. Compartment type SIR Model: (S)usceptibles to (I)nfectives to (R)ecovered J. M. Dunn (QUT) QUT Seminar 08.08.2014 36 / 41
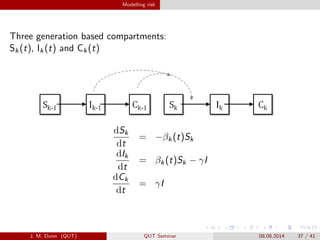
- 37. Modelling risk Three generation based compartments: Sk(t), Ik(t) and Ck(t) dSk dt = ?ª┬k(t)Sk dIk dt = ª┬k(t)Sk ? ª├I dCk dt = ª├I J. M. Dunn (QUT) QUT Seminar 08.08.2014 37 / 41
- 38. Modelling risk Force of Infection The force of infection is related to the unfed nymphs from the previous year k ? 1 ª┬k(t) = 1 DN ª═k ?ZN(t)qN. with the proportion of infected unfed nymphs, ª═k, in year k is given by ª═k = 365 0 aL(t)?p Ik?1 Nk?1 dt J. M. Dunn (QUT) QUT Seminar 08.08.2014 38 / 41
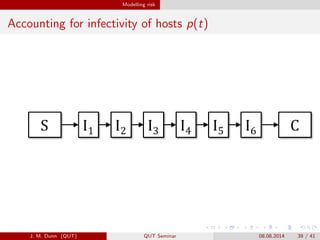
- 39. Modelling risk Accounting for infectivity of hosts p(t) J. M. Dunn (QUT) QUT Seminar 08.08.2014 39 / 41
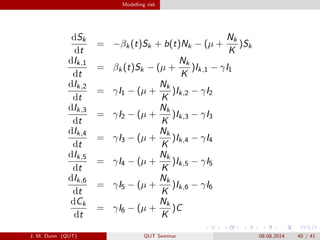
- 40. Modelling risk dSk dt = ?ª┬k(t)Sk + b(t)Nk ? (? + Nk K )Sk dIk,1 dt = ª┬k(t)Sk ? (? + Nk K )Ik,1 ? ª├I1 dIk,2 dt = ª├I1 ? (? + Nk K )Ik,2 ? ª├I2 dIk,3 dt = ª├I2 ? (? + Nk K )Ik,3 ? ª├I3 dIk,4 dt = ª├I3 ? (? + Nk K )Ik,4 ? ª├I4 dIk,5 dt = ª├I4 ? (? + Nk K )Ik,5 ? ª├I5 dIk,6 dt = ª├I5 ? (? + Nk K )Ik,6 ? ª├I6 dCk dt = ª├I6 ? (? + Nk K )C J. M. Dunn (QUT) QUT Seminar 08.08.2014 40 / 41
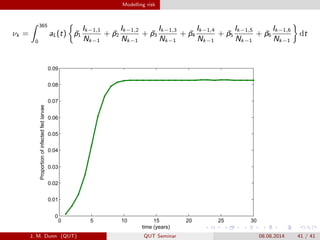
- 41. Modelling risk ª═k = 365 0 aL(t) ?p1 Ik?1,1 Nk?1 + ?p2 Ik?1,2 Nk?1 + ?p3 Ik?1,3 Nk?1 + ?p4 Ik?1,4 Nk?1 + ?p5 Ik?1,5 Nk?1 + ?p6 Ik?1,6 Nk?1 dt 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 0 0.01 0.02 0.03 0.04 0.05 0.06 0.07 0.08 0.09 time (years) Proportionofinfectedfedlarvae J. M. Dunn (QUT) QUT Seminar 08.08.2014 41 / 41