Skelet
- 2. ÐĢÐÐÐÐ ÐĄÐÐÐÐÐĒÐ âĒ ÐÐÐĒÐÐÐ Ð ÐÐ ÐÐÐÐÐÐÐĢ, ÐĻÐĒÐÐĒÐ ÐĢÐÐĢÐĒÐ ÐÐĻÐÐ ÐÐ ÐÐÐÐ, ÐĄÐÐĢÐÐ ÐÐÐ ÐÐĄÐÐÐÐÐĶ ÐÐÐĻÐÐÐÐÐ
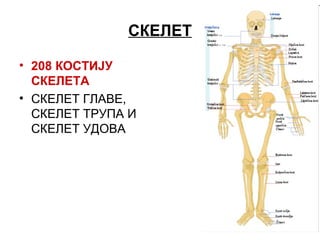
- 3. ÐĄÐÐÐÐÐĒ âĒ 208 ÐÐÐĄÐĒÐÐÐĢ ÐĄÐÐÐÐÐĒÐ âĒ ÐĄÐÐÐÐÐĒ ÐÐÐÐÐ, ÐĄÐÐÐÐÐĒ ÐĒÐ ÐĢÐÐ Ð ÐĄÐÐÐÐÐĒ ÐĢÐÐÐÐ
- 4. ÐÐÐĄÐĒÐ ÐÐÐÐÐ âĒ ÐÐÐĄÐĒÐ ÐÐÐÐÐÐ â 8 ÐÐÐĄÐĒÐÐÐĢ âĒ ÐÐÐÐĄÐÐÐĒÐ- ÐĻÐĒÐÐĒÐ ÐÐÐÐÐ, ÐĄÐÐÐÐÐÐ ÐĻÐÐÐÐÐÐÐ
- 5. ÐÐÐĄÐĒÐ ÐÐÐÐÐ âĒ ÐÐÐĄÐĒÐ ÐÐÐĶÐ â 15 ÐÐÐĄÐĒÐÐÐĢ âĒ ÐÐÐÐ ÐÐÐÐÐĶÐ ÐÐ ÐÐÐÐÐÐ ÐÐÐÐÐÐÐ
- 7. ÐÐÐĄÐĒÐ ÐĒÐ ÐĢÐÐ âĒ ÐÐЧÐÐ ÐÐ ÐĄÐÐĄÐĒÐÐÐÐÐÐ ÐÐ 33- 34 ÐÐЧÐÐÐÐ ÐÐ ÐĻÐÐÐÐ. âĒ ÐÐÐÐÐÐÐ ÐÐĒÐÐÐÐÐÐ ÐĄÐĢ ÐÐ ÐÐĒÐÐ ÐÐ ÐĻÐÐÐÐÐÐ, ÐÐÐÐÐÐÐ ÐĄÐĢ ÐĄÐÐÐÐÐÐĄÐÐ. âĒ ÐÐ ÐĄÐÐ ÐÐ ÐĻÐÐÐÐÐÐ ÐĄÐĢ ÐĄÐ ÐÐĄÐÐ ÐĢ ÐÐ ÐĄÐÐĢ ÐÐÐĄÐĒ.
- 8. ÐÐÐĄÐĒÐ ÐĒÐ ÐĢÐÐ âĒ Ð ÐÐÐÐ ÐÐ ÐĻÐÐÐÐÐÐ ÐĄÐĢ ÐÐÐÐ ÐÐÐÐÐ Ð ÐÐ ÐÐÐ Ð ÐÐÐÐĢ ÐÐÐ ÐĒÐ ÐĒÐЧÐÐĢ ÐÐÐĄÐĒ. âĒ ÐĢ ÐÐÐÐÐÐĢ ÐÐЧÐÐ ÐÐÐÐÐÐ ÐĄÐ ÐÐЧÐÐÐÐ ÐÐÐÐÐÐÐ âĒ ÐĄÐÐÐÐÐÐÐ ÐÐ ÐÐ ÐÐÐÐÐÐ ÐÐЧÐÐ ÐĢ ÐĄÐĒÐ ÐÐÐĢ Ð ÐÐÐĪÐÐÐ ÐÐ ÐÐÐÐ ÐÐÐÐÐÐĄÐĒ.
- 12. ÐÐÐĄÐĒÐ ÐĒÐ ÐĢÐÐ âĒ ÐÐ ÐĢÐÐÐ ÐÐÐĻ ÐĻÐĒÐÐĒÐ ÐĄÐ ÐĶÐ Ð ÐÐÐĢÐÐ âĒ 12 ÐÐÐ Ð Ð ÐÐÐÐ Ð âĒ 7 ÐÐÐ Ð ÐÐ ÐÐÐÐĨ, 3 ÐÐÐ Ð ÐÐÐÐÐ Ð 2 ÐÐÐ Ð ÐÐÐĒÐÐĨ Ð ÐÐÐÐ Ð
- 13. ÐÐÐĄÐĒÐ ÐĢÐÐÐÐ 126 ÐÐÐĄÐĒÐÐÐĢ âĒ Ð ÐÐÐÐÐ ÐÐÐÐÐĄ â ÐÐÐÐÐĒÐÐĶÐ Ð ÐÐÐĢЧÐÐ ÐÐÐĄÐĒ âĒ ÐÐÐĄÐĒÐ ÐÐÐÐÐÐÐĒÐÐĶÐ (Ð ÐÐÐÐÐ ÐÐÐĄÐĒ), ÐÐÐÐÐÐÐĒÐÐĶÐ (ÐÐÐÐÐĒÐÐ Ð ÐÐÐЧÐÐÐ ÐÐÐĄÐĒ) Ð ÐÐÐĄÐĒÐ ÐĻÐÐÐ (27. ÐÐÐĄÐĒÐÐÐĢ)
- 15. ÐÐÐĄÐĒÐ ÐĢÐÐÐÐ 126 ÐÐÐĄÐĒÐÐÐĢ âĒ ÐÐÐ ÐÐЧÐÐ ÐÐÐÐÐĄ (ÐÐÐÐ ÐÐÐЧÐ, ÐÐ ÐÐÐÐÐЧÐ, ÐĄÐÐÐÐÐЧÐ), ÐÐÐĒÐÐÐÐÐÐÐĶÐ (ÐÐĢÐĒÐÐ ÐÐÐĄÐĒ), ÐÐÐĒÐÐÐÐÐÐÐĶÐ (ÐÐÐÐÐÐЧРРÐÐÐĄÐÐ ÐÐÐĄÐĒ), ÐĄÐĒÐÐÐÐÐ (26 ÐÐÐĄÐĒÐÐÐĢ)
- 16. ÐÐÐĄÐĒÐ ÐĢÐÐÐÐ 126 ÐÐÐĄÐĒÐÐÐĢ âĒ ЧÐÐĻÐÐĶÐ ÐÐ ÐĒÐ ÐÐĢÐÐÐÐĄÐĒÐ ÐÐÐĄÐĒ ÐÐÐÐÐÐ ÐÐÐÐ ÐÐ ÐÐÐÐÐÐÐÐÐ ÐĄÐÐÐÐÐÐÐ ÐÐÐÐ ÐĢÐÐÐÐ ÐÐ. âĒ Ð ÐÐÐÐ ÐĒÐÐÐÐÐ ÐĄÐĢ ÐÐÐĪÐÐ ÐÐÐĶÐÐÐ ÐĄÐĒÐÐÐÐÐ ÐÐÐÐ ÐĄÐ ÐĄÐÐĢÐĻÐĒÐ ÐĄÐÐÐ ÐĄÐĒÐÐÐÐÐ.
- 18. ÐÐÐÐÐÐÐÐ âĒ ÐÐĢÐ, ÐÐÐÐÐÐ, ÐÐÐÐÐĒÐÐ, Ð ÐÐÐÐÐ ÐÐÐÐÐ
- 20. ÐÐÐĒÐÐÐ 1. ÐÐÐĻÐĒÐ ÐĄÐĢ ÐÐÐĄÐĒÐ ÐÐÐÐÐÐ ÐÐÐÐÐÐ ÐĻÐÐÐÐÐÐÐ? 2. ÐÐÐÐ ÐÐ ÐÐÐĄÐĒ ÐÐÐÐÐÐÐ Ð ÐÐÐÐ ÐÐÐÐÐÐÐ? 3. ÐÐÐÐ ÐÐ ÐĢÐÐÐÐ ÐĨÐ ÐĄÐÐÐÐÐĶÐ ÐÐÐÐÐÐĢ ÐÐ ÐĻÐÐÐÐÐÐ? 4. ÐÐÐÐÐÐ 3 ÐÐÐÐÐ ÐÐ ÐÐÐĄÐĒÐ ÐÐÐĶÐ! 5. ÐÐÐÐ ÐÐ ÐĨÐÐÐÐÐÐ ÐÐÐ ÐÐÐĢÐÐĢ ÐÐÐ ÐÐ ÐÐĄÐĒÐÐĶÐÐÐ ÐĄÐÐÐÐÐĒÐ? 6. ÐĻÐĒÐ ÐÐ ÐĄÐÐÐÐÐÐÐ Ð ÐĻÐĒÐ ÐÐÐĪÐÐÐ