Solving Inequalities Using Proper functions .ppt
Download as PPT, PDF0 likes11 views
How to solve for inequalities
1 of 27
Download to read offline

























Recommended
Solving and Graphing Inequalities.pptSolving and Graphing Inequalities.ppt



Solving and Graphing Inequalities.pptSolving and Graphing Inequalities.pptAreejAhmed38
╠²
Solving and Graphing Inequalities.pptSolving and Graphing Inequalities.ppt



Solving and Graphing Inequalities.pptSultanTomasII
╠²
This document provides information about solving and graphing inequalities. It defines inequalities and the symbols used such as <, Ōēż, >, Ōēź. It explains that inequalities have solutions that satisfy the given condition, unlike equations which have specific values. The document shows how to solve different types of inequalities algebraically by adding or subtracting from both sides and how to determine the direction of the shading or dashed line when graphing the solutions on a number line. It also discusses absolute value inequalities and graphing linear inequalities in two variables.solving inequalities .pptx



solving inequalities .pptxJonalyn34
╠²
An inequality is like an equation but uses inequality symbols like <, Ōēż, >, Ōēź. Inequalities relate two quantities and can be solved using the same steps as equations. When graphing inequalities, closed circles are used for Ōēż and Ōēź, and open circles for < and >. Examples show how to solve different inequalities algebraically and graph the solutions on a number line. The document provides practice solving and graphing several inequalities.Solving inequalities



Solving inequalitiesIta Rodriguez
╠²
This presentation helps algebra students understand how to graph and solve inequalities. There are one-step, multi-step, and compound inequalities.Inequalities mathematics grade nine igcse.ppt



Inequalities mathematics grade nine igcse.pptMisterTono
╠²
- Students learn to represent inequalities on a number line using different signs such as <, Ōēż, >, Ōēź.
- They learn to solve inequalities algebraically using the same steps as solving equations, such as adding/subtracting the same number to both sides.
- A key rule is that if multiplying or dividing by a negative number, the inequality sign must be switched (e.g. from < to >).
- Examples of solving multi-step inequalities and real-world word problems are provided to illustrate the concepts and skills.0



0Dreams4school
╠²
The document provides information and examples about solving and graphing inequalities. It defines different types of inequalities using symbols like <, Ōēż, >, Ōēź and explains what they mean. It gives examples of writing inequalities based on number lines and solving simple one-variable inequalities by adding or subtracting values from both sides. The document also discusses absolute value inequalities and how to split them into two cases. Finally, it introduces how to graph linear inequalities in two variables on a coordinate plane.Lecture 7 (inequalities)



Lecture 7 (inequalities)HarithaRanasinghe
╠²
1) An inequality is a mathematical statement that uses inequality symbols like <, Ōēż, >, Ōēź to show the relationship between two quantities.
2) When graphing inequalities on a number line, closed circles are used for Ōēż and Ōēź, and open circles are used for < and >.
3) Linear inequalities in two variables can be written as Ax + By < C, Ax + By > C, Ax + By Ōēż C, or Ax + By Ōēź C. An ordered pair (x,y) is a solution if it makes the inequality true.Number and operations review1



Number and operations review1Institute of Applied Technology
╠²
This document provides an overview of several topics in number and operations that may be covered on the SAT, including properties of integers, operations with integers, rational numbers and fractions, number lines, squares and square roots, scientific notation, elementary number theory, ratios, proportions, percents, sequences, and arithmetic and geometric sequences. Sample problems are included to illustrate key concepts.Real numbers system



Real numbers systemPradeep Agrawal
╠²
The document discusses the real number system. It defines rational and irrational numbers, and provides examples of each. Rational numbers can be written as fractions, while irrational numbers can only be written as non-terminating and non-repeating decimals. The document also covers operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division on integers, using rules like keeping or changing signs depending on whether the signs are the same or different.Inequalities ppt revised



Inequalities ppt revisedtroxellm
╠²
Here are the steps to solve each inequality and graph the solution:
1) m + 14 < 4
-14 -14
m < -10
Graph: m < -10
2) -7 > y-1
+1 +1
-6 > y
y < -6
Graph: y < -6
3) (-3)k < 10(-3)
-3
k > -30
Graph: k > -30
4) 2x + 5 Ōēż x + 1
-x -x
x + 5 Ōēż 1
-5 -5
x Ōēż -4
Graph: x Ōēż -4Nts book for gat general



Nts book for gat generalMuhammad Tawakal Shah
╠²
The document discusses standards for educational and professional testing. It provides information about the National Testing Service Pakistan Overseas Scholarship Scheme for PhD Studies. It covers topics like quantitative ability, general mathematics review including arithmetic, exponents and roots, inequalities, fractions, decimals, and comparing fractions. The mathematics review section provides formulas, properties, and examples for key mathematical concepts to help candidates prepare.Nts book-for-gat-general



Nts book-for-gat-generaldiaryinc
╠²
The document discusses standards for educational and professional testing. It provides information about the National Testing Service Pakistan Overseas Scholarship Scheme for PhD Studies. The document covers topics like quantitative ability, general mathematics review including arithmetic, exponents and roots, inequalities, fractions, decimals, and comparing fractions. It aims to refresh knowledge of basic mathematical concepts essential for testing.Interesting integers 1



Interesting integers 1amycheek
╠²
The document defines integers and their properties like positive and negative numbers. It introduces rules for adding and subtracting integers, such as adding numbers with the same sign and subtracting numbers with different signs. It also explains how to use a number line to visualize adding integers and proves that subtracting a negative number is the same as adding a positive number.Interesting integers



Interesting integersmathteacher13
╠²
The document defines integers and their properties like positive and negative numbers. It introduces rules for adding and subtracting integers, such as adding numbers with the same sign and subtracting numbers with different signs. It also explains how to use a number line to visualize adding integers. Finally, it demonstrates how to prove that subtracting a negative number is the same as adding a positive number by using the subtraction checking method.Interesting integers



Interesting integersmathteacher13
╠²
The document defines integers and their properties like positive and negative numbers. It introduces rules for adding and subtracting integers, such as adding numbers with the same sign and subtracting numbers with different signs. It also explains how to use a number line to visualize adding integers and proves that subtracting a negative number is the same as adding a positive number.Adding subtracting integers



Adding subtracting integersAmro Soliman
╠²
The document defines integers and their properties like positive and negative numbers. It introduces rules for adding and subtracting integers, such as adding numbers with the same sign and subtracting numbers with different signs. It also explains how to use a number line to demonstrate adding integers and proves that subtracting a negative number is the same as adding a positive number.Interesting integers 1



Interesting integers 1amycheek
╠²
The document defines integers and their properties like positive and negative numbers. It introduces rules for adding and subtracting integers, such as keeping the sign the same for addition if signs are the same, and changing the sign for subtraction if subtracting a negative number. It also shows how to use a number line to demonstrate adding integers and verifies the subtraction rule works by using the subtraction checking method.Adding subtracting integers



Adding subtracting integersAmro Soliman
╠²
The document defines integers and their properties like positive and negative numbers. It introduces rules for adding and subtracting integers, such as adding numbers with the same sign and subtracting numbers with different signs. It also explains how to use a number line to demonstrate adding integers and proves that subtracting a negative number is the same as adding a positive number.Adding Subtracting Integers



Adding Subtracting IntegersMr. M
╠²
The document defines integers and their properties like positive and negative numbers. It introduces rules for adding and subtracting integers, such as adding numbers with the same sign and subtracting numbers with different signs. It also explains how to use a number line to demonstrate adding integers and proves that subtracting a negative number is the same as adding a positive number.Interesting integers



Interesting integersmathteacher13
╠²
The document defines integers and their properties like positive and negative numbers. It introduces rules for adding and subtracting integers, such as keeping the sign the same when adding like signs and changing the sign when subtracting a negative number. It provides examples and checks to prove the rules are true, like using a number line to model addition and checking subtraction using the inverse operation of addition.Daily Lesson Intro to inequalities. pptx



Daily Lesson Intro to inequalities. pptxjeymararizalapayumob
╠²
This document contains an agenda for a math lesson on inequalities including:
- A warm up problem about students going trick or treating or a haunted house
- An introduction to inequalities explaining the symbols <, Ōēż, >, Ōēź and what they mean
- How to graph inequalities on a number line using open and closed circles
- Steps for solving inequalities by undoing operations and keeping the same operations on both sides
- Examples of solving various inequalities and graphing the solution sets on a number lineRational irrational and_real_number_practice



Rational irrational and_real_number_practiceeixarc
╠²
The document discusses real numbers and their classification. It defines real numbers as any number that can be found on the number line, including rational and irrational numbers. Rational numbers are those that can be written as fractions, with decimal forms that terminate or repeat. Irrational numbers cannot be written as fractions and have non-terminating, non-repeating decimal forms. Examples of rational numbers given include integers and fractions, while examples of irrational numbers include ŽĆ and square roots of non-perfect squares. The document provides examples of classifying numbers as rational or irrational and ordering them on the number line.Interesting Integers.ppt



Interesting Integers.pptGangalapudiBhaskerre
╠²
This document defines integers and the rules for adding and subtracting them. It defines positive and negative numbers, opposites, and absolute value. It then presents two rules for adding integers: 1) if signs are the same, add the numbers and use that sign, and 2) if signs are different, subtract the smaller number from the larger and use the sign of the number with the larger absolute value. It also explains that subtracting a negative number is the same as adding a positive number. Examples are provided to illustrate the rules and a number line model is presented. The document checks understanding through practice problems.Solving Absolute Value Equations and Inequalities.ppt



Solving Absolute Value Equations and Inequalities.pptFarhanPerdanaRamaden1
╠²
This document provides information and examples for solving absolute value equations and inequalities. It begins with definitions of absolute value and discusses how absolute value equations can have two solutions since the expression inside the absolute value can be positive or negative. Examples are provided for solving absolute value equations by setting the expression equal to both its positive and negative values. The document also discusses how to solve absolute value inequalities by splitting them into "and" or "or" statements and provides examples of solving and graphing various absolute value inequalities.Pre-Algebra Final Review



Pre-Algebra Final ReviewAndrea B.
╠²
Add & Subtract Integers
Multiply & Divide Integers
Add & Subtract Fractions
Multiply & Divide Fractions
One & Two Step Equations
Combining Like TermsHow to use Init Hooks in Odoo 18 - Odoo ║▌║▌▀Żs



How to use Init Hooks in Odoo 18 - Odoo ║▌║▌▀ŻsCeline George
╠²
In this slide, weŌĆÖll discuss on how to use Init Hooks in Odoo 18. In Odoo, Init Hooks are essential functions specified as strings in the __init__ file of a module.Blind Spots in AI and Formulation Science Knowledge Pyramid (Updated Perspect...



Blind Spots in AI and Formulation Science Knowledge Pyramid (Updated Perspect...Ajaz Hussain
╠²
This presentation delves into the systemic blind spots within pharmaceutical science and regulatory systems, emphasizing the significance of "inactive ingredients" and their influence on therapeutic equivalence. These blind spots, indicative of normalized systemic failures, go beyond mere chance occurrences and are ingrained deeply enough to compromise decision-making processes and erode trust.
Historical instances like the 1938 FD&C Act and the Generic Drug Scandals underscore how crisis-triggered reforms often fail to address the fundamental issues, perpetuating inefficiencies and hazards.
The narrative advocates a shift from reactive crisis management to proactive, adaptable systems prioritizing continuous enhancement. Key hurdles involve challenging outdated assumptions regarding bioavailability, inadequately funded research ventures, and the impact of vague language in regulatory frameworks.
The rise of large language models (LLMs) presents promising solutions, albeit with accompanying risks necessitating thorough validation and seamless integration.
Tackling these blind spots demands a holistic approach, embracing adaptive learning and a steadfast commitment to self-improvement. By nurturing curiosity, refining regulatory terminology, and judiciously harnessing new technologies, the pharmaceutical sector can progress towards better public health service delivery and ensure the safety, efficacy, and real-world impact of drug products.More Related Content
Similar to Solving Inequalities Using Proper functions .ppt (20)
Lecture 7 (inequalities)



Lecture 7 (inequalities)HarithaRanasinghe
╠²
1) An inequality is a mathematical statement that uses inequality symbols like <, Ōēż, >, Ōēź to show the relationship between two quantities.
2) When graphing inequalities on a number line, closed circles are used for Ōēż and Ōēź, and open circles are used for < and >.
3) Linear inequalities in two variables can be written as Ax + By < C, Ax + By > C, Ax + By Ōēż C, or Ax + By Ōēź C. An ordered pair (x,y) is a solution if it makes the inequality true.Number and operations review1



Number and operations review1Institute of Applied Technology
╠²
This document provides an overview of several topics in number and operations that may be covered on the SAT, including properties of integers, operations with integers, rational numbers and fractions, number lines, squares and square roots, scientific notation, elementary number theory, ratios, proportions, percents, sequences, and arithmetic and geometric sequences. Sample problems are included to illustrate key concepts.Real numbers system



Real numbers systemPradeep Agrawal
╠²
The document discusses the real number system. It defines rational and irrational numbers, and provides examples of each. Rational numbers can be written as fractions, while irrational numbers can only be written as non-terminating and non-repeating decimals. The document also covers operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division on integers, using rules like keeping or changing signs depending on whether the signs are the same or different.Inequalities ppt revised



Inequalities ppt revisedtroxellm
╠²
Here are the steps to solve each inequality and graph the solution:
1) m + 14 < 4
-14 -14
m < -10
Graph: m < -10
2) -7 > y-1
+1 +1
-6 > y
y < -6
Graph: y < -6
3) (-3)k < 10(-3)
-3
k > -30
Graph: k > -30
4) 2x + 5 Ōēż x + 1
-x -x
x + 5 Ōēż 1
-5 -5
x Ōēż -4
Graph: x Ōēż -4Nts book for gat general



Nts book for gat generalMuhammad Tawakal Shah
╠²
The document discusses standards for educational and professional testing. It provides information about the National Testing Service Pakistan Overseas Scholarship Scheme for PhD Studies. It covers topics like quantitative ability, general mathematics review including arithmetic, exponents and roots, inequalities, fractions, decimals, and comparing fractions. The mathematics review section provides formulas, properties, and examples for key mathematical concepts to help candidates prepare.Nts book-for-gat-general



Nts book-for-gat-generaldiaryinc
╠²
The document discusses standards for educational and professional testing. It provides information about the National Testing Service Pakistan Overseas Scholarship Scheme for PhD Studies. The document covers topics like quantitative ability, general mathematics review including arithmetic, exponents and roots, inequalities, fractions, decimals, and comparing fractions. It aims to refresh knowledge of basic mathematical concepts essential for testing.Interesting integers 1



Interesting integers 1amycheek
╠²
The document defines integers and their properties like positive and negative numbers. It introduces rules for adding and subtracting integers, such as adding numbers with the same sign and subtracting numbers with different signs. It also explains how to use a number line to visualize adding integers and proves that subtracting a negative number is the same as adding a positive number.Interesting integers



Interesting integersmathteacher13
╠²
The document defines integers and their properties like positive and negative numbers. It introduces rules for adding and subtracting integers, such as adding numbers with the same sign and subtracting numbers with different signs. It also explains how to use a number line to visualize adding integers. Finally, it demonstrates how to prove that subtracting a negative number is the same as adding a positive number by using the subtraction checking method.Interesting integers



Interesting integersmathteacher13
╠²
The document defines integers and their properties like positive and negative numbers. It introduces rules for adding and subtracting integers, such as adding numbers with the same sign and subtracting numbers with different signs. It also explains how to use a number line to visualize adding integers and proves that subtracting a negative number is the same as adding a positive number.Adding subtracting integers



Adding subtracting integersAmro Soliman
╠²
The document defines integers and their properties like positive and negative numbers. It introduces rules for adding and subtracting integers, such as adding numbers with the same sign and subtracting numbers with different signs. It also explains how to use a number line to demonstrate adding integers and proves that subtracting a negative number is the same as adding a positive number.Interesting integers 1



Interesting integers 1amycheek
╠²
The document defines integers and their properties like positive and negative numbers. It introduces rules for adding and subtracting integers, such as keeping the sign the same for addition if signs are the same, and changing the sign for subtraction if subtracting a negative number. It also shows how to use a number line to demonstrate adding integers and verifies the subtraction rule works by using the subtraction checking method.Adding subtracting integers



Adding subtracting integersAmro Soliman
╠²
The document defines integers and their properties like positive and negative numbers. It introduces rules for adding and subtracting integers, such as adding numbers with the same sign and subtracting numbers with different signs. It also explains how to use a number line to demonstrate adding integers and proves that subtracting a negative number is the same as adding a positive number.Adding Subtracting Integers



Adding Subtracting IntegersMr. M
╠²
The document defines integers and their properties like positive and negative numbers. It introduces rules for adding and subtracting integers, such as adding numbers with the same sign and subtracting numbers with different signs. It also explains how to use a number line to demonstrate adding integers and proves that subtracting a negative number is the same as adding a positive number.Interesting integers



Interesting integersmathteacher13
╠²
The document defines integers and their properties like positive and negative numbers. It introduces rules for adding and subtracting integers, such as keeping the sign the same when adding like signs and changing the sign when subtracting a negative number. It provides examples and checks to prove the rules are true, like using a number line to model addition and checking subtraction using the inverse operation of addition.Daily Lesson Intro to inequalities. pptx



Daily Lesson Intro to inequalities. pptxjeymararizalapayumob
╠²
This document contains an agenda for a math lesson on inequalities including:
- A warm up problem about students going trick or treating or a haunted house
- An introduction to inequalities explaining the symbols <, Ōēż, >, Ōēź and what they mean
- How to graph inequalities on a number line using open and closed circles
- Steps for solving inequalities by undoing operations and keeping the same operations on both sides
- Examples of solving various inequalities and graphing the solution sets on a number lineRational irrational and_real_number_practice



Rational irrational and_real_number_practiceeixarc
╠²
The document discusses real numbers and their classification. It defines real numbers as any number that can be found on the number line, including rational and irrational numbers. Rational numbers are those that can be written as fractions, with decimal forms that terminate or repeat. Irrational numbers cannot be written as fractions and have non-terminating, non-repeating decimal forms. Examples of rational numbers given include integers and fractions, while examples of irrational numbers include ŽĆ and square roots of non-perfect squares. The document provides examples of classifying numbers as rational or irrational and ordering them on the number line.Interesting Integers.ppt



Interesting Integers.pptGangalapudiBhaskerre
╠²
This document defines integers and the rules for adding and subtracting them. It defines positive and negative numbers, opposites, and absolute value. It then presents two rules for adding integers: 1) if signs are the same, add the numbers and use that sign, and 2) if signs are different, subtract the smaller number from the larger and use the sign of the number with the larger absolute value. It also explains that subtracting a negative number is the same as adding a positive number. Examples are provided to illustrate the rules and a number line model is presented. The document checks understanding through practice problems.Solving Absolute Value Equations and Inequalities.ppt



Solving Absolute Value Equations and Inequalities.pptFarhanPerdanaRamaden1
╠²
This document provides information and examples for solving absolute value equations and inequalities. It begins with definitions of absolute value and discusses how absolute value equations can have two solutions since the expression inside the absolute value can be positive or negative. Examples are provided for solving absolute value equations by setting the expression equal to both its positive and negative values. The document also discusses how to solve absolute value inequalities by splitting them into "and" or "or" statements and provides examples of solving and graphing various absolute value inequalities.Pre-Algebra Final Review



Pre-Algebra Final ReviewAndrea B.
╠²
Add & Subtract Integers
Multiply & Divide Integers
Add & Subtract Fractions
Multiply & Divide Fractions
One & Two Step Equations
Combining Like TermsRecently uploaded (20)
How to use Init Hooks in Odoo 18 - Odoo ║▌║▌▀Żs



How to use Init Hooks in Odoo 18 - Odoo ║▌║▌▀ŻsCeline George
╠²
In this slide, weŌĆÖll discuss on how to use Init Hooks in Odoo 18. In Odoo, Init Hooks are essential functions specified as strings in the __init__ file of a module.Blind Spots in AI and Formulation Science Knowledge Pyramid (Updated Perspect...



Blind Spots in AI and Formulation Science Knowledge Pyramid (Updated Perspect...Ajaz Hussain
╠²
This presentation delves into the systemic blind spots within pharmaceutical science and regulatory systems, emphasizing the significance of "inactive ingredients" and their influence on therapeutic equivalence. These blind spots, indicative of normalized systemic failures, go beyond mere chance occurrences and are ingrained deeply enough to compromise decision-making processes and erode trust.
Historical instances like the 1938 FD&C Act and the Generic Drug Scandals underscore how crisis-triggered reforms often fail to address the fundamental issues, perpetuating inefficiencies and hazards.
The narrative advocates a shift from reactive crisis management to proactive, adaptable systems prioritizing continuous enhancement. Key hurdles involve challenging outdated assumptions regarding bioavailability, inadequately funded research ventures, and the impact of vague language in regulatory frameworks.
The rise of large language models (LLMs) presents promising solutions, albeit with accompanying risks necessitating thorough validation and seamless integration.
Tackling these blind spots demands a holistic approach, embracing adaptive learning and a steadfast commitment to self-improvement. By nurturing curiosity, refining regulatory terminology, and judiciously harnessing new technologies, the pharmaceutical sector can progress towards better public health service delivery and ensure the safety, efficacy, and real-world impact of drug products.APM People Interest Network Conference - Oliver Randall & David Bovis - Own Y...



APM People Interest Network Conference - Oliver Randall & David Bovis - Own Y...Association for Project Management
╠²
APM People Interest Network Conference 2025
- Autonomy, Teams and Tension
- Oliver Randall & David Bovis
- Own Your Autonomy
Oliver Randall
Consultant, Tribe365
Oliver is a career project professional since 2011 and started volunteering with APM in 2016 and has since chaired the People Interest Network and the North East Regional Network. Oliver has been consulting in culture, leadership and behaviours since 2019 and co-developed HPTM┬«ŌĆ»an off the shelf high performance framework for teams and organisations and is currently working with SAS (Stellenbosch Academy for Sport) developing the culture, leadership and behaviours framework for future elite sportspeople whilst also holding down work as a project manager in the NHS at North Tees and Hartlepool Foundation Trust.
David Bovis
Consultant, Duxinaroe
A Leadership and Culture Change expert, David is the originator of BTFAŌäó and The Dux Model.
With a Masters in Applied Neuroscience from the Institute of Organisational Neuroscience, he is widely regarded as the ŌĆśGo-ToŌĆÖ expert in the field, recognised as an inspiring keynote speaker and change strategist.
He has an industrial engineering background, majoring in TPS / Lean. David worked his way up from his apprenticeship to earn his seat at the C-suite table. His career spans several industries, including Automotive, Aerospace, Defence, Space, Heavy Industries and Elec-Mech / polymer contract manufacture.
Published in LondonŌĆÖs Evening Standard quarterly business supplement, James CaanŌĆÖs ŌĆśYour businessŌĆÖ Magazine, ŌĆśQuality WorldŌĆÖ, the Lean Management Journal and Cambridge Universities ŌĆśPMAŌĆÖ, he works as comfortably with leaders from FTSE and Fortune 100 companies as he does owner-managers in SMEŌĆÖs. He is passionate about helping leaders understand the neurological root cause of a high-performance culture and sustainable change, in business.
Session | Own Your Autonomy ŌĆō The Importance of Autonomy in Project Management
#OwnYourAutonomy is aiming to be a global APM initiative to position everyone to take a more conscious role in their decision making process leading to increased outcomes for everyone and contribute to ŌĆ£a world in which all projects succeedŌĆØ.
We want everyone to join the journey.
#OwnYourAutonomy is the culmination of 3 years of collaborative exploration within the Leadership Focus Group which is part of the APM People Interest Network. The work has been pulled together using the 5 HPTM® Systems and the BTFA neuroscience leadership programme.
https://www.linkedin.com/showcase/apm-people-network/about/How to Configure Flexible Working Schedule in Odoo 18 Employee



How to Configure Flexible Working Schedule in Odoo 18 EmployeeCeline George
╠²
In this slide, weŌĆÖll discuss on how to configure flexible working schedule in Odoo 18 Employee module. In Odoo 18, the Employee module offers powerful tools to configure and manage flexible working schedules tailored to your organization's needs.FESTIVAL: SINULOG & THINGYAN-LESSON 4.pptx



FESTIVAL: SINULOG & THINGYAN-LESSON 4.pptxDanmarieMuli1
╠²
Sinulog Festival of Cebu City, and Thingyan Festival of Myanmar.Kaun TALHA quiz Prelims - El Dorado 2025



Kaun TALHA quiz Prelims - El Dorado 2025Conquiztadors- the Quiz Society of Sri Venkateswara College
╠²
Prelims of Kaun TALHA : a Travel, Architecture, Lifestyle, Heritage and Activism quiz, organized by Conquiztadors, the Quiz society of Sri Venkateswara College under their annual quizzing fest El Dorado 2025. How to Setup WhatsApp in Odoo 17 - Odoo ║▌║▌▀Żs



How to Setup WhatsApp in Odoo 17 - Odoo ║▌║▌▀ŻsCeline George
╠²
Integrate WhatsApp into Odoo using the WhatsApp Business API or third-party modules to enhance communication. This integration enables automated messaging and customer interaction management within Odoo 17.APM People Interest Network Conference - Tim Lyons - The neurological levels ...



APM People Interest Network Conference - Tim Lyons - The neurological levels ...Association for Project Management
╠²
APM People Interest Network Conference 2025
-Autonomy, Teams and Tension: Projects under stress
-Tim Lyons
-The neurological levels of
team-working: Harmony and tensions
With a background in projects spanning more than 40 years, Tim Lyons specialised in the delivery of large, complex, multi-disciplinary programmes for clients including Crossrail, Network Rail, ExxonMobil, Siemens and in patent development. His first career was in broadcasting, where he designed and built commercial radio station studios in Manchester, Cardiff and Bristol, also working as a presenter and programme producer. Tim now writes and presents extensively on matters relating to the human and neurological aspects of projects, including communication, ethics and coaching. He holds a MasterŌĆÖs degree in NLP, is an NLP Master Practitioner and International Coach. He is the Deputy Lead for APMŌĆÖs People Interest Network.
Session | The Neurological Levels of Team-working: Harmony and Tensions
Understanding how teams really work at conscious and unconscious levels is critical to a harmonious workplace. This session uncovers what those levels are, how to use them to detect and avoid tensions and how to smooth the management of change by checking you have considered all of them.Essentials of a Good PMO, presented by Aalok Sonawala



Essentials of a Good PMO, presented by Aalok SonawalaAssociation for Project Management
╠²
APM event hosted by the South Wales and West of England Network (SWWE Network)
Speaker: Aalok Sonawala
The SWWE Regional Network were very pleased to welcome Aalok Sonawala, Head of PMO, National Programmes, Rider Levett Bucknall on 26 February, to BAWA for our first face to face event of 2025. Aalok is a member of APMŌĆÖs Thames Valley Regional Network and also speaks to members of APMŌĆÖs PMO Interest Network, which aims to facilitate collaboration and learning, offer unbiased advice and guidance.
Tonight, Aalok planned to discuss the importance of a PMO within project-based organisations, the different types of PMO and their key elements, PMO governance and centres of excellence.
PMOŌĆÖs within an organisation can be centralised, hub and spoke with a central PMO with satellite PMOs globally, or embedded within projects. The appropriate structure will be determined by the specific business needs of the organisation. The PMO sits above PM delivery and the supply chain delivery teams.
For further information about the event please click here.Digital Tools with AI for e-Content Development.pptx



Digital Tools with AI for e-Content Development.pptxDr. Sarita Anand
╠²
This ppt is useful for not only for B.Ed., M.Ed., M.A. (Education) or any other PG level students or Ph.D. scholars but also for the school, college and university teachers who are interested to prepare an e-content with AI for their students and others.Computer Application in Business (commerce)



Computer Application in Business (commerce)Sudar Sudar
╠²
The main objectives
1. To introduce the concept of computer and its various parts. 2. To explain the concept of data base management system and Management information system.
3. To provide insight about networking and basics of internet
Recall various terms of computer and its part
Understand the meaning of software, operating system, programming language and its features
Comparing Data Vs Information and its management system Understanding about various concepts of management information system
Explain about networking and elements based on internet
1. Recall the various concepts relating to computer and its various parts
2 Understand the meaning of softwareŌĆÖs, operating system etc
3 Understanding the meaning and utility of database management system
4 Evaluate the various aspects of management information system
5 Generating more ideas regarding the use of internet for business purpose QuickBooks Desktop to QuickBooks Online How to Make the Move



QuickBooks Desktop to QuickBooks Online How to Make the MoveTechSoup
╠²
If you use QuickBooks Desktop and are stressing about moving to QuickBooks Online, in this webinar, get your questions answered and learn tips and tricks to make the process easier for you.
Key Questions:
* When is the best time to make the shift to QuickBooks Online?
* Will my current version of QuickBooks Desktop stop working?
* I have a really old version of QuickBooks. What should I do?
* I run my payroll in QuickBooks Desktop now. How is that affected?
*Does it bring over all my historical data? Are there things that don't come over?
* What are the main differences between QuickBooks Desktop and QuickBooks Online?
* And moreHow to Modify Existing Web Pages in Odoo 18



How to Modify Existing Web Pages in Odoo 18Celine George
╠²
In this slide, weŌĆÖll discuss on how to modify existing web pages in Odoo 18. Web pages in Odoo 18 can also gather user data through user-friendly forms, encourage interaction through engaging features. Rass MELAI : an Internet MELA Quiz Finals - El Dorado 2025



Rass MELAI : an Internet MELA Quiz Finals - El Dorado 2025Conquiztadors- the Quiz Society of Sri Venkateswara College
╠²
Finals of Rass MELAI : a Music, Entertainment, Literature, Arts and Internet Culture Quiz organized by Conquiztadors, the Quiz society of Sri Venkateswara College under their annual quizzing fest El Dorado 2025. EDL 290F Week 3 - Mountaintop Views (2025).pdf



EDL 290F Week 3 - Mountaintop Views (2025).pdfLiz Walsh-Trevino
╠²
EDL 290F Week 3 - Mountaintop Views (2025).pdfHow to Configure Restaurants in Odoo 17 Point of Sale



How to Configure Restaurants in Odoo 17 Point of SaleCeline George
╠²
Odoo, a versatile and integrated business management software, excels with its robust Point of Sale (POS) module. This guide delves into the intricacies of configuring restaurants in Odoo 17 POS, unlocking numerous possibilities for streamlined operations and enhanced customer experiences.Adventure Activities Final By H R Gohil Sir



Adventure Activities Final By H R Gohil SirGUJARATCOMMERCECOLLE
╠²
Adventure Activities Final By H R Gohil SirLesson Plan M1 2024 Lesson Plan M1 2024 Lesson Plan M1 2024 Lesson Plan M1...



Lesson Plan M1 2024 Lesson Plan M1 2024 Lesson Plan M1 2024 Lesson Plan M1...pinkdvil200
╠²
Lesson Plan M1 2024 Lesson Plan M1 2024 Lesson Plan M1 2024 APM People Interest Network Conference - Oliver Randall & David Bovis - Own Y...



APM People Interest Network Conference - Oliver Randall & David Bovis - Own Y...Association for Project Management
╠²
Kaun TALHA quiz Prelims - El Dorado 2025



Kaun TALHA quiz Prelims - El Dorado 2025Conquiztadors- the Quiz Society of Sri Venkateswara College
╠²
APM People Interest Network Conference - Tim Lyons - The neurological levels ...



APM People Interest Network Conference - Tim Lyons - The neurological levels ...Association for Project Management
╠²
Rass MELAI : an Internet MELA Quiz Finals - El Dorado 2025



Rass MELAI : an Internet MELA Quiz Finals - El Dorado 2025Conquiztadors- the Quiz Society of Sri Venkateswara College
╠²
Solving Inequalities Using Proper functions .ppt
- 2. An inequality is like an equation, but instead of an equal sign (=) it has one of these signs: < : less than Ōēż : less than or equal to > : greater than Ōēź : greater than or equal to
- 3. What do Inequalities mean? ŌĆó A mathematical sentence that uses one of the inequality symbols to state the relationship between two quantities.
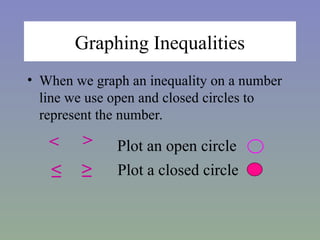
- 4. Graphing Inequalities ŌĆó When we graph an inequality on a number line we use open and closed circles to represent the number. < < Plot a closed circle Ōēż Ōēź Plot an open circle
- 5. x < 5 means that whatever value x has, it must be less than 5. Try to name ten numbers that are less than 5!
- 6. Numbers less than 5 are to the left of 5 on the number line. 0 5 10 15 -20 -15 -10 -5 -25 20 25 ŌĆó If you said 4, 3, 2, 1, 0, -1, -2, -3, etc., you are right. ŌĆó There are also numbers in between the integers, like 2.5, 1/2, -7.9, etc. ŌĆó The number 5 would not be a correct answer, though, because 5 is not less than 5.
- 7. x Ōēź -2 means that whatever value x has, it must be greater than or equal to -2. Try to name ten numbers that are greater than or equal to -2
- 8. Numbers greater than -2 are to the right of -2 on the number line. 0 5 10 15 -20 -15 -10 -5 -25 20 25 ŌĆó If you said -1, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, etc., you are right. ŌĆó There are also numbers in between the integers, like -1/2, 0.2, 3.1, 5.5, etc. ŌĆó The number -2 would also be a correct answer, because of the phrase, ŌĆ£or equal toŌĆØ. -2
- 9. Homework
- 10. Solving an Inequality ŌĆó Solve much like you would an equation. ŌĆó Always undo addition or subtraction first, then multiplication or division. ŌĆó Remember whatever is done to one side of the inequality must be done to the other side. The goal is to get the variable by itself.
- 11. Properties to Know for Solving Inequalities Addition and Subtraction ŌĆóAdding c to both sides of an inequality just shifts everything along, and the inequality stays the same. ŌĆóIf a < b, then a + c < b + c Example: Alex has less coins than Billy. ŌĆóIf both Alex and Billy get 3 more coins each, Alex will still have less coins than Billy. ŌĆóLikewise: ŌĆóIf a < b, then a ŌłÆ c < b ŌłÆ c ŌĆóIf a > b, then a + c > b + c, and ŌĆóIf a > b, then a ŌłÆ c > b ŌłÆ c ŌĆóSo adding (or subtracting) the same value to both a and b will not change the inequality
- 12. Properties to Know for Solving Inequalities ŌĆó Multiplication and Division ŌĆó When we multiply both a and b by a positive number, the inequality stays the same. ŌĆó But when we multiply both a and b by a negative number, the inequality swaps over! Notice that a<b becomes b<a after multiplying by (-2) But the inequality stays the same when multiplying by +3 ŌĆó Here are the rules: ŌĆó If a < b, and c is positive, then ac < bc ŌĆó If a < b, and c is negative, then ac > bc (inequality swaps over!) ŌĆó A "positive" example: Alex's score of 3 is lower than Billy's score of 7. ŌĆó a < b ŌĆó If both Alex and Billy manage to double their scores (├Ś2), Alex's score will still be lower than Billy's score. ŌĆó 2a < 2b ŌĆó But when multiplying by a negative the opposite happens: ŌĆó But if the scores become minuses, then Alex loses 3 points and Billy loses 7 points ŌĆó So Alex has now done better than Billy! ŌĆó -a > -b ŌĆó The same is true for division ŌĆō flip the sign of the inequality if dividing by a negative number
- 13. Solve an Inequality w + 5 < 8 - 5 -5 w < 3 All numbers less than 3 are solutions to this problem! 0 5 10 15 -20 -15 -10 -5 -25 20 25
- 14. 1 step Examples 8 + r Ōēź -2 -8 -8 r -10 All numbers greater than-10 (including -10) Ōēź 0 5 10 15 -20 -15 -10 -5 -25 20 25
- 15. 1 step Examples 2x > -2 2 2 x > -1 All numbers greater than -1 make this problem true! 0 5 10 15 -20 -15 -10 -5 -25 20 25
- 16. 2 step Examples 2h + 8 Ōēż 24 -8 -8 2h Ōēż 16 2 2 h Ōēż 8 All numbers less than 8 (including 8) 0 5 10 15 -20 -15 -10 -5 -25 20 25
- 17. Be Aware of Cases Involving Multiplying and Dividing Inequalities with Negative Numbers ŌĆó Multiplication Example ŌĆó Division Example
- 18. One More Case ŌĆó Solve Inequalities with the variable on both sides
- 19. Your TurnŌĆ”. ŌĆó Solve the inequality and graph the answer. 1. x + 3 > -4 x > -7 2. 6d > 24 d > 4 3. 2x - 8 < 14 x < 11 4. -2c ŌĆō 4 < 2 *c Ōēź-3 noticed in this problem you had to flip the inequality
- 21. Be sure to know the properties affecting inequalities. ŌĆó Addition and Subtraction: Adding(or subtracting) c to both sides of an inequality just shifts everything along, and the inequality stays the same. ŌĆó If a < b, then a + c < b + c ŌĆó If a < b, then a - c < b - c
- 22. Be sure to know the properties affecting inequalities. ŌĆóMultiplication and Division: When we multiply both a and b by a positive number, the inequality stays the same. ŌĆóBut when we multiply both a and b by a negative number, the inequality swaps over! Notice that a<b becomes b<a after multiplying by (-2) But the inequality stays the same when multiplying by +3 ŌĆóThe same is true for division ŌĆō flip the sign of the inequality if dividing by a negative number
- 23. REAL-LIFE APPLICATION PROBLEMS LetŌĆÖs look at some
- 24. Real-Life Application Hint: 90 x 6 90% = 540 pts. You are taking a history course in which your grade is based on six 100 point tests. To earn an A in class, you must have a total of at least 90%. You have scored an 83, 89, 95, 98, and 92 on the first five tests. What is the least amount of points you can earn on the sixth test in order to earn an A in the course? 83+89+95+98+92= 457 457 - 457 + T Ōēż 540 - 457 T Ōēż 83
- 25. Example 2 ŌĆó f/3 Ōēź 4 ŌĆó f/3 Ō¢¬ 3 Ōēź 4 Ō¢¬ 3 ŌĆó F Ōēź 12 To play a board game, there must be at least 4 people on each team. You divide your friends into 3 groups. Write and solve an inequality to represent the number of friends playing the game.
- 26. Example 3: ŌĆó 0.50 x +45 Ōēż 50 ŌĆó 0.50 x +45 -45 Ōēż 50 -45 ŌĆó 0.50 x Ōēż 5 ŌĆó 0.50 x / 0.50 Ōēż 5 /0.50 ŌĆó x Ōēż 10 You budget $50 a month for your cell phone plan. You pay $45 for your minutes and 250 text messages. You are charged an extra $0.50 for picture messages. Write and solve an inequality to find the number of picture messages you can send without going over your budget.
- 27. Go Forth and Prosper! More Practice available on teacher webpage




