Ó╣āÓĖÜÓĖäÓĖ¦ÓĖ▓ÓĖĪÓĖŻÓĖ╣Ó╣ē Ó╣ĆÓĖŻÓĖĘÓ╣łÓĖŁÓĖćÓĖĢÓĖŻÓĖĄÓ╣éÓĖüÓĖōÓĖĪÓĖ┤ÓĖĢÓĖ┤
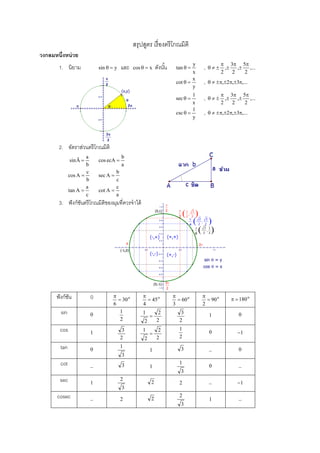
- 1. ÓĖ¬ÓĖŻÓĖĖÓĖøÓĖ¬ÓĖ╣ÓĖĢÓĖŻ Ó╣ĆÓĖŻÓĖĘÓ╣łÓĖŁÓĖćÓĖĢÓĖŻÓĖĄÓ╣éÓĖüÓĖōÓĖĪÓĖ┤ÓĖĢÓĖ┤ ÓĖ¦ÓĖćÓĖüÓĖźÓĖĪÓĖ½ÓĖÖÓĖČÓ╣łÓĖćÓĖ½ÓĖÖÓ╣łÓĖ¦ÓĖó x y tan ’ĆĮ’ü▒ ,... 2 5 , 2 3 , 2 ’ü░ ’é▒ ’ü░ ’é▒ ’ü░ ’é▒’é╣’ü▒1. ,ÓĖÖÓĖ┤ÓĖóÓĖ▓ÓĖĪ ysin ’ĆĮ’ü▒ Ó╣üÓĖźÓĖ░ xcos ÓĖöÓĖ▒ÓĖćÓĖÖÓĖ▒Ó╣ēÓĖÖ’ü▒ ’ĆĮ y x cot ’ĆĮ’ü▒ , ,...3,2, ’ü░’é▒’ü░’é▒’ü░’é▒’é╣’ü▒ x 1 sec ’ĆĮ’ü▒ , ,... 2 5 , 2 3 , 2 ’ü░ ’é▒ ’ü░ ’é▒ ’ü░ ’é▒’é╣’ü▒ y 1 csc ’ĆĮ’ü▒ , ,...3,2, ’ü░’é▒’ü░’é▒’ü░’é▒’é╣’ü▒ 2. ÓĖŁÓĖ▒ÓĖĢÓĖŻÓĖ▓ÓĖ¬Ó╣łÓĖ¦ÓĖÖÓĖĢÓĖŻÓĖĄÓ╣éÓĖüÓĖōÓĖĪÓĖ┤ÓĖĢÓĖ┤ b a ├äsin ’ĆĮ a b ecAcos ’ĆĮ b c Acos ’ĆĮ c b Asec ’ĆĮ c a Atan ’ĆĮ a c Acot ’ĆĮ 3. ÓĖ¤ÓĖ▒ÓĖćÓĖüÓ╣īÓĖŖÓĖ▒ÓĖÖÓĖĢÓĖŻÓĖĄÓ╣éÓĖüÓĖōÓĖĪÓĖ┤ÓĖĢÓĖ┤ÓĖéÓĖŁÓĖćÓĖĪÓĖĖÓĖĪÓĖŚÓĖĄÓ╣łÓĖäÓĖ¦ÓĖŻÓĖłÓ╣ŹÓĖ▓Ó╣äÓĖöÓ╣ē ÓĖ¤ÓĖ▒ÓĖćÓĖüÓ╣īÓĖŖÓĖ▒ÓĖÖ 0 o 30 6 ’ĆĮ ’ü░ o 45 4 ’ĆĮ ’ü░ o 60 3 ’ĆĮ ’ü░ o 90 2 ’ĆĮ ’ü░ o 180’ĆĮ’ü░ sin 0 2 1 2 2 2 1 ’ĆĮ 2 3 1 0 cos 1 2 3 2 2 2 1 ’ĆĮ 2 1 0 1’ĆŁ tan 0 3 1 1 3 _ 0 cot _ 3 1 3 1 0 _ sec 1 3 2 2 2 _ 1’ĆŁ cosec _ 2 2 3 2 1 _
- 2. 4. ÓĖüÓĖ▓ÓĖŻÓĖ½ÓĖ▓ÓĖäÓ╣łÓĖ▓ÓĖéÓĖŁÓĖćÓĖ¤ÓĖ▒ÓĖćÓĖüÓ╣īÓĖŖÓĖ▒ÓĖÖÓĖĢÓĖŻÓĖĄÓ╣éÓĖüÓĖōÓĖéÓĖŁÓĖćÓĖĪÓĖĖÓĖĪÓĖøÓĖŻÓĖ░ÓĖüÓĖŁÓĖÜÓĖŚÓĖĄÓ╣łÓĖäÓ╣łÓĖ▓ÓĖéÓĖŁÓĖćÓĖ¤ÓĖ▒ÓĖćÓĖüÓ╣īÓĖŖÓĖ▒ÓĖÖÓ╣äÓĖĪÓ╣łÓ╣ĆÓĖøÓĖźÓĖĄÓ╣łÓĖóÓĖÖÓ╣üÓĖøÓĖźÓĖć 2 0 ’ü░ ’Ć╝’ü▒’Ć╝ÓĖ¢Ó╣ēÓĖ▓ÓĖüÓ╣ŹÓĖ▓ÓĖ½ÓĖÖÓĖöÓ╣āÓĖ½Ó╣ē ’ü▒’ĆŁ’ü░ ÓĖŁÓĖóÓĖ╣Ó╣ł ÓĖäÓĖ¦ÓĖŁÓĖöÓĖŻÓĖ▒ÓĖÖÓĖĢÓ╣ī 2 ÓĖŁÓĖóÓĖ╣Ó╣ł ÓĖäÓĖ¦ÓĖŁÓĖöÓĖŻÓĖ▒ÓĖÖÓĖĢÓ╣ī 3 ÓĖŁÓĖóÓĖ╣Ó╣ł ÓĖäÓĖ¦ÓĖŁÓĖöÓĖŻÓĖ▒ÓĖÖÓĖĢÓ╣ī 4 ÓĖŁÓĖóÓĖ╣Ó╣ł ÓĖäÓĖ¦ÓĖŁÓĖöÓĖŻÓĖ▒ÓĖÖÓĖĢÓ╣ī 4’ü▒’ĆŁ’ü░2’ü▒’Ć½’ü░ ’ü▒’ĆŁ ’ü▒’ĆĮ’ü▒’ĆŁ’ü░ sin)sin( ’ü▒’ĆŁ’ĆĮ’ü▒’Ć½’ü░ sin)sin( ’ü▒’ĆŁ’ĆĮ’ü▒’ĆŁ’ü░ sin)2sin( ’ü▒’ĆŁ’ĆĮ’ü▒’ĆŁ sin)sin( ’ü▒’ĆŁ’ĆĮ’ü▒’ĆŁ’ü░ cos)cos( ’ü▒’ĆŁ’ĆĮ’ü▒’Ć½’ü░ cos)cos( ’ü▒’ĆĮ’ü▒’ĆŁ’ü░ cos)2cos( ’ü▒’ĆĮ’ü▒’ĆŁ cos)cos( ’ü▒’ĆŁ’ĆĮ’ü▒’ĆŁ’ü░ tan)tan( tan( ) tan’ü░ ’Ć½ ’ü▒ ’ĆĮ ’ü▒ ’ü▒’ĆŁ’ĆĮ’ü▒’ĆŁ’ü░ tan)2tan( ’ü▒’ĆŁ’ĆĮ’ü▒’ĆŁ tan)tan( ÓĖüÓĖŻÓĖōÓĖĄÓĖŚÓĖĄÓ╣łÓĖĪÓĖĖÓĖĪÓ╣ĆÓĖøÓ╣ćÓĖÖÓĖŁÓĖćÓĖ©ÓĖ▓ ÓĖüÓ╣ćÓ╣ĆÓĖŖÓ╣łÓĖÖÓ╣ĆÓĖöÓĖĄÓĖóÓĖ¦ÓĖüÓĖ▒ÓĖÖ ’ü▒’ĆŁo 180 ÓĖŁÓĖóÓĖ╣Ó╣ł ÓĖäÓĖ¦ÓĖŁÓĖöÓĖŻÓĖ▒ÓĖÖÓĖĢÓ╣ī 2 ÓĖŁÓĖóÓĖ╣Ó╣ł ÓĖäÓĖ¦ÓĖŁÓĖöÓĖŻÓĖ▒ÓĖÖÓĖĢÓ╣ī 3 ÓĖŁÓĖóÓĖ╣Ó╣ł ÓĖäÓĖ¦ÓĖŁÓĖöÓĖŻÓĖ▒ÓĖÖÓĖĢÓ╣ī 4 ÓĖŁÓĖóÓĖ╣Ó╣ł ÓĖäÓĖ¦ÓĖŁÓĖöÓĖŻÓĖ▒ÓĖÖÓĖĢÓ╣ī 4’ü▒’Ć½o 180 ’ü▒’ĆŁo 360 ’ü▒’ĆŁ ’ü▒’ĆĮ’ü▒’ĆŁ sin)180sin( o ’ü▒’ĆŁ’ĆĮ’ü▒’Ć½ sin)180sin( o ’ü▒’ĆŁ’ĆĮ’ü▒’ĆŁ sin)360sin( o ’ü▒’ĆŁ’ĆĮ’ü▒’ĆŁ sin)sin( ’ü▒’ĆŁ’ĆĮ’ü▒’ĆŁ cos)180cos( o ’ü▒’ĆŁ’ĆĮ’ü▒’Ć½ cos)180cos( o ’ü▒’ĆĮ’ü▒’ĆŁ cos)360cos( o ’ü▒’ĆĮ’ü▒’ĆŁ cos)cos( ’ü▒’ĆŁ’ĆĮ’ü▒’ĆŁ tan)180tan( o ’ü▒’ĆŁ’ĆĮ’ü▒’Ć½ tan)180tan( o ’ü▒’ĆŁ’ĆĮ’ü▒’ĆŁ tan)360tan( o ’ü▒’ĆŁ’ĆĮ’ü▒’ĆŁ tan)tan( Ó╣āÓĖÖÓĖŚÓ╣ŹÓĖ▓ÓĖÖÓĖŁÓĖćÓ╣ĆÓĖöÓĖĄÓĖóÓĖ¦ÓĖüÓĖ▒ÓĖÖÓĖ¢Ó╣ēÓĖ▓ Ó╣üÓĖźÓĖ░Ó╣ĆÓĖøÓ╣ćÓĖÖÓĖ¤ÓĖ▒ÓĖćÓĖüÓ╣īÓĖŖÓĖ▒ÓĖÖÓĖéÓĖŁÓĖćÓĖĪÓĖĖÓĖĪÓĖŚÓĖĄÓ╣łÓ╣ĆÓĖüÓĖ┤ÓĖÖÓĖŻÓĖŁÓĖÜIn ’āÄ ’ü▒’ĆŁ’ĆĮ’ü▒’ĆŁ’ü░ sin)n2sin( ’ü▒’ĆĮ’ü▒’Ć½’ü░ sin)n2sin( ’ü▒’ĆĮ’ü▒’ĆŁ’ü░ cos)n2cos( ’ü▒’ĆĮ’ü▒’Ć½’ü░ cos)n2cos( ’ü▒’ĆŁ’ĆĮ’ü▒’ĆŁ’ü░ tan)n2tan( ’ü▒’ĆŁ’ĆĮ’ü▒’Ć½’ü░ tan)n2tan( ÓĖ½ÓĖĪÓĖ▓ÓĖóÓ╣ĆÓĖ½ÓĖĢÓĖĖ ÓĖ¬ÓĖ╣ÓĖĢÓĖŻÓ╣ĆÓĖ½ÓĖźÓ╣łÓĖ▓ÓĖÖÓĖĄÓ╣ēÓ╣āÓĖŖÓ╣ēÓ╣äÓĖöÓ╣ēÓĖüÓĖ▒ÓĖÜ ÓĖŚÓĖĖÓĖüÓĖéÓĖÖÓĖ▓ÓĖöÓĖéÓĖŁÓĖćÓĖĪÓĖĖÓĖĪÓĖ½ÓĖŻÓĖĘÓĖŁÓĖłÓ╣ŹÓĖ▓ÓĖÖÓĖ¦ÓĖÖÓĖłÓĖŻÓĖ┤ÓĖćÓ╣āÓĖö Ó╣å’ü▒ ÓĖüÓĖ▓ÓĖŻÓĖ½ÓĖ▓ÓĖäÓ╣łÓĖ▓ÓĖéÓĖŁÓĖćÓĖ¤ÓĖ▒ÓĖćÓĖüÓ╣īÓĖŖÓĖ▒ÓĖÖÓĖĢÓĖŻÓĖĄÓ╣éÓĖüÓĖōÓĖéÓĖŁÓĖćÓĖĪÓĖĖÓĖĪÓĖøÓĖŻÓĖ░ÓĖüÓĖŁÓĖÜÓĖŚÓĖĄÓ╣łÓĖäÓ╣łÓĖ▓ÓĖéÓĖŁÓĖćÓĖ¤ÓĖ▒ÓĖćÓĖüÓ╣īÓĖŖÓĖ▒ÓĖÖÓĖĢÓ╣ēÓĖŁÓĖćÓ╣ĆÓĖøÓĖźÓĖĄÓ╣łÓĖóÓĖÖÓ╣üÓĖøÓĖźÓĖćÓĖ¤ÓĖ▒ÓĖćÓĖüÓ╣īÓĖŖÓĖ▒ÓĖÖ (co-function) ’ü▒’ĆŁ ’ü░ 2 3 ’ü▒’Ć½ ’ü░ 2 3 ’ü▒’ĆŁ ’ü░ 2 ’ü▒’Ć½ ’ü░ 2 ÓĖŁÓĖóÓĖ╣Ó╣ł ÓĖäÓĖ¦ÓĖŁÓĖöÓĖŻÓĖ▒ÓĖÖÓĖĢÓ╣ī 1 ÓĖŁÓĖóÓĖ╣Ó╣ł ÓĖäÓĖ¦ÓĖŁÓĖöÓĖŻÓĖ▒ÓĖÖÓĖĢÓ╣ī 2 ÓĖŁÓĖóÓĖ╣Ó╣ł ÓĖäÓĖ¦ÓĖŁÓĖöÓĖŻÓĖ▒ÓĖÖÓĖĢÓ╣ī 3 ÓĖŁÓĖóÓĖ╣Ó╣ł ÓĖäÓĖ¦ÓĖŁÓĖöÓĖŻÓĖ▒ÓĖÖÓĖĢÓ╣ī 4 ’ü▒’ĆĮ’ü▒’ĆŁ ’ü░ cos) 2 sin( ’ü▒’ĆĮ’ü▒’Ć½ ’ü░ cos) 2 sin( ’ü▒’ĆŁ’ĆĮ’ü▒’ĆŁ ’ü░ cos) 2 3 sin( ’ü▒’ĆŁ’ĆĮ’ü▒’Ć½ ’ü░ cos) 2 3 sin( ’ü▒’ĆĮ’ü▒’ĆŁ ’ü░ sin) 2 cos( ’ü▒’ĆŁ’ĆĮ’ü▒’Ć½ ’ü░ sin) 2 cos( ’ü▒’ĆŁ’ĆĮ’ü▒’ĆŁ ’ü░ sin) 2 3 cos( ’ü▒’ĆĮ’ü▒’Ć½ ’ü░ sin) 2 3 cos( ’ü▒’ĆĮ’ü▒’ĆŁ ’ü░ cot) 2 tan( ’ü▒’ĆŁ’ĆĮ’ü▒’Ć½ ’ü░ cot) 2 tan( ’ü▒’ĆĮ’ü▒’ĆŁ ’ü░ cot) 2 3 tan( ’ü▒’ĆŁ’ĆĮ’ü▒’Ć½ ’ü░ cot) 2 3 tan( ÓĖüÓĖŻÓĖōÓĖĄÓĖŚÓĖĄÓ╣łÓĖĪÓĖĖÓĖĪÓ╣ĆÓĖøÓ╣ćÓĖÖÓĖŁÓĖćÓĖ©ÓĖ▓ ÓĖüÓ╣ćÓ╣ĆÓĖŖÓ╣łÓĖÖÓ╣ĆÓĖöÓĖĄÓĖóÓĖ¦ÓĖüÓĖ▒ÓĖÖ ’ü▒’ĆŁo 90 ÓĖŁÓĖóÓĖ╣Ó╣ł ÓĖäÓĖ¦ÓĖŁÓĖöÓĖŻÓĖ▒ÓĖÖÓĖĢÓ╣ī 1 ÓĖŁÓĖóÓĖ╣Ó╣ł ÓĖäÓĖ¦ÓĖŁÓĖöÓĖŻÓĖ▒ÓĖÖÓĖĢÓ╣ī 2 ÓĖŁÓĖóÓĖ╣Ó╣łÓĖäÓĖ¦ÓĖŁÓĖöÓĖŻÓĖ▒ÓĖÖÓĖĢÓ╣ī 3 ÓĖŁÓĖóÓĖ╣Ó╣łÓĖäÓĖ¦ÓĖŁÓĖöÓĖŻÓĖ▒ÓĖÖÓĖĢÓ╣ī 4’ü▒’Ć½o 90 ’ü▒’ĆŁo 270 ’ü▒’Ć½o 270 ’ü▒’ĆĮ’ü▒’ĆŁ cos)90sin( o ’ü▒’ĆĮ’ü▒’Ć½ cos)90sin( o ’ü▒’ĆŁ’ĆĮ’ü▒’ĆŁ cos)270sin( o ’ü▒’ĆŁ’ĆĮ’ü▒’Ć½ cos)270sin( o ’ü▒’ĆĮ’ü▒’ĆŁ sin)90cos( o ’ü▒’ĆŁ’ĆĮ’ü▒’Ć½ sin)90cos( o ’ü▒’ĆŁ’ĆĮ’ü▒’ĆŁ sin)270cos( o ’ü▒’ĆĮ’ü▒’Ć½ sin)270cos( o ’ü▒’ĆĮ’ü▒’ĆŁ cot)90tan( o ’ü▒’ĆŁ’ĆĮ’ü▒’Ć½ cot)90tan( o ’ü▒’ĆĮ’ü▒’ĆŁ cot)270tan( o ’ü▒’ĆŁ’ĆĮ’ü▒’Ć½ cot)270tan( o 22 ba ’Ć½’é▒5. ÓĖäÓ╣łÓĖ▓ÓĖ¬ÓĖ╣ÓĖćÓĖ¬ÓĖĖÓĖöÓ╣üÓĖźÓĖ░ÓĖĢÓ╣ŹÓ╣łÓĖ▓ÓĖ¬ÓĖĖÓĖöÓĖéÓĖŁÓĖć ÓĖäÓĖĘÓĖŁ’ü▒’Ć½’ü▒ cosbsina
- 3. 6. Ó╣ĆÓĖŁÓĖüÓĖźÓĖ▒ÓĖüÓĖ®ÓĖōÓ╣īÓĖ×ÓĖĘÓ╣ēÓĖÖÓĖÉÓĖ▓ÓĖÖÓĖŚÓĖĄÓ╣łÓĖäÓĖ¦ÓĖŻÓĖŚÓĖŻÓĖ▓ÓĖÜ ÓĖüÓ╣ŹÓĖ▓ÓĖ½ÓĖÖÓĖöÓ╣āÓĖ½Ó╣ē Ó╣ĆÓĖøÓ╣ćÓĖÖ ÓĖĪÓĖĖÓĖĪ , ÓĖäÓĖ¦ÓĖ▓ÓĖĪÓĖóÓĖ▓ÓĖ¦ÓĖ¬Ó╣łÓĖ¦ÓĖÖÓ╣éÓĖäÓ╣ēÓĖć ÓĖ½ÓĖŻÓĖĘÓĖŁ ÓĖłÓ╣ŹÓĖ▓ÓĖÖÓĖ¦ÓĖÖÓĖłÓĖŻÓĖ┤ÓĖćÓ╣āÓĖö Ó╣å’ü▒ 1cossin 22 ’ĆĮ’ü▒’Ć½’ü▒ ’ü▒’ĆŁ’é▒’ĆĮ’ü▒’é« 2 cos1sin ÓĖłÓĖ░Ó╣ĆÓĖźÓĖĘÓĖŁÓĖü + ÓĖ½ÓĖŻÓĖĘÓĖŁ ŌĆō ÓĖĢÓ╣ēÓĖŁÓĖćÓĖéÓĖČÓ╣ēÓĖÖÓĖŁÓĖóÓĖ╣Ó╣łÓĖüÓĖ▒ÓĖÜ ’ü▒ ’ü▒’ĆŁ’é▒’ĆĮ’ü▒’é« 2 sin1cos ÓĖłÓĖ░Ó╣ĆÓĖźÓĖĘÓĖŁÓĖü + ÓĖ½ÓĖŻÓĖĘÓĖŁ ŌĆō ÓĖĢÓ╣ēÓĖŁÓĖćÓĖéÓĖČÓ╣ēÓĖÖÓĖŁÓĖóÓĖ╣Ó╣łÓĖüÓĖ▒ÓĖÜ ’ü▒ Ó╣üÓĖźÓĖ░’ü▒’ĆĮ’ü▒’Ć½ 22 eccoscot1 ’ü▒’ĆĮ’ü▒’Ć½ 22 sectan1 ÓĖüÓĖŻÓĖ▓ÓĖ¤ÓĖéÓĖŁÓĖćÓĖ¤ÓĖ▒ÓĖćÓĖüÓ╣īÓĖŖÓĖ▒ÓĖÖÓĖĢÓĖŻÓĖĄÓ╣éÓĖüÓĖōÓĖĪÓĖ┤ÓĖĢÓĖ┤ ÓĖ¤ÓĖ▒ÓĖćÓĖüÓ╣īÓĖŖÓĖ▒ÓĖÖ ÓĖüÓĖŻÓĖ▓ÓĖ¤ Ó╣éÓĖöÓ╣ĆÓĖĪÓĖÖ Ó╣ĆÓĖŻÓĖÖÓĖłÓ╣ī ÓĖäÓĖ▓ÓĖÜ Ó╣üÓĖŁÓĖĪÓĖ×ÓĖźÓĖ┤ÓĖłÓĖ╣ÓĖö xsiny ’ĆĮ R ]1,1[’ĆŁ ’ü░2 xcosy ’ĆĮ R ]1,1[’ĆŁ ’ü░2 xtany ’ĆĮ ’ā»’āŠ ’ā» ’āĮ ’ā╝ ’ā»’ā« ’ā» ’āŁ ’ā¼ ’ü░’āĘ ’āĖ ’āČ ’ā¦ ’ā© ’ā” ’Ć½ ’é╣ 2 1n2 xx In ’āÄ R ’ü░ xcoty ’ĆĮ ’ü╗ ’üĮ’ü░’é╣ nxx In ’āÄ R ’ü░ xsecy ’ĆĮ ’ā»’āŠ ’ā» ’āĮ ’ā╝ ’ā»’ā« ’ā» ’āŁ ’ā¼ ’ü░’āĘ ’āĖ ’āČ ’ā¦ ’ā© ’ā” ’Ć½ ’é╣ 2 1n2 xx In ’āÄ ),1[]1,( ’éź’āł’ĆŁ’ĆŁ’éź ’ü░2 ecxcosy ’ĆĮ ’ü╗ ’üĮ’ü░’é╣ nxx In ’āÄ ),1[]1,( ’éź’āł’ĆŁ’ĆŁ’éź ’ü░2
- 4. ÓĖ¬ÓĖ╣ÓĖĢÓĖŻÓĖ¤ÓĖ▒ÓĖćÓĖüÓ╣īÓĖŖÓĖ▒ÓĖÖÓĖĢÓĖŻÓĖĄÓ╣éÓĖüÓĖōÓĖĪÓĖ┤ÓĖĢÓĖ┤ÓĖéÓĖŁÓĖćÓĖ£ÓĖźÓĖÜÓĖ¦ÓĖüÓ╣üÓĖźÓĖ░ÓĖ£ÓĖźÓĖĢÓ╣łÓĖ▓ÓĖćÓĖéÓĖŁÓĖćÓĖĪÓĖĖÓĖĪÓĖ½ÓĖŻÓĖĘÓĖŁÓĖłÓ╣ŹÓĖ▓ÓĖÖÓĖ¦ÓĖÖÓĖłÓĖŻÓĖ┤ÓĖć )BAsin( ’Ć½ ’ĆĮ BsinAcosBcosAsin ’āŚ’Ć½’āŚ )BAsin( ’ĆŁ ’ĆĮ BsinAcosBcosAsin ’āŚ’ĆŁ’āŚ )BAcos( ’Ć½ ’ĆĮ BsinAsinBcosAcos ’āŚ’ĆŁ’āŚ )BAcos( ’ĆŁ ’ĆĮ BsinAsinBcosAcos ’āŚ’Ć½’āŚ )BAtan( ’Ć½ ’ĆĮ BtanAtan1 BtanAtan ’āŚ’ĆŁ ’Ć½ )BAtan( ’ĆŁ ’ĆĮ BtanAtan1 BtanAtan ’āŚ’Ć½ ’ĆŁ )BAcot( ’Ć½ ’ĆĮ AcotBcot 1BcotAcot ’Ć½ ’ĆŁ’āŚ )BAcot( ’ĆŁ ’ĆĮ AcotBcot 1BcotAcot ’ĆŁ ’Ć½’āŚ ÓĖ¬ÓĖ╣ÓĖĢÓĖŻÓĖ¤ÓĖ▒ÓĖćÓĖüÓ╣īÓĖŖÓĖ▒ÓĖÖÓĖĢÓĖŻÓĖĄÓ╣éÓĖüÓĖōÓĖĪÓĖ┤ÓĖĢÓĖ┤ÓĖéÓĖŁÓĖćÓĖĪÓĖĖÓĖĪ 2 Ó╣ĆÓĖŚÓ╣łÓĖ▓ 2 A cos 2 A sin2 ’āŚA2sin ÓĖ½ÓĖŻÓĖĘÓĖŁ’ĆĮ AcosAsin2 ’āŚ Asin ’ĆĮ 2 A sin 2 A cos 22 ’ĆŁA2cos ÓĖ½ÓĖŻÓĖĘÓĖŁ’ĆĮ AsinAcos 22 ’ĆŁ Acos ’ĆĮ 1 2 A cos2 2 ’ĆŁÓĖ½ÓĖŻÓĖĘÓĖŁ’ĆĮ 1Acos2 2 ’ĆŁ Acos ’ĆĮ 2 A sin21 2 ’ĆŁ’ĆĮ Asin21 2 ’ĆŁ ÓĖ½ÓĖŻÓĖĘÓĖŁ Acos ’ĆĮ 2 A tan1 2 A tan2 2 ’ĆŁ A2tan ’ĆĮ Atan1 2 ’ĆŁ Atan2 AtanÓĖ½ÓĖŻÓĖĘÓĖŁ ’ĆĮ A2cot ’ĆĮ Acot2 1Acot2 ’ĆŁ Atan1 Atan2 2 ’ĆŁ Atan1 Atan2 2 ’Ć½ Ó╣ĆÓĖÖÓĖĘÓ╣łÓĖŁÓĖćÓĖłÓĖ▓ÓĖü Ó╣ĆÓĖŻÓĖ▓ÓĖ¬ÓĖ▓ÓĖĪÓĖ▓ÓĖŻÓĖ¢ÓĖ½ÓĖ▓A2tan ’ĆĮ A2sin ’ĆĮ ’ĆĮ Atan1 Atan1 2 2 ’Ć½ ’ĆŁ A2cos ÓĖ¬ÓĖ╣ÓĖĢÓĖŻÓĖ¤ÓĖ▒ÓĖćÓĖüÓ╣īÓĖŖÓĖ▒ÓĖÖÓĖĢÓĖŻÓĖĄÓ╣éÓĖüÓĖōÓĖĪÓĖ┤ÓĖĢÓĖ┤ÓĖéÓĖŁÓĖćÓĖĪÓĖĖÓĖĪ 3 Ó╣ĆÓĖŚÓ╣łÓĖ▓ ’ĆĮA3sin Asin4Asin3 3 ’ĆŁ A3cos ’ĆĮ Acos3Acos4 3 ’ĆŁ A3tan ’ĆĮ Atan31 AtanAtan3 2 3 ’ĆŁ ’ĆŁ A3cot ’ĆĮ 1cot3 Acot3Acot 2 3 ’ĆŁ ’ĆŁ ÓĖ¬ÓĖ╣ÓĖĢÓĖŻÓĖ¤ÓĖ▒ÓĖćÓĖüÓ╣īÓĖŖÓĖ▒ÓĖÖÓĖĢÓĖŻÓĖĄÓ╣éÓĖüÓĖōÓĖĪÓĖ┤ÓĖĢÓĖ┤ÓĖéÓĖŁÓĖćÓĖĪÓĖĖÓĖĪÓĖäÓĖŻÓĖČÓ╣łÓĖć 2 A2cos1’ĆŁ ’é▒Asin2 ’ĆĮ 2 A2cos1’ĆŁ ÓĖ½ÓĖŻÓĖĘÓĖŁ Asin ’ĆĮ 2 A2cos1’Ć½ ’é▒’ĆĮAcos2 2 A2cos1’Ć½ ÓĖ½ÓĖŻÓĖĘÓĖŁ Acos ’ĆĮ
- 5. A2cos1 A2cos1 ’Ć½ ’ĆŁ ’é▒’ĆĮAtan2 A2cos1 A2cos1 ’Ć½ ’ĆŁ ÓĖ½ÓĖŻÓĖĘÓĖŁ Atan ’ĆĮ ÓĖäÓ╣łÓĖ▓ÓĖéÓĖŁÓĖćÓĖ¤ÓĖ▒ÓĖćÓĖüÓ╣īÓĖŖÓĖ▒ÓĖÖÓĖéÓĖŁÓĖćÓĖĪÓĖĖÓĖĪÓĖÜÓĖ▓ÓĖćÓĖĪÓĖĖÓĖĪÓĖŚÓĖĄÓ╣łÓĖäÓĖ¦ÓĖŻÓĖŚÓĖŻÓĖ▓ÓĖÜ o ’ĆĮ o ’ĆĮ15sin 75cos 4 26 22 13 ’ĆŁ ’ĆĮ ’ĆŁ ’ĆĮo o ’ĆĮ75sin 15cos 4 26 22 13 ’Ć½ ’ĆĮ ’Ć½ ’ĆĮo o ’ĆĮ15tan 75cot 13 13 ’Ć½ ’ĆŁ o ’ĆĮ o ’ĆĮ75tan 15cot 13 13 ’ĆŁ ’Ć½ o 18sin ’ĆĮ ’ĆĮo 72cos 4 15 ’ĆŁ ’ĆĮo 18cos o 72sin ’ĆĮ 4 5210 ’Ć½ o 36cos ’ĆĮ ’ĆĮo 54sin 4 15 ’Ć½ ’ĆĮo o ’ĆĮ36sin 54cos 4 5210 ’ĆŁ o ’ĆĮ o ’ĆĮ5.22sin 5.67cos 2 22 ’ĆŁ ’ĆĮo o ’ĆĮ5.22cos 5.67sin 2 22 ’Ć½ ÓĖ¬ÓĖ╣ÓĖĢÓĖŻÓĖüÓĖ▓ÓĖŻÓ╣ĆÓĖøÓĖźÓĖĄÓ╣łÓĖóÓĖÖÓĖ£ÓĖźÓĖäÓĖ╣ÓĖōÓĖéÓĖŁÓĖćÓĖ¤ÓĖ▒ÓĖćÓĖüÓ╣īÓĖŖÓĖ▒ÓĖÖÓ╣ĆÓĖøÓ╣ćÓĖÖÓĖ£ÓĖźÓĖÜÓĖ¦ÓĖüÓĖ½ÓĖŻÓĖĘÓĖŁÓĖ£ÓĖźÓĖĢÓ╣łÓĖ▓ÓĖćÓĖéÓĖŁÓĖćÓĖ¤ÓĖ▒ÓĖćÓĖüÓ╣īÓĖŖÓĖ▒ÓĖÖ BcosAsin2 ’āŚ ’ĆĮ )BAsin()BAsin( ’ĆŁ’Ć½’Ć½ ÓĖ½ÓĖŻÓĖĘÓĖŁ cossin2 ’āŚ )diffsin()sumsin( ’Ć½’ĆĮ BsinAcos2 ’āŚ ’ĆĮ )BAsin()BAsin( ’ĆŁ’ĆŁ’Ć½ ÓĖ½ÓĖŻÓĖĘÓĖŁ )diffsin()sumsin( ’ĆŁsincos2 ’āŚ ’ĆĮ BcosAcos2 ’āŚ ’ĆĮ )BAcos()BAcos( ’ĆŁ’Ć½’Ć½ ÓĖ½ÓĖŻÓĖĘÓĖŁ coscos2 ’āŚ )diffcos()sumcos( ’Ć½’ĆĮ BsinAsin2 ’āŚ ’ĆĮ )BAcos()BAcos( ’Ć½’ĆŁ’ĆŁ ÓĖ½ÓĖŻÓĖĘÓĖŁ sinsin2 ’āŚ )sumcos()diffcos( ’ĆŁ’ĆĮ ÓĖ¬ÓĖ╣ÓĖĢÓĖŻÓĖüÓĖ▓ÓĖŻÓ╣ĆÓĖøÓĖźÓĖĄÓ╣łÓĖóÓĖÖÓĖ£ÓĖźÓĖÜÓĖ¦ÓĖüÓĖ½ÓĖŻÓĖĘÓĖŁÓĖ£ÓĖźÓĖĢÓ╣łÓĖ▓ÓĖćÓĖéÓĖŁÓĖćÓĖ¤ÓĖ▒ÓĖćÓĖüÓ╣īÓĖŖÓĖ▒ÓĖÖÓ╣ĆÓĖøÓ╣ćÓĖÖÓĖ£ÓĖźÓĖäÓĖ╣ÓĖōÓĖéÓĖŁÓĖćÓĖ¤ÓĖ▒ÓĖćÓĖüÓ╣īÓĖŖÓĖ▒ÓĖÖ ’ĆĮ ’āĘ ’āĖ ’āČ ’ā¦ ’ā© ’ā” ’ĆŁ ’āŚ’āĘ ’āĖ ’āČ ’ā¦ ’ā© ’ā” ’Ć½ 2 BA cos 2 BA sin2BsinAsin ’Ć½ ’ĆĮ ’āĘ ’āĖ ’āČ ’ā¦ ’ā© ’ā” ’ĆŁ ’āŚ’āĘ ’āĖ ’āČ ’ā¦ ’ā© ’ā” ’Ć½ 2 BA sin 2 BA cos2BsinAsin ’ĆŁ ’ĆĮ ’āĘ ’āĖ ’āČ ’ā¦ ’ā© ’ā” ’ĆŁ ’āŚ’āĘ ’āĖ ’āČ ’ā¦ ’ā© ’ā” ’Ć½ 2 BA cos 2 BA cos2BcosAcos ’Ć½ BcosAcos ’ĆŁ ’ĆĮ ’āĘ ’āĖ ’āČ ’ā¦ ’ā© ’ā” ’ĆŁ ’āŚ’āĘ ’āĖ ’āČ ’ā¦ ’ā© ’ā” ’Ć½ 2 AB sin 2 BA sin2 ’āĘ ’āĖ ’āČ ’ā¦ ’ā© ’ā” ’ĆŁ ’āŚ’āĘ ’āĖ ’āČ ’ā¦ ’ā© ’ā” ’Ć½ ’ĆŁ 2 BA sin 2 BA sin2ÓĖ½ÓĖŻÓĖĘÓĖŁ’ĆĮ ooo 80sin40sin20sin ’āŚ’āŚ ’ĆĮ 8 3 ÓĖ½ÓĖŻÓĖĘÓĖŁ ’ĆĮ 16 3oooo 80sin60sin40sin20sin ’āŚ’āŚ’āŚ ooo 80cos40cos20cos ’āŚ’āŚ ’ĆĮ 8 1 ÓĖ½ÓĖŻÓĖĘÓĖŁ ’ĆĮ 16 1oooo 80cos60cos40cos20cos ’āŚ’āŚ’āŚ
- 6. ÓĖŁÓĖ┤ÓĖÖÓ╣ĆÓĖ¦ÓĖŁÓĖŻÓ╣īÓĖ¬ÓĖéÓĖŁÓĖćÓĖ¤ÓĖ▒ÓĖćÓĖüÓ╣īÓĖŖÓĖ▒ÓĖÖÓĖĢÓĖŻÓĖĄÓ╣éÓĖüÓĖōÓĖĪÓĖ┤ÓĖĢÓĖ┤ ÓĖ¤ÓĖ▒ÓĖćÓĖüÓ╣īÓĖŖÓĖ▒ÓĖÖÓĖĢÓĖŻÓĖĄÓ╣éÓĖüÓĖōÓĖĪÓĖ┤ÓĖĢÓĖ┤ ÓĖŁÓĖ┤ÓĖÖÓ╣ĆÓĖ¦ÓĖŁÓĖŻÓ╣īÓĖ¬ÓĖéÓĖŁÓĖćÓĖ¤ÓĖ▒ÓĖćÓĖüÓ╣īÓĖŖÓĖ▒ÓĖÖ ÓĖ¤ÓĖ▒ÓĖćÓĖüÓ╣īÓĖŖÓĖ▒ÓĖÖÓĖŁÓĖ┤ÓĖÖÓ╣ĆÓĖ¦ÓĖŁÓĖŻÓ╣īÓĖ¬ Ó╣éÓĖöÓ╣ĆÓĖĪÓĖÖÓĖéÓĖŁÓĖć Ó╣ĆÓĖŻÓĖłÓĖÖÓ╣īÓĖéÓĖŁÓĖć ÓĖ¤ÓĖ▒ÓĖćÓĖüÓ╣īÓĖŖÓĖ▒ÓĖÖÓĖŁÓĖ┤ÓĖÖÓ╣ĆÓĖ¦ÓĖŁÓĖŻÓ╣īÓĖ¬ ÓĖ¤ÓĖ▒ÓĖćÓĖüÓ╣īÓĖŖÓĖ▒ÓĖÖÓĖŁÓĖ┤ÓĖÖÓ╣ĆÓĖ¦ÓĖŁÓĖŻÓ╣īÓĖ¬ xsiny ’ĆĮ ysinx ’ĆĮ xarcsiny ’ĆĮ ÓĖ½ÓĖŻÓĖĘÓĖŁ xsiny 1’ĆŁ ’ĆĮ ]1,1[’ĆŁ ’ā║ ’ā╗ ’ā╣ ’ā¬ ’ā½ ’ā® ’ü░’ü░ ’ĆŁ 2 , 2 xcosy ’ĆĮ ycosx ’ĆĮ xarccosy ’ĆĮ ÓĖ½ÓĖŻÓĖĘÓĖŁ xcosy 1’ĆŁ ’ĆĮ ]1,1[’ĆŁ ’üø ’üØ’ü░,0 xtany ’ĆĮ ytanx ’ĆĮ xarctany ’ĆĮ ÓĖ¬ÓĖ╣ÓĖĢÓĖŻÓĖäÓĖ¦ÓĖ▓ÓĖĪÓĖ¬ÓĖ▒ÓĖĪÓĖ×ÓĖ▒ÓĖÖÓĖśÓ╣īÓĖéÓĖŁÓĖćÓĖ¤ÓĖ▒ÓĖćÓĖüÓ╣īÓĖŖÓĖ▒ÓĖÖÓĖŁÓĖ┤ÓĖÖÓ╣ĆÓĖ¦ÓĖŁÓĖŻÓ╣īÓĖ¬ÓĖĢÓĖŻÓĖĄÓ╣éÓĖüÓĖōÓĖĪÓĖ┤ÓĖĢÓĖ┤ 1. )xarcsin(’ĆŁ ’ĆĮ xarcsin’ĆŁ ’é½ ’üø ’üØ1,1x ’ĆŁ’āÄ 2. )xarccos(’ĆŁ ’ĆĮ xarccos’ĆŁ’ü░ ’é½ ’üø ’üØ1,1x ’ĆŁ’āÄ 3. )xarctan(’ĆŁ ’ĆĮ xarctan’ĆŁ ’é½ Rx ’āÄ 4. ’ĆĮ)xsin(arcsin x ’é½ ’üø ’üØ1,1x ’ĆŁ’āÄ Ó╣üÓĖźÓĖ░ ’ĆĮ)xarcsin(sin x ’é½ ’ā║ ’ā╗ ’ā╣ ’ā¬ ’ā½ ’ā® ’ü░’ü░ ’ĆŁ’āÄ 2 , 2 x ÓĖöÓĖ▒ÓĖćÓĖÖÓĖ▒Ó╣ēÓĖÖ ’ĆĮ)xsin(arcsin )xarcsin(sin ’é½ ’üø ’üØ1,1x ’ĆŁ’āÄ 5. ’ĆĮ)xcos(arccos x ’é½ ’üø ’üØ1,1x ’ĆŁ’āÄ Ó╣üÓĖźÓĖ░ ’ĆĮ)xarccos(cos x ’é½ ’üø ’üØ’ü░’āÄ ,0x ÓĖöÓĖ▒ÓĖćÓĖÖÓĖ▒Ó╣ēÓĖÖ ’ĆĮ)xcos(arccos )xarccos(cos ’é½ ’üø ’üØ1,1x ’ĆŁ’āÄ 6. )xtan(arctan ’ĆĮ x ’é½ Rx ’āÄ Ó╣üÓĖźÓĖ░ )xarctan(tan ’ĆĮ x ’é½ ’āĘ ’āĖ ’āČ ’ā¦ ’ā© ’ā” ’ü░’ü░ ’ĆŁ’āÄ 2 , 2 x ÓĖöÓĖ▒ÓĖćÓĖÖÓĖ▒Ó╣ēÓĖÖ )xtan(arctan ’ĆĮ )xarctan(tan ’é½ ’āĘ ’āĖ ’āČ ’ā¦ ’ā© ’ā” ’ü░’ü░ ’ĆŁ’āÄ 2 , 2 x ÓĖ½ÓĖŻÓĖĘÓĖŁ xtany 1’ĆŁ ’ĆĮ R ’āĘ ’āĖ ’āČ ’ā¦ ’ā© ’ā” ’ü░’ü░ ’ĆŁ 2 , 2 ÓĖ½ÓĖŻÓĖĘÓĖŁxcoty ’ĆĮ ycotx ’ĆĮ xcotarcy ’ĆĮ xcoty 1’ĆŁ ’ĆĮ R ),0( ’ü░ xsecy ’ĆĮ ysecx ’ĆĮ xsecarcy ’ĆĮ ÓĖ½ÓĖŻÓĖĘÓĖŁ xsecy 1’ĆŁ ’ĆĮ )1,1(R ’ĆŁ’ĆŁ ’üø ’üØ ’āŠ ’āĮ ’ā╝ ’ā« ’āŁ ’ā¼’ü░ ’ĆŁ’ü░ 2 ,0 xcscy ’ĆĮ ycscx ’ĆĮ xcscarcy ’ĆĮ ÓĖ½ÓĖŻÓĖĘÓĖŁ xcscy 1’ĆŁ ’ĆĮ )1,1(R ’ĆŁ’ĆŁ ’ü╗ ’üĮ0 2 , 2 ’ĆŁ’ā║ ’ā╗ ’ā╣ ’ā¬ ’ā½ ’ā® ’ü░’ü░ ’ĆŁ
- 7. 7. ’ĆĮ)xcotarccot( x ’é½ Rx ’āÄ Ó╣üÓĖźÓĖ░ ’ĆĮ)xcot(cotarc x ’é½ ),0(x ’ü░’āÄ ÓĖöÓĖ▒ÓĖćÓĖÖÓĖ▒Ó╣ēÓĖÖ ’ĆĮ)xcotarccot( )xcot(cotarc ’é½ ),0(x ’ü░’āÄ 8. ’ĆĮ)xsecarcsec( x ’é½ )1,1(Rx ’ĆŁ’ĆŁ’āÄ Ó╣üÓĖźÓĖ░ ’ĆĮ)xsec(secarc x ’é½ ’üø ’üØ ’āŠ ’āĮ ’ā╝ ’ā« ’āŁ ’ā¼’ü░ ’ĆŁ’ü░’āÄ 2 ,0x ÓĖöÓĖ▒ÓĖćÓĖÖÓĖ▒Ó╣ēÓĖÖ ’é½ ’üø ’üØ ’āŠ ’āĮ ’ā╝ ’ā« ’āŁ ’ā¼’ü░ ’ĆŁ’ü░’āÄ 2 ,0x’ĆĮ)xsecarcsec( )xsec(secarc 9. ’ĆĮ)xcscarccsc( x ’é½ )1,1(Rx ’ĆŁ’ĆŁ’āÄ Ó╣üÓĖźÓĖ░ ’ĆĮ)xcsc(cscarc x ’é½ ’ü╗ ’üĮ0 2 , 2 x ’ĆŁ’ā║ ’ā╗ ’ā╣ ’ā¬ ’ā½ ’ā® ’ü░’ü░ ’ĆŁ’āÄ ÓĖöÓĖ▒ÓĖćÓĖÖÓĖ▒Ó╣ēÓĖÖ ’ĆĮ)xsecarcsec( )xsec(secarc ’é½ )1,1(Rx ’ĆŁ’ĆŁ’āÄ 10. yarctanxarctan ’Ć½ ’ĆĮ xy1 yx arctan ’ĆŁ ’Ć½ ’é½ 2 yarctanxarctan 2 ’ü░ ’Ć╝’Ć½’Ć╝ ’ü░ ’ĆŁ yarctanxarctan ’ĆŁ ’ĆĮ xy1 yx arctan ’Ć½ ’ĆŁ ’é½ 2 yarctanxarctan 2 ’ü░ ’Ć╝’Ć½’Ć╝ ’ü░ ’ĆŁ yarctanxarctan ’Ć½ ’ĆĮ xy1 yx arctan ’ĆŁ ’Ć½ ’Ć½’ü░ ’é½ 2 yarctanxarctan ’ü░ ’ĆŠ’Ć½ yarctanxarctan ’Ć½ ’ĆĮ xy1 yx arctan ’ĆŁ ’Ć½ ’Ć½’ü░’ĆŁ ’é½ 2 yarctanxarctan ’ü░ ’ĆŁ’Ć╝’Ć½ ’ĆĮ 2 x1 x2 arctan ’ĆŁ 11. xarctan2 12. xarcsin ’ĆĮ 2 x1arccos ’ĆŁ ’ĆĮ 2 x1 x arctan ’ĆŁ ’ĆĮ x x1 cotarc 2 ’ĆŁ ’ĆĮ 2 x1 1 secarc ’ĆŁ ’ĆĮ x 1 cscarc 13. xarccosxarcsin ’Ć½ ’ĆĮ 2 ’ü░ ’é½ ’üø ’üØ1,1x ’ĆŁ’āÄ xcotarcxarctan ’Ć½ ’ĆĮ 2 ’ü░ ’é½ Rx ’āÄ xcscarcxsecarc ’Ć½ ’ĆĮ 2 ’ü░ ’é½ ’Ć© ’Ć®1,1Rx ’ĆŁ’ĆŁ’āÄ ÓĖüÓĖ▓ÓĖŻÓ╣üÓĖüÓ╣ēÓĖ¬ÓĖĪÓĖüÓĖ▓ÓĖŻÓĖĢÓĖŻÓĖĄÓ╣éÓĖüÓĖōÓĖĪÓĖ┤ÓĖĢÓĖ┤ 1. ÓĖ¢Ó╣ēÓĖ▓Ó╣éÓĖłÓĖŚÓĖóÓ╣īÓĖüÓ╣ŹÓĖ▓ÓĖ½ÓĖÖÓĖö Ó╣ĆÓĖŁÓĖüÓĖĀÓĖ×ÓĖ¬ÓĖ▒ÓĖĪÓĖ×ÓĖ▒ÓĖŚÓĖśÓ╣ī ÓĖĢÓ╣ēÓĖŁÓĖćÓĖĢÓĖŁÓĖÜÓ╣āÓĖÖÓĖŻÓĖ╣ÓĖøÓĖéÓĖŁÓĖćÓ╣ĆÓĖŗÓĖĢÓĖłÓ╣ŹÓĖ▓ÓĖüÓĖ▒ÓĖö 2. ÓĖ¢Ó╣ēÓĖ▓Ó╣éÓĖłÓĖŚÓĖóÓ╣īÓ╣äÓĖĪÓ╣łÓĖüÓ╣ŹÓĖ▓ÓĖ½ÓĖÖÓĖö Ó╣ĆÓĖŁÓĖüÓĖĀÓĖ×ÓĖ¬ÓĖ▒ÓĖĪÓĖ×ÓĖ▒ÓĖŚÓĖśÓ╣ī ÓĖĢÓ╣ēÓĖŁÓĖćÓĖĢÓĖŁÓĖÜÓ╣āÓĖÖÓĖŻÓĖ╣ÓĖøÓĖŚÓĖ▒Ó╣łÓĖ¦Ó╣äÓĖø Ó╣üÓĖźÓĖ░ÓĖüÓ╣ŹÓĖ▓ÓĖ½ÓĖÖÓĖöÓ╣āÓĖ½Ó╣ē Ó╣ĆÓĖŁÓĖüÓĖĀÓĖ×ÓĖ¬ÓĖ▒ÓĖĪÓĖ×ÓĖ▒ÓĖŚÓĖśÓ╣ī R’ĆĮ ÓĖöÓĖ▒ÓĖćÓĖÖÓĖĄÓ╣ē 2.1 ÓĖ¢Ó╣ēÓĖ▓ ÓĖäÓ╣ŹÓĖ▓ÓĖĢÓĖŁÓĖÜÓĖéÓĖŁÓĖćÓĖ¬ÓĖĪÓĖüÓĖ▓ÓĖŻ ÓĖäÓĖĘÓĖŁ’ü▒’ĆĮ sinxsin ’ü▒’ĆŁ’Ć½’ü░’ĆĮ n )1(nx 2.2 ÓĖ¢Ó╣ēÓĖ▓ ÓĖäÓ╣ŹÓĖ▓ÓĖĢÓĖŁÓĖÜÓĖéÓĖŁÓĖćÓĖ¬ÓĖĪÓĖüÓĖ▓ÓĖŻ ÓĖäÓĖĘÓĖŁ’ü▒’ĆĮ cosxcos ’ü▒’é▒’ü░’ĆĮ n2x
- 8. 2.3 ÓĖ¢Ó╣ēÓĖ▓ ÓĖäÓ╣ŹÓĖ▓ÓĖĢÓĖŁÓĖÜÓĖéÓĖŁÓĖćÓĖ¬ÓĖĪÓĖüÓĖ▓ÓĖŻ ÓĖäÓĖĘÓĖŁ’ü▒’ĆĮ tanxtan ’ü▒’Ć½’ü░’ĆĮ nx 3. ÓĖ½ÓĖźÓĖ▒ÓĖüÓĖŚÓĖĄÓ╣łÓĖäÓĖ¦ÓĖŻÓĖäÓ╣ŹÓĖ▓ÓĖÖÓĖČÓĖćÓĖ¢ÓĖČÓĖćÓ╣ĆÓĖüÓĖĄÓ╣łÓĖóÓĖ¦ÓĖüÓĖ▒ÓĖÜÓ╣ĆÓĖŻÓĖĘÓ╣łÓĖŁÓĖćÓĖüÓĖ▓ÓĖŻÓ╣üÓĖüÓ╣ēÓĖ¬ÓĖĪÓĖüÓĖ▓ÓĖŻ ÓĖäÓĖĘÓĖŁ 3.1 ÓĖüÓĖ▓ÓĖŻÓ╣üÓĖøÓĖźÓĖćÓĖŚÓĖĖÓĖüÓĖäÓ╣łÓĖ▓ÓĖéÓĖŁÓĖćÓĖĢÓĖ▒ÓĖ¦Ó╣üÓĖøÓĖŻÓ╣āÓĖ½Ó╣ēÓ╣ĆÓĖøÓ╣ćÓĖÖÓĖ¤ÓĖ▒ÓĖćÓĖüÓ╣īÓĖŖÓĖ▒ÓĖÖÓ╣ĆÓĖöÓĖĄÓĖóÓĖ¦ÓĖüÓĖ▒ÓĖÖÓ╣üÓĖźÓĖ░ÓĖĪÓĖĖÓĖĪÓ╣ĆÓĖöÓĖĄÓĖóÓĖ¦ÓĖüÓĖ▒ÓĖÖ 3.2 ÓĖüÓĖ▓ÓĖŻÓ╣üÓĖóÓĖüÓĖĢÓĖ▒ÓĖ¦ÓĖøÓĖŻÓĖ░ÓĖüÓĖŁÓĖÜ ÓĖüÓĖ▓ÓĖŻÓ╣üÓĖüÓ╣ēÓĖŁÓĖ¬ÓĖĪÓĖüÓĖ▓ÓĖŻÓĖĢÓĖŻÓĖĄÓ╣éÓĖüÓĖōÓĖĪÓĖ┤ÓĖĢÓĖ┤ Ó╣āÓĖŖÓ╣ēÓĖ½ÓĖźÓĖ▒ÓĖüÓ╣ĆÓĖ½ÓĖĪÓĖĘÓĖŁÓĖÖÓĖüÓĖ▒ÓĖÜÓĖüÓĖ▓ÓĖŻÓ╣üÓĖüÓ╣ēÓĖ¬ÓĖĪÓĖüÓĖ▓ÓĖŻÓ╣āÓĖÖÓĖŻÓĖ░ÓĖÜÓĖÜÓĖłÓ╣ŹÓĖ▓ÓĖÖÓĖ¦ÓĖÖÓĖłÓĖŻÓĖ┤ÓĖć Ó╣éÓĖöÓĖóÓĖĪÓĖĄÓĖäÓ╣łÓĖ▓ÓĖéÓĖŁÓĖćÓĖ¤ÓĖ▒ÓĖćÓĖüÓ╣īÓĖŖÓĖ▒ÓĖÖÓĖĢÓĖŻÓĖĄÓ╣éÓĖüÓĖōÓĖĪÓĖ┤ÓĖĢÓĖ┤Ó╣ĆÓĖøÓ╣ćÓĖÖÓĖĢÓĖ▒ÓĖ¦Ó╣üÓĖøÓĖŻÓ╣āÓĖö Ó╣å ÓĖüÓĖ▓ÓĖŻÓ╣üÓĖüÓ╣ēÓĖŻÓĖ╣ÓĖøÓĖ¬ÓĖ▓ÓĖĪÓ╣ĆÓĖ½ÓĖźÓĖĄÓ╣łÓĖóÓĖĪ Ó╣āÓĖŖÓ╣ēÓĖ½ÓĖźÓĖ▒ÓĖüÓĖöÓĖ▒ÓĖćÓĖÖÓĖĄÓ╣ēÓĖäÓĖĘÓĖŁ 1. ÓĖ¢Ó╣ēÓĖ▓ÓĖ¬ÓĖ▓ÓĖĪÓ╣ĆÓĖ½ÓĖźÓĖĄÓ╣łÓĖóÓĖĪÓĖöÓĖ▒ÓĖćÓĖüÓĖźÓ╣łÓĖ▓ÓĖ¦ÓĖÖÓĖ▒Ó╣ēÓĖÖÓ╣ĆÓĖøÓ╣ćÓĖÖÓĖ¬ÓĖ▓ÓĖĪÓ╣ĆÓĖ½ÓĖźÓĖĄÓ╣łÓĖóÓĖĪÓĖĪÓĖĖÓĖĪÓĖēÓĖ▓ÓĖüÓ╣āÓĖŖÓ╣ē 1.1 ÓĖŚÓĖżÓĖ®ÓĖÄÓĖĄÓĖÜÓĖŚÓĖ×ÓĖĄÓĖśÓĖ▓ÓĖüÓĖŁÓĖŻÓĖ▒ÓĖ¬ 1.2 ÓĖŁÓĖ▒ÓĖĢÓĖŻÓĖ▓ÓĖ¬Ó╣łÓĖ¦ÓĖÖÓĖĢÓĖŻÓĖĄÓ╣éÓĖüÓĖōÓĖĪÓĖ┤ÓĖĢÓĖ┤ 2. ÓĖ¢Ó╣ēÓĖ▓ÓĖ¬ÓĖ▓ÓĖĪÓ╣ĆÓĖ½ÓĖźÓĖĄÓ╣łÓĖóÓĖĪÓĖÖÓĖ▒Ó╣ēÓĖÖÓ╣ĆÓĖøÓ╣ćÓĖÖÓĖŻÓĖ╣ÓĖøÓĖ¬ÓĖ▓ÓĖĪÓ╣ĆÓĖ½ÓĖźÓĖĄÓ╣łÓĖóÓĖĪÓ╣āÓĖö Ó╣å Ó╣āÓĖŖÓ╣ē Csin c Bsin b Asin a ’ĆĮ’ĆĮ2.1 ÓĖüÓĖÄÓĖéÓĖŁÓĖćÓ╣äÓĖŗÓĖÖÓ╣ī ÓĖäÓĖĘÓĖŁ 2.2 ÓĖüÓĖÄÓĖéÓĖŁÓĖćÓ╣éÓĖäÓ╣äÓĖŗÓĖÖÓ╣ī ÓĖäÓĖĘÓĖŁ bc2 acb AcosAcosbc2cba 222 222 ’ĆŁ’Ć½ ’ĆĮ’é«’ĆŁ’Ć½’ĆĮ ac2 bca BcosBcosac2cab 222 222 ’ĆŁ’Ć½ ’ĆĮ’é«’ĆŁ’Ć½’ĆĮ ab2 cba CcosCcosab2bac 222 222 ’ĆŁ’Ć½ ’ĆĮ’é«’ĆŁ’Ć½’ĆĮ 2.3 ÓĖüÓĖÄÓĖéÓĖŁÓĖćÓ╣éÓĖøÓĖŻÓ╣ĆÓĖłÓĖüÓĖŖÓĖ▒ÓĖÖ BcoscCcosba ’Ć½’ĆĮ AcoscCcosab ’Ć½’ĆĮ AcosbBcosac ’Ć½’ĆĮ ’é┤’ĆĮ 2 1 ÓĖÉÓĖ▓ÓĖÖ ÓĖ¬ÓĖ╣ÓĖć3. ÓĖüÓĖ▓ÓĖŻÓĖ½ÓĖ▓ÓĖ×ÓĖĘÓ╣ēÓĖÖÓĖŚÓĖĄÓ╣łÓĖŻÓĖ╣ÓĖøÓĖ¬ÓĖ▓ÓĖĪÓ╣ĆÓĖ½ÓĖźÓĖĄÓ╣łÓĖóÓĖĪ ’é┤ Csinab 2 1 ’é┤’ĆĮ )cs)(bs)(as(s ’ĆŁ’ĆŁ’ĆŁ’ĆĮ )cba( 2 1 Ó╣éÓĖöÓĖóÓĖŚÓĖĄÓ╣ł s ’Ć½’Ć½’é┤’ĆĮ 4. ÓĖüÓĖ▓ÓĖŻÓĖ½ÓĖ▓ÓĖ×ÓĖĘÓ╣ēÓĖÖÓĖŚÓĖĄÓ╣łÓĖéÓĖŁÓĖćÓĖŻÓĖ╣ÓĖøÓĖ¬ÓĖ▓ÓĖĪÓ╣ĆÓĖ½ÓĖźÓĖĄÓ╣łÓĖóÓĖĪÓĖÉÓĖ▓ÓĖÖÓ╣éÓĖäÓ╣ēÓĖć ’é┤’ĆĮ 2 1 ÓĖÉÓĖ▓ÓĖÖÓ╣éÓĖäÓ╣ēÓĖć ÓĖŻÓĖ▒ÓĖ©ÓĖĪÓĖĄ ÓĖĢÓĖ▓ÓĖŻÓĖ▓ÓĖćÓĖ½ÓĖÖÓ╣łÓĖ¦ÓĖó4.1 Ó╣ĆÓĖĪÓĖĘÓ╣łÓĖŁÓĖŚÓĖŻÓĖ▓ÓĖÜÓĖäÓĖ¦ÓĖ▓ÓĖĪÓĖóÓĖ▓ÓĖ¦ÓĖÉÓĖ▓ÓĖÖÓ╣éÓĖäÓ╣ēÓĖć ’é┤ 1 r 2 ’ĆĮ ’é┤ ’é┤’ü¼ 4..2 Ó╣ĆÓĖĪÓĖĘÓ╣łÓĖŁÓĖŚÓĖŻÓĖ▓ÓĖÜÓĖéÓĖÖÓĖ▓ÓĖöÓĖéÓĖŁÓĖćÓĖĪÓĖĖÓĖĪÓĖŚÓĖĄÓ╣łÓĖłÓĖĖÓĖöÓĖ©ÓĖ╣ÓĖÖÓĖóÓ╣īÓĖüÓĖźÓĖ▓ÓĖć 2 o r 360 ’ü░’é┤ ’ü▒ ’ĆĮ ÓĖĢÓĖ▓ÓĖŻÓĖ▓ÓĖćÓĖ½ÓĖÖÓ╣łÓĖ¦ÓĖó 2 r 2 ’ü░’é┤ ’ü░ ’ü▒ ’ĆĮ


![6. Ó╣ĆÓĖŁÓĖüÓĖźÓĖ▒ÓĖüÓĖ®ÓĖōÓ╣īÓĖ×ÓĖĘÓ╣ēÓĖÖÓĖÉÓĖ▓ÓĖÖÓĖŚÓĖĄÓ╣łÓĖäÓĖ¦ÓĖŻÓĖŚÓĖŻÓĖ▓ÓĖÜ
ÓĖüÓ╣ŹÓĖ▓ÓĖ½ÓĖÖÓĖöÓ╣āÓĖ½Ó╣ē Ó╣ĆÓĖøÓ╣ćÓĖÖ ÓĖĪÓĖĖÓĖĪ , ÓĖäÓĖ¦ÓĖ▓ÓĖĪÓĖóÓĖ▓ÓĖ¦ÓĖ¬Ó╣łÓĖ¦ÓĖÖÓ╣éÓĖäÓ╣ēÓĖć ÓĖ½ÓĖŻÓĖĘÓĖŁ ÓĖłÓ╣ŹÓĖ▓ÓĖÖÓĖ¦ÓĖÖÓĖłÓĖŻÓĖ┤ÓĖćÓ╣āÓĖö Ó╣å’ü▒
1cossin 22
’ĆĮ’ü▒’Ć½’ü▒ ’ü▒’ĆŁ’é▒’ĆĮ’ü▒’é« 2
cos1sin ÓĖłÓĖ░Ó╣ĆÓĖźÓĖĘÓĖŁÓĖü + ÓĖ½ÓĖŻÓĖĘÓĖŁ ŌĆō ÓĖĢÓ╣ēÓĖŁÓĖćÓĖéÓĖČÓ╣ēÓĖÖÓĖŁÓĖóÓĖ╣Ó╣łÓĖüÓĖ▒ÓĖÜ ’ü▒
’ü▒’ĆŁ’é▒’ĆĮ’ü▒’é« 2
sin1cos ÓĖłÓĖ░Ó╣ĆÓĖźÓĖĘÓĖŁÓĖü + ÓĖ½ÓĖŻÓĖĘÓĖŁ ŌĆō ÓĖĢÓ╣ēÓĖŁÓĖćÓĖéÓĖČÓ╣ēÓĖÖÓĖŁÓĖóÓĖ╣Ó╣łÓĖüÓĖ▒ÓĖÜ ’ü▒
Ó╣üÓĖźÓĖ░’ü▒’ĆĮ’ü▒’Ć½ 22
eccoscot1 ’ü▒’ĆĮ’ü▒’Ć½ 22
sectan1
ÓĖüÓĖŻÓĖ▓ÓĖ¤ÓĖéÓĖŁÓĖćÓĖ¤ÓĖ▒ÓĖćÓĖüÓ╣īÓĖŖÓĖ▒ÓĖÖÓĖĢÓĖŻÓĖĄÓ╣éÓĖüÓĖōÓĖĪÓĖ┤ÓĖĢÓĖ┤
ÓĖ¤ÓĖ▒ÓĖćÓĖüÓ╣īÓĖŖÓĖ▒ÓĖÖ ÓĖüÓĖŻÓĖ▓ÓĖ¤ Ó╣éÓĖöÓ╣ĆÓĖĪÓĖÖ Ó╣ĆÓĖŻÓĖÖÓĖłÓ╣ī ÓĖäÓĖ▓ÓĖÜ
Ó╣üÓĖŁÓĖĪÓĖ×ÓĖźÓĖ┤ÓĖłÓĖ╣ÓĖö
xsiny ’ĆĮ R ]1,1[’ĆŁ ’ü░2
xcosy ’ĆĮ R ]1,1[’ĆŁ ’ü░2
xtany ’ĆĮ
’ā»’āŠ
’ā»
’āĮ
’ā╝
’ā»’ā«
’ā»
’āŁ
’ā¼
’ü░’āĘ
’āĖ
’āČ
’ā¦
’ā©
’ā” ’Ć½
’é╣
2
1n2
xx
In ’āÄ
R ’ü░
xcoty ’ĆĮ ’ü╗ ’üĮ’ü░’é╣ nxx
In ’āÄ
R ’ü░
xsecy ’ĆĮ
’ā»’āŠ
’ā»
’āĮ
’ā╝
’ā»’ā«
’ā»
’āŁ
’ā¼
’ü░’āĘ
’āĖ
’āČ
’ā¦
’ā©
’ā” ’Ć½
’é╣
2
1n2
xx
In ’āÄ
),1[]1,( ’éź’āł’ĆŁ’ĆŁ’éź ’ü░2
ecxcosy ’ĆĮ
’ü╗ ’üĮ’ü░’é╣ nxx
In ’āÄ
),1[]1,( ’éź’āł’ĆŁ’ĆŁ’éź ’ü░2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/random-130701062145-phpapp01/85/-3-320.jpg)


![ÓĖŁÓĖ┤ÓĖÖÓ╣ĆÓĖ¦ÓĖŁÓĖŻÓ╣īÓĖ¬ÓĖéÓĖŁÓĖćÓĖ¤ÓĖ▒ÓĖćÓĖüÓ╣īÓĖŖÓĖ▒ÓĖÖÓĖĢÓĖŻÓĖĄÓ╣éÓĖüÓĖōÓĖĪÓĖ┤ÓĖĢÓĖ┤
ÓĖ¤ÓĖ▒ÓĖćÓĖüÓ╣īÓĖŖÓĖ▒ÓĖÖÓĖĢÓĖŻÓĖĄÓ╣éÓĖüÓĖōÓĖĪÓĖ┤ÓĖĢÓĖ┤ ÓĖŁÓĖ┤ÓĖÖÓ╣ĆÓĖ¦ÓĖŁÓĖŻÓ╣īÓĖ¬ÓĖéÓĖŁÓĖćÓĖ¤ÓĖ▒ÓĖćÓĖüÓ╣īÓĖŖÓĖ▒ÓĖÖ ÓĖ¤ÓĖ▒ÓĖćÓĖüÓ╣īÓĖŖÓĖ▒ÓĖÖÓĖŁÓĖ┤ÓĖÖÓ╣ĆÓĖ¦ÓĖŁÓĖŻÓ╣īÓĖ¬ Ó╣éÓĖöÓ╣ĆÓĖĪÓĖÖÓĖéÓĖŁÓĖć Ó╣ĆÓĖŻÓĖłÓĖÖÓ╣īÓĖéÓĖŁÓĖć
ÓĖ¤ÓĖ▒ÓĖćÓĖüÓ╣īÓĖŖÓĖ▒ÓĖÖÓĖŁÓĖ┤ÓĖÖÓ╣ĆÓĖ¦ÓĖŁÓĖŻÓ╣īÓĖ¬ ÓĖ¤ÓĖ▒ÓĖćÓĖüÓ╣īÓĖŖÓĖ▒ÓĖÖÓĖŁÓĖ┤ÓĖÖÓ╣ĆÓĖ¦ÓĖŁÓĖŻÓ╣īÓĖ¬
xsiny ’ĆĮ ysinx ’ĆĮ xarcsiny ’ĆĮ ÓĖ½ÓĖŻÓĖĘÓĖŁ
xsiny 1’ĆŁ
’ĆĮ
]1,1[’ĆŁ
’ā║
’ā╗
’ā╣
’ā¬
’ā½
’ā® ’ü░’ü░
’ĆŁ
2
,
2
xcosy ’ĆĮ ycosx ’ĆĮ xarccosy ’ĆĮ ÓĖ½ÓĖŻÓĖĘÓĖŁ
xcosy 1’ĆŁ
’ĆĮ
]1,1[’ĆŁ
’üø ’üØ’ü░,0
xtany ’ĆĮ ytanx ’ĆĮ xarctany ’ĆĮ
ÓĖ¬ÓĖ╣ÓĖĢÓĖŻÓĖäÓĖ¦ÓĖ▓ÓĖĪÓĖ¬ÓĖ▒ÓĖĪÓĖ×ÓĖ▒ÓĖÖÓĖśÓ╣īÓĖéÓĖŁÓĖćÓĖ¤ÓĖ▒ÓĖćÓĖüÓ╣īÓĖŖÓĖ▒ÓĖÖÓĖŁÓĖ┤ÓĖÖÓ╣ĆÓĖ¦ÓĖŁÓĖŻÓ╣īÓĖ¬ÓĖĢÓĖŻÓĖĄÓ╣éÓĖüÓĖōÓĖĪÓĖ┤ÓĖĢÓĖ┤
1. )xarcsin(’ĆŁ ’ĆĮ xarcsin’ĆŁ ’é½ ’üø ’üØ1,1x ’ĆŁ’āÄ
2. )xarccos(’ĆŁ ’ĆĮ xarccos’ĆŁ’ü░ ’é½ ’üø ’üØ1,1x ’ĆŁ’āÄ
3. )xarctan(’ĆŁ ’ĆĮ xarctan’ĆŁ ’é½ Rx ’āÄ
4. ’ĆĮ)xsin(arcsin x ’é½ ’üø ’üØ1,1x ’ĆŁ’āÄ Ó╣üÓĖźÓĖ░
’ĆĮ)xarcsin(sin x ’é½ ’ā║
’ā╗
’ā╣
’ā¬
’ā½
’ā® ’ü░’ü░
’ĆŁ’āÄ
2
,
2
x ÓĖöÓĖ▒ÓĖćÓĖÖÓĖ▒Ó╣ēÓĖÖ
’ĆĮ)xsin(arcsin )xarcsin(sin ’é½ ’üø ’üØ1,1x ’ĆŁ’āÄ
5. ’ĆĮ)xcos(arccos x ’é½ ’üø ’üØ1,1x ’ĆŁ’āÄ Ó╣üÓĖźÓĖ░
’ĆĮ)xarccos(cos x ’é½ ’üø ’üØ’ü░’āÄ ,0x ÓĖöÓĖ▒ÓĖćÓĖÖÓĖ▒Ó╣ēÓĖÖ
’ĆĮ)xcos(arccos )xarccos(cos ’é½ ’üø ’üØ1,1x ’ĆŁ’āÄ
6. )xtan(arctan ’ĆĮ x ’é½ Rx ’āÄ Ó╣üÓĖźÓĖ░
)xarctan(tan ’ĆĮ x ’é½ ’āĘ
’āĖ
’āČ
’ā¦
’ā©
’ā” ’ü░’ü░
’ĆŁ’āÄ
2
,
2
x ÓĖöÓĖ▒ÓĖćÓĖÖÓĖ▒Ó╣ēÓĖÖ
)xtan(arctan ’ĆĮ )xarctan(tan ’é½ ’āĘ
’āĖ
’āČ
’ā¦
’ā©
’ā” ’ü░’ü░
’ĆŁ’āÄ
2
,
2
x
ÓĖ½ÓĖŻÓĖĘÓĖŁ
xtany 1’ĆŁ
’ĆĮ
R ’āĘ
’āĖ
’āČ
’ā¦
’ā©
’ā” ’ü░’ü░
’ĆŁ
2
,
2
ÓĖ½ÓĖŻÓĖĘÓĖŁxcoty ’ĆĮ ycotx ’ĆĮ xcotarcy ’ĆĮ
xcoty 1’ĆŁ
’ĆĮ
R
),0( ’ü░
xsecy ’ĆĮ ysecx ’ĆĮ xsecarcy ’ĆĮ ÓĖ½ÓĖŻÓĖĘÓĖŁ
xsecy 1’ĆŁ
’ĆĮ
)1,1(R ’ĆŁ’ĆŁ ’üø ’üØ
’āŠ
’āĮ
’ā╝
’ā«
’āŁ
’ā¼’ü░
’ĆŁ’ü░
2
,0
xcscy ’ĆĮ ycscx ’ĆĮ xcscarcy ’ĆĮ ÓĖ½ÓĖŻÓĖĘÓĖŁ
xcscy 1’ĆŁ
’ĆĮ
)1,1(R ’ĆŁ’ĆŁ ’ü╗ ’üĮ0
2
,
2
’ĆŁ’ā║
’ā╗
’ā╣
’ā¬
’ā½
’ā® ’ü░’ü░
’ĆŁ](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/random-130701062145-phpapp01/85/-6-320.jpg)






























































