1 of 25
Downloaded 131 times
























Recommended
Three mile island (nuclear power plant) accident



Three mile island (nuclear power plant) accidentGAURAV KUMAR
Ěý
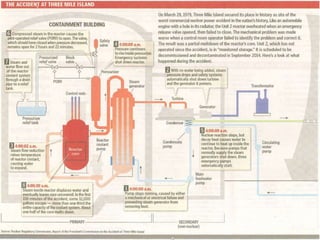
The Three Mile Island accident in 1979 was caused by failures in the non-nuclear systems that prevented the removal of heat from the reactor core. The pilot-operated relief valve failed to close which caused the loss of coolant and overheating of the reactor. This led to a partial meltdown of the nuclear fuel. The accident highlighted issues with plant design, operator training, emergency response, and strengthened safety requirements. It cost over $500 million to decontaminate and over $2-3 billion in additional capital expenditures but resulted in no deaths and only small amounts of radiation release.Three Mile Island Case Study



Three Mile Island Case StudyAsmita Bari
Ěý
It is a case study about Three Mile Island nuclear power plant accident which happened on 1979 in Pennsylvania(USA)The three mile island vaibhav 



The three mile island vaibhav vaibhav mangal
Ěý
The Three Mile Island accident in 1979 was the most significant nuclear accident in U.S. history. It began with a minor malfunction that caused the reactor to shut down, but a relief valve failed to close. Over almost 16 hours, operators struggled to determine the problem and solution. Small amounts of radioactive gases were released, leading to the voluntary evacuation of 140,000 people within a 20-mile radius, though maximum radiation exposure was less than 100 mrem. The cleanup took 12 years and cost $973 million, and the plant did not restart until 1985. While no health effects were found, it highlighted needs for improved operator training and safety systems.Three Mile Island Meltdown



Three Mile Island Meltdownkvnsutton75
Ěý
Human error led to a meltdown at the Three Mile Island nuclear power plant on March 28, 1979. A stuck open valve in the plant drained cooling water from the reactor core. Operators did not recognize that this was a loss of coolant accident. As the core heated up with no cooling, steam began forming within it. Operators further reduced the flow of water to the core, allowing damage to begin. Within two hours, the zirconium cladding around the fuel rods began to fail, releasing radioactive gases and indicating the start of core damage.Cash Study of Three Mile Island of Nuclear Melt Down



Cash Study of Three Mile Island of Nuclear Melt DownAshish Kavaiya
Ěý
The Three Mile Island nuclear power plant is located on the Susquehanna River in Pennsylvania, USA, 16 km from the state capital, Harrisburg, a city of 90 000.
It has two 900 MW(e) units with pressurized water reactors designed by Babcock and Wilcox.
The second unit of the site started commercial operation on December 30, 1978.
Nuclear Power Plant Disaster



Nuclear Power Plant DisasterZulkarnaen Zasni
Ěý
The document summarizes two major nuclear power plant disasters - Chernobyl in 1986 and Three Mile Island in 1979. It describes the causes of the accidents, their impacts, and lessons learned. The Chernobyl accident was caused by flawed reactor design and human error, resulting in a massive uncontrolled radioactive release. It directly caused 28 deaths and long term health impacts. Three Mile Island's partial core meltdown released some radiation but no direct health effects. It highlighted operational and communication issues. Both led to improved global nuclear safety standards and cooperation.Fukushima daichi disaster



Fukushima daichi disasterGiannis Bitharas
Ěý
The 2011 TĹŤhoku earthquake and tsunami caused a nuclear accident at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant. The 9.0 magnitude earthquake damaged the plant but backup diesel generators provided power for cooling. However, a 14 meter tsunami then flooded the generators, causing a complete loss of power and cooling capability. This led to three nuclear meltdowns, hydrogen-air explosions, and the release of radioactive material into the environment, forcing the evacuation of over 80,000 people within a 20km radius. The accident occurred due to inadequate safety provisions against earthquakes and tsunamis at the plant despite known risks and recommendations for upgrades.Nuclear Reactors, Materials, and Waste CIKR Sector: Case Study of the Nuclea...



Nuclear Reactors, Materials, and Waste CIKR Sector: Case Study of the Nuclea...Lindsey Landolfi
Ěý
The document provides information about the 1979 Three Mile Island nuclear accident in Pennsylvania through images, maps, and text. It discusses the accident's progression, including the partial meltdown in the reactor core and the release of radioactive gases. It also examines the emergency response, media coverage, investigations conducted afterward, debates around nuclear power, and lingering impacts on public perception and policy.Chernobyl disaster



Chernobyl disasterlalitmali8
Ěý
The Chernobyl nuclear disaster was the worst nuclear power plant accident in history. In 1986, during a safety test at the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant in Pripyat, Ukraine, then part of the Soviet Union, there was a sudden power surge and steam explosion that destroyed reactor number four. Large amounts of radioactive material were released into the environment, contaminating over 150,000 square kilometers of land. Over 100,000 people had to be evacuated and many suffered long-term health effects such as increased cancer rates due to exposure to radiation. The disaster was a result of flawed reactor design and human error during the poorly planned safety test. It highlighted issues with safety culture and communication within the Soviet nuclear industry.Chernobyl Nuclear Disaster - 1986



Chernobyl Nuclear Disaster - 1986ArnavDixit6
Ěý
The Chernobyl disaster was the worst nuclear power plant accident in history. In 1986, a flawed reactor design and human error caused an explosion and fire that released radiation into the atmosphere. Over 30 people died immediately from radiation exposure. The radioactive fallout spread over much of Europe. Long term impacts included increased cancer rates and contamination of surrounding land and water. The disaster demonstrated the importance of safety in nuclear power and providing emergency response plans for such accidents.Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster



Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disasterAnkitGiri15
Ěý
An earthquake and tsunami on March 11, 2011 disabled the power and cooling systems of three reactors at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant in Japan, causing a nuclear accident. Hydrogen explosions occurred at reactors 1 and 3, and an explosion due to rising pressure happened at reactor 2. By March 16th, 50% of the plant was on fire. The disaster, rated a 7 on the International Nuclear Event Scale, resulted in high radioactive release and economic losses of 150 billion euros for Japan, while increasing cancer risks and damaging the surrounding environment.The Space Shuttle Disasters



The Space Shuttle DisastersDon W. Lewis
Ěý
The document summarizes the story of Rodney Rocha, an engineer who warned NASA about potential damage to the Columbia space shuttle from foam insulation striking its wing during launch. Rocha and others requested clearer images of the impact and consideration of inspecting the wing, but NASA dismissed concerns, believing foam strikes could not be dangerous. Upon reentry, superheated gases entered a breach in the wing caused by the foam, leading to the destruction of Columbia and loss of the seven-member crew.Chernobyl Disaster



Chernobyl DisasterDao Tran
Ěý
This document discusses the 1986 Chernobyl nuclear disaster in Ukraine. It provides context about the disaster, including that reactor 4 at the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant exploded on April 26, 1986, causing the worst nuclear power plant accident in history. It then discusses the short-term and long-term effects of the disaster, as well as factors that contributed to it like safety violations and issues with the reactor design. It also analyzes the response and leadership after the disaster, criticizing the Soviet government's coverup and secrecy but praising the efforts of cleanup workers. Lastly, it outlines leadership lessons learned from Chernobyl around predicting risks, response planning, and leader characteristics like decision-making and problem-Chernobyl



ChernobylBen Dover
Ěý
The 1986 Chernobyl nuclear disaster in Ukraine was caused by a flawed Soviet reactor design and mistakes made by the plant's untrained operators. During a test with safety protocols deactivated, a series of errors caused a power surge and steam explosion, destroying the reactor and releasing massive amounts of radioactive materials into the atmosphere. The accident spread radioactive fallout across much of Europe and is considered the worst nuclear power plant disaster in history due to the huge amount of radiation released.Deepwater Horizon Oil Spill Overview Presentation



Deepwater Horizon Oil Spill Overview PresentationRichard Allaway
Ěý
The Deepwater Horizon oil rig exploded in the Gulf of Mexico 1,500 meters below the surface and 66 km off the coast of Louisiana, killing 11 workers. Over the next 36 hours, the rig burned and eventually sank, leaving a damaged wellhead that was leaking oil into the Gulf. For months, oil gushed from the wellhead at an estimated rate of up to 40,000 barrels per day, spreading across 1,500 square km of the Gulf and reaching the coasts of Louisiana, Florida, and elsewhere in the Gulf region due to ocean currents. The well was finally capped on July 15, over 80 days after the initial explosion.Deepwater Horizon Oil Spill



Deepwater Horizon Oil Spilltifftai
Ěý
A short slideshow to teach about what went wrong and how they tried to stop the leak. Made for 6-8 graders"Three Mile Island Accident"



"Three Mile Island Accident"Pawitra Masa-ah
Ěý
On March 28, 1979, there was a partial meltdown of one of the reactors at the Three Mile Island Nuclear Generating Station near Harrisburg, Pennsylvania. It remains the most significant accident in U.S. commercial nuclear energy history. A series of mechanical and human errors led to a partial meltdown of the reactor core and a small release of radioactive gases into the environment. The cleanup effort took around 12 years and cost approximately $973 million to complete.Deep Water Horizon Oil Spill (B. P. Oil Spill)



Deep Water Horizon Oil Spill (B. P. Oil Spill)Syed Ali Roshan
Ěý
This presentation contains information about the massive tragedy that took place near the Gulf of Mexico, which took the lives of 11 crew members.
Let me know in the comments if you want me to upload a video of myself presenting this presentation. Chernobyl Disaster.



Chernobyl Disaster.Hareem_syed
Ěý
A small, compact case study on the Chernobyl disaster. I have made this presentation because I deeply grieve for the loss of every person who suffered by the hand of the horrendous disaster.FUKUSHIMA DISASTER.pptx



FUKUSHIMA DISASTER.pptxanikchandel
Ěý
Fukushima Disaster and its introduction, Fukushima accident , causes and their impacts on people , social life , economy , nature and our environment and their solutionsFukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station Accident April19 2011



Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station Accident April19 2011Joe Miller
Ěý
This document provides an overview of the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear accident that occurred in 2011 following an earthquake and tsunami in Japan. It discusses the plant designs, accident progression, spent fuel pools, radiological releases, and impact on US reactors. Key events included the loss of off-site power and emergency diesel generators due to flooding, melting of reactor cores due to lack of cooling, hydrogen explosions, and venting of radioactive gases. Lessons learned included enhancing backup cooling capabilities and emergency procedures for extreme events.Chernobyl disaster



Chernobyl disasterLokeswar
Ěý
Chernobyl disaster and what are the lessons we have to learn especially India which having 21 Nuclear Centers or Plants
Reference Video Link is given below
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=R9JSGU8MRb0
Chernobyl case study



Chernobyl case studySKS
Ěý
The Chernobyl disaster was the worst nuclear power plant accident in history. In 1986, Reactor 4 of the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant in Ukraine exploded and caught fire during a safety test, releasing massive amounts of radiation into the atmosphere. Over 100,000 people were evacuated and hundreds of square miles of land were severely contaminated, with higher rates of cancer and other illnesses reported among those exposed. The cleanup required thousands of liquidators and cost billions. While a sarcophagus was constructed to contain the reactor, the effects of the radiation release continue to impact the region for decades to come.Chernobyl disaster



Chernobyl disasteroffineha
Ěý
The Chernobyl nuclear disaster of 1986 was the worst nuclear power plant accident in history. It occurred during a safety test at the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant in Ukraine. The explosions and fire released large quantities of radioactive particles into the atmosphere that spread over much of the western Soviet Union and Europe. Over 100,000 people were evacuated from the most contaminated areas near the plant. The accident exposed hundreds of thousands of recovery workers to high levels of radiation and caused an increase in reported cases of thyroid cancer. Long-term health and environmental effects of the Chernobyl accident are still being investigated.Fukushima Daiichi Byu Presentation



Fukushima Daiichi Byu PresentationJoe Miller
Ěý
This presentation provides an overview of the nuclear accidents that occurred at the Fukushima I power plant on March 11, 2011.Ioc jaipur oil storage depot incident



Ioc jaipur oil storage depot incidentHarshithGade
Ěý
Ioc jaipur oil storage depot incident
what has happened?
timelines
Factors effecting
Vapour cloud explosion(VCE)
source of ignition
summary
a video on incident
references
Challenger disaster



Challenger disasterjackConsideration
Ěý
The Challenger space shuttle broke apart 73 seconds after launch on January 27, 1986, killing all seven crew members. An O-ring seal on one of the solid rocket boosters failed at liftoff, allowing pressurized gas to reach the external fuel tank and cause the shuttle to disassemble. Engineers had warned NASA of the failure risk from O-ring damage in cold weather but the concerns were not addressed, resulting in the loss of Challenger and her crew.Chernobyl tragedy



Chernobyl tragedySharat045
Ěý
The Chernobyl disaster of 1986 was the worst nuclear power accident in history. During a systems test of Reactor 4, a surge in power caused two explosions that released radiation into the atmosphere. Over 100,000 people had to be evacuated from the surrounding area in Ukraine and Belarus. The incident was caused by an unstable reactor design combined with human error and safety violations during the test. It resulted in many deaths and long-term health and environmental effects.More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Chernobyl disaster



Chernobyl disasterlalitmali8
Ěý
The Chernobyl nuclear disaster was the worst nuclear power plant accident in history. In 1986, during a safety test at the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant in Pripyat, Ukraine, then part of the Soviet Union, there was a sudden power surge and steam explosion that destroyed reactor number four. Large amounts of radioactive material were released into the environment, contaminating over 150,000 square kilometers of land. Over 100,000 people had to be evacuated and many suffered long-term health effects such as increased cancer rates due to exposure to radiation. The disaster was a result of flawed reactor design and human error during the poorly planned safety test. It highlighted issues with safety culture and communication within the Soviet nuclear industry.Chernobyl Nuclear Disaster - 1986



Chernobyl Nuclear Disaster - 1986ArnavDixit6
Ěý
The Chernobyl disaster was the worst nuclear power plant accident in history. In 1986, a flawed reactor design and human error caused an explosion and fire that released radiation into the atmosphere. Over 30 people died immediately from radiation exposure. The radioactive fallout spread over much of Europe. Long term impacts included increased cancer rates and contamination of surrounding land and water. The disaster demonstrated the importance of safety in nuclear power and providing emergency response plans for such accidents.Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster



Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disasterAnkitGiri15
Ěý
An earthquake and tsunami on March 11, 2011 disabled the power and cooling systems of three reactors at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant in Japan, causing a nuclear accident. Hydrogen explosions occurred at reactors 1 and 3, and an explosion due to rising pressure happened at reactor 2. By March 16th, 50% of the plant was on fire. The disaster, rated a 7 on the International Nuclear Event Scale, resulted in high radioactive release and economic losses of 150 billion euros for Japan, while increasing cancer risks and damaging the surrounding environment.The Space Shuttle Disasters



The Space Shuttle DisastersDon W. Lewis
Ěý
The document summarizes the story of Rodney Rocha, an engineer who warned NASA about potential damage to the Columbia space shuttle from foam insulation striking its wing during launch. Rocha and others requested clearer images of the impact and consideration of inspecting the wing, but NASA dismissed concerns, believing foam strikes could not be dangerous. Upon reentry, superheated gases entered a breach in the wing caused by the foam, leading to the destruction of Columbia and loss of the seven-member crew.Chernobyl Disaster



Chernobyl DisasterDao Tran
Ěý
This document discusses the 1986 Chernobyl nuclear disaster in Ukraine. It provides context about the disaster, including that reactor 4 at the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant exploded on April 26, 1986, causing the worst nuclear power plant accident in history. It then discusses the short-term and long-term effects of the disaster, as well as factors that contributed to it like safety violations and issues with the reactor design. It also analyzes the response and leadership after the disaster, criticizing the Soviet government's coverup and secrecy but praising the efforts of cleanup workers. Lastly, it outlines leadership lessons learned from Chernobyl around predicting risks, response planning, and leader characteristics like decision-making and problem-Chernobyl



ChernobylBen Dover
Ěý
The 1986 Chernobyl nuclear disaster in Ukraine was caused by a flawed Soviet reactor design and mistakes made by the plant's untrained operators. During a test with safety protocols deactivated, a series of errors caused a power surge and steam explosion, destroying the reactor and releasing massive amounts of radioactive materials into the atmosphere. The accident spread radioactive fallout across much of Europe and is considered the worst nuclear power plant disaster in history due to the huge amount of radiation released.Deepwater Horizon Oil Spill Overview Presentation



Deepwater Horizon Oil Spill Overview PresentationRichard Allaway
Ěý
The Deepwater Horizon oil rig exploded in the Gulf of Mexico 1,500 meters below the surface and 66 km off the coast of Louisiana, killing 11 workers. Over the next 36 hours, the rig burned and eventually sank, leaving a damaged wellhead that was leaking oil into the Gulf. For months, oil gushed from the wellhead at an estimated rate of up to 40,000 barrels per day, spreading across 1,500 square km of the Gulf and reaching the coasts of Louisiana, Florida, and elsewhere in the Gulf region due to ocean currents. The well was finally capped on July 15, over 80 days after the initial explosion.Deepwater Horizon Oil Spill



Deepwater Horizon Oil Spilltifftai
Ěý
A short slideshow to teach about what went wrong and how they tried to stop the leak. Made for 6-8 graders"Three Mile Island Accident"



"Three Mile Island Accident"Pawitra Masa-ah
Ěý
On March 28, 1979, there was a partial meltdown of one of the reactors at the Three Mile Island Nuclear Generating Station near Harrisburg, Pennsylvania. It remains the most significant accident in U.S. commercial nuclear energy history. A series of mechanical and human errors led to a partial meltdown of the reactor core and a small release of radioactive gases into the environment. The cleanup effort took around 12 years and cost approximately $973 million to complete.Deep Water Horizon Oil Spill (B. P. Oil Spill)



Deep Water Horizon Oil Spill (B. P. Oil Spill)Syed Ali Roshan
Ěý
This presentation contains information about the massive tragedy that took place near the Gulf of Mexico, which took the lives of 11 crew members.
Let me know in the comments if you want me to upload a video of myself presenting this presentation. Chernobyl Disaster.



Chernobyl Disaster.Hareem_syed
Ěý
A small, compact case study on the Chernobyl disaster. I have made this presentation because I deeply grieve for the loss of every person who suffered by the hand of the horrendous disaster.FUKUSHIMA DISASTER.pptx



FUKUSHIMA DISASTER.pptxanikchandel
Ěý
Fukushima Disaster and its introduction, Fukushima accident , causes and their impacts on people , social life , economy , nature and our environment and their solutionsFukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station Accident April19 2011



Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station Accident April19 2011Joe Miller
Ěý
This document provides an overview of the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear accident that occurred in 2011 following an earthquake and tsunami in Japan. It discusses the plant designs, accident progression, spent fuel pools, radiological releases, and impact on US reactors. Key events included the loss of off-site power and emergency diesel generators due to flooding, melting of reactor cores due to lack of cooling, hydrogen explosions, and venting of radioactive gases. Lessons learned included enhancing backup cooling capabilities and emergency procedures for extreme events.Chernobyl disaster



Chernobyl disasterLokeswar
Ěý
Chernobyl disaster and what are the lessons we have to learn especially India which having 21 Nuclear Centers or Plants
Reference Video Link is given below
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=R9JSGU8MRb0
Chernobyl case study



Chernobyl case studySKS
Ěý
The Chernobyl disaster was the worst nuclear power plant accident in history. In 1986, Reactor 4 of the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant in Ukraine exploded and caught fire during a safety test, releasing massive amounts of radiation into the atmosphere. Over 100,000 people were evacuated and hundreds of square miles of land were severely contaminated, with higher rates of cancer and other illnesses reported among those exposed. The cleanup required thousands of liquidators and cost billions. While a sarcophagus was constructed to contain the reactor, the effects of the radiation release continue to impact the region for decades to come.Chernobyl disaster



Chernobyl disasteroffineha
Ěý
The Chernobyl nuclear disaster of 1986 was the worst nuclear power plant accident in history. It occurred during a safety test at the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant in Ukraine. The explosions and fire released large quantities of radioactive particles into the atmosphere that spread over much of the western Soviet Union and Europe. Over 100,000 people were evacuated from the most contaminated areas near the plant. The accident exposed hundreds of thousands of recovery workers to high levels of radiation and caused an increase in reported cases of thyroid cancer. Long-term health and environmental effects of the Chernobyl accident are still being investigated.Fukushima Daiichi Byu Presentation



Fukushima Daiichi Byu PresentationJoe Miller
Ěý
This presentation provides an overview of the nuclear accidents that occurred at the Fukushima I power plant on March 11, 2011.Ioc jaipur oil storage depot incident



Ioc jaipur oil storage depot incidentHarshithGade
Ěý
Ioc jaipur oil storage depot incident
what has happened?
timelines
Factors effecting
Vapour cloud explosion(VCE)
source of ignition
summary
a video on incident
references
Challenger disaster



Challenger disasterjackConsideration
Ěý
The Challenger space shuttle broke apart 73 seconds after launch on January 27, 1986, killing all seven crew members. An O-ring seal on one of the solid rocket boosters failed at liftoff, allowing pressurized gas to reach the external fuel tank and cause the shuttle to disassemble. Engineers had warned NASA of the failure risk from O-ring damage in cold weather but the concerns were not addressed, resulting in the loss of Challenger and her crew.Chernobyl tragedy



Chernobyl tragedySharat045
Ěý
The Chernobyl disaster of 1986 was the worst nuclear power accident in history. During a systems test of Reactor 4, a surge in power caused two explosions that released radiation into the atmosphere. Over 100,000 people had to be evacuated from the surrounding area in Ukraine and Belarus. The incident was caused by an unstable reactor design combined with human error and safety violations during the test. It resulted in many deaths and long-term health and environmental effects.