Topic: Curriculum Development Process.pptx
- 1. Curriculum & Instructions Presenter: Sobia Alvi Program: M.Phil. Education Course Title: Curriculum & Instructions Department of Education Khawaja Fareed University of Engineering & Information Technology (RYK)
- 3. Concept of Curriculum Introduction Curriculum development is a process through which an institute or the instructor designs or creates a plan for a course or program. Furthermore, it is not a stagnant approach and includes continuous improvement wherein, the content is reviewed, revised and updated according to the needs and demands. Curriculum management is the process of developing, maintaining, and improving the quality of curricula for various educational intuitions. The curriculum manager is responsible for designing and developing the curriculum with a range of content, training programs, teaching methodologies, and assessment techniques for students, learners, and employees. The developed curriculum should meet the educational standards set by the government and academic bodies. What is Curriculum Strategy? Curriculum strategy involves the process of defining goals, objectives, and levels to develop a curriculum that adheres to the given requirements (or finds solutions to the existing problems/ gaps in teaching). It streamlines the elements of the curriculum by defining the relationships between them. What makes a quality curriculum is the time and energy spent developing the curriculum strategy.
- 4. 01 02 03 04 Teaching/ Learning Methodologies Elements of Curriculum Development Content of Curriculum Evaluation of Curriculum Objectives of Curriculum
- 5. Explicit ŌĆó Also known as overt or official curriculum, it details the steps to follow to properly implement the curricula to arrive at the intended outcome. Implicit/ Hidden ŌĆó Different learning aspects contribute to implicit curricula. It is a by-product of implementing explicit curricula. Absent/ Excluded ŌĆó Absent or null curriculum is the one that is not taught or excluded from the developed curricula. It could be intentional or unintentional. 3 Types of Curriculum
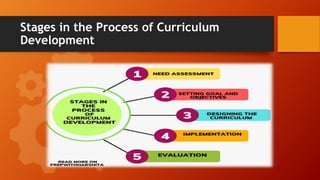
- 6. Process of Curriculum Development The curriculum development process consists of the following six stages. Step 1: Assessing the educational needs Step 2: Formulating objectives and learning goals Step 3: Careful selection of learning experiences to accomplish these objectives Step 4: The selecting the rich and valuable content through which teachers can offer the learning experiences. Step 5: Organizing and integrating learning experiences with relevant content keeping in mind the teaching-learning process Step 6: Timely and accurate evaluation of all the above phases.
- 7. Types of Curriculum Development Models 1) Learner-Centered Design The learner-centered design focuses on the understanding that each learner has different characteristics. The teachers or instructors are to give opportunities to the learners to take ownership of a project or assignment. 2) Subject-Centered Design Subject-centered design is a traditional approach to curriculum that focuses on a particular Subject matter or discipline rather than on the individual. Additionally, during the curriculum development process, this approach includes four subtypes of curriculum designs: subject-area design, discipline design, broad-field design, and correlation design. 3) Problem-Centered Design Problem-centered design is an approach that focuses on developing problem-solving skills, thinking and communication skills. This is a student-centric strategy wherein the learners are given problematic situations and encouraged to solve them after careful observation.
- 8. Stages of Curriculum Development
- 9. Stages in the Process of Curriculum Development
- 10. Principles of Curriculum Development The principles of the curriculum are norms, values, moralities, and philosophies that will benefit teachers, students, and the whole education system. The curriculum and instructional strategy are essential components of imparting knowledge to students. ’āś Totality of Experiences ’āś Child-Centeredness ’āś Conservation and Creativity ’āś Integration ’āś Flexibility ’āś Utility ’āś Character Formation ’āś Mental Discipline ’āś Social Fulfillment
- 11. Factors Affecting Curriculum Development
- 12. Tips and Strategies for Curriculum Creators Focus on the students rather than on creating the best lesson plan. The ultimate goal should be to do whatŌĆÖs best for the learners. ’āś Talk to other experts, teachers, etc., from the industry and consider their inputs. ’āś Make use of technology to design the curriculum. There are different software applications to assist you. ’āś Avoid pre-packaged curricula. The curriculum needs to be tailor made for the intended outcome. ’āś Take time to design and develop the curriculum. DonŌĆÖt rush through the process or skip stages. ’āś Make changes to the curriculum if necessary. It is acceptable and even expected if the curriculum doesnŌĆÖt align with the intended outcomes. ’āś Create a proper evaluation and feedback system to get inputs about the curriculum. Take feedback from students and teachers.
- 13. REFERENCES 1. https://prepwithharshita.com/stages-in-the-process-of-curriculum-development/ 2. https://www.iitms.co.in/blog/curriculum-development-models.html 3. https://www.prepai.io/blog/tips-and-strategies-for-curriculum- creators/?utm_source=prepaiwebsite&utm_medium=demo-btn 4. https://prepwithharshita.com/tag/meaning-of-curriculum-and-organizing-curriculum- components/
Editor's Notes
- #3: Notes to presenter: What is your purpose for sharing this reflection? Is it at the end of a unit or project? Are you sharing this reflection, at the attainment of a learning goal you set for yourself? Is it at the end of a course? State your purpose for the reflection or even the purpose of the learning experience or learning goal. Be clear and be specific in stating your purpose.
- #4: Notes to presenter: Description of what you learned in your own words on one side. Include information about the topic Details about the topic will also be helpful here. Tell the story of your learning experience. Just like a story there should always be a beginning, middle and an end. On the other side, you can add a graphic that provides evidence of what you learned. Feel free to use more than one slide to reflect upon your process. It also helps to add some video of your process.
- #5: Notes to presenter: What did you think at first? What obstacles did you encounter along the way? How did you overcome those obstacles? What images can you add to support your process? This SmartArt allows you add images and text to help outline your process. If a picture is worth a thousand words, then pictures and words should help you communicate this reflection on learning perfectly! You can always click on Insert>SmartArt to change this graphic or select the graphic and click on the Design contextual menu to change the colors. Feel free to use more than one slide to reflect upon your process. It also helps to add some video of your process.
- #6: Notes to presenter: What was important about this learning experience? How is it relevant to your course, yourself, or your society or community? Why is this significant? This SmartArt allows you add images and text to help outline your process. If a picture is worth a thousand words, then pictures and words should help you communicate this reflection on learning perfectly! You can always click on Insert>SmartArt to change this graphic or select the graphic and click on the Design contextual menu to change the colors.