UNIT. 4. Rivers.pptx, river system, tribuary
- 1. UNIT.4. RIVERS AND TECTONIC PLATES 4.1. Definition of Rivers River is a natural stream of flowing water in definite channel. Sometimes, it is referred to large mass of water flowing in a specific valley. The valley that river water flows from upstream toward the downstream is also called river channel or River course. The term River System is referred to the combination of main river with its tributaries, its delta and its distributaries. River discharge is the volume of water flowing through a river channel; measured at any given point in cubic metres per second.
- 2. Rivers may begin from the following areas: ’üČ Springs ’üČ Lakes ’üČ Glaciers and Snow ’üČ Highlands areas which receive heavy and evenly distributed rainfalls. Once a river forms, it will typically flow downhill. The movement the river makes is its current, or its flow. The flow among rivers varies; the shortest (Roe River) is 210 feet long, while the longest (Nile River) is over 4,000 miles long. The point where a river starts its flow is known as river source while its ending point is called river mouth. the land that surrounds the channel is the riverbank. The flow of river from source to mouth is known as River Course. The smaller river that joins into the main river is called Tributary.Tributary flows into the bigger river at the river confluence. The smaller channels that split from the big river are called Distributaries. The areas where distributaries scattered as fingers at the fan shaped mouth or ending area is called River Delta.
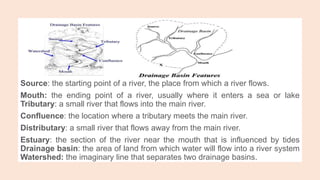
- 3. Source: the starting point of a river, the place from which a river flows. Mouth: the ending point of a river, usually where it enters a sea or lake Tributary: a small river that flows into the main river. Confluence: the location where a tributary meets the main river. Distributary: a small river that flows away from the main river. Estuary: the section of the river near the mouth that is influenced by tides Drainage basin: the area of land from which water will flow into a river system Watershed: the imaginary line that separates two drainage basins.
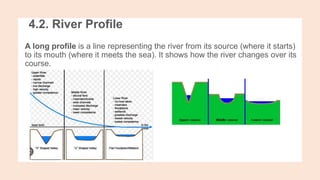
- 4. 4.2. River Profile A long profile is a line representing the river from its source (where it starts) to its mouth (where it meets the sea). It shows how the river changes over its course.
- 5. Upper course - in the upper course, where the river starts, there is often an upland area. The river's load is large in the upper course, as it more erosive area. ŌĆó middle course - The section of the river which comes between the upper and lower course. It is usually wider than the upper course and the water flows slowly. Tributary is a stream or river that flows into another stream or river instead of flowing into the sea. ŌĆó Lower course - in the lower course, the land is a lot flatter. The river's load is fine sediment, as erosion has broken down the rocks.
- 6. The upper course is marked by a V-shaped valley, with steep sides and a shallow channel. The middle course is marked by gently sloping valley sides and a wider and deeper channel. The lower course is a very wide, nearly flat valley and usually has a wide, deep channel. A. as the river flows downhill there is an increase in vertical erosion. The channel is shallow and narrow because there is not a lot of water in the channel. B. As the river flows into the middle course, there is some vertical erosion but more lateral erosion. The channel is wider and deeper as a result. C. In the lower course there is a lot less erosion, with only some lateral erosion. The channel is at its widest and deepest.
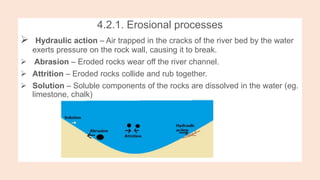
- 7. 4.2.1. Erosional processes ’āś Hydraulic action ŌĆō Air trapped in the cracks of the river bed by the water exerts pressure on the rock wall, causing it to break. ’āś Abrasion ŌĆō Eroded rocks wear off the river channel. ’āś Attrition ŌĆō Eroded rocks collide and rub together. ’āś Solution ŌĆō Soluble components of the rocks are dissolved in the water (eg. limestone, chalk)
- 8. 4.2.2.Transport processes The river picks up sediment and carries it downstream in different ways. Light loads are carried longer distance than heavy materials transferred from eroded areas to the accumulation zone. ŌĆó Traction ŌĆō Heavy boulders are rolled along the river bed ŌĆó Saltation ŌĆō Small rocks are bounced along the river bed ŌĆó Suspension ŌĆō Light particles (eg. sand grains) are transported in the water ŌĆó Solution ŌĆō Dissolved particles are carried along by the river. ŌĆó Flotation ŌĆō Light objects, eg. wood, float on the river surface
- 9. 4.2.3. Deposition Deposition occurs when the river does not have enough speed to carry the load (eg. delta, inner bends of meander or during dry spells). The velocity of a stream may slow down due to a reduction in rainfall, increased evaporation and more friction with the river bed. 4.3. Erosional and Depositional Features (Landforms) Waterfalls, gorges and plunge pools 1. form in the upper course where hard rock is layered horizontally above soft rock 2. soft rock is less resistant to erosion and is worn away. 3. hard rock forms an overhang, creating a Knick point. 4. plunge pool develops at base of Knick point as force of water erodes soft rock.
- 10. 5) hard rock eventually unsupported by soft rock below, causing the overhang to collapse. 6) plunge pool enlarges as hard rock erodes it. 7) waterfall retreats upstream and gorge may form
- 11. V-shaped valleys V-shaped valleys typically form in the upper course of a river, where water flows at high velocity and forcefully cuts into the surrounding mountains and hills. Potholes. Potholes are smooth, rounded hollows in the bedrock of the river.
- 12. 1. in the upper course 2. when flowing water encounters bedload (stones are trapped in hollows on the river bed). 3. forced over bedload and down cuts behind it (eddie currents). 4. currents cause differential erosion (hydraulic action and abrasion). 5. small holes are formed and widened by currents. 6. deep vertical erosion lowers river bed Rapids 1. form in the upper course 2. hard rock and soft rock layered diagonally (no obvious breaks of slope). 3. soft rock is less resistant, so it is eroded faster than hard rock. 4. hard rock remains, resulting in bumps along the river bed.
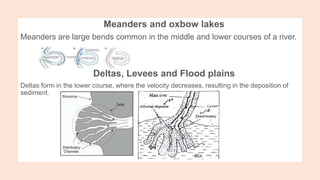
- 13. Meanders and oxbow lakes Meanders are large bends common in the middle and lower courses of a river. Deltas, Levees and Flood plains Deltas form in the lower course, where the velocity decreases, resulting in the deposition of sediment.
- 14. How floodplains form: ŌĆó river overflows at times of high discharge and spreads over surrounding flat land ŌĆó river velocity decreases, resulting in deposition ŌĆó flood plains build up with success floods over the years. How levees form: Levees may form in course material is deposited at the edge of the river channel and forms and natural embankment. 4.4. Significance of Rivers to Man Positive Effects of Rivers: 1. Rivers are both local and international boundaries demarcating between independent countries or regions within the same state. 2. Some rivers are navigable which can be used for transporting loads, livestock and even people from one location to another using small vessels.
- 15. 3. Rivers aid international trade facilitating movement and flow of supply of goods from suppliers to their consumers who are in different locations. 4. The organic matters brought down by river waters provide valuable food for fish and spawning purposes and even for industrial purposes. 5. Rivers provide natural ground or sites for the generation of hydroelectric power. 6. Rivers provide building materials because deposited loads like clay and gravels are used for construction purposes. 7. Rivers are sources of water used for irrigation, domestic use and even industrial purpose. 8. Rivers are site provides us for recreational and entertainment centers like swimming. 9. Rivers have some attractive scenes/ features like waterfalls and ox-bow lakes which are touristsŌĆÖ attractions. 10.Rivers are fishing grounds were many fishers caught species of fish for both consumption or for sale.
- 16. Negative Effects of Rivers: 1. Soil erosion. River water leads soil erosion. 2. Rivers are hostages of snails and mosquitoes which can cause water borne diseases like bilharzia and malaria respectively. 3. Rivers are habitats of dangerous wild animals like crocodiles and snakes. 4. Rivers can cause flooding which leads loss of life and properties. Practice questions 1. List the three types of river erosion. 2. Define the terms: river, basin, Source, Mouth. 3. List and define the four processes of erosion. 4. What is the deposition? 5. State four processes of river transportation.

























![Landforms[1]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/landforms1-120317150027-phpapp01-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)















































