More Related Content Similar to Agingand posturalcontrol (6) PDF
City Rehab Center - Case documentation by Park, PT
Moonkyu Lee ╠²
PDF
City Rehab Center - Case documentation by Jin, PT
Moonkyu Lee ╠²
PPTX
Ļ│╝ĒĢÖĒāÉĻĄ¼-01 ļģĖĒÖöņÖĆ ņĢłĒŗ░ņŚÉņØ┤ņ¦Ģ.pptx
sciencepeople ╠²
PDF
Age related memory loss ļé┤ Ļ▒┤ļ¦Øņ”Ø ņĀĢņāüņØĖĻ░Ć?
Jahee Lee ╠²
PPT
ņĀĢņŗĀĻ░äĒśĖĒĢÖ1 3ņ░©ņŗ£ ņØĖĻ░äņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ņØ┤ĒĢ┤_v1-2
sujaubuns ╠²
PPT
ņĀĢņŗĀĻ░äĒśĖĒĢÖ1 3ņ░©ņŗ£ ņØĖĻ░äņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ņØ┤ĒĢ┤_v1-2
sujaubuns ╠²
2. ’üĮ Model of Aging
’üĮ Behavioral indicators of instability
’üĮ Age- related changes in the systems of postural
control
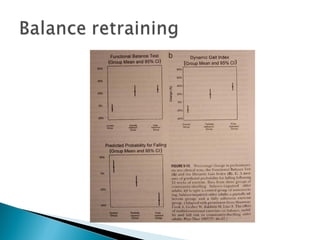
’üĮ Balance retraining
3. ŌĆó Focus
ŌĆō ļéśņØ┤ņÖĆ Ļ┤Č─ļĀ©ļÉ£ Postural Control ņØś ļ│ĆĒÖö .
ŌĆō ļéśņØ┤ņÖĆ Ļ┤Č─ļĀ©ļÉ£ system ņØś ļ│ĆĒÖöļŖö dysfunction ņØä
dysfunction ņØĆ ļśÉ instability ņØä ņ┤łļלĒĢ£ļŗż .
ŌĆō Training ņØĆ system ņĢłņŚÉņä£ balance function ņØä Ē¢źņāü
ņŗ£Ēé¼ ņłś ņ׳ļŗż .
5. ’üĮ Two general categories
ŌŚ” 1 Primary Aging
’é¢ internal causes of aging
’é¢ The life span is genetically determined
ŌŚ” 2 Secondary Aging
’é¢ External causes of aging
’é¢ Result of interaction with the environment
’é¢ Radiation, pollutants, bacteria, viruses. Foods, toxinŌĆ”ŌĆ”
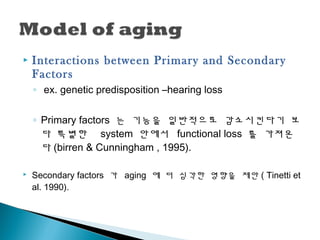
7. ’üĮ Interactions between Primary and Secondary
Factors
ŌŚ” ex. genetic predisposition ŌĆōhearing loss
ŌŚ” Primary factors ļŖö ĻĖ░ļŖźņØä ņØ╝ļ░śņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ Ļ░Éņåīņŗ£Ēé©ļŗżĻĖ░ ļ│┤
ļŗż ĒŖ╣ļ│äĒĢ£ system ņĢłņŚÉņä£ functional loss ļź╝ Ļ░ĆņĀĖņś©
ļŗż (birren & Cunningham , 1995).
’üĮ Secondary factors Ļ░Ć aging ņŚÉ ļŹö ņŗ¼Ļ░üĒĢ£ ņśüĒ¢źņØä ņĀ£ņĢł ( Tinetti et
al. 1990).
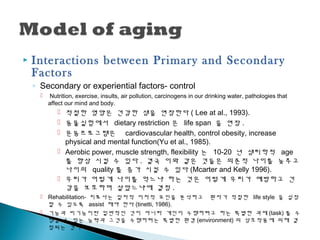
8. ’üĮ Interactions between Primary and Secondary
Factors
ŌŚ” Secondary or experiential factors- control
’é¢ Nutrition, exercise, insults, air pollution, carcinogens in our drinking water, pathologies that
affect our mind and body.
’é¢ ņĀüņĀłĒĢ£ ņśüņ¢æņØĆ Ļ▒┤Ļ░ĢĒĢ£ ņāØņØä ņŚ░ņןĒĢ£ļŗż ( Lee at al., 1993).
’é¢ ļÅÖļ¼╝ņŗżĒŚśņŚÉņä£ dietary restriction ņØĆ life span ņØä ņŚ░ņן .
’é¢ ņÜ┤ļÅÖĒöäļĪ£ĻĘĖļשņØĆ cardiovascular health, control obesity, increase
physical and mental function(Yu et al., 1985).
’é¢ Aerobic power, muscle strength, flexibility ļŖö 10-20 ļģä ņāØļ”¼ĒĢÖņĀü age
ļź╝ Ē¢źņāü ņŗ£Ēé¼ ņłś ņ׳ļŗż . Ļ▓░ĻĄŁ ņØ┤ņÖĆ Ļ░ÖņØĆ Ļ▓āļōżņØĆ ņØśņĪ┤ņĀü ļéśņØ┤ļź╝ ļŖ”ņČöĻ│Ā
ļéśņØ┤ņØś quality ļź╝ ņ”ØĻ░Ć ņŗ£Ēé¼ ņłś ņ׳ļŗż (Mcarter and Kelly 1996).
’é¢ ņÜ░ļ”¼Ļ░Ć ņ¢┤ļ¢╗Ļ▓ī ļéśņØ┤ļź╝ ļ©╣ļŖÉļāÉ ĒĢśļŖö Ļ▓āņØĆ ņ¢┤ļ¢╗Ļ▓ī ņÜ░ļ”¼Ļ░Ć ņśłļ░®ĒĢśĻ│Ā Ļ▒┤
Ļ░ĢņØä ļ│┤ĒśĖĒĢśļ®░ ņé┤ņĢśļŖÉļāÉņŚÉ Ļ▓░ņĀĢ .
’é¢ Rehabilitation- ņ╣śļŻīņé¼ļŖö ņØ╝ņ░©ņĀü ņØ┤ņ░©ņĀü ņÜöņØĖņØä ļČäņäØĒĢśĻ│Ā ĒÖśņ×ÉĻ░Ć ņĀüņĀłĒĢ£ life style ņØä ņäżņĀĢ
ĒĢĀ ņłś ņ׳ļÅäļĪØ assist ĒĢ┤ņĢ╝ ĒĢ£ļŗż (tinetti, 1986).
’é¢ ĻĖ░ļŖźĻ│╝ ļ╣äĻĖ░ļŖźņØ┤ļ×Ć ņØ╝ļ░śņĀüņØĖ Ļ▓āņØ┤ ņĢäļŗłļØ╝ Ļ░£ņØĖņØ┤ ņłśĒ¢ēĒĢśļĀżĻ│Ā ĒĢśļŖö ĒŖ╣ļ│äĒĢ£ Ļ│╝ņĀ£ (task) ļź╝ ņłś
Ē¢ēĒĢĀ ņłś ņ׳ļŖö ļŖźļĀźĻ│╝ ĻĘĖĻ▓āņØä ņłśĒ¢ēĒĢśļĀżļŖö ĒŖ╣ļ│äĒĢ£ ĒÖśĻ▓Į (environment) ņØś ņāüĒśĖņ×æņÜ®ņŚÉ ņØśĒĢ┤ Ļ▓░
ņĀĢļÉśļŖö Ļ▓āņØ┤ļŗż .
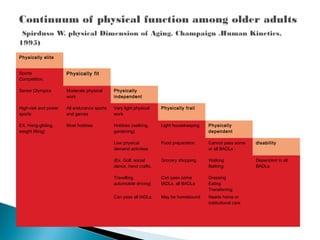
10. Physically elite
Sports
Competition,
Physically fit
Senior Olympics Moderate physical
work
Physically
independent
High-risk and power
sports
All endurance sports
and games
Very light physical
work
Physically frail
EX. Hang-gliding,
weight lifting)
Most hobbies Hobbies (walking,
gardening)
Light housekeeping Physically
dependent
Low physical
demand activities
Food preparation Cannot pass some
or all BADLs :
disability
(Ex. Golf, social
dance, hand crafts,
Grocery shopping Walking
Bathing
Dependent in all
BADLs
Travelling,
automobile driving)
Can pass some
IADLs, all BADLs
Dressing
Eating
Transferring
Can pass all IADLs May be homebound Needs home or
institutional care
12. ’üĮ Defining Falls
ŌŚ” ņ×äņāü : falling ņØĆ ļĢģņŚÉ ļäśņ¢┤ņ¦ĆĻ▒░ļéś ļĢģņŚÉ ļäśņ¢┤ņĀĖ ņ׳ļŖö ņāüĒā£ļĪ£ ļ░£
Ļ▓¼ļÉśļŖö Ļ▓ā .
’é¢ ņśłņÖĖņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ņØśļÅäĒĢśņ¦Ć ņĢŖĻ▓ī ĻĘ╝ņ▓śņØś Ēæ£ļ®┤ņŚÉ ņĀæņ┤ē ( ņØśņ×É ļ▓Įļ®┤ ) ĒĢ┤ņä£ ĻĘĀĒśĢņØä ĒÜī
ļ│ĄĒĢśļŖö Ļ▓āņØä ĒżĒĢ© .
ŌŚ” ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ĒÖśĻ▓Į : (safety harness) limit of base of support ļ░¢ņ£╝ļĪ£
center of mass Ļ░Ć ļ░¢ņ£╝ļĪ£ ļéśĻ░ĆļŖö ņāüĒÖ®ņØä falling or loss of
balance ļĪ£ ņĀĢņØś
’é¢ ļŗ©ņĀÉ stepping ĒżĒĢ© ( ļ╣äļĪØ ņĀŖņØĆņØ┤ņÖĆ ļģĖņØĖņØś strategy Ļ░Ć ļŗżļź╝ņ¦ĆļØ╝ļÅä )
ŌŚ” ņĢ×ņ£╝ļĪ£ ļ¦ÉĒĢĀ falling ņŚÉļŖö ņ¦Ćņ¦Ćļ®┤ņØĆ floor ļ┐Éļ¦ī ņĢäļŗłļØ╝ ņØśņ×É ļ▓Į
ļ®┤ļÅä ĒżĒĢ©
13. ’üĮ Risk factors for falls
ŌŚ” ĒåĄĻ│äņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ falling ņØĆ 75 ņäĖ ņØ┤ņāüņŚÉņä£ 7th
cause of death (Ochs et all.1985).
ŌŚ” ņ¦ĆņŚŁņé¼ĒÜīņŚÉ Ļ▒░ņŻ╝ĒĢśļŖö 65 ņäĖ ņØ┤ņāüņØś ļģĖņØĖņØś Falling rate ļŖö ļģäļŗ╣ 33%, ņŚ¼ņä▒ņØ┤
ļé©ņä▒ļ│┤ļŗż ļŹöņÜ▒ ļ╣łļ▓ł ( Campbell et al, 1991. Nevitt et al 1989).
ŌŚ” Loss of Balance ņŚÉ ņśüĒ¢źņØä ļ»Ėņ╣śļŖö ņÜöņåīļŖö ļ¼┤ņŚćņØĖĻ░Ć ?
’é¢ Single Cause(Vertigo, Sensory neuropathy, postural hypotention)
’é¢ Multiple Cause (Extrinsic factors : Ļ│äļŗ© , ņ¢æĒāäņ×É ,poor light & Intrinsic factors :
Physiological, musculoskeletal, psychosocial factors( Tineti et al, 1986, Campbell et al,
1989).
ŌŚ” Falling ņØĆ Ļ░£ņØĖņĀüņØĖ ņÜöņåī ĒĢśļéśļ¦īņ£╝ļĪ£ Ļ▓░ņĀĢļÉśļŖö Ļ▓āņØ┤ ņĢäļŗłļØ╝ ĒŖ╣ļ│äĒĢ£
environment ņŚÉņä£ ĒŖ╣ļ│äĒĢ£ Task ļź╝ ņłśĒ¢ēĒĢśļŖö Ļ░£ņØĖļōżņØś ņāüĒśĖ ņ×æņÜ®ņŚÉņä£
ļéśĒāĆļé£ļŗż .
14. ŌĆó Risk factors
ŌĆō Individual factors : age >64 ļé© < ņŚ¼
ŌĆō Psychological factors : Depressed or anxious fear of a falling. ņé¼ĒÜī
ņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ Ļ│Āļ”ĮļÉ£ ĒÖśĻ▓Į ( ņŻ╝ļŗ╣ 1 ĒÜī ņØ┤ĒĢśņØś ņÖĖņČ£ ) (Nevitt et al. 1999)
ŌĆō ĒÖśĻ▓ĮņĀü ņÜöņåī Ļ│äļŗ© , ņ¢æĒāäņ×É , ļ»Ėļüäļ¤¼ņÜ┤ Ēæ£ļ®┤ , poor lighting
(Rvbenstem 1988, Dheldon, 1980).
ŌĆō Lipisitz ļŖö ņ¦ĆņŚŁņé¼ĒÜīņŚÉ Ļ▒░ņŻ╝ĒĢśļŖö 70 ņäĖ ņØ┤ņāüņØś ļģĖņØĖļōżņØś falling ņØś
ņĀäņłśļź╝ ņĪ░ņé¼ ņøÉņØĖņØä ĒīīņĢģĒ¢łļŗż .
ŌĆó Ļ░ÉņåīļÉ£ ņŗĀņ▓┤ņĀü ĒÖ£ļÅÖ , Ļ░ÉņåīļÉ£ ĻĘ╝ņ£äļČĆ ĻĘ╝ļĀź , Ļ░ÉņåīļÉ£ Quiet stance stability,
ŌĆó ņØ┤ņÖĖņŚÉ knee arthritis, stroke impairment of gait, hypotension, psychotropic drug
ŌĆō ļģĖņØĖņØś falling ņŚÉļŖö multiple factors ļōżņØ┤ ņĪ┤ņ×¼ĒĢśļ®░ ņØ┤ ņŚ¼ļ¤¼ ņÜöņØĖ
ļōżņØĆ ĻĄÉņĀĢņØ┤ Ļ░ĆļŖźĒĢ£ ņÜöņåīļōżļĪ£ ĻĄ¼ņä▒ļÉśņ¢┤ņ׳ļŗż .
15. ŌĆó ļģĖņØĖĻ│╝ ĒĢ©Ļ╗ś ņØ╝ņØä ĒĢ┤ņĢ╝ ĒĢśļŖö ņ╣śļŻīņé¼ļōżņØĆ falling ņŚÉ Ļ┤Č─ņŚ¼ļÉ£ ļé┤ . ņÖĖņĀü
ņÜöņåīļōżņØä ņłÖņ¦ĆĒĢ┤ņä£ ĒŖ╣ļ│äĒĢ£ ņāüĒÖ®ņŚÉņä£ ļéśĒāĆļéśļŖö falling ņØä Ļ░Éņåī ņŗ£Ēéż
Ļ▒░ļéś ĻĄÉņĀĢĒĢĀ ņłś ņ׳ņ¢┤ņĢ╝ ĒĢ£ļŗż (Lipsitz et al, 1999).
ŌĆó Falling ņŚÉ ļåÆņØĆ ņ£äĒŚśņØä Ļ░Ćņ¦ä ļīĆņāüņ×ÉļōżņØĆ ĻĘĀĒśĢĻ│╝ Ļ┤Č─ļĀ©ļÉ£ functional
skill( ņĢēĻĖ░ , ņä£ĻĖ░ , ņä£ņä£ reaching, 360* ļÅīĻ│Ā ņä£ĻĖ░ , ņĢēņØĆ ņāüĒā£ņŚÉņä£ ņä£
ĻĖ░ , ļČĆņČĢ ņŚåņØ┤ Ļ▒ĘĻĖ░ ) ņØä ņĖĪņĀĢĒĢ£ Ļ▓░Ļ│╝ ņØ┤ ļæśņØĆ ņä£ļĪ£ ņāüĻ┤Č─Ļ┤Č─Ļ│äĻ░Ć ņ׳
ļŗż (Tinetti et al1996 ; Mathias, 1986).
ŌĆó ņĢ×ņ£╝ļĪ£ ļģĖņØĖļōżņØś balance function ņØä ņØ┤ĒĢ┤ĒĢśĻĖ░ ņ£äĒĢśņŚ¼ normal
postural control ņŚÉ Ļ┤Č─ļĀ© ļÉś ļ¦ÄņØĆ ļ│Ćņłśļōż ņżæ ļģĖņØĖļōżņØś stability &
mobility ņŚÉ Ļ┤Č─ļĀ©ļÉ£ ņÜöņåīļōż ņżæ ļé┤ņĀü ņÜöņØĖņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢśņŚ¼ ņé┤ĒÄ┤ļ│┤ļÅäļĪØ ĒĢ£ļŗż .
17. ’üĮ Age- Related Changes in the systems of Postural Control
ŌŚ” Musculoskeletal System
’é¢ Muscle Strength
’é¢ Range of Motion
ŌŚ” Neuromuscular System
’é¢ Changes in Quiet Stance
’é¢ Changes in Motor Strategies
’é¢ Adapting movement to changing tasks and environments
ŌŚ” Sensory systems
’é¢ Changes in individual Sensory
’é¢ somatosensory system
’é¢ Vision
’é¢ Vestibular
’é¢ Multisensory Deficit
’é¢ Anticipatory postural abilities
’é¢ Cognitive Issues and posture control
18. ŌĆó 1 musculoskeletal system
ŌĆō Muscle strength
ŌĆó Strength ļŖö ļéśņØ┤Ļ░Ć ļōżļ®░ Ļ░ÉņåīĒĢ£ļŗż . ĒĢśņ¦ĆņØś Ļ▓ĮņÜ░ 30-80 ļīĆļź╝ ļ╣äĻĄÉĒĢ┤ņä£ 40%
Ļ░Éņåī (Aniansson, 1986).
ŌĆó ņØ┤ņÖĆ Ļ░ÖņØĆ ņāüĒÖ®ņØĆ ļäśņ¢┤ņ¦ä Ļ▓ĮĒŚśņØ┤ ņ׳ļŖö nursing home ņŚÉ Ļ▒░ņŻ╝ĒĢśļŖö ļģĖņØĖļōżņŚÉĻ▓ī
ļŖö Ēø©ņö¼ ņŗ¼Ļ░üĒĢśĻ▓ī ļéśĒāĆļé£ļŗż . ļäśņ¢┤ņ¦ä ņé¼ļ×īņØś Ļ▓ĮņÜ░ ļäśņ¢┤ņ¦Ćņ¦Ć ņĢŖņØĆ Ļ▓ĮņÜ░ņŚÉ ļ╣äĒĢ┤
knee, ankle ņØś strength ļŖö Ļ░üĻ░ü ┬Į, ┬╝ ņłśņżĆņØ┤ņŚłļŗż (whipple et al., 1987).
ŌĆō Endurance
ŌĆó ļéśņØ┤ņŚÉ ļö░ļØ╝ Ļ░ÉņåīĒĢśņ¦Ćļ¦ī strength ņŚÉ ļ╣äĒĢ┤ ļ¦ÄņØ┤ ņ×öņĪ┤ĒĢ£ļŗż .
ŌĆó ļéśņØ┤Ļ░Ć ļōżņ¢┤Ļ░Ćļ®┤ņä£ muscle size ļŖö ņ×æņĢäņ¦ĆĻ│Ā Muscle mass ļŖö ņāüņ¦ĆņŚÉ ļ╣äĒĢ┤ ĒĢśņ¦Ć
ņŚÉņä£ Ēü¼Ļ▓ī Ļ░ÉņåīĒĢ£ļŗż (Medina., 1996)
ŌĆó Muscle cell die-’āĀ connective tissue, fat
ŌĆó Muscle fiber type: Type II fast twitch >Type I ļ╣ĀļźĖ ļ╣äņ£©ļĪ£ Ļ░Éņåī (timiras., 1994).
ŌĆó Motor unit(large & small myelinate fiber) Ļ░Éņåī & neuromuscular junction
(Medina., 1996).
19. ŌĆó 1 musculoskeletal system
ŌĆó Maximal isometric force Ļ░Éņåī
ŌĆó Muscle fatigue ļ╣©ļØ╝ņ¦ĆĻ│Ā tension ņØä ļ¦īļō£ļŖö ņåŹļÅäĻ░Ć Ļ░ÉņåīĒĢśļ»ĆļĪ£ concentric contraction>
eccentric contraction
ŌĆó Rapid velocity contraction > Slow velocity contraction.
ŌĆó Strength ņÖĆ physical function ņØś Ļ┤Č─Ļ│ä
ŌĆō functional status ņØś 20% Ļ░Ć strength ņŚÉ ņØśĒĢ┤ ņäżļ¬ģ (Buchner and Lateur, 1991).
ŌĆó Physical function ņŚÉ ĒĢäņÜöĒĢ£ strength ļŖö task ņŚÉ ļŗ¼ļĀĖļŗż .
ŌĆō Ex. 80 ņäĖ ņŚ¼ņä▒ņØĆ quadriceps m. ņØśņ×ÉņŚÉņä£ ņØ╝ņ¢┤ļéśļŖöļŹ░ ĒĢäņÜöĒĢ£ ņŚŁņ╣ś ņØ┤ĒĢśņØ╝ Ļ▓ĮņÜ░Ļ░Ć ĒØöĒĢś
ļŗż (young, 1986).
ŌĆó Task ņŚÉ ĒĢäņÜöĒĢ£ ņŚŁņ╣ś ņØ┤ĒĢśļĪ£ strength Ļ░Ć ļ¢©ņ¢┤ņ¦ĆĻ▓ī ļÉśļ®┤ functional disability Ļ░Ć ņāØĻĖ░Ļ▓ī ļÉ£ļŗż
.
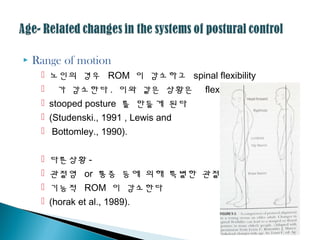
20. ’üĮ Range of motion
’é¢ ļģĖņØĖņØś Ļ▓ĮņÜ░ ROM ņØ┤ Ļ░ÉņåīĒĢśĻ│Ā spinal flexibility
’é¢ Ļ░Ć Ļ░ÉņåīĒĢ£ļŗż . ņØ┤ņÖĆ Ļ░ÖņØĆ ņāüĒÖ®ņØĆ flexed,
’é¢ stooped posture ļź╝ ļ¦īļōżĻ▓ī ļÉ£ļŗż
’é¢ (Studenski., 1991 , Lewis and
’é¢ Bottomley., 1990).
’é¢ ļŗżļźĖņāüĒÖ® -
’é¢ Ļ┤Č─ņĀłņŚ╝ or ĒåĄņ”Ø ļō▒ņŚÉ ņØśĒĢ┤ ĒŖ╣ļ│äĒĢ£ Ļ┤Č─ņĀłņØś
’é¢ ĻĖ░ļŖźņĀü ROM ņØ┤ Ļ░ÉņåīĒĢ£ļŗż
’é¢ (horak et al., 1989).
22. ’üĮ Neuromuscular system
ŌŚ” Changes in quiet stance
ŌŚ” Changes in motor strategies during perturbed stance
ŌŚ” Adapting Movements to changing tasks and
environments
23. ’üĮ Changes in quiet stance
ŌŚ” Postural Sway ŌĆōbalance function ņØś global indicator (Sheldon., 1963).
ŌŚ” ņĄ£ĻĘ╝ stabilometer or static force plate ļź╝ ņØ┤ņÜ® Ļ░üĻĖ░ ļŗżļźĖ age Ļ░ä
ņØś spontaneous sway ļź╝ ņĖĪņĀĢ .
ŌŚ” 40-80 ņäĖ ņŗĀĻ▓ĮĒĢÖņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ļ¼ĖņĀ£ņŚåļŖö 500 ļ¬ģņØä ļīĆņāüņ£╝ļĪ£ postural sway ņĖĪņĀĢ .
10 ļģä Ļ░äĻ▓®ņ£╝ļĪ£ postural sway ņ”ØĻ░Ć 80 ņäĖ Ļ╣īņ¦Ć Ļ│äņåŹņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ņ”ØĻ░Ć
(Toupet et al,. 1992).
ŌŚ” ļäśņ¢┤ņ¦ä ņĀüņØ┤ ņŚåļŖö Ļ▒┤Ļ░ĢĒĢ£ ļģĖņØĖņØä ļīĆņāüņ£╝ļĪ£ spontaneous sway ļź╝ ņĖĪņĀĢĒĢ£
Ļ▓░Ļ│╝ ņĀŖņØĆņØ┤ņŚÉ ļ╣äĒĢ┤ ĒåĄĻ│äņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ sway ļ▓öņ£äĻ░Ć ņØśļ»Ė ņ׳Ļ▓ī ņ”ØĻ░ĆļÉśņŚłĻ│Ā ļäś
ņ¢┤ņ¦ä Ļ▓ĮĒŚśņØ┤ ņ׳ļŖö ļģĖņØĖĻĄ░ņØś Ļ▓ĮņÜ░ Ļ░Ćņן ļ¦ÄņØ┤ ņ”ØĻ░Ć ļÉśņ¢┤ ņ׳ņŚłļŗż
(Shumway-cook., 1997).
24. ’üĮ Changes in quiet stance
ŌŚ” Ferine(1992) ņ¢æļĪ£ņøÉņŚÉ ņłśņÜ®ļÉ£ ļģĖņØĖļōżņØś sway amplitude & velocity ņĖĪņĀĢ .
’é¢ Sway velocity (Not amplitude) ņØś Ļ▓ĮņÜ░ ĒĢ£ļ▓łļÅä ņĢł ļäśņ¢┤ņ¦ä ļģĖņØĖļ│┤ļŗż ĒĢ£ļ▓łņØ┤ļØ╝ļÅä ļäśņ¢┤ņ¦ä
ļģĖņØĖņØś Ļ▓ĮņÜ░ ņØśļ»Ė ņ׳Ļ▓ī ņ”ØĻ░ĆļÉśņ¢┤ ņ׳ņŚłļŗż .
’é¢ ĒŖ╣ļ│äĒĢ£ ņØĖĻĄ¼ņ¦æļŗ©ņØś Ļ▓ĮņÜ░ ņĀäņ▓┤ņĀüņØĖ sway ļ│┤ļŗż sway velocity Ļ░Ć ļ│┤ļŗż balance ļ¼ĖņĀ£
ņŚÉ ļ»╝Ļ░ÉĒĢśĻ▓ī ņ×æņÜ® .
ŌŚ” Patla(1990) ņĀĢņāüņĀüņØĖ quiet stance ņāüĒā£ņŚÉņä£ spontaneous sway ņĖĪņĀĢņØĆ
balance control ņØä ņĖĪņĀĢĒĢśļŖöļŹ░ ņĀüņĀłĒĢśņ¦Ć ļ¬╗ĒĢśļŗż .
’é¢ tenderm stance ŌĆō with eye open VS close
’é¢ Horak(1992) ņŗĀĻ▓ĮĒĢÖņĀü ņ¦łĒÖśņØä Ļ░Ćņ¦ä ņŚ¼ļ¤¼ ĒÖśņ×É (such as parkinsonŌĆÖs disease) ļōżņØś Ļ▓ĮņÜ░
quiet stance ņŚÉņä£ ļéśĒāĆļé£ sway ļŖö ņĀĢņāü Ēś╣ņØĆ ĻĘĖ ņØ┤ĒĢśļĪ£ ņĖĪņĀĢ ļÉśņŚłļŗż .
25. ’üĮ Changes in motor strategies during perturbed stance
ŌŚ” ļģĖņØĖņØś Ļ▓ĮņÜ░ņÖĖļČĆņŚÉņä£ Ēś╝ļ×Ćļ│ĆņłśĻ░Ć ņāØĻĖĖ Ļ▓ĮņÜ░ balance ļź╝ ņ£Āņ¦ĆĒĢĀ ļĢī ņĀüņĀłĒĢ£
timing, force, muscle ļō▒ļō▒ņØś muscle response ļź╝ ņĪ░ņ¦üĒĢśļŖö synergy ļŖźļĀźņØĆ ņ¢┤
ļŖÉ ņĀĢļÅäņØĖĻ░Ć ?
’é¢ Moving platform (balance perturbation)
’é¢ EMG( postural m. onset latency, duration, magnitude)
’é¢ Kinematics( changes in COM, perturbated balance joint angle)
’é¢ Kinetics( force(COP) Ļ░Ć pertubated ļÉśņŚłņØä ļĢī ļ░śņØæĻ│╝ ĒÜīļ│Ą ņŗ£ ļ░śņØæ .
ŌŚ” Wollacott(1986) postural m. ņØś pertubated ļÉśņŚłņØä ņŗ£ ļ░śņØæ ĒŖ╣ņ¦Ģ
’é¢ 61 ┬▒ 78 vs. 19 ┬▒ 38 ņØś muscle response organization ņØĆ ļ╣äņŖĘ .
’é¢ Response characteristic ņé¼ņØ┤ņØś ņ░©ņØ┤ņĀÉ
’é¢ Nashner ļō▒ (1983) ņØĆ ņØ┤ņÖĆĻ░ÖņØĆ response dysfunction ņØĆ CNS dysfunction ņØ┤ ņ׳ļŖö ĒÖś
ņ×ÉņŚÉĻ▓īņä£ļÅä ļ░£Ļ▓¼ ļÉśņŚłļŗż .
26. ’üĮ Changes in motor strategies during perturbed stance
ŌŚ” Horak and mancherter( 1999) ļŖö ņĀŖņØĆņØ┤ļōżņŚÉ ļ╣äĒĢ┤ ļģĖņØĖļōżņØś Ļ▓ĮņÜ░ hip strategy
ļź╝ ņé¼ņÜ®
’é¢ ankle m. weakness, peripheral sensory function loss ļ│æņĀüņØĖ condition.
ŌŚ” Horak (1999) ņØĆ hip strategy’āĀ falling down
ŌŚ” Lin1998,Wollactt,1999
27. ’üĮ Adapting movements to changing tasks and environments
ŌŚ” ļ¼ĖņĀ£ņĀ£ĻĖ░ : Perturbation ņØś Ēü¼ĻĖ░ņÖĆ ņåŹļÅäļź╝ ļŗ¼ļ”¼ ĒĢśļ®░ ļÅÖņŗ£ņŚÉ ņŻ╝ļ│Ć ĒÖśĻ▓ĮņØä ļ│Ć
ĒÖö ņŗ£ņ╝£ balance condition ņØä ļ│ĆĒÖö ņŗ£ņ╝░ņØä ļĢī response ļŖö ņ¢┤ļ¢╗Ļ▓ī ņĀüņØæĒĢśļ®░
ļ│ĆĒÖö ĒĢĀĻ╣ī ? (Lin.,1998 ; Woolacott et al. 1999)
’é¢ Ļ░Ćņäż . Ļ░üĻĖ░ ļŗżļźĖ Ēü¼ĻĖ░ņØś perturbation ņØä ņĀ£Ļ│Ą Ē¢łņØäņŗ£ stable vs. unstable old adults ņØś
ĒÜ©Ļ│╝ņĀü ļīĆņØæņŚÉļŖö ņ░©ņØ┤Ļ░Ć ņ׳ņØä Ļ▓āņØ┤ļŗż .
’é¢ ļīĆņāüņ×É . Young(25 ┬▒ 4) stable(76 ┬▒6) & unstable(74 ┬▒ 4) old adults (dynamic gait index,
berg functional balance test, test of self ŌĆōperceived balance ability)
’é¢ ņŗżĒŚśļ░®ļ▓Ģ . Slow and small forward perturbation(fast and large) ņŚÉņä£ 3 Ļ░Ćņ¦Ć ĻĘ╝ņ£Ī (tibialis
anerior, quadriceps, abdominalis) ņØś onset latencies ļź╝ ņĪ░ņé¼
’é¢ Ļ▓░Ļ│╝ . Slow and small forward perturbation - ņĀŖņØĆņØ┤ņŚÉ ļ╣äĒĢ┤ ļģĖņØĖ group ņØĆ delay
’é¢ fast and large perturbation -unstable old adults ļ¦ī ņĀŖņØĆņØ┤ņŚÉ ļ╣äĒĢ┤ ņ”ØĻ░Ć
’é¢ Ļ▓░ļĪĀ . Stable old adults ņØś Ļ▓ĮņÜ░ slow-small perturbation ņŚÉņä£ sensing ņŚÉ ņ¢┤ļĀżņøĆņØä ļ│┤
ņØ┤Ļ│Ā large scale perturbation ņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ┤ņä£ļŖö ņĀüņĀłĒĢ£ ļ░śņØæņØä ļ│┤ņØĖļŗż .
’é¢ Unstable old adults ņØś Ļ▓ĮņÜ░ muscle response amplitude ņØś ĒÖ£ņä▒ļÅäļź╝ ņĪ░ņé¼ĒĢ£ Ļ▓░Ļ│╝ TA
response Ļ░Ć ĒśäņĀĆĒ׳ ņ×æĻ▓ī ļéśĒāĆļé¼ļŗż .
29. ’üĮ Adapting movements to changing tasks and environments
ŌŚ” Lin(1998) Wollacott(1989)
’é¢ ļģĖņØĖļōżņØ┤ Ļ░üĻ░ü ļŗżļźĖ Ēü¼ĻĖ░ņÖĆ ņåŹļÅäņØś
’é¢ perturbation ņŚÉ ņé¼ņÜ®ĒĢśļŖö voluntary
’é¢ capacity ņØś maximal capacity ļź╝
’é¢ ņĖĪņĀĢĒ¢łļŗż .
’é¢ Gastrocnemius capacity
’é¢ ĻĘĖļ”╝ņŚÉņä£ ļ│Ė Ļ▓āĻ│╝ Ļ░ÖņØ┤
’é¢ ņĀŖņØĆņØ┤ņÖĆ ļģĖņØĖ ļ¬©ļæÉ small
’é¢ perturbation ņŚÉņä£ ņĀäņ▓┤ max ņØś
’é¢ 20% unstable old adults ņØś Ļ▓ĮņÜ░
’é¢ 40% ņé¼ņÜ®
30. ’üĮ Adapting movements to changing tasks and environments
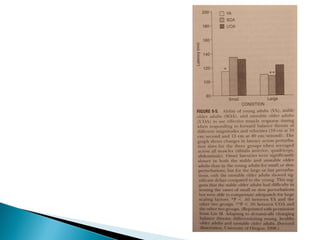
ŌŚ” Muscle response characteristics ņÖĆ behavior change ņÖĆņØś Ļ┤Č─Ļ│äļź╝ ņĢīņĢäļ│┤ĻĖ░ ņ£ä
ĒĢ┤ 3 group ņØä ļ╣äļööņśż ļČäņäØ
ŌŚ” Step ņØ┤ ĒĢäņÜöĒĢśņ¦Ć ņĢŖņØĆ slow- small perturbation ņŚÉņä£ 3group ņØś strategy ņØś ņ░©ņØ┤
’é¢ Stable & unstable old adults- ankle strategy<hip strategy
’é¢ unstable old adults ŌĆō knee bending both hand
’é¢ Large-fast perturbation ŌĆō stepping
31. ’üĮ Adapting movements to changing tasks and environments
ŌŚ” Perturbations & ļéśņØ┤ņŚÉ ļö░ļźĖ postural response ĒŖ╣ņ¦ĢņØ┤ ļŗżļź┤Ļ▓ī
ļéśĒāĆļéśļŖö ņØ┤ņ£ĀļŖö ?
’é¢ ņ×äņāüņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ļ│┤ņĢśņØä ļĢī ļģĖņØĖļōżņØĆ ņĀŖņØĆņØ┤ļōżĻ│╝ ļ╣äĻĄÉ Ē¢łņØä ļĢī muscle strength Ļ░Ć ņØśļ»Ė ņ׳Ļ▓ī ņ×æņĢśļŗż .
’é¢ Muscle strength Ļ▓Ćņé¼Ļ▓░Ļ│╝ņÖĆ functional balance test ņĀÉņłśņÖĆ ņØśļ»Ė ņ׳ļŖö ņāüĻ┤Č─Ļ┤Č─Ļ│äĻ░Ć ņ׳ņŚłļŗż .
’é¢ Vibration & proprioceptive score ņŚÉņä£ unstable ļģĖņØĖņØ┤ ļŗżļźĖ ļæÉ ņ¦æļŗ©ņŚÉ ļ╣äĻĄÉĒĢ┤ ĒśäņĀĆĒ׳ ļé«ņØĆ ņĀÉņłś
ļź╝ ļéśĒāĆļāłļŗż .
’é¢ Poor cutaneous vibration score ņÖĆ high peak angular displacement ņŚÉņä£ ņØśļ»Ė ņ׳ļŖö ņāüĻ┤Č─Ļ┤Č─Ļ│äĻ░Ć ņ׳
ņŚłļŗż .
32. ’üĮ Adapting movements to changing tasks and environments
’üĮ ņÜöņĢĮ
’üĮ Stable and unstable old adults ļ¬©ļæÉ posture control ņŚÉ ņśüĒ¢źņØä
ļ»Ėņ╣śļŖö motor system ņŚÉ ļ│ĆĒÖöĻ░Ć ņāØĻ▓╝ļŗż .
’üĮ Motor system ņØś ļ│ĆĒÖöņŚÉļŖö
1. Muscle weakness.
2. Impaired timing and organization among synergistic muscle
activated in response to instability.
3. Limitation in the ability to adapt movement for balance in
response to changing task and environmental demands.
34. ’üĮ Sensory system
ŌŚ” Changes in individual sensory systems
’é¢ Somatosensory
’é¢ Vision
’é¢ Vestibular
’é¢ Multisensory deficit
35. posture & Sensory system
ŌŚ” Sensory system ņØś ļ│ĆĒÖöĻ░Ć posture & balance control ņŚÉ ņ¢┤ļ¢╗Ļ▓ī ņśüĒ¢źņØä ļ»Ė
ņ╣śļŖöĻ░Ć ?
’üĮ Change in individual sensory systems
ŌŚ” Somatosensory system
’é¢ Kenshalo(1979) vibratory sensory threshold : 90 ņäĖ Ļ╣īņ¦Ć ņ”ØĻ░Ć
’é¢ Vibratory threshold : ņāüņ¦Ć < ĒĢśņ¦Ć
’é¢ Whanger and Wang 1974 :
’é¢ Bruce 1980: tactile sensation
’é¢ Meissner end organs and pacinian corpuscle ņ¢æĻ│╝ ņ¦łņØś ļ¼ĖņĀ£
’é¢ ĻĖ░ļŖźņĀü ĒÜ©Ļ│╝ļŖö receptor ņØś ņåÉņŗżļÉ£ ņł½ņ×ÉņŚÉ ņÜ░ņäĀņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ņśüĒ¢ź
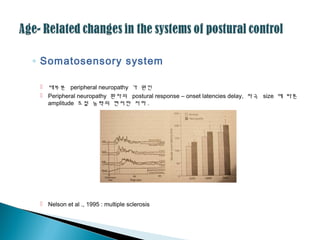
36. ŌŚ” Somatosensory system
’é¢ ļīĆļČĆļČä peripheral neuropathy Ļ░Ć ņøÉņØĖ
’é¢ Peripheral neuropathy ĒÖśņ×ÉņØś postural response ŌĆō onset latencies delay, ņ×ÉĻĘ╣ size ņŚÉ ļö░ļźĖ
amplitude ņĪ░ņĀł ļŖźļĀźņØś ĒśäņĀĆĒĢ£ ņĀĆĒĢś .
’é¢ Nelson et al ., 1995 : multiple sclerosis
37. ’üĮ Vision
’é¢ Retina
’é¢ Visual threshold
’é¢ Visual field
’é¢ Visual acuity
’é¢ Visual contrast sensitivity
’é¢ Cataract
’é¢ Macular degeneration
’é¢ Peripheral vision loss- chemical retinal or brain disease
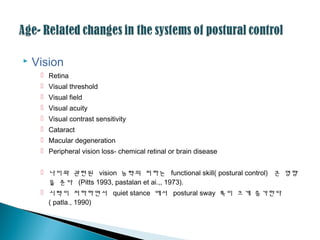
’é¢ ļéśņØ┤ņÖĆ Ļ┤Č─ļĀ©ļÉ£ vision ļŖźļĀźņØś ņĀĆĒĢśļŖö functional skill( postural control) Ēü░ ņśüĒ¢ź
ņØä ņżĆļŗż (Pitts 1993, pastalan et ai.,, 1973).
’é¢ ņŗ£ļĀźņØ┤ ņĀĆĒĢśĒĢśļ®┤ņä£ quiet stance ņŚÉņä£ postural sway ĒÅŁņØ┤ Ēü¼Ļ▓ī ņ”ØĻ░ĆĒĢ£ļŗż
( patla., 1990)
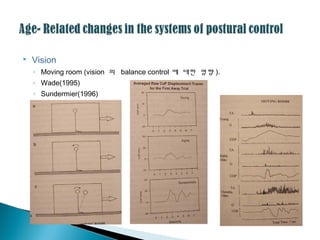
38. ’üĮ Vision
ŌŚ” Moving room (vision ņØś balance control ņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ņśüĒ¢ź ).
ŌŚ” Wade(1995)
ŌŚ” Sundermier(1996)
39. Vestibular
Rosenhall and rubin,1975: 70 age vestibular hair &cell 40%
Black and Nashner,1985 : reference system (compared and
calibrated)
Vestibular System ĻĖ░ļŖź
Visual system & somatosensory system ņāüĒśĖ ņČ®ļÅīņØ┤ ņāØĻĖĖ ļĢī ņżæņÜö
ņä▒
Vision & somatosensory system ņØś ņČ®ļÅī ņŗ£ ņÖäļ▓ĮĒĢ£ reference
system ņØś ņŗĀļó░ņä▒ņØ┤ ļ¢©ņ¢┤ņ¦ł Ļ▓ĮņÜ░ dizziness or unsteadiness ņØś
ņøÉņØĖņØä ļ¦īļōĀļŗż .
40. Multisensory Deficit
ĒĢśļéśņØ┤ņāüņØś sensory ņåÉņāüņØä ņØśļ»ĖĒĢśļŖö Ļ▓āņ£╝ļĪ£ balance & mobility ņŚÉ ļŹöņÜ▒ ņ╗żļŗżļ×Ć ņśüĒ¢źņØä ļ»Ėņ╣£ļŗż .
Adapting senses for postural control
Wolfson et al,1985; Wollacott et al., 1986 ļōżņØĆ posturography testing ņØä ņØ┤ņÜ® Ļ▒┤Ļ░ĢĒĢ£ ļģĖņØĖļōżņØś quite stance ļÅÖņĢł
ņŚÉ ļ│ĆĒÖöĒĢśļŖö condition ņŚÉ sensory adaptation
’üĮ 1.somatosensory & visual input ņŚÉ ņśüĒ¢źņØ┤ ņŚåņ£╝ļ®┤
’üĮ (5,6) ņĀŖņØĆņØ┤ņÖĆ ļģĖņØĖĻ│╝ ņ░©ņØ┤Ļ░Ć ņŚåļŗż
’üĮ 2. condition 5,6 ņŚÉņä£ ļģĖņØĖņØś 50% ļŖö ĻĘĀĒśĢņØä ņ×āņŚłĻ│Ā ,
’üĮ ņ▓½ ļ▓łņ¦Ė ņŗ£ļÅäņŚÉņä£ assist ĒĢäņÜöĒ¢łļŗż . ĻĘĖļ”¼Ļ│Ā ļæÉ ļ▓łņ¦Ė
’üĮ ņŗ£ļÅäņŚÉņä£ ļČĆĒä░ļŖö ĻĘĀĒśĢņØä ņ¢┤ļĀĄņ¦Ćļ¦ī ņ£Āņ¦Ć Ē¢łļŖöļŹ░ ņØ┤ļ¤░
’üĮ Ļ▓āņ£╝ļĪ£ ļ│┤ņĢä postural control ņØä ņ£äĒĢ£ sensory adapt
’üĮ ļŖźļĀźņØ┤ ņ׳ļŖö Ļ▓āņ£╝ļĪ£ ļ│┤ņØĖļŗż ĒĢśņ¦Ćļ¦ī ņØ┤ļŖö ņŚ░ņŖĄļ¦īņØä
’üĮ ĒåĄĒĢ┤ņä£ļ¦ī Ļ░ĆļŖźĒ¢łļŗż (wollacott et al. 1986).
’üĮ 3. ļģĖņØĖļōżņØś postural control ņØĆ single sense ņØś ņĀĢĒÖĢņä▒ņØ┤
’üĮ Ļ░ÉņåīĒĢśĻ▒░ļéś Ļ░ÉĻ░üņØä ņØ┤ņÜ®ĒĢĀ ņłś ņ׳ļŖö ļŖźļĀźņØ┤ Ļ░ÉņåīĒĢ£ Ļ▓ĮņÜ░
’üĮ postural sway Ļ░Ć ņ”ØĻ░Ć Ē¢łļŗż . Ļ▒┤Ļ░ĢĒĢ£ ļģĖņØĖņØś Ļ▓ĮņÜ░ļØ╝ļÅä ļæÉ Ļ░£ņØś
’üĮ Ļ░ÉĻ░üņØ┤ Ļ░Éņåī Ē¢łņØä Ļ▓ĮņÜ░ postural steadiness ņŚÉ ņŗ¼Ļ░üĒĢ£ ņśüĒ¢źņØä ļ»Ėņ│żļŗż .
41. ’üĮ Adapting senses for postural control
’üĮ Horak ļō▒ 1989 ņØĆ quite stance ļÅÖņĢł ļ│ĆĒÖöĒĢśļŖö sensory information ņŚÉ adaptation ĒĢśļŖö ļŖźļĀźņŚÉ
ļīĆĒĢśņŚ¼ ņŚ░ĻĄ¼
Ļ│╝Ļ▒░ļĀźņāü ļäśņ¢┤ņ¦ä ņĀü ņŚåļŖö 70 ņäĖ ļģĖņØĖ (asymptoatics)
ļäśņ¢┤ņ¦ä ņĀüņØ┤ ņ׳ļŖö 70 ņäĖ ļģĖņØĖ (symptomatic)
ņĀŖņØĆņØ┤ (20-39)
Condition 3 ņŚÉņä£ ļæÉ ļģĖņØĖ group ņØś 20 % ĻĘĀĒśĢņØä ņ×āņØī
Asymptomatic ļģĖņØĖ condition 6 40% ļäśņ¢┤ņ¦É ļīĆņĪ░ņĀü
ņ£╝ļĪ£ ņĀŖņØĆ ņ¦æļŗ©ņØĆ 10% ļäśņ¢┤ņ¦É
Symptomatic ņ¦æļŗ©ņØś Ļ▓ĮņÜ░ 4,5,6 ņŚÉņä£ Ļ▒░ņØś ļīĆļČĆļČä
ĻĘĀĒśĢņØä ņ×āņØī
ļģĖņØĖļōżņØ┤ ĻĘĀĒśĢņØä ņ£Āņ¦Ć ĒĢĀ ļĢī ļōżņ¢┤ņśżļŖö ļŗżļźĖ Ļ░ÉĻ░ü ņĀĢļ│┤ ņżæ ĒĢäņÜöĒĢ£ ņĀĢļ│┤ļź╝ ņäĀĒāØĒĢśļŖö ļŖźļĀźĻ│╝ Ēśäņ×¼Ļ╣īņ¦Ć
ņØśņĪ┤ĒĢśļŹś Ļ░ÉĻ░üņĀĢļ│┤ļź╝ ļ│ĆĻ▓ĮĒĢśļŖö ļŖźļĀźņØ┤ postural control ņŚÉ ņżæņÜöĒĢ£ ņśüĒ¢źņØä ļ»Ėņ╣£ļŗż , ĒŖ╣Ē׳
symptomatic ĒĢ£ ļģĖņØĖļōżņŚÉĻ▓īļŖö ļŹöņÜ▒ ņżæņÜöĒĢ£ ļ¼ĖņĀ£ņØ┤ļŗż (Horak et al., 1989)
42. ’üĮ Adapting senses for postural control
’üĮ Wollacott 1989 ļō▒ņØĆ ļ░£ĒīÉņØä ĒÜīņĀäņŗ£Ēéżļ®┤ņä£ Ļ░ÉĻ░üņĀüņØæņØä ņŚ░ĻĄ¼Ē¢łļŖöļŹ░ Ļ▒┤
Ļ░ĢĒĢ£ ļģĖņØĖņØś Ļ▓ĮņÜ░ ņ▓½ļ▓łņ¦Ė ņŗ£ļÅäņŚÉņä£ 50% ņØ┤ņāüņØ┤ ļäśņ¢┤ņĪīļŗż ĒĢśņ¦Ćļ¦ī ļŗż
ņØī ņŗ£ļÅäņŚÉņä£ļŖö ļīĆņāüņ×ÉļōżņØś ļīĆļČĆļČäņØ┤ ĻĘĀĒśĢņØä ņ£Āņ¦Ć ĒĢĀ ņłś ņ׳ņŚłļŖöļŹ░ ņØ┤
ņÖĆ Ļ░ÖņØĆ ņé¼ņŗżņØĆ ļģĖņØĖļōżņŚÉĻ▓īņä£ postural control ņŚÉ ņĀüņØæ ļŖźļĀźņØ┤ ņāüļŗ╣Ē׳
ļŖÉļ”¼ļŗżļŖö Ļ▓āņØä ļ│┤ņŚ¼ņŻ╝ļŖö Ļ▓āņØ┤ļŗż .
’üĮ Wollacott et al., 196 ; Horack et al ., 1989 ; peterka & black., 1990emdeh
ņ£äņÖĆ Ļ░ÖņØ┤ ņ▓½ ļ▓łņ¦Ė ņŗ£ļÅäņŚÉņä£ ļäśņ¢┤ņ¦ĆļŖö Ļ▓ĮĒ¢źņØä ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ ļ░£Ēæ£ Ē¢łļŗż .
’üĮ ņØ┤ņÖĆ Ļ░ÖņØĆ ņé¼ņŗżņØĆ adaptability ņ×Éņ▓┤Ļ░Ć ņĢł ļÉ£ļŗżĻĖ░ ļ│┤ļŗż ļŖ”Ļ▓ī ņ¦äĒ¢ēļÉśļŖö
Ļ▓āņ£╝ļĪ£ ļ│┤ņØ┤Ļ│Ā ņāłļĪŁĻ▒░ļéś ņØĖņ£äņĀüņØĖ ņāüĒÖ®ņŚÉņä£ ļäśņ¢┤ņ¦ĆļŖö Ļ▓ĮĒ¢źņØĆ
anticipatory mechanism ņØś ļ¼ĖņĀ£ļĪ£ ļéśĒāĆļéĀ ņłś ņ׳ļŗżĻ│Ā ņĀ£ņĢłĒ¢łļŗż .
43. ’üĮ Adapting senses for postural control
ŌŚ” Nerve system function : aging ņŚÉ ļö░ļźĖ Ēö╝ĒĢĀ ņłś ņŚåļŖö ļŖźļĀź Ļ░Éņåī or postural function ņŚÉ ņśü
Ē¢źņØä ļ»Ėņ╣śļŖö ĒŖ╣ļ│äĒĢ£ subsystem ņØś borderline pathology ņØś Ļ▓░Ļ│╝ņØĖĻ░Ć ?
ŌŚ” Postural sway ņ░ĖņŚ¼ĒĢśļŖö ļīĆņāüņ×Éļź╝ ļīĆņāüņ£╝ļĪ£ borderline pathology Ļ▓Ćņé¼ņŗ£Ē¢ē
’é¢ ņ×ÉņŗĀņØ┤ ņŖżņŖżļĪ£ Ļ▒┤Ļ░ĢĒĢśļŗżĻ│Ā ļ»┐Ļ│Ā ņ׳ļŖö ļģĖņØĖ ņżæ ņŗĀĻ▓ĮĒĢÖņĀü ņåÉņāüņØ┤ ņ׳ļŖö group ļ░£Ļ▓¼
’é¢ ņŗĀĻ▓ĮĒĢÖņ×ÉļŖö ņØ┤ļōżņŚÉĻ▓ī borderline pathology Ļ░Ć ņ׳ļŗżĻ│Ā ņ¦äļŗż .
’é¢ Ex. DTR + OR - , Mild peripheral deficits, Disital weakness in TA & GCM, Abnormal
nystagmusŌĆ”
’é¢ ņŗĀĻ▓ĮĒĢÖņĀü ņåÉņāüņØ┤ ņ׳ļŖö ļģĖņØĖņØ┤ ņĀäņ▓┤ ĻĘĀĒśĢņØä ņ×āņØĆ ļīĆņāüņ×ÉņØś 58% ļź╝ ņ░©ņ¦Ć
’é¢ Aging ņ×Éņ▓┤ņØś ļ¼ĖņĀ£ļØ╝ĻĖ░ļ│┤ļŗ© sensory system ņ×Éņ▓┤ pathologies ņżæņÜöņä▒ņØä ļéśĒāĆļé┤Ļ│Ā ņ׳
ļŗż .
44. ’üĮ Anticipatory Postural Abilities
’üĮ ņĀĢņØś
’üĮ Anticipatory process : ĒŖ╣ļ│äĒĢ£ task or ĒÖśĻ▓ĮņŚÉ ĒĢäņÜöĒĢ£ ņĀüņĀłĒĢ£ motor and sensory strategies ļź╝ ņäĀĒāØĒĢśļŖö ļŖźļĀź .
’üĮ Postural adjustment : voluntary movement ļź╝ ĒĢśĻĖ░ ņĀä ņŗĀņ▓┤ļź╝ ņĢłņĀĢņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ĒĢśĻĖ░ ņ£äĒĢśņŚ¼ ņØ┤ļŻ©ņ¢┤ņ¦ĆļŖö ņØ╝ļĀ©ņØś ļÅÖņ×æ .
’üĮ Kokii(1980) anticipatory postural adjustment ņÖĆ ļéśņØ┤ņØś ņŚ░Ļ┤Č─ņä▒ ņŚÉ Ļ┤Č─ĒĢ£ ņĄ£ņ┤łņØś ņŚ░ĻĄ¼
’üĮ ļīĆņāüņ×É : ņĀŖņØĆņØ┤ (19-29) middle old adults(60-69), very old (90-99)
’üĮ ņŗżĒŚśļ░®ļ▓Ģ : ĒĢ£ļ░£ņØä ļĢģņŚÉ ņ¦Ćņ¦Ć (postural response) ĒĢśĻ│Ā ļŗżļźĖ ĒĢ£ļ░£ņØä ĻĄ¼ļČĆļ”¼ļŖö (prime mover response) Ļ│╝ņĀ£ļź╝ ņé┤ĒÄ┤ļ│┤Ļ│Ā ņĢł
ņĀĢņĀüņØĖ ņåŹļÅäņÖĆ ļ╣ĀļźĖ ņåŹļÅäļź╝ ņÜöĻĄ¼ĒĢĀ ļĢīļĪ£ ļéśļłäņ¢┤ ņŗżĒŚś .
’üĮ Ļ▓░Ļ│╝
’üĮ ļģĖņØĖ ļæÉ ņ¦æļŗ©ņØś Ļ▓ĮņÜ░ postural response & prime mover response ņØś muscle response latency Ļ░Ć ņĀŖņØĆņØ┤ņŚÉ ļ╣äĒĢ┤ ļŖÉļ”¼Ļ▓ī
ļéśņÖöļŗż .
’üĮ ļ╣ĀļźĖ ņåŹļÅäņŚÉņä£ļŖö ļģĖņØĖļ¬©ļæÉ a) postural & prime mover muscle ņé¼ņØ┤ņØś correlation Ļ░Éņåī b) onset of postural & prime
mover muscle ņé¼ņØ┤ņØś period ņØ┤ Ļ░Éņåī . Very old ņØś Ļ▓ĮņÜ░ postural & prime mover muscles ļŖö Ļ▒░ņØś ļÅÖņŗ£ņŚÉ activation ļÉś
ņŚłļŗż . Prime mover ņĀäņŚÉ postural muscles ņØ┤ ņČ®ļČäĒ׳ activation ņĢłļÉ£ Ļ▓āņØ┤ ĻĘĀĒśĢņØä ņ×āņØĆ Ļ▓āņØ┤ļØ╝Ļ│Ā Ļ▓░ļĪĀ
45. ’üĮ Anticipatory Postural Abilities
ŌŚ” Anticipatory manner ŌĆōpostural muscle response synergies ņØś ĒÖ£ņä▒ĒÖöņÖĆ aging ņØś Ļ┤Č─
Ļ│ä (Inglin and Wollacott).
’é¢ ļīĆņāüņ×É : ņĀŖņØĆņØ┤ ( ĒÅēĻĘĀ 26 ņäĖ ) ļģĖņØĖ ( ĒÅēĻĘĀ 71 ņäĖ )
’é¢ ņŗ£ĒŚśļé┤ņÜ® : ņŗ£Ļ░üņĀü ņ×ÉĻĘ╣ņŚÉ ļö░ļØ╝ ņ¢┤Ļ╣©ņ£äņ╣śņŚÉ ņ׳ļŖö ĒĢĖļōżņØä ņ×ĪņĢä ļŗ╣ĻĖ░Ļ▒░ļéś ļ»ĖļŖö Ļ│╝ņĀ£
’é¢ Ļ▓░Ļ│╝ : postural m. onset latencies Ļ░Ć ļģĖņØĖņŚÉĻ▓īņä£ ĻĖĖĻ▓ī ļéśĒāĆļé¼ļŗż .
’é¢ ņØ┤ļ░¢ņŚÉ ņŗżĒŚśņŚÉņä£ļÅä ļģĖņØĖļōżņØĆ task ņØś ļ│Ąņ×Īņä▒ņŚÉ ļö░ļØ╝ onset latencies ļŖö ļŹöņÜ▒ ĻĖĖņ¢┤ņ¦ĆļŖö Ļ▓Į
Ē¢źņØä ļ│┤ņśĆļŗż .
’é¢ Ļ▓░ļĪĀ : ļ¦ÄņØĆ ļģĖņØĖļōżņØĆ ļ╣Āļź┤Ļ│Ā ĒÜ©Ļ│╝ņĀüņØĖ anticipatory postural adjustment ļŖźļĀźņŚÉ ļ¼ĖņĀ£Ļ░Ć ņ׳ļŖö
Ļ▓āņ£╝ļĪ£ ļéśĒāĆļé¼Ļ│Ā voluntary reaction time ņØ┤ ņ”ØĻ░ĆĒĢśļŖö Ļ▓āņØĆ ņĢłņĀĢņä▒ņØä ņ”ØĻ░Ćņŗ£ĒéżĻĖ░ ņ£äĒĢ£ ņŗ£Ļ░ä
ņØä ļ▓äļŖö Ļ▓āņØ┤Ļ▒░ļéś postural m. weakness or voluntary control system ņØś ļ¼ĖņĀ£ļĪ£ ņāØĻ░üļÉ£ļŗż .
’é¢ ļ¼╝Ļ▒┤ņØä ļōżĻ▒░ļéś ņś«ĻĖ░ļŖö ņØ╝ļĀ©ņØś Ē¢ēļÅÖ
’é¢ voluntary movement ņÖĆ Ļ┤Č─ļĀ©ļÉ£ ļ¬ĖņØś ņĢłņĀĢņä▒ņØä Ļ░¢ņČöļŖö ļŖźļĀźņØ┤ ĒśäņĀĆĒ׳ Ļ░ÉņåīĒĢ£ ļģĖņØĖņŚÉĻ▓ī
falling ņØś ņøÉņØĖņØä ņĀ£Ļ│Ą ĒĢĀ ņłś ņ׳ļŗż .
46. ’üĮ Cognitive issues and posture control
Ļ░üĻĖ░ ļŗżļźĖ ĒÖśĻ▓ĮņŚÉņä£ balance ability ņŚÉ
attentional capacity Ļ░Ć
ņ¢┤ļ¢╗Ļ▓ī ņśüĒ¢źņØä ļ»Ėņ╣śļŖöĻ░Ć ?
Teasdal (1993) ļō▒ņØĆ cop ņĖĪņĀĢņØä ĒåĄĒĢ┤ņä£
24 ņäĖ ņĀŖņØĆņØ┤ 8 ļ¬ģĻ│╝ 71 ņäĖ ļģĖņØĖ 9 ļ¬ģņØä ņĢēņØĆ
ņāüĒā£ (control condition) ņä£ņä£ ļłłņØä ļ£©Ļ│Ā
Ļ░ÉņØĆ ņāüĒā£ņŚÉņä£ ļ░öļŗźņØä normal & foam ņ£╝ļĪ£
ĻĄ¼ļ│äĒĢ┤ņä£ ņ▓ŁĻ░üņĀü cue(attention task) ņŚÉ
ļö░ļØ╝ ļ▓©ņØä ļłäļź┤ļŖö ņŗżĒŚś .
Attention ņØś ņ¢æņØĆ task Ļ░Ć Ļ░Ćņ¦ĆĻ│Ā ņ׳ļŖö instability ņØś ņĀĢļÅäņÖĆ Ļ┤Č─Ļ│äĻ░Ć ņ׳ļŗż .
ĻĘĖļ”¼Ļ│Ā ļģĖņØĖņØś Ļ▓ĮņÜ░ ļ│┤ļŗż ļ¦ÄņØĆ attention ņØ┤ ĒĢäņÜöĒĢśļŗż .
47. ’üĮ Cognitive issues and posture control
ŌŚ” Shumway ŌĆō cook (1997)
’é¢ ņĀŖņØĆņØ┤ņÖĆ Ļ▒┤Ļ░ĢĒĢ£ ļģĖņØĖ , ļäśņ¢┤ņ¦ä Ļ▓ĮĒŚśņØ┤ ņ׳ļŖö ļģĖņØĖņØä ļīĆņāüņ£╝ļĪ£
normal vs. foam surface ņŚÉņä£ cognitive ĻĖ░ļŖźņØ┤ ĒĢäņÜöĒĢ£
postural task ļź╝ ņłśĒ¢ē ņŗ£ņ╝░ļŗż .
’é¢ ņĀŖņØĆņØ┤ņÖĆ Ļ▒┤Ļ░ĢĒĢ£ ļģĖņØĖļōżņØś ņ░©ņØ┤ņĀÉņØĆ task ņØś ļ│Ąņ×Īņä▒ņØ┤ ņ”ØĻ░ĆļÉś
ņŚłņØäļĢīņŚÉļ¦ī ļéśĒāĆļé¼ļŗż . ņ”ē task ņØś ļ│Ąņ×Īņä▒ņØ┤ ņ”ØĻ░ĆĒĢśĻ▒░ļéś
challenging postural condition ņŚÉņä£ļ¦ī ļ¼ĖņĀ£Ļ░Ć ļ░£ņāØ .
’é¢ ĻĘĀĒśĢņŚÉ ļ¼ĖņĀ£Ļ░Ć ņ׳ļŖö ļģĖņØĖļōżņØś Ļ▓ĮņÜ░ Ļ░äļŗ©ĒĢ£ task ņŚÉņä£ļÅä ļ¼Ė
ņĀ£Ļ░Ć ļ░£ņāØ . Normal quiet stance ņŗ£ attention ņŚÉ ņĀ£ĒĢ£ņØ┤ ņ׳ļŖö
ļģĖņØĖņØś Ļ▓ĮņÜ░ attention ņØ┤ ĒĢäņÜöĒĢ£ Ļ│╝ņĀ£ļŖö falling ņØś ņ£äĒŚśņä▒ņØä
ņ”ØĻ░Ćņŗ£Ēé©ļŗż .
49. ’üĮ Strength training
’üĮ Aerobic conditioning
’üĮ Balance training
’üĮ Combined exercise programs
’üĮ Chandler and Hedley 1996
50. ’üĮ Strength training
ŌŚ” ļģĖņØĖļōżņŚÉĻ▓ī Ļ░Ćņן ņĀüņĀłĒĢśĻ│Ā ĒÜ©Ļ│╝ņĀüņØĖ training ļ░®ļ▓ĢņØĆ ?
ŌŚ” Aniansson et al (1984) ): ļé© (74-86) 86 ņŚ¼ (63-84) 2/weeks 10 Ļ░£
ņøö low intensity strengthening training -
ŌŚ” Ļ▓░Ļ│╝ 6~13% isometric knee extensor , fast twitch fiber
ŌŚ” Frontera et al (1988) : ļé© (60-72) 3/weeks 12 ņŻ╝ high
intensity( 80%) strengthening training -
ŌŚ” Ļ▓░Ļ│╝ 1rep max power(knee extensor) 107-226%
’üĮ Balance control or gait skill ļĪ£ transfer ĒĢśļŖöĻ░Ć ?
51. ’üĮ Strength training
ŌŚ” Ļ▒┤Ļ░ĢĒĢ£ ļģĖņØĖļōżņŚÉĻ▓īņä£ gait velocity or ņØśņ×ÉņŚÉņä£ ņØ╝ņ¢┤ļéśļŖö ņŗ£Ļ░äņØś Ļ░Éņåī ļō▒ņØś functional
skill ņŚÉļŖö ļ│ĆĒÖö ņŚåļŗż (Judge et al., 1994).
ŌŚ” ĒĢ£ļ░£ļĪ£ ņä£ĻĖ░ ļō▒ņØś ņŗ£Ļ░äņØ┤ ņ”ØĻ░ĆļŖö ņ׳ņŚłņ¦Ćļ¦ī ļŗżļźĖ ĒĢŁļ¬®ņØś ļ│ĆĒÖöļŖö ņŚåņŚłļŗż (Wolfson et al.,
1994).
ŌŚ” Fiatarone(1990,1994). ņŗ£ņäżņŚÉ Ļ▒░ņŻ╝ĒĢśĻ│Ā ņ׳ļŖö ĻĘ╝ļĀźņØ┤ ņĢĮĒĢ£ ļģĖņØĖļōżņØä (90 ņäĖ ) ļīĆņāüņ£╝ļĪ£
strengthening training( 3/weeks,12 ņŻ╝ quadriceps, hamstring, abductors m. ŌĆō high
resistance ex.)-174% for 1 rep max. : functional measure ņ”ØĻ░Ć ( tendom gait speed 48%
ņ”ØĻ░Ć ļæÉ ļ¬ģņØĆ ļŹö ņØ┤ņāü ņ¦ĆĒīĪņØ┤ļź╝ ņé¼ņÜ®ĒĢśņ¦Ć ņĢŖņĢäļÅä ļÉśĻ▓ī ļÉśņŚłļŗż .
ŌŚ” ņÜöņĢĮ
ŌŚ” High-resistance strengthening ņØ┤ low-resistance strengthening training ļ│┤ļŗż ĒÜ©Ļ│╝ņĀüņØ┤Ļ│Ā
functional effect ļŖö frail old adult ņŚÉĻ▓ī ĒÜ©Ļ│╝ņĀüņØ┤ļŗż .
52. ’üĮ Aerobic conditioning
ŌŚ” Resting heart rate & vo2 max ļź╝ ņ”ØĻ░Ćņŗ£ĒéżĻ│Ā , well-
being (sleep .productivityŌĆ”) ļō▒ņØä Ē¢źņāü ņŗ£Ēéżļŗż .
ŌŚ” ĒĢśņ¦Ćļ¦ī balance function ņŚÉ ņśüĒ¢źņØä ņŻ╝ļŖöņ¦ĆļŖö ĒÖĢņŗżĒĢśņ¦Ć
ņĢŖļŗż ( chandler and Hadley 1996).
53. ’üĮ Balance training
ŌŚ” Wolf et al(1993,1996) ļ¼┤ņ×æņ£äļĪ£ 3 ņ¦æļŗ©ņØä ļéśļłĀ 3 Ļ░Ćņ¦Ć ĒøłļĀ© ĒÜ©Ļ│╝ļź╝ ļ╣äĻĄÉ .
’é¢ ļīĆņāüņ×É : ņ¦ĆņŚŁņé¼ĒÜīņŚÉ Ļ▒░ņŻ╝ĒĢśļŖö 76┬▒5 ļģĖņØĖ .
’é¢ Balance training : Static balance training(balance recovery on a balance
platform), dynamic balance(TŌĆÖai chi) vs. wellness discussion.
’é¢ 2/weeks 15 ņŻ╝
’é¢ Dynamic balance training : falling risk ratio 0.63 Ļ░Éņåī
’é¢ Static balance training : ĒåĄĻ│äņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ņ░©ņØ┤ ņŚåņØī
54. ’üĮ Combined exercise programs
ŌŚ” Judge et al(1993) ņ¦ĆņŚŁņé¼ĒÜī Ļ▒░ņŻ╝ĒĢśļŖö 62-75 ņäĖ ļģĖņØĖļōżņŚÉĻ▓ī low-
extremity resistance training, brisk walking, tŌĆÖai chi training vs flexibility
training. 3/weeks 6 months
ŌŚ” Shumway cook(1997)-multidementional exercise program(low extremity
strengthening ex. Flexibility ex. Static and dynamic balance training,
aerobic ex walking).
ŌŚ” 1 group 5-7/weeks
ŌŚ” 2 group 1-4/weeks
ŌŚ” Control group 21 ņäĖ ņĀŖņØĆņØ┤
56. ’üĮ Sensory orientation training
ŌŚ” Hu and Wollacott(1994) sensory input ņØä Ļ░Éņåīņŗ£ĒéżĻ▒░ļéś ļ│ĆĒÖöņŗ£Ēé¼ ņłś ņ׳ļŖö ņĪ░Ļ▒┤
ņŚÉņä£ ņØ┤ņÖĆĻ░ÖņØĆ ņāüĒÖ®ņØä intergration ĒĢśĻ│Ā ļŗżļźĖ sensory input ņŚÉ ņ┤łņĀÉņØä ļ¦×ņČ£ ņłś
ņ׳ļŖö ņāüĒÖ®ņØä ļ¦īļōżņ¢┤ training effect ļź╝ ņé┤ĒÄ┤ļ│┤ņĢśļŗż .
’é¢ Normal support surface, eye open, head natural.
’é¢ Normal support surface, eye close, head natural.
’é¢ Normal support surface, eye open, head extended
’é¢ Normal support surface, eye close, head extended
’é¢ Foam
59. 1. AGING ņØś ļæÉ ļ¬©ļŹĖ a)CNS ņØś ļ¬©ļōĀ level ņŚÉņä£ ņĀäļ░śņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ neuron function ņØ┤ ņ¦üņäĀņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ Ļ░ÉņåīĒĢ£ļŗżļŖö Ļ░£ļģÉĻ│╝
b) ļéśņØ┤Ļ░Ć ļō£ļŖö ļÅÖņĢł CNS ļŖö CNS ņŚÉ ĒŖ╣ļ│äĒĢ£ ļČĆņ£äņŚÉ ļ»Ėņ╣śļŖö ĒŖ╣ļ│äĒĢ£ ņ¦łĒÖśņØ┤ļéś ņ×¼ĒĢ┤Ļ░Ć ņŚåļŗżļ®┤ ņŻĮĻĖ░ ņĀäĻ╣īņ¦Ć ĻĖ░ļŖź
ņØĆ ņóŗĻ▓ī ņ£Āņ¦Ć ļÉ£ļŗż .
2. Aging ņŚÉ ņśüĒ¢źņØä ļ»Ėņ╣śļŖö ņÜöņåīļĪ£ primary & secondary factors Ļ░Ć Ļ│ĀļĀż ļÉĀ ņłś ņ׳ļŖöļŹ░ ņ▓½ņ¦Ė ņÜöņåīļŖö ņ£ĀņĀäņĀü ņÜöņåīņÖĆ
Ļ░ÖņØĆ Ļ▓āņ£╝ļĪ£ system ņØś neural function ņØś Ēö╝ĒĢĀ ņłś ņŚåļŖö Ļ░Éņåīļź╝ ņ┤łļלĒĢ£ļŗż . ļæÉ ļ▓łņ¦Ė ņÜöņåīļŖö Ļ▓ĮĒŚśĻ│╝ nutrition,
exercise, insults and pathologies ļź╝ ĒżĒĢ©ĒĢ£ļŗż .
3. ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ņ×ÉļōżņØĆ ļ¬©ļōĀ ļģĖņØĖļōżņØ┤ ņāüļŗ╣Ē׳ heterogeneity ĒĢśļŗżļŖö Ļ▓āņØä ļ░£Ļ▓¼Ē¢łļŗż . ņØ┤Ļ▓āņØĆ ļ¬©ļōĀ ļģĖņØĖļōżņŚÉĻ▓ī physical
capability Ļ░Ć ņØ╝ļ░śņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ļÅÖņØ╝ĒĢśĻ▓ī Ļ░ÉņåīĒĢśņ¦Ć ņĢŖļŖöļŗżļŖö Ļ▓āņØä ņØśļ»ĖĒĢ£ļŗż .
4. Falling ņØĆ 70 ņäĖ ņØ┤ņāüņØś ļģĖņØĖņŚÉĻ▓īņä£ 7th
ņé¼ļ¦ØņøÉņØĖņØ┤ļŗż . falling ņØś ņøÉņØĖņØĆ ļģĖņØĖļōżņŚÉĻ▓ī ņŚ¼ļ¤¼ ļ│Ąņ×ĪĒĢśĻ▓ī ļéśĒāĆļé£ļŗż .
Intrinsic physiological & Extrinsic Environmental factors Ļ░Ć ņŚ¼ĻĖ░ņŚÉ ņåŹĒĢ£ļŗż . Posture & balance ability ņØś ņĀĆĒĢśļź╝ ņØ┤
ĒĢ┤ĒĢ£ļŗżļŖö Ļ▓āņØĆ ļģĖņØĖņØś falling ņØä ļ¦ēņØä ņłś ņ׳ļŖö ņ×äņāüņĀüņØĖ ņØ╝Ļ│╝ Ļ┤Č─ļĀ©ņØ┤ ņ׳ļŗż .
5. Falling Ļ│╝ imbalance risk ļź╝ Ļ░Ćņ¦ĆĻ│Ā ņ׳ļŖö ļģĖņØĖņØś balance ņĀĆĒĢśņŚÉ ņśüĒ¢źņØä ļ»Ėņ╣śļŖö ņÜöņåīļŖö ļ¦ÄņØ┤ ņĪ┤ņ×¼ĒĢ£ļŗż . ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ņ×É
ļōżņØĆ ļ¬©ļōĀ system ņŚÉņä£ ņāØĻĖ░ļŖö ņ¢┤ļ¢ĀĒĢ£ impairment ļØ╝ļÅä balance control ņŚÉ ņśüĒ¢źņØä ļ»Ėņ╣£ļŗżĻ│Ā ļ│┤Ļ│ĀĒ¢łļŗż . ĒĢśņ¦Ćļ¦ī
ļéÖņāüĒĢ£ ļ¬©ļōĀ ļģĖņØĖļōżņØś ĒŖ╣ņä▒ņØä ĒīīņĢģĒĢĀ ņłś ņ׳ļŖö ņ¢┤ļ¢ĀĒĢ£ pattern ņØĆ ļ░£Ļ▓¼ĒĢśņ¦Ć ļ¬╗Ē¢łļŗż .
6. ĻĖŹņĀĢņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ļ¦ÄņØĆ ļģĖņØĖļōżņØ┤ ņĀŖņØĆņØ┤ņÖĆ ĻĘĀĒśĢļŖźļĀźņŚÉņä£ ĒÅēļō▒ĒĢśļŗż . ļŗżļź┤Ļ▓ī ļ¦ÉĒĢśņ×Éļ®┤ balance ņĀĆĒĢśļŖö aging ņØś Ēö╝ĒĢĀ ņłś
ņŚåļŖö Ļ▓░Ļ│╝ļØ╝Ļ│Ā ĒĢĀ ņłś ņŚåļŗż . Ļ▓ĮĒŚśņĀü ņÜöņåī ņśłļź╝ ļōżņ×Éļ®┤ ņÜ┤ļÅÖņØĆ good balance ļź╝ ņ£Āņ¦ĆĒĢĀ ņłś ņ׳Ļ▓ī ĒĢśĻ│Ā ļéśņØ┤ļōĀ ņé¼
ļ×īņØś falling Ļ│╝ Ļ░ÖņØĆ Ļ▓āļōżņØä Ļ░Éņåīņŗ£ņ╝£ņżĆļŗż .
Editor's Notes #4: ņśżļŖśņØĆ aging ņØś ļ¬©ļōĀ ļ®┤ņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ┤ņä£ ļŗżļŻ©ņ¦ĆļŖö ņĢŖņØä Ļ▓üļŗłļŗż ņśżļŖś ņ┤łņĀÉņØä ļæś ļČĆļČäņØĆ posture control ņŚÉ ņśüĒ¢źņØä ļ»Ėņ╣śļŖö ļéśņØ┤ņŚÉ ņ׳ņŖĄļŗłļŗż,
ļéśņØ┤ņÖĆ Ļ┤Č─Ļ│äĒĢ£ ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ ņ×ÉļŻīļź╝ ņ░ĖĻ│Ā Ē¢łņØä ļĢī
dysfunctionņØĆ instabilityļź╝ ņ┤łļלĒ¢łĻ│Ā ,
Traing ņØś ĒÜ©Ļ│╝ņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢśņŚ¼ ņżæņĀÉņØä ļæÉĻ│Ā Ļ░ĢņØśļź╝ ņŗ£ņ×æĒĢśĻ▓ĀņŖĄļŗłļŗż.
#5: ļģĖņö©ļŖö 90ņØĖļŹ░ ļ¦łļØ╝ĒåżļŖź ĒĢś ņłś ņ׳ļŖöļŹ░ ņØ┤ņö©ļŖö 70ņäĖ ņ×äņŚÉļÅä ļČłĻĄ¼ĒĢśĻ│Ā nursing home ņŚÉ ņ׳ņ£╝ļ®░ ņØśņ×Éņ░©ņŚÉ ņØśņ¦ĆĒĢśĻ│Ā ĒÖöņןņŗżņŚÉ Ļ░ł Ļ▓ĮņÜ░ņŚÉļÅä ļČĆņČĢņØ┤ ĒĢäņÜöĒĢśļŗż ņÖ£ ņØ┤ļ¤░ ļ¼ĖņĀ£Ļ░Ć ļéśĒāĆļéśļŖöĻ░Ć ņĀĢĒÖĢĒ׳ ņØ┤ ļ¼ĖņĀ£ņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ┤ņä£ ņĀĢĒÖĢĒ׳ ļŗĄļ│ĆĒĢśĻĖ░ļŖö ņ¢┤ļĀĄņŖĄļŗłļŗż. ļ¦ÄņØĆ ņÜöņåīļōżņØ┤ Ļ▒┤Ļ░ĢĻ│╝ mobility ņŚÉ ņśüĒ¢źņØä ļ»Ėņ╣śĻĖ░ ļĢīļ¼Ėņ×ģļŗłļŗż.
#6: ļ¦ÄņØĆ ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ļź╝ ĒåĄĒĢ┤ņä£ agingņØś ņ¦äĒ¢ēņØĆ ļ¦ÄņØĆ ņ¢æņØś sensory ņÖĆ motor process ņØś Ļ░Éņåīļź╝ ņĢ╝ĻĖ░ņŗ£Ēé©ļŗżļŖö Ļ▓░ļĪĀņØä ļāłņŖĄļŗłļŗż. ĒĢśņ¦Ćļ¦ī Ļ│╝ĒĢÖņ×ÉļōżņØĆ ņ¢┤ļ¢╗Ļ▓ī ĻĘĖļ”¼Ļ│Ā ņÖ£ aging dl ņ¦äĒ¢ēļÉśļŖöņ¦ĆņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ┤ņä£ļŖö ļÅÖņØśĒĢśņ¦Ć ņĢŖĻ│Ā ņ׳ņŖĄļŗłļŗż,
ļ¦ÄņØĆ aging model ļōżņØ┤ ņ׳ņ¦Ćļ¦ī Ēü¼Ļ▓ī ļæÉĻ░Ćņ¦ĆļĪ£ ĻĄ¼ļČäĒĢ┤ņä£ ņäżļ¬ģņØä ĒĢśņ×Éļ®┤ ļŗżņØī ļæÉ Ļ░Ćņ¦ĆļĪ£ ļéśļłĀ ļ│╝ ņłś ņ׳Ļ▓ĀņŖĄļŗłļŗż.
ņ▓½ ļ▓łņ¦Ė categoryļŖö agingņØś ņøÉņØĖņØä ļé┤ņĀüņØĖ Ļ▓āņŚÉ ņ┤łņĀÉņØä ļ¦×ņČöĻ│Ā life spanņØĆ ņ£ĀņĀäņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ Ļ▓░ņĀĢļÉ£ļŗżĻ│Ā ļ│┤ļŖö Ļ▓¼ĒĢ┤ ņ×ģļŗłļŗż.
ņØ┤ Ļ┤Č─ņĀÉņŚÉ ļö░ļź┤ļ®┤ organismņØĆ ņāØņØ┤ ņŗ£ņ×æĒĢĀļĢī ļ¬©ļōĀ system ņØ┤ ņĀĢņĀÉņŚÉ ņ£äņ╣ś Ē¢łļŗżĻ░Ć ņŗ£Ļ░äņØ┤ ņ¦Ćļéśļ®┤ņä£ system ņØś cell ļōżņØ┤ ĒŖ╣ņĀĢ ņŗ£Ļ░äņŚÉ ĒīīĻ┤┤ļÉśĻĖ░ ņŗ£ņ×æĒĢśĻ│Ā ņŻĮņØīņŚÉ ņØ┤ļź┤Ļ▓ī ļÉ£ļŗżļŖö Ļ┤Č─ņĀÉņ£╝ļĪ£ ĒŖ╣ļ│äĒĢ£ ņ£ĀņĀäņĀü program ņØ┤ ļ®┤ņŚŁ system ņØä ĒīīĻ┤┤ĒĢśĻ▒░ļéś neuroendocrine ņØä ĒīīĻ┤┤ĒĢśņŚ¼ ņŻĮņØīņ£╝ļĪ£ ņØ┤ļüłļŗżĻ│Ā ņāØĻ░üĒĢśĻ│Ā ņØ┤ļź╝ aging ņØś primary aging ņ£╝ļĪ£ ĻĘ£ņĀĢĒ¢łņŖĄļŗłļŗż.
ļæÉļ▓łņ¦Ė category ņŚÉņä£ aging ņØĆ external cause Ļ░Ć primary ņøÉņØĖņ£╝ļĪ£ ļ│┤ļŖö Ļ┤Č─ņĀÉņ×ģļŗłļŗż. ņØ┤ Ļ░ĆņäżņØĆ life span ņØĆ damage ļ¦ī ņŚåļŗżļ®┤ ĒĢ£Ļ│äĻ░Ć ņŚåļŗżĻ│Ā ļ│┤ļ®░
ĒÖśĻ▓ĮņĀüņØĖ ņÜöņØĖĻ│╝ņØś ņāüĒśĖ ņ×æņÜ®ņŚÉ ņØśĒĢ┤ life span d Ļ▓░ņĀĢļÉ£ļŗżĻ│Āļ│┤Ļ│Ā ņ׳ļŖö Ļ▓¼ĒĢ┤ņØ┤ļŗż ņØ┤ Ļ░ĆņäżņŚÉ ļö░ļź┤ļ®┤ ĒŖ╣ļ│äĒĢ£ system ņØś ĻĖ░ļŖźļōżņØĆ ĒŖ╣ļ│äĒĢ£ ņ¦łļ│æņØ┤ļéś Ēü░ ņ×¼ĒĢ┤ņŚÉ ņØśĒĢ┤ system funtionņØ┤ Ēü¼Ļ▓ī Ļ░ÉņåīĒĢśņ¦Ćļ¦ī ņĢŖļŖöļŗżļ®┤ ņŻĮĻĖ░ņĀäĻ╣īņ¦Ć ļåÆņØĆ ĻĖ░ļŖźņØä ņ£Āņ¦ĆĒĢ£ļŗżĻ│Ā ļ│┤Ļ│Ā ņ׳ļŗż.
#7: ņØ┤ ļæÉ ļ¬©ļŹĖņØĆ aging ņŚÉ ļö░ļźĖ functional loss ļź╝ ļ¦żņÜ░ ļŗżļźĖ ņŗ£Ļ░üņ£╝ļĪ£ ļ│┤Ļ▓ī ļÉ®ļŗłļŗż.
ļ©╝ņĀĆ ņ▓½ ļ▓łņ¦Ė ļ¬©ļŹĖņØś Ļ▓ĮņÜ░ ļéśņØ┤ņÖĆ ĒĢ©Ļ╗ś Ļ▓░ņĀĢļÉśļŖö nerve system ņØĆ ļ╣äĻ┤Č─ņĀüņØ┤ļŗż. ņ”ē neuronal loss ļŖö Ēö╝ĒĢĀ ņłś ņŚåļŖö ņØ╝ņØ┤ļ®░ ļÅÖņŗ£ņŚÉ ĻĖ░ļŖźņĀü ņĀĆĒĢś ņŚŁņŗ£ ļéśņØ┤ņŚÉ ļö░ļØ╝ ļŗ╣ņŚ░Ē׳ ļéśĒāĆļéśļŖö Ļ▓āņ£╝ļĪ£ ņāØĻ░üĒĢśļŖöļŹ░ ņØ┤ Ļ▓ĮņÜ░ self-limiting Ļ░£ļģÉņØä Ļ░Ćņ¦ĆĻ▓ī ĒĢ®ļŗłļŗż. ņØ┤ņÖĆ Ļ░ÖņØĆ ņāØĻ░üļōżņØĆ medical professional ļōżņŚÉĻ▓īļÅä ļČĆņĀüņĀłĒĢ£ ņé¼Ļ│Ā ļ░®ņŗØņØä Ļ│Āņ░®ĒÖö ĒĢĀ ņłś ņ׳Ļ▓ī ĒĢ®ļŗłļŗż. ņ”ē ļéśņØ┤Ļ░Ć ļō£ņŗĀ ļČäļōżņØś MMT ņŗ£ ļéśņØ┤ļź╝ Ļ│ĀļĀż ņóŗĻ▓ī ĒÅēĻ░Ć ĒĢĀ ņłś ņ׳Ļ▓ī ļ¦īļō£ļŖöļŹ░ , ņØ┤ļŖö ĻĘĖļōżņØś ļŖźļĀźņŚÉ ĻĄ┤ļĀłļź╝ ņöīņÜ░ļŖö ņØ╝ņØ┤ ļÉĀ ņłś ņ׳ņŖĄļŗłļŗż.
ļ░śļ®┤ņŚÉ ļæÉ ļ▓łņ¦Ė Ļ░£ļģÉņØĆ ņóĆļŹö ļéÖĻ┤Č─ņĀüņØĖ Ļ┤Č─ņĀÉņØä Ļ░¢Ļ▓ī ĒĢśļŖöļŹ░ ņĀüņĀłĒĢ£ Ļ▓ĮĒŚśņĀü ņÜöņåīļź╝ ņĀ£Ļ│ĄĒĢśĻ│Ā Ļ│Ā, ņśłņāüņ╣ś ņĢŖņØĆ ņ¦łĒÖśņØä ļ¦ēņĢäņżĆļŗżļ®┤ CNS ņØś ņĀüņĀłĒĢ£ ĻĖ░ļŖźņØä ĻĖ░ļīĆ ĒĢĀ ņłś ņ׳Ļ▓ī ĒĢ┤ ņżŹļŗłļŗż. Optimal Ļ▓ĮĒŚśņĀü ņÜöņåīņŚÉļŖö healthy & active life Ļ░Ć ĒżĒĢ©ņØ┤ ļÉśĻ│Ā ņØ┤ļ¤░ Ļ┤Č─ņĀÉņ£╝ļĪ£ ļģĖņØĖņØä ĒÅēĻ░ĆĒĢ£ļŗżļ®┤ ļģĖņØĖņØś ĻĖ░ļŖźņØ┤ ļ¢©ņ¢┤ņĪīņØä Ļ▓ĮņÜ░ ļŗżņŗ£ ĻĖ░ļŖźņØä ĒÜīļ│Ąņŗ£Ēé¼ ņłś ņ׳ļŖö ņ×¼ĒÖ£ ņĀäļץņØä ņ×æĻ▓ī ļ¦īļōż Ļ▓üļŗłļŗż.
#8: Primary & secondary ņÜöņåīļŖö aging process ņĢłņŚÉņä£ ņä£ļĪ£ ņāüĒśĖņ×æņÜ®ņØä ĒĢ®ļŗłļŗż.
ņśłļź╝ ļōżņ×Éļ®┤ ņ£ĀņĀäņĀü ņÜöņåīļŖö ĒŖ╣ļ│ä ņ¦łĒÖśņØś ņ¦äĒ¢ēņŚÉ ņÜ░ņäĀņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ņ×æņÜ®ņØä ĒĢ®ļŗłļŗż.
ņ▓ŁĻ░ü neuronņØś degeration gene ņØä Ļ░Ćņ¦ä ņé¼ļ×īņØś Ļ▓ĮņÜ░ ļéśņØ┤Ļ░Ć ļōżļ®┤ hearing loss ļĪ£ Ļ│ĀņāØņØä ĒĢśĻ▓ī ļÉĀĻ▓üļŗłļŗż ņØ┤Ļ▓ĮņÜ░ ĒÖśĻ▓ĮņĀü ņÜöņåīņÖĆ ņāüĒśĖ ņ×æņÜ®ņØä ĒĢśĻ▓īļÉśļ®┤ hearing loss Ļ░Ć ļŹöņÜ▒ Ļ░ĆņåŹĒÖö ļÉĀĻ▓āņ£╝ļĪ£ ņśłņāü ĒĢĀ ņłś ņ׳ņŖĄļŗłļŗż. ņÖ£ļāÉļ®┤ ņ£ĀņĀäņĀü ņÜöņåī ņÖĆ ĒÖśĻ▓ĮņĀü ņÜöņåīļŖö combination ļÉśĻĖ░ ļĢīļ¼Ėņ×ģļŗłļŗż.
#9: Secondary or experiental factors ļōżņØĆ ļ│┤ļŗż contol ĒĢśĻĖ░ ņēĮĻĖ░ ļĢīļ¼Ėņ×ģļŗłļŗż.
ņŚ¼ĻĖ░ņŚÉļŖö ŌĆ”ŌĆ”.ņśüņ¢æ
ņØ┤ļĀćļō»ņØ┤ ņĢ× ĻĘĖļ”╝ņØś ļæÉ ļģĖņØĖņØś Ļ▓ĮņÜ░ļź╝ Ļ▓░ņĀĢņ¦ĆņØĆ ņÜöņåīļØ╝ļŖö Ļ▓āļōżņØĆ primary aging & secondary aging ņØś ņĪ░ĒÖöņåŹ ņŚÉņä£ ļéśĒāĆļé£ Ļ▓āņ£╝ļĪ£ ņāØĻ░üĒĢĀ ņłś ņ׳Ļ│Ā ļÅÖņŗ£ņŚÉ neural aging ņØ┤ļ×Ć primary & secondary factor Ļ░äņŚÉ ļ¬©ļōĀ functionemfņØ┤ ļÅÖņŗ£ņŚÉ Ļ░ÉņåīļÉśļŖö Ļ▓āņØ┤ ņĢäļŗłļØ╝ ĒŖ╣ņłśĒĢ£ ņŗĀĻ▓ĮĒĢÖņĀü ĒśĢĒā£ Ēś╣ņØĆ ĻĖ░ļŖźņŚÉ ņĀ£ĒĢ£ļÉśņ¢┤ņ¦äļŗżĻ│Ā ļ│╝ ņłśņ׳Ļ▓ĀņŖĄļŗłļŗż.
ņØ┤Ļ▓āņØ┤ ņØ┤ļ▓ł recture ļź╝ ĒåĄĒĢ┤ ņ¦ĆņåŹņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ņØ┤ļüīĻ│Ā Ļ░ł ņŻ╝ņĀ£ļĪ£ņä£ŌĆ”..ĻĖ░ļŖźĻ│╝ ļ╣äĻĖ░ļŖźļ”¼ļØ╝ļŖöĻ▓āņØĆ ņØ╝ļ░śņĀüņØĖĻ▓āņØ┤ ņĢäļŗłļØ╝ Ļ░£ņØĖņØ┤ ņłśĒ¢ēĒĢśļĀżĻ│Ā ĒĢśļŖö ĒŖ╣ļ│äĒĢ£ŌĆ”ŌĆ”
#10: 32Ļ░£ņØś ĒĢŁļ¬®ņŚÉļŖö musculoskeletal, NEUROLOGICAL, CARDIOVASCULAR, any history of falls Ļ░Ć ĒżĒĢ©ļÉśņ¢┤ ņ׳ņ¢┤ņ£╝ļ®░ ņØ┤ ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ņØś Ļ▓░ļĪĀņØĆ ļģĖņØĖņØś gait cycle ņŚÉņä£ ļ│ĆĒÖöĻ░Ć ļéśĒāĆļé£ļŗżļŖö Ļ▓āņØĆ ņĀĢņāüņØ┤ ņĢäļŗłļØ╝ ņ¢┤ļ¢ż pathologyņŚÉ ĻĖ░ņØĖĒĢ£ļŗżļŖö Ļ▓░ļĪĀņØä ļé┤ņŚłļŗż.
ņØ┤ņāüņØś ņé¼ņŗżļōżļĪ£ ļģĖņØĖļōżņØĆ heterogeneity Ļ░Ć ņ׳ļŗżļŖö Ļ▓āņØä ņØśļ»Ė ĒĢśļŖöĻ▓āņ£╝ļĪ£ ņØ┤Ļ▓āņØĆ ļģĖņØĖļōżņŚÉĻ▓ī ļéśĒāĆļé£ļŗżĻ│Ā ļ»┐Ļ│Ā ņ׳ļŖö ņŗĀņ▓┤ļŖźļĀźņØś Ļ░Éņåīļź╝ ĒÖĢņŗĀĒĢśļŖöļŹ░ ļ¼ĖņĀ£Ļ░Ć ņ׳ņØä ņłś ņ׳ļŗżļŖö Ļ▓āņØä ņØśļ»ĖĒĢśļŖö Ļ▓āņØ┤ĻĖ░ļÅä ĒĢ®ļŗłļŗż.
#13: ļéÖņāüņØś ņøÉņØĖņŚÉļŖö ņŚ¼ļ¤¼ Ļ░Ćņ¦ĆĻ░Ć ņ׳ņØä ņłś ņ׳Ļ▓Āņ¦Ćļ¦ī ļ©╝ņĀĆ ņĀĢņØśļź╝ ĒÖĢņŗżĒ׳ ĒĢ┤ ļæś ĒĢäņÜöĻ░Ć ņ׳Ļ▓ĀņŖĄļŗłļŗż. ĻĘĖļ”¼Ļ│Ā fallingņØś ļŗżļźĖ categories ņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ┤ņä£ļÅä ņĢīņĢäļæś ĒĢäņÜöĻ░Ć ņ׳ņŖĄļŗłļŗż.
ņÖ£ļāÉĒĢśļ®┤ ņØ┤ņÖĆ Ļ░ÖņØĆ ņ¦ĆņŗØļōżņØ┤ ņ╣śļŻīņé¼ļōżņŚÉĻ▓ī ļģĖņØĖņØ┤ ļäśņ¢┤ņ¦ĆļŖö ļ│Ėņ¦łņĀüņØĖ ļ¼ĖņĀ£ņÖĆ ļäśņ¢┤ņ¦ĆļŖö ļ╣łļÅäņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ┤ņä£ ņ¢┤ļ¢╗Ļ▓ī ļŹö ĒÜ©Ļ│╝ņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ļīĆņ▓śĒĢĀ ņłś ņ׳ļŖöĻ░Ć ? ļØ╝ļŖö ņ¦łļ¼ĖņŚÉ ņóŗņØĆ ĒĢ┤ļŗĄņØä ņżä ņłś ņ׳ņØäĻ▓āņØ┤Ļ│Ā ļéśņĢäĻ░Ć ņŚ¼ļ¤¼ ņóģļźśņØś balance risk ņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ņāüĒÖ®ņŚÉ ņĀüņĀłĒ׳ ņ×¼ĒÖ£ ņĀäļץņØä ņäĖņÜĖ ņłś ņ׳Ļ▓ī ļÉĀ Ļ▓ā ņ×ģļŗłļŗż,
FallingņØĆ ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ĒÖśĻ▓Įļ│┤ļŗż ņ×äņāüņŚÉņä£ ļ│┤ļŗż ļŗżļź┤Ļ▓ī ņĀĢņØśļÉśņ¢┤ ņ¦æļŗłļŗż
ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ĒÖśĻ▓ĮņŚÉņä£ļŖö ņĢłņĀĢņä▒ņØä ņżæņÜöņŗ£ ĒĢśĻĖ░ ļĢīļ¼ĖņŚÉ harnessļź╝ ņ▒äņøī ņŗżĒŚśņØä ĒĢśĻĖ░ ļĢīļ¼ĖņŚÉ steppingņØä ĒåĄĒĢ┤ ņĢłņĀĢņä▒ņØä Ļ│äņåŹ ņ£Āņ¦ĆĒĢĀ ņłś ņ׳ļŖö ņāüĒÖ®ļÅä falling ņ£╝ļĪ£ ĒżĒĢ©ļÉśņ¢┤ņ¦æļŗłļŗż.
ļö░ļØ╝ņä£ falls Ļ░Ć ņŚ¼ļ¤¼ ņāüĒÖ®ņŚÉņä£ Ļ░üĻĖ░ ļŗżļź┤Ļ▓ī ņĀĢņØśļÉśņ¢┤ņ¦ĆĻĖ░ ļĢīļ¼ĖņŚÉ ņ×äņāüņŚÉ ņ׳ļŖö ņé¼ļ×īļōżņŚÉĻ▓īļŖö ņ¢┤ļ¢ż ņØśļ»ĖņØś falls ņØĖņ¦Ć ņĢīņĢäļæś ĒĢäņÜöĻ░Ć ņ׳ņŖĄļŗłļŗż.
#15: ļģĖņØĖĻ│╝ ĒĢ©Ļ╗ś ņØ╝ņØä ĒĢ┤ņĢ╝ ĒĢśļŖö ņ╣śļŻīņé¼ļōżņØĆ falling ņŚÉ Ļ┤Č─ņŚ¼ļÉ£ ļé┤.ņÖĖņĀü ņÜöņåīļōżņØä ņłÖņ¦ĆĒĢ┤ņä£ ĒŖ╣ļ│äĒĢ£ ņāüĒÖ®ņŚÉņä£ ļéśĒāĆļéśļŖö fallingņØä Ļ░Éņåī ņŗ£ĒéżĻ▒░ļéś ĻĄÉņĀĢĒĢĀ ņłś ņ׳ņ¢┤ņĢ╝ ĒĢ£ļŗż(Lipsitz et al, 1999).
Falling ņŚÉ ļåÆņØĆ ņ£äĒŚśņØä Ļ░Ćņ¦ä ļīĆņāüņ×ÉļōżņØĆ ĻĘĀĒśĢĻ│╝ Ļ┤Č─ļĀ©ļÉ£ functional skill(ņĢēĻĖ░, ņä£ĻĖ░,ņä£ņä£ reaching, 360* ļÅīĻ│Ā ņä£ĻĖ░, ņĢēņØĆ ņāüĒā£ņŚÉņä£ ņä£ĻĖ░, ļČĆņČĢ ņŚåņØ┤ Ļ▒ĘĻĖ░)ņØä ņĖĪņĀĢĒĢ£ Ļ▓░Ļ│╝ ņØ┤ ļæśņØĆ ņä£ļĪ£ ņāüĻ┤Č─ņØ┤ ņ׳ļŗż(Tinetti et al1996, Mathias, 1986).
ņĢ×ņ£╝ļĪ£ ļģĖņØĖļōżņØś balance functionņØä ņØ┤ĒĢ┤ĒĢśĻĖ░ ņ£äĒĢśņŚ¼ normal postural control ņŚÉ Ļ┤Č─ļĀ© ļÉś ļ¦ÄņØĆ ļ│Ćņłśļōż ņżæ ļģĖņØĖļōżņØś stability & mobilityņŚÉ ņóŗņ¦Ć ņĢŖņØĆ ņÜöņåīļōż ņżæ ļé┤ņĀü ņÜöņØĖņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢśņŚ¼ ņé┤ĒÄ┤ļ│┤ļÅäļĪØ ĒĢ£ļŗż.
#16: ļ│┤ļŗż ņĄ£ĻĘ╝ ļģĖņØĖļōżņØś balance functionņØä ņØ┤ĒĢ┤ĒĢśĻĖ░ ņ£äĒĢ┤ normal postural control Ļ│╝ Ļ┤Č─ļĀ©ļÉ£ ļ¦ÄņØĆ ļ│ĆņłśļōżņØä ĒÅēĻ░ĆĒ¢łĻ│Ā ļģĖņØĖļōżņØś stabilityņÖĆ mobilityņŚÉ ņóŗņ¦Ć ņĢŖņØĆ ņśüĒ¢źņØä ļ»Ėņ╣śļŖö ņÜöņØĖļōżņØä ņ░ŠņĢäļāłņŖĄļŗłļŗż.
#18: ļŗżļōż ĻĖ░ņ¢ĄĒĢśņŗ£Ļ▓Āņ¦Ćļ¦ī ņśłņĀä recture ņŗ£Ļ░äņŚÉ postural control ņŚÉ ņśüĒ¢źņØä ļ»Ėņ╣śļŖö ļ¦ÄņØĆ systemņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢśņŚ¼ ņé┤ĒÄ┤ ļ│┤ņĢśņŖĄļŗłļŗż ņŚ¼ĻĖ░ņŚÉņä£ļŖö ļģĖņØĖļōżņØś falling Ļ│╝ Ļ┤Č─Ļ│äļÉ£ systemņØ┤ ņ¢┤ļ¢╗Ļ▓ī ļ│ĆĒĢśļŖöņ¦Ć ņé┤ĒÄ┤ļ│┤ļÅäļĪØ ĒĢśĻ▓ĀņŖĄļŗłļŗż.
#21: ņØ┤Ļ▓ĮņÜ░ postural alignment ņØś ļ│ĆĒÖöņÖĆ Ļ┤Č─Ļ│äĻ░Ć ņ׳ļŖöļŹ░ ņŚ¼ĻĖ░ņŚÉņä£ center of mass Ļ░Ć heel ļÆżņ¬Įņ£╝ļĪ£ ņØ┤ļÅÖĒĢśļŖö ļ│┤ņāüņ×æņÜ®ņØ┤ ņāØĻĖ░Ļ▓ī ļÉ®ļŗłļŗż.
#24: ņĀäĒåĄņĀü ļ░®ļ▓Ģņ£╝ļĪ£ ļģĖņØĖļōżņŚÉĻ▓ī balance functionņØä ĒÅēĻ░ĆĒĢśļŖö ļ░®ļ▓Ģņ£╝ļĪ£ balance controlņØś global indicator ļĪ£ ņä£ ņ׳ļŖö ļÅÖņĢłņŚÉ ļéśĒāĆļéśļŖö ņ×Éļ░£ņĀüņØĖl sway ļź╝ ņé¼ņÜ®ĒĢ┤ ņÖöņŖĄļŗłļŗż.
#25: Quite stance ņāüĒā£ņŚÉņä£ COP Ēś╣ņØĆ spontaneous sway ņØś ļ│ĆĒÖöĒĢśļŖö Ēü¼ĻĖ░ļéś ņåŹļÅäņØś ļ│ĆĒÖö ņĀĢļÅäļź╝ ņĖĪņĀĢĒĢśļŖöĻ▓āņØä balance controlņØś ņĀĢĒÖĢĒĢ£ ņĖĪņĀĢņØ┤ļØ╝Ļ│Ā ņŚ¼Ļ▓© ņÖöĻ│Ā ņ┤łņ░ĮĻĖ░ ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ļōżņØĆ Ļ▓░ļĪĀņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ņØ┤ņÖĆ Ļ░ÖņØ┤ ĒĢ┤ņÖöļŗż . ĻĘĖļ”¼Ļ│Ā Ļ▓░ļĪĀņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ļģĖņØĖņØś balance function dl dirrks Ļ░Éņåī Ē¢łļŗżĻ│Ā Ļ▓░ļĪĀņØä ņ¦ĆņŚłņŚłļŗż
ĒĢśņ¦Ćļ¦ī patla ļŖö ŌĆ”ŌĆ”
ņ”ē normal quite stance ņāüĒā£ņŚÉņä£ ĻĘĖĻ▓ī Ēś╝ļ×ĆņØä ņŻ╝ļŖö ņāüĒÖ®ņØ┤ ņŚåĻĖ░ ļĢīļ¼ĖņŚÉ ļ¦ÄņØĆ Ļ▓ĮņÜ░ņŚÉņä£ balance capacity Ļ░Ć ņóŗĻ▓ī ļéśņś©ļŗżĻ│Ā ņ¦ĆņĀüĒ¢łļŗż.
patla ļŖö COPņØś ļ¦ÄņØĆ ņØ┤ļÅÖņØĆ ņØ╝ļ░śņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ poor balance control system ņØś ļ░śņ×æņÜ®ņ£╝ļĪ£ ļéśĒāĆļé£ļŗżĻ│Ā ļ│┤ņĢśļŖöļŹ░ ņØ╝ļČĆ ļģĖņØĖļōżņØś Ļ▓ĮņÜ░ limit of stability ņĢłņŚÉņä£ ĻĘĀĒśĢņØä ņל ņ£Āņ¦ĆĒĢśļŖö ļÅÖņĢł sensory system ņ£╝ļĪ£ļČĆĒä░ Ēśä ņ×ÉņäĖņØś Ļ┤Č─ĒĢ£ ļ¦ÄņØĆ ņĀĢļ│┤ļź╝ ļ░øĻĖ░ ņ£äĒĢ┤ ņØ╝ļČĆļ¤¼ high- frequency COP Ēś╝ļÅłņØä ņé¼ņÜ®ĒĢ£ļŗżĻ│Ā ņŻ╝ņןĒĢśļ®┤ņä£
Balance ņĖĪņĀĢņØĆ static balance ļź╝ ļÅäņĀä ļ░øļŖö tenderm stance ņÖĆ Ļ░ÖņØĆ ņ×ÉņäĖĻ░Ć ņóŗļŗżĻ│ĀļÅä ņŻ╝ņןĒ¢łļŗż.
Stiffness Ļ░Ć ņ”ØĻ░ĆļÉśĻ│Ā rigidityņŚÉ ņØśĒĢ┤ sway Ļ░Ć ņĀ£ĒĢ£ļÉśņŚłĻĖ░ ļĢīļ¼ĖņØ┤ļŗż ņØ┤Ļ▓ā ļśÉĒĢ£ ļģĖņØĖļōżņŚÉĻ▓ī normal quite stance & ļłłņØä ļ£©Ļ│Ā ņĖĪņĀĢĒĢśļŖö Ļ▓āņØ┤ ĻĘĖļŗżņ¦Ć ņóŗņ¦Ćļ¦īņØĆ ņĢŖņØĆ ņØ┤ņ£ĀĻ░Ć ļÉśĻĖ░ļÅä Ē¢łļŗż.
#26: ļīĆļČĆļČäņØś ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ļōżņØĆ ņÖĖņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ balanceļź╝ ņ£äĒśæĒĢĀ ņłś ņ׳ļŖö moving paltform ņØä ņé¼ņÜ®Ē¢łļŗż.
ņØ┤ļĢī balance controlņØä ņĖĪņĀĢĒĢśļŖö ĒĢŁļ¬®ņŚÉļŖö EMGŌĆ”.
ļō▒ņØ┤ ņ׳ļŗż.
ļŗżņØī ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ļōżņØĆ ļéśņØ┤ņÖĆ Ļ┤Č─ļĀ©ļÉ£ falls ņŚÉ Ļ┤Č─ļĀ©ļÉ£ ļ│ĆņłśļōżņØś ļ│ĆĒÖöņŚÉ Ļ┤Č─ĒĢ£ ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ Ļ▓░Ļ│╝ļōżņØ┤ļŗż.
Wollacoot ņØś ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ļŖö ļéśņØ┤ņÖĆ Ļ┤Č─ļĀ©ĒĢ┤ņä£ ĻĘĀĒśĢņØ┤ Ēś╝ļ×ĆņŖżļ¤ĮĻ▓ī ļÉĀļĢī postural M.ņØś ļ░śņØæ ĒŖ╣ņ¦ĢņØä ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ĒĢ£ ņ▓½ļ▓łņ¦Ė ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ņØ┤ļŗż
Muscle RESPONSEļŖö ņØ╝ļ░śņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ņĀ£ņØ╝ļ©╝ņĀĆ ankle M. ņØ┤ stretch ehlldj ĒÖ£ņä▒ĒÖö ļÉśĻ│Ā thigh m. ņØś ņ£Śņ¬Įņ£╝ļĪ£ ņĀäļŗ¼ ļÉ£ļŗżĻ│Ā Ē¢łļŗż.
ļģĖņØĖļōżņØś Ļ▓ĮņÜ░ backward sway ņØś ņøÉņØĖņ£╝ļĪ£ ankle dorsiflextion ņŚÉ ĒåĄĻ│äņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ņāüļŗ╣Ē׳ ļŖÉļ”░ onset latencies Ļ░Ć ļ│┤ņśĆļŗż.
ļŹ¦ļČÖņŚ¼ ņØ╝ļČĆ ļģĖņØĖļōżņØĆ proximal m. ļōżņØ┤ disital m. ļōżņŚÉ ļ╣äĒĢ┤ ļ©╝ņĀĆ ņłśņČĢĒ¢łļŗż.
ļģĖņØĖļōżņØś Ļ▓ĮņÜ░ ņĀŖņØĆņØ┤ņŚÉ ļ╣äĒĢ┤ ņ×ÉņŻ╝ agonist ļ┐É ļ¦ī ņĢäļŗłļØ╝ antagonistĻ╣īņ¦Ć ņØ┤ņÜ® ĒĢśļŖö coactivation ņØä ļ│┤ņØ┤ļŖöļŹ░ ņĀŖņØĆņØ┤ļōżņŚÉ ļ╣äĒĢ┤ ļ│┤ņāüņ×æņÜ®ņØä ļ│┤ļŗż ļ¦ÄņØĆ Ļ┤Č─ņĀłņŚÉņä£ ļ│┤ļŗż stiff ĒĢśĻ▓ī ĒĢśļŖö Ļ▓ĮĒ¢źņØä ļ│┤ņśĆļŗż.
#27: ņĀŖņØĆņØ┤ļōżņŚÉ ļ╣äĒĢ┤ ļģĖņØĖļōżņØĆ ĒåĄĻ│äņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ņ£ĀņØśĒĢśĻ▓ī hip strategy ļź╝ ņé¼ņÜ® ĒĢ£ļŗżĻ│Ā Ē¢łņŖĄļŗłļŗż.
Hip strategy ņØś Ļ▓ĮņÜ░ ņĀŖņØĆņé¼ļ×īļōżņØĆ ņŻ╝ļĪ£ ņÖĖļČĆņŚÉņä£ ļōżņ¢┤ņśżļŖö Ēś╝ļ×ĆņØś ņĀĢļÅäĻ░Ć Ēü┤ļĢī ankle torque ļ¦īņ£╝ļĪ£ balanceļź╝ ļŗżņŗ£ ņ×ĪĻĖ░ ņ¢┤ļĀżņÜĖ ļĢī ņé¼ņÜ®ĒĢśļŖöļŹ░ ļģĖņØĖļōżņØś Ļ▓ĮņÜ░ ņØ╝ļ░śņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ hip strategy ļź╝ balance control ņé¼ņÜ®ĒĢśļŖö Ļ▓āņ£╝ļĪ£ ļéśņÖöļŖöļŹ░ ņØ┤ļŖö ankle m. ņØś ņĢĮĒÖöļéś peripheral sensory function loss ļō▒ņØś ļ│æņĀüņØĖ conditionņŚÉ ĻĖ░ņØĖĒĢ£ļŗżļŖö Ļ░ĆņäżņØä ļéśņĢśļŗż.
ļäśņ¢┤ņ¦ĆļŖö ļģĖņØĖ ņżæ ĒŖ╣Ē׳ ļ»Ėļüäļ¤¼ņĀĖ ļäśņ¢┤ņ¦ĆļŖö ļģĖņØĖņØś Ļ▓ĮņÜ░ Ēæ£ļ®┤ņŚÉņä£ hip strategy ņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢŁĒĢ┤ņä£ shearing force ļź╝ ņ×ĪņĢäņżä ņłś ņŚåņ¢┤ņä£ ļéśĒāĆļéśĻĖ░ ņēĮļŗżĻ│Ā ņŻ╝ņןĒ¢łļŗż ļ¦łņ╣ś ņ¢╝ņØīņ▓śļ¤╝
ņĄ£ĻĘ╝ ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ļōżņØĆ ņØ┤ ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ļōżņØä ĒÖĢļīĆĒĢ┤ņä£ ņĀŖņØĆ ņé¼ļ×īĻ│╝ ļģĖņØĖ(ļ¼ĖņĀ£ ņ£Āļ¼┤) Ļ│╝ ļ╣äĻĄÉĒ¢łļŗż.
ĻĘĖļ”╝ņØĆ anterior platform ņøĆņ¦üņ×äņŚÉ ļö░ļźĖ posterior sway Ļ▓░Ļ│╝ņŚÉ ļö░ļźĖ muscle response ņ×ģļŗłļŗż
ņĀäņ▓┤ņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ onset latency ļŖö ņĀŖņØĆņØ┤ ļ¼ĖņĀ£ņŚåļŖö ļģĖņØĖ , ļ¼ĖņĀ£ ņ׳ļŖö ļģĖņØĖņØś ņł£ņä£ņśĆļŗż.
#28: ņ┤łņ░ĮĻĖ░ ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ļōżņØś Ļ▓ĮņÜ░ ĒĢ£Ļ░Ćņ¦Ć ļ│ĆņłśņŚÉ ļö░ļźĖ balance ļ│ĆĒÖöļōżņØä ņé┤ĒÄ┤ņÖöļŖöļŹ░ ņØ┤ņĀä ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ļōżļĪ£ ļģĖņØĖļōżņØ┤ ņé¼ņÜ®ĒĢśļŖö strategy Ļ░Ć ļŗżļźĖ response ļź╝ ņé¼ņÜ®ĒĢśļŖö ņØ┤ņ£ĀĻ░Ć ņ¢┤ņ®īļ®┤ muscle weakness Ļ░ÉņåīļÉ£ ankle joint sensation, joint stiffness ņÖĆ Ļ░ÖņØĆ ņĀ£ĒĢ£ļÉ£ ņāüĒÖ®ņŚÉ ņĀüņØæĒĢśļŖö ņłśļŗ©ņØĖņ¦ĆļÅä ļ¬©ļź┤ļŖö ņØ╝ņØ┤ļŗż. ņśłļź╝ ļōżņ¢┤ ankle joint ņŚÉ ņČ®ļČäĒĢ£ force ļź╝ ņāØņä▒ĒĢĀ ņłś ņŚåņØä ļĢī ļ│┤ņāüņ×æņÜ®ņ£╝ļĪ£ hip strategyļź╝ ņé¼ņÜ®ĒĢśĻ▓ī ļÉĀ ņłś ņ׳ļŗż. ļŹ¦ļČÖņØ┤ņ×Éļ®┤ ĻĘĀĒśĢņŚÉ ļ¼ĖņĀ£Ļ░Ć ņ׳ļŖö ļģĖņØĖņØś Ļ▓ĮņÜ░ ļ│┤ļŗż ņŗ¼Ļ░üĒĢ£ ņŗĀĻ▓ĮĻ│ä ļśÉļŖö ĻĘ╝Ļ│©Ļ▓®Ļ│äņŚÉ ņĀ£ĒĢ£ņØ┤ ņ׳ļŖö Ļ▓āņ£╝ļĪ£ ļ│┤ņØ┤ļ®░ ņØ┤ņŚÉļö░ļźĖ limited response capacity Ļ░Ć ļéśĒāĆļéśĻ▓ī ļÉ£ļŗż ĻĘĖļלņä£ ņØ┤ ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ļŖö ļŗżņØīĻ│╝ Ļ░ÖņØĆ ņ¦łļ¼ĖļōżņŚÉ ļŗĄņØä ĻĄ¼ĒĢśĻ│Āņ×É ĒĢ£ļŗż..
3Ļ░Ćņ¦Ć test ņŚÉņä£ ņāüņ£ä ┬╝ ĒĢśņ£ä1/4 Ļ│╝Ļ▒░ ļéÖņāüņØä ļ╣äĻĄÉ Ē¢łņØäĻ▓ĮņÜ░ unstable 0.63 stableruddn 0.06 ņĀŖņØĆņØ┤ 0
ņ×æņØĆ perturbation ņŚÉņä£ļÅä ĻĘĖļĀćĻ▓ī ļéśņÖöļŗż
ņØ┤ņÖĆ Ļ░ÖņØĆ ņé¼ņŗżņØĆ stable & unstable group ņØś ņĀ£ĒĢ£ļÉ£ response capacityļź╝ ļ│┤ņŚ¼ņŻ╝ļŖö Ļ▓āņØ┤ļŗż.
#30: ļīĆņāüņ×ÉļōżņŚÉĻ▓ī ņŚäņ¦Ćļ░£Ļ░ĆļØĮņŚÉ ņĄ£ļīĆĒĢ£ ĒלņØä ņŻ╝ļØ╝Ļ│Ā ļ¦ÉĒĢśĻ│Ā gastrocnemius m. capacityļź╝ ņé┤ĒÄ┤ ļ│┤ņĢśņŖĄļŗłļŗż.
ņĀŖņØĆņØ┤ņÖĆ ļģĖņØĖ ļ¬©ļæÉ ņ×æņØĆ Ēś╝ļ×ĆņåŹ ņŚÉņäĀ ņĀäņ▓┤ ļŖźļĀź ņżæ 20%ņØś Ēלļ¦ī ņé¼ņÜ®Ē¢łņ¦Ćļ¦ī unstable ļģĖņØĖņØś Ļ▓ĮņÜ░ 40%ņØś ĒלņØä ņé¼ņÜ®ĒĢśļŖöĻ▓āņØä ļ│╝ ņłś ņ׳ņŚłĻ│Ā
Perturbatin velocityļź╝ 40Cm/second ļĪ£ ņ”ØĻ░Ć ņŗ£ņ╝░ņØäļĢÉ ļģĖņØĖņØ┤ ņĀŖņØĆņØ┤ņŚÉ ļ╣äĒĢ┤ ļŹöņÜ▒ ļ¦ÄņØĆ capacityļź╝ ņé¼ņÜ®ĒĢ£ Ļ▓āņØä ņé┤ĒÄ┤ļ│╝ ņłś ņ׳ņŚłļŗż.
#31: Stepping dl ĒĢäņÜöĒĢśņ¦Ć ņĢŖļŖö slow, small pertubationņŚÉņä£ 3 group dl ņāüņÜ®ĒĢśļŖö strategies ļŖö ņÖäņĀäĒ׳ ļŗżļźĖ Ļ▓āņØ┤ņŚłļŗż.
Stable & unstable ļģĖņØĖņØś Ļ▓ĮņÜ░ ņĀŖņØĆņØ┤ļōżņŚÉ ļ╣äĻĄÉĒĢ┤ņä£ ankle strategyļź╝ ņĀüĻ▓ī ņé¼ņÜ®ĒĢśĻ│Ā hip strategyļź╝ ļŹöņÜ▒ ļ¦ÄņØ┤ ņé¼ņÜ®ĒĢśļŖö Ļ▓āņØ┤ ļ│┤ņśĆļŗż.
ļŹ¦ļČÖņØ┤ņ×Éļ®┤ unstable ļģĖņØĖņØś Ļ▓ĮņÜ░ ĻĘĀĒśĢņØä ņ×ĪĻĖ░ ņ£äĒĢ┤ knee bending & ņ¢æ ĒīöņØä ņØ┤ņÜ® ĒĢśļŖö Ļ▓ā Ļ╣īņ¦Ć Ļ┤Č─ņ░░ņØ┤ ļÉśņŚłļŗż.
ņØ┤ņÖĆ Ļ░ÖņØĆ ņ░©ņØ┤ļŖö faster pertubatin ņŚÉņä£ ļŹöņÜ▒ Ēü¼Ļ▓ī ļéśĒāĆļé¼ļŖöļŹ░ ļģĖņØĖļōżņØĆ ņĀŖņØĆņØ┤ļōżņØ┤ ankle hip strategyļ¦īņØä ņØ┤ņÜ® ņä£ ņ׳ļŖö ļÅÖņĢłņŚÉļÅä stepping ņØä ņé¼ņÜ®ĒĢśļŖö Ļ▓āņØ┤ ļéśĒāĆļé¼ļŗż.
ņŚ¼ĻĖ░ņŚÉņä£ ļéśĒāĆļé£ cop ņØś change response ļź╝ ĻĘĖļ”╝ņŚÉņä£ ņé┤ĒÄ┤ļ│╝ ņłś ņ׳ļŗż.
ņĀŖņØĆņØ┤ļōżņØś Ļ▓ĮņÜ░ platform pertubation ņØ┤ ņŻ╝ņ¢┤ņĪīņØäļĢī ĒÜ©Ļ│╝ņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ņĢłņĀĢņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ cop ļź╝ ņĀ£ ņ×Éļ”¼ļĪ£ Ļ░ĆņĀĖĻ░ĆļŖö Ļ▓āņØ┤ Ļ┤Č─ņ░░ļÉśņ¢┤ņ¦Ćļéś ļģĖņØĖļōżņØś Ļ▓ĮņÜ░ ņĢłņĀĢņĀüņØĖ ņ×ÉņäĖņŚÉ ļ╣äĒĢ┤ copņØś oscillationņØ┤ ļ¦ÄņØ┤ ņ”ØĻ░ĆļÉśņŚłĻ│Ā unstable ļģĖņØĖņØś Ļ▓ĮņÜ░ cop Ļ░Ć Ļ░Ćņן ļ¦ÄņØ┤ ļ░¢ņ£╝ļĪ£ ņØ┤ļÅÖļÉśĻ│Ā Ļ▓░ļĪĀņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ņĢłņĀĢņĀüņØĖ ņ×ÉņäĖļź╝ ņ×ĪĻĖ░ ņ£äĒĢ┤ copļź╝ ņĀ£ ņ£äņ╣ś ņŗ£ĒéżļŖöļŹ░ ņŗ£Ļ░äņØ┤ ņĀ£ņØ╝ ļ¦ÄņØ┤ ĒĢäņÜöĒĢśĻ▓ī ļÉśņŚłļŗż.
#36: whanger ļŗżņłśņØś ļģĖņØĖļīĆņāüņ×ÉņŚÉĻ▓īņä£ vibratory response ļź╝ ĻĖ░ļĪØ ĒĢĀ ņłś ņŚåņŚłļŗż.
Touch stimuli ņØś ņŚŁņ╣ś ņ”ØĻ░ĆņŚÉ ļö░ļØ╝ ļéśņØ┤ņŚÉ ļö░ļØ╝ tactile sensation Ļ░Éņåī
ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ņ×ÉļōżņØĆ meissner end organs and pacinian corpuscle ņŚÉ ņØśĒĢ┤ļéśĒāĆļéśļŖö fine touch, pressure, vibration sensation ļō▒ņØ┤ Ļ░ÉņåīĒĢśļŖö Ļ▓āņ£╝ļĪ£ ļéśļéśļé¼ļŖöļŹ░
AgingņØĆ messiner end organs Ļ│╝ pacinian corpuscle ņØś ņ¢æĻ│╝ ņ¦łņŚÉ ņśüĒ¢źņØä ļ░øņĢśĻ│Ā ĻĖ░ļŖźņĀü ĒÜ©Ļ│╝ļŖö receptors ņØś ņåÉņŗżļÉ£ ņł½ņ×ÉņŚÉ ņØśĒĢ┤ ņÜ░ņäĀņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ņśüĒ¢źņØä ļ░øņĢśļŗż.
#37: Receptor loss ņÖĆ ļŹöļČłņ¢┤ peripheral receptor ņØś sensory fiber ņżæ 30%ņŚÉ innervation ņŚÉ Ļ░ÉņåīĻ░Ć ņ׳ļŖö Ļ▓āņ£╝ļĪ£ ņĢīļĀżņĀĖ ņ׳ņŚłļŖöļŹ░ ļīĆļČĆļČäņØś ņøÉņØĖņØĆ peripheral neuropathy Ļ░Ć ņøÉņØĖņØĖ Ļ▓āņ£╝ļĪ£ ļ░ØĒśĆņĪīņŖĄļŗłļŗż.
Pheripheral neuropathy Ļ░Ć ņ׳ļŖö ļģĖņØĖņØśĻ▓ĮņÜ░ vision & vestibular system ņŚÉ ņØśņĪ┤ļÅäļŖö ļŹöņÜ▒ ņ╗żņ¦ĆĻ▓ī ļÉ£ļŗż.
Somatosensory system neuropathyņŚÉ ņØśĒĢ£ Ļ▓░ĒĢ©ņØ┤ņ׳ļŖö ļģĖņØĖņØś postural response ļź╝ ņé┤ĒÄ┤ ļ│┤ņĢśņØä Ļ▓ĮņÜ░ ĻĘĖļ”╝ 9-8
Platform ņŚÉ ņØśĒĢ┤ ņāØĻĖ░ļŖö Ēś╝ļ×ĆņŚÉ ļ░śņØæĒĢśļŖö onset latencies Ļ░Ć ļŖ”ņČ░ņ¦äĻ▓āņØ┤ ļ│┤ņØ┤Ļ│Ā ņ×ÉĻĘ╣ size ņÖĆ Ļ┤Č─ļĀ©ĒĢ┤ņä£ amplitude ļź╝ ņĪ░ņĀłĒĢśļŖö ļŖźļĀźņØ┤ ĒśäņĀĆĒ׳ ļ¢©ņ¢┤ņ¦äĻ▓āņØä ņé┤ĒÄ┤ ļ│╝ ņłś ņ׳ņŚłļŗż.
9-8ŃģĀ ņØś ĻĘĖļ”╝ņØĆ ņĀĢņāüņØĖĻ│╝ preipheral neuropathy Ļ░Ć ņ׳ļŖö ņé¼ļ×īņØś muscle onset latencies ļź╝ ļ╣äĻĄÉĒĢ£Ļ▒░ņ×ģļŗłļŗż.
Inglis ļō▒ņØĆ ĻĖ░ļĪØĒĢ£ ļ¬©ļōĀ Ńä▒Ńä┤ņ£ĪļōżņØś ļōĘ Ļ▓░Ļ│╝ ļģĖņØĖļōżņŚÉĻ▓īņä£ ļŖÉļ”¼Ļ▓ī ļéśņÖöļŗżĻ│Ā Ē¢łņ£╝ļ®░
Nelson ņØĆ multiple sclerosis ļź╝ Ļ░Ćņ¦ĆĻ│Ā ņ׳ļŖö ĒÖśņ×ÉņÖĆ neuropathy Ļ░Ć ņ׳ļŖö ļģĖņØĖņØśņØ┤ ļ╣äņŖĘĒĢ£ ņ¢æņāüņØ┤ ņ׳ļŗżĻ│Ā Ē¢łļŗż.
#38: ļ╣ø ņ×Éņ▓┤Ļ░Ć ņĀüĻ▓ī ņĀäļŗ¼ļÉśĻ│Ā ļ¼╝ņ▓┤ļź╝ ļ│┤ļŖöļŹ░ ĒĢäņÜöĒĢ£ ņĄ£ņåīĒĢ£ņØś ļ╣øņØ┤ ņ”ØĻ░ĆĒĢśļ®░ ļ×┤ļö® ņØś Ļ░Éņåī ņŗ£ļĀźĻ┤Č─ņ░░ ļŖźļĀźņØś ņĢäņ╣┤ļĪ£ņøĆņØ┤ ļ¢©ņ¢┤ņ¦ĆĻ▓īļÉśĻ│Ā , ņĀĢņ¦ĆņāüĒā£ ļ¼╝Ļ▒┤ņØś ļ¬ģļÅäļź╝ ĻĄ¼ļ│äĒĢĀ ņłś ņ׳ļŖö ļŖźļĀźņØ┤ ļ¢©ņ¢┤ņ¦Ćļ®░ ļ░▒ļé┤ņן Ļ░üļ¦ēņØś ļ░śļ¼Ė ļō▒ņØ┤ ļéśĒāĆļéśĻĖ░ ņēĮļŗżĻ│Ā ļ│┤Ļ│ĀļÉśņ¢┤ņ׳ļŗż.
ņØ┤ņÖĆĻ░ÖņØĆ ņé¼ņŗżļōżņØĆ functional skill ņØś ņĀäļ░śņŚÉ Ļ▒Ėņ│É ņśüĒ¢źņØä ņŻ╝Ļ▓ī ļÉ£ļŗż.
ņŚÉļź╝ ļōżņ¢┤ ļ¦ÄņØĆ ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ļōżņŚÉņä£ ņŗ£Ļ░üņØä ņ░©ļŗ© Ē¢łņØä Ļ▓ĮņÜ░ ļéśņØ┤Ļ░Ć ļōżļ®░ ļŹöņÜ▒ quiet stance ņāüĒā£ņŚÉņä£ sway Ļ░Ć ņ”ØĻ░ĆļÉ£ļŗżĻ│Ā ļ░£Ēæ£Ē¢łļŗż.
#39: VisionņØś balance control ņŚÉ ņśüĒ¢ÉņØä ņé┤ĒÄ┤ļ│┤ļŖö ļ░®ļ▓Ģņ£╝ļĪ£ Ļ░Ćņן ļīĆņżæņĀüņØĖ ļ░®ļ▓ĢņØĆ moving room test ņØĖļŹ░ ņŗ£Ļ░üņŚÉ Ēś╝ļ×ĆņØä ņŻ╝ņ¢┤ postural responseļź╝ ņĖĪņĀĢĒĢśļŖö ļ░®ļ▓Ģņ×ģļŗłļŗż.
WadeļŖö cop ļź╝ ņĖĪņĀĢĒĢśļ®░ moving roomņŚÉņä£ visual flow ņØś ĒÜ©Ļ│╝ļź╝ ņŗżĒŚś Ē¢łļŖöļŹ░ Ļ▓░ļĪĀņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ Ļ▒┤Ļ░ĢĒĢ£ ļģĖņØĖļōżļÅä ņĀŖņØĆņØ┤ņŚÉ ļ╣äĻĄÉĒĢ┤ņä£ ļ│┤ļŗż ļ¦ÄņØĆ sway Ļ░Ć ļéśĒāĆļéśļŖÉ Ļ▓āņØä ļ│┤ņĢśņØä ļĢī ņØ┤ ņøÉņØĖņØĆ somatosensory system information ņØś Ļ░ÉņåīņŚÉ ĻĖ░ņØĖĒĢśļŖö Ļ▓āņ£╝ļĪ£ Ļ▓░ļĪĀņØä ņ¦ĆņŚłņŖĄļŗłļŗż.
ĻĘĖļ”╝ A ļ░®ņØ┤ ņĢ×ņ£╝ļĪ£ ņøĆņ¦üņØ╝ ļĢī ļīĆņāüņ×ÉļŖö ļÆżņ¬Įņ£╝ļĪ£ sway(B) ņĢ×ņ¬Įņ£╝ļĪ£ ┬®
Ļ░ĆņÜ┤ļŹ░ ĻĘĖļ”╝ cop Ļ░Ć Ļ░ü group ņØś postural response ļź╝ ļ│┤ņŚ¼ņŻ╝Ļ│Ā ņ׳ļŗż Ļ▓░ļĪĀņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ symptomatic ĒĢ£ ļģĖņØĖņØś Ļ▓ĮņÜ░ visual flow reliance ņŚÉ ņ░©ņØ┤Ļ░Ć ņ׳ļŖö Ļ▓āņ£╝ļĪ£ ļéśĒāĆļé¼Ļ│Ā ņØ┤ļōżņØĆ ļ░®ņØ┤ ļ®łņČś ĒøäņŚÉņä£ ņ¦ĆņåŹņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ cop oscillation ņØ┤ Ļ┤Č─ņ░░ ļÉśņŚłļŗż. ļśÉĒĢ£ ņ×ÉņäĖļź╝ ļŗżņŗ£ Ļ│Āņ│É ņ×ĪņØä ļĢī ņØ┤ļōżņØĆ higher levels of sheer force ļź╝ ņé¼ņÜ® ĒĢśļŖö Ļ▓āņ£╝ļĪ£ ņØ┤ļŖö hip strategy ļź╝ ņé¼ņÜ®ĒĢ£ Ļ▓āņ£╝ļĪ£ ļ│┤ņŚ¼ņ¦äļŗż
#40: Vestibular system ņØś ĻĖ░ļŖź ņżæ ĒĢśļéśļŖö vision Ļ│╝ somatosensory system ņØś ņÖäļ▓ĮĒĢ£ reference system ņ£╝ļĪ£ ņ”ē ļ╣äĻĄÉ ņĖĪņĀĢ ĒĢśļŖö ĻĖ░Ļ┤Č─ņ£╝ļĪ£ ņŚŁĒĢĀņØä ĒĢ£ļŗż.
ĒŖ╣Ē׳ vestibular system ņØĆ vision & somatosensory system ņØ┤l ņāüĒśĖ ņČ®ļÅīņØ┤ ņāØĻĖĖ ļĢī ĻĘĖ ņŚŁĒĢĀņØ┤ ļŹöņÜ▒ ņżæņÜöĒĢ┤ņ¦äļŗż ņ”ē vestibular system ņŚÉ ļ¼ĖņĀ£Ļ░Ć ņ׳ļŖö ļģĖņØĖņØś Ļ▓ĮņÜ░ ĒÖśĻ▓ĮņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ vision & somatosensory system ņØ┤ ņČ®ļÅīņØ┤ ņāØĻĖĖ ņłś ņ׳ļŖö ĒÖśĻ▓ĮņŚÉ ļģĖņČ£ļÉĀ ļĢī dizzness & unsteadness ļź╝ ļ│┤ņØ┤ļŖö ņøÉņØĖņØ┤ ļÉ£ļŗż.,
#41: ļ¦ÄņØĆ ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ņ×ÉļōżņØĆ postural control ņØä ĒĢśĻĖ░ ņ£äĒĢ£ Ļ░ÉĻ░üņĀĢļ│┤ļź╝ ņØ╝ņĀĢņĀĢļÅä ņĀ£Ļ▒░ĒĢśĻ▓ī ļÉśļ®┤ ņØ╝ļČĆ ļģĖņØĖļōżņŚÉĻ▓īņä£ sensory system ņØś ĻĖ░ļŖźņĀü ņĀĆĒĢśĻ░Ć ļ░£ņāØ ļÉś ļśæļ░öļĪ£ ņä£ ņ׳ļŖö Ļ▓āņØä ņ£Āņ¦ĆĒĢśĻĖ░ļÅä ņ¢┤ļĀżņÜ┤ ņāüĒā£Ļ░Ć ļÉśņŚłļŗż.
#45: 70-80 ņäĖ ļģĖņØĖļōżņØś Ļ▓ĮņÜ░ ņØ┤ postural adjustment ņŚÉ ļ¼ĖņĀ£Ļ░Ć ļéśĒāĆļéśļŖöļŹ░ ņ¦ĆņåŹņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ movementļź╝ ĒĢśļ®┤ņä£ balance adjustment ļź╝ ĒåĄĒĢ®ĒĢśļŖö ļŖźļĀźņØ┤ ļ¢©ņ¢┤ņĪīļŗż. ņśłļź╝ ļōżņ×Éļ®┤ ļ¼╝Ļ▒┤ņØä ļōżĻ│Ā ņś«ĻĖ░ļŖö ņØ╝ļō▒ŌĆ”
Anticipatory postural adjustment ņÖĆ aging Ļ│╝ņØś Ļ┤Č─Ļ│äļź╝ ņĀ£ņØ╝ ņ▓śņØī ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ĒĢ£ ņé¼ļ×īņØĆ ļ¤¼ņŗ£ņĢä Ļ│╝ĒĢÖņ×É kokii ļĪ£ņä£
ņĀĢņāüņä▒ņØĖņØś Ļ▓ĮņÜ░ ņä£ņä£ voluntary movement ļź╝ ņłśĒ¢ēĒĢśĻĖ░ ņĀäņŚÉ anticipatory movement Ļ░Ć ņØ╝ņ¢┤ļéśņä£ balance control dl ņØ┤ļŻ©ņ¢┤ ņ¦ĆļŖöļŹ░ (postural response synergies) ņśłļź╝ ļōżņ¢┤ ņä£ņ׳ļŖö ņāüĒā£ņŚÉņä£ ĒĢĖļōżņØä ņ×ĪņĢäļŗ╣ĻĖ░ļŖö Ļ│╝ņĀ£ļź╝ ņłśĒ¢ēĒĢśļŖö Ļ▓ĮņÜ░ ņ▓½ļ▓łņ¦Ė GCM ņØ┤ ĒÖ£ņä▒ĒÖöļÉśĻ│Ā, hamstring, TRUNK extensor, ņł£ņ£╝ļĪ£ ĒÖ£ņä▒ĒÖö ļÉśĻ│Ā prime mover muscle ņØĖ biceps Ļ░Ć ņøĆņ¦üņśĆļŗż.
#50: ļģĖņØĖļōżņØś Ļ▓ĮņÜ░ ņŚ¼ļ¤¼ ĻĖ░ļŖźņØś ņĀĆĒĢśļĪ£ postural control ņØś ļŖźļĀźņØ┤ Ļ░ÉņåīĒ¢łļŗż. ņØ┤ļĀćĻ▓ī Ļ░ÉņåīĒĢ£ balance ĻĖ░ļŖźņØä training ņØä ĒåĄĒĢ┤ņä£ Ļ░ĆļŖźĒĢĀĻ╣ī?
ņØ╝ļŗ© ņÜ┤ļÅÖņØ┤ Ļ▒┤Ļ░ĢĻ│╝ fitnessņŚÉ ņżæņÜöĒĢ£ ņÜöņåīļØ╝ļŖöĻ▓āņØĆ ļäōĻ▓ī ļ░øņĢäļōżņŚ¼ ņÖöļŗż.
ļ¦ÄņØĆ ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ņ×ÉļōżņØ┤ standing balance ļź╝ ņ”Øņ¦äņŗ£ĒéżĻĖ░ ņ£äĒĢ┤ functional test ļź╝ ĒåĄĒĢ┤ņä£ training program ņØä test ĒĢśĻ│Ā design ņØä Ē¢łļŖöļŹ░
ņØ┤ training program ņØĆ ļŗżņØīĻ│╝ Ļ░ÖņØ┤ 4Ļ░Ćņ¦Ć categoriesļĪ£ ĻĄ¼ļČäļÉ£ļŗż.
#54: Dynamic balance group ņŚÉņä£ ĻĘĀĒśĢ ĒøłļĀ©ņØ┤ ļŹöņÜ▒ ĒÜ©Ļ│╝ņĀüņØĖĻ▓āņ£╝ļĪ£ ļéśņÖöĻ│Ā, ĻĘĖļ░¢ņŚÉ cardiovascular endurance strength ROM ļō▒ņŚÉļŖö ļ│ĆĒĢ©ņØ┤ ņŚåņŚłļŗż.
Ļ▓░ļĪĀņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ single leg stand & functional base of support & balance function
#55: ņŚ¼ļ¤¼ system ņŚÉ ņśüĒ¢źņØä ļ»Ėņ╣śļŖö ex. Program ņØä ņŗżņŗ£Ē¢łņØä Ļ▓ĮņÜ░ balance function ņØ┤ ņ”ØĻ░ĆĒĢśļŖöĻ░Ć? ļīĆļČĆļČä ĒöäļĪ£ĻĘĖļשņŚÉ strengthening, aerobic & balance coordination dl ĒżĒĢ©ļÉ£ļŗż.
Ļ▓░Ļ│╝ļŖö ņ▓½ ļ▓łņ¦Ė ņ¦æļŗ©ņŚÉņä£ļ¦ī ĻĘĀĒśĢņØś ņ”ØĻ░ĆĻ░Ć ļ│┤ņśĆļŗż. Single leg stance center of force displacement Ļ░Ć ņ▓½ņ¦Ė ņ¦æļŗ©ņŚÉņä£ 18%ņØś Ļ░ÉņåīĻ░Ć ļ│┤ņśĆļŗż
-balance & mobility ņŚÉ Ļ┤Č─ļĀ©ļÉ£ Clinical test ļ┐Éļ¦ī ņĢäļŗłļØ╝ falling risk ļź╝ Ļ░üĻ░ü 3Ļ░£ ņ¦æļŗ©ņŚÉņä£ ņŗżņŗ£Ē¢łļŗż.
#56: Functional balance test & dynamic gait index emd clinical test ļź╝ ņłśĒ¢ēĒ¢łĻ│Ā ņÜ┤ļÅÖ program ņŚÉ ņ░ĖņŚ¼ĒĢ£ ņ¦æļŗ©ņØĆ control ņ¦æļŗ©ņŚÉ ļ╣äĒĢ┤ ņĖĪņĀĢļÉ£ ļ¬©ļōĀ 3Ļ░£ņØś ņĖĪņĀĢņŚÉņä£ ņØśļ»Ė ņ׳Ļ▓ī ņóŗĻ▓ī ļéśĒāĆļé¼ļŗż.
#58: ņŗżĒŚśĻ▓░Ļ│╝ ņ▓½ļéĀļČĆĒä░ ļ¦łņ¦Ćļ¦ē ļéĀĻ╣īņ¦Ć sway ņĀĢļÅäĻ░Ć ņØśļ»Ė ņ׳Ļ▓ī ņ”Øņ¦äļÉśņŚłļŖöļŹ░ (all foam surface condition & eye closed head extended on normal surface)
ņĪ░Ļ▒┤ņŚÉņä£ļ¦ī ņ”ØĻ░ĆļÉśņŚłļŗż.
9-14ļŖö training group ņĢłņŚÉ ļīĆņāüņ×É ņżæ ĒĢ£ ļ¬ģņØś 10ņØ╝ ļÅÖņĢłņØś sway Ļ░Éņåīļź╝ ļ│┤ņŚ¼ņŻ╝Ļ│Ā ņ׳ļŗż sensory organization training dl ļŗżļźĖ balance taskņŚÉ transfer ļÉśņŚłņØäĻ╣ī
ņŚÉ
Sensory training effectļŖö ņŚ¼ļ¤¼ clininc ņŚÉņä£ ņé¼ņÜ®ļÉśņ¢┤ņ¦ĆļŖö sensory organization test ņŚÉ transfer ļÉśņŚłļŗż( one legged stance test.
ĻĘĖ ļ░¢ņŚÉļÅä platform perturbation ņŗ£ muscle response pattern ņŚÉļÅä ļ│ĆĒÖöĻ░Ć ņāØĻ▓╝ļŗż.ŌĆöless coactivation of antagonist muscle.
Ēøłļ│Ćļ░øņØĆ ļīĆņāüņ×ÉņØś ĒÜ©Ļ│╝ļŖö 4ņŻ╝Ļ╣īņ¦Ć ņ¦ĆņåŹļÉśņŚłļŗż.