1 of 25
Download to read offline


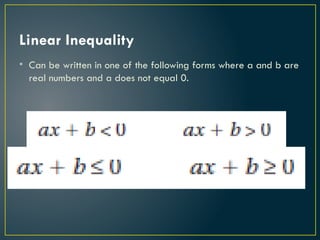


















Recommended
Solving Absolute Value Equations and Inequalities.ppt



Solving Absolute Value Equations and Inequalities.pptFarhanPerdanaRamaden1
Ěý
This document provides information and examples for solving absolute value equations and inequalities. It begins with definitions of absolute value and discusses how absolute value equations can have two solutions since the expression inside the absolute value can be positive or negative. Examples are provided for solving absolute value equations by setting the expression equal to both its positive and negative values. The document also discusses how to solve absolute value inequalities by splitting them into "and" or "or" statements and provides examples of solving and graphing various absolute value inequalities.Inequalities mathematics grade nine igcse.ppt



Inequalities mathematics grade nine igcse.pptMisterTono
Ěý
- Students learn to represent inequalities on a number line using different signs such as <, ≤, >, ≥.
- They learn to solve inequalities algebraically using the same steps as solving equations, such as adding/subtracting the same number to both sides.
- A key rule is that if multiplying or dividing by a negative number, the inequality sign must be switched (e.g. from < to >).
- Examples of solving multi-step inequalities and real-world word problems are provided to illustrate the concepts and skills.Solving and Graphing Inequalities.ppt



Solving and Graphing Inequalities.pptSultanTomasII
Ěý
This document provides information about solving and graphing inequalities. It defines inequalities and the symbols used such as <, ≤, >, ≥. It explains that inequalities have solutions that satisfy the given condition, unlike equations which have specific values. The document shows how to solve different types of inequalities algebraically by adding or subtracting from both sides and how to determine the direction of the shading or dashed line when graphing the solutions on a number line. It also discusses absolute value inequalities and graphing linear inequalities in two variables.Solving and Graphing Inequalities.pptSolving and Graphing Inequalities.ppt



Solving and Graphing Inequalities.pptSolving and Graphing Inequalities.pptAreejAhmed38
Ěý
Solving and Graphing Inequalities.ppt(7) Lesson 6.6



(7) Lesson 6.6wzuri
Ěý
The document provides examples for solving word problems using the work backward strategy. It includes three example problems and their answers:
1) Miguel had originally $27 based on spending amounts for food and ice cream and having $9 left which was 1/3 of the original.
2) Curtis' starting vet bill balance was $160 based on an $80 original bill, $40 added for medicine, and now owing $120.
3) The number is 21 based on dividing a number by 3, adding 5 to the quotient, and subtracting 2 to get 10.4.5 notes



4.5 notesnglaze10
Ěý
This document defines absolute value and discusses solving absolute value equations in 3 sentences or less:
Absolute value is the distance between zero and a number on the number line, and absolute value equations can be solved by rewriting the equation as two separate equations setting the absolute value expression equal to both its positive and negative values. The document provides examples of solving absolute value equations, identifying when an equation has no solution, and applying absolute value to word problems involving acceptable ranges.(7) Lesson 6.8



(7) Lesson 6.8wzuri
Ěý
The document provides examples of solving two-step inequalities and writing and solving word problems as inequalities. It begins with six examples of solving two-step inequalities by combining like terms and then isolating the variable, including graphing the solution sets on number lines. The next examples involve writing and solving word problems as inequalities, such as writing an inequality to represent the number of magazine subscriptions needed to earn $35. The document concludes by reviewing the process of solving two-step inequalities.Solving inequalities



Solving inequalitiesIta Rodriguez
Ěý
This presentation helps algebra students understand how to graph and solve inequalities. There are one-step, multi-step, and compound inequalities.Absolute Value Inequalities



Absolute Value Inequalitiesswartzje
Ěý
This document discusses how to solve absolute value inequalities by:
1) Determining whether the absolute value is greater than or less than the variable, which indicates a disjunction or conjunction graph.
2) Solving the inequality for both possibilities of the expression inside the absolute value being positive or negative.
3) Combining the solutions from both possibilities using the appropriate inequality symbol (>, <, etc.) to obtain the final solution set.PRIMER GRADO ECUACIONES Y DESIGUALDADES EN UNA VARIABLE.pdf



PRIMER GRADO ECUACIONES Y DESIGUALDADES EN UNA VARIABLE.pdfedwinllantoy2
Ěý
This document provides an overview of solving first degree equations and inequalities in one variable. It defines key terms like equations, solutions, and properties of equality. It then explains the steps and properties used to solve equations with one or multiple operations, like addition, subtraction, multiplication and division. Examples are provided to demonstrate solving different types of equations and checking solutions. The document also discusses simplifying equations before solving by combining like terms.Oct. 20, 2014



Oct. 20, 2014khyps13
Ěý
This document contains notes from a math class that covered several topics:
- Warm-up with Khan Academy on fractions and percents
- Reviewing fraction and percent conversions
- Solving absolute value equations
- The notes provide examples and steps for solving absolute value equations, changing fractions to decimals, and ordering fractions using cross-multiplication. Examples are worked through to demonstrate the process.Linear equations review



Linear equations reviewjulienorman80065
Ěý
This document provides instruction on solving linear equations. It includes definitions of key terms used in linear equations like linear equation, non-linear equation, solution, and coefficient. It outlines objectives like identifying the number of solutions an equation has, solving single and multi-step linear equations, and writing mathematical expressions from word problems as linear or non-linear equations. Examples of solving various types of linear equations are provided along with explanations of the expected solutions. Practice problems are included for students to work through.2.-Linear-Equation-and-Inequalities-Copy2.pptx



2.-Linear-Equation-and-Inequalities-Copy2.pptxmelecio maneclang
Ěý
This document provides an overview of linear inequalities and equations for a mathematics class. It defines key terms like linear inequality, solution set, and graphs examples of solving different types of linear inequalities. Students are asked to solve sample inequalities, write the solution sets using set notation, and graph the solutions. The document compares linear inequalities and equations, and covers various properties for solving inequalities, including addition/subtraction, multiplication/division, and dealing with negative numbers.MIT Math Syllabus 10-3 Lesson 6: Equations



MIT Math Syllabus 10-3 Lesson 6: EquationsLawrence De Vera
Ěý
This document provides information about equations, including definitions, properties, and steps to solve different types of equations. It defines an equation as a statement about the equality of two expressions. Equations can be solved to find all values that satisfy the equation. The key properties of equality, including addition/subtraction and multiplication/division properties, allow equivalent equations to be formed in order to solve equations. The document discusses linear equations, absolute value equations, formulas, and using equations to model real-world situations.November 30, 2015



November 30, 2015khyps13
Ěý
The document provides an introduction and overview of inequalities for a math class. It includes:
1) A discussion of the key differences between equations and inequalities, noting that inequalities can have a range of solutions rather than a single value.
2) Examples of how to write inequalities using appropriate symbols (<, >, ≤, ≥) and an explanation of open vs. closed circles on a number line.
3) Steps for solving linear inequalities, with the reminder that the inequality sign must be flipped when multiplying or dividing both sides by a negative number.
4) Practice problems for students to solve and graph inequalities on a number line.1



1Dreams4school
Ěý
This document discusses solving and graphing linear inequalities. It explains what inequalities are, different inequality symbols, and how to solve linear inequalities using addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. It also notes that when multiplying or dividing by a negative number, the inequality symbol must be reversed. Examples are provided to demonstrate how to solve linear inequalities algebraically and graph the solution sets on a number line. The document encourages supporting female education to eliminate inequality.Lecture 7 (inequalities)



Lecture 7 (inequalities)HarithaRanasinghe
Ěý
1) An inequality is a mathematical statement that uses inequality symbols like <, ≤, >, ≥ to show the relationship between two quantities.
2) When graphing inequalities on a number line, closed circles are used for ≤ and ≥, and open circles are used for < and >.
3) Linear inequalities in two variables can be written as Ax + By < C, Ax + By > C, Ax + By ≤ C, or Ax + By ≥ C. An ordered pair (x,y) is a solution if it makes the inequality true.Equations Revision



Equations Revisionandrewhickson
Ěý
1) The document outlines objectives and methods for solving linear equations, including solving single equations, equations with fractions, and simultaneous equations.
2) Key methods discussed are transposing terms, multiplying/dividing both sides by the same amount to isolate the variable, and using substitution or elimination for simultaneous equations.
3) Examples are provided to illustrate solving single equations with various operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication and division as well as equations containing fractions or brackets.presentation-111004200224-phpapp02.pptx



presentation-111004200224-phpapp02.pptxJennilynBalusdan3
Ěý
This document provides examples of solving various types of linear equations and inequalities in one variable. It demonstrates solving equations and inequalities using properties of equality and inequality, such as adding or subtracting the same quantity to both sides. It also discusses representing and solving4.4 notes



4.4 notesnglaze10
Ěý
This document discusses solving compound inequalities, which contain two inequalities joined by "and" or "or". It provides examples of writing compound inequalities from word phrases and graphing the solutions. Examples are given of solving compound inequalities containing "and" or "or" and graphing the solutions.Algebra 1. 9.7 Lesson. Absolute Value



Algebra 1. 9.7 Lesson. Absolute Valuedmatkeson21
Ěý
The document discusses solving absolute value equations. It begins with examples of absolute value equations and their solutions. It then provides additional examples and special cases of absolute value equations, explaining how to set them up as cases and solve for the solutions. It also includes a word problem example about gas mileage and the absolute value equation used to find the minimum and maximum values.Solving and graphing inequalities lecture



Solving and graphing inequalities lectureDaisy Zambrano
Ěý
This document provides an overview of a lesson on solving and graphing inequalities. It includes student objectives like understanding properties of inequalities, solving singular and absolute value inequalities, and applying inequalities to real-life situations. Examples are provided to demonstrate solving different types of inequalities step-by-step and graphing the solutions. Students are asked to apply what they've learned to solve practice problems independently and discuss questions in pairs. The lesson aims to build students' skills in reasoning with inequalities.Solving and graphing inequalities lecture 1



Solving and graphing inequalities lecture 1Daisy Zambrano
Ěý
This document provides an overview of a lesson on solving and graphing inequalities. It includes student objectives like understanding properties of inequalities and learning how to solve singular and absolute value inequalities. Examples are provided to demonstrate solving different types of inequalities step-by-step and graphing the solutions. Real-world examples like parking restrictions are used to illustrate how inequalities apply in daily life. Formative assessments like a KWL chart and discussion questions are incorporated to check understanding.(7) Lesson 6.4



(7) Lesson 6.4wzuri
Ěý
Here are the key steps to solve this type of problem:
1) Write the equation relating the quantities: b + 6 = 18
2) Undo the addition by subtracting 6 from both sides: b = 18 - 6
3) Simplify: b = 12
To check the solution, substitute b = 12 back into the original equation:
12 + 6 = 18
18 = 18
The check confirms that b = 12 is indeed the solution.
By learning the process of undoing operations methodically, I can set up and solve two-step equations to find the value of a variable. This helps explain what it means for two quantities to be equal - the operations performed on both sides result inSolving Inequalities.ppt



Solving Inequalities.pptnuriyesan
Ěý
This document discusses solving inequalities:
- Inequalities use signs like <, ≤, >, ≥ instead of = and represent relationships between quantities.
- Graphing inequalities follows rules where the direction of the arrow indicates whether it is open or closed.
- Solving inequalities uses the same properties as solving equations, except when multiplying or dividing by a negative number the sign must be switched.
- Multi-step inequalities are solved by performing the same operations as equations and checking signs remain correct.Solving Inequalitiesmath sixt grade ineq



Solving Inequalitiesmath sixt grade ineqjsalerno2
Ěý
This document discusses solving inequalities. It introduces inequality signs such as <, ≤, >, ≥ and their meanings. It explains how to graph inequalities by using arrows pointing in the direction of the sign. The document then covers solving one-step and multi-step inequalities by applying properties of inequalities, such as switching the sign when multiplying or dividing by a negative number. Examples are provided to illustrate solving different types of inequalities step-by-step.More Related Content
Similar to Algebra Inequality presentation power point.pptx (20)
Solving inequalities



Solving inequalitiesIta Rodriguez
Ěý
This presentation helps algebra students understand how to graph and solve inequalities. There are one-step, multi-step, and compound inequalities.Absolute Value Inequalities



Absolute Value Inequalitiesswartzje
Ěý
This document discusses how to solve absolute value inequalities by:
1) Determining whether the absolute value is greater than or less than the variable, which indicates a disjunction or conjunction graph.
2) Solving the inequality for both possibilities of the expression inside the absolute value being positive or negative.
3) Combining the solutions from both possibilities using the appropriate inequality symbol (>, <, etc.) to obtain the final solution set.PRIMER GRADO ECUACIONES Y DESIGUALDADES EN UNA VARIABLE.pdf



PRIMER GRADO ECUACIONES Y DESIGUALDADES EN UNA VARIABLE.pdfedwinllantoy2
Ěý
This document provides an overview of solving first degree equations and inequalities in one variable. It defines key terms like equations, solutions, and properties of equality. It then explains the steps and properties used to solve equations with one or multiple operations, like addition, subtraction, multiplication and division. Examples are provided to demonstrate solving different types of equations and checking solutions. The document also discusses simplifying equations before solving by combining like terms.Oct. 20, 2014



Oct. 20, 2014khyps13
Ěý
This document contains notes from a math class that covered several topics:
- Warm-up with Khan Academy on fractions and percents
- Reviewing fraction and percent conversions
- Solving absolute value equations
- The notes provide examples and steps for solving absolute value equations, changing fractions to decimals, and ordering fractions using cross-multiplication. Examples are worked through to demonstrate the process.Linear equations review



Linear equations reviewjulienorman80065
Ěý
This document provides instruction on solving linear equations. It includes definitions of key terms used in linear equations like linear equation, non-linear equation, solution, and coefficient. It outlines objectives like identifying the number of solutions an equation has, solving single and multi-step linear equations, and writing mathematical expressions from word problems as linear or non-linear equations. Examples of solving various types of linear equations are provided along with explanations of the expected solutions. Practice problems are included for students to work through.2.-Linear-Equation-and-Inequalities-Copy2.pptx



2.-Linear-Equation-and-Inequalities-Copy2.pptxmelecio maneclang
Ěý
This document provides an overview of linear inequalities and equations for a mathematics class. It defines key terms like linear inequality, solution set, and graphs examples of solving different types of linear inequalities. Students are asked to solve sample inequalities, write the solution sets using set notation, and graph the solutions. The document compares linear inequalities and equations, and covers various properties for solving inequalities, including addition/subtraction, multiplication/division, and dealing with negative numbers.MIT Math Syllabus 10-3 Lesson 6: Equations



MIT Math Syllabus 10-3 Lesson 6: EquationsLawrence De Vera
Ěý
This document provides information about equations, including definitions, properties, and steps to solve different types of equations. It defines an equation as a statement about the equality of two expressions. Equations can be solved to find all values that satisfy the equation. The key properties of equality, including addition/subtraction and multiplication/division properties, allow equivalent equations to be formed in order to solve equations. The document discusses linear equations, absolute value equations, formulas, and using equations to model real-world situations.November 30, 2015



November 30, 2015khyps13
Ěý
The document provides an introduction and overview of inequalities for a math class. It includes:
1) A discussion of the key differences between equations and inequalities, noting that inequalities can have a range of solutions rather than a single value.
2) Examples of how to write inequalities using appropriate symbols (<, >, ≤, ≥) and an explanation of open vs. closed circles on a number line.
3) Steps for solving linear inequalities, with the reminder that the inequality sign must be flipped when multiplying or dividing both sides by a negative number.
4) Practice problems for students to solve and graph inequalities on a number line.1



1Dreams4school
Ěý
This document discusses solving and graphing linear inequalities. It explains what inequalities are, different inequality symbols, and how to solve linear inequalities using addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. It also notes that when multiplying or dividing by a negative number, the inequality symbol must be reversed. Examples are provided to demonstrate how to solve linear inequalities algebraically and graph the solution sets on a number line. The document encourages supporting female education to eliminate inequality.Lecture 7 (inequalities)



Lecture 7 (inequalities)HarithaRanasinghe
Ěý
1) An inequality is a mathematical statement that uses inequality symbols like <, ≤, >, ≥ to show the relationship between two quantities.
2) When graphing inequalities on a number line, closed circles are used for ≤ and ≥, and open circles are used for < and >.
3) Linear inequalities in two variables can be written as Ax + By < C, Ax + By > C, Ax + By ≤ C, or Ax + By ≥ C. An ordered pair (x,y) is a solution if it makes the inequality true.Equations Revision



Equations Revisionandrewhickson
Ěý
1) The document outlines objectives and methods for solving linear equations, including solving single equations, equations with fractions, and simultaneous equations.
2) Key methods discussed are transposing terms, multiplying/dividing both sides by the same amount to isolate the variable, and using substitution or elimination for simultaneous equations.
3) Examples are provided to illustrate solving single equations with various operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication and division as well as equations containing fractions or brackets.presentation-111004200224-phpapp02.pptx



presentation-111004200224-phpapp02.pptxJennilynBalusdan3
Ěý
This document provides examples of solving various types of linear equations and inequalities in one variable. It demonstrates solving equations and inequalities using properties of equality and inequality, such as adding or subtracting the same quantity to both sides. It also discusses representing and solving4.4 notes



4.4 notesnglaze10
Ěý
This document discusses solving compound inequalities, which contain two inequalities joined by "and" or "or". It provides examples of writing compound inequalities from word phrases and graphing the solutions. Examples are given of solving compound inequalities containing "and" or "or" and graphing the solutions.Algebra 1. 9.7 Lesson. Absolute Value



Algebra 1. 9.7 Lesson. Absolute Valuedmatkeson21
Ěý
The document discusses solving absolute value equations. It begins with examples of absolute value equations and their solutions. It then provides additional examples and special cases of absolute value equations, explaining how to set them up as cases and solve for the solutions. It also includes a word problem example about gas mileage and the absolute value equation used to find the minimum and maximum values.Solving and graphing inequalities lecture



Solving and graphing inequalities lectureDaisy Zambrano
Ěý
This document provides an overview of a lesson on solving and graphing inequalities. It includes student objectives like understanding properties of inequalities, solving singular and absolute value inequalities, and applying inequalities to real-life situations. Examples are provided to demonstrate solving different types of inequalities step-by-step and graphing the solutions. Students are asked to apply what they've learned to solve practice problems independently and discuss questions in pairs. The lesson aims to build students' skills in reasoning with inequalities.Solving and graphing inequalities lecture 1



Solving and graphing inequalities lecture 1Daisy Zambrano
Ěý
This document provides an overview of a lesson on solving and graphing inequalities. It includes student objectives like understanding properties of inequalities and learning how to solve singular and absolute value inequalities. Examples are provided to demonstrate solving different types of inequalities step-by-step and graphing the solutions. Real-world examples like parking restrictions are used to illustrate how inequalities apply in daily life. Formative assessments like a KWL chart and discussion questions are incorporated to check understanding.(7) Lesson 6.4



(7) Lesson 6.4wzuri
Ěý
Here are the key steps to solve this type of problem:
1) Write the equation relating the quantities: b + 6 = 18
2) Undo the addition by subtracting 6 from both sides: b = 18 - 6
3) Simplify: b = 12
To check the solution, substitute b = 12 back into the original equation:
12 + 6 = 18
18 = 18
The check confirms that b = 12 is indeed the solution.
By learning the process of undoing operations methodically, I can set up and solve two-step equations to find the value of a variable. This helps explain what it means for two quantities to be equal - the operations performed on both sides result inSolving Inequalities.ppt



Solving Inequalities.pptnuriyesan
Ěý
This document discusses solving inequalities:
- Inequalities use signs like <, ≤, >, ≥ instead of = and represent relationships between quantities.
- Graphing inequalities follows rules where the direction of the arrow indicates whether it is open or closed.
- Solving inequalities uses the same properties as solving equations, except when multiplying or dividing by a negative number the sign must be switched.
- Multi-step inequalities are solved by performing the same operations as equations and checking signs remain correct.Solving Inequalitiesmath sixt grade ineq



Solving Inequalitiesmath sixt grade ineqjsalerno2
Ěý
This document discusses solving inequalities. It introduces inequality signs such as <, ≤, >, ≥ and their meanings. It explains how to graph inequalities by using arrows pointing in the direction of the sign. The document then covers solving one-step and multi-step inequalities by applying properties of inequalities, such as switching the sign when multiplying or dividing by a negative number. Examples are provided to illustrate solving different types of inequalities step-by-step.More from Chuu5 (8)
Edexcel IGCSE-Drawing and Interpretation Histograms.pptx



Edexcel IGCSE-Drawing and Interpretation Histograms.pptxChuu5
Ěý
These slides are used for GCSE students.Recently uploaded (20)
QuickBooks Desktop to QuickBooks Online How to Make the Move



QuickBooks Desktop to QuickBooks Online How to Make the MoveTechSoup
Ěý
If you use QuickBooks Desktop and are stressing about moving to QuickBooks Online, in this webinar, get your questions answered and learn tips and tricks to make the process easier for you.
Key Questions:
* When is the best time to make the shift to QuickBooks Online?
* Will my current version of QuickBooks Desktop stop working?
* I have a really old version of QuickBooks. What should I do?
* I run my payroll in QuickBooks Desktop now. How is that affected?
*Does it bring over all my historical data? Are there things that don't come over?
* What are the main differences between QuickBooks Desktop and QuickBooks Online?
* And moreFESTIVAL: SINULOG & THINGYAN-LESSON 4.pptx



FESTIVAL: SINULOG & THINGYAN-LESSON 4.pptxDanmarieMuli1
Ěý
Sinulog Festival of Cebu City, and Thingyan Festival of Myanmar.How to Configure Flexible Working Schedule in Odoo 18 Employee



How to Configure Flexible Working Schedule in Odoo 18 EmployeeCeline George
Ěý
In this slide, we’ll discuss on how to configure flexible working schedule in Odoo 18 Employee module. In Odoo 18, the Employee module offers powerful tools to configure and manage flexible working schedules tailored to your organization's needs.Kaun TALHA quiz Prelims - El Dorado 2025



Kaun TALHA quiz Prelims - El Dorado 2025Conquiztadors- the Quiz Society of Sri Venkateswara College
Ěý
Prelims of Kaun TALHA : a Travel, Architecture, Lifestyle, Heritage and Activism quiz, organized by Conquiztadors, the Quiz society of Sri Venkateswara College under their annual quizzing fest El Dorado 2025. Useful environment methods in Odoo 18 - Odoo şÝşÝߣs



Useful environment methods in Odoo 18 - Odoo şÝşÝߣsCeline George
Ěý
In this slide we’ll discuss on the useful environment methods in Odoo 18. In Odoo 18, environment methods play a crucial role in simplifying model interactions and enhancing data processing within the ORM framework.How to Setup WhatsApp in Odoo 17 - Odoo şÝşÝߣs



How to Setup WhatsApp in Odoo 17 - Odoo şÝşÝߣsCeline George
Ěý
Integrate WhatsApp into Odoo using the WhatsApp Business API or third-party modules to enhance communication. This integration enables automated messaging and customer interaction management within Odoo 17.SOCIAL CHANGE(a change in the institutional and normative structure of societ...



SOCIAL CHANGE(a change in the institutional and normative structure of societ...DrNidhiAgarwal
Ěý
This PPT is showing the effect of social changes in human life and it is very understandable to the students with easy language.in this contents are Itroduction, definition,Factors affecting social changes ,Main technological factors, Social change and stress , what is eustress and how social changes give impact of the human's life.Eng7-Q4-Lesson 1 Part 1 Understanding Discipline-Specific Words, Voice, and T...



Eng7-Q4-Lesson 1 Part 1 Understanding Discipline-Specific Words, Voice, and T...sandynavergas1
Ěý
Understanding Discipline-Specific Words, Voice, and Technical TermsHow to Modify Existing Web Pages in Odoo 18



How to Modify Existing Web Pages in Odoo 18Celine George
Ěý
In this slide, we’ll discuss on how to modify existing web pages in Odoo 18. Web pages in Odoo 18 can also gather user data through user-friendly forms, encourage interaction through engaging features. Digital Tools with AI for e-Content Development.pptx



Digital Tools with AI for e-Content Development.pptxDr. Sarita Anand
Ěý
This ppt is useful for not only for B.Ed., M.Ed., M.A. (Education) or any other PG level students or Ph.D. scholars but also for the school, college and university teachers who are interested to prepare an e-content with AI for their students and others.Lesson Plan M1 2024 Lesson Plan M1 2024 Lesson Plan M1 2024 Lesson Plan M1...



Lesson Plan M1 2024 Lesson Plan M1 2024 Lesson Plan M1 2024 Lesson Plan M1...pinkdvil200
Ěý
Lesson Plan M1 2024 Lesson Plan M1 2024 Lesson Plan M1 2024 Rass MELAI : an Internet MELA Quiz Finals - El Dorado 2025



Rass MELAI : an Internet MELA Quiz Finals - El Dorado 2025Conquiztadors- the Quiz Society of Sri Venkateswara College
Ěý
Finals of Rass MELAI : a Music, Entertainment, Literature, Arts and Internet Culture Quiz organized by Conquiztadors, the Quiz society of Sri Venkateswara College under their annual quizzing fest El Dorado 2025. How to use Init Hooks in Odoo 18 - Odoo şÝşÝߣs



How to use Init Hooks in Odoo 18 - Odoo şÝşÝߣsCeline George
Ěý
In this slide, we’ll discuss on how to use Init Hooks in Odoo 18. In Odoo, Init Hooks are essential functions specified as strings in the __init__ file of a module.Kaun TALHA quiz Finals -- El Dorado 2025



Kaun TALHA quiz Finals -- El Dorado 2025Conquiztadors- the Quiz Society of Sri Venkateswara College
Ěý
Finals of Kaun TALHA : a Travel, Architecture, Lifestyle, Heritage and Activism quiz, organized by Conquiztadors, the Quiz society of Sri Venkateswara College under their annual quizzing fest El Dorado 2025. The Constitution, Government and Law making bodies .



The Constitution, Government and Law making bodies .saanidhyapatel09
Ěý
This PowerPoint presentation provides an insightful overview of the Constitution, covering its key principles, features, and significance. It explains the fundamental rights, duties, structure of government, and the importance of constitutional law in governance. Ideal for students, educators, and anyone interested in understanding the foundation of a nation’s legal framework.
N.C. DPI's 2023 Language Diversity Briefing



N.C. DPI's 2023 Language Diversity BriefingMebane Rash
Ěý
The number of languages spoken in NC public schools.Principle and Practices of Animal Breeding || Boby Basnet



Principle and Practices of Animal Breeding || Boby BasnetBoby Basnet
Ěý
Principle and Practices of Animal Breeding Full Note
|| Assistant Professor Boby Basnet ||IAAS || AFU || PU || FUKaun TALHA quiz Prelims - El Dorado 2025



Kaun TALHA quiz Prelims - El Dorado 2025Conquiztadors- the Quiz Society of Sri Venkateswara College
Ěý
Rass MELAI : an Internet MELA Quiz Finals - El Dorado 2025



Rass MELAI : an Internet MELA Quiz Finals - El Dorado 2025Conquiztadors- the Quiz Society of Sri Venkateswara College
Ěý
Kaun TALHA quiz Finals -- El Dorado 2025



Kaun TALHA quiz Finals -- El Dorado 2025Conquiztadors- the Quiz Society of Sri Venkateswara College
Ěý
Algebra Inequality presentation power point.pptx
- 1. 1.6: Solve Linear Inequalities I can: Solve a linear and/or compound inequality and graph the solution set. Manipulate a formula to solve for a particular variable.
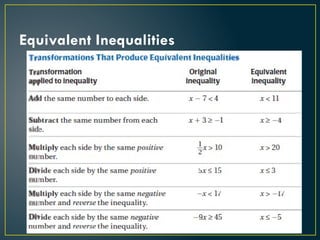
- 2. Key Vocabulary • Linear Inequality • Compound Inequality • Equivalent Inequalities
- 3. Linear Inequality • Can be written in one of the following forms where a and b are real numbers and a does not equal 0.
- 5. Compound Inequality • Consists of two simple inequalities joined by “and” or “or”
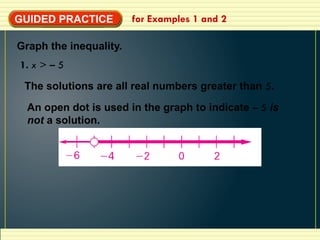
- 7. GUIDED PRACTICE for Examples 1 and 2 Graph the inequality. 1. x > – 5 The solutions are all real numbers greater than 5. An open dot is used in the graph to indicate – 5 is not a solution.
- 8. GUIDED PRACTICE for Examples 1 and 2 Graph the inequality. 2. x ≤ 3 The solutions are all real numbers less than or equal to 3. A closed dot is used in the graph to indicate 2 is a solution.
- 9. GUIDED PRACTICE for Examples 1 and 2 Graph the inequality. 3. – 3 ≤ x < 1 The solutions are all real numbers that are greater than or equalt to – 3 and less than 1.
- 10. GUIDED PRACTICE for Examples 1 and 2 Graph the inequality. 4. x < 1 or x ≥ 2 The solutions are all real numbers that are less than 1 or greater than or equal to 2.
- 11. Why? • Near the end of the semester or school year, I have students ask me what scores they must get on a final in order to earn a particular grade. You can use linear inequalities to answer this question. • You budgeted x amount of dollars for movies. You have already spend $50 of the amount. You can use inequalities to determine staying under budget or reaching your budgeted target.
- 16. GUIDED PRACTICE for Examples 3 and 4 Solve the inequality. Then graph the solution. 5. 4x + 9 < 25 4x + 9 < 25 Write original inequality. 4x < 16 Subtract 9 from each side. x < 4 Divide each side by 4. 6. 1 – 3x ≥ – 14 1 – 3x ≥ – 14 Write original inequality. – 3x ≥ – 15 Subtract –1 from each side. x ≤ 5
- 17. GUIDED PRACTICE for Examples 3 and 4 Solve the inequality. Then graph the solution. 7. 5x – 7 ≤ 6x 8. 3 – x > x – 9 5x – 7 ≤ 6x Write original inequality. x > – 7 Subtract 5x from each side. 3 – x > x – 9 Write original inequality. 3 – 2x > – 9 – 2x > – 12 x < 6 Subtract x from each side. Subtract 3 from each side. Divide each side by –2 and reverse.
- 19. EXAMPLE 6 Solve an “or” compound inequality Solve 3x + 5 ≤ 11 or 5x – 7 ≥ 23 . Then graph the solution. SOLUTION A solution of this compound inequality is a solution of either of its parts. First Inequality Second Inequality 3x + 5 ≤ 11 3x ≤ 6 x ≤ 2 Write first inequality. Subtract 5 from each side. Divide each side by 3. 5x – 7 ≥ 23 5x ≥ 30 x ≥ 6 Write second inequality. Add 7 to each side. Divide each side by 5.
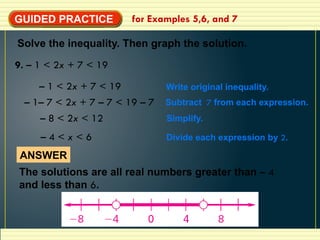
- 20. GUIDED PRACTICE for Examples 5,6, and 7 Solve the inequality. Then graph the solution. 9. – 1 < 2x + 7 < 19 – 1 < 2x + 7 < 19 Write original inequality. Subtract 7 from each expression. Simplify. Divide each expression by 2. – 1– 7 < 2x + 7 – 7 < 19 – 7 – 8 < 2x < 12 – 4 < x < 6 ANSWER The solutions are all real numbers greater than – 4 and less than 6.
- 21. GUIDED PRACTICE for Examples 5,6 and 7 Solve the inequality. Then graph the solution. 10. – 8 ≤ – x – 5 ≤ 6 – 8 ≤– x – 5 ≤ 6 – 8+5 ≤– x – 5 + 5 ≤ 6 + 5 – 3 ≤– x ≤ 11 – 11 ≤ x ≤ 3 Write original inequality. Add 5 to each expression. Simplify. The solutions are all real numbers greater than and equal to – 11 and less than and equal to 3. ANSWER
- 22. GUIDED PRACTICE for Examples 5,6 and 7 Solve the inequality. Then graph the solution. 11. x + 4 ≤ 9 or x – 3 ≥ 7 SOLUTION A solution of this compound inequality is a solution of either of its parts. First Inequality Second Inequality x ≤ 5 Write first inequality. Subtract 4 from each side. x ≥ 10 Write second inequality. Add 3 to each side. x + 4 ≤ 9 x – 3 ≥ 7
- 23. GUIDED PRACTICE for Examples 5,6 and 7 ANSWER The graph is shown below. The solutions are all real numbers. less than or equal to 5 or greater than or equal to 10.
- 24. GUIDED PRACTICE for Examples 5,6 and 7 Solve the inequality. Then graph the solution. 12. 3x – 1 < – 1 or 2x + 5 ≥ 11 SOLUTION A solution of this compound inequality is a solution of either of its parts. First Inequality Second Inequality 3x ≤ 0 x ≤ 0 Write first inequality. Add 1 each side . Divide each side by 3. 2x + 5 ≥ 11 2x ≥ 6 x ≥ 3 Write second inequality. Subtract 5 from each side Divide each side by 5. 3x – 1< – 1
- 25. GUIDED PRACTICE for Examples 5,6 and 7 less than 0 or greater than or equal to 3. ANSWER The graph is shown below. The solutions are all real numbers.











