AP_Physics_2_-_Ch_22_and_23_Reflection_and_Mirrors.ppt
0 likes23 views
1) Light can be reflected, absorbed, or refracted when interacting with mirrors and lenses. The law of reflection states that the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection. 2) For a flat plane mirror, the image location is the same distance behind the mirror as the object is in front. The image is virtual, upright, and the same size as the object. 3) Concave mirrors can focus light to a real, inverted, and enlarged or reduced image location that can be calculated using the mirror equation. Ray diagrams and calculations of magnification can be used to determine image characteristics.
1 of 19
Download to read offline

















Recommended
reflection_and_mirrors



reflection_and_mirrorsBhagyashree92
╠²
1) Light can be reflected, absorbed, or refracted. When light reflects off a flat surface, the law of reflection states that the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection.
2) A mirror forms a virtual image that is located behind the mirror on the opposite side of the object. The image distance from the mirror is equal to the object distance from the mirror.
3) Spherical mirrors can be either converging or diverging. A converging mirror focuses parallel light rays to a focal point in front using ray diagrams to determine the characteristics of the real image formed.Reflection and Mirrors



Reflection and Mirrorsitutor
╠²
Light is an electromagnetic wave that can be reflected, absorbed, or refracted. The law of reflection states that the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection. Mirrors can form either real or virtual images. Concave mirrors focus parallel light rays to a focal point, forming real, inverted, and reduced images between the focal point and center of curvature. The mirror equation and magnification equation can be used to calculate the location and characteristics of an image formed by a spherical mirror.Mirrors.pptx



Mirrors.pptxJanleTolentinoMercen
╠²
This document discusses light, reflection, and mirrors. It begins by providing facts about light, including that it is a form of electromagnetic energy and part of the electromagnetic spectrum. It then discusses how light can be reflected, absorbed, or refracted. Rays are introduced as a way to represent the direction light travels. Reflection of light off mirrors is explained, including that rays are always perpendicular to wave fronts. Real images from mirrors are described as appearing on the same side of the mirror as the object. Concave and convex mirrors are contrasted, and ray diagrams are used to determine image characteristics such as size, position, and orientation for different object positions with concave mirrors. The mirror equation and magnification equation are also introduced forLight - PModelo.pptx



Light - PModelo.pptxPercyBrendaModelo
╠²
This document provides an overview of light and optics concepts. It begins with the nature of light and properties of light such as reflection and refraction. It then discusses Snell's law and its application to the refraction of light. The remainder of the document focuses on mirrors and lenses, including definitions of real and virtual images, examples of different types of curved mirrors and their imaging properties, as well as examples of convex and concave lenses and how they are used to correct vision. Worked examples are provided for solving problems using the mirror and lens equations.pdf_20230526_055232_0000.pdf



pdf_20230526_055232_0000.pdfkritdarshil
╠²
This document provides an overview of reflection of light and image formation using spherical mirrors. It defines key terms like focal length, radius of curvature, and center of curvature. It explains that reflection occurs when light rays bounce off a smooth, polished surface. The document also describes the laws of reflection and discusses image characteristics for plane mirrors and convex and concave spherical mirrors in different scenarios depending on the object's position. Formulas for mirror equation and magnification are also provided. Real and virtual images and signs in the sign convention are defined. Finally, uses of concave mirrors are outlined.Concave and convex



Concave and convexBonbonArboleda
╠²
Today's lesson covers image formation using plane mirrors, concave mirrors, and convex mirrors. Students must learn to draw ray diagrams and solve the mirror equations to determine the characteristics of images such as orientation, size, and location. Ray diagrams use two or more principle rays to locate the image. The mirror equations describe the relationships between object and image distances and focal length. Images formed by concave mirrors can be real or virtual depending on the object position, while convex mirrors always form virtual upright images.reflection in curved mirror.ppt



reflection in curved mirror.pptEugeneMorada
╠²
The document provides guidance on safety practices during the COVID-19 pandemic, including maintaining physical distance, good hygiene, wearing face masks and limiting exposure. It also discusses the properties of concave mirrors and how light rays behave when reflecting off of one. Key points covered include that concave mirrors can form real or virtual images that are upright or inverted, and can be magnified, minified or the same size as the object. Ray diagrams are demonstrated as a way to determine the characteristics of an image formed by a concave mirror.RAY-DIAGRAM.ppt for the grade 10 quarter 3



RAY-DIAGRAM.ppt for the grade 10 quarter 3eddiesonvasquez
╠²
A ray diagram is a graphical representation of the behavior of light as it passes through a lens or a mirror. Here's a basic overview of how to draw a ray diagram:
# Types of Ray Diagrams
1. *Converging Lens Ray Diagram*: Shows how light rays converge to form a real image.
2. *Diverging Lens Ray Diagram*: Shows how light rays diverge to form a virtual image.
3. *Mirror Ray Diagram*: Shows how light rays reflect off a mirror to form an image.
# Steps to Draw a Ray Diagram
1. *Draw the Lens or Mirror*: Represent the lens or mirror as a vertical line or a curved line.
2. *Draw the Object*: Draw an arrow or a line to represent the object being observed.
3. *Draw the Rays*: Draw several rays emanating from the object, each representing a different path of light.
4. *Show Refraction or Reflection*: Show how the rays bend (refract) or bounce (reflect) off the lens or mirror.
5. *Draw the Image*: Draw the image formed by the converging or diverging rays.
# Key Components of a Ray Diagram
1. *Object*: The object being observed.
2. *Lens or Mirror*: The optical component that bends or reflects light.
3. *Rays*: The paths of light as they pass through the lens or mirror.
4. *Image*: The resulting image formed by the converging or diverging rays.
5. *Focal Point*: The point at which parallel rays converge after passing through a lens.
# Tips for Drawing Ray Diagrams
1. *Use a ruler*: Draw straight lines to represent the lens or mirror and the rays.
2. *Use a pencil*: Draw lightly so you can easily erase and correct mistakes.
3. *Label the components*: Clearly label the object, lens or mirror, rays, image, and focal point.
4. *Practice, practice, practice*: The more you practice drawing ray diagrams, the more comfortable you'll become with the process.pdf_20230526_053308_0000.pdf



pdf_20230526_053308_0000.pdfkritdarshil
╠²
1. The document provides information about reflection of light and image formation using spherical mirrors. It discusses the basics of reflection, types of spherical mirrors including concave and convex, and image formation based on the position of the object in front of these mirrors.
2. Formulas for mirror equation and magnification are presented, along with the sign convention used in spherical mirrors where the object distance is always negative.
3. Uses of concave mirrors are highlighted including in torches, solar devices, shaving mirrors, and dentistry due to the ability to produce magnified images.class20 123456789abcdefghijklmnopdrstuvwxyz



class20 123456789abcdefghijklmnopdrstuvwxyzsailavanyar1
╠²
dj9rjgfmgifmgimf fgkf kv k vknvk tgjflsm9wd;skskpofkdodmogcpkpglm,pg0;k09rovfgEspejos 



Espejos gmonzonvenet
╠²
The document discusses reflection of light and sound waves. It defines reflection as the change in direction of a ray or wave at the boundary between two mediums, causing it to return to the initial medium. Regular or specular reflection occurs on very smooth surfaces, following the laws that the incident, reflected, and normal rays are in the same plane at the point of incidence, and the angles of incidence and reflection are equal. Diffuse reflection occurs on rough surfaces, scattering the light in different directions.Spherical mirror by Kshitiz Rai



Spherical mirror by Kshitiz Rai26sep98
╠²
This document discusses virtual and real images formed by mirrors. Virtual images cannot be projected onto a screen and are always on the opposite side of the mirror from the object. Real images can be projected onto a screen and are on the same side of the mirror as the object. Concave mirrors form real, inverted images between the focal point and center of curvature for objects beyond the center of curvature. Ray diagrams are used to determine the nature and position of images formed by concave mirrors depending on the object's position relative to the focal point and center of curvature. The mirror equation can also be used to calculate the position of images.Reflection of Light in Mirrors - Science 10 (S10FE-IIg-h-50-52)



Reflection of Light in Mirrors - Science 10 (S10FE-IIg-h-50-52)Rolly Franco
╠²
Lesson 1: Reflection of Light in Plane Mirrors
Lesson 2: Reflection of Light in Spherical Mirrors
Lesson 3: Optical Instruments (Camera, Microscope, Telescope)
Reference:
DepEd K12. (2019, July). Science Grade 10 LearnerŌĆÖs Materials. [PDF File]. Retrieved from https://www.depedk12.com/2019/07/science-grade-10-learners-materials-pdf.htmlReflection of the light in the mirror.pptx



Reflection of the light in the mirror.pptxkriselcello
╠²
This document provides an overview of light reflection and spherical mirrors. It begins with definitions of key concepts like reflection, convex mirrors, concave mirrors, and plane mirrors. Examples are given to illustrate the properties of each type of mirror. The key parts of spherical mirrors like the principal axis, focal point, and radius of curvature are summarized. Methods for predicting images using ray diagrams are described. The differences between images formed by concave and convex mirrors are explained. Finally, the mirror equation for calculating image properties is introduced along with sign conventions.Reflection ray optics light chapter



Reflection ray optics light chapterAbishekThiyagarajan
╠²
reflection light chapter ncert class 7 and 8 reflection ppt light chapter ppt on reflection part of light chapter class7 and 8Light 1.pptx



Light 1.pptxFrankySetiono
╠²
This document summarizes key properties of light and reflection:
1) Light propagates as an electromagnetic wave that does not require a medium and travels in straight lines at a very fast speed. Objects are visible because they reflect light into our eyes.
2) Reflection follows the law that the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection. Reflection can be specular from smooth surfaces or diffuse from rough surfaces. Mirrors use the principle of reflection.
3) Plane mirrors form virtual upright images that are the same size and as far behind the mirror as the object is in front. The image is laterally reversed left to right. Spherical mirrors can also form images.Light full chaptet 10 cbse x 



Light full chaptet 10 cbse x RAVNEET NAGI
╠²
The document discusses the laws of reflection and image formation using spherical mirrors. It defines key terms like normal, angle of incidence, angle of reflection, focal length, pole, radius of curvature, etc. Rules for image formation using concave and convex mirrors are explained along with diagrams. Characteristics of the image like nature, position and size are defined based on the position of the object in front of the concave mirror. Sign convention for spherical mirrors is also explained. Examples of questions from NCERT on image formation and characteristics are summarized.1 Reflaction Of Light



1 Reflaction Of LightHamsiah Dahalan
╠²
The document discusses the reflection of light, including the laws of reflection and how images are formed using plane mirrors and curved mirrors. It explains that light rays reflect such that the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection, and the image formed by a plane mirror is the same distance behind the mirror as the object is in front of it. It also describes characteristics of images formed by convex and concave mirrors depending on the position of the object.Light



LightMussaOmary3
╠²
1. The document discusses the properties and behavior of light as it interacts with mirrors and lenses. It defines key terms used to describe concave and convex mirrors such as focal length, radius of curvature, and center of curvature.
2. Rules are provided for how light rays behave when hitting different types of mirrors, such as rays parallel to the principal axis passing through the focal point after reflecting off a concave mirror.
3. Examples are given of how the position, size, and nature of images formed by mirrors depend on the position of the object, such as a concave mirror always producing a diminished, virtual image between the focal point and mirror.fdocuments.net_optics-lecture-2-book-chapter-3435.ppt



fdocuments.net_optics-lecture-2-book-chapter-3435.pptPedramMaghsoudi4
╠²
An image is a reproduction of an object via light that can either be real, forming on a surface, or virtual, requiring an observer. Real images are produced by concave mirrors and converging lenses, whereas virtual images are produced by flat mirrors. A real image occurs where rays converge and a virtual image where rays appear to converge. Concave mirrors form real images when the object is outside the focal point and virtual images when inside the focal point. Lenses also form real or virtual images depending on if the object is outside or inside the focal point. Diffraction occurs when light encounters an obstacle comparable in size to its wavelength, spreading the waves and creating interference patterns like Newton's rings.Geometric optics



Geometric opticsJessabeth Aluba
╠²
This document provides an overview of geometric optics, including the ray model of light, reflection, refraction, and image formation using plane mirrors, spherical mirrors, and thin lenses. Key concepts covered include the types of images that can be formed (real or virtual), sign conventions, lateral magnification, focal points and lengths, and graphical methods for solving problems involving mirrors and lenses. Sample problems are worked through as examples.Reflection of light (Physics)



Reflection of light (Physics)Sheikh Amman
╠²
Light propagates in straight lines and can be reflected, refracted, and diffracted when interacting with matter. Reflection occurs when light hits a smooth surface and bounces back into the same medium at the same angle. Regular reflection occurs from plane mirrors where the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection. Spherical mirrors can be concave or convex. Concave mirrors form real, inverted images, while convex mirrors form virtual, upright images. The mirror equation relates the focal length and distances of the object and image.1 Reflaction Of Light



1 Reflaction Of LightHamsiah Dahalan
╠²
The document discusses the reflection of light, including the laws of reflection which state that the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection and that the incident ray, reflected ray, and normal all lie in the same plane. It also discusses image formation using plane mirrors, including that the image is laterally inverted and as far behind the mirror as the object is in front of it. Convex and concave mirrors are also discussed, including their focal points and how light rays behave depending on the object's position relative to the focal point.Mate, a short story by Kate Grenvile.pptx



Mate, a short story by Kate Grenvile.pptxLiny Jenifer
╠²
A powerpoint presentation on the short story Mate by Kate Greenville. This presentation provides information on Kate Greenville, a character list, plot summary and critical analysis of the short story.The Dravidian Languages: Tamil, Telugu, Kannada, Malayalam, Brahui, Kuvi, Tulu



The Dravidian Languages: Tamil, Telugu, Kannada, Malayalam, Brahui, Kuvi, TuluDrIArulAram
╠²
The Dravidian Languages by Arul AramMore Related Content
Similar to AP_Physics_2_-_Ch_22_and_23_Reflection_and_Mirrors.ppt (20)
pdf_20230526_053308_0000.pdf



pdf_20230526_053308_0000.pdfkritdarshil
╠²
1. The document provides information about reflection of light and image formation using spherical mirrors. It discusses the basics of reflection, types of spherical mirrors including concave and convex, and image formation based on the position of the object in front of these mirrors.
2. Formulas for mirror equation and magnification are presented, along with the sign convention used in spherical mirrors where the object distance is always negative.
3. Uses of concave mirrors are highlighted including in torches, solar devices, shaving mirrors, and dentistry due to the ability to produce magnified images.class20 123456789abcdefghijklmnopdrstuvwxyz



class20 123456789abcdefghijklmnopdrstuvwxyzsailavanyar1
╠²
dj9rjgfmgifmgimf fgkf kv k vknvk tgjflsm9wd;skskpofkdodmogcpkpglm,pg0;k09rovfgEspejos 



Espejos gmonzonvenet
╠²
The document discusses reflection of light and sound waves. It defines reflection as the change in direction of a ray or wave at the boundary between two mediums, causing it to return to the initial medium. Regular or specular reflection occurs on very smooth surfaces, following the laws that the incident, reflected, and normal rays are in the same plane at the point of incidence, and the angles of incidence and reflection are equal. Diffuse reflection occurs on rough surfaces, scattering the light in different directions.Spherical mirror by Kshitiz Rai



Spherical mirror by Kshitiz Rai26sep98
╠²
This document discusses virtual and real images formed by mirrors. Virtual images cannot be projected onto a screen and are always on the opposite side of the mirror from the object. Real images can be projected onto a screen and are on the same side of the mirror as the object. Concave mirrors form real, inverted images between the focal point and center of curvature for objects beyond the center of curvature. Ray diagrams are used to determine the nature and position of images formed by concave mirrors depending on the object's position relative to the focal point and center of curvature. The mirror equation can also be used to calculate the position of images.Reflection of Light in Mirrors - Science 10 (S10FE-IIg-h-50-52)



Reflection of Light in Mirrors - Science 10 (S10FE-IIg-h-50-52)Rolly Franco
╠²
Lesson 1: Reflection of Light in Plane Mirrors
Lesson 2: Reflection of Light in Spherical Mirrors
Lesson 3: Optical Instruments (Camera, Microscope, Telescope)
Reference:
DepEd K12. (2019, July). Science Grade 10 LearnerŌĆÖs Materials. [PDF File]. Retrieved from https://www.depedk12.com/2019/07/science-grade-10-learners-materials-pdf.htmlReflection of the light in the mirror.pptx



Reflection of the light in the mirror.pptxkriselcello
╠²
This document provides an overview of light reflection and spherical mirrors. It begins with definitions of key concepts like reflection, convex mirrors, concave mirrors, and plane mirrors. Examples are given to illustrate the properties of each type of mirror. The key parts of spherical mirrors like the principal axis, focal point, and radius of curvature are summarized. Methods for predicting images using ray diagrams are described. The differences between images formed by concave and convex mirrors are explained. Finally, the mirror equation for calculating image properties is introduced along with sign conventions.Reflection ray optics light chapter



Reflection ray optics light chapterAbishekThiyagarajan
╠²
reflection light chapter ncert class 7 and 8 reflection ppt light chapter ppt on reflection part of light chapter class7 and 8Light 1.pptx



Light 1.pptxFrankySetiono
╠²
This document summarizes key properties of light and reflection:
1) Light propagates as an electromagnetic wave that does not require a medium and travels in straight lines at a very fast speed. Objects are visible because they reflect light into our eyes.
2) Reflection follows the law that the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection. Reflection can be specular from smooth surfaces or diffuse from rough surfaces. Mirrors use the principle of reflection.
3) Plane mirrors form virtual upright images that are the same size and as far behind the mirror as the object is in front. The image is laterally reversed left to right. Spherical mirrors can also form images.Light full chaptet 10 cbse x 



Light full chaptet 10 cbse x RAVNEET NAGI
╠²
The document discusses the laws of reflection and image formation using spherical mirrors. It defines key terms like normal, angle of incidence, angle of reflection, focal length, pole, radius of curvature, etc. Rules for image formation using concave and convex mirrors are explained along with diagrams. Characteristics of the image like nature, position and size are defined based on the position of the object in front of the concave mirror. Sign convention for spherical mirrors is also explained. Examples of questions from NCERT on image formation and characteristics are summarized.1 Reflaction Of Light



1 Reflaction Of LightHamsiah Dahalan
╠²
The document discusses the reflection of light, including the laws of reflection and how images are formed using plane mirrors and curved mirrors. It explains that light rays reflect such that the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection, and the image formed by a plane mirror is the same distance behind the mirror as the object is in front of it. It also describes characteristics of images formed by convex and concave mirrors depending on the position of the object.Light



LightMussaOmary3
╠²
1. The document discusses the properties and behavior of light as it interacts with mirrors and lenses. It defines key terms used to describe concave and convex mirrors such as focal length, radius of curvature, and center of curvature.
2. Rules are provided for how light rays behave when hitting different types of mirrors, such as rays parallel to the principal axis passing through the focal point after reflecting off a concave mirror.
3. Examples are given of how the position, size, and nature of images formed by mirrors depend on the position of the object, such as a concave mirror always producing a diminished, virtual image between the focal point and mirror.fdocuments.net_optics-lecture-2-book-chapter-3435.ppt



fdocuments.net_optics-lecture-2-book-chapter-3435.pptPedramMaghsoudi4
╠²
An image is a reproduction of an object via light that can either be real, forming on a surface, or virtual, requiring an observer. Real images are produced by concave mirrors and converging lenses, whereas virtual images are produced by flat mirrors. A real image occurs where rays converge and a virtual image where rays appear to converge. Concave mirrors form real images when the object is outside the focal point and virtual images when inside the focal point. Lenses also form real or virtual images depending on if the object is outside or inside the focal point. Diffraction occurs when light encounters an obstacle comparable in size to its wavelength, spreading the waves and creating interference patterns like Newton's rings.Geometric optics



Geometric opticsJessabeth Aluba
╠²
This document provides an overview of geometric optics, including the ray model of light, reflection, refraction, and image formation using plane mirrors, spherical mirrors, and thin lenses. Key concepts covered include the types of images that can be formed (real or virtual), sign conventions, lateral magnification, focal points and lengths, and graphical methods for solving problems involving mirrors and lenses. Sample problems are worked through as examples.Reflection of light (Physics)



Reflection of light (Physics)Sheikh Amman
╠²
Light propagates in straight lines and can be reflected, refracted, and diffracted when interacting with matter. Reflection occurs when light hits a smooth surface and bounces back into the same medium at the same angle. Regular reflection occurs from plane mirrors where the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection. Spherical mirrors can be concave or convex. Concave mirrors form real, inverted images, while convex mirrors form virtual, upright images. The mirror equation relates the focal length and distances of the object and image.1 Reflaction Of Light



1 Reflaction Of LightHamsiah Dahalan
╠²
The document discusses the reflection of light, including the laws of reflection which state that the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection and that the incident ray, reflected ray, and normal all lie in the same plane. It also discusses image formation using plane mirrors, including that the image is laterally inverted and as far behind the mirror as the object is in front of it. Convex and concave mirrors are also discussed, including their focal points and how light rays behave depending on the object's position relative to the focal point.Recently uploaded (20)
Mate, a short story by Kate Grenvile.pptx



Mate, a short story by Kate Grenvile.pptxLiny Jenifer
╠²
A powerpoint presentation on the short story Mate by Kate Greenville. This presentation provides information on Kate Greenville, a character list, plot summary and critical analysis of the short story.The Dravidian Languages: Tamil, Telugu, Kannada, Malayalam, Brahui, Kuvi, Tulu



The Dravidian Languages: Tamil, Telugu, Kannada, Malayalam, Brahui, Kuvi, TuluDrIArulAram
╠²
The Dravidian Languages by Arul AramFESTIVAL: SINULOG & THINGYAN-LESSON 4.pptx



FESTIVAL: SINULOG & THINGYAN-LESSON 4.pptxDanmarieMuli1
╠²
Sinulog Festival of Cebu City, and Thingyan Festival of Myanmar.How to Setup WhatsApp in Odoo 17 - Odoo ║▌║▌▀Żs



How to Setup WhatsApp in Odoo 17 - Odoo ║▌║▌▀ŻsCeline George
╠²
Integrate WhatsApp into Odoo using the WhatsApp Business API or third-party modules to enhance communication. This integration enables automated messaging and customer interaction management within Odoo 17.QuickBooks Desktop to QuickBooks Online How to Make the Move



QuickBooks Desktop to QuickBooks Online How to Make the MoveTechSoup
╠²
If you use QuickBooks Desktop and are stressing about moving to QuickBooks Online, in this webinar, get your questions answered and learn tips and tricks to make the process easier for you.
Key Questions:
* When is the best time to make the shift to QuickBooks Online?
* Will my current version of QuickBooks Desktop stop working?
* I have a really old version of QuickBooks. What should I do?
* I run my payroll in QuickBooks Desktop now. How is that affected?
*Does it bring over all my historical data? Are there things that don't come over?
* What are the main differences between QuickBooks Desktop and QuickBooks Online?
* And moreHow to attach file using upload button Odoo 18



How to attach file using upload button Odoo 18Celine George
╠²
In this slide, weŌĆÖll discuss on how to attach file using upload button Odoo 18. Odoo features a dedicated model, 'ir.attachments,' designed for storing attachments submitted by end users. We can see the process of utilizing the 'ir.attachments' model to enable file uploads through web forms in this slide.POWERPOINT-PRESENTATION_DM-NO.017-S.2025.pptx



POWERPOINT-PRESENTATION_DM-NO.017-S.2025.pptxMarilenQuintoSimbula
╠²
Rubric level Summary for Teacher 1 to 3, Proficient Teacher. Guide in assessing MOV presented.SOCIAL CHANGE(a change in the institutional and normative structure of societ...



SOCIAL CHANGE(a change in the institutional and normative structure of societ...DrNidhiAgarwal
╠²
This PPT is showing the effect of social changes in human life and it is very understandable to the students with easy language.in this contents are Itroduction, definition,Factors affecting social changes ,Main technological factors, Social change and stress , what is eustress and how social changes give impact of the human's life.How to Modify Existing Web Pages in Odoo 18



How to Modify Existing Web Pages in Odoo 18Celine George
╠²
In this slide, weŌĆÖll discuss on how to modify existing web pages in Odoo 18. Web pages in Odoo 18 can also gather user data through user-friendly forms, encourage interaction through engaging features. Blind Spots in AI and Formulation Science Knowledge Pyramid (Updated Perspect...



Blind Spots in AI and Formulation Science Knowledge Pyramid (Updated Perspect...Ajaz Hussain
╠²
This presentation delves into the systemic blind spots within pharmaceutical science and regulatory systems, emphasizing the significance of "inactive ingredients" and their influence on therapeutic equivalence. These blind spots, indicative of normalized systemic failures, go beyond mere chance occurrences and are ingrained deeply enough to compromise decision-making processes and erode trust.
Historical instances like the 1938 FD&C Act and the Generic Drug Scandals underscore how crisis-triggered reforms often fail to address the fundamental issues, perpetuating inefficiencies and hazards.
The narrative advocates a shift from reactive crisis management to proactive, adaptable systems prioritizing continuous enhancement. Key hurdles involve challenging outdated assumptions regarding bioavailability, inadequately funded research ventures, and the impact of vague language in regulatory frameworks.
The rise of large language models (LLMs) presents promising solutions, albeit with accompanying risks necessitating thorough validation and seamless integration.
Tackling these blind spots demands a holistic approach, embracing adaptive learning and a steadfast commitment to self-improvement. By nurturing curiosity, refining regulatory terminology, and judiciously harnessing new technologies, the pharmaceutical sector can progress towards better public health service delivery and ensure the safety, efficacy, and real-world impact of drug products.Computer Application in Business (commerce)



Computer Application in Business (commerce)Sudar Sudar
╠²
The main objectives
1. To introduce the concept of computer and its various parts. 2. To explain the concept of data base management system and Management information system.
3. To provide insight about networking and basics of internet
Recall various terms of computer and its part
Understand the meaning of software, operating system, programming language and its features
Comparing Data Vs Information and its management system Understanding about various concepts of management information system
Explain about networking and elements based on internet
1. Recall the various concepts relating to computer and its various parts
2 Understand the meaning of softwareŌĆÖs, operating system etc
3 Understanding the meaning and utility of database management system
4 Evaluate the various aspects of management information system
5 Generating more ideas regarding the use of internet for business purpose APM People Interest Network Conference - Oliver Randall & David Bovis - Own Y...



APM People Interest Network Conference - Oliver Randall & David Bovis - Own Y...Association for Project Management
╠²
APM People Interest Network Conference 2025
- Autonomy, Teams and Tension
- Oliver Randall & David Bovis
- Own Your Autonomy
Oliver Randall
Consultant, Tribe365
Oliver is a career project professional since 2011 and started volunteering with APM in 2016 and has since chaired the People Interest Network and the North East Regional Network. Oliver has been consulting in culture, leadership and behaviours since 2019 and co-developed HPTM┬«ŌĆ»an off the shelf high performance framework for teams and organisations and is currently working with SAS (Stellenbosch Academy for Sport) developing the culture, leadership and behaviours framework for future elite sportspeople whilst also holding down work as a project manager in the NHS at North Tees and Hartlepool Foundation Trust.
David Bovis
Consultant, Duxinaroe
A Leadership and Culture Change expert, David is the originator of BTFAŌäó and The Dux Model.
With a Masters in Applied Neuroscience from the Institute of Organisational Neuroscience, he is widely regarded as the ŌĆśGo-ToŌĆÖ expert in the field, recognised as an inspiring keynote speaker and change strategist.
He has an industrial engineering background, majoring in TPS / Lean. David worked his way up from his apprenticeship to earn his seat at the C-suite table. His career spans several industries, including Automotive, Aerospace, Defence, Space, Heavy Industries and Elec-Mech / polymer contract manufacture.
Published in LondonŌĆÖs Evening Standard quarterly business supplement, James CaanŌĆÖs ŌĆśYour businessŌĆÖ Magazine, ŌĆśQuality WorldŌĆÖ, the Lean Management Journal and Cambridge Universities ŌĆśPMAŌĆÖ, he works as comfortably with leaders from FTSE and Fortune 100 companies as he does owner-managers in SMEŌĆÖs. He is passionate about helping leaders understand the neurological root cause of a high-performance culture and sustainable change, in business.
Session | Own Your Autonomy ŌĆō The Importance of Autonomy in Project Management
#OwnYourAutonomy is aiming to be a global APM initiative to position everyone to take a more conscious role in their decision making process leading to increased outcomes for everyone and contribute to ŌĆ£a world in which all projects succeedŌĆØ.
We want everyone to join the journey.
#OwnYourAutonomy is the culmination of 3 years of collaborative exploration within the Leadership Focus Group which is part of the APM People Interest Network. The work has been pulled together using the 5 HPTM® Systems and the BTFA neuroscience leadership programme.
https://www.linkedin.com/showcase/apm-people-network/about/Eng7-Q4-Lesson 1 Part 1 Understanding Discipline-Specific Words, Voice, and T...



Eng7-Q4-Lesson 1 Part 1 Understanding Discipline-Specific Words, Voice, and T...sandynavergas1
╠²
Understanding Discipline-Specific Words, Voice, and Technical TermsInformation Technology for class X CBSE skill Subject



Information Technology for class X CBSE skill SubjectVEENAKSHI PATHAK
╠²
These questions are based on cbse booklet for 10th class information technology subject code 402. these questions are sufficient for exam for first lesion. This subject give benefit to students and good marks. if any student weak in one main subject it can replace with these marks.APM People Interest Network Conference - Oliver Randall & David Bovis - Own Y...



APM People Interest Network Conference - Oliver Randall & David Bovis - Own Y...Association for Project Management
╠²
AP_Physics_2_-_Ch_22_and_23_Reflection_and_Mirrors.ppt
- 1. Light, Reflection, & Mirrors AP Physics 2
- 2. Facts about Light ’ü« It is a form of Electromagnetic Energy ’ü« It is a part of the Electromagnetic Spectrum and the only part we can really see
- 3. Facts about Light The speed of light, c, is constant in a vacuum. Light can be: ŌĆóREFLECTED ŌĆóABSORBED ŌĆóREFRACTED Light is an electromagnetic wave in that it has wave like properties which can be influenced by electric and magnetic fields.
- 4. The Law of ŌĆ£REFLECTIONŌĆØ The Law of Reflection states that- " the angle of incidence (incoming ray) equals the angle of reflection (outgoing ray)" The law works for FLAT, PLANE surfaces only. The angles are measured from a perpendicular line to the surface called a NORMAL. NORMAL
- 5. Plane Mirror Suppose we had a flat , plane mirror mounted vertically. A candle is placed 10 cm in front of the mirror. WHERE IS THE IMAGE OF THE CANDLE LOCATED? mirror Object Distance, Do = 10 cm Same side as the object? On the surface of the mirror? Behind the mirror?
- 6. Plane Mirror Suppose we had a flat , plane mirror mounted vertically. A candle is placed 10 cm in front of the mirror. WHERE IS THE IMAGE OF THE CANDLE LOCATED? mirror Object Distance, Do = 10 cm Image Distance, Di = 10 cm Do=Di, and the heights are equal as well Virtual Image
- 7. Virtual Images Virtual Images are basically images which cannot be visually projected on a screen. If this box gave off light, we could project an image of this box on to a screen provided the screen was on the SAME SIDE as the box. You would not be able to project the image of the vase or your face in a mirror on a screen, therefore it is a virtual image. CONCLUSION: VIRTUAL IMAGES are ALWAYS on the OPPOSITE side of the mirror relative to the object.
- 8. Real Image Real Images are ones you can project on to a screen. For MIRRORS they always appear on the SAME SIDE of the mirror as the object. object image The characteristics of the image, however, may be different from the original object. These characteristics are: ŌĆóSIZE (reduced,enlarged,same size) ŌĆóPOSITION (same side, opposite side) ŌĆóORIENTATION (right side up, inverted) What if the mirror isnŌĆÖt flat?
- 9. Spherical Mirrors ŌĆō Concave & Convex Also called CONVERGING mirror Also called DIVERGING mirror
- 10. Converging (Concave) Mirror A converging mirror is one that is spherical in nature by which it can FOCUS parallel light rays to a point directly in front of its surface. Every spherical mirror can do this and this special point is at a ŌĆ£fixedŌĆØ position for every mirror. We call this point the FOCAL POINT. To find this point you MUST use light from ŌĆ£infinityŌĆØ Light from an ŌĆ£infiniteŌĆØ distance, most likely the sun.
- 11. Converging (Concave) Mirror Since the mirror is spherical it technically has a CENTER OF CURVATURE, C. The focal point happens to be HALF this distance. We also draw a line through the center of the mirror and call it the PRINCIPAL AXIS. f C C f 2 2 ’ĆĮ ’ĆĮ
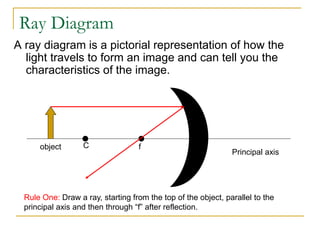
- 12. Ray Diagram A ray diagram is a pictorial representation of how the light travels to form an image and can tell you the characteristics of the image. Principal axis f C object Rule One: Draw a ray, starting from the top of the object, parallel to the principal axis and then through ŌĆ£fŌĆØ after reflection.
- 13. Ray Diagrams Principal axis f C object Rule Two: Draw a ray, starting from the top of the object, through the focal point, then parallel to the principal axis after reflection.
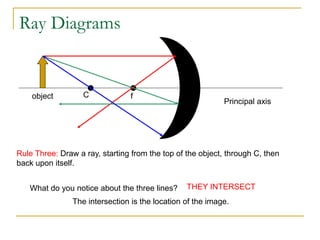
- 14. Ray Diagrams Principal axis f C object Rule Three: Draw a ray, starting from the top of the object, through C, then back upon itself. What do you notice about the three lines? THEY INTERSECT The intersection is the location of the image.
- 15. Ray Diagram ŌĆō Image Characteristics Principal axis f C object After getting the intersection, draw an arrow down from the principal axis to the point of intersection. Then ask yourself these questions: 1) Is the image on the SAME or OPPOSITE side of the mirror as the object? Same, therefore it is a REAL IMAGE. 2) Is the image ENLARGED or REDUCED? 3) Is the image INVERTED or RIGHT SIDE UP?
- 16. The Mirror/Lens Equation Is there any OTHER way to predict image characteristics besides the ray diagram? YES! One way is to use the MIRROR/LENS equation to CALCULATE the position of the image. i o d d f 1 1 1 ’Ć½ ’ĆĮ
- 17. Mirror/Lens Equation Assume that a certain concave spherical mirror has a focal length of 10.0 cm. Locate the image for an object distance of 25 cm and describe the imageŌĆÖs characteristics. ’ĆĮ ’Ć½ ’ĆĮ ’é« ’Ć½ ’ĆĮ i i i o d d d d f 1 25 1 10 1 1 1 1 16.67 cm What does this tell us? First we know the image is BETWEEN ŌĆ£CŌĆØ & ŌĆ£fŌĆØ. Since the image distance is POSITIVE the image is a REAL IMAGE. Real image = positive image distance Virtual image = negative image distance What about the size and orientation?
- 18. Magnification Equation To calculate the orientation and size of the image we use the MAGNIFICATION EQUATION. x M M h h d d M o i o i 67 . 0 25 67 . 16 ’ĆŁ ’ĆĮ ’ĆŁ ’ĆĮ ’ĆĮ ’ĆŁ ’ĆĮ Here is how this works: ŌĆóIf we get a POSITIVE magnification, the image is UPRIGHT. ŌĆóIf we get a NEGATIVE magnification, the image is INVERTED ŌĆóIf the magnification value is GREATER than 1, the image is ENLARGED. ŌĆóIf the magnification value is LESS than 1, the image is REDUCED. ŌĆóIf the magnification value is EQUAL to 1, the image is the SAME SIZE as the object. Using our previous data we see that our image was INVERTED, and REDUCED.
- 19. Example Assume that a certain concave spherical mirror has a focal length of 10.0 cm. Locate the image for an object distance of 5 cm and describe the imageŌĆÖs characteristics. ’ĆĮ ’ĆŁ ’ĆĮ ’ĆĮ ’Ć½ ’ĆĮ ’é« ’Ć½ ’ĆĮ 5 1 5 1 10 1 1 1 1 i i i i o d M d d d d f -10 cm 2x ŌĆóVIRTUAL (opposite side) ŌĆóEnlarged ŌĆóUpright Characteristics?










