Cyclin dependent kinases
Download as PPTX, PDF6 likes11,252 views
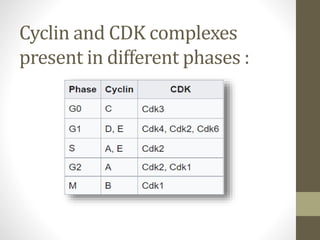
Cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) are protein kinases that regulate critical cellular processes such as the cell cycle, transcription, and differentiation. CDKs are activated when bound to cyclin proteins and phosphorylate target proteins to regulate their activity. Different cyclin-CDK complexes are involved at different phases of the cell cycle, controlling checkpoints and ensuring DNA replication only occurs once per cycle. When DNA damage is detected, CDK inhibitors like p53 and p21 are activated, halting transcription and giving time for DNA repair.
1 of 15
Downloaded 28 times












Recommended
Signal transduction 



Signal transduction KAUSHAL SAHU
Ěý
GENERAL IDEA OF SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION
DEFINATION
WHAT DOES THE TERM SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION MEANS
HISTORY
BASIC ELEMENTS IN SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION
TYPES OF SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION
SIGNALLING MOLECULE
RECEPTOR MOLECULE
MODES OF CELL CELL SIGNALING
SECOND MESSENGER
SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION PATHWAY
SOME SIGNALING PATHWAYS
SIGNIFICANCE
CONCLUSION
REFERENCE
Cell cycle regulation ppt



Cell cycle regulation pptmanojsiddartha bolthajira
Ěý
The cell cycle involves an interphase of growth and DNA replication followed by mitosis, where the cell divides. The cell cycle is regulated by cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) that drive progression between phases. CDK activity increases upon binding to cyclins and decreases when cyclins are degraded. Growth hormones like auxins and cytokinins promote cell cycle progression by increasing cyclin and CDK expression, while abscisic acid inhibits the cell cycle. Together, these regulatory mechanisms precisely control cell division.Oncogene



OncogeneBAlbeer Singh
Ěý
Oncogenes are mutated proto-oncogenes that can cause normal cells to become cancerous. Proto-oncogenes regulate cell growth and differentiation and are involved in signal transduction and mitogenic signals. They can become oncogenes through point mutations, increased expression from gene amplification, or chromosomal translocations. The first confirmed oncogene, src, was discovered in 1970. Oncogenes are classified into groups based on their functions, such as secreted growth factors, cell surface receptors, intracellular transducers, and regulators of the cell cycle. The challenge is developing cancer treatments that kill cancer cells without harming healthy cells.Cell cycle, its regulation and checkpoints



Cell cycle, its regulation and checkpointsSanju Kaladharan
Ěý
The document summarizes key aspects of the cell cycle and cell division. It discusses the phases of the cell cycle including interphase and mitosis. It describes chromosome structure and duplication. It explains the process of mitosis and cytokinesis. It also discusses regulation of the cell cycle through checkpoints at the G1/S and G2/M transitions to ensure DNA integrity before cell division.Operon 



Operon sijiskariah
Ěý
This document provides an overview of gene regulation in prokaryotes using the lac operon in E. coli as an example. It explains that genes are regulated to control which proteins are expressed at different times. The lac operon consists of structural genes that encode enzymes for lactose metabolism, as well as a regulatory gene that produces a repressor protein. In the absence of the lactose inducer, the repressor binds to the operator region and prevents transcription. When lactose is present, it binds to the repressor and causes a conformational change that prevents it from binding to the operator, allowing transcription.Cot curve 



Cot curve EmaSushan
Ěý
Cot value and Cot Curve analysis is a technique for measuring DNA complexity based on renaturation kinetics. DNA is denatured and allowed to reanneal, with larger DNA taking longer. Cot value accounts for DNA concentration, time, and buffer effects, representing repetitive sequences - lower Cot means more repeats. Examples show bacteria have nearly all single-copy DNA, while mouse has varying proportions of single-copy, middle repetitive, and highly repetitive sequences. Cot curve analysis provides information on genome size, complexity, and proportions of sequence types.Protein sorting and targeting



Protein sorting and targetingKAUSHAL SAHU
Ěý
The delivery of newly synthesized protein to their proper cellular destination, usually referred to as protein targeting or sorting.
The mode of protein transport depends chiefly on the location in the cell cytoplasm of the polysomes involved in protein synthesis.
There are two modes of protein sorting:-
1) Co - translational Transportation.
2) Post - translational Transportation.
Abzymes



Abzymesjeeva raj
Ěý
Abzymes, also known as catalytic antibodies, are monoclonal antibodies that exhibit enzymatic activity. They are able to bind to transition states of enzyme-catalyzed reactions with high specificity and affinity, stabilizing the transition state and increasing reaction rates. Abzymes can be artificially produced by immunizing animals with transition state analogs of reactions. They have potential applications in drug development, cancer treatment, and developing therapies for viral infections like HIV. Researchers have engineered an abzyme that can degrade an essential region of the HIV envelope protein, rendering the virus unable to infect cells.Telomerase



TelomeraseKashmeera N.A.
Ěý
Telomeres are repetitive nucleotide sequences located at the ends of chromosomes that protect the ends from deterioration or fusion with other chromosomes. They shorten each time a cell divides until a length is reached that triggers cell senescence or death. The enzyme telomerase maintains telomere length by adding telomeric repeats to chromosome ends using its own RNA component as a template. Telomerase is active in germ cells, stem cells, and cancer cells, allowing indefinite cell division, but not in most somatic cells, limiting their replicative lifespan.Dna replication in eukaryotes



Dna replication in eukaryotesM Vignesh
Ěý
This document describes the process of DNA replication in eukaryotes. It occurs in S phase of the cell cycle and involves three main stages: initiation, formation of the initiation complex, and elongation. Initiation requires the assembly of pre-replication complexes containing ORC, Cdc6, Cdt1 and MCM proteins. In S phase, Cdc45 and GINS are recruited to form the initiation complex. Elongation proceeds bidirectionally from replication forks, with leading strand synthesis continuous and lagging strand discontinuous via Okazaki fragments. Replication terminates at telomeres.Dna methylation ppt



Dna methylation pptIbad khan
Ěý
DNA methylation involves the addition of methyl groups to cytosine bases in DNA. It is an epigenetic process that plays an important role in normal development and diseases like cancer. Cytosine methylation occurs most widely and involves the addition of a methyl group to the C-5 position of cytosine. Methylation can repress gene expression by interfering with transcriptional protein binding or recruiting chromatin remodeling proteins. In cancer, aberrant methylation can lead to silencing of tumor suppressor genes or activation of oncogenes. Genomic imprinting involves differential gene expression based on parental origin through epigenetic mechanisms like methylation. Around 1% of genes show imprinting including IGF2 and H19. Imprinting errorsReceptor tyrosine kinases.ppt



Receptor tyrosine kinases.pptDr. Khuram Aziz
Ěý
The document discusses receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs), a class of cell surface receptors that possess intrinsic tyrosine kinase activity. RTKs are activated through ligand binding and dimerization, which leads to autophosphorylation and downstream signaling. This signaling involves phosphorylation of proteins by RTKs and recruitment of adapter proteins, and results in cellular responses like cell division, differentiation, and motility. Common to all RTKs are an extracellular ligand-binding domain, a transmembrane domain, an intracellular tyrosine kinase domain, and regulatory domains.MODELS OF REPLICATION



MODELS OF REPLICATIONKristu Jayanti College
Ěý
The document discusses three models of DNA replication:
1) Asymmetric replication - the leading and lagging strands are replicated differently due to the 5' to 3' directionality of DNA polymerase. The leading strand replicates continuously while the lagging strand replicates discontinuously in short Okazaki fragments.
2) D-loop model - replication in mitochondria where one strand is displaced to form a D-loop and replicates first before the other strand.
3) Rolling circle model - used by plasmids and viruses where one strand is nicked and displaced to be used as a template, forming multiple copies linked together in a concatemer.Oncogene and Proto-oncogene



Oncogene and Proto-oncogenevidan biology
Ěý
Proto-oncogenes are normal genes that can become oncogenes following mutations. They encode proteins involved in cell growth, proliferation, differentiation and apoptosis. Examples include HER2, Wnt, Myc, Ras and genes in the Ras signaling pathway. Mutations in proto-oncogenes convert them into oncogenes, driving uncontrolled cell growth and tumor development. Common mutations are point mutations, which result in overactive gene products by altering transcription or protein function. For example, point mutations in Ras genes are found in many cancers and keep the Ras protein constantly active.dyneins and kinesins



dyneins and kinesinsstudent
Ěý
Kinesins and dyneins are motor proteins that move along microtubules. Kinesins move cargo from the center of the cell to its periphery by moving toward the plus end of microtubules. Dyneins move cargo from the periphery to the center by moving toward the minus end of microtubules. Both use ATP hydrolysis to power their movement in 8 nm steps along microtubules in opposite directions. Dyneins are also responsible for the bending movement of cilia and flagella by generating force between adjacent microtubule doublets.Holliday junction Model by kk



Holliday junction Model by kkKAUSHAL SAHU
Ěý
INTRODUCTION
TERMENOLOGY
SITES OF HOLLIDAY JUNCTION
HOMOLOGOUS RECOMBINATION
HOLLIDAY MODEL
DOUBEL STRAND BREAK MODEL
IN PROKAYOTIC RECOMBINATION
IN EUKARYOTIC RECOMBINATION
SITE SPECIFIC RECOMBINATION
SERINE RECOMBINATION
TYROSINE RECOMBINATION
TRANSPOSITION
ILLEGITIMATE RECOMBINATION
CONCLUSION
REFRENCES
Dna damage and repair



Dna damage and repairNamrata Chhabra
Ěý
DNA damage, Types of damage, Agents causing DNA damage, DNA repair system, Implications of defective DNA repair systemRNA editing



RNA editingTenzin t
Ěý
RNA editing is a post-transcriptional process that makes discrete changes to RNA sequences. There are three main types of RNA editing: cytosine to uracil deamination, adenine to inosine deamination, and guide RNA-mediated insertion/deletion of uridine bases. Cytidine deamination is site-specific and involves enzymes like cytidine deaminase. Adenine deamination occurs in RNA secondary structures and involves enzymes like ADAR. Guide RNA editing involves hybridization of RNA to guide RNA, cleavage by an endonuclease, addition of uridine by TuTase, and ligation. RNA editing increases protein diversity and is essential for organelle development in eukaryotes.Cromatin Remodeling



Cromatin RemodelingBalaji Thorat
Ěý
1. Chromatin remodeling is the process by which chromatin structure is dynamically modified to allow access of DNA for processes like transcription.
2. There are two main types of chromatin remodeling - covalent histone modification and ATP-dependent chromatin remodeling complexes.
3. ATP-dependent complexes use energy from ATP hydrolysis to move, eject, or restructure nucleosomes, allowing access to DNA.
4. Examples of chromatin remodeling complexes include SWI/SNF, ISWI, CHD, and INO80 families, which have different activities like nucleosome sliding or histone variant exchange.Trp operon



Trp operonSKYFALL
Ěý
The trp operon contains a cluster of genes involved in tryptophan biosynthesis that are under the control of a single promoter. It was the first repressible operon discovered in E. coli in 1953. The trp operon contains structural genes that encode enzymes for tryptophan synthesis, as well as a promoter, operator, and regulatory genes. Tryptophan acts as an effector molecule that binds to the repressor protein, increasing its affinity for the operator sequence and repressing transcription when tryptophan is present. The trp operon is also regulated by transcriptional attenuation, where tryptophan levels affect the formation of termination or anti-termination hairpin loops in the mRNA.Rna polymerase



Rna polymerasepriyanka raviraj
Ěý
RNA Polymerase
Introduction
Purification
History
PRODUCTS OF RNAP
Messenger RNA
Non-coding RNA Ěýor "RNA genes
Transfer RNA
Ribosomal RNA
Micro RNA
Catalytic RNA (Ribozyme)
prokaryotic and eukaryotic
Transcription by RNA Polymerase
TYPES OF RNA POLYMERASE
Type I
Type II
Type III
Prokaryotic Transcription Unit
EXPRESSION OF A PROKARYOTIC GENE
Prokaryotic Polycistronic Message Codes for Several Different Proteins
Eukaryotic Transcription Unit
ENHANCERS AND SILENCERS
RESULT OF THE TRANSCRIPTION CYCLE
RNAP III TRANSCRIBES HUMAN MICRORNAS
RNAP I–specific subunits promote
polymerase clustering to enhance the rRNA gene
transcription cycle
RNAP II–TFIIB STRUCTURE AND
MECHANISM OF TRANSCRIPTION INITIATION
FIVE CHECKPOINTS MAINTAINING THE FIDELITY OF
TRANSCRIPTION BY RNAP IN STRUCTURAL AND
ENERGETIC DETAILSDNA Supercoiling 



DNA Supercoiling Subhranil Bhattacharjee
Ěý
This contains DNA Supercoiling , relation between Linking no,Twist and Writhe and a brief explanation of Topoisomerase Transposable elements



Transposable elementsSai Kiran Munagala
Ěý
Transportable elements are DNA Sequences that move from one location in a chromosome to another within the same chromosome or into another chromosome.
These are DNA Sequences that move from one location in a chromosome to another within the same chromosome or into another chromosome.
These are DNA Sequences that move from one location in a chromosome to another within the same chromosome or into another chromosome.
These are also known as “Jumping genes”.
Site specific recombination



Site specific recombinationRoshan Parihar
Ěý
This document discusses site-specific recombination, including the structures and mechanisms involved. It describes two classes of recombinases - tyrosine recombinases and serine recombinases. Tyrosine recombinases involve cleavage of DNA through formation of a protein-DNA bond using a tyrosine residue. Serine recombinases utilize a phosphoserine bond between DNA and a conserved serine residue. The document provides examples of applications for site-specific recombination such as tracking cell lineage, altering gene expression, and targeted gene knockout.Ribozyme



RibozymeMUMTHAS P K - KANNUR UNIVERSITY, CAMPUS, KANNUR
Ěý
Ribozymes are RNA molecules that act as enzymes and catalyze biochemical reactions. Some key points:
- Ribozymes were first proposed in the 1960s and discovered in the 1980s by Thomas Cech and Sidney Altman, who shared the 1989 Nobel Prize for the discovery.
- Common ribozyme activities include splicing and cleaving RNA and DNA. Ribozymes in the ribosome help link amino acids during protein synthesis.
- Major types of ribozymes include group I and group II introns, hammerhead, hairpin, and RNase P ribozymes. They use mechanisms like metal ion coordination and nucleophilic attacks to catalyze reactions.
- RTranscription in eukaryotes



Transcription in eukaryotesgohil sanjay bhagvanji
Ěý
This document discusses transcription in eukaryotes. It begins with definitions of transcription and describes the basic process of RNA being synthesized from a DNA template. It then covers the mechanisms of transcription, including initiation involving RNA polymerase and transcription factors, elongation, and termination. The key similarities between prokaryotic and eukaryotic transcription are that DNA acts as a template and RNA polymerase facilitates RNA synthesis. Key differences are that eukaryotic transcription occurs in the nucleus, is carried out by three classes of RNA polymerase, and RNAs are processed in the nucleus rather than the cytoplasm.DNA reparing



DNA reparingBahauddin Zakariya University lahore
Ěý
DNA repair is a collection of processes cells use to identify and correct damage to DNA molecules. Around 1 million lesions can occur per cell per day due to normal metabolic activities and environmental factors like UV light. Unrepaired lesions can alter gene transcription or cause mutations. The main types of DNA repair are direct reversal, base excision repair, nucleotide excision repair, and double-strand break repair. Cells have checkpoint mechanisms to detect DNA damage and initiate repair or induce apoptosis if damage is too severe. Defects in DNA repair can cause diseases like xeroderma pigmentosum or increase cancer risks. Telomere shortening due to factors like oxidation also contributes to cellular aging, and telomerase may help counter thisVarious model of DNA replication



Various model of DNA replicationEmaSushan
Ěý
1. There are four main models of DNA replication: rolling circle replication, theta replication, bidirectional replication of linear DNA, and telomere replication.
2. Rolling circle replication involves nicking circular DNA and using one strand as a template to produce multiple copies of the original circular DNA.
3. Theta replication occurs in prokaryotes and involves unwinding circular DNA at an origin of replication and replicating bi-directionally to form a theta-shaped structure.
4. Bidirectional replication of linear DNA involves unwinding DNA at origins of replication and using leading and lagging strand synthesis to replicate in both directions until the ends of the linear genome are reached.Cdk



CdkSuba Venkat
Ěý
Cyclin dependent kinases (CDKs) play a key regulatory role in controlling the cell cycle. CDKs form complexes with cyclins and their activity varies throughout the cell cycle. There are checkpoints that ensure DNA replication and division occur accurately. CDK-cyclin complexes promote progression through the cell cycle phases (G1, S, G2, M) by phosphorylating target proteins. Cyclin levels oscillate while CDKs are constantly present. Together they activate enzymes and proteins required for DNA replication and mitosis. Precise regulation of CDK-cyclin complexes and degradation of cyclins through ubiquitination is crucial for orderly cell cycle progression.Cell Cycle_ Usman.pptx sasgdgdb vdf g g rg g



Cell Cycle_ Usman.pptx sasgdgdb vdf g g rg gmunshi5
Ěý
The cell cycle is regulated by cyclins, cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs), and tumor suppressors. The M phase is the shortest phase and includes mitosis and cytokinesis. G1 phase duration is variable. CDKs must bind to cyclins to transition between phases and are inhibited by CDK inhibitors in the presence of errors. The Cyclin D/Cdk4 complex initiates DNA replication by phosphorylating the retinoblastoma protein (pRb). The p53 tumor suppressor inhibits DNA replication through activating pRb and initiating apoptosis in cells with irreparable DNA damage.More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Telomerase



TelomeraseKashmeera N.A.
Ěý
Telomeres are repetitive nucleotide sequences located at the ends of chromosomes that protect the ends from deterioration or fusion with other chromosomes. They shorten each time a cell divides until a length is reached that triggers cell senescence or death. The enzyme telomerase maintains telomere length by adding telomeric repeats to chromosome ends using its own RNA component as a template. Telomerase is active in germ cells, stem cells, and cancer cells, allowing indefinite cell division, but not in most somatic cells, limiting their replicative lifespan.Dna replication in eukaryotes



Dna replication in eukaryotesM Vignesh
Ěý
This document describes the process of DNA replication in eukaryotes. It occurs in S phase of the cell cycle and involves three main stages: initiation, formation of the initiation complex, and elongation. Initiation requires the assembly of pre-replication complexes containing ORC, Cdc6, Cdt1 and MCM proteins. In S phase, Cdc45 and GINS are recruited to form the initiation complex. Elongation proceeds bidirectionally from replication forks, with leading strand synthesis continuous and lagging strand discontinuous via Okazaki fragments. Replication terminates at telomeres.Dna methylation ppt



Dna methylation pptIbad khan
Ěý
DNA methylation involves the addition of methyl groups to cytosine bases in DNA. It is an epigenetic process that plays an important role in normal development and diseases like cancer. Cytosine methylation occurs most widely and involves the addition of a methyl group to the C-5 position of cytosine. Methylation can repress gene expression by interfering with transcriptional protein binding or recruiting chromatin remodeling proteins. In cancer, aberrant methylation can lead to silencing of tumor suppressor genes or activation of oncogenes. Genomic imprinting involves differential gene expression based on parental origin through epigenetic mechanisms like methylation. Around 1% of genes show imprinting including IGF2 and H19. Imprinting errorsReceptor tyrosine kinases.ppt



Receptor tyrosine kinases.pptDr. Khuram Aziz
Ěý
The document discusses receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs), a class of cell surface receptors that possess intrinsic tyrosine kinase activity. RTKs are activated through ligand binding and dimerization, which leads to autophosphorylation and downstream signaling. This signaling involves phosphorylation of proteins by RTKs and recruitment of adapter proteins, and results in cellular responses like cell division, differentiation, and motility. Common to all RTKs are an extracellular ligand-binding domain, a transmembrane domain, an intracellular tyrosine kinase domain, and regulatory domains.MODELS OF REPLICATION



MODELS OF REPLICATIONKristu Jayanti College
Ěý
The document discusses three models of DNA replication:
1) Asymmetric replication - the leading and lagging strands are replicated differently due to the 5' to 3' directionality of DNA polymerase. The leading strand replicates continuously while the lagging strand replicates discontinuously in short Okazaki fragments.
2) D-loop model - replication in mitochondria where one strand is displaced to form a D-loop and replicates first before the other strand.
3) Rolling circle model - used by plasmids and viruses where one strand is nicked and displaced to be used as a template, forming multiple copies linked together in a concatemer.Oncogene and Proto-oncogene



Oncogene and Proto-oncogenevidan biology
Ěý
Proto-oncogenes are normal genes that can become oncogenes following mutations. They encode proteins involved in cell growth, proliferation, differentiation and apoptosis. Examples include HER2, Wnt, Myc, Ras and genes in the Ras signaling pathway. Mutations in proto-oncogenes convert them into oncogenes, driving uncontrolled cell growth and tumor development. Common mutations are point mutations, which result in overactive gene products by altering transcription or protein function. For example, point mutations in Ras genes are found in many cancers and keep the Ras protein constantly active.dyneins and kinesins



dyneins and kinesinsstudent
Ěý
Kinesins and dyneins are motor proteins that move along microtubules. Kinesins move cargo from the center of the cell to its periphery by moving toward the plus end of microtubules. Dyneins move cargo from the periphery to the center by moving toward the minus end of microtubules. Both use ATP hydrolysis to power their movement in 8 nm steps along microtubules in opposite directions. Dyneins are also responsible for the bending movement of cilia and flagella by generating force between adjacent microtubule doublets.Holliday junction Model by kk



Holliday junction Model by kkKAUSHAL SAHU
Ěý
INTRODUCTION
TERMENOLOGY
SITES OF HOLLIDAY JUNCTION
HOMOLOGOUS RECOMBINATION
HOLLIDAY MODEL
DOUBEL STRAND BREAK MODEL
IN PROKAYOTIC RECOMBINATION
IN EUKARYOTIC RECOMBINATION
SITE SPECIFIC RECOMBINATION
SERINE RECOMBINATION
TYROSINE RECOMBINATION
TRANSPOSITION
ILLEGITIMATE RECOMBINATION
CONCLUSION
REFRENCES
Dna damage and repair



Dna damage and repairNamrata Chhabra
Ěý
DNA damage, Types of damage, Agents causing DNA damage, DNA repair system, Implications of defective DNA repair systemRNA editing



RNA editingTenzin t
Ěý
RNA editing is a post-transcriptional process that makes discrete changes to RNA sequences. There are three main types of RNA editing: cytosine to uracil deamination, adenine to inosine deamination, and guide RNA-mediated insertion/deletion of uridine bases. Cytidine deamination is site-specific and involves enzymes like cytidine deaminase. Adenine deamination occurs in RNA secondary structures and involves enzymes like ADAR. Guide RNA editing involves hybridization of RNA to guide RNA, cleavage by an endonuclease, addition of uridine by TuTase, and ligation. RNA editing increases protein diversity and is essential for organelle development in eukaryotes.Cromatin Remodeling



Cromatin RemodelingBalaji Thorat
Ěý
1. Chromatin remodeling is the process by which chromatin structure is dynamically modified to allow access of DNA for processes like transcription.
2. There are two main types of chromatin remodeling - covalent histone modification and ATP-dependent chromatin remodeling complexes.
3. ATP-dependent complexes use energy from ATP hydrolysis to move, eject, or restructure nucleosomes, allowing access to DNA.
4. Examples of chromatin remodeling complexes include SWI/SNF, ISWI, CHD, and INO80 families, which have different activities like nucleosome sliding or histone variant exchange.Trp operon



Trp operonSKYFALL
Ěý
The trp operon contains a cluster of genes involved in tryptophan biosynthesis that are under the control of a single promoter. It was the first repressible operon discovered in E. coli in 1953. The trp operon contains structural genes that encode enzymes for tryptophan synthesis, as well as a promoter, operator, and regulatory genes. Tryptophan acts as an effector molecule that binds to the repressor protein, increasing its affinity for the operator sequence and repressing transcription when tryptophan is present. The trp operon is also regulated by transcriptional attenuation, where tryptophan levels affect the formation of termination or anti-termination hairpin loops in the mRNA.Rna polymerase



Rna polymerasepriyanka raviraj
Ěý
RNA Polymerase
Introduction
Purification
History
PRODUCTS OF RNAP
Messenger RNA
Non-coding RNA Ěýor "RNA genes
Transfer RNA
Ribosomal RNA
Micro RNA
Catalytic RNA (Ribozyme)
prokaryotic and eukaryotic
Transcription by RNA Polymerase
TYPES OF RNA POLYMERASE
Type I
Type II
Type III
Prokaryotic Transcription Unit
EXPRESSION OF A PROKARYOTIC GENE
Prokaryotic Polycistronic Message Codes for Several Different Proteins
Eukaryotic Transcription Unit
ENHANCERS AND SILENCERS
RESULT OF THE TRANSCRIPTION CYCLE
RNAP III TRANSCRIBES HUMAN MICRORNAS
RNAP I–specific subunits promote
polymerase clustering to enhance the rRNA gene
transcription cycle
RNAP II–TFIIB STRUCTURE AND
MECHANISM OF TRANSCRIPTION INITIATION
FIVE CHECKPOINTS MAINTAINING THE FIDELITY OF
TRANSCRIPTION BY RNAP IN STRUCTURAL AND
ENERGETIC DETAILSDNA Supercoiling 



DNA Supercoiling Subhranil Bhattacharjee
Ěý
This contains DNA Supercoiling , relation between Linking no,Twist and Writhe and a brief explanation of Topoisomerase Transposable elements



Transposable elementsSai Kiran Munagala
Ěý
Transportable elements are DNA Sequences that move from one location in a chromosome to another within the same chromosome or into another chromosome.
These are DNA Sequences that move from one location in a chromosome to another within the same chromosome or into another chromosome.
These are DNA Sequences that move from one location in a chromosome to another within the same chromosome or into another chromosome.
These are also known as “Jumping genes”.
Site specific recombination



Site specific recombinationRoshan Parihar
Ěý
This document discusses site-specific recombination, including the structures and mechanisms involved. It describes two classes of recombinases - tyrosine recombinases and serine recombinases. Tyrosine recombinases involve cleavage of DNA through formation of a protein-DNA bond using a tyrosine residue. Serine recombinases utilize a phosphoserine bond between DNA and a conserved serine residue. The document provides examples of applications for site-specific recombination such as tracking cell lineage, altering gene expression, and targeted gene knockout.Ribozyme



RibozymeMUMTHAS P K - KANNUR UNIVERSITY, CAMPUS, KANNUR
Ěý
Ribozymes are RNA molecules that act as enzymes and catalyze biochemical reactions. Some key points:
- Ribozymes were first proposed in the 1960s and discovered in the 1980s by Thomas Cech and Sidney Altman, who shared the 1989 Nobel Prize for the discovery.
- Common ribozyme activities include splicing and cleaving RNA and DNA. Ribozymes in the ribosome help link amino acids during protein synthesis.
- Major types of ribozymes include group I and group II introns, hammerhead, hairpin, and RNase P ribozymes. They use mechanisms like metal ion coordination and nucleophilic attacks to catalyze reactions.
- RTranscription in eukaryotes



Transcription in eukaryotesgohil sanjay bhagvanji
Ěý
This document discusses transcription in eukaryotes. It begins with definitions of transcription and describes the basic process of RNA being synthesized from a DNA template. It then covers the mechanisms of transcription, including initiation involving RNA polymerase and transcription factors, elongation, and termination. The key similarities between prokaryotic and eukaryotic transcription are that DNA acts as a template and RNA polymerase facilitates RNA synthesis. Key differences are that eukaryotic transcription occurs in the nucleus, is carried out by three classes of RNA polymerase, and RNAs are processed in the nucleus rather than the cytoplasm.DNA reparing



DNA reparingBahauddin Zakariya University lahore
Ěý
DNA repair is a collection of processes cells use to identify and correct damage to DNA molecules. Around 1 million lesions can occur per cell per day due to normal metabolic activities and environmental factors like UV light. Unrepaired lesions can alter gene transcription or cause mutations. The main types of DNA repair are direct reversal, base excision repair, nucleotide excision repair, and double-strand break repair. Cells have checkpoint mechanisms to detect DNA damage and initiate repair or induce apoptosis if damage is too severe. Defects in DNA repair can cause diseases like xeroderma pigmentosum or increase cancer risks. Telomere shortening due to factors like oxidation also contributes to cellular aging, and telomerase may help counter thisVarious model of DNA replication



Various model of DNA replicationEmaSushan
Ěý
1. There are four main models of DNA replication: rolling circle replication, theta replication, bidirectional replication of linear DNA, and telomere replication.
2. Rolling circle replication involves nicking circular DNA and using one strand as a template to produce multiple copies of the original circular DNA.
3. Theta replication occurs in prokaryotes and involves unwinding circular DNA at an origin of replication and replicating bi-directionally to form a theta-shaped structure.
4. Bidirectional replication of linear DNA involves unwinding DNA at origins of replication and using leading and lagging strand synthesis to replicate in both directions until the ends of the linear genome are reached.Similar to Cyclin dependent kinases (20)
Cdk



CdkSuba Venkat
Ěý
Cyclin dependent kinases (CDKs) play a key regulatory role in controlling the cell cycle. CDKs form complexes with cyclins and their activity varies throughout the cell cycle. There are checkpoints that ensure DNA replication and division occur accurately. CDK-cyclin complexes promote progression through the cell cycle phases (G1, S, G2, M) by phosphorylating target proteins. Cyclin levels oscillate while CDKs are constantly present. Together they activate enzymes and proteins required for DNA replication and mitosis. Precise regulation of CDK-cyclin complexes and degradation of cyclins through ubiquitination is crucial for orderly cell cycle progression.Cell Cycle_ Usman.pptx sasgdgdb vdf g g rg g



Cell Cycle_ Usman.pptx sasgdgdb vdf g g rg gmunshi5
Ěý
The cell cycle is regulated by cyclins, cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs), and tumor suppressors. The M phase is the shortest phase and includes mitosis and cytokinesis. G1 phase duration is variable. CDKs must bind to cyclins to transition between phases and are inhibited by CDK inhibitors in the presence of errors. The Cyclin D/Cdk4 complex initiates DNA replication by phosphorylating the retinoblastoma protein (pRb). The p53 tumor suppressor inhibits DNA replication through activating pRb and initiating apoptosis in cells with irreparable DNA damage.CELL DIVISION AND ITS REGULATION.pdf



CELL DIVISION AND ITS REGULATION.pdfRAMDAS BHAT
Ěý
This document provides information on human cell cycle checkpoints and regulation. It discusses the three main cell cycle checkpoints - G1/S, G2/M, and M checkpoints. Each checkpoint verifies processes are completed before progression to the next phase. Key regulators of the cell cycle discussed include cyclins, CDKs, CDKIs, Rb protein, and p53 protein. Cyclins and CDKs control progression through different cell cycle phases, while CDKIs inhibit CDKs to arrest the cell cycle. Rb and p53 are important tumor suppressor proteins that also regulate the cell cycle.Cell cycle regulation 17BCB0016



Cell cycle regulation 17BCB0016AkanchaAgarwal1
Ěý
This presentation on "Cell Cycle regulation" takes you to the cell cycle describing the stages and checkpoints involved providing some of the evidences of cell cycle regulation. Then we will move to cyclins and cyclin dependent kinases and the mechanism they follow.
This journey in regulation of cell cycle will take a halt after a general discussion of positive and negative cell cycle regulators.
Thankyou.cell cycle



cell cycleChitresh Aggarwal
Ěý
This document provides an overview of the cell cycle, including its phases, regulation, checkpoints, and deregulation in cancer. Key points include:
- The cell cycle consists of the G1, S, G2, and M phases, during which the cell grows and divides. Cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) drive progression through the phases.
- CDK activity is regulated by cyclins, CDK inhibitors, phosphorylation, and ubiquitin-mediated degradation. The retinoblastoma protein (Rb) and E2F transcription factors also regulate the cell cycle.
- Checkpoints like G1/S, intra-S, and G2/M ensure DNACell Cycle and Dna replication.pdf very good



Cell Cycle and Dna replication.pdf very goodunspokenbuddy
Ěý
The document summarizes the key phases and checkpoints of the cell cycle, as well as the roles of cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) in regulating progression through the cell cycle. It notes that the cell cycle consists of M (mitosis), G1, S (DNA synthesis), and G2 phases, with checkpoints to detect errors and damage. Cyclins activate CDKs to phosphorylate proteins and drive progression, with Cyclin D activating CDK4/6 to promote G1/S transition, Cyclin E and A activating CDK2 to initiate DNA synthesis, and Cyclin B activating CDK1 for G2/M transition. The Rb protein also regulates the G1 checkpointCell cycle regulation 17 bcb0016



Cell cycle regulation 17 bcb0016AkanchaAgarwal1
Ěý
This presentation on "Cell Cycle regulation" takes you to the cell cycle describing the stages and checkpoints involved providing some of the evidences of cell cycle regulation. Then we will move to cyclins and cyclin dependent kinases and the mechanism they follow.
This journey in regulation of cell cycle will take a halt after a general discussion of positive and negative cell cycle regulators.
Thankyou.New Microsoft Office PowerPoint Presentation-1.pptx



New Microsoft Office PowerPoint Presentation-1.pptxShounakKamat1
Ěý
The cell cycle is a precisely programmed series of events that enables a cell to duplicate its contents and divide into two daughter cells. It consists of interphase (G1, S, G2 phases) and mitosis (M phase). Progression through the cell cycle is regulated by cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs). CDK activity is controlled by association with cyclins, CDK inhibitors, and phosphorylation. Checkpoint pathways like the G1/S, G2, and spindle assembly checkpoints ensure replication and division errors are corrected before progression. Deregulation of these checkpoint pathways can lead to genomic instability and carcinogenesis.Cell cycle regulation



Cell cycle regulationHimakaraDattaMandala1
Ěý
This slideshow contains various stages of cell cycle regulation, cell cycle checkpoints and their proteins involved in regulation. Cell cycle checkpoints transition phases.Cell cycle checkpoints, apoptosis and cancer



Cell cycle checkpoints, apoptosis and cancerSurender Rawat
Ěý
1. The document discusses various aspects of the cell cycle, including its key phases and regulating molecules. It notes that the cell cycle includes growth, DNA replication, chromosome separation, and cytokinesis.
2. Major regulatory molecules discussed include cyclins, CDKs, Rb protein, and checkpoints like START that ensure DNA damage is repaired before progression.
3. External factors like nutrients and growth signals regulate the cell cycle at transition points like the G1/S boundary through pathways involving cyclins, CDKs, and Rb.Cell cycle



Cell cycleNida Sajjad
Ěý
The cell cycle is tightly regulated by both positive and negative regulators to ensure accurate DNA replication and cell division. Positive regulators like cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) control progression through the cell cycle phases. Negative regulators including the retinoblastoma (Rb) protein and p53 protein oppose cell cycle progression in response to DNA damage or other problems. Checkpoints at the G1/S and G2/M transitions verify DNA integrity before allowing the cell to progress further. Faulty regulation of these cell cycle controllers can lead to uncontrolled cell division and cancer.Cell cycle and tumor kinetics



Cell cycle and tumor kineticsNilesh Kucha
Ěý
- The cell cycle consists of four main phases - G1, S, G2, and M. The G1, S, and G2 phases make up interphase.
- The cell cycle is tightly regulated by cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs). Different cyclin-CDK complexes control progression through the different cell cycle phases.
- Checkpoints exist to monitor DNA damage before progression into S phase and M phase. These checkpoints are regulated by proteins like ATM, ATR, Chk1, Chk2, and p53.
- Dysregulation of cell cycle control and checkpoint pathways contributes to uncontrolled cell proliferation in cancer. Both oncogenes and tumorCell Cycle, Cell cycle Check Points, Cell cycle regulation and Tumor Suppress...



Cell Cycle, Cell cycle Check Points, Cell cycle regulation and Tumor Suppress...Dr. A.D.Naveen Kumar
Ěý
An overview on Cell Cycle and CancerCELL SIGNALLING.pptx



CELL SIGNALLING.pptxJegadeshwariBhaskara
Ěý
The phenomenon of signal transduction, also known as cell signaling, pertains to the intricate mechanisms that facilitate the transfer of biological information between cells. The effective coordination of diverse specialized cell types in various tissues and organs is a prerequisite for the proper functioning of complex multicellular organisms, necessitating intercellular communication. This communication must be continuous and dynamic to maintain coordination. Additionally, cell signaling pathways play a crucial role in the mechanisms of action of numerous drugs, including both local and general anesthetics. Consequently, a fundamental understanding of cell signaling mechanisms is imperative for comprehending various pathophysiologic and pharmacologic mechanisms.Cyclin-Dependent Kinase



Cyclin-Dependent Kinasepharmdelve
Ěý
Cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) belong to a protein serine/threonine kinases whose activity depends on association with a noncatalytic regulatory subunit called a cyclin. Cyclin-dependent kinases inhibitors are vital for progression through the cell cycle and proliferation. Cell cycle and its regulation



Cell cycle and its regulationpriyanshugupta1515
Ěý
The cell cycle is regulated by cyclin-dependent kinases (Cdks) whose activity oscillates throughout the cycle. Cdks form complexes with cyclins, which activate the Cdks and determine which phase of the cycle they control. The cyclin-Cdk complexes phosphorylate target proteins to promote replication and mitosis. Progression through the cell cycle is also controlled by ubiquitin ligases and phosphorylation/dephosphorylation events. The cycle operates through a series of switches that trigger irreversible events, keeping it tightly regulated and coordinated.Cell cycle regulation Basics



Cell cycle regulation BasicsMinali Singh
Ěý
The cell cycle is the ordered series of events that leads to cell division into two daughter cells. It consists of four main phases: G1, S, G2, and M. Checkpoints ensure each step is completed before progression. Cyclins activate CDKs at specific phases - G1 cyclins activate G1 CDKs which promote DNA replication by phosphorylating Rb and activating E2Fs. S-phase CDKs activate DNA replication origins. Mitotic CDKs promote mitotic events like spindle formation and chromosome condensation. Completion of mitosis involves chromosome segregation and cyclin degradation to inactivate CDKs and allow cell division.Please answer all of #5 After the completion of S phase, F.2F functi.pdf



Please answer all of #5 After the completion of S phase, F.2F functi.pdfsiennatimbok52331
Ěý
Phosphorylation by Wee1 regulates cyclin/CDK activity by inhibiting Cdk1 through
phosphorylation. Dephosphorylation by Cdc25 activates cyclin/CDK activity by removing
inhibitory phosphates from Cdks. Binding by cyclin dependent kinase inhibitors (CKIs) regulates
cyclin/CDK activity by interacting with cyclin-CDK complexes to block their kinase activity.
Degradation of cyclins by the proteasome regulates cyclin/CDK activity by using proteasomes to
degrade cyclins after they have performed their function, providing directionality to the cell cycle.cell cycle 1st sem.pptx



cell cycle 1st sem.pptxdikshasingh649964
Ěý
The document summarizes the cell cycle and its regulation. It discusses the main phases of the cell cycle including interphase (G1, S, G2 phases) and the M phase. It also describes key cell cycle checkpoints and the proteins involved in regulating progression through the cycle, such as cyclins, CDKs, and CDK inhibitors. Precise control of the cell cycle is essential as any errors could lead to cancer.Cell Cycle, Cell cycle Check Points, Cell cycle regulation and Tumor Suppress...



Cell Cycle, Cell cycle Check Points, Cell cycle regulation and Tumor Suppress...Dr. A.D.Naveen Kumar
Ěý
More from Mandira bhosale (6)
Fluorescence microscopy presentation



Fluorescence microscopy presentationMandira bhosale
Ěý
fluorecence microscopy defination, fluorecence microscopy principle ,fluorecence microscopy working , fluorecence microscopy history ,fluorecence microscopy application ,fluorecence microscopy advantange ,fluorecence microscopy disadvantage Tm of DNA - melting temperature of DNA



Tm of DNA - melting temperature of DNAMandira bhosale
Ěý
melting temperature of DNA
Chargaff's rule on DNA & RNA
denaturation renaturation
hyperchromism
hypochromism Therapeutic enzymes working 



Therapeutic enzymes working Mandira bhosale
Ěý
enzymes working as therapeutic agents
uses off enzymes msc level information
history of therapeutic enzymesSafety measures while handling radioisotopes



Safety measures while handling radioisotopesMandira bhosale
Ěý
The document discusses the effects of radioisotopes and radiation safety. It describes the immediate and delayed health effects of radiation exposure, including bone marrow syndrome, gastrointestinal issues, and increased risk of cancer. It emphasizes the importance of minimizing time, maximizing distance, and using proper shielding (TDS) when working with radiation. The document provides guidance on safety equipment, dosimeters, waste disposal, labeling, and other laboratory rules to prevent exposure.plant growth regulators - mandira bhosale



plant growth regulators - mandira bhosaleMandira bhosale
Ěý
The document discusses various plant growth regulators (PGRs) including their classification, functions, and applications. There are five major classes of natural plant hormones: auxins, gibberellins, cytokinins, ethylene, and abscisic acid. Auxins, gibberellins and cytokinins promote growth, while abscisic acid and ethylene generally inhibit growth. PGRs are used in agriculture to promote seed germination, flowering, fruit development and stress tolerance in plants.Gel electrophoresis complete study



Gel electrophoresis complete studyMandira bhosale
Ěý
gel electrophoresis is technique which we used to separate or purify some macromolecules like DNA RNA & proteins.Recently uploaded (20)
Year 10 The Senior Phase Session 3 Term 1.pptx



Year 10 The Senior Phase Session 3 Term 1.pptxmansk2
Ěý
Year 10 The Senior Phase Session 3 Term 1.pptxDigital Tools with AI for e-Content Development.pptx



Digital Tools with AI for e-Content Development.pptxDr. Sarita Anand
Ěý
This ppt is useful for not only for B.Ed., M.Ed., M.A. (Education) or any other PG level students or Ph.D. scholars but also for the school, college and university teachers who are interested to prepare an e-content with AI for their students and others.Rass MELAI : an Internet MELA Quiz Prelims - El Dorado 2025



Rass MELAI : an Internet MELA Quiz Prelims - El Dorado 2025Conquiztadors- the Quiz Society of Sri Venkateswara College
Ěý
Prelims of Rass MELAI : a Music, Entertainment, Literature, Arts and Internet Culture Quiz organized by Conquiztadors, the Quiz society of Sri Venkateswara College under their annual quizzing fest El Dorado 2025. How to Configure Flexible Working Schedule in Odoo 18 Employee



How to Configure Flexible Working Schedule in Odoo 18 EmployeeCeline George
Ěý
In this slide, we’ll discuss on how to configure flexible working schedule in Odoo 18 Employee module. In Odoo 18, the Employee module offers powerful tools to configure and manage flexible working schedules tailored to your organization's needs.Computer Application in Business (commerce)



Computer Application in Business (commerce)Sudar Sudar
Ěý
The main objectives
1. To introduce the concept of computer and its various parts. 2. To explain the concept of data base management system and Management information system.
3. To provide insight about networking and basics of internet
Recall various terms of computer and its part
Understand the meaning of software, operating system, programming language and its features
Comparing Data Vs Information and its management system Understanding about various concepts of management information system
Explain about networking and elements based on internet
1. Recall the various concepts relating to computer and its various parts
2 Understand the meaning of software’s, operating system etc
3 Understanding the meaning and utility of database management system
4 Evaluate the various aspects of management information system
5 Generating more ideas regarding the use of internet for business purpose Kaun TALHA quiz Prelims - El Dorado 2025



Kaun TALHA quiz Prelims - El Dorado 2025Conquiztadors- the Quiz Society of Sri Venkateswara College
Ěý
Prelims of Kaun TALHA : a Travel, Architecture, Lifestyle, Heritage and Activism quiz, organized by Conquiztadors, the Quiz society of Sri Venkateswara College under their annual quizzing fest El Dorado 2025. Useful environment methods in Odoo 18 - Odoo şÝşÝߣs



Useful environment methods in Odoo 18 - Odoo şÝşÝߣsCeline George
Ěý
In this slide we’ll discuss on the useful environment methods in Odoo 18. In Odoo 18, environment methods play a crucial role in simplifying model interactions and enhancing data processing within the ORM framework.Eng7-Q4-Lesson 1 Part 1 Understanding Discipline-Specific Words, Voice, and T...



Eng7-Q4-Lesson 1 Part 1 Understanding Discipline-Specific Words, Voice, and T...sandynavergas1
Ěý
Understanding Discipline-Specific Words, Voice, and Technical TermsDatabase population in Odoo 18 - Odoo slides



Database population in Odoo 18 - Odoo slidesCeline George
Ěý
In this slide, we’ll discuss the database population in Odoo 18. In Odoo, performance analysis of the source code is more important. Database population is one of the methods used to analyze the performance of our code. Lesson Plan M1 2024 Lesson Plan M1 2024 Lesson Plan M1 2024 Lesson Plan M1...



Lesson Plan M1 2024 Lesson Plan M1 2024 Lesson Plan M1 2024 Lesson Plan M1...pinkdvil200
Ěý
Lesson Plan M1 2024 Lesson Plan M1 2024 Lesson Plan M1 2024 SOCIAL CHANGE(a change in the institutional and normative structure of societ...



SOCIAL CHANGE(a change in the institutional and normative structure of societ...DrNidhiAgarwal
Ěý
This PPT is showing the effect of social changes in human life and it is very understandable to the students with easy language.in this contents are Itroduction, definition,Factors affecting social changes ,Main technological factors, Social change and stress , what is eustress and how social changes give impact of the human's life.EDL 290F Week 3 - Mountaintop Views (2025).pdf



EDL 290F Week 3 - Mountaintop Views (2025).pdfLiz Walsh-Trevino
Ěý
EDL 290F Week 3 - Mountaintop Views (2025).pdfThe Constitution, Government and Law making bodies .



The Constitution, Government and Law making bodies .saanidhyapatel09
Ěý
This PowerPoint presentation provides an insightful overview of the Constitution, covering its key principles, features, and significance. It explains the fundamental rights, duties, structure of government, and the importance of constitutional law in governance. Ideal for students, educators, and anyone interested in understanding the foundation of a nation’s legal framework.
Mate, a short story by Kate Grenvile.pptx



Mate, a short story by Kate Grenvile.pptxLiny Jenifer
Ěý
A powerpoint presentation on the short story Mate by Kate Greenville. This presentation provides information on Kate Greenville, a character list, plot summary and critical analysis of the short story.The Dravidian Languages: Tamil, Telugu, Kannada, Malayalam, Brahui, Kuvi, Tulu



The Dravidian Languages: Tamil, Telugu, Kannada, Malayalam, Brahui, Kuvi, TuluDrIArulAram
Ěý
The Dravidian Languages by Arul AramFESTIVAL: SINULOG & THINGYAN-LESSON 4.pptx



FESTIVAL: SINULOG & THINGYAN-LESSON 4.pptxDanmarieMuli1
Ěý
Sinulog Festival of Cebu City, and Thingyan Festival of Myanmar.Rass MELAI : an Internet MELA Quiz Prelims - El Dorado 2025



Rass MELAI : an Internet MELA Quiz Prelims - El Dorado 2025Conquiztadors- the Quiz Society of Sri Venkateswara College
Ěý
Kaun TALHA quiz Prelims - El Dorado 2025



Kaun TALHA quiz Prelims - El Dorado 2025Conquiztadors- the Quiz Society of Sri Venkateswara College
Ěý
Cyclin dependent kinases
- 2. What are CDK’s? • Cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) are protein kinases involved in critical cellular processes. • They are important in the regulation and control of cell cycle. • They are also involved in regulating transcription, mRNA processing, and the differentiation of nerve cells. • They are always present in the cells in their inactive form , but the binding of a cyclin activates it, making it a functional enzyme and allowing it to modify target proteins. • CDK’s are the enzymes that phosphorylates specific target proteins and the attached phosphate group acts like a switch, making the target protein more or less active.
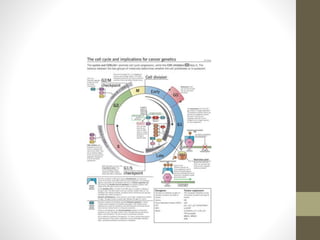
- 3. Checkpoints of cell cycle:
- 4. Cyclin and CDK complexes present in different phases :
- 9. • Tumor suppressor protein retinoblastoma (Rb) protein holding transcription factor E2F. • cyclin_-CDK complex phosphorylate the Rb protein and leads the release of E2F. • E2F can then activate transcription of the cyclin E gene. Cyclin E binds CDK2, and this complex fully phosphorylates Rb, completing its inactivation. Cyclin E also phosphorylates p27Kip1, an inhibitor of Cyclin D. Phosphorylation of p27Kip1 tags it for degradation. Degradation of this protein promotes expression of cyclin A. • During S phase, Cyclin A ensures that DNA replication only occurs ONCE per cell cycle by preventing assembly of excessive replication complexes.
- 10. • The Cyclin A-CDK2 complex also regulates DNA replication by phosphorylating certain DNA replication machinery components. • When the cell transition occur to M phase cyclin A gets replaced with cyclin B. • Cyclin B is a mitotic cyclin which binds to CDK1 to form the maturation promoting factor, or mitosis promoting factor . The concentration of MPF rises until mitosis, until its concentration falls abruptly due to degradation of Cyclin B. High concentrations of Cyclin B are necessary for cells to enter M phase, and low concentrations are needed to exit M phase.
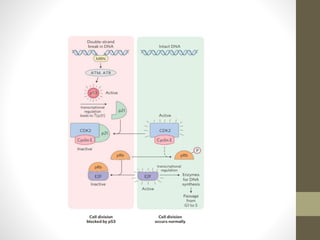
- 11. • When DNA damage is their cyclin cdk inhibitors gets activated i.e. Tumor suppressor proteins like p53,p21,p27kip1 etc. • P53 activates p21 and binds all cyclin cdk complexes and activity of Rb proteins get restored and E2F is inactivated . • Transcription gets halt and cell gets time for the repair of DNA damage.
- 14. References : • https://youtu.be/VLJF8Pf8spw • https://youtu.be/nEMMKzYQf9A • Nelson and Cox Lehninger principles of biochemistry 6th edition (chapter no.12) • https://www.khanacademy.org/science/ap-biology/cell- communication-and-cell-cycle/regulation-of-cell-cycle/a/cell- cycle-regulators
- 15. Thank you!




