Density Functional Theory by Tayyab Shabir
Download as PPTX, PDF0 likes59 views
Density Functional Theory
1 of 8
Download to read offline





Recommended
Density Functional Theory (DFT) Overview.pptx



Density Functional Theory (DFT) Overview.pptxmomnaqayyum01
╠²
Density Functional Theory (DFT) is a powerful computational method used to study the electronic structure of molecules and materials by focusing on electron density rather than the many-body wave function. DFT is preferred due to its efficiency, accuracy, and versatility, making it applicable in diverse fields like material design, catalysis, and drug discovery. When applied to the HŌééO molecule, DFT accurately predicts its molecular geometry, bond angles, and bond lengths, and provides insights into its electron density distribution, which reveals its polar nature. DFT simplifies the study of many-particle systems by reducing the problem to a manageable form, allowing for efficient calculations of large systems. The Born-Oppenheimer approximation further simplifies DFT by treating nuclear and electronic motions separately, significantly reducing the computational cost. At its core, the Hohenberg-Kohn theorem provides the theoretical foundation of DFT, stating that all properties of a quantum system can be determined by its electron density, making it a cornerstone of modern computational chemistry and materials science. In this PPT, we have explained the fundamentals of Density Functional Theory (DFT), its importance, and its application to the HŌééO molecule, along with key concepts like electron density, many-particle systems, the Born-Oppenheimer approximation, and the Hohenberg-Kohn theorem, highlighting its relevance in modern computational chemistry.Density functional theory



Density functional theorysandhya singh
╠²
This document provides an overview of density functional theory (DFT). It discusses the history and development of DFT, including the Hohenberg-Kohn and Kohn-Sham theorems. The document outlines the fundamentals of DFT, including how it uses functionals of electron density rather than wavefunctions to simplify solving the many-body Schrodinger equation. It also describes the self-consistent approach in DFT calculations and provides examples of popular DFT software packages.Molecular modeling in drug design



Molecular modeling in drug designAADHIBHAGAWAN COLLEGE OF PHARMACY, THIRUVANNAMAI, TAMIL NADU
╠²
Molecular Modeling methods # QUANTUM MECHANICS # Drug Design #
PHARMACOPHORE MODELING # MOLECULAR DOCKING #
Hartree method ppt physical chemistry



Hartree method ppt physical chemistryalikhan1414
╠²
easy slides to understand the hartree method in basic physical chemistry of BS_6th semester in Pakistani universities.Computational chemistry



Computational chemistryMattSmith321834
╠²
Computational chemistry uses computers to simulate chemical systems and solve equations that model their properties. It is considered a third pillar of scientific investigation, along with theory and experiment. There are several computational methodologies including quantum mechanics, molecular mechanics, and molecular dynamics. Computational chemistry software can be used to optimize molecular geometries, map potential energy surfaces, perform conformational analyses, and calculate many other molecular properties and reaction kinetics. These methods have improved significantly with increasing computer power over the past few decades.Interaction of small molecules with grapheen supported on metal substrates: A...



Interaction of small molecules with grapheen supported on metal substrates: A...MIHIR RANJAN SAHOO
╠²
here we study how band structure changes in graphene on Ni(111) substrate and also binding energy of water on graphene/metal interface.lecture1-230501075743-142343456580ac.ppt



lecture1-230501075743-142343456580ac.pptzulqarnain199841
╠²
density fucntional theory
Hohen kohn sham equationsRoy-document-3



Roy-document-3prasenjit roy
╠²
This document discusses thermoelectric materials and calculations using the Wien2K software. It describes the Seebeck effect and Peltier effect. It discusses using Wien2K to model materials like Mg2Si, calculate properties like density of states, band structure, and optimize volume. Modifying approximations, strain effects, and nanostructuring are discussed to increase thermoelectric figure of merit ZT by increasing power factor and decreasing thermal conductivity.SCF methods, basis sets, and integrals part III



SCF methods, basis sets, and integrals part IIIAkefAfaneh2
╠²
Some DFT implementations (such as Octopus) attempt to describe the molecular
KohnŌĆōSham orbitals on a real-space grid.
ŌĆó A 3D simulation box is chosen together with a grid spacing, for example 0.5 a0. Then,
a grid in 3D is constructed and the SCF equations are solved on the grid.
ŌĆó This is different from an MO-LCAO expansion in numerical AOs!
ŌĆó Pseudopotentials are inevitable for real-space grid methods, but they are not required
when numerical AOs are used.
ŌĆó A great advantage of the use of numerical AOs as in DMol3 is that the method is free
of the basis-set superposition error (BSSE).
ŌĆó Because exact atomic orbitals are used, the atoms in a molecule cannot improve
their orbitals arti’¼ücially using basis functions from other atoms.Computational methodologies



Computational methodologiesMattSmith321834
╠²
Computational chemistry uses mathematical and computing methods to simulate chemical processes. It can predict molecular properties, structures, interactions and reaction pathways without expensive experiments. The main computational methods are ab initio, semi-empirical, density functional theory, molecular mechanics and molecular dynamics. Geometry optimization finds the lowest energy conformation of a molecule using algorithms to minimize the potential energy surface. It is important for understanding how structure influences properties and reactivity.Ab initio md



Ab initio mdyudhaarman
╠²
The document discusses ab initio molecular dynamics simulation methods. It begins by introducing molecular dynamics and Monte Carlo simulations using empirical potentials. It then describes limitations of empirical potentials and the need for ab initio molecular dynamics which calculates the potential from quantum mechanics. The document outlines several ab initio molecular dynamics methods including Ehrenfest molecular dynamics, Born-Oppenheimer molecular dynamics, and Car-Parrinello molecular dynamics. It provides details on how these methods treat the quantum mechanical potential and classical nuclear motion.Applications of Computational Quantum Chemistry



Applications of Computational Quantum ChemistryUniversity of Kerbala, Faculty of Science, Department of Chemistry
╠²
This presentation introduces an idea about the computational quantum chemistry field and its importance and applications in different ways.Molecular mechanics and dynamics



Molecular mechanics and dynamicsAteos Foundation of Science Education and Research, Pune, M.S., India
╠²
Computational Chemistry aspects of Molecular Mechanics and Dynamics have been discussed in this presentation. Useful for the Undergraduate and Postgraduate students of Pharmacy, Drug Design and Computational Chemistryfinland.ppt



finland.pptRAMARATHI2
╠²
This document discusses challenges and open questions in nuclear density functional theory (DFT). It begins by providing background on DFT and how it has been applied to nuclei using approximations like the local density approximation. It then discusses questions around improving the nuclear energy density functional, including justifying terms from microscopic theory, improving treatment of pairing and beyond-mean-field correlations, and incorporating dynamics. The document concludes by emphasizing the need for focused theoretical efforts, international collaborations, and new experimental data to help address open questions in nuclear DFT.Advantages and applications of computational chemistry



Advantages and applications of computational chemistrymanikanthaTumarada
╠²
The document discusses computational chemistry methods for calculating various thermodynamic and electronic properties of molecules. It provides an overview of computational chemistry and the properties that can be calculated, such as structure, energy, dipole moment, polarizability, ionization potential, HOMO/LUMO energies, chemical hardness and softness. It also describes different computational methods like classical molecular mechanics and molecular dynamics, as well as quantum chemistry methods including semi-empirical, ab initio and density functional theory approaches. Specific examples are given of calculating properties like dipole moment, polarizability, ionization potential using computational methods.COMPUTATIONAL CHEMISTRY 



COMPUTATIONAL CHEMISTRY Komal Rajgire
╠²
Computational chemistry uses theoretical chemistry calculations incorporated into computer programs to calculate molecular structures and properties. It can calculate properties such as structure, energy, charge distribution, and spectroscopic quantities using methods that range from highly accurate ab initio methods to less accurate semi-empirical and molecular mechanics methods. Computational chemistry allows medicinal chemists to use computer power to measure molecular geometry, electron density, energies, and more for applications such as conformational analysis, docking ligands in receptor sites, and comparing ligands.Density Functional Theory.pptx



Density Functional Theory.pptxHassanShah396906
╠²
Density functional theory (DFT) is a computational quantum mechanics method used to investigate the electronic structure of many-body systems like molecules and solids. It functions by using functionals of the electron density rather than the many-body wavefunction. This makes calculations more efficient. DFT was developed based on the Hohenberg-Kohn theorems, which established that all ground state properties are uniquely determined by the electron density alone. This allowed modeling systems using functionals of the density rather than attempting to solve the complicated many-electron Schrodinger equation directly. DFT is now widely used in physics, chemistry, and materials science.Single Particle Appoximation Final Pres.pptx



Single Particle Appoximation Final Pres.pptxkhalilpcsir
╠²
Many Body Problems topic About Perturbation Theory Single Particle Aproximation, it Defination Working , advantgaes Limittation Future aspects , Mathemtical Formulas about Many Body Problems topic About Perturbation Theory Single Particle Aproximation, Detail of Similicity in Quantam phyisics Methods paper



paperIsabelle Pelaschier
╠²
The document discusses using machine learning to develop density functional approximations for orbital-free density functional theory calculations. Specifically, kernel ridge regression is used to approximate the kinetic energy of non-interacting fermions confined to a 1D box as a functional of electron density. This machine-learned density functional approximation achieves highly accurate energies and self-consistent densities, outperforming traditional approximations. Various kernels, cross-validation methods, and representations of the electron density are explored to optimize the machine-learned approximation.computationalchemistry_12-6.ppt



computationalchemistry_12-6.pptsami97008
╠²
Computational chemistry uses numerical simulations based on the laws of physics to model chemical structures and reactions. There are different types of computational models of varying accuracy and computational cost, including molecular mechanics, semi-empirical, ab initio, and density functional theory methods. The accuracy of calculations also depends on the basis set used to describe molecular orbitals. Computational chemistry has become an important tool for characterizing nanomaterials.Intro-QM-Chem.ppt



Intro-QM-Chem.pptsami97008
╠²
This document provides an introduction to computational quantum chemistry. It defines computational chemistry as using mathematical approximations and computer programs to solve chemical problems based on quantum mechanics. Specifically, computational quantum chemistry focuses on solving the Schr├Čdinger equation for molecular systems using approximations like the Born-Oppenheimer approximation. It discusses how computational methods can be used to calculate various molecular properties and motivates the need for approximations due to the inability to exactly solve the Schr├Čdinger equation for complex molecules. The document then provides an overview of common computational methods like Hartree-Fock, configuration interaction, M├Ėller-Plesset perturbation theory, and coupled cluster theory.Intro-QM-Chem.ppt



Intro-QM-Chem.pptAkramLaKilo1
╠²
This document provides an introduction to computational quantum chemistry. It defines computational chemistry as using mathematical approximations and computer programs to solve chemical problems based on quantum mechanics. Specifically, computational quantum chemistry focuses on solving the Schr├Čdinger equation for molecular systems using approximations like the Born-Oppenheimer approximation. It also discusses methods for approximating the wavefunction like Hartree-Fock, configuration interaction, and density functional theory as well as expanding the molecular orbitals in a basis set of atomic orbitals.9783642250750 c2



9783642250750 c2Cl├│vis Batista dos Santos
╠²
The document summarizes the hopping mechanism for charge transport in organic materials. It describes how charge transport occurs through hopping between molecules, with the hopping rate determined by Marcus electron transfer theory. It discusses methods to calculate key parameters in the Marcus rate formula, including the transfer integral between molecules and the reorganization energy, using first-principles density functional theory calculations. These parameters and the Marcus rate theory can then be used to simulate charge mobility through random walk models.Molecular and Quantum Mechanics in drug design



Molecular and Quantum Mechanics in drug designAjay Kumar
╠²
This document discusses and compares molecular mechanics and quantum mechanics methods for drug design. It provides an overview of molecular mechanics, which uses classical physics to model potential energy surfaces, and common molecular mechanics force fields such as AMBER and CHARMM. It also describes quantum mechanics principles, density functional theory, and semi-empirical methods. Key differences between molecular mechanics and quantum mechanics are noted, such as system size, time required, and accuracy. Applications of each method in drug design are mentioned.More Related Content
Similar to Density Functional Theory by Tayyab Shabir (20)
lecture1-230501075743-142343456580ac.ppt



lecture1-230501075743-142343456580ac.pptzulqarnain199841
╠²
density fucntional theory
Hohen kohn sham equationsRoy-document-3



Roy-document-3prasenjit roy
╠²
This document discusses thermoelectric materials and calculations using the Wien2K software. It describes the Seebeck effect and Peltier effect. It discusses using Wien2K to model materials like Mg2Si, calculate properties like density of states, band structure, and optimize volume. Modifying approximations, strain effects, and nanostructuring are discussed to increase thermoelectric figure of merit ZT by increasing power factor and decreasing thermal conductivity.SCF methods, basis sets, and integrals part III



SCF methods, basis sets, and integrals part IIIAkefAfaneh2
╠²
Some DFT implementations (such as Octopus) attempt to describe the molecular
KohnŌĆōSham orbitals on a real-space grid.
ŌĆó A 3D simulation box is chosen together with a grid spacing, for example 0.5 a0. Then,
a grid in 3D is constructed and the SCF equations are solved on the grid.
ŌĆó This is different from an MO-LCAO expansion in numerical AOs!
ŌĆó Pseudopotentials are inevitable for real-space grid methods, but they are not required
when numerical AOs are used.
ŌĆó A great advantage of the use of numerical AOs as in DMol3 is that the method is free
of the basis-set superposition error (BSSE).
ŌĆó Because exact atomic orbitals are used, the atoms in a molecule cannot improve
their orbitals arti’¼ücially using basis functions from other atoms.Computational methodologies



Computational methodologiesMattSmith321834
╠²
Computational chemistry uses mathematical and computing methods to simulate chemical processes. It can predict molecular properties, structures, interactions and reaction pathways without expensive experiments. The main computational methods are ab initio, semi-empirical, density functional theory, molecular mechanics and molecular dynamics. Geometry optimization finds the lowest energy conformation of a molecule using algorithms to minimize the potential energy surface. It is important for understanding how structure influences properties and reactivity.Ab initio md



Ab initio mdyudhaarman
╠²
The document discusses ab initio molecular dynamics simulation methods. It begins by introducing molecular dynamics and Monte Carlo simulations using empirical potentials. It then describes limitations of empirical potentials and the need for ab initio molecular dynamics which calculates the potential from quantum mechanics. The document outlines several ab initio molecular dynamics methods including Ehrenfest molecular dynamics, Born-Oppenheimer molecular dynamics, and Car-Parrinello molecular dynamics. It provides details on how these methods treat the quantum mechanical potential and classical nuclear motion.Applications of Computational Quantum Chemistry



Applications of Computational Quantum ChemistryUniversity of Kerbala, Faculty of Science, Department of Chemistry
╠²
This presentation introduces an idea about the computational quantum chemistry field and its importance and applications in different ways.Molecular mechanics and dynamics



Molecular mechanics and dynamicsAteos Foundation of Science Education and Research, Pune, M.S., India
╠²
Computational Chemistry aspects of Molecular Mechanics and Dynamics have been discussed in this presentation. Useful for the Undergraduate and Postgraduate students of Pharmacy, Drug Design and Computational Chemistryfinland.ppt



finland.pptRAMARATHI2
╠²
This document discusses challenges and open questions in nuclear density functional theory (DFT). It begins by providing background on DFT and how it has been applied to nuclei using approximations like the local density approximation. It then discusses questions around improving the nuclear energy density functional, including justifying terms from microscopic theory, improving treatment of pairing and beyond-mean-field correlations, and incorporating dynamics. The document concludes by emphasizing the need for focused theoretical efforts, international collaborations, and new experimental data to help address open questions in nuclear DFT.Advantages and applications of computational chemistry



Advantages and applications of computational chemistrymanikanthaTumarada
╠²
The document discusses computational chemistry methods for calculating various thermodynamic and electronic properties of molecules. It provides an overview of computational chemistry and the properties that can be calculated, such as structure, energy, dipole moment, polarizability, ionization potential, HOMO/LUMO energies, chemical hardness and softness. It also describes different computational methods like classical molecular mechanics and molecular dynamics, as well as quantum chemistry methods including semi-empirical, ab initio and density functional theory approaches. Specific examples are given of calculating properties like dipole moment, polarizability, ionization potential using computational methods.COMPUTATIONAL CHEMISTRY 



COMPUTATIONAL CHEMISTRY Komal Rajgire
╠²
Computational chemistry uses theoretical chemistry calculations incorporated into computer programs to calculate molecular structures and properties. It can calculate properties such as structure, energy, charge distribution, and spectroscopic quantities using methods that range from highly accurate ab initio methods to less accurate semi-empirical and molecular mechanics methods. Computational chemistry allows medicinal chemists to use computer power to measure molecular geometry, electron density, energies, and more for applications such as conformational analysis, docking ligands in receptor sites, and comparing ligands.Density Functional Theory.pptx



Density Functional Theory.pptxHassanShah396906
╠²
Density functional theory (DFT) is a computational quantum mechanics method used to investigate the electronic structure of many-body systems like molecules and solids. It functions by using functionals of the electron density rather than the many-body wavefunction. This makes calculations more efficient. DFT was developed based on the Hohenberg-Kohn theorems, which established that all ground state properties are uniquely determined by the electron density alone. This allowed modeling systems using functionals of the density rather than attempting to solve the complicated many-electron Schrodinger equation directly. DFT is now widely used in physics, chemistry, and materials science.Single Particle Appoximation Final Pres.pptx



Single Particle Appoximation Final Pres.pptxkhalilpcsir
╠²
Many Body Problems topic About Perturbation Theory Single Particle Aproximation, it Defination Working , advantgaes Limittation Future aspects , Mathemtical Formulas about Many Body Problems topic About Perturbation Theory Single Particle Aproximation, Detail of Similicity in Quantam phyisics Methods paper



paperIsabelle Pelaschier
╠²
The document discusses using machine learning to develop density functional approximations for orbital-free density functional theory calculations. Specifically, kernel ridge regression is used to approximate the kinetic energy of non-interacting fermions confined to a 1D box as a functional of electron density. This machine-learned density functional approximation achieves highly accurate energies and self-consistent densities, outperforming traditional approximations. Various kernels, cross-validation methods, and representations of the electron density are explored to optimize the machine-learned approximation.computationalchemistry_12-6.ppt



computationalchemistry_12-6.pptsami97008
╠²
Computational chemistry uses numerical simulations based on the laws of physics to model chemical structures and reactions. There are different types of computational models of varying accuracy and computational cost, including molecular mechanics, semi-empirical, ab initio, and density functional theory methods. The accuracy of calculations also depends on the basis set used to describe molecular orbitals. Computational chemistry has become an important tool for characterizing nanomaterials.Intro-QM-Chem.ppt



Intro-QM-Chem.pptsami97008
╠²
This document provides an introduction to computational quantum chemistry. It defines computational chemistry as using mathematical approximations and computer programs to solve chemical problems based on quantum mechanics. Specifically, computational quantum chemistry focuses on solving the Schr├Čdinger equation for molecular systems using approximations like the Born-Oppenheimer approximation. It discusses how computational methods can be used to calculate various molecular properties and motivates the need for approximations due to the inability to exactly solve the Schr├Čdinger equation for complex molecules. The document then provides an overview of common computational methods like Hartree-Fock, configuration interaction, M├Ėller-Plesset perturbation theory, and coupled cluster theory.Intro-QM-Chem.ppt



Intro-QM-Chem.pptAkramLaKilo1
╠²
This document provides an introduction to computational quantum chemistry. It defines computational chemistry as using mathematical approximations and computer programs to solve chemical problems based on quantum mechanics. Specifically, computational quantum chemistry focuses on solving the Schr├Čdinger equation for molecular systems using approximations like the Born-Oppenheimer approximation. It also discusses methods for approximating the wavefunction like Hartree-Fock, configuration interaction, and density functional theory as well as expanding the molecular orbitals in a basis set of atomic orbitals.9783642250750 c2



9783642250750 c2Cl├│vis Batista dos Santos
╠²
The document summarizes the hopping mechanism for charge transport in organic materials. It describes how charge transport occurs through hopping between molecules, with the hopping rate determined by Marcus electron transfer theory. It discusses methods to calculate key parameters in the Marcus rate formula, including the transfer integral between molecules and the reorganization energy, using first-principles density functional theory calculations. These parameters and the Marcus rate theory can then be used to simulate charge mobility through random walk models.Molecular and Quantum Mechanics in drug design



Molecular and Quantum Mechanics in drug designAjay Kumar
╠²
This document discusses and compares molecular mechanics and quantum mechanics methods for drug design. It provides an overview of molecular mechanics, which uses classical physics to model potential energy surfaces, and common molecular mechanics force fields such as AMBER and CHARMM. It also describes quantum mechanics principles, density functional theory, and semi-empirical methods. Key differences between molecular mechanics and quantum mechanics are noted, such as system size, time required, and accuracy. Applications of each method in drug design are mentioned.Applications of Computational Quantum Chemistry



Applications of Computational Quantum ChemistryUniversity of Kerbala, Faculty of Science, Department of Chemistry
╠²
Molecular mechanics and dynamics



Molecular mechanics and dynamicsAteos Foundation of Science Education and Research, Pune, M.S., India
╠²
More from TayyabShabir (6)


lesson 4--part 2.pptx



lesson 4--part 2.pptxTayyabShabir
╠²
1. The document discusses the Chinese currency Renminbi and its denomination units of yuan, jiao, and fen.
2. It provides examples of how to express monetary amounts in spoken Chinese using kuai, mao, and fen instead of yuan, jiao, and fen.
3. The document also introduces common Chinese measure words like ge, ping, ben, wan, and bei that are used when counting or referring to objects.2-SolidstatePhys(13).ppt



2-SolidstatePhys(13).pptTayyabShabir
╠²
1. The document discusses band theory and energy bands in solids, explaining that available electron energy states form bands rather than discrete energies as in atoms.
2. Materials are classified as conductors, insulators, or semiconductors based on their band structure, particularly whether the conduction and valence bands overlap or are separated by a band gap.
3. Semiconductors have a small band gap separating the almost-full valence band from the almost-empty conduction band, allowing electrical conductivity to be controlled by doping with impurities. Intrinsic semiconductors contain only the semiconductor material while extrinsic ones are doped with donor or acceptor atoms.2_current_electricity_1.ppt



2_current_electricity_1.pptTayyabShabir
╠²
This document provides an overview of key concepts related to electric current including:
- Definitions of electric current, conventional current, and drift velocity of electrons.
- Relationships between current, charge, time, and drift velocity.
- Introduction of concepts like current density, Ohm's law, resistance, and temperature dependence of resistance.
- Explanations of series and parallel combinations of resistors and cells.Recently uploaded (20)
How to use Init Hooks in Odoo 18 - Odoo ║▌║▌▀Żs



How to use Init Hooks in Odoo 18 - Odoo ║▌║▌▀ŻsCeline George
╠²
In this slide, weŌĆÖll discuss on how to use Init Hooks in Odoo 18. In Odoo, Init Hooks are essential functions specified as strings in the __init__ file of a module.How to Configure Flexible Working Schedule in Odoo 18 Employee



How to Configure Flexible Working Schedule in Odoo 18 EmployeeCeline George
╠²
In this slide, weŌĆÖll discuss on how to configure flexible working schedule in Odoo 18 Employee module. In Odoo 18, the Employee module offers powerful tools to configure and manage flexible working schedules tailored to your organization's needs.QuickBooks Desktop to QuickBooks Online How to Make the Move



QuickBooks Desktop to QuickBooks Online How to Make the MoveTechSoup
╠²
If you use QuickBooks Desktop and are stressing about moving to QuickBooks Online, in this webinar, get your questions answered and learn tips and tricks to make the process easier for you.
Key Questions:
* When is the best time to make the shift to QuickBooks Online?
* Will my current version of QuickBooks Desktop stop working?
* I have a really old version of QuickBooks. What should I do?
* I run my payroll in QuickBooks Desktop now. How is that affected?
*Does it bring over all my historical data? Are there things that don't come over?
* What are the main differences between QuickBooks Desktop and QuickBooks Online?
* And moreKaun TALHA quiz Prelims - El Dorado 2025



Kaun TALHA quiz Prelims - El Dorado 2025Conquiztadors- the Quiz Society of Sri Venkateswara College
╠²
Prelims of Kaun TALHA : a Travel, Architecture, Lifestyle, Heritage and Activism quiz, organized by Conquiztadors, the Quiz society of Sri Venkateswara College under their annual quizzing fest El Dorado 2025. A PPT Presentation on The Princess and the God: A tale of ancient India by A...



A PPT Presentation on The Princess and the God: A tale of ancient India by A...Beena E S
╠²
A PPT Presentation on The Princess and the God: A tale of ancient India by Aaron ShepardUseful environment methods in Odoo 18 - Odoo ║▌║▌▀Żs



Useful environment methods in Odoo 18 - Odoo ║▌║▌▀ŻsCeline George
╠²
In this slide weŌĆÖll discuss on the useful environment methods in Odoo 18. In Odoo 18, environment methods play a crucial role in simplifying model interactions and enhancing data processing within the ORM framework.Reordering Rules in Odoo 17 Inventory - Odoo ║▌║▌▀Żs



Reordering Rules in Odoo 17 Inventory - Odoo ║▌║▌▀ŻsCeline George
╠²
In Odoo 17, the Inventory module allows us to set up reordering rules to ensure that our stock levels are maintained, preventing stockouts. Let's explore how this feature works.How to Configure Restaurants in Odoo 17 Point of Sale



How to Configure Restaurants in Odoo 17 Point of SaleCeline George
╠²
Odoo, a versatile and integrated business management software, excels with its robust Point of Sale (POS) module. This guide delves into the intricacies of configuring restaurants in Odoo 17 POS, unlocking numerous possibilities for streamlined operations and enhanced customer experiences.How to Setup WhatsApp in Odoo 17 - Odoo ║▌║▌▀Żs



How to Setup WhatsApp in Odoo 17 - Odoo ║▌║▌▀ŻsCeline George
╠²
Integrate WhatsApp into Odoo using the WhatsApp Business API or third-party modules to enhance communication. This integration enables automated messaging and customer interaction management within Odoo 17.The Constitution, Government and Law making bodies .



The Constitution, Government and Law making bodies .saanidhyapatel09
╠²
This PowerPoint presentation provides an insightful overview of the Constitution, covering its key principles, features, and significance. It explains the fundamental rights, duties, structure of government, and the importance of constitutional law in governance. Ideal for students, educators, and anyone interested in understanding the foundation of a nationŌĆÖs legal framework.
Digital Tools with AI for e-Content Development.pptx



Digital Tools with AI for e-Content Development.pptxDr. Sarita Anand
╠²
This ppt is useful for not only for B.Ed., M.Ed., M.A. (Education) or any other PG level students or Ph.D. scholars but also for the school, college and university teachers who are interested to prepare an e-content with AI for their students and others.Essentials of a Good PMO, presented by Aalok Sonawala



Essentials of a Good PMO, presented by Aalok SonawalaAssociation for Project Management
╠²
APM event hosted by the South Wales and West of England Network (SWWE Network)
Speaker: Aalok Sonawala
The SWWE Regional Network were very pleased to welcome Aalok Sonawala, Head of PMO, National Programmes, Rider Levett Bucknall on 26 February, to BAWA for our first face to face event of 2025. Aalok is a member of APMŌĆÖs Thames Valley Regional Network and also speaks to members of APMŌĆÖs PMO Interest Network, which aims to facilitate collaboration and learning, offer unbiased advice and guidance.
Tonight, Aalok planned to discuss the importance of a PMO within project-based organisations, the different types of PMO and their key elements, PMO governance and centres of excellence.
PMOŌĆÖs within an organisation can be centralised, hub and spoke with a central PMO with satellite PMOs globally, or embedded within projects. The appropriate structure will be determined by the specific business needs of the organisation. The PMO sits above PM delivery and the supply chain delivery teams.
For further information about the event please click here.South Hornsey: The Lost Local Authority that Merged with Stoke Newington by T...



South Hornsey: The Lost Local Authority that Merged with Stoke Newington by T...History of Stoke Newington
╠²
Presented at the 24th Stoke Newington History Talks event on 27th Feb 2025
https://stokenewingtonhistory.com/stoke-newington-history-talks/Database population in Odoo 18 - Odoo slides



Database population in Odoo 18 - Odoo slidesCeline George
╠²
In this slide, weŌĆÖll discuss the database population in Odoo 18. In Odoo, performance analysis of the source code is more important. Database population is one of the methods used to analyze the performance of our code. Computer Application in Business (commerce)



Computer Application in Business (commerce)Sudar Sudar
╠²
The main objectives
1. To introduce the concept of computer and its various parts. 2. To explain the concept of data base management system and Management information system.
3. To provide insight about networking and basics of internet
Recall various terms of computer and its part
Understand the meaning of software, operating system, programming language and its features
Comparing Data Vs Information and its management system Understanding about various concepts of management information system
Explain about networking and elements based on internet
1. Recall the various concepts relating to computer and its various parts
2 Understand the meaning of softwareŌĆÖs, operating system etc
3 Understanding the meaning and utility of database management system
4 Evaluate the various aspects of management information system
5 Generating more ideas regarding the use of internet for business purpose Blind Spots in AI and Formulation Science Knowledge Pyramid (Updated Perspect...



Blind Spots in AI and Formulation Science Knowledge Pyramid (Updated Perspect...Ajaz Hussain
╠²
This presentation delves into the systemic blind spots within pharmaceutical science and regulatory systems, emphasizing the significance of "inactive ingredients" and their influence on therapeutic equivalence. These blind spots, indicative of normalized systemic failures, go beyond mere chance occurrences and are ingrained deeply enough to compromise decision-making processes and erode trust.
Historical instances like the 1938 FD&C Act and the Generic Drug Scandals underscore how crisis-triggered reforms often fail to address the fundamental issues, perpetuating inefficiencies and hazards.
The narrative advocates a shift from reactive crisis management to proactive, adaptable systems prioritizing continuous enhancement. Key hurdles involve challenging outdated assumptions regarding bioavailability, inadequately funded research ventures, and the impact of vague language in regulatory frameworks.
The rise of large language models (LLMs) presents promising solutions, albeit with accompanying risks necessitating thorough validation and seamless integration.
Tackling these blind spots demands a holistic approach, embracing adaptive learning and a steadfast commitment to self-improvement. By nurturing curiosity, refining regulatory terminology, and judiciously harnessing new technologies, the pharmaceutical sector can progress towards better public health service delivery and ensure the safety, efficacy, and real-world impact of drug products.Kaun TALHA quiz Prelims - El Dorado 2025



Kaun TALHA quiz Prelims - El Dorado 2025Conquiztadors- the Quiz Society of Sri Venkateswara College
╠²
South Hornsey: The Lost Local Authority that Merged with Stoke Newington by T...



South Hornsey: The Lost Local Authority that Merged with Stoke Newington by T...History of Stoke Newington
╠²
Density Functional Theory by Tayyab Shabir
- 1. 1 Density Functional Theory (DFT) ’üČ 1998: Nobel prize awarded to Walter Kohn Walter Kohn a Austrian- American theoretical physicist and theoretical chemist ’üČ To solve many body problems by Schr├Čdinger's equation. H’ü╣ = E’ü╣
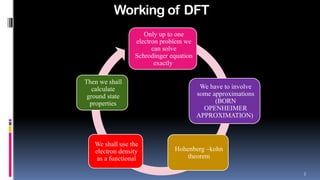
- 2. 2 Working of DFT Only up to one electron problem we can solve Schrodinger equation exactly We have to involve some approximations (BORN OPENHEIMER APPROXIMATION) Hohenberg ŌĆōkohn theorem We shall use the electron density as a functional Then we shall calculate ground state properties
- 3. ’é¦ The Hamiltonian for N-Particle system ’é¦ BORN OPPENHEIMER APPROXIMATION ØæÜØæøØæóØæÉØæÖØæÆØæ¢ Ōē½ØæÜØæÆ ŌĆó Reduced dimension from 3Ne to 3 by considering nuclei is static. ’é¦ HOHENBERG ŌĆō KOHN THEOREMS Theorem: 1 ŌĆ£The external potential vext or the ground state energy E is a unique functional of electron densityŌĆØ. Theorem: 2 ŌĆ£The electron density that minimizes the energy of the overall functional is the true ground state electron densityŌĆØ. Limitations of HK Theorems They do provide method of finding in practice however these theorems were not very helpful in real calculation. Two other scientists Kohn and Sham gave an equation which turned DFT into a practical tool. 17
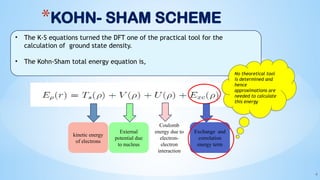
- 4. *KOHN- SHAM SCHEME 4 ŌĆó The K-S equations turned the DFT one of the practical tool for the calculation of ground state density. ŌĆó The Kohn-Sham total energy equation is, kinetic energy of electrons External potential due to nucleus Coulomb energy due to electron- electron interaction Exchange and correlation energy term No theoretical tool is determined and hence approximations are needed to calculate this energy
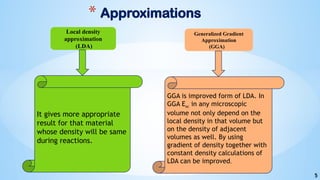
- 5. 5 * Approximations Local density approximation (LDA) Generalized Gradient Approximation (GGA) It gives more appropriate result for that material whose density will be same during reactions. GGA is improved form of LDA. In GGA Exc in any microscopic volume not only depend on the local density in that volume but on the density of adjacent volumes as well. By using gradient of density together with constant density calculations of LDA can be improved.
- 6. 6 *Amsterdam Density Functional ŌĆó Developed in 1970 ŌĆó Vrije University of Amsterdam and university of Calgary , Canada. ŌĆó Structure, Reactivity and spectra of molecules. ŌĆó Transition metal complexes and molecules with heavy atoms. 20
- 7. Computational Detail ’éĘ Structure is build from Space Group Fm-3m (no.225) ’éĘ Lattice Parameters a= 5.984Ōä½ ’éĘ Miller Indices of (001) is used to cut slab from bulk. ’éĘ Geometry Optimization ’éĘ LDA ’éĘ GGA-mPBE approximation is used. 7
Editor's Notes
- #1: DFT is a computational quantum mechanical modelling method used. DFT is used for the calculation of electric, magnetic, structural and different other properties of solids. Only up to one electron problem we can solve Schr├Čdinger's equation exactly. It is very hectic to solve the Schr├Čdinger's equation for a N- body system. In DFT instead of electronic wave function, ground state electron density Žü(r), is used to solve many body problems.
- #2: Electron density╠²is a representation of the probability of finding an╠²electron╠²in a specific location around an atom or molecule. In general, the╠²electron╠²is more likely to be found in regions with high╠²electron density. Density of electron Žü(r) only depends upon the three coordinates of position x, y and z instead of 3N-coordinates.
- #3: There are bunch of nuclei and electrons, making the equation very difficult to solve
- #4: The nuclear attraction energy part of the electronic Hamiltonian operator is called ŌĆ£external potential The part of the binding╠²energy╠²of a system of particles, such as an atomic nucleus of a solid, which is associated with electrostatic forces between the particles. Exchange correlation energy: sum of energy of interacting system. Correlation energy: interaction energy of electrons with different spin. Spin effect of electrons as well as their interaction was included.
- #5: The exchange correlation energy at any point gives the same value to that of uniform electron gas for identical density of a system. Taking the gradient of electron density improvements enhanced the accuracy of results upto large extent compared to LDA.
- #6: Amsterdam Density Functional (ADF) is particularly strong╠²in╠²understanding╠²and predicting. ADF is frequently used for studying since all elements in the periodic table can be modeled accurately
- #7: (Generalized Gradient Approximation-modified Perdew Burke Erenzerhof The lattice parameters are the quantities specifying a unit cell or the unit of the periodicity of the atomic arrangement. The lattice parameters (constants) are composed of "a, b, c," lengths of the unit cell in three dimensions, and "╬▒, ╬▓, ╬│," their mutual angles. Miller indices, group of three numbers that indicates the orientation of a plane or set of parallel planes of atoms in a crystal.









