Final Argentine
- 1. Using Wikispaces for Instruction & Computer Supported Collaborative Learning by Kimberly Brown, Maryland English Institute
- 2. Discussion What software programs or other technologies have you used in your classes? What was successful? What was unsuccessful? In your opinion, why is teaching with technology important? What are some obstacles that prevent successful use of technology in the classroom? Have you used collaborative learning strategies in your classroom? Describe.
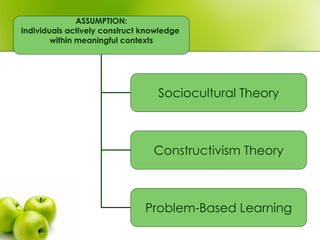
- 3. Theory Many theories support the use of computer-supported collaborative learning or CSCL. Underlying all of them is the assumption that individuals are active agents purposefully seeking and constructing knowledge within a meaningful context
- 4. ASSUMPTION: Individuals actively construct knowledge within meaningful contexts Sociocultural Theory Constructivism Theory Problem-Based Learning
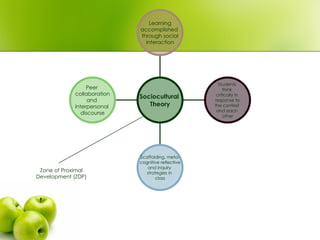
- 5. Zone of Proximal Development (ZDP) Peer collaboration and interpersonal discourse Scaffolding, meta- cognitive reflective and inquiry strategies in class Students think critically in response to the context and each other Learning accomplished through social interaction Sociocultural Theory
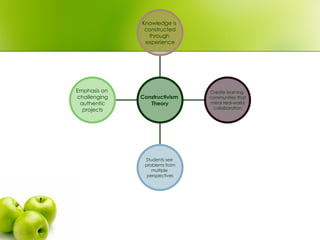
- 6. Emphasis on challenging authentic projects Students see problems from multiple perspectives Create learning communities that mirror real-world collaboration Knowledge is constructed through experience Constructivism Theory
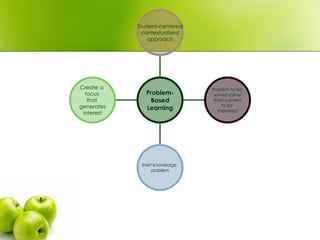
- 7. Create a focus that generates interest Inert knowledge problem Problem to be solved rather than content to be mastered Student-centered contextualized approach Problem- Based Learning
- 8. Benefits of collaborative learning? Develops higher level thinking skills Enhances student satisfaction with the learning experience Develops oral communication skills Develops social interaction skills Creates an environment of active, involved, exploratory learning Encourages diversity understanding Encourages student responsibility for learning Encourages alternate student assessment techniques Greater ability of students to view situations from others' perspectives (development of empathy)
- 9. Computer Supported Collaborative Learning Computer supported systems can support and facilitate group process and group dynamics in ways that are not achievable by face-to-face. With new developments in collaborative platforms, such as Wikisapces, we have the unique ability to collaborate across cultures.
- 10. Creating & Designing a Course Wikispace
- 11. Go to the Wikispaces main page – www.wikispaces.com
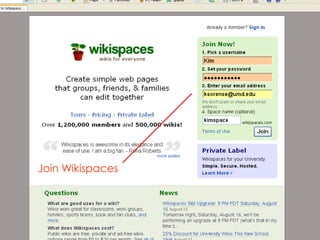
- 12. Join Wikispaces
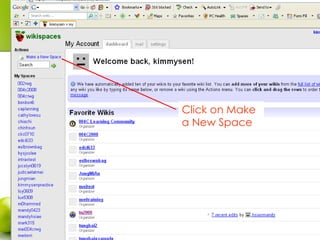
- 13. Click on Make a New Space
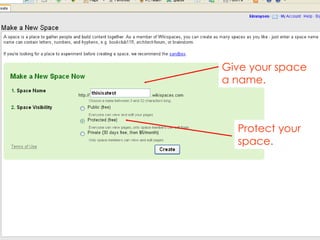
- 14. Give your space a name. Protect your space.
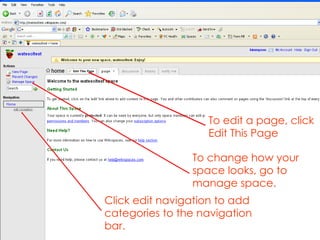
- 15. To change how your space looks, go to manage space. Click edit navigation to add categories to the navigation bar. To edit a page, click Edit This Page
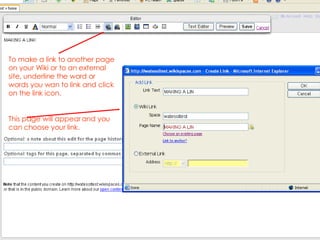
- 16. To make a link to another page on your Wiki or to an external site, underline the word or words you wan to link and click on the link icon. This page will appear and you can choose your link.
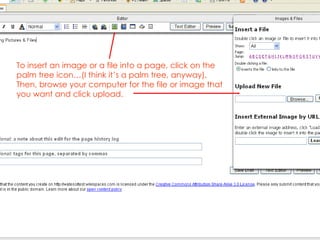
- 17. To insert an image or a file into a page, click on the palm tree icon…(I think it’s a palm tree, anyway), Then, browse your computer for the file or image that you want and click upload.
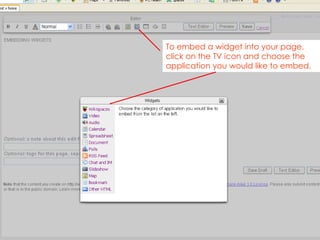
- 18. To embed a widget into your page, click on the TV icon and choose the application you would like to embed.
- 19. How can Wikis be used in instruction and computer supported collaborative learning? Uses in instruction Power Point/grades/calendars/student pages/assessment Uses in collaborative learning Collaborative Writing Collaborative projects With students in the same class With students in different schools/cities/states/countries
- 20. Examples www.tu2008.wikispaces.com www.004c2008.wikispaces.com
- 21. Teaching a Diversity Curriculum Mural Art & Intercultural Competence
- 22. Why teach about diversity? Racial, ethnic & religious diversity are key aspects of U.S. culture. Because of globalization, nearly all societies are experiencing some degree of diversification among their populations.
- 23. What is a diversity curriculum? …a curriculum that for each topic emphasizes the diversity of values & beliefs, opinions, and experiences of various groups. …a curriculum that encourages students to compare these values & beliefs, opinions, and experiences with their own.
- 24. Why is intercultural competence important? …it ensures intercultural effectiveness when living, traveling, or working abroad. …it improves students’ development of fluency in a language. …it is a crucial aspect to increasing peace.
- 25. How can mural art be used to explore diversity issues and develop intercultural competence? …murals provide a community a tool to express culture. …murals give insight into the values, beliefs, and experiences of a community. …murals often contain socio-political messages that allow students to understand a community within the larger context of society.
- 26. Exploring Washington D.C. Murals The Immigrant Experience Understanding the history of immigration to the U.S. as well as current trends and issues is essential to understanding of diversity in the U.S. In addition, mural art is an important means of expression in many cultures and has been brought to the U.S. along with the many immigrants.
- 27. Class 1 – The History of Immigration / D.C. Neighborhoods Readings & Discussion - The Context of Traditional American Values: Racial , Ethnic, Religious, and Cultural Diversity The Influence of Ethnicity on Washington D.C. Neighborhoods Students discuss the readings and compare the history of immigration to the U.S. to the history in their native countries.
- 28. Classes 2 & 3 - Exploring the Immigrant Experience Students learn reasons why people have immigrated and continue to immigrate to the U.S. Students listen to the story of an immigrant and learn about American diversity . http://www.america.gov/ Students create an immigrant profile based on an interview with an immigrant. Students compare immigration to the U.S. with immigration to their countries & discuss whether or not it is common for people from their countries to immigrate to the U.S.
- 29. Classes 4 & 5– Understanding Mural Art Students use the following website to learn to analyze mural art and begin to understand reasons for the creation of mural art through exploring famous Nicaraguan murals. Students find examples of mural art from their countries and analyze them. http://www.stanford.edu/group/arts/nicaragua/student/mural/index.html
- 30. Class 6 – D.C. Murals Students learn about the history of D.C. murals & artists and are given the field trip assignment & presentation. http://www.culturaltourismdc.org/dch_tourism2555/dch_tourism.htm?doc_id=45287&area=2517
- 31. Class 7 - The Trip Students use the following as a guide to examine the murals of D.C. Use the questions below to help find the physical context. What is the agenda of the creator? Why was it made? How does it help people? How does it promote ideas? Use the questions below to help find the social context. Who created it? Who is the audience? Use the questions below to help discover the historical context. When do you think the mural was created? What was going on at the time? Color Why do you think the artists chose the colors they did? How does the color fit the message of the mural? How does the color fit in with the physical environment? Scale How does the scale of the mural affect your impression of it? Would the affect be different if the mural were smaller or larger? Shape How does the shape affect how we interpret the mural? Light Where do you see the most light? What do you think the artist is trying to suggest through his/her use of light?
- 32. Ěý
- 33. Ěý
- 34. Ěý
- 35. Final Projects Essay: Write a two-three page essay on your analysis of one or more of the murals. Ideas: Examine various aspects of one mural. Compare &/or contrast two or more murals from the trip. Explain concepts of the mural as they relate to research done on the artist. Compare &/or contrast one or more murals from the trip with one or more other famous murals discovered through research. In your analysis, include personal reflection. How did the mural affect you? Presentation: Create a mural of your own that represents some aspect of American culture. In the creation of your mural, pay close attention to the aspects of murals that we analyzed during the trip and incorporate these into your own mural. Make sure to indicate in what type of community your mural would be painted and why. Note: You do not have to paint your mural on the side of a building. I do not expect you to be a great artist, but I do expect creativity! You may use computer graphics to create your mural if you can’t draw or paint. The main point is to demonstrate your understanding of American culture in addition to your understanding of how culture is reflected through mural art. Develop a 3-5 minute presentation during which you explain the concepts illustrated in your mural.
- 36. Unexpected positives Interaction with native/fluent speakers of English. Interaction with people from different ethnic backgrounds. Students became more integrated in the community.
- 37. A difficulty Assessment of intercultural competence.
- 38. Discussion Do you think you might have a use for Wikispaces in your classroom? In what ways might you use Wikispaces? Do you think you might create a diversity curriculum in your school? What diversity resources are available in your city?
- 39. Sources Lo Bianco, Joseph; Liddicoat, Anthony J.; Crozet Chantal. Striving for the Third Place: Intercultural Competence through Language Education . Australian National Languages and Literacy Institute, 1999. Teaching English . British Council Teaching English. 5/5/2006. http://www.teachingenglish.org.uk/think/methodology/intercultural1.shtml . http:// www.edb.utexas.edu/csclstudent/dhsiao/theories.html