Flipped classroom
0 likes65 views
In this teaching model, the events that have traditionally taken place in the classroom, now take place outside the classroom through technological tools.
1 of 12










Recommended
Flipped Learning



Flipped LearningIris Thiele Isip-Tan
╠²
This document provides an overview of flipped learning. It begins by defining flipped learning as an approach where direct instruction moves from group to individual learning spaces, allowing group space to become more interactive. It discusses designing flipped lessons using backward design and a 7-step process. This includes determining learning objectives, designing individual and group activities, and post-group activities. Challenges of flipped learning are also addressed, such as students needing to adjust to new roles and time requirements. The document provides resources for designing effective flipped lessons and addresses potential issues that may arise.Prepare your esol students for the real world with pbl google docs pres 1 - copy



Prepare your esol students for the real world with pbl google docs pres 1 - copyccruz07
╠²
This document discusses how project-based learning (PBL) can help prepare ESOL students for the real world. PBL focuses on real-world problems and promotes using all four language skills. It engages students in learning how to learn while developing language skills. Benefits include teachers acting as coaches and students improving critical thinking. Challenges for teachers include time needed and maintaining order, while students must learn independence and coordination. The document provides an example of a PBL video and outlines the PBL process and tools to guide students through projects.Flipped classroom and blended learning



Flipped classroom and blended learningKadafi Marzan
╠²
The flipped classroom model reverses traditional teaching by having students watch video lectures at home and dedicating class time to exercises and projects. This allows class time to focus on applying concepts through collaboration while giving students flexibility to learn at their own pace outside of class. Both flipped classrooms and blended learning incorporate online and in-person learning, but flipped classrooms specifically involve watching lectures as homework while blended learning combines online and face-to-face teaching in a complementary way.Loreto 5 Roslyn Halmy 2013



Loreto 5 Roslyn Halmy 2013Loreto Normanurst
╠²
This document outlines a project to implement a flipped classroom style of teaching for selected topics in a year 7 class. It will find good online resources to teach without a textbook and set up a wiki page for students to access worksheets and other materials. The flipped classroom involves students watching videos or reading about the next lesson for homework and then discussing what they learned in class. More challenging questions and problem solving activities are completed during class time. A wiki page is needed to store and allow easy access to worksheets for students, provide extra practice material, store links to videos and activities for both students and teachers, and allow absent students to catch up.Flipped classroom



Flipped classroomtabathastowers91
╠²
This document discusses the flipped classroom model of instruction. In a flipped classroom, direct instruction moves from the group learning space to the individual learning space, typically through online lecture videos for students to watch at home. Class time is used for applying concepts, clarifying understanding, and collaborating with peers. Benefits include allowing students to learn at their own pace, promoting active learning, and giving teachers more time for individualized support. Challenges include reliance on technology access and preparation of instructional content. The document outlines the key components of the flipped classroom approach.Flipped classroom



Flipped classroomstephens2042
╠²
This presentation describes flipped classroom and compares flipped classroom vs traditional method of teaching.Flipped classroom



Flipped classroomJessica Iveth de Loera Moreno
╠²
This document discusses the use of flipped classroom in foreign language teaching. It defines flipped classroom as activities traditionally done in class, such as lectures, being moved outside of class, while activities traditionally done as homework, such as problem-solving, are moved into the classroom. This allows class time to be used for active learning activities like discussions and working on difficult concepts. The document outlines how to implement flipped classroom, including creating pre-recorded videos and integrating online tools. It also discusses common approaches and steps for an effective flipped classroom model. Research has shown students have mostly positive attitudes towards flipped classroom. Benefits include personalized learning, increased motivation, and a continuous connection between teachers and students.Introduction to Online Learning_AGP



Introduction to Online Learning_AGPAnn Giralico Pearlman
╠²
This document provides considerations for developing an effective online or blended course. It recommends determining teaching style and how this aligns with how students learn today. Students have varying learning styles, so instruction should be presented in multiple ways to benefit all. Key aspects to address include course goals and outcomes, content, methods for transferring knowledge, and learning-centered assessments. The beginning steps involve evaluating the syllabus and outline to create an engaging blended or online learning experience.Mastery Learning - Flipped Classroom



Mastery Learning - Flipped ClassroomRoselle Manalo
╠²
What, why and how to implement Flipped Classroom?
Pillars of Flipped Classroom
Pros and Cons of Flipped ClassroomFlipped classroom



Flipped classroomYaritza Ovalle Firpo
╠²
The document discusses flipped classroom and blended learning models. It defines flipped classroom as transferring work outside of class like watching lectures, and using class time for hands-on activities and practice. Blended learning combines online and in-person learning, where students may learn content both online and in class. The document describes six blended learning models: Station Rotation, Lab Rotation, Individual Rotation, Flipped Classroom, Flex, and A La Carte. These models vary in how students access online content and receive support from teachers.Flipped learning



Flipped learningSurbhi Gausvami
╠²
The document discusses the flipped classroom model of education. It defines flipped classroom as a model where traditional lectures are done as homework via online video lectures, while class time is spent on exercises, projects, and discussions. The key idea is that video lectures allow students to learn foundational content on their own time, while class time can focus on application and higher-order thinking. The document traces the origins of this concept and discusses benefits like increased student engagement and preparation. It also notes that flipped learning continues evolving due to research, innovation, and new technologies.Flipped classroom presentation



Flipped classroom presentationsbrownrn
╠²
A flipped classroom reverses the traditional classroom structure by having students learn new content at home through online videos and lectures, freeing up class time for collaborative activities and hands-on practice with the teacher present. In a flipped classroom, teachers record lectures for students to watch outside of class, while class time focuses on applying the new knowledge through problem-solving and projects with the teacher available for guidance. While it requires more preparation from teachers, a flipped classroom allows students to learn at their own pace and receive more individualized attention, though some students prefer face-to-face lectures. Equipment access and student motivation must also be considered.Flipped Classroom and blended learning, pros, cons, similarities and differences



Flipped Classroom and blended learning, pros, cons, similarities and differencesROSA CALZADO
╠²
The document discusses flipped classrooms and blended learning. A flipped classroom reverses traditional teaching by delivering instructional content online outside of class and using class time for hands-on work and projects. Blended learning combines online and in-person learning, such as students attending a traditional classroom and also completing online coursework. Both approaches integrate technology into teaching. While both use online and in-person elements, blended learning uses them together, whereas flipped learning separates the online instruction and in-class application of knowledge. The document also outlines pros and cons of each approach.The flipped classroom



The flipped classroomJavier Aguirre
╠²
The document discusses the flipped classroom model of education. In a flipped classroom, instructional content is delivered to students outside of class, often through online videos, freeing up class time for more active and collaborative learning activities. During class, teachers guide students through hands-on problem solving, discussions, experiments and other engaging lessons, allowing for more personalized attention. The flipped classroom shifts the focus from a teacher-centered model to a learner-centered approach that emphasizes higher-order thinking skills.Loreto 5 Jo Kachel 2013



Loreto 5 Jo Kachel 2013Loreto Normanurst
╠²
This document summarizes the work of a teacher in the RE department who participated in the Loreto5 program in 2013. It discusses initial goals of introducing flipped learning strategies to engage students. It then describes how the teacher's work evolved throughout the year to focus on using Quia, an online tool, to create practice multiple choice questions for HSC revision. Analysis found that students who used Quia performed better. The teacher also created online tutorials and investigated options to better organize course content beyond the portal. Participation in Loreto5 provided new skills, opportunities to learn from colleagues, and inspiration to continue improving teaching practices.Ict flipped classroom presentation.



Ict flipped classroom presentation.monique ramesar
╠²
presentation about flipped classroom and the difference between traditional classroom and flipped classroom.Flipped classroom



Flipped classroomApple Shih
╠²
The document discusses the flipped classroom model of education. It notes that flipped classroom originated in the United States in 2007 and focuses on individualized learning through independent study outside of class. This allows teachers to take on more of a guiding role in classroom. The document also discusses challenges with implementing flipped classroom in Taiwan, including lack of upgraded teaching methods and ensuring quality control. It emphasizes the need for teachers to enhance their professional authority and for principals to provide strong instructional leadership.Flipped classroom



Flipped classroommrsfitzsocialstudies
╠²
The document outlines an agenda for a class on flipping the classroom, discussing the history of flipped learning through Khan Academy, defining the flipped classroom model, reviewing case studies, and discussing the pros and cons and challenges of implementing a flipped classroom approach. Teachers are then challenged to build their own flipped lesson to share online and develop an in-class activity to accompany the digital content. Team-Based Learning (TBL) Classrooms: Catalyzing Student-Centered Teaching a...



Team-Based Learning (TBL) Classrooms: Catalyzing Student-Centered Teaching a...Bradford Wheeler
╠²
Wheeler, B. (2016). Team-Based Learning (TBL) Classrooms: Catalyzing Student-Centered Teaching and Learning (SCTL). Presentation at UMass Amherst College of Engineering student development workshop series.Flipped classroom approaches



Flipped classroom approachesMatt Cornock
╠²
E-Learning Development Team Lunchtime Webinar (2 November 2015, University of York). This presentation explores concepts of flipped classroom / flipped learning design. Drawing upon literature for definitions and case studies of different learning design models. This 'design' presentation will be followed up with technical advice later in the year. The intended audience is higher education lecturers.The flipped classroom



The flipped classroomgmaneta
╠²
This is a PPT I created in order to familiarize my students with the concept of "flipped classroom" All material has been taken from Educause.Angel training agp ppt_0510



Angel training agp ppt_0510Ann Giralico Pearlman
╠²
The document provides considerations for developing an effective online or blended course. It suggests determining teaching style and how this aligns with how students learn today. Content and goals should be established to ensure students know and can do upon completion. Methods of transferring knowledge should include varied activities to engage different learning styles like visual, textual, auditory, and kinesthetic learners. Student-centered approaches with the instructor as facilitator are recommended, utilizing blended synchronous and asynchronous activities for engagement and assessment.The flipped classroom



The flipped classroomLjubica Ruzinska
╠²
In our schools, students have grown accustomed to the traditional methods of instruction where the teachers stand in front of the class lecturing the same thing to all the students present. Then, just at the end of the class, students are given homework to reinforce the learned concepts at home where they get little or no added support. As a result of this way of teaching, students are just ŌĆ£passiveŌĆØ listeners on the receiving end of a one-way communication process that encourages little critical thinking. In order to change this trend of passive listening, teacher around the globe employ technology to implement a blended learning method that ŌĆ£frees upŌĆØ class time for collaborative activities by shifting lectures out of the classroom and on the internet. This method, known as a "flipped" classroom, combines the benefits of direct instruction and active learning to engage students in the educational process.
The flipped classroom model was pioneered by two chemistry teachers, Jonathan Bergman and Aaron Sams, who inverted the traditional teaching methods by delivering lectures online as homework and moving activities into the classroom. By flipping thier lessons they were able to spend class time working directly with students on more engaging activities giving them support and hands-on instructions. There are many ways that a classroom can be flipped, but the underlying premise is that students review lecture materials outside of class and then come to class prepared to participate in instructor-guided learning activities. In the presentation I will explain the flipped classroom model and compere it with the traditional classroom. We will look at what the flipped classroom enables the teacher to do as well as discuss the benefits of the flipped classroom for the students. Lastly we will look at how I implemented the flipped classroom and made it work for my elementary students.Strategies for effective lesson planning flipped classroom



Strategies for effective lesson planning flipped classroomJames Folkestad
╠²
The document provides guidance on lesson planning for a flipped classroom. It defines a flipped classroom as one where typical lecture and homework elements are reversed - students watch video lectures at home and class time is used for exercises, projects, or discussion. The key steps in planning are: 1) Identifying learning objectives for videos and in-class activities using Bloom's Taxonomy; 2) Outlining the lesson plan using the STEPP method; 3) Developing video lectures that engage students; 4) Planning in-class activities to check understanding; and 5) Creating a timeline and being flexible. Reflection after teaching is also recommended.Flipped classroom for the 21st century



Flipped classroom for the 21st centuryThe Chinese University of Hong Kong
╠²
Find tips when implementing flipped classroom to teaching in your classroom. It will save you time and efforts with rewarding outcomes on student learning.Team Based Learning



Team Based LearningFCT at LSSU
╠²
Team-based learning is a student-centered pedagogical approach that involves assigning students to permanent teams to work on applied problems. It consists of three phases: preparation before class, a readiness assurance process in class, and application exercises. The readiness assurance process involves short individual and team tests to ensure students are prepared. Application exercises are complex problems for teams to work through together. Research shows team-based learning improves student engagement, develops skills like collaboration, and has been effectively used in medical, nursing, and other professional programs. While it requires an initial faculty time investment, team-based learning has benefits for both students and faculty.Loreto 5 Richard Munro 2013



Loreto 5 Richard Munro 2013Loreto Normanurst
╠²
The document discusses using a flipped classroom approach to teach Ancient History. It involves creating a series of video lessons on a topic that would normally take 3 classroom lessons. The videos cover content, note taking skills, essay writing skills, and how to support ideas with evidence. Student surveys found the videos helped their understanding, note taking, analysis skills, and ability to work at their own pace. Some feedback was to speak slower in videos and to allow more flexibility in essay length. Overall, flipped classroom approaches can help develop critical thinking if combined with traditional support.Flipped Classrooms



Flipped ClassroomsFederica Oradini
╠²
This document discusses flipping the classroom, which involves assigning lecture videos for students to watch at home and using class time for collaborative work and problem-solving. It provides examples of how to structure pre-class, in-class, and post-class activities. Key aspects of flipping include repurposing class time for active learning, engaging students through structured activities that integrate online and in-class work, and shifting the teacher's role from "sage on the stage" to "guide on the side." The document also offers tips for implementation such as not over-flipping courses and managing student expectations of the new approach.Flip it presentation



Flip it presentationwobt
╠²
Flip It! is a professional development resource about moving direct instruction away from group learning spaces so that these spaces can be transformed into more dynamic and interactive learning environments.educational technology and communication in education



educational technology and communication in educationBensiB
╠²
The document discusses the flipped classroom model of education. In a flipped classroom, students learn new content at home by watching video lectures. Class time is used for applying concepts, group work, discussions, and personalized guidance from the teacher. This reverses the traditional model where content is presented in class and homework is individual practice. The document outlines various flipped classroom models and discusses benefits like flexible learning and increased teacher-student interaction time.More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Mastery Learning - Flipped Classroom



Mastery Learning - Flipped ClassroomRoselle Manalo
╠²
What, why and how to implement Flipped Classroom?
Pillars of Flipped Classroom
Pros and Cons of Flipped ClassroomFlipped classroom



Flipped classroomYaritza Ovalle Firpo
╠²
The document discusses flipped classroom and blended learning models. It defines flipped classroom as transferring work outside of class like watching lectures, and using class time for hands-on activities and practice. Blended learning combines online and in-person learning, where students may learn content both online and in class. The document describes six blended learning models: Station Rotation, Lab Rotation, Individual Rotation, Flipped Classroom, Flex, and A La Carte. These models vary in how students access online content and receive support from teachers.Flipped learning



Flipped learningSurbhi Gausvami
╠²
The document discusses the flipped classroom model of education. It defines flipped classroom as a model where traditional lectures are done as homework via online video lectures, while class time is spent on exercises, projects, and discussions. The key idea is that video lectures allow students to learn foundational content on their own time, while class time can focus on application and higher-order thinking. The document traces the origins of this concept and discusses benefits like increased student engagement and preparation. It also notes that flipped learning continues evolving due to research, innovation, and new technologies.Flipped classroom presentation



Flipped classroom presentationsbrownrn
╠²
A flipped classroom reverses the traditional classroom structure by having students learn new content at home through online videos and lectures, freeing up class time for collaborative activities and hands-on practice with the teacher present. In a flipped classroom, teachers record lectures for students to watch outside of class, while class time focuses on applying the new knowledge through problem-solving and projects with the teacher available for guidance. While it requires more preparation from teachers, a flipped classroom allows students to learn at their own pace and receive more individualized attention, though some students prefer face-to-face lectures. Equipment access and student motivation must also be considered.Flipped Classroom and blended learning, pros, cons, similarities and differences



Flipped Classroom and blended learning, pros, cons, similarities and differencesROSA CALZADO
╠²
The document discusses flipped classrooms and blended learning. A flipped classroom reverses traditional teaching by delivering instructional content online outside of class and using class time for hands-on work and projects. Blended learning combines online and in-person learning, such as students attending a traditional classroom and also completing online coursework. Both approaches integrate technology into teaching. While both use online and in-person elements, blended learning uses them together, whereas flipped learning separates the online instruction and in-class application of knowledge. The document also outlines pros and cons of each approach.The flipped classroom



The flipped classroomJavier Aguirre
╠²
The document discusses the flipped classroom model of education. In a flipped classroom, instructional content is delivered to students outside of class, often through online videos, freeing up class time for more active and collaborative learning activities. During class, teachers guide students through hands-on problem solving, discussions, experiments and other engaging lessons, allowing for more personalized attention. The flipped classroom shifts the focus from a teacher-centered model to a learner-centered approach that emphasizes higher-order thinking skills.Loreto 5 Jo Kachel 2013



Loreto 5 Jo Kachel 2013Loreto Normanurst
╠²
This document summarizes the work of a teacher in the RE department who participated in the Loreto5 program in 2013. It discusses initial goals of introducing flipped learning strategies to engage students. It then describes how the teacher's work evolved throughout the year to focus on using Quia, an online tool, to create practice multiple choice questions for HSC revision. Analysis found that students who used Quia performed better. The teacher also created online tutorials and investigated options to better organize course content beyond the portal. Participation in Loreto5 provided new skills, opportunities to learn from colleagues, and inspiration to continue improving teaching practices.Ict flipped classroom presentation.



Ict flipped classroom presentation.monique ramesar
╠²
presentation about flipped classroom and the difference between traditional classroom and flipped classroom.Flipped classroom



Flipped classroomApple Shih
╠²
The document discusses the flipped classroom model of education. It notes that flipped classroom originated in the United States in 2007 and focuses on individualized learning through independent study outside of class. This allows teachers to take on more of a guiding role in classroom. The document also discusses challenges with implementing flipped classroom in Taiwan, including lack of upgraded teaching methods and ensuring quality control. It emphasizes the need for teachers to enhance their professional authority and for principals to provide strong instructional leadership.Flipped classroom



Flipped classroommrsfitzsocialstudies
╠²
The document outlines an agenda for a class on flipping the classroom, discussing the history of flipped learning through Khan Academy, defining the flipped classroom model, reviewing case studies, and discussing the pros and cons and challenges of implementing a flipped classroom approach. Teachers are then challenged to build their own flipped lesson to share online and develop an in-class activity to accompany the digital content. Team-Based Learning (TBL) Classrooms: Catalyzing Student-Centered Teaching a...



Team-Based Learning (TBL) Classrooms: Catalyzing Student-Centered Teaching a...Bradford Wheeler
╠²
Wheeler, B. (2016). Team-Based Learning (TBL) Classrooms: Catalyzing Student-Centered Teaching and Learning (SCTL). Presentation at UMass Amherst College of Engineering student development workshop series.Flipped classroom approaches



Flipped classroom approachesMatt Cornock
╠²
E-Learning Development Team Lunchtime Webinar (2 November 2015, University of York). This presentation explores concepts of flipped classroom / flipped learning design. Drawing upon literature for definitions and case studies of different learning design models. This 'design' presentation will be followed up with technical advice later in the year. The intended audience is higher education lecturers.The flipped classroom



The flipped classroomgmaneta
╠²
This is a PPT I created in order to familiarize my students with the concept of "flipped classroom" All material has been taken from Educause.Angel training agp ppt_0510



Angel training agp ppt_0510Ann Giralico Pearlman
╠²
The document provides considerations for developing an effective online or blended course. It suggests determining teaching style and how this aligns with how students learn today. Content and goals should be established to ensure students know and can do upon completion. Methods of transferring knowledge should include varied activities to engage different learning styles like visual, textual, auditory, and kinesthetic learners. Student-centered approaches with the instructor as facilitator are recommended, utilizing blended synchronous and asynchronous activities for engagement and assessment.The flipped classroom



The flipped classroomLjubica Ruzinska
╠²
In our schools, students have grown accustomed to the traditional methods of instruction where the teachers stand in front of the class lecturing the same thing to all the students present. Then, just at the end of the class, students are given homework to reinforce the learned concepts at home where they get little or no added support. As a result of this way of teaching, students are just ŌĆ£passiveŌĆØ listeners on the receiving end of a one-way communication process that encourages little critical thinking. In order to change this trend of passive listening, teacher around the globe employ technology to implement a blended learning method that ŌĆ£frees upŌĆØ class time for collaborative activities by shifting lectures out of the classroom and on the internet. This method, known as a "flipped" classroom, combines the benefits of direct instruction and active learning to engage students in the educational process.
The flipped classroom model was pioneered by two chemistry teachers, Jonathan Bergman and Aaron Sams, who inverted the traditional teaching methods by delivering lectures online as homework and moving activities into the classroom. By flipping thier lessons they were able to spend class time working directly with students on more engaging activities giving them support and hands-on instructions. There are many ways that a classroom can be flipped, but the underlying premise is that students review lecture materials outside of class and then come to class prepared to participate in instructor-guided learning activities. In the presentation I will explain the flipped classroom model and compere it with the traditional classroom. We will look at what the flipped classroom enables the teacher to do as well as discuss the benefits of the flipped classroom for the students. Lastly we will look at how I implemented the flipped classroom and made it work for my elementary students.Strategies for effective lesson planning flipped classroom



Strategies for effective lesson planning flipped classroomJames Folkestad
╠²
The document provides guidance on lesson planning for a flipped classroom. It defines a flipped classroom as one where typical lecture and homework elements are reversed - students watch video lectures at home and class time is used for exercises, projects, or discussion. The key steps in planning are: 1) Identifying learning objectives for videos and in-class activities using Bloom's Taxonomy; 2) Outlining the lesson plan using the STEPP method; 3) Developing video lectures that engage students; 4) Planning in-class activities to check understanding; and 5) Creating a timeline and being flexible. Reflection after teaching is also recommended.Flipped classroom for the 21st century



Flipped classroom for the 21st centuryThe Chinese University of Hong Kong
╠²
Find tips when implementing flipped classroom to teaching in your classroom. It will save you time and efforts with rewarding outcomes on student learning.Team Based Learning



Team Based LearningFCT at LSSU
╠²
Team-based learning is a student-centered pedagogical approach that involves assigning students to permanent teams to work on applied problems. It consists of three phases: preparation before class, a readiness assurance process in class, and application exercises. The readiness assurance process involves short individual and team tests to ensure students are prepared. Application exercises are complex problems for teams to work through together. Research shows team-based learning improves student engagement, develops skills like collaboration, and has been effectively used in medical, nursing, and other professional programs. While it requires an initial faculty time investment, team-based learning has benefits for both students and faculty.Loreto 5 Richard Munro 2013



Loreto 5 Richard Munro 2013Loreto Normanurst
╠²
The document discusses using a flipped classroom approach to teach Ancient History. It involves creating a series of video lessons on a topic that would normally take 3 classroom lessons. The videos cover content, note taking skills, essay writing skills, and how to support ideas with evidence. Student surveys found the videos helped their understanding, note taking, analysis skills, and ability to work at their own pace. Some feedback was to speak slower in videos and to allow more flexibility in essay length. Overall, flipped classroom approaches can help develop critical thinking if combined with traditional support.Flipped Classrooms



Flipped ClassroomsFederica Oradini
╠²
This document discusses flipping the classroom, which involves assigning lecture videos for students to watch at home and using class time for collaborative work and problem-solving. It provides examples of how to structure pre-class, in-class, and post-class activities. Key aspects of flipping include repurposing class time for active learning, engaging students through structured activities that integrate online and in-class work, and shifting the teacher's role from "sage on the stage" to "guide on the side." The document also offers tips for implementation such as not over-flipping courses and managing student expectations of the new approach.Similar to Flipped classroom (20)
Flip it presentation



Flip it presentationwobt
╠²
Flip It! is a professional development resource about moving direct instruction away from group learning spaces so that these spaces can be transformed into more dynamic and interactive learning environments.educational technology and communication in education



educational technology and communication in educationBensiB
╠²
The document discusses the flipped classroom model of education. In a flipped classroom, students learn new content at home by watching video lectures. Class time is used for applying concepts, group work, discussions, and personalized guidance from the teacher. This reverses the traditional model where content is presented in class and homework is individual practice. The document outlines various flipped classroom models and discusses benefits like flexible learning and increased teacher-student interaction time.Strategies and Pedagogies.pptx



Strategies and Pedagogies.pptxrosemedecillo
╠²
This document discusses various teaching strategies and pedagogies including differentiated instruction, active learning, project-based learning, inquiry-based learning, blended learning, flipped classrooms, cooperative learning, and constructivist, collaborative, integrative, reflective, and inquiry-based learning methods. It explains the benefits of each approach and provides examples of related activities and strategies to engage students in the learning process. Effective pedagogy is important as it can improve teaching quality, encourage cooperative learning, make learning less monotonous, allow students to learn in different ways, and enhance teacher-student communication.Bensi.b 38 ns edu03 with mcq



Bensi.b 38 ns edu03 with mcqBensiB
╠²
The document discusses the flipped classroom model of education. It defines flipped classroom as an approach where students learn new content through online videos and lectures at home, then do homework and projects in class with teacher guidance. This reverses the traditional model of lectures at school and homework at home. The document outlines several benefits of flipped classroom for students and teachers, such as allowing students to learn at their own pace and freeing up class time for more personalized instruction. It also describes various flipped classroom models and discusses implications of the approach.ReadytoFlip_Jan2017



ReadytoFlip_Jan2017Jackie Mo
╠²
Flipped classrooms reverse traditional teaching by having students learn new content outside of class, often through online video lectures, and doing homework in class with teacher guidance. This document discusses the origins and approaches of flipped classrooms, as well as their advantages of providing differentiated instruction, and disadvantages such as the digital divide. Key aspects of flipped classrooms are teacher surrender of control to put students in charge of their learning and using class time for applied activities and projects."Flip it" presentation



"Flip it" presentationwobt
╠²
A presentation on Flipped Learning which discusses the concept and provides some strategies, methods, tools and links.Flipped classroom - A quick guide to concepts and practice 



Flipped classroom - A quick guide to concepts and practice Richard Grieman
╠²
Flipped classroom, inverted classroom, blended classroom, flipped class, inverted class, flipped class basics, how to flip a class, how to flip a classroom, flipped class guide, flipped classroom guide, flipped classroom basics, experience with flipped classroom, experience with flipped classes, what is a flipped class, what is a flipped classroom, partially flipped classes, tools needed to flip a class, examples of flipped classroom, examples of flipped classes, flipped classroom design, designing a flipped class, designing a flipped classroom, curriculum,Itslearning blended ebook. El libro de Aprendizaje Semi presencial de Itslear...



Itslearning blended ebook. El libro de Aprendizaje Semi presencial de Itslear...Itslearning M├®xico
╠²
This document provides an overview of blended learning. It defines blended learning as a mix of online and in-person learning. Various blended learning models are described, including rotation models where students rotate between online and in-person modalities to learn the same material. Benefits of blended learning include increased student engagement, easier differentiation of instruction, and development of modern skills. The document also provides case studies of different schools implementing blended learning through flipped classroom and flexible learning models.ESOL Differentiated Instruction Presentation 



ESOL Differentiated Instruction Presentation Rebeccabrownmusic
╠²
This document discusses strategies for differentiating instruction for English language learners (ELLs). It defines differentiated instruction as modifying lesson delivery and materials based on students' backgrounds, readiness, and learning preferences. The document recommends that teachers create a supportive learning environment, differentiate instruction, encourage flexible grouping, use student diversity as a resource, and develop alternative assessments for ELLs. It provides specific strategies in each of these areas, such as simplifying language, using visuals, focusing on key vocabulary, and allowing ELLs additional time and translation resources on assessments.A flipped learning model



A flipped learning modelSHU Learning & Teaching
╠²
The document describes changes made to a TESOL module to implement a flipped learning model. Key changes included moving short language lectures online as screencasts and videos for pre-class work, and using class time for more interactive activities and applying content to practice. This aimed to give students more control over their learning and better prepare them for in-class discussions. Evaluation found that while some students engaged well with pre-work, others struggled with independent learning or found both pre- and post-work excessive. The module will be refined based on learning points around orientation, feedback, and modifying task lengths and types.Flipped Classroom - Presented By Tahira Rafiq 



Flipped Classroom - Presented By Tahira Rafiq AbdulHakeemKhagga2
╠²
PRESENTED TO: DR. SAMINAMALIK
PRESENTED BY: TAHIRARAFIQ
REG. NO. : 161-FSS/PHDEDU/F19
DEPARTMENT OF EDUCATION
INTERNATIONAL ISLAMIC UNIVERSITY, ISLAMABAD
OBJECTIVES
ŌĆó Students will able to understand that
ŌĆó What is the flipped classroom?
ŌĆó Traditional vs flipped classroom
ŌĆó What the flipped classroom enables the teacher to do?
ŌĆó What are the benefits of the students?
ŌĆó How do we implement the flipped classroom with our students?Flipping the-classroom



Flipping the-classroomAndresBrutas
╠²
This document discusses flipping the classroom model of education. It defines flipping the classroom as moving direct instruction from group to individual learning spaces so that class time can be used for dynamic, interactive learning guided by the teacher. The document outlines reasons for flipping a classroom, including allowing students to learn at their own pace and increasing interaction. It provides a 6-step process for implementing flipping: plan the lesson, record an instructional video, share the video with students, change how class time is used, separate students into groups, and have groups share their work. The goal is to use class time for active, collaborative learning activities.PPT RAIHAN & AUL.pptx



PPT RAIHAN & AUL.pptxRaihanAlbaihaq
╠²
This document discusses flipped pedagogy, specifically as it relates to chemistry education. It defines flipped teaching as assigning traditionally in-class activities like lectures as homework, and traditionally out-of-class activities like exercises as in-class work. This allows class time to be used for active learning, discussion, and problem-solving. The document outlines benefits like personalized learning and improved retention, but also drawbacks such as technological barriers. It finds that flipped learning has been shown to be effective for various chemistry topics when pre-class and in-class activities are designed well and technologies are utilized to facilitate the approach.Flipped classrooms



Flipped classroomsahmedabbas1121
╠²
The flipped classroom model reverses traditional teaching by having students gain initial content exposure outside of class, often via online lectures, and using class time for hands-on activities. It aims to increase engagement and empower students. Key aspects include short online videos, in-class application of knowledge, and communication between teachers and students. While requiring preparation, proponents argue it can improve grades and better support varied pacing.Lesson planning and elt



Lesson planning and eltMohammad Ghasemi Bagherabadi
╠²
This document discusses lesson planning and provides guidance on developing effective lessons. It outlines the advantages of having a good lesson plan, including inspiring teacher improvement, helping with evaluation, and developing confidence. It then describes the key components of a lesson plan, such as objectives, anticipatory sets, direct instruction, guided and independent practice, materials, assessment, and reflection. The document also discusses principles for designing lessons focused on specific skills, like reading, speaking, vocabulary, grammar, and listening. These include introducing new vocabulary in context, providing opportunities for student speaking practice, and incorporating strategy training. Finally, it addresses learning styles and motivation.7. the flipped classroom



7. the flipped classroom1ald
╠²
The flipped classroom model reverses traditional classroom structure by having students watch video lectures at home and devote class time to collaborative learning exercises and discussions. Teachers post short video lectures for students to view as homework, allowing class time to focus on applying the material. This gives students more control over their learning and promotes a student-centered approach through collaborative projects. While critics argue it relies on student preparation and access to technology, the flipped classroom engages students and deepens their understanding.Flipped classroom and blended learning, pros



Flipped classroom and blended learning, prosLuz Bencosme
╠²
Flipped classroom and blended learning are related but distinct pedagogical models. A flipped classroom reverses traditional lecture and homework elements by delivering instructional content, such as prerecorded lectures, online for students to engage with outside of class. This frees up class time for interactive activities and exercises. Blended learning combines online and face-to-face instruction to provide a comprehensive learning experience, with online materials complementing in-person classwork. While blended learning integrates online and in-person modes, flipped learning separates them - with online content introduced before classwork to be explored and applied. Both aim to enhance learning through technology and active engagement.Using active learning instructional strategies



Using active learning instructional strategiesEngr.Dr.Abdul Rehman Abbasi
╠²
This document discusses using active learning strategies to enhance training and learning. It defines active learning as involving students in activities that promote thinking and doing, rather than passive listening. Research shows active learning improves conceptual understanding and problem-solving over traditional lectures. The document provides examples of active learning strategies like case studies, group work, role-playing, and supplemental videos. It also addresses common problems in implementing active learning, such as reduced content coverage, preparation time, large class sizes, and student resistance to new approaches. Overall, the document advocates active learning as a best practice for developing workforce skills.Flipped classroom



Flipped classroomcrenfroe
╠²
The document discusses the flipped classroom model, where typical lecture and homework elements are reversed - short video lectures are viewed at home by students before class, while in-class time is used for exercises, projects, and discussions. It notes some common misconceptions, such as that it is easy for teachers or that teachers are replaced by computers. Best practices for the flipped classroom model include using videos for students to learn concepts at home, then applying those concepts in class through activities where teachers can better identify errors and provide support. The goal is to put more responsibility on students while giving them more control over their learning.Itslearning blended ebook. El libro de Aprendizaje Semi presencial de Itslear...



Itslearning blended ebook. El libro de Aprendizaje Semi presencial de Itslear...Itslearning M├®xico
╠²
Recently uploaded (20)
How to Configure Restaurants in Odoo 17 Point of Sale



How to Configure Restaurants in Odoo 17 Point of SaleCeline George
╠²
Odoo, a versatile and integrated business management software, excels with its robust Point of Sale (POS) module. This guide delves into the intricacies of configuring restaurants in Odoo 17 POS, unlocking numerous possibilities for streamlined operations and enhanced customer experiences.Research & Research Methods: Basic Concepts and Types.pptx



Research & Research Methods: Basic Concepts and Types.pptxDr. Sarita Anand
╠²
This ppt has been made for the students pursuing PG in social science and humanities like M.Ed., M.A. (Education), Ph.D. Scholars. It will be also beneficial for the teachers and other faculty members interested in research and teaching research concepts.Lesson Plan M1 2024 Lesson Plan M1 2024 Lesson Plan M1 2024 Lesson Plan M1...



Lesson Plan M1 2024 Lesson Plan M1 2024 Lesson Plan M1 2024 Lesson Plan M1...pinkdvil200
╠²
Lesson Plan M1 2024 Lesson Plan M1 2024 Lesson Plan M1 2024 Database population in Odoo 18 - Odoo slides



Database population in Odoo 18 - Odoo slidesCeline George
╠²
In this slide, weŌĆÖll discuss the database population in Odoo 18. In Odoo, performance analysis of the source code is more important. Database population is one of the methods used to analyze the performance of our code. Mate, a short story by Kate Grenvile.pptx



Mate, a short story by Kate Grenvile.pptxLiny Jenifer
╠²
A powerpoint presentation on the short story Mate by Kate Greenville. This presentation provides information on Kate Greenville, a character list, plot summary and critical analysis of the short story.Adventure Activities Final By H R Gohil Sir



Adventure Activities Final By H R Gohil SirGUJARATCOMMERCECOLLE
╠²
Adventure Activities Final By H R Gohil SirHow to attach file using upload button Odoo 18



How to attach file using upload button Odoo 18Celine George
╠²
In this slide, weŌĆÖll discuss on how to attach file using upload button Odoo 18. Odoo features a dedicated model, 'ir.attachments,' designed for storing attachments submitted by end users. We can see the process of utilizing the 'ir.attachments' model to enable file uploads through web forms in this slide.FESTIVAL: SINULOG & THINGYAN-LESSON 4.pptx



FESTIVAL: SINULOG & THINGYAN-LESSON 4.pptxDanmarieMuli1
╠²
Sinulog Festival of Cebu City, and Thingyan Festival of Myanmar.Digital Tools with AI for e-Content Development.pptx



Digital Tools with AI for e-Content Development.pptxDr. Sarita Anand
╠²
This ppt is useful for not only for B.Ed., M.Ed., M.A. (Education) or any other PG level students or Ph.D. scholars but also for the school, college and university teachers who are interested to prepare an e-content with AI for their students and others.POWERPOINT-PRESENTATION_DM-NO.017-S.2025.pptx



POWERPOINT-PRESENTATION_DM-NO.017-S.2025.pptxMarilenQuintoSimbula
╠²
Rubric level Summary for Teacher 1 to 3, Proficient Teacher. Guide in assessing MOV presented.How to Configure Flexible Working Schedule in Odoo 18 Employee



How to Configure Flexible Working Schedule in Odoo 18 EmployeeCeline George
╠²
In this slide, weŌĆÖll discuss on how to configure flexible working schedule in Odoo 18 Employee module. In Odoo 18, the Employee module offers powerful tools to configure and manage flexible working schedules tailored to your organization's needs.Chapter 3. Social Responsibility and Ethics in Strategic Management.pptx



Chapter 3. Social Responsibility and Ethics in Strategic Management.pptxRommel Regala
╠²
This course provides students with a comprehensive understanding of strategic management principles, frameworks, and applications in business. It explores strategic planning, environmental analysis, corporate governance, business ethics, and sustainability. The course integrates Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) to enhance global and ethical perspectives in decision-making.Useful environment methods in Odoo 18 - Odoo ║▌║▌▀Żs



Useful environment methods in Odoo 18 - Odoo ║▌║▌▀ŻsCeline George
╠²
In this slide weŌĆÖll discuss on the useful environment methods in Odoo 18. In Odoo 18, environment methods play a crucial role in simplifying model interactions and enhancing data processing within the ORM framework.Flipped classroom
- 1. 1
- 2. 2 ’ü▒ Introduction ’ü▒ Defining the Flipped Classroom ’ü▒ Description of the Flipped Classroom ’ü▒ Benefits ’ü▒ Theoretical Frameworks ’ü▒ Differences from the Traditional and Flipped Classroom ’ü▒ Advantages and Disadvantages ’ü▒ Conclusion Presentation content
- 3. Introduction Learning a language other than the mother tongue in the knowledge society constitutes a fundamental aspect since it expands study and work boundaries. However, there are various methodologies for its teaching. Currently, a model used more and more is the Flipped Classroom. In this presentation, we will have an approach to this teaching model. In addition, we will know the definition, description, some benefits, the theoretical framework, differences with the traditional method, advantages, and disadvantages.
- 4. 4 Defining the Flipped Classroom Define the flipped classroom as a classroom where what was traditionally done in class is now switched with what was done at home. So, students prepare the lessons at home as homework and complete in class the practice. Bergmann and Sams (2012):
- 5. 5 Bishop and Verleger (2013): Describe the flipped classroom as an educational technique that comprises two parts: interactive learning tasks conducted and monitored by the teacher in the classroom, and direct computer based asynchronous video lectures and close-ended problems or tests individually completed outsidethe classroom.
- 6. 6 ŌĆó The student studies the content at home using resources created by the teacher. ŌĆó he goes to face-to-face class and applies the knowledge acquired. ŌĆó The teacher's work changes, and now he must be a guide for his students. ŌĆó The teacher allows time for additional learning activities such as project-based learning or differentiated education. DESCRIPTION OF THE FLIPPED CLASSROOM
- 7. Benefits ŌŖ╣ Students learn how to think and educators learn what the students are struggling with. ŌŖ╣ Let students study at their own pace and schedule. ŌŖ╣ Large class sizes and high student-to-teacher ratios caused by economic forces may become manageable and less important. 7 ŌŖ╣ It permits teachers to be creative and to use a variety of teaching methodologies. ŌŖ╣ It allows the class to move forward in spite of student and teacher absences.
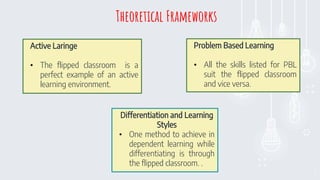
- 8. 8 Active Laringe ŌĆó The flipped classroom is a perfect example of an active learning environment. Problem Based Learning ŌĆó All the skills listed for PBL suit the flipped classroom and vice versa. Differentiation and Learning Styles ŌĆó One method to achieve in dependent learning while differentiating is through the flipped classroom. . Theoretical Frameworks
- 9. 9 DIFFERENCES FROM THE TRADITIONAL AND FLIPPED CLASSROOM FLIPPED CLASSROOM TRADITIONAL
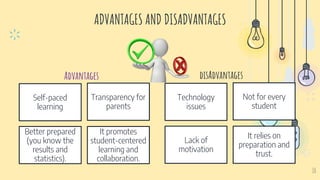
- 10. 10 ADVANTAGES AND DISADVANTAGES Self-paced learning Transparency for parents Better prepared (you know the results and statistics). It promotes student-centered learning and collaboration. Technology issues Not for every student Lack of motivation It relies on preparation and trust. Advantages disAdvantages
- 11. CONCLUSION 11 In this teaching model, the events that have traditionally taken place in the classroom, now take place outside the classroom through technological tools. The flipped classroom is one of the new forms of blended teaching that includes the use of the Internet and other technologies to enhance student learning. In addition, the teacher becomes a guide and can spend more time with his students. Also, it is a teaching model that has several advantages for both students and teachers.
- 12. 12 Thanks!







