GROUP 3 (GPS).pptxbskfkdkfjndkfkdkfkdksk
- 2. Global Positioning System ŌĆó ŌĆó ŌĆó ŌĆó ŌĆó ŌĆó The basic principle of the Global Positioning System (GPS) GPS System configuration GPS frequencies that are used Dilution of precision (DOP) The various errors of GPS Differential GPS What is W GS 84 Datum ŌĆó ŌĆó ŌĆó ŌĆó ŌĆó ŌĆó The advantages and limitation of GPS
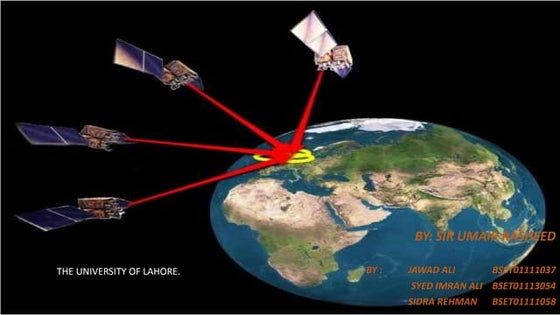
- 3. ŌĆó GPS satellites circle the earth twice a day in a very precise orbit and transmit signal information to earth. ŌĆó GPS receiver compares the time a signal was transmitted by a satellite with the time it was received. The time difference tells the GPS receiver how far away (distance) the satellite is. ŌĆó With distance measurements from a few more satellites, the receiver can determine the userŌĆÖs position and display it as a latitude and longitude. The basic principle of the Global Positioning System (GPS)
- 4. The basic principle of the Global Positioning System (GPS) ŌĆó A GPS receiver must be locked on to the signal of at least three satellites to calculate a two-dimensional position (latitude and longitude) and track movement. With four or more satellites in view, the receiver can determine the userŌĆÖs three-dimensional position (latitude, longitude and altitude).
- 5. Working Of GPS ŌŚÅ A GPS receiver can tell its own position by using the position data of itself, and compares that data with 3 or more GPS satellites. ŌŚÅ To get the distance to each satellite, the GPS transmits a signal to each satellite. The signal travels at a known speed. The system measures the time delay between the signal transmission and signal reception of the GPS signal. The signals carry information about the satelliteŌĆÖs location. Determines the position of, and distance to, at least three satellites. The receiver computes position using TRILATERATION.
- 7. Space Segment ŌĆó GPS satellites fly in circular orbits at an altitude of 20,200 km and with a period of 12 hours. ŌĆó Orbital planes are centered on the Earth. ŌĆó Each satellite makes two complete orbits each sidereal day. ŌĆó It passes over the same location on Earth once each day. ŌĆó Orbits are designed so that at the very least, six satellites are always within line of sight from any location on the planet.
- 8. Control Segment ŌĆó The Control Segment consists of 3 entities: ŌĆō Master Control Station ŌĆō Monitor Stations ŌĆō Ground Antennas ŌĆō NGA Monitor Stations ŌĆō Air Force Satellite Control Network (AFSCN) Remote Tracking Stations
- 10. Master Control Station ŌĆó The master control station, located at Falcon Air Force Base in Colorado Springs, Colorado, is responsible for overall management of the remote monitoring and transmission sites. Performs the primary control segment functions, providing command and control of the GPS constellation. Generates and uploads navigation messages and ensures the health and accuracy of the satellite constellation. Monitors navigation messages and system integrity, can reposition satellites to maintain an optimal GPS constellation. ŌĆó ŌĆó ŌĆó
- 11. Monitor Stations ŌĆó Six monitor stations are located at Falcon Air Force Base in Colorado, Cape Canaveral, Florida, Hawaii, Ascension Island in the Atlantic Ocean, Diego Garcia, and in the South Pacific Ocean. Checks the exact altitude, position, speed, and overall health of the orbiting satellites. The control segment uses measurements collected by the monitor stations to predict the behavior of each satellite's orbit and clock. The prediction data is up-linked, or transmitted, to the satellites for transmission back to the users. The control segment also ensures that the GPS satellite orbits and clocks remain within acceptable limits. A station can track up to 11 satellites at a time. This "check-up" is performed twice a day, by each station. ŌĆó ŌĆó ŌĆó ŌĆó ŌĆó ŌĆó
- 12. Ground Antennas ŌĆó ŌĆó ŌĆó ŌĆó Ground antennas monitor and track the satellites from horizon to horizon. They also transmit correction information to individual satellites. Communicate with the GPS satellites for command and control purposes. Four dedicated GPS ground antenna sites co-located with the monitor stations at Kwajalein Atoll, Ascension Island, Diego Garcia, and Cape Canaveral.
- 13. AFSCN Remote Tracking Stations ŌĆó Air Force Satellite Control Network (AFSCN) provides support for the operation, control, and maintenance of a variety of United States Department of Defense satellites. This involves continual Tracking, Telemetry, and Command (TT&C). It also provides prelaunch simulation, launch support, and early orbit support while satellites are in initial or transfer orbits and require maneuvering to their final orbit. ŌĆó ŌĆó
- 14. NGA Monitor Stations ŌĆó The NGA Monitor collects, processes, and distributes GPS observations, environmental data, and station health information. It also provides 24/7 data integrity monitoring. ŌĆó
- 15. User Segment ŌĆó ŌĆó The user's GPS receiver is the User Segment of the GPS system. GPS receivers are generally composed of an antenna, tuned to the frequencies transmitted by the satellites, receiver-processors, and a highly-stable clock (commonly a crystal oscillator). They include a display for showing location and speed information to the user. A receiver is often described by its number of channels this signifies how many satellites it can monitor simultaneously. ŌĆó ŌĆó
- 16. GPS Signals ŌĆó ŌĆó ŌĆó ŌĆó ŌĆó Coarse/Acquisition code Precision code Navigation message Almanac Data updates
- 17. GPS Frequencies ŌĆó ŌĆó ŌĆó ŌĆó ŌĆó L1 (1575.42 MHz) L2 (1227.60 MHz) L3 (1381.05 MHz) L4 (1379.913 MHz) L5 (1176.45 MHz)
- 18. Frequency Information ŌĆó ŌĆó The C/A code is transmitted on the L1 frequency as a 1.023 MHz signal. The P(Y)-code is transmitted on both the L1 and L2 frequencies as a 10.23 MHz signal. L3 is used by the Defense Support Program to signal detection of missile launches, nuclear detonations, and other applications. L4 is used for additional correction to the part of the atmosphere that is ionized by solar radiation. L5 is used as a civilian safety-of-life (SoL) signal. ŌĆó ŌĆó ŌĆó
- 19. Frequency L2C ŌĆó Launched in 2005, L2C is civilian GPS signal, designed specifically to meet commercial needs. L2C enables ionospheric correction, a technique that boosts accuracy. Delivers faster signal acquisition, enhanced reliability, and greater operating range. L2C broadcasts at a higher effective power making it easier to receive under trees and even indoors. It is estimated L2C could generate $5.8 billion in economic productivity benefits through the year 2030. ŌĆó ŌĆó ŌĆó ŌĆó
- 20. Accuracy ŌĆó The position calculated by a GPS receiver relies on three accurate measurements: ŌĆō Current time ŌĆō Position of the satellite ŌĆō Time delay for the signal The GPS signal in space will provide a "worst case" accuracy of 7.8 meters at a 95% confidence level. GPS time is accurate to about 14 nanoseconds. Higher accuracy is available today by using GPS in combination with augmentation systems. These enable real-time positioning to within a few centimeters. ŌĆó ŌĆó ŌĆó
- 21. Issues That Affect Accuracy ŌĆó Changing Atmospheric Issues: ŌĆō Radio signals travel at different velocities through the atmosphere. ŌĆō It changes the speed of the GPS signals unpredictably as they pass through the ionosphere. ŌĆō The amount of humidity in the air also has a delaying effect on the signal.
- 22. Issues That Affect Accuracy (contŌĆÖd) ŌĆó Clock Errors : ŌĆō Can occur when a GPS satellite is boosted back into a proper orbit. ŌĆō The satellite's atomic clocks experience noise and clock drift errors. GPS Jamming : ŌĆō It limits the effectiveness of the GPS signal. ŌĆō GPS jammer is a low cost device to temporarily disable the reception of the civilian coarse acquisition (C/A) code. ŌĆó
- 23. Issues That Affect Accuracy (contŌĆÖd) ŌĆó Multi-path Issues : ŌĆō The multipath effect is caused by reflection of satellite signals (radio waves) on objects. ŌĆō The reflected signal takes more time to reach the receiver than the direct signal.
- 24. Methods of Improving Accuracy ŌĆó Precision monitoring ŌĆō Dual Frequency Monitoring ŌĆō Carrier-Phase Enhancement (CPGPS) ŌĆō Relative Kinematic Positioning (RKP) ŌĆó Augmentation
- 25. A. Dual Frequency Monitoring ŌĆó Refers to systems that can compare two or more signals. ŌĆó These two frequencies are affected in two different ways. ŌĆó After monitoring these signals, itŌĆÖs possible to calculate what the error is and eliminate it. ŌĆó Receivers that have the correct decryption key can decode the P(Y)-code transmitted on signals to measure the error.
- 26. B. Carrier-Phase Enhancement (CPGPS) ŌĆó CPGPS uses the L1 carrier wave, which has a period 1000 times smaller than that of the C/A bit period, to act as an additional clock signal and resolve uncertainty. ŌĆó The phase difference error in the normal GPS amounts to between 2 and 3 meters (6 to 10 ft) of ambiguity. ŌĆó CPGPS works to within 1% of perfect transition to reduce the error to 3 centimeters (1 inch) of ambiguity. ŌĆó By eliminating this source of error, CPGPS coupled with DGPS normally realizes between 20 and 30 centimeters (8 to 12 inches) of absolute accuracy.
- 27. C. Relative Kinematic Positioning (RKP) ŌĆó Determination of range signal can be resolved to an accuracy of less than 10 centimeters (4 in). ŌĆó Resolves the number of cycles in which the signal is transmitted and received by the receiver. ŌĆó Accomplished by using a combination of DGPS correction data, transmitting GPS signal phase information and ambiguity resolution techniques via statistical tests ŌĆö possibly with processing in real-time.
- 28. ŌĆó Augmentation ŌĆō Relies on external information being integrated into the calculation process. ŌĆō Some augmentation systems transmit additional information about sources of error. ŌĆō Some provide direct measurements of how much the signal was off in the past ŌĆō Another group could provide additional navigational or vehicle information to be integrated in the calculation process.
- 29. Augmentation Systems ŌĆó Nationwide Differential GPS System (NDGPS) ŌĆō Ground-based augmentation system that provides increased accuracy and integrity of GPS information to users on U.S. land and waterways. ŌĆō The system consists of the Maritime Differential GPS System operated by the U.S. Coast Guard and an inland component funded by the Department of Transportation.
- 30. Augmentation Systems (contŌĆÖd) ŌĆó Wide Area Augmentation System (WAAS) ŌĆō Satellite-based augmentation system operated by the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA), supports aircraft navigation across North America. ŌĆó Global Differential GPS (GDGPS) ŌĆō High accuracy GPS augmentation system, developed by the NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) to support the real-time positioning, timing, and determination requirements of NASA science missions. ŌĆō Future NASA plans include using the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite System (TDRSS) to transmit via satellite a real-time differential correction message.
- 31. Applications ŌĆó Civilian ŌĆō Geotagging : Applying location coordinates to digital objects such as photographs and other documents. ŌĆō Disaster Relief/Emergency Services ŌĆō Vehicle Tracking Systems ŌĆō Person Tracking Systems ŌĆō GPS Aircraft Tracking ŌĆō Telematics: GPS technology integrated with computers and mobile communications technology in automotive navigation systems.
- 32. Applications (contŌĆÖd) ŌĆó Military ŌĆō Target Tracking: Tracking potential ground and air targets before flagging them as hostile. ŌĆō Navigation ŌĆō Missile and Projectile Guidance: Allows accurate targeting of various military weapons including cruise missiles and precision-guided munitions ŌĆō Reconnaissance ŌĆō Search and Rescue: Downed pilots can be located faster if their position is known.
- 33. Applications (contŌĆÖd) ŌĆó Other Applications ŌĆō Railroad Systems ŌĆō Recreational Activities ŌĆō Weather Prediction ŌĆō Skydiving ŌĆō And many more!