learningprocess.pptx
- 1. BY: Mr. Tauqeer Ahmed Sr. Lecturer (FUCN) Dated: 02-03-23 The Learning Process
- 2. Objectives: By the end of this lecture, students will be able to: 1- Understand the learning process 2- Discuss the some fundamental principles of learning 3- Elaborate the different theories related to learning
- 3. Definition: Learning is… A change in behavior as a result of experience or practice. The acquisition of knowledge. Knowledge gained through study. To gain knowledge of, or skill in, something through study, teaching, instruction or experience. The process of gaining knowledge. A process by which behavior is changed, shaped or controlled. The individual process of constructing understanding based on experience from a wide range of sources.
- 4. Some First Principles Learning is something all humans do Fetuses learn Infants learn Children learn Adults learn Learning is not uniquely human – all living things learn Learning evolved as an adaptation for promoting survival
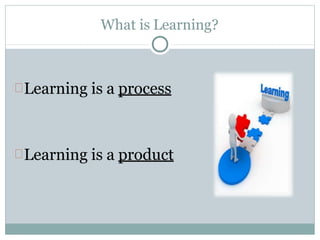
- 6. What is Learning? Learning is a process Learning is a product
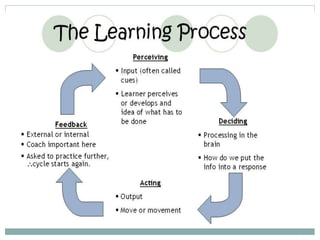
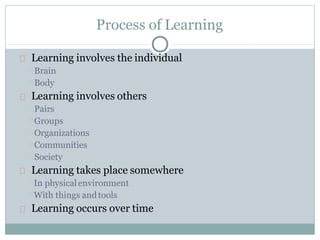
- 7. Process of Learning Learning involves the individual Brain Body Learning involves others Pairs Groups Organizations Communities Society Learning takes place somewhere In physicalenvironment With things and tools Learning occurs over time
- 8. Products of Learning Learning is about ideas and concepts Learning is about behaviors and skills Learning is about attitudes and values
- 10. Five Principles of Learning Participation: involve trainees, learn by doing Repetition: Relevance: repeat ideas & concepts to help people learn learn better when material is meaningful and related Transference: to real world using simulations Feedback: ask for it and adjust training methods to audience.
- 11. Domains Of Learning Benjamin Bloom has suggested three domains of learning:    Cognitive – To recall, calculate, discuss, analyze, problem solve, etc. Psychomotor – To dance, swim, ski, dive, drive a car, ride a bike, etc. Affective – To like something or someone, love, appreciate, fear, hate, worship, etc.
- 12. Basic Learning Principles • Learning depends upon three conditions: The readiness to learn The ability to learn The learning environment
- 13. Definition: Theories are… What is a theory? A theory provides a general explanation for observations made over time. A theory explains and predicts behavior. A theory can never be established beyond all doubt. A theory may be modified. Theories seldom have to be thrown out completely if thoroughly tested but sometimes a theory may be widely accepted for a long time and later disproved.
- 14. Broad domains of theories Behaviorism Cognitivism Social Learning Theory Social Constructivism Multiple Intelligences Brain-Based Learning
- 15. Behaviorism Confined to observable and measurable behavior Classical Conditioning - Pavlov Operant Conditioning - Skinner
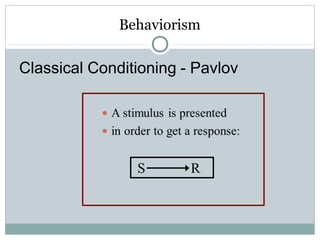
- 16. Behaviorism S R Classical Conditioning - Pavlov
- 17. Behaviorism Operant Conditioning - Skinner The response is made first, then reinforcement follows.
- 18. Behaviorism in the Classroom Rewards and punishments Responsibility for student learning rests squarely with the teacher Lecture-based, highly structured
- 19. Cognitivism Grew in response to Behaviorism Knowledge is stored cognitively as symbols Learning is the process of connecting symbols in a meaningful & memorable way Studies focused on the mental processes that facilitate symbol connection
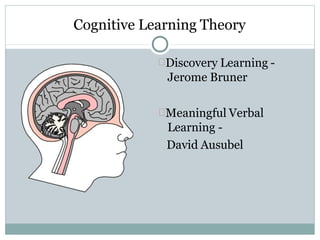
- 20. Cognitive Learning Theory Discovery Learning - Jerome Bruner Meaningful Verbal Learning - David Ausubel
- 21. Cognitivism in the Classroom Inquiry-oriented projects Opportunities for the testing of hypotheses Curiosity encouraged Staged scaffolding
- 22. Social Learning Theory (SLT) Grew out of Cognitivism A. Bandura (1973) Learning takes place through observation and sensorial experiences Imitation is the sincerest form of flattery SLT is the basis of the movement against violence in media & video games
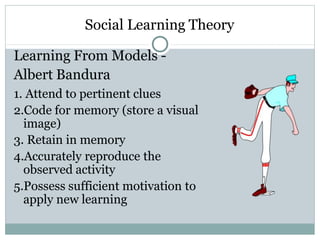
- 23. Social Learning Theory Learning From Models - Albert Bandura 1. Attend to pertinent clues 2.Code for memory (store a visual image) 3. Retain in memory 4.Accurately reproduce the observed activity 5.Possess sufficient motivation to apply new learning
- 24. SLT in the Classroom Collaborative learning and group work Modeling responses and expectations Opportunities to observe experts in action
- 25. Social Constructivism Grew out of and in response to Cognitivism, framed around metacognition Knowledge is actively constructed Learning is… A search for meaning by the learner Contextualized An inherently social activity Dialogic and recursive The responsibility of the learner Lev Vygotsky Social Learning Zone of Proximal Development
- 26. Social Constructivism in the Classroom Journaling Experiential activities Personal focus Collaborative & cooperative learning
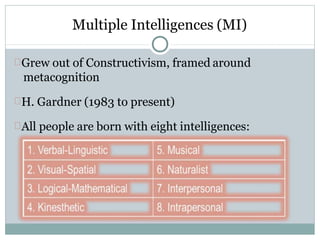
- 27. Multiple Intelligences (MI) Grew out of Constructivism, framed around metacognition H. Gardner (1983 to present) All people are born with eight intelligences:
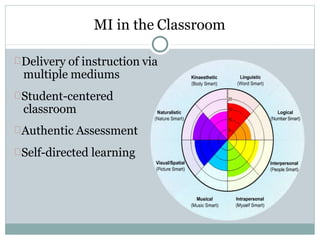
- 28. MI in the Classroom Delivery of instruction via multiple mediums Student-centered classroom Authentic Assessment Self-directed learning
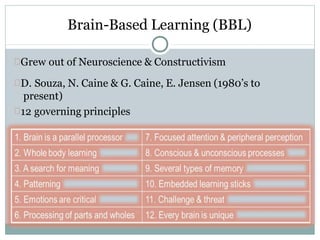
- 29. Brain-Based Learning (BBL) Grew out of Neuroscience & Constructivism D. Souza, N. Caine & G. Caine, E. Jensen (1980’s to present) 12 governing principles
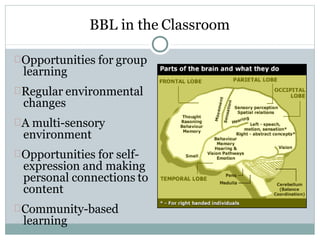
- 30. BBL in the Classroom Opportunities for group learning Regular environmental changes A multi-sensory environment Opportunities for self- expression and making personal connections to content Community-based learning
- 31. Classroom Learning Activities: Entry/Exit Tickets Free Writing/Minute Paper/Question of the Day Exercise Ice Breakers Think–Pair–Share Case Studies and Problem-Based Learning Case studies Problem-based learning Debate Interview or Role Play Interactive Demonstrations Jigsaw
- 32. REFRENCES: Bitterman; et al. (1983). "Classical Conditioning of Proboscis Extension in Honeybees (Apis mellifera)". J. Comp. Psych. J. Scott Armstrong (2012). "Natural Learning in Higher Education". Encyclopedia of the Sciences of Learning. http://www.dynamicflight.com/avcfibook/learning_ process/ http://www.authorstream.com/Presentation/tchisiri -1567544-learning-process/