Learning Theories.ppt
- 4. 1. âa persisting change in human performance or performance potential . . . (brought) about as a result of the learnerâs interaction with the environmentâ (Driscoll, 1994, pp. 8-9). 2. âthe relatively permanent change in a personâs knowledge or behavior due to experienceâ (Mayer, 1982, p. 1040). 3. âan enduring change in behavior, or in the capacity to behave in a given fashion, which results from practice or other forms of experienceâ (Shuell, 1986, p. 412). Definitions: Learning is:
- 5. Q: How do people learn? A: Nobody really knows. But there are 6 main theories: Learning Theory Behaviorism Cognitivism Social Learning Theory Social Constructivism Multiple Intelligences Brain-Based Learning
- 6. Confined to observable and measurable behavior ï§ Classical Conditioning - Pavlov ï§ Operant Conditioning - Skinner Behaviorism
- 8. ï§ Classical Conditioning - Pavlov Behaviorism S R A stimulus is presented in order to get a response:
- 9. ï§ Classical Conditioning - Pavlov Behaviorism S US UR CS US CR
- 10. ï§ Operant Conditioning - Skinner Behaviorism The response is made first, then reinforcement follows.
- 11. ïŠ Learning is defined by the outward expression of new behaviors ïŠ Focuses solely on observable behaviors ïŠ A biological basis for learning ïŠ Learning is context-independent ïŠ Classical & Operant Conditioning ïŠ Reflexes (Pavlovâs Dogs) ïŠ Feedback/Reinforcement (Skinnerâs Pigeon Box) Behaviorism
- 12. ïŠ Rewards and punishments. ïŠ Responsibility for student learning rests squarely with the teacher, teacher as deliverer with expert skills and knowledge. âĒ Rote learning/ regular practice. Behaviorism in the Classroom
- 13. ïŠ Grew in response to Behaviorism ïŠ Knowledge is stored cognitively as symbols ïŠ Learning is the process of connecting symbols in a meaningful & memorable way ïŠ Studies focused on the mental processes that facilitate symbol connection Cognitivism
- 14. ï§ Discovery Learning - Jerome Bruner ï§ Meaningful Verbal Learning - David Ausubel Cognitive Learning Theory
- 15. ï§ Discovery Learning Cognitive Learning Theory 1. Bruner said anybody can learn anything at any age, provided it is stated in terms they can understand.
- 16. ï§ Discovery Learning Cognitive Learning Theory 2. Powerful Concepts (not isolated facts) a. Transfer to many different situations b. Only possible through Discovery Learning c. Confront the learner with problems and help them find solutions. Do not present sequenced materials.
- 17. ï§ Meaningful Verbal Learning Cognitive Learning Theory Advance Organizers: New material is presented in a systematic way, and is connected to existing cognitive structures in a meaningful way.
- 18. ï§ Meaningful Verbal Learning Cognitive Learning Theory When learners have difficulty with new material, go back to the concrete anchors (Advance Organizers). Provide a Discovery approach, and theyâll learn.
- 19. ïŠ Inquiry-oriented projects ïŠ Opportunities for the testing of hypotheses ïŠ Curiosity encouraged ïŠ Staged scaffolding Cognitivism in the Classroom
- 20. ïŠ Grew out of Cognitivism ïŠ A. Bandura (1973) ïŠ Learning takes place through observation and sensorial experiences ïŠ Imitation is the sincerest form of flattery ïŠ SLT is the basis of the movement against violence in media & video games Social Learning Theory (SLT)
- 21. Learning From Models - Albert Bandura 1. Attend to pertinent clues 2. Code for memory (store a visual image) 3. Retain in memory 4. Accurately reproduce the observed activity 5. Possess sufficient motivation to apply new learning Social Learning Theory
- 22. Research indicates that the following factors influence the strength of learning from models: Social Learning Theory 1. How much power the model seems to have 2. How capable the model seems to be 3. How nurturing (caring) the model seems to be 4. How similar the learner perceives self and model 5. How many models the learner observes
- 23. Four interrelated processes establish and strengthen identification with the model: Social Learning Theory 1. Children want to be like the model 2. Children believe they are like the model 3. Children experience emotions like those the model is feeling. 4. Children act like the model.
- 24. Through identification, children come to believe they have the same characteristics as the model. Social Learning Theory When they identify with a nurturant and competent model, children feel pleased and proud. When they identify with an inadequate model, children feel unhappy and insecure.
- 25. ïŠ Collaborative learning and group work ïŠ Modeling responses and expectations ïŠ Opportunities to observe experts in action SLT in the Classroom
- 26. ïŠ Grew out of and in response to Cognitivism, framed around metacognition ïŠ Knowledge is actively constructed ïŠ Learning isâĶ ïŠ A search for meaning by the learner ïŠ Contextualized ïŠ An inherently social activity ïŠ Dialogic and recursive ïŠ The responsibility of the learner ïŠ Lev Vygotsky ïŠ Social Learning ïŠ Zone of Proximal Development Social Constructivism
- 27. ïŠ Journaling ïŠ Experiential activities ïŠ Personal focus ïŠ Collaborative & cooperative learning Social Constructivism in the Classroom
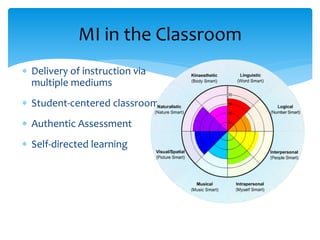
- 28. Multiple Intelligences (MI) ïŠ Grew out of Constructivism, framed around metacognition ïŠ H. Gardner (1983 to present) ïŠ All people are born with eight intelligences: ïŠ Enables students to leverage their strengths and purposefully target and develop their weaknesses 1. Verbal-Linguistic 5. Musical 2. Visual-Spatial 6. Naturalist 3. Logical-Mathematical 7. Interpersonal 4. Kinesthetic 8. Intrapersonal
- 29. ïŠ Delivery of instruction via multiple mediums ïŠ Student-centered classroom ïŠ Authentic Assessment ïŠ Self-directed learning MI in the Classroom
- 30. Brain-Based Learning (BBL) ïŠ Grew out of Neuroscience & Constructivism ïŠ D. Souza, N. Caine & G. Caine, E. Jensen (1980âs to present) ïŠ 12 governing principles 1. Brain is a parallel processor 7. Focused attention & peripheral perception 2. Whole body learning 8. Conscious & unconscious processes 3. A search for meaning 9. Several types of memory 4. Patterning 10. Embedded learning sticks 5. Emotions are critical 11. Challenge & threat 6. Processing of parts and wholes 12. Every brain is unique
- 31. ïŠ Opportunities for group learning ïŠ Regular environmental changes ïŠ A multi-sensory environment ïŠ Opportunities for self- expression and making personal connections to content ïŠ Community-based learning BBL in the Classroom
- 32. ïŠ All students are intrinsically motivated to self actualize or learn. ïŠ Learning is dependent upon meeting a hierarchy of needs (physiological, psychological and intellectual). ïŠ Learning should be reinforced. ïŠ There are many connections between the theories. ïŠ Used by teachers to understand childrenâs learning and to plan for progress. Conclusion
- 33. ïŠ facultyweb.anderson.edu/~jhaukerman/Learning%20Theory.p pt ïŠ Matthew D. Laliberte www.nercomp.org/data/media/A%20Brief%20History%20of%20 Learning%20Theory.ppt ïŠ Michael A. Lorber, Ph.D. www.learningtechnologies.ac.uk/.../PROJECT/resources/Lear ning%20Theory/Resources/learning%20theories.ppt ïŠ www.dcs.bbk.ac.uk/selene/reports/SeLeNe1.2.ppt ïŪSources: