2.Theories of Learning for master of philosophy of education
Download as PPT, PDF0 likes18 views
Philosophy
1 of 19
Download to read offline


















Recommended
Theories of learning.ppt



Theories of learning.pptSoftnessBandaKabinda
Ěý
This document provides an overview of various theories of learning, including behavioral, cognitive, social, and brain-based theories. It defines learning and discusses major theorists and concepts within each approach. Behaviorism focuses on observable behaviors and conditioning, while cognitivism examines mental processes. Social learning theory emphasizes observational learning. Constructivism views learning as an active, social process of constructing knowledge. Multiple intelligences theory proposes eight types of intelligence. Brain-based learning incorporates findings from neuroscience.Theories of Learning



Theories of LearningDr. Amjad Ali Arain
Ěý
Topic: Theories of Learning
Student Name: Ibadat
Class: M.Ed
Project Name: “Young Teachers' Professional Development (TPD)"
"Project Founder: Prof. Dr. Amjad Ali Arain
Faculty of Education, University of Sindh, Pakistan
Learning Theories.ppt



Learning Theories.pptSumairaAamir2
Ěý
“a persisting change in human performance or performance potential . . . (brought) about as a result of the learner’s interaction with the environment” understandcontemporaryissuesaffectingeducationpolicyandtheirimpactonorganizat...



understandcontemporaryissuesaffectingeducationpolicyandtheirimpactonorganizat...DavidBotchway3
Ěý
The gap model of service quality identifies five potential gaps that can lead to unsatisfactory customer experiences. The first gap is between customer expectations and management perceptions. The second gap is between management perceptions and service quality specifications. The third gap is between service quality specifications and service delivery. The fourth gap is between service delivery and what is communicated to customers. Addressing these gaps requires effective communication across departments, accurate translation of customer expectations into standards, and ensuring adequate resources support service delivery. Cultural differences must also be considered when applying this model internationally.Understand contemporary issues affecting education policy and their impact on...



Understand contemporary issues affecting education policy and their impact on...IDM Campus
Ěý
Cognition is defined as 'the mental action or process of acquiring knowledge and understanding through thought, experience, and the senses. ' At Cambridge Cognition we look at it as the mental processes relating to the input and storage of information and how that information is then used to guide your behavior
Principles of Learning



Principles of LearningLynne Tolentino
Ěý
The document discusses several theories of learning including behaviorism, cognitivism, social learning theory, social constructivism, multiple intelligences theory, and brain-based learning. It provides an overview of key aspects of each theory such as major contributors, core concepts, and implications for teaching practices. Learning is described as a complex process influenced by both internal cognitive and external social factors. 4 theories of learning



4 theories of learningBusines
Ěý
This document discusses several theories of learning. It begins by defining learning and examining key theories including behaviorism, cognitivism, social learning theory, social constructivism, multiple intelligences theory, and brain-based learning. For each theory, the document outlines major contributors, key concepts, and implications for classroom practice. It also notes some critiques of each theory. The goal is to operationally define terms related to learning theories and examine theories currently important to understanding how people learn.Learning Theory PPT.ppt



Learning Theory PPT.pptDrHarshadaSushilMuly
Ěý
This document provides an overview of several theories of learning, including behaviorism, cognitivism, social learning theory, social constructivism, multiple intelligences theory, and brain-based learning. It defines learning and examines key aspects of each theory, such as behaviorist concepts of classical and operant conditioning, cognitivist ideas of discovery learning and meaningful verbal learning, and social constructivist views of socially constructed knowledge. Critiques of each theory are also mentioned. Theories are compared and examples are given of how each informs classroom instructional practices. Source information is listed at the end.Theories of learning



Theories of learningMa Cecilla Vergara
Ěý
This document discusses several theories of learning. It begins by defining learning and examining six main theories: behaviorism, cognitivism, social learning theory, social constructivism, multiple intelligences theory, and brain-based learning. For each theory, key aspects are outlined such as important figures, core concepts, and implications for classroom instruction. Critiques of each theory are also presented. The document provides an overview of the major frameworks for understanding how people learn.Tema 4 theories of learning



Tema 4 theories of learningAmmara Khan Niazi
Ěý
This document provides an overview of various theories of learning, including behaviorism, cognitivism, social learning theory, social constructivism, multiple intelligences theory, and brain-based learning. It defines learning and examines key aspects of each theory, such as behaviorist concepts of classical and operant conditioning, cognitivist ideas of discovery learning and meaningful verbal learning, and social constructivist views of socially constructed and contextualized knowledge. The document also discusses applications of each theory for classroom instruction and potential critiques.Tema 4 theories of learning



Tema 4 theories of learningdeviealbarado
Ěý
This document provides an overview of various theories of learning, including behaviorism, cognitivism, social learning theory, social constructivism, multiple intelligences theory, and brain-based learning. It defines learning and examines key aspects of each theory, such as behaviorist concepts of classical and operant conditioning, cognitivist ideas of discovery learning and meaningful verbal learning, and constructivist notions of knowledge construction and social learning. The document also discusses applications of each theory for classroom instruction and potential critiques.Tema 4 theories of learning



Tema 4 theories of learningjyoti arya
Ěý
This document provides an overview of various theories of learning, including behaviorism, cognitivism, social learning theory, social constructivism, multiple intelligences theory, and brain-based learning. It defines learning and examines key aspects of each theory, such as behaviorist concepts of classical and operant conditioning, cognitivist ideas of discovery learning and meaningful verbal learning, and constructivist notions of knowledge construction and social learning. The document also discusses applications of each theory for classroom instruction and potential critiques.Theories of Learning



Theories of LearningMingMing Davis
Ěý
The document outlines several major theories of learning:
1. Behaviorism focuses on observable behaviors and uses reinforcement.
2. Cognitivism examines internal mental processes and meaningful learning.
3. Social learning theory emphasizes observational learning and modeling.
4. Social constructivism views knowledge as constructed through social experiences.
5. Multiple intelligences proposes eight distinct types of intelligence.
6. Brain-based learning incorporates principles from neuroscience on how the brain learns best.Tema 4 theories of learning



Tema 4 theories of learningSultan Ahmed
Ěý
This document provides an overview of several theories of learning, including:
- Behaviorism, which focuses on observable behaviors and conditioning principles. Key theorists discussed are Pavlov and Skinner.
- Cognitive learning theory, which examines internal mental processes. Key concepts are Bruner's discovery learning and Ausubel's meaningful verbal learning.
- Social learning theory, which emphasizes learning through observation and imitation. Bandura's research on modeling behavior is summarized.
- Social constructivism and multiple intelligences theory, which view knowledge as actively constructed based on social and individual contexts. Key figures discussed are Vygotsky, Gardner, and brain-based learning principles.Theories of Learning 



Theories of Learning Dr. Amjad Ali Arain
Ěý
Topic: Theories of Learning
Student Name: Kanwal Shaikh
Class: M.Ed
Project Name: “Young Teachers' Professional Development (TPD)"
"Project Founder: Prof. Dr. Amjad Ali Arain
Faculty of Education, University of Sindh, PakistanTheories of learning by dr sudhir sahu



Theories of learning by dr sudhir sahuSudhir INDIA
Ěý
The document discusses various definitions and theories of learning from different scholars over time. It defines learning as a relatively permanent change in behavior or knowledge that results from experience. It outlines several learning theories including behaviorism, which focuses on observable behaviors and conditioning; cognitivism, which views learning as the processing of information; social learning theory, which emphasizes learning through observation; and constructivism, which sees learning as an active process of constructing knowledge.theories of learning.pptx



theories of learning.pptxNabaeghaNajam1
Ěý
This document summarizes several prominent learning theories: Behaviorism, Cognitivism, Social Learning Theory, Social Constructivism, Multiple Intelligences Theory, and Brain-Based Learning. For each theory, the document outlines key aspects like underlying principles, major contributors, and examples of how each theory can be applied in classroom instruction. It also notes some common critiques of each theoretical approach. Learning Process Theories 



Learning Process Theories Marlin Singson
Ěý
This document discusses various learning theories that are important for educators to understand, including behaviorism, cognitivism, social learning theory, social constructivism, multiple intelligences theory, and brain-based learning. It defines learning and theories, explains the importance of learning theories for educators, and discusses different types of student learning and the cone of learning model. The six main learning theories covered are behaviorism, cognitivism, social learning theory, social constructivism, multiple intelligences theory, and brain-based learning.Teaching Andragogy An Overvew



Teaching Andragogy An Overvewparveenpandit2019
Ěý
This document provides an overview of andragogy, the study of adult education. It discusses key concepts in andragogy including that it focuses on "man leading" or self-directed learning as adults have accumulated life experiences. The document contrasts andragogy with earlier subject-centric models of education and outlines principles of andragogy including creating a supportive environment, collaborative learning, and dealing with obstacles to learning. It also discusses the role of teachers in balancing lecture, discussion and visual methods to operationalize abstract concepts and build critical thinking.Essential Learning Theories and Styles



Essential Learning Theories and StylesKathleen Iverson, Ph.D.
Ěý
This document provides summaries of several learning theories and styles, including:
1) Andragogy proposes that adults learn best when their experience is valued and learning is self-directed. Malcolm Knowles theorized pedagogy does not effectively teach adults.
2) Experiential learning theory by David Kolb includes concrete experience, reflection, abstract conceptualization, and active experimentation in a learning cycle.
3) Behaviorism by B.F. Skinner focuses on observable behavior and reinforcement. Constructivism holds that learners construct their own knowledge based on their experiences.
4) Social learning theory by Albert Bandura emphasizes observing and modeling others' behaviors. Learning styles like VAK/VARKScience of Reading- presentation about .pptx



Science of Reading- presentation about .pptxIleethaGroomPhD
Ěý
Adult Learning Theory meet Science of ReadingMallick Its not about the ology..its the pedagogy - M043 (1).pptx



Mallick Its not about the ology..its the pedagogy - M043 (1).pptxJennilynBalusdan3
Ěý
1. The document discusses key learning theorists and their contributions to pedagogy and educational theory. It contrasts theories of older established theorists like Vygotsky, Piaget, and Dewey with more recent experts in areas like social learning theory, transformative learning theory, and the science of learning.
2. Many theorists emphasized active engagement with content, small group work, hands-on learning, and developing critical thinking skills. Recent work has explored social and cultural aspects of learning along with the role of reflection, self-awareness, and emotional intelligence.
3. Applying different theories involves understanding various learners and using a blended approach, selectively applying strategies like problem-solving, collaborative projects, modeling behaviors, and facilitatingLearning theories, intellectual skills, cognitive skills, psychomotor skills



Learning theories, intellectual skills, cognitive skills, psychomotor skillsIjaz Ahmad
Ěý
Learning theories provide frameworks to understand how people learn. The document discusses several major learning theories including behaviorism, cognitivism, and constructivism. Behaviorism views learning as changes in observable behavior through conditioning. Cognitivism sees learning as information processing and knowledge acquisition. Constructivism proposes that learners actively construct knowledge based on their experiences. The document also examines intellectual skills like knowledge, critical thinking, problem solving, and creativity that are developed through learning. Understanding learning theories helps educators design effective instruction aligned with how people learn.theories of learning PPT very nice good amazing excellent beautiful



theories of learning PPT very nice good amazing excellent beautifulShawalNawaz3
Ěý
This PPT is about theories of learning.Learning



LearningArkabrata Bandyapadhyay
Ěý
This document provides an overview of learning and learning theories. It defines learning, discusses the domains, features, principles, and process of learning. It also summarizes four major learning theories: behaviorism, cognitivism, constructivism, and humanism. Behaviorism views learning as changes in observable behavior due to environmental influences and conditioning. Cognitivism sees learning as the processing of information in memory. Constructivism emphasizes learning through experience and knowledge construction. Humanism views learning as a personal act to fulfill one's potential.learningprocess.pptx



learningprocess.pptxMrTauqeerAhmedFacult
Ěý
The document discusses the learning process and various theories of learning. It defines learning and discusses principles such as learning involving individuals, others, environments, and occurring over time. Products of learning include ideas, behaviors, attitudes. Theories covered include behaviorism, cognitivism, social learning theory, social constructivism, and brain-based learning. Behaviorism focuses on observable behavior while cognitivism emphasizes mental processes. Social learning theory and social constructivism highlight the social aspects of learning. Brain-based learning incorporates insights from neuroscience. The document also provides examples of classroom activities aligned with different theories.More Related Content
Similar to 2.Theories of Learning for master of philosophy of education (20)
Learning Theory PPT.ppt



Learning Theory PPT.pptDrHarshadaSushilMuly
Ěý
This document provides an overview of several theories of learning, including behaviorism, cognitivism, social learning theory, social constructivism, multiple intelligences theory, and brain-based learning. It defines learning and examines key aspects of each theory, such as behaviorist concepts of classical and operant conditioning, cognitivist ideas of discovery learning and meaningful verbal learning, and social constructivist views of socially constructed knowledge. Critiques of each theory are also mentioned. Theories are compared and examples are given of how each informs classroom instructional practices. Source information is listed at the end.Theories of learning



Theories of learningMa Cecilla Vergara
Ěý
This document discusses several theories of learning. It begins by defining learning and examining six main theories: behaviorism, cognitivism, social learning theory, social constructivism, multiple intelligences theory, and brain-based learning. For each theory, key aspects are outlined such as important figures, core concepts, and implications for classroom instruction. Critiques of each theory are also presented. The document provides an overview of the major frameworks for understanding how people learn.Tema 4 theories of learning



Tema 4 theories of learningAmmara Khan Niazi
Ěý
This document provides an overview of various theories of learning, including behaviorism, cognitivism, social learning theory, social constructivism, multiple intelligences theory, and brain-based learning. It defines learning and examines key aspects of each theory, such as behaviorist concepts of classical and operant conditioning, cognitivist ideas of discovery learning and meaningful verbal learning, and social constructivist views of socially constructed and contextualized knowledge. The document also discusses applications of each theory for classroom instruction and potential critiques.Tema 4 theories of learning



Tema 4 theories of learningdeviealbarado
Ěý
This document provides an overview of various theories of learning, including behaviorism, cognitivism, social learning theory, social constructivism, multiple intelligences theory, and brain-based learning. It defines learning and examines key aspects of each theory, such as behaviorist concepts of classical and operant conditioning, cognitivist ideas of discovery learning and meaningful verbal learning, and constructivist notions of knowledge construction and social learning. The document also discusses applications of each theory for classroom instruction and potential critiques.Tema 4 theories of learning



Tema 4 theories of learningjyoti arya
Ěý
This document provides an overview of various theories of learning, including behaviorism, cognitivism, social learning theory, social constructivism, multiple intelligences theory, and brain-based learning. It defines learning and examines key aspects of each theory, such as behaviorist concepts of classical and operant conditioning, cognitivist ideas of discovery learning and meaningful verbal learning, and constructivist notions of knowledge construction and social learning. The document also discusses applications of each theory for classroom instruction and potential critiques.Theories of Learning



Theories of LearningMingMing Davis
Ěý
The document outlines several major theories of learning:
1. Behaviorism focuses on observable behaviors and uses reinforcement.
2. Cognitivism examines internal mental processes and meaningful learning.
3. Social learning theory emphasizes observational learning and modeling.
4. Social constructivism views knowledge as constructed through social experiences.
5. Multiple intelligences proposes eight distinct types of intelligence.
6. Brain-based learning incorporates principles from neuroscience on how the brain learns best.Tema 4 theories of learning



Tema 4 theories of learningSultan Ahmed
Ěý
This document provides an overview of several theories of learning, including:
- Behaviorism, which focuses on observable behaviors and conditioning principles. Key theorists discussed are Pavlov and Skinner.
- Cognitive learning theory, which examines internal mental processes. Key concepts are Bruner's discovery learning and Ausubel's meaningful verbal learning.
- Social learning theory, which emphasizes learning through observation and imitation. Bandura's research on modeling behavior is summarized.
- Social constructivism and multiple intelligences theory, which view knowledge as actively constructed based on social and individual contexts. Key figures discussed are Vygotsky, Gardner, and brain-based learning principles.Theories of Learning 



Theories of Learning Dr. Amjad Ali Arain
Ěý
Topic: Theories of Learning
Student Name: Kanwal Shaikh
Class: M.Ed
Project Name: “Young Teachers' Professional Development (TPD)"
"Project Founder: Prof. Dr. Amjad Ali Arain
Faculty of Education, University of Sindh, PakistanTheories of learning by dr sudhir sahu



Theories of learning by dr sudhir sahuSudhir INDIA
Ěý
The document discusses various definitions and theories of learning from different scholars over time. It defines learning as a relatively permanent change in behavior or knowledge that results from experience. It outlines several learning theories including behaviorism, which focuses on observable behaviors and conditioning; cognitivism, which views learning as the processing of information; social learning theory, which emphasizes learning through observation; and constructivism, which sees learning as an active process of constructing knowledge.theories of learning.pptx



theories of learning.pptxNabaeghaNajam1
Ěý
This document summarizes several prominent learning theories: Behaviorism, Cognitivism, Social Learning Theory, Social Constructivism, Multiple Intelligences Theory, and Brain-Based Learning. For each theory, the document outlines key aspects like underlying principles, major contributors, and examples of how each theory can be applied in classroom instruction. It also notes some common critiques of each theoretical approach. Learning Process Theories 



Learning Process Theories Marlin Singson
Ěý
This document discusses various learning theories that are important for educators to understand, including behaviorism, cognitivism, social learning theory, social constructivism, multiple intelligences theory, and brain-based learning. It defines learning and theories, explains the importance of learning theories for educators, and discusses different types of student learning and the cone of learning model. The six main learning theories covered are behaviorism, cognitivism, social learning theory, social constructivism, multiple intelligences theory, and brain-based learning.Teaching Andragogy An Overvew



Teaching Andragogy An Overvewparveenpandit2019
Ěý
This document provides an overview of andragogy, the study of adult education. It discusses key concepts in andragogy including that it focuses on "man leading" or self-directed learning as adults have accumulated life experiences. The document contrasts andragogy with earlier subject-centric models of education and outlines principles of andragogy including creating a supportive environment, collaborative learning, and dealing with obstacles to learning. It also discusses the role of teachers in balancing lecture, discussion and visual methods to operationalize abstract concepts and build critical thinking.Essential Learning Theories and Styles



Essential Learning Theories and StylesKathleen Iverson, Ph.D.
Ěý
This document provides summaries of several learning theories and styles, including:
1) Andragogy proposes that adults learn best when their experience is valued and learning is self-directed. Malcolm Knowles theorized pedagogy does not effectively teach adults.
2) Experiential learning theory by David Kolb includes concrete experience, reflection, abstract conceptualization, and active experimentation in a learning cycle.
3) Behaviorism by B.F. Skinner focuses on observable behavior and reinforcement. Constructivism holds that learners construct their own knowledge based on their experiences.
4) Social learning theory by Albert Bandura emphasizes observing and modeling others' behaviors. Learning styles like VAK/VARKScience of Reading- presentation about .pptx



Science of Reading- presentation about .pptxIleethaGroomPhD
Ěý
Adult Learning Theory meet Science of ReadingMallick Its not about the ology..its the pedagogy - M043 (1).pptx



Mallick Its not about the ology..its the pedagogy - M043 (1).pptxJennilynBalusdan3
Ěý
1. The document discusses key learning theorists and their contributions to pedagogy and educational theory. It contrasts theories of older established theorists like Vygotsky, Piaget, and Dewey with more recent experts in areas like social learning theory, transformative learning theory, and the science of learning.
2. Many theorists emphasized active engagement with content, small group work, hands-on learning, and developing critical thinking skills. Recent work has explored social and cultural aspects of learning along with the role of reflection, self-awareness, and emotional intelligence.
3. Applying different theories involves understanding various learners and using a blended approach, selectively applying strategies like problem-solving, collaborative projects, modeling behaviors, and facilitatingLearning theories, intellectual skills, cognitive skills, psychomotor skills



Learning theories, intellectual skills, cognitive skills, psychomotor skillsIjaz Ahmad
Ěý
Learning theories provide frameworks to understand how people learn. The document discusses several major learning theories including behaviorism, cognitivism, and constructivism. Behaviorism views learning as changes in observable behavior through conditioning. Cognitivism sees learning as information processing and knowledge acquisition. Constructivism proposes that learners actively construct knowledge based on their experiences. The document also examines intellectual skills like knowledge, critical thinking, problem solving, and creativity that are developed through learning. Understanding learning theories helps educators design effective instruction aligned with how people learn.theories of learning PPT very nice good amazing excellent beautiful



theories of learning PPT very nice good amazing excellent beautifulShawalNawaz3
Ěý
This PPT is about theories of learning.Learning



LearningArkabrata Bandyapadhyay
Ěý
This document provides an overview of learning and learning theories. It defines learning, discusses the domains, features, principles, and process of learning. It also summarizes four major learning theories: behaviorism, cognitivism, constructivism, and humanism. Behaviorism views learning as changes in observable behavior due to environmental influences and conditioning. Cognitivism sees learning as the processing of information in memory. Constructivism emphasizes learning through experience and knowledge construction. Humanism views learning as a personal act to fulfill one's potential.learningprocess.pptx



learningprocess.pptxMrTauqeerAhmedFacult
Ěý
The document discusses the learning process and various theories of learning. It defines learning and discusses principles such as learning involving individuals, others, environments, and occurring over time. Products of learning include ideas, behaviors, attitudes. Theories covered include behaviorism, cognitivism, social learning theory, social constructivism, and brain-based learning. Behaviorism focuses on observable behavior while cognitivism emphasizes mental processes. Social learning theory and social constructivism highlight the social aspects of learning. Brain-based learning incorporates insights from neuroscience. The document also provides examples of classroom activities aligned with different theories.More from FazalHayat12 (20)
TPD Unit-2.1, 2.2, 2.3, 2.4.(Teachers Professional Development)



TPD Unit-2.1, 2.2, 2.3, 2.4.(Teachers Professional Development)FazalHayat12
Ěý
PhD Education PresentationRecently uploaded (20)
Principle and Practices of Animal Breeding || Boby Basnet



Principle and Practices of Animal Breeding || Boby BasnetBoby Basnet
Ěý
Principle and Practices of Animal Breeding Full Note
|| Assistant Professor Boby Basnet ||IAAS || AFU || PU || FUAPM People Interest Network Conference - Tim Lyons - The neurological levels ...



APM People Interest Network Conference - Tim Lyons - The neurological levels ...Association for Project Management
Ěý
APM People Interest Network Conference 2025
-Autonomy, Teams and Tension: Projects under stress
-Tim Lyons
-The neurological levels of
team-working: Harmony and tensions
With a background in projects spanning more than 40 years, Tim Lyons specialised in the delivery of large, complex, multi-disciplinary programmes for clients including Crossrail, Network Rail, ExxonMobil, Siemens and in patent development. His first career was in broadcasting, where he designed and built commercial radio station studios in Manchester, Cardiff and Bristol, also working as a presenter and programme producer. Tim now writes and presents extensively on matters relating to the human and neurological aspects of projects, including communication, ethics and coaching. He holds a Master’s degree in NLP, is an NLP Master Practitioner and International Coach. He is the Deputy Lead for APM’s People Interest Network.
Session | The Neurological Levels of Team-working: Harmony and Tensions
Understanding how teams really work at conscious and unconscious levels is critical to a harmonious workplace. This session uncovers what those levels are, how to use them to detect and avoid tensions and how to smooth the management of change by checking you have considered all of them.Essentials of a Good PMO, presented by Aalok Sonawala



Essentials of a Good PMO, presented by Aalok SonawalaAssociation for Project Management
Ěý
APM event hosted by the South Wales and West of England Network (SWWE Network)
Speaker: Aalok Sonawala
The SWWE Regional Network were very pleased to welcome Aalok Sonawala, Head of PMO, National Programmes, Rider Levett Bucknall on 26 February, to BAWA for our first face to face event of 2025. Aalok is a member of APM’s Thames Valley Regional Network and also speaks to members of APM’s PMO Interest Network, which aims to facilitate collaboration and learning, offer unbiased advice and guidance.
Tonight, Aalok planned to discuss the importance of a PMO within project-based organisations, the different types of PMO and their key elements, PMO governance and centres of excellence.
PMO’s within an organisation can be centralised, hub and spoke with a central PMO with satellite PMOs globally, or embedded within projects. The appropriate structure will be determined by the specific business needs of the organisation. The PMO sits above PM delivery and the supply chain delivery teams.
For further information about the event please click here.Kaun TALHA quiz Prelims - El Dorado 2025



Kaun TALHA quiz Prelims - El Dorado 2025Conquiztadors- the Quiz Society of Sri Venkateswara College
Ěý
Prelims of Kaun TALHA : a Travel, Architecture, Lifestyle, Heritage and Activism quiz, organized by Conquiztadors, the Quiz society of Sri Venkateswara College under their annual quizzing fest El Dorado 2025. How to Setup WhatsApp in Odoo 17 - Odoo şÝşÝߣs



How to Setup WhatsApp in Odoo 17 - Odoo şÝşÝߣsCeline George
Ěý
Integrate WhatsApp into Odoo using the WhatsApp Business API or third-party modules to enhance communication. This integration enables automated messaging and customer interaction management within Odoo 17.The Constitution, Government and Law making bodies .



The Constitution, Government and Law making bodies .saanidhyapatel09
Ěý
This PowerPoint presentation provides an insightful overview of the Constitution, covering its key principles, features, and significance. It explains the fundamental rights, duties, structure of government, and the importance of constitutional law in governance. Ideal for students, educators, and anyone interested in understanding the foundation of a nation’s legal framework.
Mate, a short story by Kate Grenvile.pptx



Mate, a short story by Kate Grenvile.pptxLiny Jenifer
Ěý
A powerpoint presentation on the short story Mate by Kate Greenville. This presentation provides information on Kate Greenville, a character list, plot summary and critical analysis of the short story.FESTIVAL: SINULOG & THINGYAN-LESSON 4.pptx



FESTIVAL: SINULOG & THINGYAN-LESSON 4.pptxDanmarieMuli1
Ěý
Sinulog Festival of Cebu City, and Thingyan Festival of Myanmar.South Hornsey: The Lost Local Authority that Merged with Stoke Newington by T...



South Hornsey: The Lost Local Authority that Merged with Stoke Newington by T...History of Stoke Newington
Ěý
Presented at the 24th Stoke Newington History Talks event on 27th Feb 2025
https://stokenewingtonhistory.com/stoke-newington-history-talks/A PPT Presentation on The Princess and the God: A tale of ancient India by A...



A PPT Presentation on The Princess and the God: A tale of ancient India by A...Beena E S
Ěý
A PPT Presentation on The Princess and the God: A tale of ancient India by Aaron ShepardQuickBooks Desktop to QuickBooks Online How to Make the Move



QuickBooks Desktop to QuickBooks Online How to Make the MoveTechSoup
Ěý
If you use QuickBooks Desktop and are stressing about moving to QuickBooks Online, in this webinar, get your questions answered and learn tips and tricks to make the process easier for you.
Key Questions:
* When is the best time to make the shift to QuickBooks Online?
* Will my current version of QuickBooks Desktop stop working?
* I have a really old version of QuickBooks. What should I do?
* I run my payroll in QuickBooks Desktop now. How is that affected?
*Does it bring over all my historical data? Are there things that don't come over?
* What are the main differences between QuickBooks Desktop and QuickBooks Online?
* And moreComputer Application in Business (commerce)



Computer Application in Business (commerce)Sudar Sudar
Ěý
The main objectives
1. To introduce the concept of computer and its various parts. 2. To explain the concept of data base management system and Management information system.
3. To provide insight about networking and basics of internet
Recall various terms of computer and its part
Understand the meaning of software, operating system, programming language and its features
Comparing Data Vs Information and its management system Understanding about various concepts of management information system
Explain about networking and elements based on internet
1. Recall the various concepts relating to computer and its various parts
2 Understand the meaning of software’s, operating system etc
3 Understanding the meaning and utility of database management system
4 Evaluate the various aspects of management information system
5 Generating more ideas regarding the use of internet for business purpose TLE 7 - 3rd Topic - Hand Tools, Power Tools, Instruments, and Equipment Used ...



TLE 7 - 3rd Topic - Hand Tools, Power Tools, Instruments, and Equipment Used ...RizaBedayo
Ěý
Hand Tools, Power Tools, and Equipment in Industrial ArtsBlind Spots in AI and Formulation Science Knowledge Pyramid (Updated Perspect...



Blind Spots in AI and Formulation Science Knowledge Pyramid (Updated Perspect...Ajaz Hussain
Ěý
This presentation delves into the systemic blind spots within pharmaceutical science and regulatory systems, emphasizing the significance of "inactive ingredients" and their influence on therapeutic equivalence. These blind spots, indicative of normalized systemic failures, go beyond mere chance occurrences and are ingrained deeply enough to compromise decision-making processes and erode trust.
Historical instances like the 1938 FD&C Act and the Generic Drug Scandals underscore how crisis-triggered reforms often fail to address the fundamental issues, perpetuating inefficiencies and hazards.
The narrative advocates a shift from reactive crisis management to proactive, adaptable systems prioritizing continuous enhancement. Key hurdles involve challenging outdated assumptions regarding bioavailability, inadequately funded research ventures, and the impact of vague language in regulatory frameworks.
The rise of large language models (LLMs) presents promising solutions, albeit with accompanying risks necessitating thorough validation and seamless integration.
Tackling these blind spots demands a holistic approach, embracing adaptive learning and a steadfast commitment to self-improvement. By nurturing curiosity, refining regulatory terminology, and judiciously harnessing new technologies, the pharmaceutical sector can progress towards better public health service delivery and ensure the safety, efficacy, and real-world impact of drug products.APM People Interest Network Conference - Tim Lyons - The neurological levels ...



APM People Interest Network Conference - Tim Lyons - The neurological levels ...Association for Project Management
Ěý
Kaun TALHA quiz Prelims - El Dorado 2025



Kaun TALHA quiz Prelims - El Dorado 2025Conquiztadors- the Quiz Society of Sri Venkateswara College
Ěý
South Hornsey: The Lost Local Authority that Merged with Stoke Newington by T...



South Hornsey: The Lost Local Authority that Merged with Stoke Newington by T...History of Stoke Newington
Ěý
2.Theories of Learning for master of philosophy of education
- 1. Theories of Learning Broad Goals • Operationally define terms relevant to theories of learning. • Examine learning theories that are currently important 1
- 2. Definitions: Learning is: • “a persisting chance in human performance or performance potential (brought) about as a result of the learner’s interaction with the environment” (Driscoll, 1994, pp.8-9). • “the relatively permanent change in a person’s knowledge or behaviour due to experience (Mayer, 1982, p.1040). • “an endurign change in behaviour, or in the capacity to behave in a given fashion, which results from practice or other forms of experience” (Shuell, 1986, p.412) 2
- 3. Learning Theory Kind of Learning Theories • Behaviorism • Cognitivism • Social Learning Theory • Social Constructivism • Multiple Intelligences • Brain-Based Learning 3
- 4. Behaviourism Confined to observable and measurable behaviour • Classical conditioning – Pavlov 4 A Stimulus is presented in order to get a response S R
- 5. Behaviourism • Classical conditioning – Pavlov 5 S US UR CS US CR
- 6. Behaviourism • Operant conditioning – Skinner The response is made first, then reinforcement follows. 6
- 7. Behaviourism • Operant conditioning – Skinner The response is made first, then reinforcement follows. 7
- 8. Cognitivism • Grew in responses to Bheaviourism • Knowledge is stored cognitively as symbols • Learning is the process of connecting symbols in a meaningful & memorable way • Studies focused on the mental processes that facilitate symbol connection 8
- 9. Cognitive Learning Theory • Discovery Learning – Jerome Bruner • Meaningful Verbal Learning – David Ausubel 9
- 10. Learning Theory • Behaviourism • Social Learning Theory • Cognitive Learning Theory 10
- 11. Social Learning Theory (SLT) • Grew out of Cognitivism • A. Bandura (1973) • Learning takes place through observation and sensorial experiences • Imitation is the sincerest form of flattery • SLT is the basis of the movement against violence in media & video games. 11
- 12. Social Learning Theory Learning From Models – Albert Bandura 1. Attend to pertinent clues 2. Code for memory (Store a visual image) 3. Retain in memory 4. Accurately reproduce the observed activity 5. Possess sufficient motivation to apply new learning. 12
- 13. Social Learning Theory Research indicates that the following factors influence the strength of learning from models: 1. How much power the model seems to have 2. How capable the model seems to be 3. How nurturing (caring) the model seems to be 4. How similar the learner perceives self and model 5. How many models the learner observes 13
- 14. SLT in the Classroom • Collaboration Learning and group work • Modeling responses and expectations • Opportunities to observe experts in action 14
- 15. Critiques of Social Learning Theory • Does not take into account individuality, context, and experience as mediating factors • Suggests students learn best as passive receivers of sensory stimuli, as opposed to being active learners • Emotions and motivation not considered important or connected to learning 15
- 16. Social Constructivism • Grew out of and in response to Cognitivism, framed around metacognition • Knowledge is actively constructed • Learning is… – A search for meaning by the learner – Contextualized – An inherently social activity – Dialogic and recursive – The responsibility of the learner • Lev Vygotosky – Social learbning – Zone of Proximal Development 16
- 17. Social Constructivism in the Classroom • Journaling • Experiential activities • Personal focus • Collaborative & cooperative learning 17
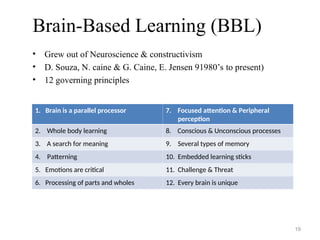
- 18. Multiple Intelligence (MI) • Grew out of constructivism, framed around metagocnition • H. Gardner (1983 to present) • All people are born with eight intelligence: Enables students to leverage their strengths and purposefully target and develop their weaknesses 18 1. Verbal – Linguistic 5. Musical 2. Visual – Spatial 6. Naturalist 3. Logical Mathematical 7. Interpersonal 4. Kinesthetic 8. Intrapersonal
- 19. Brain-Based Learning (BBL) • Grew out of Neuroscience & constructivism • D. Souza, N. caine & G. Caine, E. Jensen 91980’s to present) • 12 governing principles 19 1. Brain is a parallel processor 7. Focused attention & Peripheral perception 2. Whole body learning 8. Conscious & Unconscious processes 3. A search for meaning 9. Several types of memory 4. Patterning 10. Embedded learning sticks 5. Emotions are critical 11. Challenge & Threat 6. Processing of parts and wholes 12. Every brain is unique


























