New bicycle
- 1. SWAMI KESHVANAND INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY MANAGEMENT & GRAMOTHAN, JAIPUR. 3ME8-Basic Mechanical Engineering Lab. EXPERIMENT No. 2 Object:- Operation, Assembling and disassembling of Bicycle. Objectives :- After doing the experiment, student will be able to i) Know the principle and working of a bicycle. ii) Calculate the mechanical advantage iii) Know the different mechanisms of the bicycle iv) Recognize the different parts of the bicycle Apparatus- Bicycle, Tools Needed- Allen keys, Wrenches ,OpenEnd and rings spanners & Sockets, Screwdriver, Wire Cutters, Air Pump. Theory-The bicycle, cycle or bike, is a pedal-driven, human-powered vehicle with two wheels attached to a frame, one behind the other, with a seat for the cyclist to sit on. Bicycles work on a rather simple mechanism. There is no major electrical or mechanical principle hidden behind it. It uses two simple techniques. ï· Applying friction in brakes to stop the bicycle ï· The gear mechanism make the bicycle go faster. The main part of a bicycle is its center frame which is the base for all other parts. Apart from the frame the major parts are two wheels, a handlebar, pedals, brakes, gears, chains and a seat. Of course additional equipments like front and back lights, bells, carriages and baskets are added as extra fittings. But a bicycle can very well run without them also. Once the frame is manufactured two wheels are fitted to it first. To make the wheels move further the gear and chain mechanism is used. These are the three simple mechanisms applied in bicycle which makes it the most common, durable, household machine. Brake Mechanism: 1. To stop rotation of the wheels brakes are pulled and automatically a friction is created stopping the wheels immediately.
- 2. 2. Brakes are provided in front as well as rear wheel. Braking shoes are assembled in forks, which comes in contacts with wheel rims, when levers are pulled. 3. Braking mechanism is a mechanical system having control levers attached to handle bar. Ball bearings Mechanism: 1. The same concept used in brakes to stop the bicycle is used in ball bearings to make the bicycle run faster by reducing friction. 2. Ball bearing are found in bicycles in the fork tube, pedal, freewheels and front and back hubs of the wheels. Ball bearings make the handle bar turn smoothly, help us pedal easily and also helps smoothmovement of wheels. Free wheelMechanism: 1. The simplest freewheel device consists of two saw-toothed, spring-loaded discs pressing against each other with the toothed sides together, somewhat like a ratchet. Rotating in one direction, the saw teeth of the drive disc lock with the teeth of the driven disc, making it rotate at the same speed. If the drive disc slows down or stops rotating, the teeth of the driven disc slip over the drive disc teeth and continue rotating, producing a characteristic clicking sound proportionate to the speed difference of the driven gear relative to that of the (slower) driving gear. 2. Most bicycle freewheels use an internally step-toothed drum with two or more spring-loaded, hardened steel pawls to transmit the load. More pawls help spread the wear and give greater reliability although, unless the device is made to tolerances not normally found in bicycle components, simultaneous engagement of more than two pawls is rarely achieved. Main Parts : The main parts of a bicycle is its center frame which is the base for all other parts. Apart from the frame the major parts are 1. Two wheels and axles 2. A handlebar 3. Pedals 4. Brakes 5. Gears 6. Chains
- 3. 7. A seat 8. Additional equipments like front and back lights, bells, carriages and baskets are added as extra fittings. But a cycle can very well run without them also. Mechanicaladvantage: 1. Mechanical advantage is a measure of the force amplification achieved by using a tool, mechanical device or machine system. Ideally, the device preserves the input power and simply trades off forces against movement to obtain a desired amplification in the output force. The model for this is the law of the lever. Machine components designed to manage forces and movement in this way are called mechanisms. 2. Mechanisms of a bicycle consisting of two sprockets connected by a chain are designed to provide a specific mechanical advantage in power transmission systems. 3. The velocity v of the chain is the same when in contact with the two sprockets: where the input sprocket A meshes with the chain along the pitch radius rA and the output sprocket B meshes with this chain along the pitch radius rB.
- 4. 4. The mechanical advantage is also achieved between rear sprocketand rear wheel. Diameter of driver= D, diameter of driven= d and diameter of wheel= D1 When the driver completes one revolution then the driven also completes one revolution ÏD = Ïd
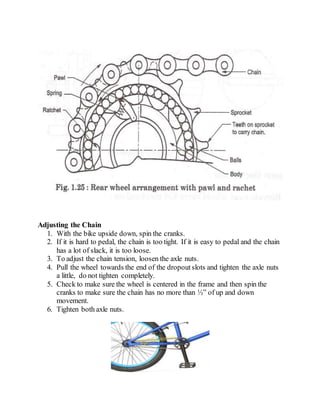
- 5. Adjusting the Chain 1. With the bike upside down, spin the cranks. 2. If it is hard to pedal, the chain is too tight. If it is easy to pedal and the chain has a lot of slack, it is too loose. 3. To adjust the chain tension, loosen the axle nuts. 4. Pull the wheel towards the end of the dropoutslots and tighten the axle nuts a little, do not tighten completely. 5. Check to make sure the wheel is centered in the frame and then spin the cranks to make sure the chain has no more than Â―â of up and down movement. 6. Tighten both axle nuts.
- 6. Disassembling of bicycle 1. Twist the pedals off the pedal cranks. Loosen the bolts or nuts that secure the brake pads in place, and then loosen the bolts securing the brakes to the frame or wheel hub. 2. Loosen the bolt that fastens the brake lever to the handlebar. Remove the grips from the ends of the handlebar. Remove the brakes and brake lever from the bicycle and set them aside. 3. Loosen the bolt that secures the seat post clamp in the locked position. Pull the seat post out of the bicycle frame. Remove the bolts that fasten the seat to the seat post; lift the seat off and set it aside. Remove the bolts securing the rear reflector, and take off the reflector and set it aside. 4. Remove the bolt securing the handlebar stem in place. Pull the stem up and out of the bicycle frame. Remove the bolt securing the handlebar clamp in place. Extract the handlebar from the handlebar clamp. 5. Remove the nuts at the front wheel to the bicycle fork. Extract the wheel from the fork. Remove the screws that fasten the front fender to the frame; remove the fender and set it aside. 6. Loosen the nuts attached to the rear axle and shift the rear wheel forward. Inspect the bicycle wheel and locate the joining link. Use a flat-head screwdriver to pry the joining link free of the bicycle chain. Remove the chain and rear wheel. 7. Remove the nut, washer and bearing assembly located on the left side of the pedal crank. Pull the crank out of the frame. Remove the chainwheel. 8. Remove the bolts, screws or nuts securing any remaining accessories to the bicycle frame; remove the accessories and set them aside. Remove the bolts, pins or fasteners securing the reflectors to the front and rear wheel. Extract the reflector from the spokes of each wheel. Assembling 1. While assembling the pump, we have to fit the parts in the reverse order, i.e. last part opened is to be fitted first. 2. We have to tighten the nuts and bolts properly. 3. After assembling the bicycle, it has to be tested for the properworking. Problem Solving 1. Bicycle got punctured- How it is to be repaired? 2. Chain tension has become less or chain has come out from free wheel-How it is to be adjusted? 3. How centering of handle bar is to be adjusted?
- 7. 4. Experiment Outcome 1. We have learnt the principle of bicycle. 2. After dissembling the bicycle, we have recognized the various parts of the bicycle and their functions.