Obesity hypoventilation syndrome HY
0 likes153 views
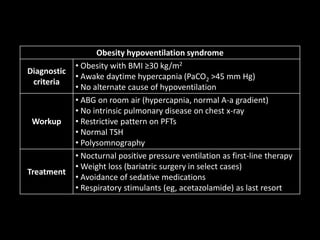
Obesity hypoventilation syndrome is diagnosed in obese patients (BMI ≥30 kg/m2) with awake hypercapnia (PaCO2 >45 mm Hg) and no other cause of hypoventilation. It is evaluated with blood gases, chest x-ray, pulmonary function tests, thyroid function tests, and polysomnography. Treatment involves nocturnal positive pressure ventilation as first-line, weight loss through bariatric surgery if needed, avoiding sedatives, and using respiratory stimulants only as a last resort.
1 of 1
Download to read offline
Ad
Recommended
Case4 3
Case4 3Ahmed Maghraby
Ěý
This document presents the case of a 70-year-old woman admitted to the ICU with hypotension, hypoxia, abdominal tenderness and distension. She developed intra-abdominal hypertension with an intra-abdominal pressure of 26 mmHg. Imaging revealed occlusion of the superior mesenteric artery near its origin with infarction of the right kidney and spleen. Her condition was too poor for surgery, so medical management was initiated for her intra-abdominal hypertension and multiple organ dysfunction.Dka and HHS pptx
Dka and HHS pptxNurulHusnaRashid1
Ěý
This document discusses diabetic emergencies including hypoglycemia, diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), and hyperglycemic hyperosmolar state (HHS). It provides details on the diagnostic criteria, symptoms, and general approach to managing patients with DKA. Key points include: DKA is caused by insulin deficiency leading to hyperglycemia and ketonemia; diagnostic criteria includes blood glucose over 11 mmol/L, ketones over 3 mmol/L, and venous pH below 7.3; symptoms include nausea, vomiting, and altered mental status; management involves assessing airway, breathing, circulation, and providing IV fluids and insulin.[Int. med] chest pain 3rd year class
[Int. med] chest pain 3rd year classMuhammad Ahmad
Ěý
Chest pain can be caused by many serious cardiac and pulmonary conditions. It is considered a medical emergency and requires prompt evaluation and treatment. Common causes of chest pain include acute coronary syndrome, aortic dissection, pulmonary embolism, pericarditis, gastroesophageal reflux disease, and psychological factors like panic attacks and anxiety. A careful history, physical exam, electrocardiogram, cardiac enzyme tests, imaging studies, and other diagnostics are used to determine the underlying cause and guide management.Acute pancreatitis case discussion
Acute pancreatitis case discussionMuhammad Asim Rana
Ěý
This document discusses three case studies of patients presenting with acute pancreatitis and its complications:
Case 1 involves a 56-year-old man with severe acute pancreatitis, respiratory failure, and multiple organ dysfunction. CT reveals pancreatic necrosis. Intensive care support is needed.
Case 2 involves a 61-year-old man whose acute pancreatitis is complicated by infection of pancreatic necrosis from bile duct stones. Surgery is eventually needed to debride necrotic tissue.
Case 3 involves a 45-year-old man whose acute pancreatitis is complicated by a pancreatic rupture and collection. Percutaneous drainage is initially done but surgery is later needed to drain solid necrotic debris from the collection. He develops aAcute pancreatitis
Acute pancreatitisNandinii Ramasenderan
Ěý
Mr. T, a 56-year-old man, presented with acute pancreatitis symptoms including epigastric pain and nausea. Investigations confirmed elevated pancreatic enzymes. He was initially treated conservatively but his condition deteriorated, requiring ICU admission and intubation. Imaging showed acute pancreatitis with peripancreatic fluid collection. Antibiotics were started after he developed a fever. Complications of acute pancreatitis like pancreatic necrosis and pseudocyst formation were discussed. The role of antibiotics, ERCP, and surgical or radiologic drainage of infected collections was also outlined.Intra-abdominal Hypertension - Abdominal Compartment Syndrome part 1
Intra-abdominal Hypertension - Abdominal Compartment Syndrome part 1International Fluid Academy
Ěý
The document discusses intra-abdominal hypertension (IAH) and abdominal compartment syndrome (ACS), emphasizing their significant impact on the morbidity and mortality of critically ill patients. It presents findings from a consensus study involving 179 ICU doctors from 15 countries, highlighting common misconceptions and knowledge gaps regarding IAH and ACS among specialists. The document also outlines definitions, measurement techniques, classifications, and risk factors associated with IAH and ACS, as well as their implications for treatment and prognosis.Acute mesentric ischemia
Acute mesentric ischemiaIbrahimAlbujays
Ěý
Acute mesenteric ischemia is a sudden reduction in blood flow to the small intestine that can be caused by blockages or issues with the arteries or veins supplying the intestine. It has a high mortality rate of 25-80% if not treated promptly. Diagnosis involves imaging like CT scans to identify abnormalities in the bowel walls or presence of gas in the blood vessels. Treatment depends on the underlying cause but may include aggressive resuscitation, antibiotics, revascularization procedures to restore blood flow, or bowel resection if parts of the intestine are found to be non-viable. Post-operative management focuses on lifelong anticoagulation to prevent future episodes.Acute pancreatits
Acute pancreatitsJawad Ahmad
Ěý
This document provides an overview of acute pancreatitis including its anatomy, epidemiology, pathophysiology, etiology, clinical presentation, workup, severity scoring, treatment, prognosis, and complications. It begins with definitions of the pancreas' anatomy and functions. It then discusses the disease's worldwide incidence, risk factors, presentations, diagnostic criteria, hematological and radiological evaluations, and key findings on imaging studies like CT scans. The document provides a comprehensive review of acute pancreatitis.Adrenal cushings
Adrenal cushingsMohammad Gamal
Ěý
This case report describes a 33-year-old male patient who presented with multiple skin lesions and chest pain. After initial treatment by a dermatologist and pulmonologist, he was found to have high blood pressure. Further investigation revealed elevated cortisol levels and a mass in his right adrenal gland. He was diagnosed with Cushing's syndrome caused by an adrenal adenoma. Cushing's syndrome results from excess glucocorticoid exposure and affects multiple body systems. Correct diagnosis requires a careful clinical assessment and laboratory tests including cortisol levels and imaging of the pituitary and adrenal glands. The patient was referred for surgical removal of the adrenal tumor as the treatment for his condition. Abdominal Compartment Syndrome
Abdominal Compartment SyndromeMarijan Tepeš
Ěý
The document presents updated consensus definitions and clinical practice guidelines for intra-abdominal hypertension and abdominal compartment syndrome from the World Society of the Abdominal Compartment Syndrome. It retains definitions from 2006 and introduces new definitions accepted by the 2012 consensus panel. It provides recommendations and suggestions regarding measuring intra-abdominal pressure, adopting standard measurement techniques, utilizing monitoring and management protocols, and using decompressive laparotomy for overt abdominal compartment syndrome. The recommendations and suggestions are assigned grades based on quality of evidence.WSACS Definitions
WSACS DefinitionsAndrew Ferguson
Ěý
This document presents definitions agreed upon by experts for intra-abdominal hypertension (IAH) and abdominal compartment syndrome (ACS). IAH is defined as an intra-abdominal pressure of 12 mmHg or higher and is graded based on severity. ACS occurs when IAH is over 20 mmHg and is associated with new organ dysfunction. The definitions standardize measurement of intra-abdominal pressure via bladder at 25 ml saline and establish abdominal perfusion pressure as key. Primary ACS originates in the abdomen while secondary ACS occurs elsewhere and can recur after initial treatment.Abdominal compartmental Syndrom
Abdominal compartmental SyndromMuhammad Badawi
Ěý
This document summarizes a case of abdominal compartment syndrome in a 26-year-old man following a road traffic accident. He developed increased ventilatory requirements, metabolic acidosis, and oliguria despite resuscitation, and was found to have a tense abdomen. Measurement found his intra-abdominal pressure to be elevated at 28cmH20, confirming abdominal compartment syndrome. He underwent decompressive laparotomy, which reduced his ventilatory needs. He developed subsequent complications but ultimately recovered with abdominal closure and pelvic fixation.General principles of surgery - medical finals revision notes
General principles of surgery - medical finals revision notesChristiane Riedinger
Ěý
1) This document provides an overview of general principles for surgical management, including pre-operative assessment and optimization of medical conditions, guidelines for fluid treatment and antibiotic prophylaxis, and considerations for specific diseases.
2) Key aspects of pre-op management discussed include reviewing medications, performing tests like ECG and imaging, addressing comorbidities, and obtaining informed consent.
3) Fluid treatment principles focus on maintaining fluid and electrolyte balance, with crystalloids being preferred to colloids due to safety concerns. Goals include compensation for losses in different fluid compartments.Damage control surgery
Damage control surgeryBashir BnYunus
Ěý
Damage control surgery involves rapidly controlling hemorrhaging and contamination through temporary closure of injuries to stabilize critically injured patients, followed by resuscitation and definitive repair once physiology is restored. It aims to prevent the lethal triad of hypothermia, acidosis, and coagulopathy. The approach has three stages - initial laparotomy and packing, ICU resuscitation, and planned reoperation once metabolic conditions improve. It has been shown to improve survival rates for severely injured trauma patients compared to traditional surgery.Upper gi bleeding
Upper gi bleedingAziza ʚïɞ
Ěý
This document provides information on the evaluation and management of upper gastrointestinal bleeding. It reviews the major causes of upper GI bleeding, important aspects of the history and physical exam, diagnostic evaluation, and acute management. A case is presented of a 67 year old man with a history of NSAID use who presents with coffee ground emesis and is found to have anemia. His likely cause is a peptic ulcer or gastritis. His initial management includes IV fluids, monitoring, PPI treatment, and GI consultation.Abdominal compartment syndrome
Abdominal compartment syndromeMEEQAT HOSPITAL
Ěý
This document discusses abdominal compartment syndrome (ACS), which refers to organ dysfunction caused by increased intra-abdominal pressure known as intra-abdominal hypertension (IAH). The key points are:
1. ACS can impair nearly every organ system but is often underdiagnosed. Diagnosis requires measuring intra-abdominal pressure via bladder catheter.
2. Management consists of supportive care initially but may require surgical decompression of the abdomen in severe cases.
3. Following decompression, temporary abdominal closure techniques are used until definitive closure can be achieved or a planned hernia results.Abdominal compartment syndrome and septic abdomen
Abdominal compartment syndrome and septic abdomenAleksandar Gluhović
Ěý
The document discusses abdominal compartment syndrome (ACS) and intra-abdominal hypertension (IAH), providing definitions, classifications, and physiological consequences related to these conditions. It outlines risk factors for IAH/ACS, management recommendations, and monitoring techniques for intra-abdominal pressure, along with the need for comprehensive intervention trials. The document emphasizes the serious implications of IAH/ACS on multiple organ systems and the importance of timely medical responses.Lower gi bleed
Lower gi bleedAsraf Hussain
Ěý
This document provides an overview of lower gastrointestinal bleeding (LGIB), including its definition, etiology, clinical features, diagnostic and therapeutic approaches. It discusses how LGIB accounts for 20% of gastrointestinal bleeding cases and can be safely managed in an outpatient setting once initial resuscitation and risk evaluation is complete. Colonoscopy is highlighted as the first-line investigation, while angiography and surgery are reserved for more severe or refractory cases. The overall mortality rate of LGIB is reported to be less than 5%.Abdominal Compartment Syndrome
Abdominal Compartment Syndromepradeep495
Ěý
The document defines key terms related to intra-abdominal pressure (IAP) including intra-abdominal hypertension (IAH) and abdominal compartment syndrome (ACS). It discusses the physiologic consequences of increased IAP on multiple organ systems. Diagnosis of ACS requires IAP measurement, typically via intravesicular bladder pressure. Management focuses on supportive care to reduce IAP as well as surgical decompression for severe or refractory cases. Complications of an open abdomen include fluid/protein loss and fistula formation.Abdominal Comparment Syndrome
Abdominal Comparment SyndromeDene W. Daugherty
Ěý
This document discusses abdominal compartment syndrome, which occurs when intra-abdominal pressure increases due to fluid accumulation in the abdominal space from trauma, surgery, edema, or tumor growth. As pressure rises, blood flow to organs is compromised, which can lead to organ dysfunction or failure and death if left untreated. Early detection and treatment are important to prevent multiple organ failure. The document defines grades of intra-abdominal hypertension and abdominal compartment syndrome and discusses causes, pathophysiology, measurement, and impact on organ systems.Intra-abdominal hypertension and abdominal compartment syndrome
Intra-abdominal hypertension and abdominal compartment syndromeNicholas Leary
Ěý
Intra-abdominal hypertension (IAH) and abdominal compartment syndrome (ACS) are conditions characterized by elevated intra-abdominal pressure, with ACS being a medical emergency. These conditions can occur in both trauma and medical patients, with a notable prevalence in critical care populations. Monitoring intra-abdominal pressure and optimizing treatment strategies are essential for managing these conditions effectively.SCORING AND RISK STRATIFICATION OF ACUTE PANCREATITIS
SCORING AND RISK STRATIFICATION OF ACUTE PANCREATITISArkaprovo Roy
Ěý
The document discusses various classification systems and severity scoring methods for acute pancreatitis (AP), including the revised Atlanta classification. It recommends early severity stratification within 48 hours using methods like Glasgow score and CRP. The APACHE II score can be used for initial assessment and monitoring of severe cases in order to predict outcomes and guide management, which may include referral to specialist units for organ failure or local complications. Accurate classification and scoring is important for individualizing treatment protocols based on severity.Management of upper gi bleeding email copy
Management of upper gi bleeding email copynadiagulnaz
Ěý
- Acute upper gastrointestinal bleeding is a common medical emergency that can have high mortality.
- Risk assessment using tools like the Blatchford and Rockall scores helps determine urgency of endoscopy and predict outcomes.
- Endoscopy within 24 hours of admission is recommended to treat bleeding lesions through methods like injection, thermal coagulation, or band ligation of varices.
- Post-endoscopic management involves PPIs, transfusions targeting a hemoglobin of 70-90 g/L, H. pylori treatment if present, and continued medications like terlipressin or beta blockers to prevent rebleeding.Arhi morb
Arhi morb Arthi Rajasankar
Ěý
Dr. Yasha, Dr. Tina, Dr. Arthi, and Dr. Janani treated a 55-year-old female patient with a retroperitoneal mass, septic shock, acute kidney injury (AKI), and severe metabolic acidosis. She presented with a history of diarrhea, vomiting, and decreased urine output. Imaging showed dilated bowel loops and ascites consistent with small intestinal obstruction. The patient was intubated, started on vasopressors, and underwent an exploratory laparotomy which revealed a retroperitoneal mass causing obstruction. Despite resuscitative measures including hemodialysis, bicarbonate infusion, and escalating vasopressors, her condition deteriorated and sheUpper git bleeding
Upper git bleeding HAMAD DHUHAYR
Ěý
A 53-year-old woman presented with abdominal pain and vomiting blood. Her symptoms indicated upper gastrointestinal bleeding. The most common causes of upper GI bleeding are esophageal varices, acute gastric erosions caused by NSAIDs, acute hemorrhagic gastritis, and chronic duodenal ulcers. Initial management involves resuscitation through intravenous fluids and blood transfusions. Endoscopy is important to localize the source of bleeding and allow for potential treatment. The endoscopy may reveal varices, ulcers, or erosions as the cause. Angiography can help diagnose bleeding from rare sources if endoscopy is inconclusive.Abdominal Compartment Syndrome
Abdominal Compartment Syndrome AlaaZeineh
Ěý
Abdominal compartment syndrome (ACS) occurs when sustained elevated intra-abdominal pressure above 20 mmHg is associated with new organ dysfunction. Risk factors include aggressive fluid resuscitation, burns over 30% total body surface area, liver transplantation, and abdominal/retroperitoneal conditions. Physiologic consequences of increased intra-abdominal pressure include decreased cardiac preload and output, impaired pulmonary and renal function, and reduced splanchnic blood flow. Definitive diagnosis requires direct measurement of intra-abdominal pressure. Management involves supportive care, surgical decompression if medical therapies fail, and temporary abdominal closure during open abdomen treatment. Failure to recognize ACS can lead to multiple organ failure and death in 40Abdominal compartment syndrome[1]
Abdominal compartment syndrome[1]Mahmoud El-saharty
Ěý
This document discusses abdominal compartment syndrome (ACS), an underrecognized cause of acute kidney injury. It defines ACS as multiple organ dysfunction caused by elevated intra-abdominal pressure. The document outlines various causes of increased intra-abdominal pressure and the physiologic manifestations of ACS, which can impact the cardiac, pulmonary, gastrointestinal, renal and neurological systems. Left untreated, ACS can lead to multi-system organ failure and death. Early detection of increased intra-abdominal pressure and treatment, including decompressive laparotomy if needed, are important to prevent complications of ACS.Weaning ventilator
Weaning ventilatorHappyFridayKnight
Ěý
This randomized controlled trial compared two spontaneous breathing trial (SBT) strategies: a 2-hour T-piece trial versus a 30-minute trial with pressure support ventilation (PSV) of 8 cmH2O. The Kaplan-Meier curves showed a significantly higher rate of successful extubation, defined as being free of invasive ventilation for 72 hours, in the PSV group compared to the T-piece group. Reasons for reintubation were not significantly different between groups. While the T-piece SBT was less well tolerated, the PSV SBT of 30 minutes was sufficient to assess breathing ability without increasing post-extubation respiratory failure rates.Vaccines during pregnancy HY
Vaccines during pregnancy HYRickettsia Rickettsii
Ěý
Vaccines during pregnancy are recommended for Tdap, inactive influenza, and Rho(D) immunoglobulin. Hepatitis B, hepatitis A, pneumococcus, haemophilus influenzae, meningococcus, and varicella-zoster immunoglobulin are indicated for high-risk patients. HPV, MMR, live attenuated influenza, and varicella are contraindicated during pregnancy.Urinary tract infection in children HY
Urinary tract infection in children HYRickettsia Rickettsii
Ěý
Urinary tract infections in children can be caused by female sex, uncircumcised males, anatomical defects, dysfunctional voiding, or constipation. Symptoms include dysuria, fever, and pain in the bladder area or back/flank. Diagnosis involves finding white blood cells and bacteria in the urine. Treatment is with antibiotic therapy and sometimes additional imaging tests.More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Adrenal cushings
Adrenal cushingsMohammad Gamal
Ěý
This case report describes a 33-year-old male patient who presented with multiple skin lesions and chest pain. After initial treatment by a dermatologist and pulmonologist, he was found to have high blood pressure. Further investigation revealed elevated cortisol levels and a mass in his right adrenal gland. He was diagnosed with Cushing's syndrome caused by an adrenal adenoma. Cushing's syndrome results from excess glucocorticoid exposure and affects multiple body systems. Correct diagnosis requires a careful clinical assessment and laboratory tests including cortisol levels and imaging of the pituitary and adrenal glands. The patient was referred for surgical removal of the adrenal tumor as the treatment for his condition. Abdominal Compartment Syndrome
Abdominal Compartment SyndromeMarijan Tepeš
Ěý
The document presents updated consensus definitions and clinical practice guidelines for intra-abdominal hypertension and abdominal compartment syndrome from the World Society of the Abdominal Compartment Syndrome. It retains definitions from 2006 and introduces new definitions accepted by the 2012 consensus panel. It provides recommendations and suggestions regarding measuring intra-abdominal pressure, adopting standard measurement techniques, utilizing monitoring and management protocols, and using decompressive laparotomy for overt abdominal compartment syndrome. The recommendations and suggestions are assigned grades based on quality of evidence.WSACS Definitions
WSACS DefinitionsAndrew Ferguson
Ěý
This document presents definitions agreed upon by experts for intra-abdominal hypertension (IAH) and abdominal compartment syndrome (ACS). IAH is defined as an intra-abdominal pressure of 12 mmHg or higher and is graded based on severity. ACS occurs when IAH is over 20 mmHg and is associated with new organ dysfunction. The definitions standardize measurement of intra-abdominal pressure via bladder at 25 ml saline and establish abdominal perfusion pressure as key. Primary ACS originates in the abdomen while secondary ACS occurs elsewhere and can recur after initial treatment.Abdominal compartmental Syndrom
Abdominal compartmental SyndromMuhammad Badawi
Ěý
This document summarizes a case of abdominal compartment syndrome in a 26-year-old man following a road traffic accident. He developed increased ventilatory requirements, metabolic acidosis, and oliguria despite resuscitation, and was found to have a tense abdomen. Measurement found his intra-abdominal pressure to be elevated at 28cmH20, confirming abdominal compartment syndrome. He underwent decompressive laparotomy, which reduced his ventilatory needs. He developed subsequent complications but ultimately recovered with abdominal closure and pelvic fixation.General principles of surgery - medical finals revision notes
General principles of surgery - medical finals revision notesChristiane Riedinger
Ěý
1) This document provides an overview of general principles for surgical management, including pre-operative assessment and optimization of medical conditions, guidelines for fluid treatment and antibiotic prophylaxis, and considerations for specific diseases.
2) Key aspects of pre-op management discussed include reviewing medications, performing tests like ECG and imaging, addressing comorbidities, and obtaining informed consent.
3) Fluid treatment principles focus on maintaining fluid and electrolyte balance, with crystalloids being preferred to colloids due to safety concerns. Goals include compensation for losses in different fluid compartments.Damage control surgery
Damage control surgeryBashir BnYunus
Ěý
Damage control surgery involves rapidly controlling hemorrhaging and contamination through temporary closure of injuries to stabilize critically injured patients, followed by resuscitation and definitive repair once physiology is restored. It aims to prevent the lethal triad of hypothermia, acidosis, and coagulopathy. The approach has three stages - initial laparotomy and packing, ICU resuscitation, and planned reoperation once metabolic conditions improve. It has been shown to improve survival rates for severely injured trauma patients compared to traditional surgery.Upper gi bleeding
Upper gi bleedingAziza ʚïɞ
Ěý
This document provides information on the evaluation and management of upper gastrointestinal bleeding. It reviews the major causes of upper GI bleeding, important aspects of the history and physical exam, diagnostic evaluation, and acute management. A case is presented of a 67 year old man with a history of NSAID use who presents with coffee ground emesis and is found to have anemia. His likely cause is a peptic ulcer or gastritis. His initial management includes IV fluids, monitoring, PPI treatment, and GI consultation.Abdominal compartment syndrome
Abdominal compartment syndromeMEEQAT HOSPITAL
Ěý
This document discusses abdominal compartment syndrome (ACS), which refers to organ dysfunction caused by increased intra-abdominal pressure known as intra-abdominal hypertension (IAH). The key points are:
1. ACS can impair nearly every organ system but is often underdiagnosed. Diagnosis requires measuring intra-abdominal pressure via bladder catheter.
2. Management consists of supportive care initially but may require surgical decompression of the abdomen in severe cases.
3. Following decompression, temporary abdominal closure techniques are used until definitive closure can be achieved or a planned hernia results.Abdominal compartment syndrome and septic abdomen
Abdominal compartment syndrome and septic abdomenAleksandar Gluhović
Ěý
The document discusses abdominal compartment syndrome (ACS) and intra-abdominal hypertension (IAH), providing definitions, classifications, and physiological consequences related to these conditions. It outlines risk factors for IAH/ACS, management recommendations, and monitoring techniques for intra-abdominal pressure, along with the need for comprehensive intervention trials. The document emphasizes the serious implications of IAH/ACS on multiple organ systems and the importance of timely medical responses.Lower gi bleed
Lower gi bleedAsraf Hussain
Ěý
This document provides an overview of lower gastrointestinal bleeding (LGIB), including its definition, etiology, clinical features, diagnostic and therapeutic approaches. It discusses how LGIB accounts for 20% of gastrointestinal bleeding cases and can be safely managed in an outpatient setting once initial resuscitation and risk evaluation is complete. Colonoscopy is highlighted as the first-line investigation, while angiography and surgery are reserved for more severe or refractory cases. The overall mortality rate of LGIB is reported to be less than 5%.Abdominal Compartment Syndrome
Abdominal Compartment Syndromepradeep495
Ěý
The document defines key terms related to intra-abdominal pressure (IAP) including intra-abdominal hypertension (IAH) and abdominal compartment syndrome (ACS). It discusses the physiologic consequences of increased IAP on multiple organ systems. Diagnosis of ACS requires IAP measurement, typically via intravesicular bladder pressure. Management focuses on supportive care to reduce IAP as well as surgical decompression for severe or refractory cases. Complications of an open abdomen include fluid/protein loss and fistula formation.Abdominal Comparment Syndrome
Abdominal Comparment SyndromeDene W. Daugherty
Ěý
This document discusses abdominal compartment syndrome, which occurs when intra-abdominal pressure increases due to fluid accumulation in the abdominal space from trauma, surgery, edema, or tumor growth. As pressure rises, blood flow to organs is compromised, which can lead to organ dysfunction or failure and death if left untreated. Early detection and treatment are important to prevent multiple organ failure. The document defines grades of intra-abdominal hypertension and abdominal compartment syndrome and discusses causes, pathophysiology, measurement, and impact on organ systems.Intra-abdominal hypertension and abdominal compartment syndrome
Intra-abdominal hypertension and abdominal compartment syndromeNicholas Leary
Ěý
Intra-abdominal hypertension (IAH) and abdominal compartment syndrome (ACS) are conditions characterized by elevated intra-abdominal pressure, with ACS being a medical emergency. These conditions can occur in both trauma and medical patients, with a notable prevalence in critical care populations. Monitoring intra-abdominal pressure and optimizing treatment strategies are essential for managing these conditions effectively.SCORING AND RISK STRATIFICATION OF ACUTE PANCREATITIS
SCORING AND RISK STRATIFICATION OF ACUTE PANCREATITISArkaprovo Roy
Ěý
The document discusses various classification systems and severity scoring methods for acute pancreatitis (AP), including the revised Atlanta classification. It recommends early severity stratification within 48 hours using methods like Glasgow score and CRP. The APACHE II score can be used for initial assessment and monitoring of severe cases in order to predict outcomes and guide management, which may include referral to specialist units for organ failure or local complications. Accurate classification and scoring is important for individualizing treatment protocols based on severity.Management of upper gi bleeding email copy
Management of upper gi bleeding email copynadiagulnaz
Ěý
- Acute upper gastrointestinal bleeding is a common medical emergency that can have high mortality.
- Risk assessment using tools like the Blatchford and Rockall scores helps determine urgency of endoscopy and predict outcomes.
- Endoscopy within 24 hours of admission is recommended to treat bleeding lesions through methods like injection, thermal coagulation, or band ligation of varices.
- Post-endoscopic management involves PPIs, transfusions targeting a hemoglobin of 70-90 g/L, H. pylori treatment if present, and continued medications like terlipressin or beta blockers to prevent rebleeding.Arhi morb
Arhi morb Arthi Rajasankar
Ěý
Dr. Yasha, Dr. Tina, Dr. Arthi, and Dr. Janani treated a 55-year-old female patient with a retroperitoneal mass, septic shock, acute kidney injury (AKI), and severe metabolic acidosis. She presented with a history of diarrhea, vomiting, and decreased urine output. Imaging showed dilated bowel loops and ascites consistent with small intestinal obstruction. The patient was intubated, started on vasopressors, and underwent an exploratory laparotomy which revealed a retroperitoneal mass causing obstruction. Despite resuscitative measures including hemodialysis, bicarbonate infusion, and escalating vasopressors, her condition deteriorated and sheUpper git bleeding
Upper git bleeding HAMAD DHUHAYR
Ěý
A 53-year-old woman presented with abdominal pain and vomiting blood. Her symptoms indicated upper gastrointestinal bleeding. The most common causes of upper GI bleeding are esophageal varices, acute gastric erosions caused by NSAIDs, acute hemorrhagic gastritis, and chronic duodenal ulcers. Initial management involves resuscitation through intravenous fluids and blood transfusions. Endoscopy is important to localize the source of bleeding and allow for potential treatment. The endoscopy may reveal varices, ulcers, or erosions as the cause. Angiography can help diagnose bleeding from rare sources if endoscopy is inconclusive.Abdominal Compartment Syndrome
Abdominal Compartment Syndrome AlaaZeineh
Ěý
Abdominal compartment syndrome (ACS) occurs when sustained elevated intra-abdominal pressure above 20 mmHg is associated with new organ dysfunction. Risk factors include aggressive fluid resuscitation, burns over 30% total body surface area, liver transplantation, and abdominal/retroperitoneal conditions. Physiologic consequences of increased intra-abdominal pressure include decreased cardiac preload and output, impaired pulmonary and renal function, and reduced splanchnic blood flow. Definitive diagnosis requires direct measurement of intra-abdominal pressure. Management involves supportive care, surgical decompression if medical therapies fail, and temporary abdominal closure during open abdomen treatment. Failure to recognize ACS can lead to multiple organ failure and death in 40Abdominal compartment syndrome[1]
Abdominal compartment syndrome[1]Mahmoud El-saharty
Ěý
This document discusses abdominal compartment syndrome (ACS), an underrecognized cause of acute kidney injury. It defines ACS as multiple organ dysfunction caused by elevated intra-abdominal pressure. The document outlines various causes of increased intra-abdominal pressure and the physiologic manifestations of ACS, which can impact the cardiac, pulmonary, gastrointestinal, renal and neurological systems. Left untreated, ACS can lead to multi-system organ failure and death. Early detection of increased intra-abdominal pressure and treatment, including decompressive laparotomy if needed, are important to prevent complications of ACS.Weaning ventilator
Weaning ventilatorHappyFridayKnight
Ěý
This randomized controlled trial compared two spontaneous breathing trial (SBT) strategies: a 2-hour T-piece trial versus a 30-minute trial with pressure support ventilation (PSV) of 8 cmH2O. The Kaplan-Meier curves showed a significantly higher rate of successful extubation, defined as being free of invasive ventilation for 72 hours, in the PSV group compared to the T-piece group. Reasons for reintubation were not significantly different between groups. While the T-piece SBT was less well tolerated, the PSV SBT of 30 minutes was sufficient to assess breathing ability without increasing post-extubation respiratory failure rates.More from Rickettsia Rickettsii (20)
Vaccines during pregnancy HY
Vaccines during pregnancy HYRickettsia Rickettsii
Ěý
Vaccines during pregnancy are recommended for Tdap, inactive influenza, and Rho(D) immunoglobulin. Hepatitis B, hepatitis A, pneumococcus, haemophilus influenzae, meningococcus, and varicella-zoster immunoglobulin are indicated for high-risk patients. HPV, MMR, live attenuated influenza, and varicella are contraindicated during pregnancy.Urinary tract infection in children HY
Urinary tract infection in children HYRickettsia Rickettsii
Ěý
Urinary tract infections in children can be caused by female sex, uncircumcised males, anatomical defects, dysfunctional voiding, or constipation. Symptoms include dysuria, fever, and pain in the bladder area or back/flank. Diagnosis involves finding white blood cells and bacteria in the urine. Treatment is with antibiotic therapy and sometimes additional imaging tests.Uric acid kidney stones HY
Uric acid kidney stones HYRickettsia Rickettsii
Ěý
Uric acid kidney stones can form when urine is too acidic, causing uric acid to precipitate into crystals and stones. Risk factors include gout, dehydration, and conditions causing low urine pH like diarrhea or diabetes. Treatment involves raising urine pH through potassium citrate to keep uric acid dissolved in the urine and prevent stone formation.Tourette syndrome HY
Tourette syndrome HYRickettsia Rickettsii
Ěý
Tourette syndrome is a disorder characterized by both multiple motor and at least one vocal tic occurring for over one year. Common motor tics include facial grimacing and head jerking, while vocal tics include grunting and yelling. Treatment options include behavioral therapy, medications that impact dopamine such as antipsychotics and tetrabenazine, and alpha-2 adrenergic receptor agonists.Systemic lupus erythematosus HY
Systemic lupus erythematosus HYRickettsia Rickettsii
Ěý
Systemic lupus erythematosus is an autoimmune disease characterized by gradual onset of symptoms such as a malar or discoid rash, joint pain, kidney problems, serosal involvement, or neurological issues. Laboratory tests typically show anemia, low white and platelet blood cell counts, positive antinuclear antibody, anti-double stranded DNA and anti-Smith tests, as well as low complement levels and increased immune complexes.Suspected gastrinoma HY
Suspected gastrinoma HYRickettsia Rickettsii
Ěý
The patient presented with multiple stomach ulcers and thickened gastric folds. To check for a possible gastrinoma, doctors measured the patient's serum gastrin level after stopping proton pump inhibitor therapy for a week, and performed a secretin stimulation test. Based on the results, further testing was recommended to localize a gastrinoma.Spikes protocol for delivering serious news HY
Spikes protocol for delivering serious news HYRickettsia Rickettsii
Ěý
The SPIKES protocol outlines six steps for delivering serious medical news to patients and their families: set the stage by arranging a private setting and introducing everyone; assess their perception of the situation; invite them to share how much information they want; provide knowledge of the situation in a clear and empathetic manner while checking for understanding; express empathy in response to emotions; and summarize by creating a follow-up plan.Side effects & risks of combination oral contraceptives HY
Side effects & risks of combination oral contraceptives HYRickettsia Rickettsii
Ěý
Combination oral contraceptives can cause side effects like breakthrough bleeding, breast tenderness, nausea, bloating, and amenorrhea. They also carry risks such as hypertension, blood clots, and increased triglycerides. However, combination oral contraceptives decrease the risk of ovarian and endometrial cancers while increasing the risk of cervical cancer.Scurvy (vitamin c deficiency) HY
Scurvy (vitamin c deficiency) HYRickettsia Rickettsii
Ěý
Scurvy is caused by vitamin C deficiency due to insufficient dietary intake of citrus fruits and vegetables. It commonly affects those with alcohol or substance use disorders and severe malnutrition. Symptoms include skin hemorrhages, bleeding gums, joint pain, fatigue, and impaired wound healing. Treatment involves oral or injected vitamin C supplementation, which resolves most symptoms within days, though excessive doses can cause side effects like abdominal pain.Retroperitoneal abdominal organs HY
Retroperitoneal abdominal organs HYRickettsia Rickettsii
Ěý
This document lists retroperitoneal abdominal organs such as the adrenal glands, aorta, inferior vena cava, parts of the duodenum, pancreas, ureters, parts of the colon, kidneys, esophagus, and parts of the rectum. It provides a mnemonic - SAD PUCKER - to help remember these retroperitoneal organs and notes that some organs like the duodenum, pancreas and colon are secondarily retroperitoneal having developed intraperitoneally and migrated retroperitoneally.Red blood cell transfusion thresholds HY
Red blood cell transfusion thresholds HYRickettsia Rickettsii
Ěý
This document provides recommendations for red blood cell transfusion thresholds based on hemoglobin levels. Transfusions are generally indicated for hemoglobin levels below 7 g/dL, may be considered for levels between 7-8 g/dL depending on factors like cardiac surgery or cancer treatment, and are not generally recommended above 10 g/dL.Panic disorder HY
Panic disorder HYRickettsia Rickettsii
Ěý
Panic disorder is characterized by recurrent, unexpected panic attacks involving physical symptoms like chest pain, palpitations, shortness of breath, trembling, and feelings of choking, as well as cognitive symptoms such as fear of losing control or dying. Treatment involves first-line therapies of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) or serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) and/or cognitive-behavioral therapy for maintenance, and benzodiazepines can be used for acute distress from panic attacks.Normal postpartum lochia HY
Normal postpartum lochia HYRickettsia Rickettsii
Ěý
Lochia rubra lasts from birth to 3-4 days postpartum and consists of dark or bright red blood and clots. Lochia serosa lasts from days 4-10 or 14 and is pink or brown blood that gradually decreases. Lochia alba lasts from days 11-6 weeks and is white or yellow and light in quantity. Lochia may increase with breastfeeding or sloughing of the placental site scab around days 7-14.Noninvasive positive pressure ventilation HY
Noninvasive positive pressure ventilation HYRickettsia Rickettsii
Ěý
Noninvasive positive pressure ventilation (NPPV) is recommended for patients with severe COPD exacerbation, cardiogenic pulmonary edema, acute respiratory failure, postoperative hypoxemic respiratory failure, and immunosuppressed patients to facilitate early extubation. Contraindications for NPPV include medical instability such as cardiac or respiratory arrest, severe acidosis, acute respiratory distress syndrome, nonrespiratory organ failure, unstable cardiac arrhythmias or hemodynamic instability, encephalopathy, or gastrointestinal bleeding. Inability to protect the airway due to being uncooperative, agitated, or unable to clear secretions with a high aspiration risk are also contraindications. Mechanical issues like a recent esophageal anastomosis orManagement of endometriosis HY
Management of endometriosis HYRickettsia Rickettsii
Ěý
This document provides guidance on managing endometriosis. It lists symptoms that could indicate suspected endometriosis such as chronic pelvic pain, painful periods, painful sex, and painful bowel movements. For patients with suspected endometriosis, the document recommends considering over-the-counter pain relievers and birth control pills initially, and performing a laparoscopy if symptoms do not improve or if there are concerns about infertility, medical contraindications, need for diagnosis, or potential malignancy.Lung cancer HY
Lung cancer HYRickettsia Rickettsii
Ěý
This document discusses the four main types of lung cancer: adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, small cell carcinoma, and large cell carcinoma. It provides information on the incidence, typical location in the lungs, and common clinical associations for each type of lung cancer. Adenocarcinoma makes up 40-50% of lung cancers and is usually located in the periphery of the lungs. Squamous cell carcinoma accounts for 20-25% of cases and is typically central. Small cell carcinoma comprises 10-15% of lung cancers and is also usually central. Large cell carcinoma represents 5-10% of lung cancers and tends to be peripheral.Leukocyte adhesion deficiency HY
Leukocyte adhesion deficiency HYRickettsia Rickettsii
Ěý
Leukocyte adhesion deficiency is caused by a defect in CD18-containing integrins, which impairs leukocyte adhesion and endothelial transmigration. This results in recurrent skin and mucosal infections without pus formation, impaired wound healing, and delayed umbilical cord separation beyond 3 weeks of age. Laboratory findings include leukocytosis and neutrophilia.Intrauterine fetal demise HY
Intrauterine fetal demise HYRickettsia Rickettsii
Ěý
Intrauterine fetal demise is defined as fetal death at 20 weeks or later. It is diagnosed by the absence of fetal cardiac activity on ultrasound. Management depends on gestational age - between 20-23 weeks dilation and evacuation or vaginal delivery is recommended, while at 24 weeks or later vaginal delivery is recommended, though cesarean delivery is an option based on maternal history. A complication can be coagulopathy if the fetus is retained for several weeks.Infectious mononucleosis HY
Infectious mononucleosis HYRickettsia Rickettsii
Ěý
Infectious mononucleosis is characterized by fever, tonsillitis or pharyngitis that may have exudates, enlarged lymph nodes in the neck, fatigue, and possibly enlargement of the liver and spleen. Complications can include airway obstruction, autoimmune conditions affecting red blood cells or platelets, and rupture of the spleen.Indications for urgent dialysis (aeiou) HY
Indications for urgent dialysis (aeiou) HYRickettsia Rickettsii
Ěý
Acidosis, electrolyte abnormalities, ingestion of toxic substances, overload states, and uremia are indications for urgent dialysis according to the AEIOU mnemonic. Specifically, metabolic acidosis with a pH below 7.1, hyperkalemia causing ECG changes or arrhythmias, ingestion of toxic alcohols, volume overload refractory to diuretics, and uremia causing encephalopathy, pericarditis or bleeding require immediate dialysis treatment.Ad
Recently uploaded (20)
How to Customize Quotation Layouts in Odoo 18
How to Customize Quotation Layouts in Odoo 18Celine George
Ěý
Customizing quotation layouts in Odoo 18 allows businesses to personalize their quotations to match branding or specific requirements. This can include adding logos, custom fields, or modifying headers and footers. M&A5 Q1 1 differentiate evolving early Philippine conventional and contempora...
M&A5 Q1 1 differentiate evolving early Philippine conventional and contempora...ErlizaRosete
Ěý
MAPEH 6 QI WEEK IAprendendo Arquitetura Framework Salesforce - Dia 02
Aprendendo Arquitetura Framework Salesforce - Dia 02Mauricio Alexandre Silva
Ěý
Aprendendo Arquitetura Framework Salesforce - Dia 02
How to use search fetch method in Odoo 18
How to use search fetch method in Odoo 18Celine George
Ěý
The search_fetch is a powerful ORM method used in Odoo for some specific addons to combine the functionality of search and read for more efficient data fetching. It might be used to search for records and fetch specific fields in a single call. It stores the result in the cache memory.CRYPTO TRADING COURSE BY FINANCEWORLD.IO
CRYPTO TRADING COURSE BY FINANCEWORLD.IOAndrewBorisenko3
Ěý
Unlock the Secrets of Crypto Trading with FinanceWorld.io!
Are you ready to dive into the exciting world of cryptocurrency trading? This comprehensive course by FinanceWorld.io is designed for beginners and intermediate traders who want to master the fundamentals of crypto markets, technical analysis, risk management, and trading strategies.
What you’ll learn:
Introduction to blockchain and cryptocurrencies
How crypto markets work
Setting up wallets and trading accounts securely
Understanding exchanges and order types
Reading charts and technical analysis basics
Essential indicators and market signals
Risk management and portfolio diversification
Real-life trading strategies and case studies
Common mistakes and how to avoid them
Who should view this course?
Aspiring crypto traders
Investors seeking additional income sources
Anyone curious about the future of decentralized finance
Why FinanceWorld.io?
Our experts make complex concepts simple, helping you gain the confidence to navigate volatile markets and capitalize on opportunities.
Ready to start your crypto journey?
View this slide deck now and take your first step towards becoming a successful crypto trader with FinanceWorld.io!Paper 107 | From Watchdog to Lapdog: Ishiguro’s Fiction and the Rise of “Godi...
Paper 107 | From Watchdog to Lapdog: Ishiguro’s Fiction and the Rise of “Godi...Rajdeep Bavaliya
Ěý
Dive into a captivating analysis where Kazuo Ishiguro’s nuanced fiction meets the stark realities of post‑2014 Indian journalism. Uncover how “Godi Media” turned from watchdog to lapdog, echoing the moral compromises of Ishiguro’s protagonists. We’ll draw parallels between restrained narrative silences and sensationalist headlines—are our media heroes or traitors? Don’t forget to follow for more deep dives!
M.A. Sem - 2 | Presentation
Presentation Season - 2
Paper - 107: The Twentieth Century Literature: From World War II to the End of the Century
Submitted Date: April 4, 2025
Paper Name: The Twentieth Century Literature: From World War II to the End of the Century
Topic: From Watchdog to Lapdog: Ishiguro’s Fiction and the Rise of “Godi Media” in Post-2014 Indian Journalism
[Please copy the link and paste it into any web browser to access the content.]
Video Link: https://youtu.be/kIEqwzhHJ54
For a more in-depth discussion of this presentation, please visit the full blog post at the following link: https://rajdeepbavaliya2.blogspot.com/2025/04/from-watchdog-to-lapdog-ishiguro-s-fiction-and-the-rise-of-godi-media-in-post-2014-indian-journalism.html
Please visit this blog to explore additional presentations from this season:
Hashtags:
#GodiMedia #Ishiguro #MediaEthics #WatchdogVsLapdog #IndianJournalism #PressFreedom #LiteraryCritique #AnArtistOfTheFloatingWorld #MediaCapture #KazuoIshiguro
Keyword Tags:
Godi Media, Ishiguro fiction, post-2014 Indian journalism, media capture, Kazuo Ishiguro analysis, watchdog to lapdog, press freedom India, media ethics, literature and media, An Artist of the Floating WorldLDMMIA Yoga S10 Free Workshop Grad Level
LDMMIA Yoga S10 Free Workshop Grad LevelLDM & Mia eStudios
Ěý
This is complete for June 17th. For the weekend of Summer Solstice
June 20th-22nd.
6/17/25: “My now Grads, You’re doing well. I applaud your efforts to continue. We all are shifting to new paradigm realities. Its rough, there’s good and bad days/weeks. However, Reiki with Yoga assistance, does work.”
6/18/25: "For those planning the Training Program Do Welcome. Happy Summer 2k25. You are not ignored and much appreciated. Our updates are ongoing and weekly since Spring. I Hope you Enjoy the Practitioner Grad Level. There's more to come. We will also be wrapping up Level One. So I can work on Levels 2 topics. Please see documents for any news updates. Also visit our websites. Every decade I release a Campus eMap. I will work on that for summer 25. We have 2 old libraries online thats open. https://ldmchapels.weebly.com "
Our Monthly Class Roster is 7,141 for 6/21.
ALL students get privacy naturally. Thx Everyone.
As a Guest Student,
You are now upgraded to Grad Level.
See Uploads for “Student Checkins” & “S9”. Thx.
Happy Summer 25.
These are also timeless.
Thank you for attending our workshops.
If you are new, do welcome.
For visual/Video style learning see our practitioner student status.
This is listed under our new training program. Updates ongoing levels 1-3 this summer. We just started Session 1 for level 1.
These are optional programs. I also would like to redo our library ebooks about Hatha and Money Yoga. THe Money Yoga was very much energy healing without the Reiki Method. An updated ebook/course will be done this year. These Projects are for *all fans, followers, teams, and Readers. TY for being presenting.LDMMIA Shop & Student News Summer Solstice 25
LDMMIA Shop & Student News Summer Solstice 25LDM & Mia eStudios
Ěý
6/18/25
Shop, Upcoming: Final Notes to Review as we Close Level One. Make sure to review the orientation and videos as well. There’s more to come and material to cover in Levels 2-3. The content will be a combination of Reiki and Yoga. Also energy topics of our spiritual collective.
Thanks again all future Practitioner Level Students. Our Levels so far are: Guest, Grad, and Practitioner. We have had over 5k Spring Views.
https://ldm-mia.creator-spring.comK12 Tableau User Group virtual event June 18, 2025
K12 Tableau User Group virtual event June 18, 2025dogden2
Ěý
National K12 Tableau User Group: June 2025 meeting slidesJune 2025 Progress Update With Board Call_In process.pptx
June 2025 Progress Update With Board Call_In process.pptxInternational Society of Service Innovation Professionals
Ěý
---
June 25 ISSIP Event - slides in process
20250618 PPre-Event Presentation Summary - Progress Update with Board Series June 25
ISSIP Website Upcoming Events Description: https://issip.org/event/semi-annual-issip-progress-call/
Register here (even if you cannot attend live online, all who register will get link to recording and slides post-event): https://docs.google.com/forms/d/e/1FAIpQLSdThrop1rafOCo4PQkYiS2XApclJuMjYONEHRMGBsceRdcQqg/viewform
This pre-event presentation: /slideshow/june-2025-progress-update-with-board-call_in-process-pptx/280718770
This pre-event recording: https://youtu.be/Shjgd5o488o
---2025 June Year 9 Presentation: Subject selection.pptx
2025 June Year 9 Presentation: Subject selection.pptxmansk2
Ěý
2025 June Year 9 Presentation: Subject selectionThis is why students from these 44 institutions have not received National Se...
This is why students from these 44 institutions have not received National Se...Kweku Zurek
Ěý
This is why students from these 44 institutions have not received National Service PIN codes (LIST)Pests of Maize: An comprehensive overview.pptx
Pests of Maize: An comprehensive overview.pptxArshad Shaikh
Ěý
Maize is susceptible to various pests that can significantly impact yields. Key pests include the fall armyworm, stem borers, cob earworms, shoot fly. These pests can cause extensive damage, from leaf feeding and stalk tunneling to grain destruction. Effective management strategies, such as integrated pest management (IPM), resistant varieties, biological control, and judicious use of chemicals, are essential to mitigate losses and ensure sustainable maize production.Q1_ENGLISH_PPT_WEEK 1 power point grade 3 Quarter 1 week 1
Q1_ENGLISH_PPT_WEEK 1 power point grade 3 Quarter 1 week 1jutaydeonne
Ěý
Grade 3 Quarter 1 Week 1 English part 2A Visual Introduction to the Prophet Jeremiah
A Visual Introduction to the Prophet JeremiahSteve Thomason
Ěý
These images will give you a visual guide to both the context and the flow of the story of the prophet Jeremiah. Feel free to use these in your study, preaching, and teaching.Paper 107 | From Watchdog to Lapdog: Ishiguro’s Fiction and the Rise of “Godi...
Paper 107 | From Watchdog to Lapdog: Ishiguro’s Fiction and the Rise of “Godi...Rajdeep Bavaliya
Ěý
June 2025 Progress Update With Board Call_In process.pptx
June 2025 Progress Update With Board Call_In process.pptxInternational Society of Service Innovation Professionals
Ěý
Ad
Obesity hypoventilation syndrome HY
- 1. Obesity hypoventilation syndrome Diagnostic criteria • Obesity with BMI ≥30 kg/m2 • Awake daytime hypercapnia (PaCO2 >45 mm Hg) • No alternate cause of hypoventilation Workup • ABG on room air (hypercapnia, normal A-a gradient) • No intrinsic pulmonary disease on chest x-ray • Restrictive pattern on PFTs • Normal TSH • Polysomnography Treatment • Nocturnal positive pressure ventilation as first-line therapy • Weight loss (bariatric surgery in select cases) • Avoidance of sedative medications • Respiratory stimulants (eg, acetazolamide) as last resort
