аєВаЄДаЄ£аЄЗаЄ™аЄ£аєЙаЄ≤аЄЗаЄВаЄ≠аЄЗ Past continuous tense
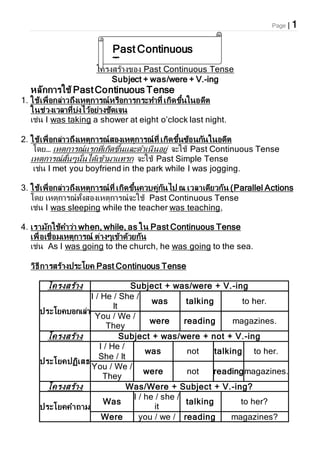
- 1. Page | 1 аєВаЄДаЄ£аЄЗаЄ™аЄ£аєЙаЄ≤аЄЗаЄВаЄ≠аЄЗ Past Continuous Tense Subject + was/were + V.-ing аЄЂаЄ•аЄ±аЄБаЄБаЄ≤аЄ£аєГаЄКаєЙ PastContinuous Tense 1. аєГаЄКаєЙаєАаЄЮаЄЈаєИаЄ≠аЄБаЄ•аєИаЄ≤аЄІаЄЦаЄґаЄЗаєАаЄЂаЄХаЄЄаЄБаЄ≤аЄ£аЄУаєМаЄЂаЄ£аЄЈаЄ≠аЄБаЄ≤аЄ£аЄБаЄ£аЄ∞аЄЧаЄ≤аЄЧаЄµаєИ аєАаЄБаЄіаЄФаЄВаЄґаєЙаЄЩаєГаЄЩаЄ≠аЄФаЄµаЄХ аєГаЄЩаЄКаєИаЄІаЄЗаєАаЄІаЄ•аЄ≤аЄЧаЄµаєИаЄЪаєИаЄЗаєДаЄІаєЙаЄ≠аЄҐаєИаЄ≤аЄЗаЄКаЄ±аЄФаєАаЄИаЄЩ аєАаЄКаєИаЄЩ I was taking a shower at eight oвАЩclock last night. 2. аєГаЄКаєЙаєАаЄЮаЄЈаєИаЄ≠аЄБаЄ•аєИаЄ≤аЄІаЄЦаЄґаЄЗаєАаЄЂаЄХаЄЄаЄБаЄ≤аЄ£аЄУаєМаЄ™аЄ≠аЄЗаєАаЄЂаЄХаЄЄаЄБаЄ≤аЄ£аЄУаєМаЄЧаЄµаєИ аєАаЄБаЄіаЄФаЄВаЄґаєЙаЄЩаЄЛаєЙаЄ≠аЄЩаЄБаЄ±аЄЩаєГаЄЩаЄ≠аЄФаЄµаЄХ аєВаЄФаЄҐвА¶ аєАаЄЂаЄХаЄЄаЄБаЄ≤аЄ£аЄУаєМаєБаЄ£аЄБаЄЧаЄµаєИаєАаЄБаЄіаЄФаЄВаЄґаєЙаЄЩаєБаЄ•аЄ∞аЄФаЄ≤аєАаЄЩаЄіаЄЩаЄ≠аЄҐаЄєаєИ аЄИаЄ∞аєГаЄКаєЙ Past Continuous Tense аєАаЄЂаЄХаЄЄаЄБаЄ≤аЄ£аЄУаєМаЄ™аЄ±аєЙаЄЩаєЖаЄЩаЄ±аєЙаЄЩаєДаЄФаєЙаєАаЄВаєЙаЄ≤аЄ°аЄ≤аєБаЄЧаЄ£аЄБ аЄИаЄ∞аєГаЄКаєЙ Past Simple Tense аєАаЄКаєИаЄЩ I met you boyfriend in the park while I was jogging. 3. аєГаЄКаєЙаєАаЄЮаЄЈаєИаЄ≠аЄБаЄ•аєИаЄ≤аЄІаЄЦаЄґаЄЗаєАаЄЂаЄХаЄЄаЄБаЄ≤аЄ£аЄУаєМаЄЧаЄµаєИ аєАаЄБаЄіаЄФаЄВаЄґаєЙаЄЩаЄДаЄІаЄЪаЄДаЄєаєИаЄБаЄ±аЄЩаєДаЄЫ аЄУ аєАаЄІаЄ•аЄ≤аєАаЄФаЄµаЄҐаЄІаЄБаЄ±аЄЩ (Parallel Actions аєВаЄФаЄҐ аєАаЄЂаЄХаЄЄаЄБаЄ≤аЄ£аЄУаєМаЄЧаЄ±аєЙаЄЗаЄ™аЄ≠аЄЗаєАаЄЂаЄХаЄЄаЄБаЄ≤аЄ£аЄУаєМаЄИаЄ∞аєГаЄКаєЙ Past Continuous Tense аєАаЄКаєИаЄЩ I was sleeping while the teacher was teaching, 4. аєАаЄ£аЄ≤аЄ°аЄ±аЄБаєГаЄКаєЙаЄДаЄ≤аЄІаєИаЄ≤ when, while, as аєГаЄЩ Past Continuous Tense аєАаЄЮаЄЈаєИаЄ≠аєАаЄКаЄЈаєИаЄ≠аЄ°аєАаЄЂаЄХаЄЄаЄБаЄ≤аЄ£аЄУаєМ аЄХаєИаЄ≤аЄЗаєЖаєАаЄВаєЙаЄ≤аЄФаєЙаЄІаЄҐаЄБаЄ±аЄЩ аєАаЄКаєИаЄЩ As I was going to the church, he was going to the sea. аЄІаЄіаЄШаЄµаЄБаЄ≤аЄ£аЄ™аЄ£аєЙаЄ≤аЄЗаЄЫаЄ£аЄ∞аєВаЄҐаЄД Past Continuous Tense аєВаЄДаЄ£аЄЗаЄ™аЄ£аєЙаЄ≤аЄЗ Subject + was/were + V.-ing аЄЫаЄ£аЄ∞аєВаЄҐаЄДаЄЪаЄ≠аЄБаєАаЄ•аєИаЄ≤ I / He / She / It was talking to her. You / We / They were reading magazines. аєВаЄДаЄ£аЄЗаЄ™аЄ£аєЙаЄ≤аЄЗ Subject + was/were + not + V.-ing аЄЫаЄ£аЄ∞аєВаЄҐаЄДаЄЫаЄПаЄіаєАаЄ™аЄШ I / He / She / It was not talking to her. You / We / They were not readingmagazines. аєВаЄДаЄ£аЄЗаЄ™аЄ£аєЙаЄ≤аЄЗ Was/Were + Subject + V.-ing? аЄЫаЄ£аЄ∞аєВаЄҐаЄДаЄДаЄ≤аЄЦаЄ≤аЄ° Was I / he / she / it talking to her? Were you / we / reading magazines? Past Continuous Tense
- 2. Page | 2 they аєВаЄДаЄ£аЄЗаЄ™аЄ£аєЙаЄ≤аЄЗ Who/What/Where/When/Why/How + was/were + Subject + V.-ing? аЄЫаЄ£аЄ∞аєВаЄҐаЄДаЄДаЄ≤аЄЦаЄ≤аЄ° Wh- Who was I / he / she / it talking to? What were you / we / they reading? Put in the verbs in brackets into the gaps. Use the Past Progressive/Present Continuous. 1. She ________________________ the lunch basket. (to pack) 2. I ________________________. (not/to whisper) 3. ________________________ he ________________________ to help? (to try) 4. The men ________________________ at the street corner. (not/to fight) 5. Frank________________________ the grass. (to cut) 6. ________________________ you ________________________ during the last lesson? (to yawn) 7. They________________________ stickers. (to swap) 8. The guest ________________________ the whole evening. (to dance) 9. We ________________________ in the tree house. (not/to hide) 10. ________________________ it ________________________ dark? (to get) **** *** Choose the past simple or past continuous: 1. What ________________________ (you / do) when I ________________________ (call) you last night? 2. I ________________________ (sit) in a caf√© when you________________________ (call). 3. When you ________________________ (arrive) at the party, who ________________________ (be) there? 4. Susie ________________________ (watch) a film when she ________________________ (hear) the noise. 5. Yesterday I ________________________ (go) to the library, next I ________________________ (have) a swim, later I ________________________ (meet) Julie for a coffee.
- 3. Page | 3 6. We ________________________ (play) tennis when John________________________ (hurt) his ankle. 7. What ________________________ (they / do) at 10pm last night? It __________________ (be) really noisy. 8. He ________________________ (take) a shower when the telephone ________________________ (ring). 9. He ________________________ (be) in the shower whenthe telephone ________________________ (ring). 10. When I ________________________ (walk) into the room, everyone ________________________ (work). **** *** пГ∞ Present Perfect Continuous Tense аЄИаЄ∞ аєАаЄЩаєЙаЄЩаЄЦаЄґаЄЗаЄДаЄІаЄ≤аЄ°аЄХаєИаЄ≠аєАаЄЩаЄЈаєИаЄ≠аЄЗаЄВаЄ≠аЄЗаЄБаЄ≤аЄ£аЄБаЄ£аЄ∞аЄЧаЄ≤ (Continuity of action)аЄ°аЄ≤аЄБаЄБаЄІаєИаЄ≤ Present Perfect Tense аєВаЄДаЄ£аЄЗаЄ™аЄ£аєЙаЄ≤аЄЗаЄВаЄ≠аЄЗ Present Perfect Continuous Tense Subject + has/have + been + V.-ing аЄЂаЄ•аЄ±аЄБаЄБаЄ≤аЄ£аєГаЄКаєЙ Present PerfectContinuous Tense 1. аєГаЄКаєЙаЄБаЄ±аЄЪаєАаЄЂаЄХаЄЄаЄБаЄ≤аЄ£аЄУаєМаЄЧаЄµаєИ аєАаЄБаЄіаЄФаЄВаЄґаєЙаЄЩаєГаЄЩаЄ≠аЄФаЄµаЄХаЄХаєИаЄ≠аєАаЄЩаЄЈаєИаЄ≠аЄЗаЄ°аЄ≤аЄҐаЄ±аЄЗаЄЫаЄ±аЄИаЄИаЄЄаЄЪаЄ±аЄЩ аєБаЄ•аЄ∞аЄҐаЄ±аЄЗаЄДаЄЗаЄФаЄ≤аєАаЄЩаЄіаЄЩаЄХаєИаЄ≠аєДаЄЫаЄ≠аЄµаЄБаєГаЄЩаЄ≠аЄЩаЄ≤аЄДаЄХаєВаЄФаЄҐаєГаЄКаєЙаЄБаЄ±аЄЪаЄДаЄ≤аЄІаєИаЄ≤sinceаєБаЄ•аЄ∞for аєАаЄКаєИаЄЩ She has been sitting here for an hour. 2. аЄДаЄ≤аЄБаЄ£аЄіаЄҐаЄ≤аЄЧаЄµаєИаєГаЄКаєЙаЄБаЄ±аЄЪ Present Perfect Continuous Tense аЄЩаЄ±аєЙаЄЩ аЄИаЄ∞аЄХаєЙаЄ≠аЄЗаєАаЄЫаєЗ аЄЩаЄДаЄ≤аЄБаЄ£аЄіаЄҐаЄ≤аЄЧаЄµаєИаєБаЄ™аЄФаЄЗаЄЦаЄґаЄЗаЄДаЄІаЄ≤аЄ°аЄХаєИаЄ≠аєАаЄЩаЄЈаєИаЄ≠аЄЗаЄЂаЄ£аЄЈаЄ≠ аЄБаЄ£аЄіаЄҐаЄ≤аЄЧаЄµаєИаєБаЄ™аЄФаЄЗаЄЦаЄґаЄЗаЄБаЄ≤аЄ£аЄБаЄ£аЄ∞аЄЧаЄ≤аЄЧаЄµаєИаЄЩаЄ≤аЄЩ (long action) аєАаЄЧаєИаЄ≤аЄЩаЄ±аєЙаЄЩ аєАаЄКаєИаЄЩ play, look, watch, learn, live, wait, eat аєБаЄ•аЄ∞аЄ≠аЄЈаєИаЄЩаєЖ аєВаЄФаЄҐаєДаЄ°аєИаЄ™аЄ≤аЄ°аЄ≤аЄ£аЄЦаєГаЄКаєЙаЄБаЄ±аЄЪаЄБаЄ£аЄіаЄҐаЄ≤аЄЧаЄµаєИаєДаЄ°аєИаєБаЄ™аЄФаЄЗаЄЦаЄґаЄЗаЄДаЄІаЄ≤аЄ°аЄХаєИаЄ≠аєАаЄЩаЄЈаєИаЄ≠аЄЗ аЄЂаЄ£аЄЈаЄ≠ аЄБаЄ£аЄіаЄҐаЄ≤аЄЧаЄµаєИаєБаЄ™аЄФаЄЗаЄЦаЄґаЄЗаЄБаЄ≤аЄ£аЄБаЄ£аЄ∞аЄЧаЄ≤аЄЧаЄµаєИаЄИаЄЪаєГаЄЩаЄЧаЄ±аЄЩаЄЧаЄµаєДаЄФаєЙ аєАаЄКаєИаЄЩ stop, prefer, arrive аєАаЄЫаєЗаЄЩаЄХаєЙаЄЩ аєАаЄКаєИаЄЩ I have been playing games since afternoon. 3. Present Perfect Continuous Tense аЄ≠аЄ≤аЄИаЄЩаЄ≤аЄ°аЄ≤аєГаЄКаєЙаєДаЄФаєЙаЄБаЄ±аЄЪаєАаЄЂаЄХаЄЄаЄБаЄ≤аЄ£аЄУаєМаЄЧаЄµаєИ аЄ™аЄіаєЙаЄЩаЄ™аЄЄаЄФаЄ•аЄЗаєБаЄ•аєЙаЄІ аєБаЄХаєИаЄ™аєИаЄЗаЄЬаЄ•аЄ°аЄ≤аЄҐаЄ±аЄЗаЄЫаЄ±аЄИаЄИаЄЄаЄЪаЄ±аЄЩ аєАаЄКаєИаЄЩ You look tired. Have you been sleeping properly? Present Perfect Continuous Tense
- 4. Page | 4 аЄІаЄіаЄШаЄµаЄБаЄ≤аЄ£аЄ™аЄ£аєЙаЄ≤аЄЗаЄЫаЄ£аЄ∞аєВаЄҐаЄД Present Perfect Continuous Tense аєВаЄДаЄ£аЄЗаЄ™аЄ£аєЙаЄ≤аЄЗ Subject + has/have + been + V.-ing аЄЫаЄ£аЄ∞аєВаЄҐаЄДаЄЪаЄ≠аЄБаєАаЄ•аєИ аЄ≤ I / You / We / They have been working in the office. He / She / It has been watchin g the television. аєВаЄДаЄ£аЄЗаЄ™аЄ£аєЙаЄ≤аЄЗ Subject + has/have + not + been + V.-ing аЄЫаЄ£аЄ∞аєВаЄҐаЄДаЄЫаЄПаЄіаєАаЄ™аЄШ I / You / We / They have not been working in the office. He / She / It has not been watching the television. аєВаЄДаЄ£аЄЗаЄ™аЄ£аєЙаЄ≤аЄЗ Has/Have + Subject + been + V.-ing? аЄЫаЄ£аЄ∞аєВаЄҐаЄДаЄДаЄ≤аЄЦаЄ≤аЄ° Have I / you / we / they been working in the office? Has he / she / it been watchin g the television? аєВаЄДаЄ£аЄЗаЄ™аЄ£аєЙаЄ≤аЄЗ Who/What/Where/When/Why/How + has/have + Subject + been + V.-ing? аЄЫаЄ£аЄ∞аєВаЄҐаЄДаЄДаЄ≤аЄЦаЄ≤аЄ° Wh- Who have I / you / we / they been Talking to? Where has he / she / it been sleeping? Put in the verbs in brackets into the gaps. Use Present Perfect Progressive/Continuous. Watch the punctuation and form sentences or questions. 1. Andrew_____________________in the country. (not/to live) 2. How long_____________________your grandparents_____________________this car? (to drive) 3. They_____________________ (not/to cycle) 4. Tony_____________________this book, but Mary has. (not/to read) 5. How long_____________________he_____________________for her? (to wait) 6. _____________________Andy_____________________on the blue car? (to work) 7. My brother_____________________hard enough. (not/to study)
- 5. Page | 5 8. How long_____________________they_____________________for a flat? (to look) 9. I_____________________my homework. (not/to do) 10. _____________________you_____________________the whole morning? (to sleep) **** *** Present Perfect Simple or Present Perfect Continuous Exercise 1. ___________________ (they / arrive) already? 2. Lucy ___________________ (run) 2000 metres today. 3. I ___________________ (clean) all morning вАУ IвАЩm fedup! 4. How long ___________________ (you / know) Simon? 5. I ___________________ (drink) more water lately, and I feel better. 6. Sorry about the mess! I ___________________ (bake). 7. How many times ___________________ (you / take) this exam? 8. He ___________________ (eat) six bars of chocolate today! 9. Julie ___________________ (cook) dinner. LetвАЩs go and eat! 10. The students ___________________ (finish) their exams. TheyвАЩre very happy. **** *** Linking words = аЄДаЄ≤аЄЂаЄ£аЄЈаЄ≠аЄБаЄ•аЄЄаєИаЄ°аЄДаЄ≤аЄЧаЄµаєИаєГаЄКаєЙаєБаЄ™аЄФаЄЗаЄДаЄІаЄ≤аЄ°аЄ™аЄ±аЄ°аЄЮаЄ±аЄЩаЄШаєМаЄ£аЄ∞аЄЂаЄІаєИаЄ≤аЄЗаЄДаЄ≤ аЄБаЄ•аЄЄаєИаЄ°аЄДаЄ≤аЄЂаЄ£аЄЈаЄ≠аЄЫаЄ£аЄ∞аєВаЄҐаЄД 1. аєБаЄ™аЄФаЄЗаЄБаЄ≤аЄ£аєАаЄЮаЄіаєИаЄ°аЄВаєЙаЄ≠аЄ°аЄєаЄ•аЄЧаЄµаєИаЄДаЄ•аєЙаЄ≠аЄҐаЄХаЄ≤аЄ°аЄБаЄ±аЄЩаєГаЄЩаєАаЄКаЄіаЄЗаЄЪаЄІаЄБ аєДаЄФаєЙаєБаЄБаєИ and, both вА¶and, too, besides (this /that), moreover, what is more, in addition (to), also, as well as (this/that), furthermore, etc аЄХаЄ±аЄІаЄ≠аЄҐаєИаЄ≤аЄЗаєАаЄКаєИаЄЩTony is both kind and helpful. 2. аєБаЄ™аЄФаЄЗаЄБаЄ≤аЄ£аєАаЄЮаЄіаєИаЄ°аЄВаєЙаЄ≠аЄ°аЄєаЄ•аЄЧаЄµаєИаЄДаЄ•аєЙаЄ≠аЄҐаЄХаЄ≤аЄ°аЄБаЄ±аЄЩаєГаЄЩаєАаЄКаЄіаЄЗаЄ•аЄЪ аєДаЄФаєЙаєБаЄБаєИ neither (вА¶ nor), nor, neither, either, etc аЄХаЄ±аЄІаЄ≠аЄҐаєИаЄ≤аЄЗаєАаЄКаєИаЄЩNeither Sue nor I went to the club. 3. аєБаЄ™аЄФаЄЗаЄДаЄІаЄ≤аЄ°аЄВаЄ±аЄФаєБаЄҐаєЙаЄЗ аєДаЄФаєЙаєБаЄБаєИ but, however, on the other hand, yet, still, etc Linker s
- 6. Page | 6 although (+ clause), in spite of (+ noun/-ing), despite (+ noun/- ing), while (+ clause), whereas (+ clause), even though (+ clause), etc аЄХаЄ±аЄІаЄ≠аЄҐаєИаЄ≤аЄЗаєАаЄКаєИаЄЩ Even though we hurried, we still missed the bus. 4. аєБаЄ™аЄФаЄЗаЄХаЄ±аЄІаЄ≠аЄҐаєИаЄ≤аЄЗ аєДаЄФаєЙаєБаЄБаєИ such as, like, for example, for instance, especially, in particular, etc аЄХаЄ±аЄІаЄ≠аЄҐаєИаЄ≤аЄЗаєАаЄКаєИаЄЩThe weather has been bad this week, and Friday in particular was very cold. 5. аєБаЄ™аЄФаЄЗаєАаЄЂаЄХаЄЄ/аЄЬаЄ• аєДаЄФаєЙаєБаЄБаєИ as, because, because of, since, for this reason, due to, so, as a result (of), etc аЄХаЄ±аЄІаЄ≠аЄҐаєИаЄ≤аЄЗаєАаЄКаєИаЄЩShe had to take a taxi because her car had run out of petrol. 6. аєБаЄ™аЄФаЄЗаєАаЄЗаЄЈаєИаЄ≠аЄЩаєДаЄВ аєДаЄФаєЙаєБаЄБаєИ if, whether, only if, in case of, in case, provided (that), providing (that), unless, as/so long as, otherwise, or (else), on condition (that), etc аЄХаЄ±аЄІаЄ≠аЄҐаєИаЄ≤аЄЗаєАаЄКаєИаЄЩJoy said she could lend me 50 as long as I paid it back by Monday. 7. аєБаЄ™аЄФаЄЗаЄИаЄЄаЄФаЄЫаЄ£аЄ∞аЄ™аЄЗаЄДаєМ аєДаЄФаєЙаєБаЄБаєИ to, so that, so as (not) to, in order (not) to, in order that, in case, etc аЄХаЄ±аЄІаЄ≠аЄҐаєИаЄ≤аЄЗаєАаЄКаєИаЄЩDavid went to the bank to get a loan. 8. аєБаЄ™аЄФаЄЗаЄЬаЄ• аєДаЄФаєЙаєБаЄБаєИ such/so вА¶ that, so, consequently, as a result, therefore, for this reason, etc аЄХаЄ±аЄІаЄ≠аЄҐаєИаЄ≤аЄЗаєАаЄКаєИаЄЩShe doesnвАЩt really like her job so she is looking for a new one. 9. аєБаЄ™аЄФаЄЗаєАаЄІаЄ•аЄ≤ аєДаЄФаєЙаєБаЄБаєИ when, whenever, as, as soon as, while, before, until/till, after, since, etc аЄХаЄ±аЄІаЄ≠аЄҐаєИаЄ≤аЄЗаєАаЄКаєИаЄЩTheyвАЩll go out as soon as I get there. 10. аєБаЄ™аЄФаЄЗаЄВаєЙаЄ≠аЄҐаЄБаєАаЄІаєЙаЄЩ аєДаЄФаєЙаєБаЄБаєИ except (for), apart from, etc аЄХаЄ±аЄІаЄ≠аЄҐаєИаЄ≤аЄЗаєАаЄКаєИаЄЩ He paid all the bills except for the electricity. 11. аЄ™аЄ£аЄ£аЄЮаЄЩаЄ≤аЄ°аєАаЄКаЄЈаєИаЄ≠аЄ°аЄДаЄІаЄ≤аЄ° аєДаЄФаєЙаєБаЄБаєИ who, whom, whose, which, what, that аЄХаЄ±аЄІаЄ≠аЄҐаєИаЄ≤аЄЗаєАаЄКаєИаЄЩThatвАЩs the man who works in the library. Choose вАШhoweverвАЩ, вАШalthoughвАЩ or вАШdespiteвАЩ: 1. ______________________ the rain, we still went to the park. 2. ______________________ it was raining, we still went to the park.
- 7. Page | 7 3. It was raining. ______________________, we still went to the park. 4. John bought the watch, ______________________ the fact that it was expensive. 5. John bough the watch. ______________________, it was expensive. 6. ______________________ it was expensive, John bought the watch. 7. I finished the homework. It, ______________________, wasnвАЩt easy. 8. I finished the homework, ______________________ it wasnвАЩt easy. 9. ______________________ the fact that it wasnвАЩt easy, I finished the homework. 10. She went for a long walk, ______________________ being cold. 11. ______________________ she was cold, she went for a long walk. 12. She was cold. She went for a long walk, ______________________. 13. The restaurant has a good reputation ______________________, the food was terrible. 14. ______________________ the restaurantвАЩs good reputation, the food was terrible. 15. ______________________ the restaurant has a good reputation, the food was terrible. **** *** must ,mustnвАЩt , have to / should, shouldnвАЩt / can , canвАЩt , could / was able to , were able to / may , might Modal Verbs аєДаЄФаєЙаєБаЄБаєИаЄДаЄ≤аЄЧаЄµаєИаєАаЄ£аЄ≤аЄЩаЄ≤аєДаЄЫаєГаЄКаєЙаєАаЄЫаєЗаЄЩаЄБаЄ£аЄіаЄҐаЄ≤аЄКаєИаЄІаЄҐаєГаЄЩаЄЫаЄ£аЄ∞аєВаЄҐаЄД аєДаЄФаєЙаєБаЄБаєИ must , mustnвАЩt , have to / should, shouldnвАЩt / can , canвАЩt , could / was able to , were able to / may , might аЄЛаЄґаєИаЄЗаЄ°аЄµаЄІаЄіаЄШаЄµаЄБаЄ≤аЄ£аЄЩаЄ≤аєДаЄЫаєГаЄКаєЙаЄФаЄ±аЄЗаЄЩаЄµаєЙ 1. must аєБаЄЫаЄ•аЄІаєИаЄ≤ аЄХаєЙаЄ≠аЄЗ пВЈ аєАаЄ£аЄ≤аєГаЄКаєЙ must аєГаЄЩаЄБаЄ≤аЄ£аєБаЄ™аЄФаЄЗаЄЦаЄґаЄЗаЄЂаЄЩаєЙаЄ≤аЄЧаЄµаєИаЄЂаЄ£аЄЈаЄ≠аЄДаЄІаЄ≤аЄ°аЄ£аЄ±аЄЪаЄЬаЄіаЄФаЄКаЄ≠аЄЪаЄЧаЄµаєИаєДаЄ°аєИаЄ™аЄ≤аЄ°аЄ≤аЄ£аЄЦаЄЫаЄПаЄіаєАаЄ™аЄШаєДаЄФаєЙ аєАаЄКаєИаЄЩ пГЉ You must always follow school rules. аЄДаЄЄаЄУаЄХаєЙаЄ≠аЄЗаЄЫаЄПаЄіаЄЪаЄ±аЄХаЄіаЄХаЄ≤аЄ°аЄБаЄПаЄВаЄ≠аЄЗаєВаЄ£аЄЗаєАаЄ£аЄµаЄҐаЄЩаєАаЄ™аЄ°аЄ≠ (itвАЩs the rule/the law.) Modal Verbs
- 8. Page | 8 пГЉ You must have the driving license before driving. аЄДаЄЄаЄУаЄХаєЙаЄ≠аЄЗаЄ°аЄµаєГаЄЪаЄ≠аЄЩаЄЄаЄНаЄ≤аЄХаЄВаЄ±аЄЪаЄВаЄµаєИ аЄБаєИаЄ≠аЄЩаЄВаЄ±аЄЪаЄ£аЄЦ (it is the low.) (аЄЂаЄ•аЄ±аЄЗ must аЄХаєЙаЄ≠аЄЗаЄХаЄ≤аЄ°аЄФаєЙаЄІаЄҐаЄБаЄ£аЄіаЄҐаЄ≤ (verb) аЄКаєИаЄ≠аЄЗ 1 аєАаЄ™аЄ°аЄ≠ 2. mustn't аєБаЄЫаЄ•аЄІаєИаЄ≤ аЄХаєЙаЄ≠аЄЗаєДаЄ°аєИ аєАаЄ£аЄ≤аєГаЄКаєЙ mustnвАЩt аєГаЄЩаЄБаЄ≤аЄ£аєБаЄ™аЄФаЄЗаЄЦаЄґаЄЗаЄБаЄ≤аЄ£аєДаЄ°аєИаЄ≠аЄЩаЄЄаЄНаЄ≤аЄХ (аЄВаєЙаЄ≠аЄЂаєЙаЄ≤аЄ°) аєАаЄКаєИаЄЩ пГЉ You mustnвАЩt park here. аЄДаЄЄаЄУаЄХаєЙаЄ≠аЄЗаєДаЄ°аєИаЄИаЄ≠аЄФаЄ£аЄЦаЄЧаЄµаєИаЄЩаЄµаєИ (it isnвАЩt allowed.) 3. have to аєБаЄЫаЄ•аЄІаєИаЄ≤ аЄХаєЙаЄ≠аЄЗ пВЈ аєАаЄ£аЄ≤аєГаЄКаєЙ have to аєГаЄЩаЄБаЄ≤аЄ£аєБаЄ™аЄФаЄЗаЄЦаЄґаЄЗаЄДаЄІаЄ≤аЄ°аЄИаЄ≤аєАаЄЫаєЗаЄЩаЄХаєЙаЄ≠аЄЗаЄЫаЄПаЄіаЄЪаЄ±аЄХаЄіаЄХаЄ≤аЄ° аєАаЄКаєИаЄЩ пГЉ You have to be quiet in the library. аЄДаЄЄаЄУаЄХаєЙаЄ≠аЄЗаєАаЄЗаЄµаЄҐаЄЪаєГаЄЩаЄЂаєЙаЄ≠аЄЗаЄ™аЄ°аЄЄаЄФ пГЉ We have to study hard for history exam. (itвАЩs necessary.) 4. don't have to аєБаЄЫаЄ•аЄІаєИаЄ≤ аЄХаєЙаЄ≠аЄЗаєДаЄ°аєИ пВЈ аєАаЄ£аЄ≤аєГаЄКаєЙ donвАЩt have to аєГаЄЩаЄБаЄ≤аЄ£аєБаЄ™аЄФаЄЗаЄЦаЄґаЄЗаЄДаЄІаЄ≤аЄ°аєДаЄ°аєИаЄИаЄ≤аєАаЄЫаєЗаЄЩаЄЧаЄµаєИаЄХаєЙаЄ≠аЄЗаЄЫаЄПаЄіаЄЪаЄ±аЄХаЄіаЄХаЄ≤аЄ° аєАаЄКаєИаЄЩ пГЉ You donвАЩt have to wear a tie for the party. аЄДаЄЄаЄУаєДаЄ°аєИаЄИаЄ≤аєАаЄЫаєЗаЄЩаЄХаєЙаЄ≠аЄЗаєГаЄ™аєИаєДаЄЧаЄЩаєМ аєДаЄЫаЄЗаЄ≤аЄЩаЄЫаЄ≤аЄ£аєМаЄХаЄµаєЙ (it isnвАЩt necessary. вАУ it shows no obligation.) аЄВаєЙаЄ≠аЄДаЄІаЄ£аЄИаЄ≤ пБґ аєАаЄ£аЄ≤аєГаЄКаєЙ must / mustnвАЩt аєГаЄЩ present tense аєАаЄЧаєИаЄ≤аЄЩаЄ±аєЙаЄЩ пБґ аєАаЄ£аЄ≤аЄ™аЄ≤аЄ°аЄ≤аЄ£аЄЦаєГаЄКаєЙ have to аєДаЄФаєЙаЄБаЄ±аЄЪаЄЧаЄЄаЄБаєЖ tense пВЈ аєАаЄ£аЄ≤аєГаЄКаєЙаЄЧаЄ±аєЙаЄЗ may аєБаЄ•аЄ∞ might аєАаЄ°аЄЈаєИаЄ≠аєАаЄ£аЄ≤аЄХаєЙаЄ≠аЄЗаЄБаЄ≤аЄ£аЄДаЄІаЄ≤аЄ°аЄ™аЄЄаЄ†аЄ≤аЄЮаЄ°аЄ≤аЄБаЄБаЄІаєИаЄ≤ аЄЛаЄґаєИаЄЗ might аєГаЄКаєЙаєАаЄЫаєЗаЄЩаЄЧаЄ≤аЄЗаЄБаЄ≤аЄ£аЄ°аЄ≤аЄБаЄБаЄІаєИаЄ≤ may аєАаЄ™аЄµаЄҐаЄ≠аЄµаЄБ пВЈ аєАаЄ£аЄ≤аєГаЄКаєЙ may аєАаЄ°аЄЈаєИаЄ≠аєАаЄ£аЄ≤аЄДаЄіаЄФаЄІаєИаЄ≤аЄЪаЄ≤аЄЗаЄ™аЄіаєИаЄЗаЄЪаЄ≤аЄЗаЄ≠аЄҐаєИаЄ≤аЄЗаЄЩаЄ±аєЙаЄЩаєАаЄЫаєЗаЄЩаєДаЄЫаєДаЄФаєЙаЄЧаЄµаєИаЄИаЄ∞аєАаЄБаЄіаЄФаЄВаЄґаєЙаЄЩ пВЈ аєАаЄ£аЄ≤аєГаЄКаєЙ might аєАаЄ°аЄЈаєИаЄ≠аєАаЄ£аЄ≤аЄДаЄіаЄФаЄІаєИаЄ≤аЄЪаЄ≤аЄЗаЄ™аЄіаєИаЄЗаЄЪаЄ≤аЄЗаЄ≠аЄҐаєИаЄ≤аЄЗаЄЩаЄ±аєЙаєАаЄЫаєЗаЄЩаєДаЄЫаєДаЄ°аєИаєДаЄФаєЙаЄЧаЄµаєИаЄИаЄ∞аєАаЄБаЄіаЄФаЄВаЄґаєЙаЄЩ пГЉ It could be dangerous to swim alone. (аЄ°аЄ±аЄЩаЄ≠аЄ≤аЄИаєАаЄЫаєЗаЄЩаЄ≠аЄ±аЄЩаЄХаЄ£аЄ≤аЄҐаєГаЄЩаЄБаЄ≤аЄ£аЄІаєИаЄ≤аЄҐаЄЩаєЙаЄ≤аЄДаЄЩаєАаЄФаЄµаЄҐаЄІ) пГЉ It may be dangerous to swim alone. пГЉ It might be dangerous to swim alone. аЄДаЄ≤аЄ®аЄ±аЄЮаЄЧаєМаЄЧаЄµаєИаєАаЄБаЄµаєИаЄҐаЄІаЄБаЄ±аЄЪ Modal Verbs аєДаЄФаєЙаєБаЄБаєИ obligation = аЄЂаЄЩаєЙаЄ≤аЄЧаЄµаєИ, prohibition = аЄВаєЙаЄ≠аЄЂаєЙаЄ≤аЄ°, recommendation = аЄБаЄ≤аЄ£аєБаЄЩаЄ∞аЄЩаЄ≤, possibility = аЄДаЄІаЄ≤аЄ°аєАаЄЫаєЗаЄЩаєДаЄЫаєДаЄФаєЙ , rule = аЄБаЄП, necessary = аЄДаЄІаЄ≤аЄ°аЄИаЄ≤аєАаЄЫаєЗаЄЩ, advice = аЄДаЄ≤аєБаЄЩаЄ∞аЄЩаЄ≤, ability = аЄДаЄІаЄ≤аЄ°аЄ™аЄ≤аЄ°аЄ≤аЄ£аЄЦ, permission = аЄВаЄ≠аЄ≠аЄЩаЄЄаЄНаЄ≤аЄХ,Request = аЄВаЄ≠, suggestion = аЄБаЄ≤аЄ£аєБаЄЩаЄ∞аЄЩаЄ≤ 5. should / shouldnвАЩt аєБаЄЫаЄ•аЄІаєИаЄ≤ аЄДаЄІаЄ£ / аєДаЄ°аєИаЄДаЄІаЄ£ пВЈ аєАаЄ£аЄ≤аєГаЄКаєЙ should / shouldnвАЩt аєГаЄЩаЄБаЄ≤аЄ£аєГаЄЂаєЙаЄДаЄ≤аєБаЄЩаЄ∞аЄЩаЄ≤аЄЧаЄµаєИаЄЩаєИаЄ≤аєАаЄКаЄЈаєИаЄ≠аЄЦаЄЈаЄ≠ аєАаЄКаєИаЄЩ пГЉ You should be careful on the road. аЄДаЄЄаЄУаЄДаЄІаЄ£аЄ£аЄ∞аЄ°аЄ±аЄФаЄ£аЄ∞аЄІаЄ±аЄЗаЄЪаЄЩаЄЦаЄЩаЄЩ пГЉ You should relax if you feel tired. аЄДаЄЄаЄУаЄДаЄІаЄ£аЄЮаЄ±аЄБаЄЬаєИаЄ≠аЄЩаЄЦаєЙаЄ≤аЄДаЄЄаЄУаєАаЄЂаЄЩаЄЈаєИаЄ≠аЄҐ (it is a good idea.) пГЉ You shouldnвАЩt go out on your own at night. аЄДаЄЄаЄУаєДаЄ°аєИаЄДаЄІаЄ£аЄ≠аЄ≠аЄБаєДаЄЫаЄВаєЙаЄ≤аЄЗаЄЩаЄ≠аЄБаЄДаЄЩаєАаЄФаЄµаЄҐаЄІаЄХаЄ≠аЄЩаЄБаЄ•аЄ≤аЄЗаЄДаЄЈаЄЩ 6. can / canвАЩt аєБаЄЫаЄ•аЄІаєИаЄ≤ аЄ™аЄ≤аЄ°аЄ≤аЄ£аЄЦ, аєДаЄ°аєИаЄ™аЄ≤аЄ°аЄ≤аЄ£аЄЦ
- 9. Page | 9 пВЈ аєАаЄ£аЄ≤аєГаЄКаєЙ can аєГаЄЩаЄБаЄ≤аЄ£аєБаЄ™аЄФаЄЗаЄЦаЄґаЄЗаЄДаЄІаЄ≤аЄ°аЄ™аЄ≤аЄ°аЄ≤аЄ£аЄЦаєГаЄЩаЄЫаЄ±аЄИаЄИаЄЄаЄЪаЄ±аЄЩ аєАаЄКаєИаЄЩ пГЉ He can speak four languages. (he has the ability.) пВЈ аєАаЄ£аЄ≤аєГаЄКаєЙ can аєГаЄЩаЄБаЄ≤аЄ£аЄВаЄ≠аЄ≠аЄЩаЄЄаЄНаЄ≤аЄХ аєАаЄКаєИаЄЩ пГЉ Can I use your phone? (May I?) пВЈ аєАаЄ£аЄ≤аєГаЄЂаєЙаЄДаЄІаЄ≤аЄ°аЄ≠аЄЩаЄЄаЄНаЄ≤аЄХ аєАаЄКаєИаЄЩ Yes, you can use my car. (you are allowed.) пВЈ аєАаЄ£аЄ≤аєГаЄКаєЙ can аєГаЄЩаЄБаЄ≤аЄ£аЄВаЄ≠ аєАаЄКаєИаЄЩ Can I have some coffee, please? пВЈ аєАаЄ£аЄ≤аєГаЄКаєЙ can аєГаЄЩаЄБаЄ≤аЄ£аєБаЄЩаЄ∞аЄЩаЄ≤ аєАаЄКаєИаЄЩ пГЉ You can write her a letter and tell her how you feel. (Why donвАЩt youвА¶.?) пВЈ аєАаЄ£аЄ≤аєГаЄКаєЙ can аєГаЄЩаЄБаЄ≤аЄ£аєБаЄ™аЄФаЄЗаЄЦаЄґаЄЗаЄДаЄІаЄ≤аЄ°аєАаЄЫаєЗаЄЩаєДаЄЫаєДаЄФаєЙ (аЄ™аЄ≤аЄДаЄ±аЄН) аєАаЄКаєИаЄЩ пГЉ Jellyfish can sting you very badly. (аєБаЄ°аЄЗаЄБаЄ£аЄ∞аЄЮаЄ£аЄЄаЄЩаЄ™аЄ≤аЄ°аЄ≤аЄ£аЄЦаЄХаєИаЄ≠аЄҐаЄДаЄЄаЄУаЄ≠аЄҐаєИаЄ≤аЄЗаєАаЄИаєЗаЄЪаЄЫаЄІаЄФ) пГЉ He can win the race. (itвАЩs possible.) пВЈ аєАаЄ£аЄ≤аєГаЄКаєЙ canвАЩt аєГаЄЩаЄБаЄ≤аЄ£аЄЫаЄПаЄіаєАаЄ™аЄШаЄБаЄ≤аЄ£аЄВаЄ≠аЄ≠аЄЩаЄЄаЄНаЄ≤аЄХ аєАаЄКаєИаЄЩ пГЉ No, you canвАЩt play outside; it is raining. (you arenвАЩt allowed.) пВЈ аєАаЄ£аЄ≤аєГаЄКаєЙ could аєГаЄЩаЄБаЄ≤аЄ£аЄВаЄ≠аЄ≠аЄЩаЄЄаЄНаЄ≤аЄХ аЄЂаЄ£аЄЈаЄ≠ аЄВаЄ≠ (аЄЪаЄ≤аЄЗаЄ™аЄіаєИаЄЗаЄЪаЄ≤аЄЗаЄ≠аЄҐаєИаЄ≤аЄЗ) аєАаЄКаєИаЄЩ пГЉ Could I use your computer, please? (more polite than can) пВЈ аєГаЄЩаЄБаЄ≤аЄ£аєБаЄ™аЄФаЄЗаЄЦаЄґаЄЗаЄДаЄІаЄ≤аЄ°аЄ™аЄ≤аЄ°аЄ≤аЄ£аЄЦаЄЧаЄ±аєИаЄІаєЖаєДаЄЫаєГаЄЩаЄ≠аЄФаЄµаЄХ аєАаЄКаєИаЄЩ пГЉ I could run very fast when I was fourteen. (I had the ability.) 7. was able to / were able to аєБаЄЫаЄ•аЄІаєИаЄ≤ аЄ™аЄ≤аЄ°аЄ≤аЄ£аЄЦ пВЈ аєАаЄ£аЄ≤аєГаЄКаєЙ was able to / were able to аєГаЄЩаЄБаЄ≤аЄ£аєБаЄ™аЄФаЄЗаЄІаєИаЄ≤аєГаЄДаЄ£аЄЪаЄ≤аЄЗаЄДаЄЩаЄ°аЄµаЄДаЄІаЄ≤аЄ°аЄ™аЄ≤аЄ°аЄ≤аЄ£аЄЦаєГаЄЩаЄБаЄ≤аЄ£аЄЧаЄ≤аЄЪаЄ≤аЄЗаЄ™аЄіаєИаЄЗаЄЪаЄ≤аЄЗаЄ≠аЄҐаєИаЄ≤аЄЗаєГаЄЩаЄ™аЄЦаЄ≤аЄЩаЄБаЄ≤ аЄ£аЄУаєМаЄЧаЄµаєИаєДаЄ°аєИаЄШаЄ£аЄ£аЄ°аЄФаЄ≤аєГаЄЩаЄ≠аЄФаЄµаЄХ аєАаЄКаєИаЄЩ пГЉ Although it was dark, Steve was able to find his way. (he managed to.) 8. may, might, could be аєБаЄЫаЄ•аЄІаєИаЄ≤ аЄ≠аЄ≤аЄИаЄИаЄ∞ пВЈ аєАаЄ£аЄ≤аєГаЄКаєЙ may / might аєГаЄЩаЄБаЄ≤аЄ£аєБаЄ™аЄФаЄЗаЄЦаЄґаЄЗаЄДаЄІаЄ≤аЄ°аєАаЄЫаєЗаЄЩаєДаЄЫаєДаЄФаєЙаєАаЄЮаЄµаЄҐаЄЗаєАаЄ•аєЗаЄБаЄЩаєЙаЄ≠аЄҐ (аЄДаЄ≤аЄФаЄДаЄ∞аєАаЄЩ) аєАаЄКаєИаЄЩ пГЉ It may / might happen again. (itвАЩs possible.) пВЈ аєГаЄЩаЄБаЄ≤аЄ£аЄВаЄ≠аЄ≠аЄЩаЄЄаЄНаЄ≤аЄХ аЄЛаЄґаєИаЄЗ may аєГаЄКаєЙаєАаЄЫаєЗаЄЩаЄЧаЄ≤аЄЗаЄБаЄ≤аЄ£аЄ°аЄ≤аЄБаЄБаЄІаєИаЄ≤ can аєАаЄКаєИаЄЩ пГЉ May I come in? аЄЂаЄ£аЄЈаЄ≠ May I go now? Put in вАШcanвАЩ / вАШcanвАЩtвАЩ / вАШcouldвАЩ / вАШcouldnвАЩtвАЩ. If none is possible, use вАШbe able toвАЩ in the correct tense: 1. _________________ you swim when you were 10? 2. We ________________ get to the meeting on time yesterday because the train was delayed by one hour. 3. He _________________ arrive at the party on time, even after missing the train, so he was very pleased.
- 10. Page | 10 4. HeвАЩs amazing, he _________________ speak 5 languages including Chinese. 5. I _________________ drive a car until I was 34, then I moved to the countryside so I had to learn. 6. I looked everywhere for my glasses but I _________________ find them anywhere. 7. I searched for your house for ages, luckily I _________________ find it in the end. 8. SheвАЩs 7 years old but she _________________ read yet вАУ her parents are getting her extra lessons. 9. I read the book three times but I _________________understand it. 10. James _________________ speak Japanese when he lived in Japan, but heвАЩs forgotten most of it now. **** ***