rasha osman critical thinking final.pptx
- 1. HTI December 2024 Seminar on Critical Thinking Rasha Osman
- 2. Table Contents ’ā╝Definition ’ā╝Introduction ’ā╝About Critical Thinkers ’ā╝Critical Thinking Skills ’ā╝The Critical Thinking Process ’ā╝Benefits of Critical Thinking ’ā╝Conclusion 2
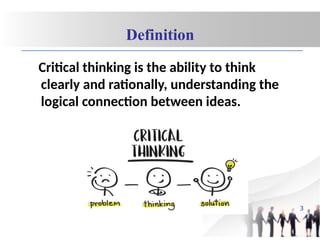
- 3. Definition Critical thinking is the ability to think clearly and rationally, understanding the logical connection between ideas. 3
- 4. Introduction ŌĆó Critical thinking has been the subject of much debate and thought since the time of early Greek philosophers such as Plato and Socrates and has continued to be a subject of discussion into the modern age, for example the ability to recognise fake news. ŌĆó Critical thinking might be described as the ability to engage in reflective and independent thinking. 4
- 5. 5
- 6. About Critical Thinkers ŌĆó Critical thinkers rigorously question ideas and assumptions rather than accepting them at face value. They will always seek to determine whether the ideas, arguments and findings represent the entire picture and are open to finding that they do not. ŌĆó Critical thinkers will identify, analyse and solve problems systematically rather than by intuition or instinct. 6
- 7. Critical Thinking Skills ŌĆó Understand the links between ideas. ŌĆó Determine the importance and relevance of arguments and ideas. ŌĆó Recognise, build and appraise arguments. ŌĆó Identify inconsistencies and errors in reasoning. ŌĆó Approach problems in a consistent and systematic way. ŌĆó Reflect on the justification of their own assumptions, beliefs and values. ŌŚÅŌŚÅŌŚÅ 7
- 8. Critical Thinking Skills ŌĆó Critical thinking is thinking about things in certain ways so as to arrive at the best possible solution in the circumstances that the thinker is aware of. ŌĆó In more everyday language, it is a way of thinking about whatever is presently occupying your mind so that you come to the best possible conclusion. ŌŚÅŌŚÅŌŚÅ 8
- 9. Critical Thinking Skills ŌĆó The skills that we need in order to be able to think critically are varied and include observation, analysis, interpretation, reflection, evaluation, inference, explanation, problem solving, and decision making. ŌŚÅŌŚÅŌŚÅ 9
- 10. Critical Thinking Skills ŌĆó Think about a topic or issue in an objective and critical way. ŌĆó Identify the different arguments there are in relation to a particular issue. ŌĆó Evaluate a point of view to determine how strong or valid it is. ŌĆó Recognise any weaknesses or negative points that there are in the evidence or argument. ŌŚÅŌŚÅŌŚÅ 10
- 11. Critical Thinking Skills ŌĆó Notice what implications there might be behind a statement or argument. ŌĆó Provide structured reasoning and support for an argument that we wish to make. ŌŚÅŌŚÅŌŚÅ 11
- 12. 12
- 13. The Critical Thinking Process ŌĆó You should be aware that none of us think critically all the time. ŌĆó Sometimes we think in almost any way but critically, for example when our self-control is affected by anger, grief or joy or when we are feeling just plain ŌĆśbloody mindedŌĆÖ. ŌŚÅŌŚÅŌŚÅ 13
- 14. The Critical Thinking Process ŌĆó On the other hand, the good news is that, since our critical thinking ability varies according to our current mindset, most of the time we can learn to improve our critical thinking ability by developing certain routine activities and applying them to all problems that present themselves. 14
- 15. Benefit of Critical Thinking ŌĆó Almost all decisions we make and implement donŌĆÖt prove disastrous if we find reasons to abandon them. ŌĆó However, our decision making will be infinitely better and more likely to lead to success if, when we reach a tentative conclusion, we pause and consider the impact on the people and activities around us. ŌŚÅŌŚÅŌŚÅ 15
- 16. Benefit of Critical Thinking ŌĆó In many cases, consideration of one element from a different perspective will reveal potential dangers in pursuing our decision. ŌĆó For instance, moving a business activity to a new location may improve potential output considerably but it may also lead to the loss of skilled workers if the distance moved is too great. ŌŚÅŌŚÅŌŚÅ 16
- 17. 17
- 18. Wh. Questions ’ā╝ What ’ā╝ When ’ā╝ Where ’ā╝ Why ’ā╝ How 18
- 19. Questions of Opinion ’ā╝ What do you think ’ā╝ What is your opinion ’ā╝ Do you think 19
- 20. References ŌĆó Exploring the connections between Philosophy for Children and character education: Some implications for moral education?Andrew Peterson & Brendan Bentley - 2015 - Journal of Philosophy in Schools 2 (2):48-70. ŌĆó Educating for Good Thinking: Virtues, Skills, or Both?Jason Baehr - 2023 - Informal Logic 43 (2):173-203. ŌĆó Educating for Intellectual Virtues: From Theory to Practice.Jason Baehr - 2013 - Journal of Philosophy of Education 47 (2):248-262. ŌĆó Educating against intellectual vices.Noel L. Clemente - 2024 - Ethics and Education 19 (1):109-123.
- 21. Thanks
Editor's Notes
- #2: SAY: Before we wrap up the course, letŌĆÖs review what we have learned today. During this course, we have <READ the bullets from the slide.> GO to next slide.
- #3: SAY: Before we wrap up the course, letŌĆÖs review what we have learned today. During this course, we have <READ the bullets from the slide.> GO to next slide.
- #4: SAY: Before we wrap up the course, letŌĆÖs review what we have learned today. During this course, we have <READ the bullets from the slide.> GO to next slide.
- #5: SAY: The purpose of epidemiology in public health practice is to discover the agent, host, and environmental factors that affect health; determine the relative importance of causes of illness, disability, and death; identify those segments of the population that have the greatest risk from specific causes of ill health; and evaluate the effectiveness of health programs and services in improving population health. GO to next slide.
- #6: SAY: The purpose of epidemiology in public health practice is to discover the agent, host, and environmental factors that affect health; determine the relative importance of causes of illness, disability, and death; identify those segments of the population that have the greatest risk from specific causes of ill health; and evaluate the effectiveness of health programs and services in improving population health. GO to next slide.
- #7: SAY: The purpose of epidemiology in public health practice is to discover the agent, host, and environmental factors that affect health; determine the relative importance of causes of illness, disability, and death; identify those segments of the population that have the greatest risk from specific causes of ill health; and evaluate the effectiveness of health programs and services in improving population health. GO to next slide.
- #8: SAY: The purpose of epidemiology in public health practice is to discover the agent, host, and environmental factors that affect health; determine the relative importance of causes of illness, disability, and death; identify those segments of the population that have the greatest risk from specific causes of ill health; and evaluate the effectiveness of health programs and services in improving population health. GO to next slide.
- #9: SAY: The purpose of epidemiology in public health practice is to discover the agent, host, and environmental factors that affect health; determine the relative importance of causes of illness, disability, and death; identify those segments of the population that have the greatest risk from specific causes of ill health; and evaluate the effectiveness of health programs and services in improving population health. GO to next slide.
- #10: SAY: The purpose of epidemiology in public health practice is to discover the agent, host, and environmental factors that affect health; determine the relative importance of causes of illness, disability, and death; identify those segments of the population that have the greatest risk from specific causes of ill health; and evaluate the effectiveness of health programs and services in improving population health. GO to next slide.
- #11: SAY: The purpose of epidemiology in public health practice is to discover the agent, host, and environmental factors that affect health; determine the relative importance of causes of illness, disability, and death; identify those segments of the population that have the greatest risk from specific causes of ill health; and evaluate the effectiveness of health programs and services in improving population health. GO to next slide.
- #13: SAY: The purpose of epidemiology in public health practice is to discover the agent, host, and environmental factors that affect health; determine the relative importance of causes of illness, disability, and death; identify those segments of the population that have the greatest risk from specific causes of ill health; and evaluate the effectiveness of health programs and services in improving population health. GO to next slide.
- #14: SAY: The purpose of epidemiology in public health practice is to discover the agent, host, and environmental factors that affect health; determine the relative importance of causes of illness, disability, and death; identify those segments of the population that have the greatest risk from specific causes of ill health; and evaluate the effectiveness of health programs and services in improving population health. GO to next slide.
- #15: SAY: The purpose of epidemiology in public health practice is to discover the agent, host, and environmental factors that affect health; determine the relative importance of causes of illness, disability, and death; identify those segments of the population that have the greatest risk from specific causes of ill health; and evaluate the effectiveness of health programs and services in improving population health. GO to next slide.
- #16: SAY: The purpose of epidemiology in public health practice is to discover the agent, host, and environmental factors that affect health; determine the relative importance of causes of illness, disability, and death; identify those segments of the population that have the greatest risk from specific causes of ill health; and evaluate the effectiveness of health programs and services in improving population health. GO to next slide.
- #18: SAY: The purpose of epidemiology in public health practice is to discover the agent, host, and environmental factors that affect health; determine the relative importance of causes of illness, disability, and death; identify those segments of the population that have the greatest risk from specific causes of ill health; and evaluate the effectiveness of health programs and services in improving population health. GO to next slide.
- #19: SAY: The purpose of epidemiology in public health practice is to discover the agent, host, and environmental factors that affect health; determine the relative importance of causes of illness, disability, and death; identify those segments of the population that have the greatest risk from specific causes of ill health; and evaluate the effectiveness of health programs and services in improving population health. GO to next slide.