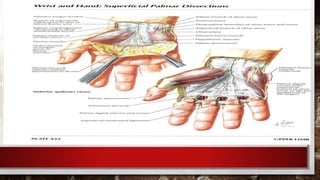
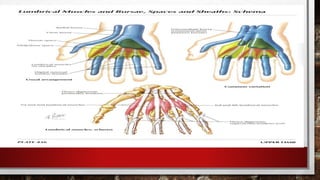
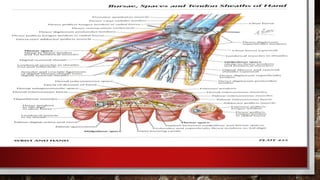
–≥–∞—Ä, —Å–∞—Ä–≤—É—É–Ω—ã –≥—ç–º—Ç—ç–ª
- 5. –ó–ê–í–¨ –•–≠–õ–ë–≠–Ý–¢ –Ø–°–ù–´ –•–£–ì–ê–Ý–ê–õ –ì–∞—Ä —Å–∞—Ä–≤–∞–π–Ω –∞–ª–≥–∞–∞—Ä –¥–∞—Ä–∂ —É–Ω–∞—Ö–∞–¥ –≥–æ–ª–¥—É—É —Ö—É–≥–∞—Ä–¥–∞–≥. –ì–æ–ª–¥—É—É –¥—É–Ω–¥—É—É—Ä–∞–∞ —Ö—É–≤–∞–∞–≥–¥–∞–≥–¥–∞–∂ —Ö—É–≥–∞—Ä–¥–∞–≥. –•—É–≥–∞—Ä–ª—ã–≥ “Ø–µ: ‚Ä¢ –¥–æ—Ç—É—É—Ä, ‚Ä¢ –≥–∞–¥—É—É—Ä –≥—ç–∂ —è–ª–≥–∞–Ω–∞. –û–Ω–æ—à–ª–æ—Ö–≥“Ø–π ”©–Ω–≥”©—Ä—Å–Ω”©”©—Å –±—É–≥—É–π–≥–∞–∞—Ä –±–∞–π–Ω–≥–∞ ”©–≤–¥”©—Ö, —Ö”©–¥”©–ª–≥”©”©–Ω —Ö—è–∑–≥–∞–∞—Ä–ª–∞–≥–¥–∞—Ö, —Ö”©–¥”©–ª–º”©—Ä–ª”©—Ö —á–∞–¥–≤–∞—Ä –±—É—É—Ä–¥–∞–≥.
- 6. •Оношлогоо: ердийн 2 тусгалаар рентген зураг авахад завь хэлбэрт яс бүхэлдээ тодорхой харагдахгүй тул хажуугаас нь 450 налуу өнцгөөр 3 дахь тусгалаар авсан зурагт завь хэлбэрт яс бүхэлдээ харагдана. Шинж тэмдэг: • бугуй бага зэрэг хавдах, • хөдөлгөхөд өвдөх, • хөдөлгөөн хязгаарлагдахыг зарим өвчтөн анзаарахгүй хугацаа алддаг. • Эрхий гэдийлгэхэд ар ёроолд нь үүсдэг хонхрын ёроолыг дарахад хөндүүр, хавдартай, шууны шөвөгний орчимд дарах, эрхий долоовор хурууг туушид нь түлхэхэд, сарвууг гэдийлгэхэд өвдөлт нэмэгдэнэ.
- 7. Эмчилгээ: • завь хэлбэрт яс хугарахад тэжээгч судас тасарснаас ба бугуйн яснууд ясны хальсгүй тул бороололт муу байдаг. • Бугуйн үеэр хөдөлж байхад завь хэлбэрт ясны хугархайнууд бороолохгүй. • Гөлтгөнө боолтыг тохойн үенээс хурууны уг хүртэл битүү гөлтгөнө боолт хийж чиг бэхэлгээ хийдэг. Сарвууг эрхий чигт бага зэрэг хазайлгаж гөлтгөнө боолт хийдэг. • Бороололгүй удсан хугарлыг мэс заслаар эмчилнэ.
- 8. –•–∞–≥–∞—Å —Å–∞—Ä —è—Å–Ω—ã —Ö—É–≥–∞—Ä–∞–ª –•–æ–≤–æ—Ä —Ç–æ—Ö–∏–æ–ª–¥–æ–Ω–æ. –°–∞—Ä–≤—É—É–≥ –±–æ–≥—Ç–æ—Å–Ω—ã —á–∏–≥—Ç –º—É—Ä–∏–π–∂ –∞–ª–≥–∞–∞—Ä –¥–∞—Ä–∂ —É–Ω–∞—Ö–∞–¥ —Ö—É–≥–∞—Ä–¥–∞–≥. –ì–æ–ª–¥—É—É —à–∞—Ö–∞–≥–¥–∞–∂, –±—è—Ü–∞—Ä—á —Ö—É–≥–∞—Ä–¥–∞–≥. –®–∏–Ω–∂ —Ç—ç–º–¥—ç–≥, –æ–Ω–æ—à: ‚Ä¢ –±—É–≥—É–π–Ω “Ø–µ–Ω–∏–π –∞—Ä –≥–æ–ª–¥ –∂–∏–∂–∏–≥ —Ö–∞–≤–¥–∞—Ä—Ç–∞–π, ‚Ä¢ –¥–∞—Ä–∞—Ö–∞–¥ —Ö”©–Ω–¥“Ø“Ø—Ä –±–∞–π–¥–∞–≥. ‚Ä¢ –î—É–Ω–¥ —è–¥–∞–º —Ö—É—Ä—É—É–≥ —É—Ä—Ç–∞–∞—à –Ω—å —Ç“Ø–ª—Ö—ç—Ö, —Å–∞—Ä–≤—É—É–≥ –≥—ç–¥–∏–π–ª–≥—ç—Ö—ç–¥ —Ö–∞–≥–∞—Å —Å–∞—Ä —è—Å–Ω—ã –æ—Ä—á–∏–º –∏—Ö ”©–≤–¥”©–Ω”©. ‚Ä¢ –Ý–µ–Ω—Ç–≥–µ–Ω –∑—É—Ä–∞–≥ –∞–≤—á –æ–Ω–æ—à–ª–æ–Ω–æ.
- 9. Эрхий хурууны алга-хурууны шивнүүр хоорондын үений хажуугийн холбоос тасрах Эрхийг гэнэт хэтэрхий гэдийлгэхэд алга-хурууны шивнүүр хоорондын холбоос тасарч болох юм. Заримдаа жижиг ясыг огло татаж холбоос тасардаг. Үүнээс болж ямар нэг юмыг атгахыг завдах, эрхийн өндөгөөр бусад хурууны чимхэхэд эрхийн угийн шивнүүр хагас мултрах хандлагатай болдог. Атгах, чимхэх үйлдэл бол эрхийн гол үүрэг юм.
- 12. –®–∏–Ω–∂ —Ç—ç–º–¥—ç–≥, –æ–Ω–æ—à–ª–æ–≥–æ–æ: —ç—Ä—Ö–∏–π–Ω ”©–Ω–¥–≥–∏–π–≥ –¥–∞—Ä–∞—Ö–∞–¥ —É–≥–Ω—ã “Ø–µ—ç—Ä –∞–ª–≥–∞–Ω —Ç–∏–π—à –æ–≤–æ–π–∂ —Ç–∞—Ö–∏–π–¥–∞–≥. –Ý–µ–Ω—Ç–≥–µ–Ω –∑—É—Ä–∞–≥ –¥—ç—ç—Ä —ç—Ä—Ö–∏–π —Ö–∞–≥–∞—Å –º—É–ª—Ç–∞—Ä—Å–∞–Ω, —è—Å —ç–º—Ç—ç—Ä—Å—ç–Ω –±–∞–π–¥–∞–≥. –≠–º—á–∏–ª–≥—ç—ç: —ç—Ä—Ö–∏–π–≥ –¥–æ–ª–æ–æ–≤–æ—Ä —Ö—É—Ä—É—É–Ω—ã —á–∏–≥—Ç –±–∞–≥–∞ –∑—ç—Ä—ç–≥ –±”©—Ö–∏–π–ª–≥”©—Å”©–Ω –±–∞–π—Ä–ª–∞–ª–¥ –≥”©–ª—Ç–≥”©–Ω”© –∞—Ä–∞–≤—á–Ω—ã —á–∏–≥ —à—É—É–Ω—ã –¥—É–Ω–¥ —Ö—ç—Å—ç–≥ —Ö“Ø—Ä—Ç—ç–ª —Ç–∞–≤—å–¥–∞–≥. –ò–π–º –∞—Ä–≥–∞–∞—Ä –∑–∞—Å—Ä–∞—Ö–≥“Ø–π –±–æ–ª –º—ç—Å –∑–∞—Å–ª–∞–∞—Ä —Ç–∞—Å–∞—Ä—Å–∞–Ω —Ö–æ–ª–±–æ–æ—Å—ã–≥ –±–∞–π—Ä–∞–Ω–¥ –Ω—å –±–∞—Ä—å–∂ –æ—ë–¥–æ–≥.
- 13. Алганы I шивнүүрийн суурь хэсгийн хугарал Хурууны уртааш тэнхлэгээр түлхэхэд алга хавчих байрлалтай байсан I шивнүүрийг гэнэт хүчтэй нугалснаас ийм хугарал үүсдэг. Ялангуяа гар бөмбөгөөр тоглох, ачаа ачих зэрэг ажиллагааны үед ийм хугарал үүсдэг. Хугарлыг 2 хуваадаг: Нэг дэх хугарлын үед зөвхөн шивнүүрийн суурины урд дотор талын буюу богтос талын хасаг хугарна. Хуруу алганы шивнүүрийн хамт ар тийш мултардаг. Үүнийг Беннетийн хугарал-мултрал гэнэ. Хоёр дахь хэлбэрийн хугарлын үед алганы шивнүүрийн суурь хэсэг нугалах байрлалаар хугарна. Хугарлын шугам үе дайралгүй түүнээс 1.5 см доогуур гардаг. Үзүүр талын хугархайн үзүүр ар тйиш зөрж сойдог.
- 14. Шинж тэмдэг, оношлогоо: • хуруу хагас атгах байрлалтай, • шивнүүрийн ар талд түүний суурь орчим овойж дарах, хөдөлгөхөд хөндүүр. Хуруунаас татах, түлхэхэд овгор орчинд өвдөж, хөдлөх ёсгүй хэсгээр хөдөлж, хааяа яс хавирч мэдэгдэнэ. • Хурууг татаж гэдийлгэхэд тахир нь арилаад тавихад дахин тахийдаг. • Хоёр тусгалаас рентген зураг авч эцсийн онош тогтоодог. Эмчилгээ: хэсгийн мэдээ алдуулалт хийнэ. Туслагч II, III хуруу, бугуйнаас хөдлөлгүй барина. аравч чиг тавиад битүү гөлтгөнө боолт хийдэг. Мэс засал эмчилгээ: Засраагүй, хялбархан зөрөмтгий алганы шивнүүрийн хугарлыг мэс заслаар эмчилнэ.
- 15. Алганы II, III, IV, V шивнүүрийн их биеийн хугарал Юманд шууд дарагдсан, хавчигдсан, цохигдсоноос голдуу алганы шивнүүр хугардаг. Гэмтэл учруулсан хүчний онцлогоос болж ташуу, мушгирсан, бяцарсан, хааяа шигдмэл, хөндлөн хугарал тохиолдоно. Шивнүүрийн аль ч түвшинд хугардаг. Ганц шивнүүрийн хугархай зөрөх нь ховор, их төлөв алганы ар тийш овойж тахийдаг. Хэд хэдэн шивнүүр хугарахад хажуугийн зөрөө үүсдэг.
- 17. –®–∏–Ω–∂ —Ç—ç–º–¥—ç–≥, –æ–Ω–æ—à–ª–æ–≥–æ–æ: –•—É–≥–∞—Ä—Ö–∞–π–Ω –∑”©—Ä”©”©–≥ —Ç—ç–º—Ç—ç—Ä—á “Ø–∑—ç—ç–¥ —Ç–∞–Ω–∏—Ö–∞–¥ –∞–º–∞—Ä—Ö–∞–Ω , —Ü—É—Å —Ö—É—Ä—Å–∞–Ω, –∞—Ä —Ç–∏–π—à –æ–≤–æ–π—Å–æ–Ω –Ω—å –∏–ª —Ö–∞—Ä–∞–≥–¥–∞–Ω–∞. –•—É—Ä—É—É–≥ —ç–≥—Ü—ç—ç—Ä –Ω—å —Ç–∞—Ç–∞—Ö, —Ç“Ø–ª—Ö—ç—Ö –±–∞ —Ö—É–≥–∞—Ä–ª—ã–Ω –æ—Ä—á–∏–º–¥ –¥–∞—Ä–∞—Ö–∞–¥ —Ö—É–≥–∞—Ä–ª—ã–Ω —Ö—ç—Å—ç–≥—Ç ”©–≤–¥”©–Ω”©. –•–∞–∞—è–∞ —è—Å —Ö–∞–≤–∏—Ä—á –º—ç–¥—ç–≥–¥—ç–Ω—ç. –Ý–µ–Ω—Ç–≥–µ–Ω –∑—É—Ä–∞–≥ —Ö–æ–π–¥, —É—Ä–¥, 350 —Ç–∞—à—É—É —Ç—É—Å–≥–∞–ª–∞–∞—Ä –∞–≤—á —Ö—É–≥–∞—Ä–ª—ã–Ω –±–∞–π–¥–ª—ã–≥ —Ç–æ–¥–æ—Ä—Ö–æ–π –º—ç–¥–Ω—ç. –≠–º—á–∏–ª–≥—ç—ç: –∑”©—Ä”©”©–≥“Ø–π –±–æ–ª –∞—Ä–∞–≤—á –±“Ø—Ö–∏–π –≥”©–ª—Ç–≥”©–Ω”© –±–æ–æ–ª—Ç —Ö–∞—Ä—å—Ç, —Å–∞—Ä–≤—É—É–≥ —Ö–∞–≤—Å—Ä—É—É–ª–∞–Ω —Ö–∏–π–¥—ç–≥. –¢–∞—Ö–∏–π—Å–∞–Ω –∑”©—Ä”©”©—Ç—ç–π —Ö—É–≥–∞—Ä–ª—ã–≥ –∑–∞—Å–∞—Ö—ã–Ω —Ç—É–ª–¥ —Ö—ç—Å–≥–∏–π–Ω –º—ç–¥—ç—ç–≥“Ø–π–∂“ؓؖª—ç–≥ —Ö–∏–π–≥—ç—ç–¥ –∞—Ä —Ç–∏–π—à –æ–≤–æ–π—Å–æ–Ω “Ø–∑“ؓؗĖ∏–π–≥ –Ω—ç–≥ —Ö—É—Ä—É—É–Ω—ã ”©–Ω–¥–≥”©”©—Ä –∞–ª–≥–∞–≥—ã —á–∏–≥—Ç –Ω”©–≥”©”© –≥–∞—Ä—ã–Ω —Ö—É—Ä—É—É–≥–∞–∞—Ä —à–∏–≤–Ω“Ø“Ø—Ä–∏–π–Ω —Ç–æ–ª–≥–æ–π–≥ –∞–ª–≥–∞–Ω —Ç–∞–ª–∞–∞—Å —Ç—É—Å —Ç—É—Å —Å”©—Ä–≥“ؓؖª—ç–Ω –¥–∞—Ä–∂ —ç–≤–ª“ؓؖª–¥—ç–≥.
- 18. Хурууны хугарал Үйлдвэрлэлийн ба гэр ахуйн нөхцөлд хуруу голлож гэмтдэг. Ялангуяа ил хугарал элбэг байдаг. Ил хугаралд мэс заслын анхны цэгцэлгээ хийдэг. Хурууны шивнүүрийн хугарал: үений дотуур, үе хавьцаа, шивнүүрийн их биеийн хугарал гэж ялгадаг. Хурууны хугарлын нэлээд нь суурь шивнүүрийн хугарал байдаг. Голдуу түүний дээд хэсгээр хугардаг. Хурууны үе мултарч хугарахад үений ирмэгээс том, жижиг хэсэг сэлтэрдэг. Ингэснээр үений бат тогтвортой байдал алдагддаг.
- 19. Хумстай үений шивнүүр голдуу юманд цохигдох, хавчигдах, дарагдахад хугардаг. Ихэнхдээ бяцарсан хугарал үүсэж хумсны дотуур цус хуралдана. Хумстай шивнүүрийг гэнэт хүчтэй нугалахад шивнүүрийн суурь хэсэгт бэхлэгдсэн тэнийлгэгч булчингийн шөрмөс бэхэлгээнээсээ тасардаг. Шинж тэмдэг: шивнүүрийн их бие хугараад зөрвөл хуруу тахийж богино болдог. Яс овойсныг барьж мэдэх бөгөөд хурууны уртааш тэнхлэгийн дагуу дарах буюу татахад хугарлаар өвдөж яс хавирч мэдэгдэнэ. Шивнүүрийн үений хугарлын үед тэр хэсэгт хавдаж хөдөлгөхөд их өвдөнө.
- 20. Эмчилгээ: засалтыг нямбай хийх ёстой. Хугархайнууд муу эвлэж бороолбол хурууны үйл ажиллагаа ноцтой алдах тул жинхэнэ анатомийг нь сэргээх явдал хамгийн чухал. Ар тийш тахийж бороолбол нугалах, алган тийш тахийвал тэнийлгэх хөдөлгөөн хязгаарлагдана. Хугархайн үзүүр, бороо, наалдац зэрэгт нугалагч шөрмөсний бүрээс гэмтсэнээс хурууны хөдөлгөөн хязгаарлагдана. Гэмтлийн үрэвсэл арилтал цус, хаван сорогдож шимэгдтэл засалт хийснээс хойш 2-3 долоо хоног сайн чиг бэхэлгээ хийнэ. Чиг бэхэлгээ хийхдээ гэмтсэн хурууг эгц байрлалд байлгана. Эрүүл хурууг оролцуулахыг хориглоно. Бэхлээгүй хуруу, гарын үеүдийг байнга хөдөлгөх нь чухал. Зөвхөн идэвхтэй хөдөлгөөн хийх ёстой.