Summary scm
Download as PPT, PDF1 like879 views
This document discusses key topics in supply chain management (SCM) including outsourcing logistics services, order management, transportation, warehousing, inventory management, packaging, supplier selection, system design, and international logistics structures. It provides definitions and overviews of supply chains, SCM, third-party logistics (3PL) providers, electronic commerce and logistics, order management, packaging, transportation modes, warehouse location analysis, warehousing management, inventory management, supplier selection, logistics system design, and international logistics structures.
1 of 28
Downloaded 17 times


























Recommended
Logistics Management, BBA III Year Notes, Osmania University



Logistics Management, BBA III Year Notes, Osmania UniversityBalasri Kamarapu
Ã˝
Inbound, Internal and Outbound Logistics in SCM, Developing the Logistics organization for effective Supply Chain Management, development of Integrated Logistics Strategy, Logistics in Maximizing profitability and cash flow, 3PL, 4PL, International Logistics, Reverse Logistics.Supply chain management



Supply chain managementbabak mahmoodi
Ã˝
The document discusses supply chain management and supply network design. It defines a supply network as including all upstream and downstream operations linked together. Considering the whole network helps with understanding competitiveness, identifying important links, and focusing on long-term issues. Location decisions are influenced by both supply-side factors like labor, land, and transportation costs, and demand-side factors like customer convenience. Supply chain management involves coordinating the flow of goods and services from raw materials to the final customer.Logistics Management & Material Handeling



Logistics Management & Material HandelingSana Fatima
Ã˝
1. The document discusses logistics management concepts including key logistics activities, total cost concept, and relationship between logistics activities and costs.
2. It outlines 13 common logistics activities such as customer service, demand forecasting, inventory management, and transportation. These activities need to be integrated to improve efficiency.
3. The total cost concept aims to reduce overall logistics costs by analyzing trade-offs between order processing, inventory carrying, transportation, and other costs.Principles Of Logistics Management



Principles Of Logistics ManagementYvonne
Ã˝
This document discusses principles of logistics management. It defines logistics management as planning, implementing, and controlling the efficient flow of goods from origin to consumption to meet customer needs. Logistics plays an important role in the economy by creating time and place utility, and plays a key role in organizations by supporting marketing and adding value through possession, time, and place utility. The document outlines key components and activities of logistics management including demand forecasting, inventory management, transportation, and customer service.Logistics in business



Logistics in businessAmit Kulkarni
Ã˝
Logistics management involves ensuring the right materials are in the right place at the right time. The objectives of logistics include customer satisfaction, understanding customer needs, managing uncertainty, responding to globalization, effective information flow, and cost reduction. Careers in logistics are growing and include positions in inventory control, warehousing, transportation, consulting, and logistics administration. Key aspects of logistics management are location, staffing, taxation, product and supplier development, packaging, transportation, order fulfillment, inventory management, and customer management. Planning considers performance measures, processes, systems, organizational requirements, inventory, supply, and transportation.Logistics management



Logistics managementMayank Garg
Ã˝
Logistics involves planning and implementing the efficient movement and storage of goods and services from the supplier to the customer. It includes activities like transportation, warehousing, inventory management, and order fulfillment. Logistics aims to meet customer needs cost effectively and ensure the right materials are delivered at the right time. Key logistics activities involve customer service, inventory planning, procurement, transportation, and distribution center operations. Logistics provides benefits like risk reduction and better productivity but also faces challenges around speed, customer service, and data management.Fed ex warehousing overview



Fed ex warehousing overviewsavvyavarma
Ã˝
FedEx uses a hybrid warehousing strategy that is decentralized internationally but centralized nationally. This allows them to have warehouses close to customers internationally to reduce delivery times, while taking advantage of economies of scale within countries by operating fewer, larger warehouses. When implementing a warehouse management system, FedEx considers the physical characteristics and storage requirements of each item, as well as warehouse dimensions and capacities. It also decides on configuration details like placement and retrieval processes. A successful implementation requires input from warehouse operations to understand daily processes without disrupting regular activities.raymond tarr- paper



raymond tarr- paperray tarr
Ã˝
Packaging optimization can significantly reduce supply chain costs by improving how products are packaged for shipping. The efficiency of the supply chain depends on both the network of movement as well as the physical characteristics of the product. By designing packaging to better fit pallets and trucks, companies can impact key shipping rate factors like density and reduce logistics expenses. Through packaging assessments and cost-benefit analyses of improvement options, optimization programs can be developed to streamline packaging systems, lower costs, and enhance supply chain efficiencies. Examples of opportunities include reducing package weight and size, improving density, and designing packaging that better withstands distribution damage.Logistics management 



Logistics management Arbaz Khan
Ã˝
Logistics management involves planning, implementing, and controlling the flow of materials and goods from the origin to the point of use. The objectives of logistics management are to have the right quality and quantity of products available at the right place and time at reduced costs. Logistics management applies to business, military operations, events, and services. It aims to optimize material flow through an organization to customers while reducing inventory, ensuring reliable delivery, minimizing freight and damage costs, and allowing quick response.New Normal and New Supply Chain Management -- Part 2



New Normal and New Supply Chain Management -- Part 2Tom Craig
Ã˝
With the pandemic, companies around the world confirmed the strategic and critical importance of SCM. All the time that the pandemic has gone on. The new, post-pandemic supply chain management is key to much that companies, both manufacturers and retailers, have to do. E-commerce. Supply chain resilience. Reshore. And the impact of the pandemic-- Inventory. Understand your end-to-end supply chain. Change is not an option.Logistics management



Logistics managementNavin Raj Saroj
Ã˝
The document discusses various aspects of logistics management including definitions, objectives, importance and key concepts. It defines logistics as the process of optimizing the flow of materials and supplies through an organization to deliver products to customers. The objectives of logistics are to make the right products available in the right place at the right time, while achieving customer satisfaction and lowest cost. It also discusses the importance of logistics in physical distribution, reverse logistics, material handling, packaging and the paradigm shift in viewing logistics operations as an integrated system rather than separate functions.3pl and 4pl



3pl and 4plHammaduddin
Ã˝
Third-party logistics (3PL) providers are companies that provide logistics services like transportation, warehousing, and distribution for other companies. 3PLs allow companies to focus on their core business while outsourcing logistics functions. Common types of 3PLs include transportation-based, warehouse/distribution-based, and financial-based providers. Using 3PLs can help companies save time and money, expand markets, and focus on their strengths. However, there are also risks like loss of control and visibility with customers. Choosing the right 3PL requires thorough due diligence and establishing clear expectations, performance measures, and a process for managing the relationship.Customer oriented logistics management



Customer oriented logistics managementAruzmahajan
Ã˝
The document discusses logistics management and customer-oriented logistics. It describes logistics as the transport of goods to customers and logistics management as meeting customer demands through planning, control and implementation of movement and storage. The objectives of logistics management are outlined as cost reduction, capital reduction and service improvement. Key facilities decisions, warehousing functions and decisions are also summarized.Introduction 2 Logistics



Introduction 2 LogisticsYoussef Serroukh
Ã˝
This document provides an introduction to logistics. It defines logistics as the planning and management of the flow of goods and services. Logistics involves activities like transportation, warehousing, inventory management, and customer service. The document also discusses the importance of logistics and how it has evolved over time to integrate functions across supply chains on a global scale.Supply Chain Management Resilience



Supply Chain Management ResilienceTom Craig
Ã˝
A lesson from the pandemic is the strategic and critical importance of supply chain management. With that goes the need for supply chain resilience. Both inside and outside four walls. It started out about technology, but as the pandemic continued, logistics and logistics infrastructure is showing as a key for supply chain resilience. View these for content that may assist you to make your supply chain resilient.Bey syl scm



Bey syl scmAhmed Sharif
Ã˝
Supply chain management involves managing all efforts to produce and deliver a final product or service. This includes sourcing raw materials, manufacturing, inventory management, distribution, and delivery to customers. The supply chain includes suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, and customers. Effective supply chain management can lower costs and improve customer service. It requires coordinating processes like procurement, manufacturing, and replenishment across the chain.Warehouse decesion model



Warehouse decesion modelKeshar Khadka
Ã˝
This presentation insight the importance of strategic decision while allocating new warehouse or distribution point.Scm ppt



Scm pptprakrati27
Ã˝
Logistics involves managing the flow of goods and information from suppliers to customers. It includes transportation, warehousing, inventory management, and other processes involved in procurement, distribution, and delivery. The goal of logistics is to deliver the right product to the right customer at the right time and place while minimizing costs and meeting customer requirements. Logistics management aims to control material and information flows efficiently and effectively across the supply chain.Introduction to Logistics Management



Introduction to Logistics ManagementLitunya Laurean
Ã˝
A brief overview of logistics management covering the following: the aim of logistics, components of logistics, major functions of logistics and the phases of logistics management.1 introduction



1 introductionKaterina Berezovskaya
Ã˝
This document provides an introduction to a logistics management course. It outlines the course description, learning objectives, textbooks, grading policy and schedule. The course will cover topics such as logistics systems and supply chain management. It will include lectures, videos, group exercises and case study discussions. Students will be graded based on assignments, midterm exam, case study presentation and a final project. The goal is for students to understand the strategic role of supply chains and how to solve business problems through logistics.Logistics main



Logistics mainm_laddha
Ã˝
The document discusses the key elements and functions of logistics management. It defines logistics as the process of planning and executing the efficient movement and storage of raw materials, work-in-process inventory, and finished goods from point of origin to point of consumption. The main elements of logistics include procurement, inventory management, transportation, warehousing, material handling, and packaging. The key logistics functions involve information systems, transportation, inventory control, warehousing, material handling, and network design. The document also outlines several important concepts and operating objectives in logistics like rapid response, minimum variance, and life cycle support.Supply chain sustainability is a holistic perspective of supply chain process...



Supply chain sustainability is a holistic perspective of supply chain process...Narendra Chaudhary
Ã˝
This document discusses several topics related to supply chain management and logistics. It discusses supply chain sustainability, demand-driven manufacturing, third-party logistics (3PL), demand flow scheduling systems, reducing supply chain costs through optimizing logistics management, and just-in-time manufacturing. The key ideas are that supply chain sustainability aims to reduce waste and costs through collaboration, demand-driven manufacturing produces goods based on customer orders rather than forecasts, 3PL providers manage outsourced logistics services, and optimizing logistics is important for controlling international trade costs.Logistic management



Logistic managementjimcyvarghese
Ã˝
Logistic management and supply chain management are critical for businesses. Logistics involves planning, implementing, and controlling the flow of materials and finished goods from suppliers to customers. It has become more important with globalization, a focus on integrated supply chain management, and the outsourcing of non-core functions. Effective logistics can provide both cost leadership and differentiated products and services by optimizing activities across the value chain.Implementig the strategy



Implementig the strategyosmanbakkal
Ã˝
The document discusses implementing logistics strategies by relating them to lower level decisions, examining areas like supply chain structure, facility location, and capacity. It also covers managing change when implementing new strategies, noting that change must be carefully managed as most people resist rapid or complex changes but will accept changes given enough time. The case study of Ralston Energy Systems describes how outsourcing logistics to a third party provider brought benefits like flexible warehousing and reduced costs.Supply Chain Management Basics: 3PLs - One Size Does Not Fit All



Supply Chain Management Basics: 3PLs - One Size Does Not Fit AllAngela Carver
Ã˝
This document discusses third-party logistics providers (3PLs) and factors to consider when selecting one. It notes that 3PLs now offer a wider range of services beyond traditional transportation and warehousing, including global, IT, and value-added services. When evaluating 3PLs, the document recommends considering their technology capabilities, company culture, infrastructure, ease of doing business, key performance metrics, and intangible services. Selecting the best-fit 3PL can help shippers reduce costs, improve customer satisfaction, access global expertise, and reduce risk.Distribution Strategies



Distribution StrategiesSUDARSHAN KUMAR PATEL
Ã˝
The document discusses various distribution strategies and concepts. It begins by defining distribution strategies and describing different channel types like intensive, selective, and exclusive distribution. It then discusses direct shipping and its advantages and challenges. Other concepts covered include intermediate inventory points distribution, traditional warehousing versus cross-docking versus centralized pooling strategies, transportation and transhipment.Logistics Management



Logistics ManagementNarendra Chaudhary
Ã˝
This document provides an overview of logistics management. It defines logistics as managing the flow of materials and finished goods from suppliers to customers. This includes transportation, warehousing, inventory management, and information systems. The objectives of an effective logistics system are to ensure the right goods are delivered to customers in the correct quantities, locations, times and at the lowest overall cost while meeting quality standards. Key aspects of logistics discussed include distribution and warehousing management, physical distribution, and reducing supply chain costs.Integrated logistics and supply chain framework



Integrated logistics and supply chain frameworkbarvie
Ã˝
The document provides an overview of supply chain and logistics concepts for students. It defines key terms like supply chain management, logistics management, and physical distribution. It also outlines the typical flow of activities in a company's supply chain, from sales forecasting to order fulfillment. The goal is for students to understand the roles and importance of effective logistics and supply chain management.1 introduction



1 introductionSagar Mhatre
Ã˝
This document provides an introduction and overview of a logistics management course. It includes sections on introducing the instructor and course objectives, an outline of course topics, a description of assignments and grading, and the course schedule. The key topics covered are an introduction to logistics and supply chain management, the relationship between material and information flow, how logistics contributes to competitive advantage, and factors to consider in developing a supply chain strategy.Fundamentals of Logistics.pptx



Fundamentals of Logistics.pptxssuserba946c
Ã˝
Introduction
• The Broad Scope of Logistics
• Definitions
– Logistics
– Logistics Management
• Logistics – A System Concept
– Logistics Mix
• Logistics Functions
• * Scope / Activities of Logistics
• Inbound Logistics [Upstream Logistics]
• Outbound Logistics [Downstream Logistics]
• Manufacturing LogisticsMore Related Content
What's hot (20)
Logistics management 



Logistics management Arbaz Khan
Ã˝
Logistics management involves planning, implementing, and controlling the flow of materials and goods from the origin to the point of use. The objectives of logistics management are to have the right quality and quantity of products available at the right place and time at reduced costs. Logistics management applies to business, military operations, events, and services. It aims to optimize material flow through an organization to customers while reducing inventory, ensuring reliable delivery, minimizing freight and damage costs, and allowing quick response.New Normal and New Supply Chain Management -- Part 2



New Normal and New Supply Chain Management -- Part 2Tom Craig
Ã˝
With the pandemic, companies around the world confirmed the strategic and critical importance of SCM. All the time that the pandemic has gone on. The new, post-pandemic supply chain management is key to much that companies, both manufacturers and retailers, have to do. E-commerce. Supply chain resilience. Reshore. And the impact of the pandemic-- Inventory. Understand your end-to-end supply chain. Change is not an option.Logistics management



Logistics managementNavin Raj Saroj
Ã˝
The document discusses various aspects of logistics management including definitions, objectives, importance and key concepts. It defines logistics as the process of optimizing the flow of materials and supplies through an organization to deliver products to customers. The objectives of logistics are to make the right products available in the right place at the right time, while achieving customer satisfaction and lowest cost. It also discusses the importance of logistics in physical distribution, reverse logistics, material handling, packaging and the paradigm shift in viewing logistics operations as an integrated system rather than separate functions.3pl and 4pl



3pl and 4plHammaduddin
Ã˝
Third-party logistics (3PL) providers are companies that provide logistics services like transportation, warehousing, and distribution for other companies. 3PLs allow companies to focus on their core business while outsourcing logistics functions. Common types of 3PLs include transportation-based, warehouse/distribution-based, and financial-based providers. Using 3PLs can help companies save time and money, expand markets, and focus on their strengths. However, there are also risks like loss of control and visibility with customers. Choosing the right 3PL requires thorough due diligence and establishing clear expectations, performance measures, and a process for managing the relationship.Customer oriented logistics management



Customer oriented logistics managementAruzmahajan
Ã˝
The document discusses logistics management and customer-oriented logistics. It describes logistics as the transport of goods to customers and logistics management as meeting customer demands through planning, control and implementation of movement and storage. The objectives of logistics management are outlined as cost reduction, capital reduction and service improvement. Key facilities decisions, warehousing functions and decisions are also summarized.Introduction 2 Logistics



Introduction 2 LogisticsYoussef Serroukh
Ã˝
This document provides an introduction to logistics. It defines logistics as the planning and management of the flow of goods and services. Logistics involves activities like transportation, warehousing, inventory management, and customer service. The document also discusses the importance of logistics and how it has evolved over time to integrate functions across supply chains on a global scale.Supply Chain Management Resilience



Supply Chain Management ResilienceTom Craig
Ã˝
A lesson from the pandemic is the strategic and critical importance of supply chain management. With that goes the need for supply chain resilience. Both inside and outside four walls. It started out about technology, but as the pandemic continued, logistics and logistics infrastructure is showing as a key for supply chain resilience. View these for content that may assist you to make your supply chain resilient.Bey syl scm



Bey syl scmAhmed Sharif
Ã˝
Supply chain management involves managing all efforts to produce and deliver a final product or service. This includes sourcing raw materials, manufacturing, inventory management, distribution, and delivery to customers. The supply chain includes suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, and customers. Effective supply chain management can lower costs and improve customer service. It requires coordinating processes like procurement, manufacturing, and replenishment across the chain.Warehouse decesion model



Warehouse decesion modelKeshar Khadka
Ã˝
This presentation insight the importance of strategic decision while allocating new warehouse or distribution point.Scm ppt



Scm pptprakrati27
Ã˝
Logistics involves managing the flow of goods and information from suppliers to customers. It includes transportation, warehousing, inventory management, and other processes involved in procurement, distribution, and delivery. The goal of logistics is to deliver the right product to the right customer at the right time and place while minimizing costs and meeting customer requirements. Logistics management aims to control material and information flows efficiently and effectively across the supply chain.Introduction to Logistics Management



Introduction to Logistics ManagementLitunya Laurean
Ã˝
A brief overview of logistics management covering the following: the aim of logistics, components of logistics, major functions of logistics and the phases of logistics management.1 introduction



1 introductionKaterina Berezovskaya
Ã˝
This document provides an introduction to a logistics management course. It outlines the course description, learning objectives, textbooks, grading policy and schedule. The course will cover topics such as logistics systems and supply chain management. It will include lectures, videos, group exercises and case study discussions. Students will be graded based on assignments, midterm exam, case study presentation and a final project. The goal is for students to understand the strategic role of supply chains and how to solve business problems through logistics.Logistics main



Logistics mainm_laddha
Ã˝
The document discusses the key elements and functions of logistics management. It defines logistics as the process of planning and executing the efficient movement and storage of raw materials, work-in-process inventory, and finished goods from point of origin to point of consumption. The main elements of logistics include procurement, inventory management, transportation, warehousing, material handling, and packaging. The key logistics functions involve information systems, transportation, inventory control, warehousing, material handling, and network design. The document also outlines several important concepts and operating objectives in logistics like rapid response, minimum variance, and life cycle support.Supply chain sustainability is a holistic perspective of supply chain process...



Supply chain sustainability is a holistic perspective of supply chain process...Narendra Chaudhary
Ã˝
This document discusses several topics related to supply chain management and logistics. It discusses supply chain sustainability, demand-driven manufacturing, third-party logistics (3PL), demand flow scheduling systems, reducing supply chain costs through optimizing logistics management, and just-in-time manufacturing. The key ideas are that supply chain sustainability aims to reduce waste and costs through collaboration, demand-driven manufacturing produces goods based on customer orders rather than forecasts, 3PL providers manage outsourced logistics services, and optimizing logistics is important for controlling international trade costs.Logistic management



Logistic managementjimcyvarghese
Ã˝
Logistic management and supply chain management are critical for businesses. Logistics involves planning, implementing, and controlling the flow of materials and finished goods from suppliers to customers. It has become more important with globalization, a focus on integrated supply chain management, and the outsourcing of non-core functions. Effective logistics can provide both cost leadership and differentiated products and services by optimizing activities across the value chain.Implementig the strategy



Implementig the strategyosmanbakkal
Ã˝
The document discusses implementing logistics strategies by relating them to lower level decisions, examining areas like supply chain structure, facility location, and capacity. It also covers managing change when implementing new strategies, noting that change must be carefully managed as most people resist rapid or complex changes but will accept changes given enough time. The case study of Ralston Energy Systems describes how outsourcing logistics to a third party provider brought benefits like flexible warehousing and reduced costs.Supply Chain Management Basics: 3PLs - One Size Does Not Fit All



Supply Chain Management Basics: 3PLs - One Size Does Not Fit AllAngela Carver
Ã˝
This document discusses third-party logistics providers (3PLs) and factors to consider when selecting one. It notes that 3PLs now offer a wider range of services beyond traditional transportation and warehousing, including global, IT, and value-added services. When evaluating 3PLs, the document recommends considering their technology capabilities, company culture, infrastructure, ease of doing business, key performance metrics, and intangible services. Selecting the best-fit 3PL can help shippers reduce costs, improve customer satisfaction, access global expertise, and reduce risk.Distribution Strategies



Distribution StrategiesSUDARSHAN KUMAR PATEL
Ã˝
The document discusses various distribution strategies and concepts. It begins by defining distribution strategies and describing different channel types like intensive, selective, and exclusive distribution. It then discusses direct shipping and its advantages and challenges. Other concepts covered include intermediate inventory points distribution, traditional warehousing versus cross-docking versus centralized pooling strategies, transportation and transhipment.Logistics Management



Logistics ManagementNarendra Chaudhary
Ã˝
This document provides an overview of logistics management. It defines logistics as managing the flow of materials and finished goods from suppliers to customers. This includes transportation, warehousing, inventory management, and information systems. The objectives of an effective logistics system are to ensure the right goods are delivered to customers in the correct quantities, locations, times and at the lowest overall cost while meeting quality standards. Key aspects of logistics discussed include distribution and warehousing management, physical distribution, and reducing supply chain costs.Integrated logistics and supply chain framework



Integrated logistics and supply chain frameworkbarvie
Ã˝
The document provides an overview of supply chain and logistics concepts for students. It defines key terms like supply chain management, logistics management, and physical distribution. It also outlines the typical flow of activities in a company's supply chain, from sales forecasting to order fulfillment. The goal is for students to understand the roles and importance of effective logistics and supply chain management.Supply chain sustainability is a holistic perspective of supply chain process...



Supply chain sustainability is a holistic perspective of supply chain process...Narendra Chaudhary
Ã˝
Similar to Summary scm (20)
1 introduction



1 introductionSagar Mhatre
Ã˝
This document provides an introduction and overview of a logistics management course. It includes sections on introducing the instructor and course objectives, an outline of course topics, a description of assignments and grading, and the course schedule. The key topics covered are an introduction to logistics and supply chain management, the relationship between material and information flow, how logistics contributes to competitive advantage, and factors to consider in developing a supply chain strategy.Fundamentals of Logistics.pptx



Fundamentals of Logistics.pptxssuserba946c
Ã˝
Introduction
• The Broad Scope of Logistics
• Definitions
– Logistics
– Logistics Management
• Logistics – A System Concept
– Logistics Mix
• Logistics Functions
• * Scope / Activities of Logistics
• Inbound Logistics [Upstream Logistics]
• Outbound Logistics [Downstream Logistics]
• Manufacturing LogisticsChap0011



Chap0011Jayne Dissette
Ã˝
The document provides an overview of supply chain management. It discusses key concepts like the components of a supply chain including suppliers, facilities, functions, and activities. It also covers topics such as supply chain management, global supply chains, procurement, inventory management, logistics, and challenges in creating an effective supply chain. The overall goal of supply chain management is to match supply and demand as effectively and efficiently as possible.Supply Chain Risk Management



Supply Chain Risk ManagementIhab Rizk CISCM, FIATA
Ã˝
This document provides an overview of supply chain management concepts. It defines key terms like logistics and supply chain management. It then discusses various components of a supply chain like facilities, inventory, transportation, and information and how decisions around these components can impact efficiency and responsiveness. The document also examines sourcing, pricing and supply chain collaboration strategies and how they relate to the competitive strategy.Third party logistic



Third party logisticPrakash Raj
Ã˝
The document discusses third party logistics (3PL). It defines 3PL as using third party businesses to outsource elements of distribution, warehousing, and fulfillment. This allows companies to focus on their core business while 3PL providers handle logistics functions. The document outlines the advantages of 3PL, such as reduced costs, lower capital requirements, and increased flexibility. It also discusses some disadvantages like loss of control and challenges with returns processing. Finally, it describes different types of 3PL providers based on the services offered.Logistic management



Logistic managementNabeel Shaikh
Ã˝
India has steadily liberalized its trade policies since the 1990s, reducing average tariffs and eliminating many import restrictions. However, it still maintains some protectionist policies like higher agricultural tariffs and restrictions on foreign investment in retail. The government's foreign trade policy aims to benefit consumers by facilitating imports needed to stimulate the economy. India is pursuing new regional and bilateral trade agreements and playing a leadership role in global trade negotiations. The World Bank provides analytical reports and workshops to support India's trade policy reforms and strategy in international negotiations, focusing on sectors like services, horticulture, and barriers to professional movement.supply chain mgt



supply chain mgtHarman Mangat
Ã˝
The document defines key concepts in supply chain management, including defining a supply chain as a network of organizations working together to deliver products to customers. It discusses the role of supply chain management in coordinating activities like production, inventory, location, transportation, and information across organizations. The goal of supply chain management is to increase sales to customers while reducing inventory and expenses. It also stresses the importance of aligning a company's supply chain strategy with its overall business strategy and market.The logistics system



The logistics systemVincenzo Presutto
Ã˝
What is the company's logistics system? Because logistics is increasingly important? How do you design a new logistics system?Unit 3 Forecasting systems design - Understanding the system



Unit 3 Forecasting systems design - Understanding the systemAnanya A
Ã˝
. Understand Supply Chain Dynamics:
Gain a comprehensive understanding of the entire supply chain, including procurement, production, logistics, and distribution. Recognize how different stages of the supply chain may influence demand.
2. Collaborate with Stakeholders:
Involve key stakeholders from different departments such as sales, marketing, production, and logistics. Their insights and expertise will provide valuable information for accurate forecasting.
3. Data Integration:
Integrate data from various sources within the supply chain, including historical sales data, inventory levels, supplier performance, and external factors such as market trends or economic indicators.
4. Demand Segmentation:
Segment your products or services based on characteristics that affect demand, such as seasonality, product life cycle, or customer demographics. Differentiated forecasting methods may be applied to each segment.
5. Technology Selection:
Choose forecasting technologies that integrate seamlessly with other SCM systems. This might include Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems, Warehouse Management Systems (WMS), and Transportation Management Systems (TMS).
6. Consider Lead Times and Variability:
Account for lead times in the supply chain when forecasting. Understand the variability in lead times and demand patterns to optimize inventory levels and reduce the risk of stockouts or overstocking.
7. Dynamic Models for Supply Chain Events:
Design dynamic forecasting models that can adapt to sudden events in the supply chain, such as disruptions in the supply network, changes in supplier capabilities, or unexpected demand fluctuations.
8. Demand Shaping Strategies:
Implement demand shaping strategies to influence customer demand positively. This may involve promotions, discounts, or other marketing initiatives to align with forecasted demand.
9. Risk Assessment:
Incorporate risk assessments into the forecasting process. Identify potential risks and uncertainties in the supply chain, such as geopolitical issues, natural disasters, or supplier reliability, and develop contingency plans.
10. Real-time Visibility:
Aim for real-time visibility into supply chain activities. Use technologies like IoT devices, RFID, and advanced analytics to monitor the movement of goods, track inventory levels, and gather real-time data for more accurate forecasting.
11. Performance Metrics:
Establish key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure the accuracy and effectiveness of the forecasting system. Regularly assess forecast accuracy, bias, and other relevant metrics to identify areas for improvement.
12. Continuous Improvement:
Emphasize a culture of continuous improvement. Regularly review and update forecasting models based on changing market conditions, technology advancements, and feedback from actual performance.
13. Sustainability Considerations:
Consider sustainability factors in forecasting, such as the environmental impact of production and transportation. 2011.2.14 marketing



2011.2.14 marketingStephan Langdon
Ã˝
The document discusses key concepts in supply chain management including defining supply chains, supply chain management, and the benefits of a supply chain orientation. It outlines important processes like customer relationship management, demand management, and order fulfillment. It also discusses logistical components, trends like advanced technology and outsourcing, and rankings of top healthcare supply chains.Introduction of logistics management.pptx



Introduction of logistics management.pptxRajeevRanjan743854
Ã˝
The document discusses logistics and supply chain management. It defines logistics and key concepts. Logistics involves planning and controlling the flow of goods and services. The goals of logistics systems are to ensure the right products are delivered to customers in the right quantities, at the right locations and times, in usable condition, and at the lowest total cost. Elements of logistics systems include transportation, warehousing, inventory management, packaging, and information systems.Role of-merchant-in-supply chain managment



Role of-merchant-in-supply chain managmentBangladesh University of Textiles
Ã˝
This document discusses supply chain management in the apparel industry. It provides definitions of supply chain management and describes key aspects of apparel supply chains, including typical links such as raw material suppliers, manufacturers, export channels, and retail networks. It also discusses the roles of merchandisers in managing apparel supply chain efficiency and outlines some trends in supply chain management like increased use of technology.8 session 8_distribution strategy cfvg 2012



8 session 8_distribution strategy cfvg 2012kimsach
Ã˝
The document discusses various distribution strategies used in supply chain management. It describes centralized and decentralized distribution control approaches. It then covers traditional distribution strategies like direct shipping, warehousing, cross-docking and provides details on how cross-docking operations work. The document also discusses other strategies like transshipment, pool distribution, hub-and-spoke models and milk-run systems. It analyzes the strategies based on factors like inventory levels, handling costs and transportation costs.Study of supply chain management with special reference to fed ex



Study of supply chain management with special reference to fed exchinar.khar
Ã˝
The document provides an overview of supply chain management (SCM) with a focus on FedEx. It discusses what SCM is, the problems it addresses, and key activities/functions. SCM aims to fulfill customer demands efficiently through integrated business processes from original suppliers to end users. The primary objective is efficiency across the supply chain to match demand with supply using minimal inventory. Key issues addressed by SCM include distribution network configuration, distribution strategy, trade-offs in logistical activities, information sharing, inventory management, and cash flow coordination. The document then discusses logistics management and its role in governing supply chain functions at strategic, operational and tactical levels.3 pl



3 plBashaSyed8
Ã˝
Third-party logistics (3PL) providers offer outsourced logistics services that involve managing procurement and fulfillment activities. 3PL services include transportation, warehousing, freight forwarding, reverse logistics, and courier shipping. Companies choose 3PL to reduce costs, improve efficiency, and focus on their core competencies. While 3PL provides benefits, it also results in loss of control over logistics and a more distant relationship with clients.SUPPLY CHAIN OVERVIEW



SUPPLY CHAIN OVERVIEWLambert Rodriguez
Ã˝
This document provides an overview of supply chain management and logistics. It discusses the origin and evolution of logistics, defines key terms like supply chain and logistics, and outlines the scope and key components of logistics in business. It also covers topics like logistics decision making, system design and planning, distribution networks, and transportation. The document aims to give the reader a comprehensive introduction to concepts in supply chain management and logistics.Key concepts of supply chain management



Key concepts of supply chain managementHpm India
Ã˝
This document discusses key concepts of supply chain management. It defines a supply chain as the network of activities required to deliver goods or services to consumers, including production, inventory, location, transportation, and information. The goal of supply chain management is to increase throughput while reducing inventory and operating expenses. It also discusses how companies can align their supply chain with their business strategy and market.Supply chain management 



Supply chain management MANNU KUMAR
Ã˝
The document discusses supply chain management concepts through a case study on Walmart's supply chain operations and another case study on Tata Nano's target costing approach.
The key points are:
1) Walmart simplified its supply chain by reducing inventory and using information to track goods more efficiently. This allowed faster transportation and delivery to stores.
2) Tata Nano used target costing to design the Nano, assigning cost targets to components to drive costs out of the supply chain. This involved reducing inventory, eliminating delays, and optimizing transportation networks.
3) Effective supply chain management can improve both efficiency through reduced costs and responsiveness through faster fulfillment of customer demand.More from btecexpert (20)
Rm group



Rm groupbtecexpert
Ã˝
The document summarizes an analysis of opening a new supermarket mall in the city of Erqi. It discusses the mall's opportunities such as its central location and transport facilities. Threats include high rent costs and competition from nearby department stores and large shopping malls. A SWOT analysis is provided comparing the new mall to competitors like Walmart. Market research shows the area has potential for commercial development. The conclusion recommends opening a large supermarket at the proposed site, due to its high commercial value and accessibility.Rm assignment2



Rm assignment2btecexpert
Ã˝
The group has been assigned as business consultants to an Australian Retail Group. They must submit a 2,500-word report on a large Chinese retail institution in Zhengzhou and make a presentation of no more than 30 slides to the chairman. The report should include an industry analysis, competitor analysis, retail strategy analysis, consumer behavior analysis, retail site evaluation criteria, and a conclusion discussing what was learned and suggestions for improvement.Trade theories



Trade theoriesbtecexpert
Ã˝
This document contains key terms and concepts related to international trade theories and economic history, including references to world wars, the industrial revolution, and trade theories from Adam Smith to new trade theory. Some of the major topics covered include comparative advantage, absolute advantage, mercantilism, theories of international trade such as Ricardo's model and Heckscher-Ohlin theory, as well as concepts like national competitive advantage, firm strategy, and productivity.Rm assignment



Rm assignmentbtecexpert
Ã˝
The document provides guidance for an assignment on analyzing a retail store. Students are instructed to select a topic from a list of store types, observe the store's retail strategy, and write a report analyzing the store's type, location, merchandise, prices, atmosphere, services, promotion, processes, and customers. The report should be 1,000 to 1,500 words in length and address these various elements of the retail strategy.Assignment 2



Assignment 2btecexpert
Ã˝
This document outlines a research project on improving a college canteen. It discusses collecting secondary data on student usage patterns and satisfaction levels. Primary data will be gathered through questionnaires with students to identify areas for improvement. Findings will be analyzed and recommendations made to address dissatisfied students and other issues identified.Research methods1



Research methods1btecexpert
Ã˝
This document outlines different research methods used to collect data, including primary and secondary sources, observation, experiments, surveys, sampling techniques, survey approaches, questionnaire structures, and survey administration frequencies. Primary data is collected directly from original sources like observation or experiments, while secondary data comes from existing sources. Sampling can be probability-based using random, systematic, or stratified methods, or non-probability based like convenience or judgmental sampling. Surveys are commonly conducted by post, telephone, or in-person interviews using either unstructured or structured questionnaires that may be administered in-house or outsourced. Surveys can also vary in frequency from ad hoc to continuous collection.

210social responsibilities



210social responsibilitiesbtecexpert
Ã˝
Corporate social responsibilities and promoting social responsibility in supply chain management. The document discusses key concepts like stakeholders and CSR. It outlines IBM's environmental responsibilities to stakeholders, including efficient raw material use, recycling, and energy saving. The document also suggests ways for IBM to screen suppliers, including questionnaires and compliance with standards. It describes IBM's strategies for promoting CSR among suppliers, such as audits, learning programs, and industry collaboration. IBM's CSR initiatives have strengthened its relationships with suppliers by assisting them to improve and sharing best practices.206global sourcing



206global sourcingbtecexpert
Ã˝
Global sourcing involves identifying, selecting, and developing suppliers globally, including outsourcing partners. Common activities outsourced include resource-intensive tasks requiring specialist skills or changing technologies. Outsourcing purchasing is more common where purchasing is non-core, the supplier base is small and proven, and items supplied are non-strategic and low risk/cost. Benefits of outsourcing include reduced costs and staffing needs, increased flexibility, and focus on core business functions, while potential problems include reduced quality control, dependence on few suppliers, and loss of skills/expertise. Implementing outsourcing requires careful planning and management of supplier relationships.208 internationalpurchasingspecialists



208 internationalpurchasingspecialistsbtecexpert
Ã˝
International purchasing specialists (IPS) act as intermediaries between international buyers and sellers. They use their expertise in local markets and industries to identify suppliers that match buyers' needs, help negotiate deals, and manage the relationship. IPS provide a range of services including market research, arranging meetings between buyers and sellers, assisting with communications, advising on logistics and documentation, and keeping clients informed on industry trends. Hiring an IPS widens sourcing options, can lower costs or improve quality, saves time, and eases the challenges of international procurement.

Summary scm
- 2. Topics SC and SCM Outsourcing services IT support, ecommerce and logistics Order management Transportation management Warehousing location and management Inventory management Packaging issues Selection of suppliers System design International issues and logistics structure
- 3. About Supply Chains… A supply chain “encompasses all activities associated with the flow and transformation of goods from the raw material stage (extraction), through to the end user, as well as the associated information flows.” Holmes Instititute, 2007
- 4. Supply Chain Management Supply chain management is “the systemic, strategic coordination of the traditional business functions and the tactics across these business functions within a particular company and across businesses in the supply chain, for the purposes of improving the long-term performance of the individual companies and the supply chain as a whole.” Holmes Instititute, 2007
- 5. Key Attributes of Supply Chain Management Customer power Today's customers want to be treated as individuals and business to be conducted on their terms Long-term orientation Relational exchanges. Building up relations based on a win – win situation Transactional exchanges Short term relationship win – lose situation Leveraging technology Extranets. Allowing one supply chain party to have virtually instantaneous visibility too the same data as other parties in the supply chain. Allows a more proactive approach. Enhanced communication across organizations Real time dataflow between parties Holmes Instititute, 2007
- 6. Third-Party Logistics (3PL) A third-party logistics provider is a firm that provides outsourced logistics services to companies for part or all of their supply chain management function. Third party logistics providers typically specialize in integrated warehousing and transportation services that can be scaled and customized to customer’s needs based on market conditions and the demands and delivery service requirements for their products and materials. Holmes Instititute, 2007
- 7. Discuss What is a 3PL company? Discuss any three functions performed by a 3PL company, give examples where appropriate.
- 8. Electronic Commerce and Logistics E-fulfillment Many logistical functions and activities occur More, smaller orders Order management and information management systems must handle large volumes of orders Smaller orders dictate open-case picking Traditional Fulfillment Many logistical functions and activities occur Fewer, larger orders Order management system is set up to handle orders from resellers, not consumers Full-case picking Warehouse set up to handle large volume orders
- 9. Electronic Commerce and Logistics E-fulfillment Products slotted to facilitate picking smaller orders Totes and push carts used Packaging is small cartons, envelopes, bags suited to holding small quantities Traditional Fulfillment Warehouse set up to handle large volume orders Variety of materials handling equipment used Packaging generally cartons that hold large volume orders
- 10. Electronic Commerce and Logistics E-fulfillment Transportation companies used with extensive delivery networks; experience in parcel shipments Outbound shipments usually picked up by vans Return rates much higher and from ultimate consumers Traditional Fulfillment Transportation methods and companies vary by request of buyer Outbound shipments may be picked up by tractor trailers or railcars Return rates lower and from resellers
- 11. Order Management Order management is the activities that take place in the period between the time a firm receives an order and the time a warehouse is notified to ship the goods to fill that order. Order planning-connected to sales forecasting Order transmittal Order processing Order picking and assembly Order delivery
- 12. Order Management Order cycle defined by the seller: time from when an order is received to when the goods arrive at the customer’s dock. Order cycle defined by the buyer: time from when an order is placed to when the goods are received. Also called replenishment cycle Getting shorter More precise delivery times Customer can track orders Quality is important and is benchmarked
- 13. Discuss Explain the term order cycle. Describe the four stages of the ‘order cycle’ in detail.
- 14. Packaging Protective functions of packaging Enclose materials Restrain materials from undesired movement Separate contents to prevent undesired contact Cushion contents from outside vibrations and shocks Support the weight of identical containers stacked above Position the contents to provide maximum protection Provide for uniform weight distribution Provide exterior surface for labeling Be tamperproof Be safe for consumers or others Give examples, where appropriate
- 15. Discuss What are the 5 modes of transportation in logistics? Explain and give examples, where appropriate.
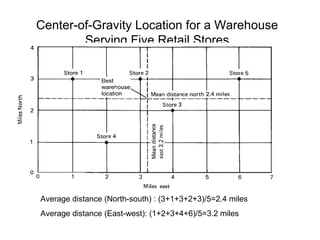
- 16. Center-of-Gravity Location for a Warehouse Serving Five Retail Stores Average distance (North-south) : (3+1+3+2+3)/5=2.4 miles Average distance (East-west): (1+2+3+4+6)/5=3.2 miles
- 17. Discuss You are representing a new brand of wine from France to be distributed in whole China. How would you like to solve your warehouse location problem using the concept of “Centre of gravity approach”? Illustrate your answer and make your assumptions where appropriate.
- 18. Warehousing Management Warehousing emphasizes storage of products. Distribution centers emphasize rapid movement of products through the facility. Throughput is the amount of product entering and leaving a facility in a given time period. Regrouping function Accumulating (increasing quantity) Allocating (reducing quantity) Assorting (building up a variety of products) Sorting (separating products into grades and qualities)
- 19. Discuss Discuss some of the value-added activities that can be performed by warehouses and distribution centers
- 20. Inventory management ABC analysis JIT VMI Reversed logistics EOQ Carrying costs Stockout costs Safety stocks
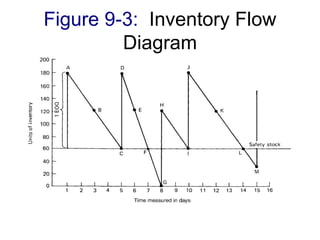
- 21. Figure 9-3: Inventory Flow Diagram
- 22. Discuss How can inventory flow diagrams be useful to a logistic manager? Illustrate your answer using an example, where appropriate.
- 23. Supplier Selection and Management Supplier management is charged with keeping existing suppliers happy Selecting vendors depends on: Delivery Facilities and capacity, geographic location Performance history Price and quality Technical capability Warranties and claim policies
- 24. Discuss What criteria would be important when selecting a supplier for a local shop of your choice? Discuss and give example where appropriate.
- 25. Logistics System Design Product audit Existing facilities audit Vendor audit Customer audit Channels audit Competition audit Environmental sensitivity audit
- 26. Discuss Name the seven types of comprehensive logistics systems audits that should be performed. Which do you view as the most important? The least important? Why?
- 27. Logistics structure Order management Transportation management Warehousing location and management Inventory management Packaging issues IT support
- 28. Discuss Your friend, David, is importing tropical food items from Malaysia to China. He will distribute these products to retailers all over Zhengzhou. What advice would you give to him to set up his logistic structure in Zhengzhou?











