Transformer
Download as PPTX, PDF8 likes517 views
(1)Introduction (2)Types of transformer (3)Principle (4)Construction (5)Working (6)Efficiency (7)Energy losses
1 of 11
Downloaded 247 times








Recommended
Transformer



TransformerDeepak Patel
Ėý
The document summarizes key aspects of transformers:
1. Transformers transfer electric power from one circuit to another through electromagnetic induction without changing frequency. They are used to step up or step down AC voltage for power transmission or distribution.
2. The working principle is based on electromagnetic induction - a changing magnetic field in the primary winding induces a voltage in the secondary winding.
3. Main components are the primary and secondary windings wrapped around a laminated steel core to maximize the magnetic flux between coils.Transformers 1



Transformers 1SHREYAS321
Ėý
A transformer transfers power from one circuit to another through electromagnetic induction without changing frequency. It works on the principle of mutual induction between two coils - the primary and secondary windings. When an alternating current flows through the primary, it produces an alternating magnetic flux that induces an alternating voltage in the secondary. Transformers come in two main construction types - core type with windings on either side of the core, and shell type with windings sandwiched between core limbs. Efficiency losses include copper losses from winding resistance and iron losses from hysteresis and eddy currents in the core.Forward convertor



Forward convertorzeshana
Ėý
The forward converter uses a transformer to step up or down an input dc voltage and provide isolation for the load. It operates in two modes: when the switch is on, the input voltage is applied to the primary winding and power is transferred to the secondary winding and load; when the switch is off, the secondary inductor maintains current through a freewheeling diode. Key aspects of design include transformer turn ratio selection, inductor and capacitor sizing, and duty cycle adjustment for output voltage control. Benefits include better transformer utilization, filtered output, input-output isolation, and higher efficiency compared to flyback converters for power levels of 100-200 watts.Transformer



TransformerAshvani Shukla
Ėý
construction of transformer , core , winding , theory of operation , equivalent circuit of transformer,emf equation of transformer,type of transformertransformer slide prsentation 



transformer slide prsentation abu jubayer
Ėý
This document provides an overview of transformers, including their structure, working principle, construction, losses, and applications. Transformers are devices that change AC electric power at one voltage level to another through magnetic coupling of two coils. They allow interchange of electric energy between circuits without a direct connection. The transformer consists of a primary coil, secondary coil, and magnetic core. When an alternating current flows through the primary, it induces a changing magnetic flux that is transferred to the secondary coil to induce voltage. Transformers experience losses from copper, hysteresis, and eddy currents. They are used widely in power transmission and applications like televisions and cameras.Transformer a short presentation



Transformer a short presentationshakil2604
Ėý
A transformer transfers electrical energy from one circuit to another through electromagnetic induction. It works by using two coils - a primary winding that receives energy from an alternating current source, and a secondary winding that delivers energy to a load. As the magnetic field in the primary coil fluctuates, it induces an alternating voltage in the secondary coil. This allows the transformer to increase or decrease voltage levels while keeping frequency constant. Common transformer types include power transformers used in electrical equipment and autotransformers with a single winding and movable tap to select different output voltages.Transformer



TransformerMinhaj Hussain
Ėý
The document discusses transformers, including their construction, principle of operation, types (step-up and step-down), applications, and history. A transformer is a device that changes alternating current voltages through inductive coupling between two coils. It consists of a primary coil, secondary coil, and iron core. The principle is based on Faraday's law of induction. Transformers are used to increase or decrease voltages for power transmission or electronic devices and were an important development in the history of electricity.Autotransformer



Autotransformerpapusahu
Ėý
The document discusses autotransformers, which are transformers with a single winding that acts on itself rather than having separate primary and secondary windings. Autotransformers can be used to step up or step down voltages and have advantages over two-winding transformers like reduced material costs. However, they pose safety risks if the common connection fails and do not provide electrical isolation between input and output. Autotransformers are commonly used to compensate for voltage drops on power lines or reduce motor voltages during starting. transformer



transformerNITIN MAGAR
Ėý
it contain transformer basic beginer of electrical being helpful that gets idea about transformer workiTransformers



TransformersSoumyaRanjanDas13
Ėý
PPT ON PRACTICAL TRANSFORMERS IN A PLANT, THEIR VARIOUS PARTS , TYPES AND TESTS PERFORMED ON A TRANSFORMERS.Transformer



TransformerAbhay Laxane
Ėý
A perfect PPT on Transformer including - Intro. , Defn , Construction , Working , Types , Etc. by Abhay M. Laxane Distribution transformer



Distribution transformerEngr Muhammad Imran
Ėý
Distribution transformers are used to reduce high primary voltages to lower utilization voltages for consumers. They come in various types including large distribution transformers used to receive energy from high voltage levels and distribute to substations or industries, and single-phase pole mounted transformers used for residential overhead distribution. Voltage regulation is the percentage difference between no-load and full-load voltages, and is affected by the voltage drop due to current flowing through the transformer windings. Losses in distribution transformers include core losses, copper losses from winding resistance, and stray losses from stray fluxes.Transformer



TransformerAugustien Raju
Ėý
A transformer consists of two coils with a mutual magnetic field that allows it to convert alternating current of one voltage to another without changing frequency. It works on the principle of electromagnetic induction between the primary and secondary windings. There are several types of losses that occur in transformers like copper, eddy current, and hysteresis losses. The ratio of voltages out to voltages in depends on the turns ratio of the number of windings in the primary coil to the secondary coil. Transformers can either step up or step down voltages and are used widely in power transmission and applications requiring different voltages.Transformer



Transformer9737932664
Ėý
A transformer transfers electrical energy between two circuits through electromagnetic induction. It works by using a primary coil to produce a varying magnetic field that induces a voltage in a secondary coil. This allows transformers to increase or decrease voltage levels in an electrical circuit. The number of turns in each coil and the ratio of their turns determines the relationship between the voltages in the primary and secondary circuits. Transformers are commonly used to increase voltage for power transmission over long distances and decrease voltage for safe use in electronic devices.TRANSFORMER PPT 



TRANSFORMER PPT Rakesh Raushan
Ėý
This document provides information about transformers, including:
1) Transformers work by mutual inductance between two coils linked by a magnetic flux, allowing conversion of voltages while keeping frequency the same.
2) Transformers consist of two inductive windings and a laminated steel core to reduce losses. They are classified based on factors like phase, core type, cooling method, and application.
3) Transformers experience losses from hysteresis in the core, eddy currents, and resistive heating of windings. Proper design aims to minimize different types of losses depending on the transformer's role.Transformer ppt download



Transformer ppt downloadANKUSHKUMAR407
Ėý
This document provides an overview of transformers. It discusses that transformers are used to transfer electrical energy between AC circuits by inducing a voltage in one circuit from another via electromagnetic induction. The basic principles of a transformer are explained, including that an alternating current in the primary winding produces an alternating magnetic flux that induces a voltage in the secondary winding. Different types of transformer cores are described. It also notes that transformers cannot operate on DC and discusses some applications of transformers such as stepping up or down voltages for power transmission or measurements.Presentation report of transformer



Presentation report of transformerWasiqueKhan5
Ėý
A transformer is a static device that transfers electrical energy between two circuits through electromagnetic induction. It consists of two or more coils wound around an iron core. The coil connected to the power source is the primary winding, and the coil that provides power to the load is the secondary winding. Transformers are used to change the voltage levels in electrical systems. They are categorized as power transformers or electronic transformers based on their power ratings and applications. Power transformers are used in power generation, transmission and distribution systems to increase or decrease voltage levels, while electronic transformers operate at lower voltages and power levels in devices like computers and TVs.TYPES OF TRANSFORMER ,COMPARISON BETWEEN CORE AND SHELL |DAY4||IN HINDI|BASIC...



TYPES OF TRANSFORMER ,COMPARISON BETWEEN CORE AND SHELL |DAY4||IN HINDI|BASIC...Prasant Kumar
Ėý
#TYPES_OF_TRANSFORMER
#COMPARISON_CORE_SHELL_TYPE_TRANSFORMER
#CLASSIFICATION_OF_TRANSFORMER
#COMPARISON BETWEEN CORE AND SHELL TYPE TRANSFORMER
#CORE TYPE TRANSFORMER
#SHELL TYPE TRANSFORMER
#BASIC ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING
#SINGLE PHASE TRANSFORMER
#Topic - ELECTRICAL TRANSFORMER
~ Link of all sessions are.
DAY 1 (Need/Definition)
https://youtu.be/BvaykFJ_NoE
DAY 2 (Working principle and Construction)
https://youtu.be/06rgxocihaM
DAY 3 (EMF equation and Turns Ratio)
https://youtu.be/g7e5xBPmv3Y
DAY 4 (Classification of Transformer)
https://youtu.be/6NP5L4MlvY4Power quality notes unit 1 



Power quality notes unit 1 Dilip kumar
Ėý
This document discusses power quality and defines it as any deviation from the normal sinusoidal voltage or current waveform. It covers various power quality issues like voltage sags, swells, fluctuations, harmonics, interruptions and more. It explains the causes and impacts of different power quality problems. The document also discusses classification of issues, measurement and evaluation of power quality as well as relevant standards from organizations like IEEE.Electrical Transformer



Electrical TransformerAnaseem Hanini
Ėý
Transformer
Working Principle
A transformer is an fixed electrical device.
Function : transforms the voltage level .
The principle of operation is mutual induction.
Transformer Parts And Construction:
Primary Winding of Transformer.
Magnetic Core of Transformer.
Secondary Winding of Transformer.
TYPES OF TRANSFORMERS
based on Voltage Level:
1.Step-Down Transformer
2. Step-Up Transformer
Transformer, it's types and cooling methods with power factor, percentage imp...



Transformer, it's types and cooling methods with power factor, percentage imp...Urooj Abid
Ėý
A transformer transfers power between two circuits through electromagnetic induction without a physical connection. It consists of two windings - a primary and secondary circuit. There are different types of transformers including step-up/step-down transformers which increase/decrease voltage, core and shell type transformers based on winding construction, and single, two or three winding transformers. Transformers are essential devices that allow efficient transmission and distribution of electric power.Transformer



TransformerPramod Singh
Ėý
The document discusses the construction and working of transformers. It explains that a transformer transfers electrical power from one alternating current circuit to another through mutual induction without direct electrical contact. It has a primary winding that receives input power and a secondary winding that delivers output power. The transformer works by inducing voltage in the secondary winding through a changing magnetic field generated by the primary winding around a shared ferromagnetic core. The document further describes step-up and step-down transformers, classifications, losses, and applications of transformers.ELECTRICAL TECHNOLOGY- Transformers



ELECTRICAL TECHNOLOGY- TransformersAimi Khairina
Ėý
This document discusses transformers, including:
- Transformers change AC electrical power at one voltage level into another voltage level through magnetic fields, without changing frequency.
- They have two coils, a primary and secondary, that are magnetically linked but electrically isolated.
- Transformers can either step up or step down voltage depending on the ratio of turns in the primary and secondary coils.
- The main types are core-type transformers, which have cylindrical coils around a central core, and shell-type transformers, which have disc-shaped coil layers stacked together.Full transformer



Full transformerPrateek Anandpara
Ėý
here all MAJOR TOPICS OF TRANSFORMER IS MAINTAIN & WHICH HELPFULL FOR REVISION AND LEANING AND TEACHING AUTO TRANSFORMER AND THREE PHASE TRANSFORMER



AUTO TRANSFORMER AND THREE PHASE TRANSFORMERfarhanurrahman6
Ėý
- An autotransformer has a single winding that acts as both the primary and secondary winding. It uses less copper than a two-winding transformer, resulting in lower costs. However, it does not provide isolation between primary and secondary voltages.
- Key features include higher efficiency, smaller size, superior voltage regulation, and lower losses compared to a two-winding transformer. The output power depends on the transformation ratio. Savings in copper increases as the ratio approaches 1.
- Common three-phase transformer connections include star-star, delta-delta, star-delta, and delta-star, which determine how line voltages and currents are distributed across the windings.Transformer ppt.



Transformer ppt.MohitDhiman36
Ėý
WHAT IS TRANSFORMER, DEFINE TRANSFORMER, TYPES OF TRANSFORMER, RATINGS OF TRANSFORMERS, MANUFACTURING PROCESS OF TRANSFORMER, PARTS OF TRANSFORMER, TESTS OF TRANSFORMER, COSTING OF COPPER.Transformer - Detailed Presentation 50 slids



Transformer - Detailed Presentation 50 slidsAbhi Kushwaha
Ėý
1. Transformers have on-load and off-load tap changers that allow adjusting the transformer's output voltage without interrupting the load current. On-load tap changers can adjust voltage while energized using fast-acting switches, while off-load tap changers require de-energizing the transformer to change taps.
2. On-load tap changers are commonly used in power generation and distribution transformers to control voltage as load and line conditions vary. They monitor voltage and raise or lower taps using an automatic voltage regulator. Off-load tap changers are typically used in solar and wind projects where the generator voltage is low-voltage.
3. The on-load tap changer maintains uninterruptedTransformer basics



Transformer basicsAtheenaPandian Enterprises
Ėý
The Basics of electronics can be studied also through the link http://bit.ly/2PPv0mv
A transformer is a passive electrical device that transfers electrical energy from one electrical circuit to one or more circuits. newmicrosoftofficepowerpointpresentation-160805121228 (1).pdf



newmicrosoftofficepowerpointpresentation-160805121228 (1).pdfDineshThallapelly
Ėý
Transformers allow for efficient transfer of alternating current from one circuit to another with a change in voltage. They work on the principle of electromagnetic induction between two coils linked by a magnetic core. There are different types including single and three phase transformers based on the number of phases, and core and shell types based on construction. Transformers can step up or step down voltage and are used for applications like power transmission, distribution to homes and industries, and in electronic devices. Practical transformers have losses not present in an ideal transformer.Transformers seminar



Transformers seminarvinayvickky
Ėý
types of transformers,seminar on transformers,
What is Transformer,
Working principle,
Types of transformers,
Ideal and practical transformer,
Applications of transformers.
More Related Content
What's hot (20)
transformer



transformerNITIN MAGAR
Ėý
it contain transformer basic beginer of electrical being helpful that gets idea about transformer workiTransformers



TransformersSoumyaRanjanDas13
Ėý
PPT ON PRACTICAL TRANSFORMERS IN A PLANT, THEIR VARIOUS PARTS , TYPES AND TESTS PERFORMED ON A TRANSFORMERS.Transformer



TransformerAbhay Laxane
Ėý
A perfect PPT on Transformer including - Intro. , Defn , Construction , Working , Types , Etc. by Abhay M. Laxane Distribution transformer



Distribution transformerEngr Muhammad Imran
Ėý
Distribution transformers are used to reduce high primary voltages to lower utilization voltages for consumers. They come in various types including large distribution transformers used to receive energy from high voltage levels and distribute to substations or industries, and single-phase pole mounted transformers used for residential overhead distribution. Voltage regulation is the percentage difference between no-load and full-load voltages, and is affected by the voltage drop due to current flowing through the transformer windings. Losses in distribution transformers include core losses, copper losses from winding resistance, and stray losses from stray fluxes.Transformer



TransformerAugustien Raju
Ėý
A transformer consists of two coils with a mutual magnetic field that allows it to convert alternating current of one voltage to another without changing frequency. It works on the principle of electromagnetic induction between the primary and secondary windings. There are several types of losses that occur in transformers like copper, eddy current, and hysteresis losses. The ratio of voltages out to voltages in depends on the turns ratio of the number of windings in the primary coil to the secondary coil. Transformers can either step up or step down voltages and are used widely in power transmission and applications requiring different voltages.Transformer



Transformer9737932664
Ėý
A transformer transfers electrical energy between two circuits through electromagnetic induction. It works by using a primary coil to produce a varying magnetic field that induces a voltage in a secondary coil. This allows transformers to increase or decrease voltage levels in an electrical circuit. The number of turns in each coil and the ratio of their turns determines the relationship between the voltages in the primary and secondary circuits. Transformers are commonly used to increase voltage for power transmission over long distances and decrease voltage for safe use in electronic devices.TRANSFORMER PPT 



TRANSFORMER PPT Rakesh Raushan
Ėý
This document provides information about transformers, including:
1) Transformers work by mutual inductance between two coils linked by a magnetic flux, allowing conversion of voltages while keeping frequency the same.
2) Transformers consist of two inductive windings and a laminated steel core to reduce losses. They are classified based on factors like phase, core type, cooling method, and application.
3) Transformers experience losses from hysteresis in the core, eddy currents, and resistive heating of windings. Proper design aims to minimize different types of losses depending on the transformer's role.Transformer ppt download



Transformer ppt downloadANKUSHKUMAR407
Ėý
This document provides an overview of transformers. It discusses that transformers are used to transfer electrical energy between AC circuits by inducing a voltage in one circuit from another via electromagnetic induction. The basic principles of a transformer are explained, including that an alternating current in the primary winding produces an alternating magnetic flux that induces a voltage in the secondary winding. Different types of transformer cores are described. It also notes that transformers cannot operate on DC and discusses some applications of transformers such as stepping up or down voltages for power transmission or measurements.Presentation report of transformer



Presentation report of transformerWasiqueKhan5
Ėý
A transformer is a static device that transfers electrical energy between two circuits through electromagnetic induction. It consists of two or more coils wound around an iron core. The coil connected to the power source is the primary winding, and the coil that provides power to the load is the secondary winding. Transformers are used to change the voltage levels in electrical systems. They are categorized as power transformers or electronic transformers based on their power ratings and applications. Power transformers are used in power generation, transmission and distribution systems to increase or decrease voltage levels, while electronic transformers operate at lower voltages and power levels in devices like computers and TVs.TYPES OF TRANSFORMER ,COMPARISON BETWEEN CORE AND SHELL |DAY4||IN HINDI|BASIC...



TYPES OF TRANSFORMER ,COMPARISON BETWEEN CORE AND SHELL |DAY4||IN HINDI|BASIC...Prasant Kumar
Ėý
#TYPES_OF_TRANSFORMER
#COMPARISON_CORE_SHELL_TYPE_TRANSFORMER
#CLASSIFICATION_OF_TRANSFORMER
#COMPARISON BETWEEN CORE AND SHELL TYPE TRANSFORMER
#CORE TYPE TRANSFORMER
#SHELL TYPE TRANSFORMER
#BASIC ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING
#SINGLE PHASE TRANSFORMER
#Topic - ELECTRICAL TRANSFORMER
~ Link of all sessions are.
DAY 1 (Need/Definition)
https://youtu.be/BvaykFJ_NoE
DAY 2 (Working principle and Construction)
https://youtu.be/06rgxocihaM
DAY 3 (EMF equation and Turns Ratio)
https://youtu.be/g7e5xBPmv3Y
DAY 4 (Classification of Transformer)
https://youtu.be/6NP5L4MlvY4Power quality notes unit 1 



Power quality notes unit 1 Dilip kumar
Ėý
This document discusses power quality and defines it as any deviation from the normal sinusoidal voltage or current waveform. It covers various power quality issues like voltage sags, swells, fluctuations, harmonics, interruptions and more. It explains the causes and impacts of different power quality problems. The document also discusses classification of issues, measurement and evaluation of power quality as well as relevant standards from organizations like IEEE.Electrical Transformer



Electrical TransformerAnaseem Hanini
Ėý
Transformer
Working Principle
A transformer is an fixed electrical device.
Function : transforms the voltage level .
The principle of operation is mutual induction.
Transformer Parts And Construction:
Primary Winding of Transformer.
Magnetic Core of Transformer.
Secondary Winding of Transformer.
TYPES OF TRANSFORMERS
based on Voltage Level:
1.Step-Down Transformer
2. Step-Up Transformer
Transformer, it's types and cooling methods with power factor, percentage imp...



Transformer, it's types and cooling methods with power factor, percentage imp...Urooj Abid
Ėý
A transformer transfers power between two circuits through electromagnetic induction without a physical connection. It consists of two windings - a primary and secondary circuit. There are different types of transformers including step-up/step-down transformers which increase/decrease voltage, core and shell type transformers based on winding construction, and single, two or three winding transformers. Transformers are essential devices that allow efficient transmission and distribution of electric power.Transformer



TransformerPramod Singh
Ėý
The document discusses the construction and working of transformers. It explains that a transformer transfers electrical power from one alternating current circuit to another through mutual induction without direct electrical contact. It has a primary winding that receives input power and a secondary winding that delivers output power. The transformer works by inducing voltage in the secondary winding through a changing magnetic field generated by the primary winding around a shared ferromagnetic core. The document further describes step-up and step-down transformers, classifications, losses, and applications of transformers.ELECTRICAL TECHNOLOGY- Transformers



ELECTRICAL TECHNOLOGY- TransformersAimi Khairina
Ėý
This document discusses transformers, including:
- Transformers change AC electrical power at one voltage level into another voltage level through magnetic fields, without changing frequency.
- They have two coils, a primary and secondary, that are magnetically linked but electrically isolated.
- Transformers can either step up or step down voltage depending on the ratio of turns in the primary and secondary coils.
- The main types are core-type transformers, which have cylindrical coils around a central core, and shell-type transformers, which have disc-shaped coil layers stacked together.Full transformer



Full transformerPrateek Anandpara
Ėý
here all MAJOR TOPICS OF TRANSFORMER IS MAINTAIN & WHICH HELPFULL FOR REVISION AND LEANING AND TEACHING AUTO TRANSFORMER AND THREE PHASE TRANSFORMER



AUTO TRANSFORMER AND THREE PHASE TRANSFORMERfarhanurrahman6
Ėý
- An autotransformer has a single winding that acts as both the primary and secondary winding. It uses less copper than a two-winding transformer, resulting in lower costs. However, it does not provide isolation between primary and secondary voltages.
- Key features include higher efficiency, smaller size, superior voltage regulation, and lower losses compared to a two-winding transformer. The output power depends on the transformation ratio. Savings in copper increases as the ratio approaches 1.
- Common three-phase transformer connections include star-star, delta-delta, star-delta, and delta-star, which determine how line voltages and currents are distributed across the windings.Transformer ppt.



Transformer ppt.MohitDhiman36
Ėý
WHAT IS TRANSFORMER, DEFINE TRANSFORMER, TYPES OF TRANSFORMER, RATINGS OF TRANSFORMERS, MANUFACTURING PROCESS OF TRANSFORMER, PARTS OF TRANSFORMER, TESTS OF TRANSFORMER, COSTING OF COPPER.Transformer - Detailed Presentation 50 slids



Transformer - Detailed Presentation 50 slidsAbhi Kushwaha
Ėý
1. Transformers have on-load and off-load tap changers that allow adjusting the transformer's output voltage without interrupting the load current. On-load tap changers can adjust voltage while energized using fast-acting switches, while off-load tap changers require de-energizing the transformer to change taps.
2. On-load tap changers are commonly used in power generation and distribution transformers to control voltage as load and line conditions vary. They monitor voltage and raise or lower taps using an automatic voltage regulator. Off-load tap changers are typically used in solar and wind projects where the generator voltage is low-voltage.
3. The on-load tap changer maintains uninterruptedTransformer basics



Transformer basicsAtheenaPandian Enterprises
Ėý
The Basics of electronics can be studied also through the link http://bit.ly/2PPv0mv
A transformer is a passive electrical device that transfers electrical energy from one electrical circuit to one or more circuits. Similar to Transformer (20)
newmicrosoftofficepowerpointpresentation-160805121228 (1).pdf



newmicrosoftofficepowerpointpresentation-160805121228 (1).pdfDineshThallapelly
Ėý
Transformers allow for efficient transfer of alternating current from one circuit to another with a change in voltage. They work on the principle of electromagnetic induction between two coils linked by a magnetic core. There are different types including single and three phase transformers based on the number of phases, and core and shell types based on construction. Transformers can step up or step down voltage and are used for applications like power transmission, distribution to homes and industries, and in electronic devices. Practical transformers have losses not present in an ideal transformer.Transformers seminar



Transformers seminarvinayvickky
Ėý
types of transformers,seminar on transformers,
What is Transformer,
Working principle,
Types of transformers,
Ideal and practical transformer,
Applications of transformers.
Tansformer @dheeraj upadhyay



Tansformer @dheeraj upadhyayDheeraj Upadhyay
Ėý
- A transformer is a static device that converts alternating current voltages to different voltages while keeping frequency the same through electromagnetic induction.
- It works on the principle of mutual induction between two coils - an alternating current in the primary coil induces an alternating voltage in the secondary coil.
- Transformers are used extensively in power transmission to increase voltage for long distance transmission lines and then reduce voltage for safe distribution, as well as in electronics to step down voltages for low-voltage circuits.BEE.pdf



BEE.pdfloharesadanand
Ėý
This document discusses transformers, including:
- Their history from Edison's DC power system to Tesla's development of AC power transmission.
- How a transformer works using mutual induction to change the voltage of alternating current between a primary and secondary coil.
- The basic construction of a transformer with an iron core and two insulated coils.
- The main types of transformers including step-up, step-down, auto, poly-phase, leakage, resonant, and instrument transformers.Transformer



TransformerPriyanka Jakhar
Ėý
A transformer is a device that converts alternating voltages from one level to another. It works on the principle of mutual induction between two coils linked by a magnetic field. A step-up transformer increases voltage and decreases current, while a step-down transformer decreases voltage and increases current. Real transformers are not 100% efficient due to energy losses from copper windings, flux leakage, hysteresis in the iron core, and eddy currents. However, transformers remain essential for power transmission and applications requiring different voltage levels.Transformer 



Transformer Hari Shiyam Prakash T
Ėý
- Transformers transfer electrical energy from one circuit to another through mutual induction between two windings, and can change the voltage but not the frequency.
- They work on the principle of Faraday's law of induction, where a changing magnetic field in the primary coil induces an electromagnetic force (EMF) in the secondary coil.
- Transformers are classified based on factors like performance, construction, voltages, applications, cooling, and input supply, and can be used to step up or step down voltages.Transformer-History,Type And More Detail



Transformer-History,Type And More DetailAdeel Rasheed
Ėý
On these šÝšÝßĢs I describe History, Introduction, Construction, Working and Principle, Types of Transformer, Ideal Transformer and Uses of Transformer.
Transformer construction,types and working



Transformer construction,types and workingmaharshi dayanand university rohtak
Ėý
this is good for electrical engineering students to present seminar in your college or university....A PPT On What is Electrical Power Transformers, It's Types and How it's Works?



A PPT On What is Electrical Power Transformers, It's Types and How it's Works?Pankaj Tiwari
Ėý
A Complete Details About the Electrical Power Transformer, Types Of Transformers and How's it Electrical Transformers Works. Transformers details construction.pptx



Transformers details construction.pptxDesktopPC7
Ėý
Transformers work on the principle of mutual induction to transmit and distribute power in AC circuits. A changing current in one coil induces an EMF in a neighboring coil. Transformers can convert high voltage, low current into low voltage, high current. The ratio of the number of turns in the primary and secondary coils determines the turns ratio, which describes how the transformer will step up or step down voltage. Common applications of transformers include increasing or decreasing voltage for welding machines, X-ray tubes, mobile phone charging, and transmitting current through power lines.transformer breif introduction HV and LV Connection



transformer breif introduction HV and LV Connectionfarasatali30
Ėý
Transformers work on the principle of mutual induction to transmit and distribute power in AC circuits. A changing current in one coil induces an EMF in a neighboring coil. Transformers can convert high voltage, low current into low voltage, high current. The ratio of the number of turns in the primary and secondary coils determines the turns ratio, which dictates how the voltage and current are altered. Common applications of transformers include increasing or decreasing voltages for appliances, welding machines, and mobile device charging.Transformer



TransformerHemantChoudhary65
Ėý
This document discusses the construction and working of transformers. It begins with an introduction that defines a transformer as a device that changes AC electric power at one voltage level to another through magnetic coupling of two coils. It then covers the main topics of the structure and working principle of transformers, the different types of constructions including core and shell types, losses in transformers including copper, hysteresis and eddy current losses, the differences between ideal and practical transformers, and applications such as in transmission and distribution of power.Tansformer 



Tansformer sajedulsuvo
Ėý
A transformer works on the principle of mutual induction between two coils. It converts high voltage alternating current to low voltage and vice versa while keeping frequency the same. A transformer consists of a primary coil, secondary coil, and core. When current flows through the primary coil, it induces an alternating magnetic flux in the core. This changing flux induces an alternating voltage in the secondary coil. There are two main types of construction for transformers: core type and shell type. Transformers experience iron losses from hysteresis and eddy currents in the core as well as copper losses from resistance in the windings.Topic 7 Transformer



Topic 7 TransformerAMZAD KHAN
Ėý
A transformer transfers power between two circuits without physical contact by using electromagnetic induction. It consists of two coils called the primary and secondary windings. Changes in the primary winding's magnetic flux induce voltage in the secondary winding according to Faraday's law of induction. There are different types of transformers classified by their application, voltage ratios, core material, and winding arrangements, such as step-up transformers which increase voltage and step-down transformers which decrease voltage from one circuit to another. Common transformer cores use either air or iron to provide a flux path between the windings.Transformer



TransformerS M Milu
Ėý
A single phase transformer works by electromagnetic induction to transfer electrical energy from one circuit to another without a direct connection. It uses a primary coil and secondary coil wound around an iron core to induce a voltage in the secondary coil from the primary coil's magnetic field. Transformers can be used to step up or step down voltages depending on whether the secondary coil has more or fewer turns than the primary coil. They allow efficient transmission of power over long distances by increasing voltage to reduce current and transmission losses.what is a Transformer ??



what is a Transformer ??arunavasava
Ėý
The document summarizes the basics of a transformer. It explains that a transformer transfers electrical energy from one circuit to another through mutual induction of two coils, the primary and secondary. It works for alternating current but not direct current since it requires a changing current. Transformers can be classified by their cooling system, core type, output voltage, number of phases, power rating, and intended use. Common applications include impedance matching, voltage transformation for power transmission and distribution, and use in devices like voltmeters and rectifiers.Recently uploaded (20)
How to Setup WhatsApp in Odoo 17 - Odoo šÝšÝßĢs



How to Setup WhatsApp in Odoo 17 - Odoo šÝšÝßĢsCeline George
Ėý
Integrate WhatsApp into Odoo using the WhatsApp Business API or third-party modules to enhance communication. This integration enables automated messaging and customer interaction management within Odoo 17.How to Manage Putaway Rule in Odoo 17 Inventory



How to Manage Putaway Rule in Odoo 17 InventoryCeline George
Ėý
Inventory management is a critical aspect of any business involved in manufacturing or selling products.
Odoo 17 offers a robust inventory management system that can handle complex operations and optimize warehouse efficiency. Rass MELAI : an Internet MELA Quiz Finals - El Dorado 2025



Rass MELAI : an Internet MELA Quiz Finals - El Dorado 2025Conquiztadors- the Quiz Society of Sri Venkateswara College
Ėý
Finals of Rass MELAI : a Music, Entertainment, Literature, Arts and Internet Culture Quiz organized by Conquiztadors, the Quiz society of Sri Venkateswara College under their annual quizzing fest El Dorado 2025. The Story Behind the Abney Park Restoration Project by Tom Walker



The Story Behind the Abney Park Restoration Project by Tom WalkerHistory of Stoke Newington
Ėý
Presented at the 24th Stoke Newington History Talks event on 27th Feb 2025
https://stokenewingtonhistory.com/stoke-newington-history-talks/Digital Tools with AI for e-Content Development.pptx



Digital Tools with AI for e-Content Development.pptxDr. Sarita Anand
Ėý
This ppt is useful for not only for B.Ed., M.Ed., M.A. (Education) or any other PG level students or Ph.D. scholars but also for the school, college and university teachers who are interested to prepare an e-content with AI for their students and others.The Constitution, Government and Law making bodies .



The Constitution, Government and Law making bodies .saanidhyapatel09
Ėý
This PowerPoint presentation provides an insightful overview of the Constitution, covering its key principles, features, and significance. It explains the fundamental rights, duties, structure of government, and the importance of constitutional law in governance. Ideal for students, educators, and anyone interested in understanding the foundation of a nationâs legal framework.
Lesson Plan M1 2024 Lesson Plan M1 2024 Lesson Plan M1 2024 Lesson Plan M1...



Lesson Plan M1 2024 Lesson Plan M1 2024 Lesson Plan M1 2024 Lesson Plan M1...pinkdvil200
Ėý
Lesson Plan M1 2024 Lesson Plan M1 2024 Lesson Plan M1 2024 Essentials of a Good PMO, presented by Aalok Sonawala



Essentials of a Good PMO, presented by Aalok SonawalaAssociation for Project Management
Ėý
APM event hosted by the South Wales and West of England Network (SWWE Network)
Speaker: Aalok Sonawala
The SWWE Regional Network were very pleased to welcome Aalok Sonawala, Head of PMO, National Programmes, Rider Levett Bucknall on 26 February, to BAWA for our first face to face event of 2025. Aalok is a member of APMâs Thames Valley Regional Network and also speaks to members of APMâs PMO Interest Network, which aims to facilitate collaboration and learning, offer unbiased advice and guidance.
Tonight, Aalok planned to discuss the importance of a PMO within project-based organisations, the different types of PMO and their key elements, PMO governance and centres of excellence.
PMOâs within an organisation can be centralised, hub and spoke with a central PMO with satellite PMOs globally, or embedded within projects. The appropriate structure will be determined by the specific business needs of the organisation. The PMO sits above PM delivery and the supply chain delivery teams.
For further information about the event please click here.How to Configure Flexible Working Schedule in Odoo 18 Employee



How to Configure Flexible Working Schedule in Odoo 18 EmployeeCeline George
Ėý
In this slide, weâll discuss on how to configure flexible working schedule in Odoo 18 Employee module. In Odoo 18, the Employee module offers powerful tools to configure and manage flexible working schedules tailored to your organization's needs.Adventure Activities Final By H R Gohil Sir



Adventure Activities Final By H R Gohil SirGUJARATCOMMERCECOLLE
Ėý
Adventure Activities Final By H R Gohil SirAPM People Interest Network Conference - Tim Lyons - The neurological levels ...



APM People Interest Network Conference - Tim Lyons - The neurological levels ...Association for Project Management
Ėý
APM People Interest Network Conference 2025
-Autonomy, Teams and Tension: Projects under stress
-Tim Lyons
-The neurological levels of
team-working: Harmony and tensions
With a background in projects spanning more than 40 years, Tim Lyons specialised in the delivery of large, complex, multi-disciplinary programmes for clients including Crossrail, Network Rail, ExxonMobil, Siemens and in patent development. His first career was in broadcasting, where he designed and built commercial radio station studios in Manchester, Cardiff and Bristol, also working as a presenter and programme producer. Tim now writes and presents extensively on matters relating to the human and neurological aspects of projects, including communication, ethics and coaching. He holds a Masterâs degree in NLP, is an NLP Master Practitioner and International Coach. He is the Deputy Lead for APMâs People Interest Network.
Session | The Neurological Levels of Team-working: Harmony and Tensions
Understanding how teams really work at conscious and unconscious levels is critical to a harmonious workplace. This session uncovers what those levels are, how to use them to detect and avoid tensions and how to smooth the management of change by checking you have considered all of them.Kaun TALHA quiz Prelims - El Dorado 2025



Kaun TALHA quiz Prelims - El Dorado 2025Conquiztadors- the Quiz Society of Sri Venkateswara College
Ėý
Prelims of Kaun TALHA : a Travel, Architecture, Lifestyle, Heritage and Activism quiz, organized by Conquiztadors, the Quiz society of Sri Venkateswara College under their annual quizzing fest El Dorado 2025. How to Modify Existing Web Pages in Odoo 18



How to Modify Existing Web Pages in Odoo 18Celine George
Ėý
In this slide, weâll discuss on how to modify existing web pages in Odoo 18. Web pages in Odoo 18 can also gather user data through user-friendly forms, encourage interaction through engaging features. APM People Interest Network Conference - Oliver Randall & David Bovis - Own Y...



APM People Interest Network Conference - Oliver Randall & David Bovis - Own Y...Association for Project Management
Ėý
APM People Interest Network Conference 2025
- Autonomy, Teams and Tension
- Oliver Randall & David Bovis
- Own Your Autonomy
Oliver Randall
Consultant, Tribe365
Oliver is a career project professional since 2011 and started volunteering with APM in 2016 and has since chaired the People Interest Network and the North East Regional Network. Oliver has been consulting in culture, leadership and behaviours since 2019 and co-developed HPTMÂŪâŊan off the shelf high performance framework for teams and organisations and is currently working with SAS (Stellenbosch Academy for Sport) developing the culture, leadership and behaviours framework for future elite sportspeople whilst also holding down work as a project manager in the NHS at North Tees and Hartlepool Foundation Trust.
David Bovis
Consultant, Duxinaroe
A Leadership and Culture Change expert, David is the originator of BTFAâĒ and The Dux Model.
With a Masters in Applied Neuroscience from the Institute of Organisational Neuroscience, he is widely regarded as the âGo-Toâ expert in the field, recognised as an inspiring keynote speaker and change strategist.
He has an industrial engineering background, majoring in TPS / Lean. David worked his way up from his apprenticeship to earn his seat at the C-suite table. His career spans several industries, including Automotive, Aerospace, Defence, Space, Heavy Industries and Elec-Mech / polymer contract manufacture.
Published in Londonâs Evening Standard quarterly business supplement, James Caanâs âYour businessâ Magazine, âQuality Worldâ, the Lean Management Journal and Cambridge Universities âPMAâ, he works as comfortably with leaders from FTSE and Fortune 100 companies as he does owner-managers in SMEâs. He is passionate about helping leaders understand the neurological root cause of a high-performance culture and sustainable change, in business.
Session | Own Your Autonomy â The Importance of Autonomy in Project Management
#OwnYourAutonomy is aiming to be a global APM initiative to position everyone to take a more conscious role in their decision making process leading to increased outcomes for everyone and contribute to âa world in which all projects succeedâ.
We want everyone to join the journey.
#OwnYourAutonomy is the culmination of 3 years of collaborative exploration within the Leadership Focus Group which is part of the APM People Interest Network. The work has been pulled together using the 5 HPTMÂŪ Systems and the BTFA neuroscience leadership programme.
https://www.linkedin.com/showcase/apm-people-network/about/Computer Application in Business (commerce)



Computer Application in Business (commerce)Sudar Sudar
Ėý
The main objectives
1. To introduce the concept of computer and its various parts. 2. To explain the concept of data base management system and Management information system.
3. To provide insight about networking and basics of internet
Recall various terms of computer and its part
Understand the meaning of software, operating system, programming language and its features
Comparing Data Vs Information and its management system Understanding about various concepts of management information system
Explain about networking and elements based on internet
1. Recall the various concepts relating to computer and its various parts
2 Understand the meaning of softwareâs, operating system etc
3 Understanding the meaning and utility of database management system
4 Evaluate the various aspects of management information system
5 Generating more ideas regarding the use of internet for business purpose South Hornsey: The Lost Local Authority that Merged with Stoke Newington by T...



South Hornsey: The Lost Local Authority that Merged with Stoke Newington by T...History of Stoke Newington
Ėý
Presented at the 24th Stoke Newington History Talks event on 27th Feb 2025
https://stokenewingtonhistory.com/stoke-newington-history-talks/Rass MELAI : an Internet MELA Quiz Finals - El Dorado 2025



Rass MELAI : an Internet MELA Quiz Finals - El Dorado 2025Conquiztadors- the Quiz Society of Sri Venkateswara College
Ėý
APM People Interest Network Conference - Tim Lyons - The neurological levels ...



APM People Interest Network Conference - Tim Lyons - The neurological levels ...Association for Project Management
Ėý
Kaun TALHA quiz Prelims - El Dorado 2025



Kaun TALHA quiz Prelims - El Dorado 2025Conquiztadors- the Quiz Society of Sri Venkateswara College
Ėý
APM People Interest Network Conference - Oliver Randall & David Bovis - Own Y...



APM People Interest Network Conference - Oliver Randall & David Bovis - Own Y...Association for Project Management
Ėý
South Hornsey: The Lost Local Authority that Merged with Stoke Newington by T...



South Hornsey: The Lost Local Authority that Merged with Stoke Newington by T...History of Stoke Newington
Ėý
Transformer
- 1. TRANSFORMER
- 2. Contents ï Introduction ï Types of transformer ï Principle ï Construction ï Working ï Efficiency ï Energy losses
- 3. Introduction ï A transformer is a static electromagnetic device that transforms one alternating current into another of different voltage and current. ï It is a device used to change the voltage.
- 4. Types of Transformer ï Step up transformer- It is used to convert low voltage to high voltage or high current to low current. ï Step down transformer- It is used to convert high voltage to low voltage or low current to high current.
- 5. Principle ï Transformer system is based on the principle of mutual induction.
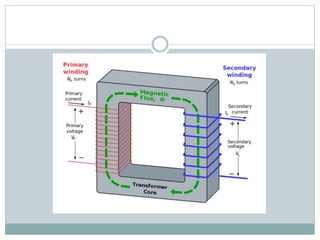
- 6. Construction ï Transformer consist of two coil insulates from each other. They are wounded on a soft iron core. One of the coil is called primary coil and other is called as secondary coil.
- 8. Working ï This equation is equal to a constant k called transformation ratio. ï For step up k>1 and for step down k<1.
- 9. Efficiency ï It can be defined as,
- 10. Energy Losses in Transformer ï Flux linkage ï Resistance of the windings ï Eddy current ï Hysteresis








