UNIT 3 MAPEH 6 LESSON 1 SCREEN PRINTING- ARTS.pptx
Download as PPTX, PDF0 likes46 views
ctto
1 of 15
Download to read offline














Recommended
Screen printing



Screen printingNazmusShakib22
╠²
This presentation provides an overview of screen printing. It discusses the basic screen printing process where a mesh is used to transfer ink to a substrate using a squeegee. It also outlines some of the key items needed for screen printing like screens, squeegees, and inks. The presentation describes different types of screen printing including hand screen printing, semi-automatic flat screen printing, and rotary screen printing. It concludes with advantages like durable vibrant colors on a variety of materials and disadvantages like long set up times.Screen Printing.pptx



Screen Printing.pptxJESSICACAMET1
╠²
Screen printing is a printing technique that uses a mesh screen to transfer ink onto a substrate. It involves using a squeegee to force ink through the mesh openings to print an image. Multiple screens can be used to print multi-colored images. There are different methods of screen printing including hand, semi-automatic, and rotary screen printing. Hand screen printing allows for precise printing but requires skill while rotary screen printing is faster but uses cylindrical screens. Screen printing offers durable prints in vivid colors on a variety of materials but has long set-up times.Screen Printing Technology (Screen Printing Frames, Screen Printing Press, Su...



Screen Printing Technology (Screen Printing Frames, Screen Printing Press, Su...Ajjay Kumar Gupta
╠²
Screen printing is a printing technique whereby a mesh is used to transfer ink onto a substrate, except in areas made impermeable to the ink by a blocking stencil. Screen printing is also a stencil method of print making in which a design is imposed on a screen of polyester or other fine mesh, with blank areas coated with an impermeable substance.
See more
https://goo.gl/Rkw9rA
https://goo.gl/TTuhMC
https://goo.gl/EJ7x26
Contact us
Email: npcs.ei@gmail.com , info@entrepreneurindia.co
Tel: +91-11-23843955, 23845654, 23845886, 8800733955
Mobile: +91-9811043595
Website : www.entrepreneurindia.co , www.niir.org
Tags
Process technology book on screen printing, Screen Printing Technology book, Aluminum Frames: Screen Printing, Aluminum Screen Printing Frames, best screen printing small business, Business start-up, Great Opportunity for Startup, How does printing work?, how to do screen printing, How To Screen Print -Step by Step process, how to screen print t shirts, How to screen print your own t-shirts, How to Screen Printing on Fabric, How to Start a Screen Print Business, How to start a screen printing business, How to start a successful screen printing business, How to start screen printing Industry in India, How to Start Your Own Screen Printing Business, Is screen printing a good business?, Most Profitable screen printing Business Ideas, New Screen Printing Technology, new small scale ideas in screen printing industry, Printing on unusual surfaces, Printing processes, Printing Surfaces, profitable small and cottage scale industries,project for startups, screen print kit, screen printing Based Small Scale Industries Projects, screen printing business plan, screen printing business profit, screen printing business start up cost, screen printing Business, screen printing frame India, screen printing frame making, screen printing frames, screen printing Industry in India, screen printing materials, Screen Printing Press, screen printing process, screen printing process step by step, screen printing Projects, screen printing technique, Screen Printing Technology, screen printing tutorial, screen printing wood frames, Screens and Screen Printing Frames, Setting up and opening your screen printing Business, Setting up of screen printing Units, Small scale Commercial screen printing, Small Scale screen printing Projects, Small Start-up Business Project, Start Up India, Stand Up India, Starting a screen printing Business, Starting Your Own Screen Printing Business, Start-up Business Plan for screen printing, startup ideas, Startup Project, Startup Project for screen printing, startup project plan, surface printing techniques, The Printing Process - How Offset Printing Works, The Printing Process: Screen Printing, T-shirt Screen PrintingPrinting



Printingahad003
╠²
Screen printing and digital printing are two common textile printing methods. Screen printing uses a woven mesh screen to support an ink-blocking stencil and applies ink through the open areas of the screen onto the fabric below. Digital printing uses inkjet printing technology to place micro-sized ink droplets onto fabric directly from a computer design file. Both methods allow for localized color application and flexible designs, while digital printing enables very small minimum runs due to not requiring prepared screens. Key factors in choosing a printing method include design requirements, cost, minimum order quantities, and the desired finish.Screen printing in textile printing sector



Screen printing in textile printing sectorHasibul Haque Chowdhury
╠²
Now we are in the age of printing, textile printing becomes popular day by day. Screen printing has been taken large place in textile printing sector. Trying to give a short description on it.What is Screen Printing?



What is Screen Printing?FESPA
╠²
Screen printing is a printing technique that involves forcing ink through a mesh screen to deposit it onto a substrate. It can be used on a wide variety of materials and products from t-shirts and textiles to technical components. Modern screen printing uses advanced machines that can print colors automatically and rapidly in multiple layers onto flat and rounded surfaces. It remains a versatile printing method that can create detailed, multi-colored images for art, graphics, and industrial applications.FINAL REPORT c



FINAL REPORT cKapil Rana
╠²
This document provides information on the process of automatic glass printing machine. It discusses screen printing, which uses a stencil and ink to print the same design on glass or other surfaces. The machine uses components like a chain drive, reduction gearbox, and cams powered by a single motor to automatically move and rotate glass pieces on a conveyor to be printed on all sides. The document outlines the materials, process, and technical details involved in screen printing and creating an automatic machine to perform the process.Printing



PrintingSabeema
╠²
S. MAGDOOM SABEEMA
ASSISTANT PROFESSOR
DEPARTMENT OF COSTUME DESIGN AND FASHION
V.V.VANNIAPERUMAL COLLEGE FOR WOMEN
VIRUDHUNAGARPigment printing 130103023



Pigment printing 130103023BGMEA University Of Fashion & Technology
╠²
Pigment printing is a textile printing technique that involves applying insoluble pigments mixed with a binder and thickener only to defined areas of fabric to create a pattern. It does not require washing after printing like other techniques since the binder fixes the pigment. Pigment printing can be done on many fiber types at high speeds, making it economical. The process involves preparing a printing paste, applying it using screen or roller printing, then drying and curing the printed fabric without an after-treatment wash.Pigment printing



Pigment printingKarcahi university
╠²
The document discusses pigment printing, which is a type of textile printing where insoluble pigments are fixed to fabric using a binder. Pigment printing pastes contain thickening agents, binders, and other auxiliaries. It is the most economical printing process as it does not require washing after printing. Screen printing and roller printing are common methods used to apply pigment pastes to fabric in defined patterns.Screen printing



Screen printingashrafulislam293
╠²
Screen printing is a printing technique where a mesh is used to transfer ink onto a substrate, except in areas made impermeable to the ink by a blocking stencil. A blade or squeegee is moved across the screen to fill the open mesh apertures with ink, and a reverse stroke then causes the screen to touch the substrate momentarily along a line of contact.Garment Printing Solutions



Garment Printing SolutionsAbhishek Raj
╠²
This document provides information on various garment printing methods and their costs. It discusses traditional methods like block printing and screen printing as well as digital methods like direct-to-garment (DTG) printing and sublimation printing. Specific printing techniques are outlined, such as plastisol, discharge, and foil printing. Production processes, suitable fabrics, costs per print, and minimum order quantities are compared for each method. In conclusion, the document serves as a guide for selecting printing styles based on needs and budgets.Printing



PrintingBannari Amman Institute of Technology
╠²
Printing techniques were summarized including:
1. Printing involves applying dyes or pigments locally to fabrics to create designs through techniques like screen printing and block printing.
2. Screen printing uses a mesh screen to block ink from transferring in some areas to create sharp-edged images, while block printing carves designs into wooden blocks.
3. Other techniques include discharge printing which dyes the whole fabric and then removes dye in a pattern, and resist printing which applies a dye-repelling substance before dyeing.Direct printing



Direct printingSajjad Ali
╠²
This document discusses different types of direct printing techniques. Direct printing involves applying dye directly to fabric using blocks, screens, or rollers to create patterns. The key types discussed are block printing, roller printing, screen printing, flat screen printing, and rotary screen printing. Block printing is the oldest method and involves manually pressing carved wooden blocks into fabric. Roller printing uses engraved metal rollers to print continuously on fabric. Screen printing applies dye through cutout stencils or printed screens. Flat and rotary screen printing are automated versions of screen printing using machines.Printing



PrintingMd. Mazadul Hasan Shishir
╠²
This document provides information about various printing methods used in the textile industry. It begins by describing direct printing, resist printing, and discharge printing. It then lists and provides brief descriptions of different types of printing methods, such as screen printing, flock printing, foil printing, heat transfer printing, and dye sublimation printing. The document also includes diagrams of screen printing and rotary screen printing processes. It provides more detailed explanations of techniques like block printing, dye sublimation printing, heat transfer printing, and batik.Printing 



Printing Amit kumar
╠²
This document provides information about various printing methods and processes. It begins by describing direct printing, resist printing, and discharge printing methods. It then discusses different types of printing methods known, including screen printing, and provides steps for processes like design to screen and after production primary printing inspection. The document also includes descriptions of specific printing techniques like roller printing, block printing, dye sublimation printing, and heat transfer printing. It concludes by comparing automatic print versus hand print.Textile printing & Finishing machinery



Textile printing & Finishing machineryMdToukir1
╠²
1. The document discusses various types of printing and finishing machinery used in the textile industry, including block printing machines, roller printing machines, stencil printing machines, and digital printing machines.
2. It describes specific printing processes like hand block printing and roller printing in detail. Finishing machinery discussed include mercerizing machines and softening machines.
3. Printing and finishing machinery play a crucial role in the textile industry by allowing for design, improving fabric quality, and making textiles suitable for various end uses.Textile Printing & Finishing Machinery



Textile Printing & Finishing MachineryMdToukirAhmedSrabon
╠²
1. The document discusses various types of printing and finishing machinery used in the textile industry, including block printing machines, roller printing machines, stencil printing machines, and digital printing machines.
2. It describes specific printing processes like hand block printing and roller printing in detail. Hand block printing uses carved wooden blocks to apply color while roller printing uses rollers for precise repeating patterns.
3. Important finishing machinery discussed include mercerizing machines, which improve cotton luster, and softening machines, which apply softening agents to fabrics.
4. Printing and finishing machinery play a crucial role in textile production and quality by allowing for designs, durability, and making fabrics suitable for various end uses.Lecture 8 digital printing of textiles (condensed)



Lecture 8 digital printing of textiles (condensed)Adane Nega
╠²
Digital printing of textiles allows for mass customization by printing designs directly from digital files without screens or plates. It provides benefits like quick design changes and short runs but adoption has been slow due to limitations in printing speed. Improvements are being made and digital printing is gaining acceptance for applications like sampling and short runs while conventional printing remains dominant for bulk production. In the future, further increases in printing speeds may allow digital printing to compete for more bulk production applications and even be used in a woven format with multiple printers.Lecture 8 digital printing of textiles (condensed)



Lecture 8 digital printing of textiles (condensed)Adane Nega
╠²
Digital printing of textiles is an emerging technology that offers several advantages over traditional analog printing methods. It allows for mass customization through computer-controlled inkjet printing without the need for screens or plates. While adoption has been slow due to issues like speed and cost, digital printing is growing in niche applications like sampling and small batch production. As inkjet printer speeds increase to compete with traditional methods and as the technology matures, digital printing is poised to transform the textile printing industry.Lecture 8 digital printing of textiles (condensed)



Lecture 8 digital printing of textiles (condensed)Adane Nega
╠²
Digital printing of textiles allows for mass customization by printing designs directly from digital files without screens or plates. It provides benefits like quick design changes and short runs but adoption has been slow due to limitations in printing speed. Improvements are being made and digital printing is gaining acceptance for applications like sampling and short runs while conventional printing remains dominant for bulk production. In the future, further increases in printing speeds may allow digital printing to compete for more bulk production applications and even be used in a woven format like looms.Lecture 8 digital printing of textiles (condensed)



Lecture 8 digital printing of textiles (condensed)Adane Nega
╠²
Digital printing of textiles is an emerging technology that offers several advantages over traditional analog printing methods. Digital printing uses electronic design files and inkjet printing heads rather than physical screens or rollers. It allows for mass customization, quick design changes, and reduced waste. While the technology is gaining ground in niche markets like sampling, wider adoption has been slowed by issues like printing speeds and the high costs of inks and printers needed for bulk production. Continued improvements may allow digital printing to compete with conventional rotary screen printing for medium-sized runs in the future.Lecture 8 digital printing of textiles (condensed)



Lecture 8 digital printing of textiles (condensed)Adane Nega
╠²
Digital printing of textiles allows for mass customization by printing designs directly from digital files without screens or plates. It provides benefits like quick design changes and short runs but adoption has been slow due to limitations in printing speed. Improvements in inkjet printing technology aim to increase speeds to compete with conventional rotary screen printing for bulk production. While digital printing is established for sampling, the future vision is for it to also enable small batch production directly from computer designs.MIRACLE OF SCREEN PRINTING MACHINE BUSINESS IN 7 DAYS & NIGHTS.pdf



MIRACLE OF SCREEN PRINTING MACHINE BUSINESS IN 7 DAYS & NIGHTS.pdfseri bangash
╠²
https://seribangash.com/
An apparatus used for screen printing is a screen printing machine, in which ink is forced onto a substrate through a mesh screen. It is made up of a frame, a mesh screen that is stretched tightly, and an ink application squeegee. This machine produces strong, colorful prints on a variety of materials, including paper, fabric, metal, and plastic. It is utilized in many different sectors.Screen printing



Screen printingGlobe Trotter
╠²
Screen printing is a stencil printing process where ink is forced through a mesh fabric screen to which a design cut from film has been attached. The key steps are cutting a stencil design from film and adhering it to a stretched mesh screen, then using a squeegee to force ink through the open areas of the screen onto the printing surface below. Screen printing has been used for centuries and grew with industrialization. It allows printing on various surfaces and materials and is well-suited for printing stationary, t-shirts, and other items. The process involves preparing the screen and stencil, printing, cleaning, and removing the stencil.Textile Printing Presentation



Textile Printing PresentationMazedin Reza
╠²
This document discusses different methods of textile printing. It begins by explaining the basic process of printing designs on fabric using blocks, rollers or screens to apply color. It then compares automatic and hand printing methods. The main methods covered are direct, discharge and resist printing. Specific techniques like block, screen and digital printing are explained in terms of how they work, their advantages and disadvantages. The document provides an overview of the various techniques used in textile printing.Lecture 8 digital printing of textiles



Lecture 8 digital printing of textilesAdane Nega
╠²
This document summarizes digital printing of textiles using inkjet technology. It discusses how digital printing works by transferring a design file digitally to an inkjet printer, without the need for screens or plates. The key steps are outlined as master design, scanning, transferring the design data to the inkjet printer via software, and printing onto the fabric surface without contact. Various inkjet technologies like thermal, piezo and continuous inkjet are described along with their advantages and disadvantages. Factors important for inkjet printing of textiles like inks, pretreated fabrics, and software are also summarized.Lecture 8 digital printing of textiles



Lecture 8 digital printing of textilesAdane Nega
╠²
The document discusses digital printing of textiles compared to analog printing methods. Digital printing involves storing the design electronically and using an inkjet printer to apply the design to fabric without screens or plates. It has advantages over analog methods like quicker turnaround times, lower costs for short runs, and more design flexibility. The two main inkjet technologies discussed are continuous inkjet which uses electrically-charged droplets, and drop-on-demand inkjet which forms droplets only as needed using thermal or piezoelectric methods.UNIT 3 LESSON 3 RELIGOUS EDUCATION 4- THE CATHOLIC SOCIAL TEACHING [Autosaved...



UNIT 3 LESSON 3 RELIGOUS EDUCATION 4- THE CATHOLIC SOCIAL TEACHING [Autosaved...CarljohnCallos
╠²
cttoMore Related Content
Similar to UNIT 3 MAPEH 6 LESSON 1 SCREEN PRINTING- ARTS.pptx (20)
Pigment printing 130103023



Pigment printing 130103023BGMEA University Of Fashion & Technology
╠²
Pigment printing is a textile printing technique that involves applying insoluble pigments mixed with a binder and thickener only to defined areas of fabric to create a pattern. It does not require washing after printing like other techniques since the binder fixes the pigment. Pigment printing can be done on many fiber types at high speeds, making it economical. The process involves preparing a printing paste, applying it using screen or roller printing, then drying and curing the printed fabric without an after-treatment wash.Pigment printing



Pigment printingKarcahi university
╠²
The document discusses pigment printing, which is a type of textile printing where insoluble pigments are fixed to fabric using a binder. Pigment printing pastes contain thickening agents, binders, and other auxiliaries. It is the most economical printing process as it does not require washing after printing. Screen printing and roller printing are common methods used to apply pigment pastes to fabric in defined patterns.Screen printing



Screen printingashrafulislam293
╠²
Screen printing is a printing technique where a mesh is used to transfer ink onto a substrate, except in areas made impermeable to the ink by a blocking stencil. A blade or squeegee is moved across the screen to fill the open mesh apertures with ink, and a reverse stroke then causes the screen to touch the substrate momentarily along a line of contact.Garment Printing Solutions



Garment Printing SolutionsAbhishek Raj
╠²
This document provides information on various garment printing methods and their costs. It discusses traditional methods like block printing and screen printing as well as digital methods like direct-to-garment (DTG) printing and sublimation printing. Specific printing techniques are outlined, such as plastisol, discharge, and foil printing. Production processes, suitable fabrics, costs per print, and minimum order quantities are compared for each method. In conclusion, the document serves as a guide for selecting printing styles based on needs and budgets.Printing



PrintingBannari Amman Institute of Technology
╠²
Printing techniques were summarized including:
1. Printing involves applying dyes or pigments locally to fabrics to create designs through techniques like screen printing and block printing.
2. Screen printing uses a mesh screen to block ink from transferring in some areas to create sharp-edged images, while block printing carves designs into wooden blocks.
3. Other techniques include discharge printing which dyes the whole fabric and then removes dye in a pattern, and resist printing which applies a dye-repelling substance before dyeing.Direct printing



Direct printingSajjad Ali
╠²
This document discusses different types of direct printing techniques. Direct printing involves applying dye directly to fabric using blocks, screens, or rollers to create patterns. The key types discussed are block printing, roller printing, screen printing, flat screen printing, and rotary screen printing. Block printing is the oldest method and involves manually pressing carved wooden blocks into fabric. Roller printing uses engraved metal rollers to print continuously on fabric. Screen printing applies dye through cutout stencils or printed screens. Flat and rotary screen printing are automated versions of screen printing using machines.Printing



PrintingMd. Mazadul Hasan Shishir
╠²
This document provides information about various printing methods used in the textile industry. It begins by describing direct printing, resist printing, and discharge printing. It then lists and provides brief descriptions of different types of printing methods, such as screen printing, flock printing, foil printing, heat transfer printing, and dye sublimation printing. The document also includes diagrams of screen printing and rotary screen printing processes. It provides more detailed explanations of techniques like block printing, dye sublimation printing, heat transfer printing, and batik.Printing 



Printing Amit kumar
╠²
This document provides information about various printing methods and processes. It begins by describing direct printing, resist printing, and discharge printing methods. It then discusses different types of printing methods known, including screen printing, and provides steps for processes like design to screen and after production primary printing inspection. The document also includes descriptions of specific printing techniques like roller printing, block printing, dye sublimation printing, and heat transfer printing. It concludes by comparing automatic print versus hand print.Textile printing & Finishing machinery



Textile printing & Finishing machineryMdToukir1
╠²
1. The document discusses various types of printing and finishing machinery used in the textile industry, including block printing machines, roller printing machines, stencil printing machines, and digital printing machines.
2. It describes specific printing processes like hand block printing and roller printing in detail. Finishing machinery discussed include mercerizing machines and softening machines.
3. Printing and finishing machinery play a crucial role in the textile industry by allowing for design, improving fabric quality, and making textiles suitable for various end uses.Textile Printing & Finishing Machinery



Textile Printing & Finishing MachineryMdToukirAhmedSrabon
╠²
1. The document discusses various types of printing and finishing machinery used in the textile industry, including block printing machines, roller printing machines, stencil printing machines, and digital printing machines.
2. It describes specific printing processes like hand block printing and roller printing in detail. Hand block printing uses carved wooden blocks to apply color while roller printing uses rollers for precise repeating patterns.
3. Important finishing machinery discussed include mercerizing machines, which improve cotton luster, and softening machines, which apply softening agents to fabrics.
4. Printing and finishing machinery play a crucial role in textile production and quality by allowing for designs, durability, and making fabrics suitable for various end uses.Lecture 8 digital printing of textiles (condensed)



Lecture 8 digital printing of textiles (condensed)Adane Nega
╠²
Digital printing of textiles allows for mass customization by printing designs directly from digital files without screens or plates. It provides benefits like quick design changes and short runs but adoption has been slow due to limitations in printing speed. Improvements are being made and digital printing is gaining acceptance for applications like sampling and short runs while conventional printing remains dominant for bulk production. In the future, further increases in printing speeds may allow digital printing to compete for more bulk production applications and even be used in a woven format with multiple printers.Lecture 8 digital printing of textiles (condensed)



Lecture 8 digital printing of textiles (condensed)Adane Nega
╠²
Digital printing of textiles is an emerging technology that offers several advantages over traditional analog printing methods. It allows for mass customization through computer-controlled inkjet printing without the need for screens or plates. While adoption has been slow due to issues like speed and cost, digital printing is growing in niche applications like sampling and small batch production. As inkjet printer speeds increase to compete with traditional methods and as the technology matures, digital printing is poised to transform the textile printing industry.Lecture 8 digital printing of textiles (condensed)



Lecture 8 digital printing of textiles (condensed)Adane Nega
╠²
Digital printing of textiles allows for mass customization by printing designs directly from digital files without screens or plates. It provides benefits like quick design changes and short runs but adoption has been slow due to limitations in printing speed. Improvements are being made and digital printing is gaining acceptance for applications like sampling and short runs while conventional printing remains dominant for bulk production. In the future, further increases in printing speeds may allow digital printing to compete for more bulk production applications and even be used in a woven format like looms.Lecture 8 digital printing of textiles (condensed)



Lecture 8 digital printing of textiles (condensed)Adane Nega
╠²
Digital printing of textiles is an emerging technology that offers several advantages over traditional analog printing methods. Digital printing uses electronic design files and inkjet printing heads rather than physical screens or rollers. It allows for mass customization, quick design changes, and reduced waste. While the technology is gaining ground in niche markets like sampling, wider adoption has been slowed by issues like printing speeds and the high costs of inks and printers needed for bulk production. Continued improvements may allow digital printing to compete with conventional rotary screen printing for medium-sized runs in the future.Lecture 8 digital printing of textiles (condensed)



Lecture 8 digital printing of textiles (condensed)Adane Nega
╠²
Digital printing of textiles allows for mass customization by printing designs directly from digital files without screens or plates. It provides benefits like quick design changes and short runs but adoption has been slow due to limitations in printing speed. Improvements in inkjet printing technology aim to increase speeds to compete with conventional rotary screen printing for bulk production. While digital printing is established for sampling, the future vision is for it to also enable small batch production directly from computer designs.MIRACLE OF SCREEN PRINTING MACHINE BUSINESS IN 7 DAYS & NIGHTS.pdf



MIRACLE OF SCREEN PRINTING MACHINE BUSINESS IN 7 DAYS & NIGHTS.pdfseri bangash
╠²
https://seribangash.com/
An apparatus used for screen printing is a screen printing machine, in which ink is forced onto a substrate through a mesh screen. It is made up of a frame, a mesh screen that is stretched tightly, and an ink application squeegee. This machine produces strong, colorful prints on a variety of materials, including paper, fabric, metal, and plastic. It is utilized in many different sectors.Screen printing



Screen printingGlobe Trotter
╠²
Screen printing is a stencil printing process where ink is forced through a mesh fabric screen to which a design cut from film has been attached. The key steps are cutting a stencil design from film and adhering it to a stretched mesh screen, then using a squeegee to force ink through the open areas of the screen onto the printing surface below. Screen printing has been used for centuries and grew with industrialization. It allows printing on various surfaces and materials and is well-suited for printing stationary, t-shirts, and other items. The process involves preparing the screen and stencil, printing, cleaning, and removing the stencil.Textile Printing Presentation



Textile Printing PresentationMazedin Reza
╠²
This document discusses different methods of textile printing. It begins by explaining the basic process of printing designs on fabric using blocks, rollers or screens to apply color. It then compares automatic and hand printing methods. The main methods covered are direct, discharge and resist printing. Specific techniques like block, screen and digital printing are explained in terms of how they work, their advantages and disadvantages. The document provides an overview of the various techniques used in textile printing.Lecture 8 digital printing of textiles



Lecture 8 digital printing of textilesAdane Nega
╠²
This document summarizes digital printing of textiles using inkjet technology. It discusses how digital printing works by transferring a design file digitally to an inkjet printer, without the need for screens or plates. The key steps are outlined as master design, scanning, transferring the design data to the inkjet printer via software, and printing onto the fabric surface without contact. Various inkjet technologies like thermal, piezo and continuous inkjet are described along with their advantages and disadvantages. Factors important for inkjet printing of textiles like inks, pretreated fabrics, and software are also summarized.Lecture 8 digital printing of textiles



Lecture 8 digital printing of textilesAdane Nega
╠²
The document discusses digital printing of textiles compared to analog printing methods. Digital printing involves storing the design electronically and using an inkjet printer to apply the design to fabric without screens or plates. It has advantages over analog methods like quicker turnaround times, lower costs for short runs, and more design flexibility. The two main inkjet technologies discussed are continuous inkjet which uses electrically-charged droplets, and drop-on-demand inkjet which forms droplets only as needed using thermal or piezoelectric methods.More from CarljohnCallos (20)
UNIT 3 LESSON 3 RELIGOUS EDUCATION 4- THE CATHOLIC SOCIAL TEACHING [Autosaved...



UNIT 3 LESSON 3 RELIGOUS EDUCATION 4- THE CATHOLIC SOCIAL TEACHING [Autosaved...CarljohnCallos
╠²
cttoBusiness Finance CHapter 2 Lesson 5 Tools in Managing Cash Receivables and pp...



Business Finance CHapter 2 Lesson 5 Tools in Managing Cash Receivables and pp...CarljohnCallos
╠²
cttoUnit 2 Business Finance Chapter 1 Lesson 1 SOurces of funds for business oper...



Unit 2 Business Finance Chapter 1 Lesson 1 SOurces of funds for business oper...CarljohnCallos
╠²
cttoRecently uploaded (20)
Rass MELAI : an Internet MELA Quiz Finals - El Dorado 2025



Rass MELAI : an Internet MELA Quiz Finals - El Dorado 2025Conquiztadors- the Quiz Society of Sri Venkateswara College
╠²
Finals of Rass MELAI : a Music, Entertainment, Literature, Arts and Internet Culture Quiz organized by Conquiztadors, the Quiz society of Sri Venkateswara College under their annual quizzing fest El Dorado 2025. Database population in Odoo 18 - Odoo slides



Database population in Odoo 18 - Odoo slidesCeline George
╠²
In this slide, weŌĆÖll discuss the database population in Odoo 18. In Odoo, performance analysis of the source code is more important. Database population is one of the methods used to analyze the performance of our code. QuickBooks Desktop to QuickBooks Online How to Make the Move



QuickBooks Desktop to QuickBooks Online How to Make the MoveTechSoup
╠²
If you use QuickBooks Desktop and are stressing about moving to QuickBooks Online, in this webinar, get your questions answered and learn tips and tricks to make the process easier for you.
Key Questions:
* When is the best time to make the shift to QuickBooks Online?
* Will my current version of QuickBooks Desktop stop working?
* I have a really old version of QuickBooks. What should I do?
* I run my payroll in QuickBooks Desktop now. How is that affected?
*Does it bring over all my historical data? Are there things that don't come over?
* What are the main differences between QuickBooks Desktop and QuickBooks Online?
* And moreYear 10 The Senior Phase Session 3 Term 1.pptx



Year 10 The Senior Phase Session 3 Term 1.pptxmansk2
╠²
Year 10 The Senior Phase Session 3 Term 1.pptxInformation Technology for class X CBSE skill Subject



Information Technology for class X CBSE skill SubjectVEENAKSHI PATHAK
╠²
These questions are based on cbse booklet for 10th class information technology subject code 402. these questions are sufficient for exam for first lesion. This subject give benefit to students and good marks. if any student weak in one main subject it can replace with these marks.Blind spots in AI and Formulation Science, IFPAC 2025.pdf



Blind spots in AI and Formulation Science, IFPAC 2025.pdfAjaz Hussain
╠²
The intersection of AI and pharmaceutical formulation science highlights significant blind spotsŌĆösystemic gaps in pharmaceutical development, regulatory oversight, quality assurance, and the ethical use of AIŌĆöthat could jeopardize patient safety and undermine public trust. To move forward effectively, we must address these normalized blind spots, which may arise from outdated assumptions, errors, gaps in previous knowledge, and biases in language or regulatory inertia. This is essential to ensure that AI and formulation science are developed as tools for patient-centered and ethical healthcare.How to Configure Flexible Working Schedule in Odoo 18 Employee



How to Configure Flexible Working Schedule in Odoo 18 EmployeeCeline George
╠²
In this slide, weŌĆÖll discuss on how to configure flexible working schedule in Odoo 18 Employee module. In Odoo 18, the Employee module offers powerful tools to configure and manage flexible working schedules tailored to your organization's needs.Mate, a short story by Kate Grenvile.pptx



Mate, a short story by Kate Grenvile.pptxLiny Jenifer
╠²
A powerpoint presentation on the short story Mate by Kate Greenville. This presentation provides information on Kate Greenville, a character list, plot summary and critical analysis of the short story.The Dravidian Languages: Tamil, Telugu, Kannada, Malayalam, Brahui, Kuvi, Tulu



The Dravidian Languages: Tamil, Telugu, Kannada, Malayalam, Brahui, Kuvi, TuluDrIArulAram
╠²
The Dravidian Languages by Arul AramKaun TALHA quiz Prelims - El Dorado 2025



Kaun TALHA quiz Prelims - El Dorado 2025Conquiztadors- the Quiz Society of Sri Venkateswara College
╠²
Prelims of Kaun TALHA : a Travel, Architecture, Lifestyle, Heritage and Activism quiz, organized by Conquiztadors, the Quiz society of Sri Venkateswara College under their annual quizzing fest El Dorado 2025. Essentials of a Good PMO, presented by Aalok Sonawala



Essentials of a Good PMO, presented by Aalok SonawalaAssociation for Project Management
╠²
APM event hosted by the South Wales and West of England Network (SWWE Network)
Speaker: Aalok Sonawala
The SWWE Regional Network were very pleased to welcome Aalok Sonawala, Head of PMO, National Programmes, Rider Levett Bucknall on 26 February, to BAWA for our first face to face event of 2025. Aalok is a member of APMŌĆÖs Thames Valley Regional Network and also speaks to members of APMŌĆÖs PMO Interest Network, which aims to facilitate collaboration and learning, offer unbiased advice and guidance.
Tonight, Aalok planned to discuss the importance of a PMO within project-based organisations, the different types of PMO and their key elements, PMO governance and centres of excellence.
PMOŌĆÖs within an organisation can be centralised, hub and spoke with a central PMO with satellite PMOs globally, or embedded within projects. The appropriate structure will be determined by the specific business needs of the organisation. The PMO sits above PM delivery and the supply chain delivery teams.
For further information about the event please click here.The Constitution, Government and Law making bodies .



The Constitution, Government and Law making bodies .saanidhyapatel09
╠²
This PowerPoint presentation provides an insightful overview of the Constitution, covering its key principles, features, and significance. It explains the fundamental rights, duties, structure of government, and the importance of constitutional law in governance. Ideal for students, educators, and anyone interested in understanding the foundation of a nationŌĆÖs legal framework.
A PPT Presentation on The Princess and the God: A tale of ancient India by A...



A PPT Presentation on The Princess and the God: A tale of ancient India by A...Beena E S
╠²
A PPT Presentation on The Princess and the God: A tale of ancient India by Aaron ShepardHow to use Init Hooks in Odoo 18 - Odoo ║▌║▌▀Żs



How to use Init Hooks in Odoo 18 - Odoo ║▌║▌▀ŻsCeline George
╠²
In this slide, weŌĆÖll discuss on how to use Init Hooks in Odoo 18. In Odoo, Init Hooks are essential functions specified as strings in the __init__ file of a module.Rass MELAI : an Internet MELA Quiz Finals - El Dorado 2025



Rass MELAI : an Internet MELA Quiz Finals - El Dorado 2025Conquiztadors- the Quiz Society of Sri Venkateswara College
╠²
Kaun TALHA quiz Prelims - El Dorado 2025



Kaun TALHA quiz Prelims - El Dorado 2025Conquiztadors- the Quiz Society of Sri Venkateswara College
╠²
UNIT 3 MAPEH 6 LESSON 1 SCREEN PRINTING- ARTS.pptx
- 2. 2 Introduction to screen printing INDEX Preparation For Screen Printing Required Items For Screen Printing
- 3. 3 Types of Screen Printing INDEX Advantages Disadvantages
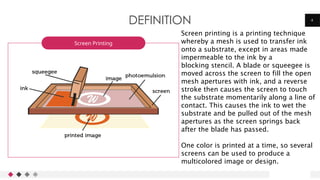
- 4. 4 Screen printing is a printing technique whereby a mesh is used to transfer ink onto a substrate, except in areas made impermeable to the ink by a blocking stencil. A blade or squeegee is moved across the screen to fill the open mesh apertures with ink, and a reverse stroke then causes the screen to touch the substrate momentarily along a line of contact. This causes the ink to wet the substrate and be pulled out of the mesh apertures as the screen springs back after the blade has passed. One color is printed at a time, so several screens can be used to produce a multicolored image or design. Screen Printing DEFINITION
- 5. 5 REQUIRED ITEMS FOR SCREEN PRINTING ’ü▒ It refers to the number of the threads per inch of fabric. ’ü▒ The usual mesh of screen employed for cotton and silk printing is 80 threads per inch. Screen Screen Frames ’ü▒ .There are two types of screen frames(metal & wood) ’ü▒ Screen frames are usually 26╦Ø├Ś55╦Ø and 23├Ś55╦Ø for printing 45╦Ø wide cloth.
- 6. 6 REQUIRED ITEMS FOR SCREEN PRINTING ’ü▒ Silk- Multifilament Weave ’ü▒ Nylon- Multifilament or monofilament ’ü▒ Polyester- Multifilament or Monofilament Screen Fabric Types Squeegee ’ü▒ squeegee is moved across the screen to fill the open mesh apertures with ink
- 7. 7 PREPARATION OF SCREEN Photochemical method is the most widely used for preparing the screen. This based on the principle that when a coating of a solution of ammonium dichromate-gelatin or ammonium dichromate- polyvinyl alcohol is dried and exposed to light, insolubilisation takes place. Other method for screen preparation is lacquer and laser screen.
- 8. 8 TYPES OF SCREEN PRINTING 2. Rotary Screen Printing Upcoming Deposits 1. Flat(bed) screen printing Fully Automatic Flat Screen Printing Semi Automatic Flat Screen Printing Hand Screen Printing
- 9. Hand Screen Printing is a technique that allows to print, with greater accuracy, large and bright images on any type of fabric. It is an ancient technique, that has envolved over time and is still one of the most common for textile printing. Hand Screen printing is made with just a frame, ink and a stencils. The stencil is the negative of the image you want to print and is in waterproofing material. After mounting the fabric on the frame and placing the stencil, the ink is spread. The operation have to be repeated several times if working with multiple colors. In this case, the fabric must dry completely between one color and the next. The technique of Hand Screen Printing, while being less prone to human error, requires a high level of competence: the craftsman who makes the press must be familiar with the pigments used and the fabric, to be sure of obtaining a good results. SLIDE 6
- 10. Semi Automatic Flat Screen Printing The manual process has been semi automated by mounting the screen in a carriage and driving the squeegee mechanically across the screen. Long tables, typically 20-60m long, are used and some provision is usually made for drying the printed fabric. Semi automated flat screen printing is still very popular where the scale of production is not large or where capital investment is limited. In both hand and semi-automatic flat screen printing the colors are printed one after another with time for drying, which means that the situation approaches ŌĆśwet-on-dryŌĆÖ printing. SLIDE 6
- 11. Rotary Screen Printing In basic operation, rotary screen and flat screen- printing machines are very similar. Both use the same type of in-feed device, glue through, rotating blanket, dryer and fixation equipment. The process involves initially feeding fabric onto the rubber blanket. As the fabric travels under the rotary screens, the screens turn the white fabric. During printing, the paste is pressed through the surface via openings in order to obtain the desired design. The cylindrical screens allow more screens to be arranged per unit length than is the case with flat screen printing. Speed range from 30 to 50 m/min. The standard internal circumference of cylindrical screens is 640 - 640.1 mm. However, other dimensions are also ┬Ę possible. SLIDE 6
- 12. 12 Advantages ’ü▒ The inks used are very durable, the colors are extremely vivid, particularly for outdoor uses, making this a unique reproduction technique. ’ü▒ We can print on a very large variety of materials and objects, and that we can choose from a plethora of special inks. ’ü▒ This is a very flexible printing technology, with no limitation on the thickness. Advantages of Screen Printing
- 13. 13 Disadvantages ’ü▒ The major disadvantage in Screen Printing is the amount of time it takes to set up a job. ’ü▒ So preparation times are particularly long, particularly in high quality applications. ’ü▒ This means that, as a method, it is financially impractical for the production of a single item, particularly for color printing advertising applications. Disadvantages of Screen Printing








![OM Unit 2 Leson 1 Nature of Staffing [Autosaved].pptx](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/omunit2leson1natureofstaffingautosaved-241202224728-4630628e-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)













