Workshop Article on management Monkey version-II.pptx
- 1. ByWilliam Oncken, Jr., and Donald L.Wass MANAGEMENT TIME WHOŌĆÖS GOT THE MONKEY Presented By Group-I WORKSHOP PRESENTATON
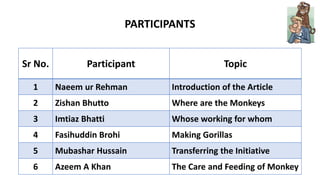
- 2. PARTICIPANTS Sr No. Participant Topic 1 Naeem ur Rehman Introduction of the Article 2 Zishan Bhutto Where are the Monkeys 3 Imtiaz Bhatti Whose working for whom 4 Fasihuddin Brohi Making Gorillas 5 Mubashar Hussain Transferring the Initiative 6 Azeem A Khan The Care and Feeding of Monkey
- 3. Introduction of the Article By Engr. Naeem Ur Rehman
- 4. WhoŌĆÖs got the monkey? The tale of an overburdened manager who allows his employees to delegate responsibilities upward.
- 5. AGENDA ’āś Learning Objective ’āś What is a monkey? ’āś How do you get monkeys? ’āś What is the process? ’āś Why do we manage Other People Monkeys? (OPMŌĆÖs) ’āś How do we manage all our monkeys? ’āś How do we prioritize?
- 6. LEARNING OBJECTIVE ’āś Time management is working on the right thing at the right time. ’āś To accomplish time management, you must give your task on the top priority assigned by boss (Feed your monkeys). ’āś Let other people work their problems (Let them feed their monkeys). ’āś Prioritize the work based on value (Use Magic Quadrant).
- 7. WHAT ARE THE MONKEYS ’āś Monkeys are issues/actions that people bring to you to solve. ’āś The monkey on your back ŌĆō It is metaphor describes issues/problems and the ownership of issues /problems.
- 8. WHAT ARE THE MONKEYS ’āś Issues may be problems, tasks or other items at work that you need to resolve. ’āś They can come from just about anywhere, without warning and you have to manage them.
- 9. WHAT IS MONKEY MANAGEMENT Imagine someone walking into your office with a Monkey on their back. They say, ŌĆ£I have this problem, there is a monkey on my back, and I would like to put the monkey on your backŌĆØ. What would you say? ŌĆ£Great! Load it up, add it to the dozen I have already?ŌĆØ
- 10. MONKEY TRANSFERENCE The process of transferring problems from one owner to a another owner. Leads to following Results:- 1. Generate Stress. 2. Prevent you from working on your assigned higher priority tasks. 3. Prevent you from being perceived as effective.
- 11. Introduction 1.MANAGERSare running out ofTIME? 2.SUBORDINATESare running out ofWORK?
- 12. CAN YOU RELATE TO THIS? How is it possible that I am working overtime and still running out of time, every day, while it seems like everyone else goes home right on time as if they donŌĆÖt have enough to do? ?
- 13. THREE KINDS OF TIME MANAGEMENT Bossimposed time workgiven by boss-Must do (Direct Penalty) Systemimposed time workfrom peers- Must do (Lesser Penalty) Self imposedtime work youagrees to do-Choice Based (No Penalty)
- 14. Self Imposed Time Discretionary Time workgiven by boss-Must do Direct Penalty Subordinateimposed time workfrom peers- Must do Lesser Penalty
- 15. THREE KINDS OF TIME MANAGEMENT ’āś Rest time for managerŌĆśsown self ŌåÆ DISCRETIONARYTIME ’āś Self imposed time CANCONVERTto ŌåÆ SUBORDINATEIMPOSEDTIME Maximize Discretionary Time Minimize: Subordinate Imposed Time
- 16. Where Are the Monkeys By Engr. Zishan
- 17. WHEREŌĆÖS THEMONKEY? Wegot a problem Let me think about it & IŌĆÖll let you know The manager has becomesubordinate to hissubordinate Monkey Ōēł A problem needed to solved
- 18. SOMEOTHER INSTANCES WHERE THE MONKEY GETS TRANSFERRED TO MANAGERŌĆÖS BACK ’āś When subordinate asks for help and managerŌĆÖs words are ŌĆ£let me know how I can helpŌĆØ implies the subordinate has to get approval of manager so she/he has to checks up on manager. ’āś Manager does not respond to a memo and subordinateasks for the follow up. ’āś Manager respond to a new employee that he will draft initial points to discuss it with the subordinate for his objectives of new job. New employeewill not do job until told. MANAGERWILL GETFRUSTRATEDWITHALLTHEMONKEYS
- 19. Getting Rid of the Monkey By Engr. Imtiaz ul Hassan Bhatti
- 21. GETTING RIDOFTHEMONKEY ’āś The subordinate will happy that his problem entertained. ’āś The manager will also happy to see the monkey back to and the subordinate will not be waiting for the manager, instead, the manager will be waiting for the subordinate.
- 22. EXAMPLES 1. Project Manager and subordinate on report Writing 2. Sales Manager and Client about the product.
- 23. RULES TO GET RID OF MONKEYS 1. Make appointments. 2. Give the monkey back. 3. Set priorities. 4. Say no. 5. Train your subordinates or colleagues.
- 24. Making Time for Gorillas By Engr. Fasihuddin Brohi
- 25. MAKING TIME FOR GORILLAS What is a Gorilla? ’āś A ŌĆ£GorillaŌĆØ is a strategic endeavor that requires manager attention to dramatically improve the business. ’āś As with most Executives, each day can seem like an endless stream of meetings followed by a series of urgent tasks and decisions that we inherit from our subordinates. ’āś Some of the decision are warranted, but the vast majority come about because we accept our subordinatesŌĆÖ ŌĆ£MonkeysŌĆØ. These Monkeys prevent us from doing other high-value work (ŌĆ£GorillasŌĆØ) which are both important to the business and career-building.
- 26. MAKING TIME FOR GORILLAS Command and Control ’āś Today, managers are desperate for a way to free up their time, but command and control is the status quo. Managers feel that they are not allowed to empower their subordinates to make decisions. Too dangerous. Too risky. ’āś ThatŌĆÖs why OnckenŌĆÖs messageŌĆögive the monkey back to its rightful ownerŌĆö involves a critically important paradigm shift. Many managers working today owe him a debt of gratitude. ’āś Command and control as a management philosophy is all but dead, and ŌĆ£empowermentŌĆØ is the word of the day in most organizations trying to thrive in global, intensely competitive markets.
- 27. MAKING TIME FOR GORILLAS ’āś But command and control stubbornly remains a common practice. ’āś Bosses cannot just give a monkey back to their subordinates and then merrily get on with their own business. Empowering subordinates is hard and complicated work. ’āś The reason: when you give problems back to subordinates to solve themselves, you have to be sure that they have both the desire and the ability to do so. As every executive knows, that isnŌĆÖt always the case.
- 28. MAKING TIME FOR GORILLAS Empowerment ’āś Empowerment often means you have to develop people, which is initially much more time consuming than solving the problem on your own. ’āś Just as important, empowerment can only thrive when the whole organization buys into it. ’āś Managers need to be rewarded for delegating decisions and developing people.
- 29. MAKING TIME FOR GORILLAS Delegation ’āś The most important lesson about empowerment is that effective delegation which depends on a trusting relationship between a manager and his subordinate. ’āś To delegate effectively, executives need to establish a running dialogue with subordinates. They need to establish a partnership. ’āś After all, if subordinates are afraid of failing in front of their boss, theyŌĆÖll keep coming back for help rather than truly take initiative.
- 30. MAKING TIME FOR GORILLAS ’āś Nearly all the managers agree that their people are underutilized in their present jobs. ’āś When Managers see others gain power, information, or recognition, for instance, they experience ŌĆ£a feeling of deficiencyŌĆØŌĆöa sense that something is being taken from them. ’āś Managers can easily give back or refuse monkeys, but many managers may subconsciously fear that a subordinate taking the initiative will make them appear a little less strong and a little more vulnerable.
- 31. Making Time for Gorillas ’āś Managers who live with integrity according to a principle based value system are most likely to sustain an empowering style of leadership. ’āś Half or more of managerŌĆÖs time is spent on matters that are urgent but not important. TheyŌĆÖre trapped in an endless cycle of dealing with other peopleŌĆÖs monkeys, yet theyŌĆÖre reluctant to help those people take their own initiative. ’āś As a result, theyŌĆÖre often too busy to spend the time they need on the real gorillas in their organization.
- 32. Transferring the Initiatives By Engr. Mubashar Hussain
- 33. TRANSFERRING THE INITIATIVES When we say that manager has to transfer initiative then we are describing that manager actually showing some confidence in his junior that his junior is in position that he can handle the whatever problem is and junior should describe the problem and solve it by himself .In this way monkey lies on junior and will not come manager.
- 34. TRANSFERRING THE INITIATIVES 1. WAIT,until told 2. ASK,what to do; 3. RECOMMEND,then take resulting action; 4. ACT,but advise at once; 5. ACTONYOUROWN,then routinely report
- 35. 1. WAIT UNTIL TOLD ’āś Monkey lies with manger. ’āś Junior has no monkey. ’āś Problem piles up. ’āś Wastage of valuable time of manager and organization. ’āś Manger has not enough time and content /confidence. ’āś Manager has avoid such initiatives.
- 36. 2. ASK,WHAT TO DO ’āś Monkey lies with junior ’āś Shows manager has control over time ’āś Shows no control on content ’āś this initiative reduce hold of management over junior
- 37. 3. RECOMMEND, THEN TAKE RESULTING ACTION ’āś If manager have enough control on monkey ’āś Understand the monkey. ’āś What can he do? ’āś He immediately recommends what junior has to do. ’āś What action he has to take. ’āś Manager will give recommendation. ’āś Junior just have to follow it. ’āś Monkey lies on junior.
- 38. 4. ACT,BUT ADVISE AT ONCE ’āś Manager take the monkey with him. ’āś He acts and take actions. ’āś Tell the junior exactly what he has to do. ’āś Actually manager advising him. ’āś This better practice.
- 39. 5. ACT ON YOUR OWN, then routinely report (highestinitiative) ’āś Manager tells the junior ,act upon your own. ’āś Monkey on the junior. ’āś Report him on monkey routinely. ’āś Get advise from manager. ’āś Shows confidence in juniors.
- 40. TRANSFERRING THE INITIATIVES ’āś Firs two initiatives ’āś Wait until told & ask what to do ’āś Monkey lies with manager ’āś These are not best initiatives ’āś Put bad impressions on juniors ’āś Fifth Initiative is best one ’āś Routinely report is best method ’āś Manager has no monkey on his back ’āś junior do the work with confidence due to confidence of manager in him
- 41. The Care and Feeding of Monkey By Engr. Azeem Anwar Khan
- 42. RULES FOR MANAGING MONKEYS Rule 1. Monkeys should be fed or shot. Otherwise, they will starve to death, and the manager will waste valuable time on postmortems or attempted resurrections. Rule 2. The monkey population should be kept below the maximum number the manager has time to feed. Subordinates will find time to work as many monkeys as he or she finds time to feed, but no more. It shouldnŌĆÖt take more than five to 15 minutes to feed a properly maintained monkey.
- 43. RULES FOR MANAGING MONKEYS Rule 3. Monkeys should be fed by appointment only. The manager should not have to hunt down starving monkeys and feed them on a catch-as- catch- can basis. Rule 4. Monkeys should be fed face-to-face or by telephone, but never by mail. (Remember ŌĆō with mail, the next move will be the managerŌĆÖs.) Documentation may add to the feeding process, but it cannot take the place of feeding.
- 44. ŌĆ£Get control over the timing and content of what youdoŌĆØ Rule 5. Every monkey should have an assigned next feeding time and degree of initiative. These may be revised at any time by mutual consent but never allowed to become vague or indefinite. Otherwise, the monkey will either starve to death or wind up on the managerŌĆÖs back. ŌĆ£Get control over the timing RULES FOR MANAGING MONKEYS
- 45. GROUND RULES ŌĆ£At no time while I am helping you with this or any other problem will your problem become my problem. The instant your problem becomes mine, you no longer have a problem. I cannot help a person who hasnŌĆÖt got a problemŌĆØ Ō¢Ā The monkey will leave on subordinateŌĆÖs back. Ō¢Ā Subordinates can discuss their problem at given time by manager. Ō¢Ā Manager will not make any move alone. They will discuss it together only. The manager will not have to shut his/her doors, His monkeys are gone. They will return but byappointment.
Editor's Notes
- #21: In the next morning manger reaches office late and 5 subordinates are waiting outside his office to discuss their monkey with manager. Manager calls them one by one . The purpose of interview is to take the monkey, place it on the desk between them, and figure out together next move/action for subordinates Each subordinate shall try their monkey should be decided by manager. Here Manager should Start Questioning What he has done so far? What challenges he is facing? What solutions he has considered? Manager just only guide about the process and set the dead line to finish the work. In this way manager can return the monkey to subordinate. By using above technique manager can return the monkey to respective subordinate.
- #22: If manager took the monkey, then subordinate would be happy and waiting of manager for solution. But manager has returned the monkey to sub ordinate. Now has enough time to feed their own monkey. He will not be over burdened
- #23: Example 1: You are a project manager and one of your subordinate comes to you with a problem. He says he doesn't know how to write a report for the client and asks you to do it for him. You realize that this is a monkey that he is trying to pass on to you. Instead of taking the monkey, you give it back to him. You ask him what he has done so far, what challenges he is facing, and what solutions he has considered. You guide him through the process of writing a report, but you don't do it for him. You also set a deadline for him to finish the report and check in with him regularly. By doing this, you help him develop his skills and confidence, and you also free up your time for your own work.- Example 2: You are a sales manager and one of your clients comes to you with a problem. He says he is unhappy with the product he bought from you and asks you to give him a refund. You realize that this is a monkey that he is trying to shift to you. Instead of taking the monkey, you ask him some questions to understand his situation better. After questioning you find out that he is not using the product correctly and that he has not read the user manual. You explain to him how to use the product properly and offer him some additional support and training. You also show him some recommendations and reviews from other satisfied customers. By doing this, you address his concerns and turn him into a loyal customer, and you also avoid losing money and reputation.
- #24: Make appointments. Don't let your subordinates or colleagues interrupt you with their problems whenever they want. Schedule a specific time to discuss the issue and stick to it. Give the monkey back. When someone brings you a problem, don't take responsibility for it. Ask them what their proposed solution is, and encourage them to take ownership of the problem. Set priorities. When you have multiple monkeys on your desk, it can be overwhelming. Decide which ones are urgent and important, and which ones can wait or be delegated.- Say no. Sometimes, you just have to say no. If the problem is not related to your goals or responsibilities, or if you don't have the time or resources to handle it, politely decline to take the monkey. Train your subordinates or colleagues. One of the reasons why people transfer their monkeys to you is because they lack the skills or confidence to deal with them themselves. You can help them by providing feedback, coaching, and mentoring By following these tips, you can free up your time and energy for your own work, and also empower your subordinates or colleagues to become more independent and accountable. I hope this helps you manage your time better.