Drip Irrigation 7fjfjfifididifififfifi.pptx
- 2. Irrigation Managements 2+1=3 Dr Asmatullah Durani Email: dorani_2000@yahoo.com WhatsApp; 0787888434 Phone No. 0730564575 Drip or trickle Irrigation
- 3. Drip or trickle Irrigation ŌĆó Drip irrigation is a micro irrigation method in which the rate of water application is very low and without any pressure. i.e., drop by drop ŌĆó Drip irrigation is based on the basic concept of irrigation only the roots zone of crop , rather than the entire land surface on which the crop is grow.
- 4. Drip or trickle ▒§░∙░∙Š▒▓Ą▓╣│┘Š▒┤Ū▓įŌĆ”
- 5. History of drip irrigation system ŌĆó ŌĆ½ž»ž¦ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦┘łž©ž«┘łž▒ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž│┘Ŗž│ž¬┘ģŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘Š┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌®ž¦┘äŌĆ¼ ( 1940 ) ŌĆ½ž»ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘Ŗ┘łŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦ž│ž▒ž¦ž”┘Ŗ┘ä┘ŖŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦┘åž¼┘å┘Ŗž▒ž│┘Ŗ┘ģ┌垦ž©ž¦┘äž│ŌĆ¼ ( Symcha blass ) ŌĆ½┘Š┘å┘ł┘ģŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘Ŗ┘łŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘Šž¦┘Ŗ┘ŠŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ä┘Ŗ┌®ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž┤┘łŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ŖŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»ž│ž¦žŁ┘ŖŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¬┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘Š┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌®ž¬┘ä┘łŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž│ž▒┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģž╣┘ä┘ł┘ģŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦┘łŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©┘Ŗž¦ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘Ŗ┘ŖŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘Š┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌®ž¦┘äŌĆ¼ ( 1964 ) ŌĆ½ž»ž¦ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌ē┘ł┘äŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»ž¦┘łž©ž«┘łž▒ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ä┘ģ┌ō┘å┘ŖŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž│┘Ŗž│ž¬┘ģŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž▒ž¦┘ģ┘å┌üž¬┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌®┌ō┘łŌĆ¼ . ŌĆ½┌å┘ŖŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž┤┘ä┘ģ┘ŖŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘Š┘Ŗ┌ō█ŹŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¬ž▒ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ŠŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦┘Ŗ┘ŖŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘Š┘łž▒┘ŖŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘Ŗ┘ŖŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦┘垬ž┤ž¦ž▒ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¬ž▒ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦ž│ž¬ž▒ž¦┘ä┘Ŗž¦ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦┘łŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦┘ģž▒┘Ŗ┌®┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģž¬žŁž»┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦┘Ŗž¦ž¦┘䞬┘łŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¬┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘łž┤┘ł┘łŌĆ¼ . ŌĆ½┌å┘ŖŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¬ž▒ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌®ž¦┘äŌĆ¼ ( 1988 ) ŌĆ½┘Š┘łž▒┘ŖŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘Š┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘å┘ł┘ģ┘ł┌ō┘ŖŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž│┘Ŗž│ž¬┘ģŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž©ž¦┘åž»┘ŖŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»ž¦┘łž©ž«┘łž▒ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž│ž¦žŁ┘ŖŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģ┘éž»ž¦ž▒ŌĆ¼ ( 1055000 ) ŌĆ½┘ć┌®ž¬ž¦ž▒ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¬┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘łž▒ž│┘Ŗž»┘łŌĆ¼ . ŌĆ½┌å┘ŖŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘å┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘łž▒┌üŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘Šž»┘ŖŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌ē┘ł┘äŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦┘łž©ž«┘łž▒ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘äž▒┘ł┘å┌®┘ŖŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž│ž¦žŁ┘ŖŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘Š┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦ž│ž¦ž│ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦┘ģž▒┘Ŗ┌®┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ä┘ģ┌ō┘ŖŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ģ┘éŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦┘ģŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘äž▒┘ŖŌĆ¼ . ŌĆ½┌å┘ŖŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»ž¦ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌ē┘ł┘äŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž│┘Ŗž│ž¬┘ģŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘Š┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»┘ł┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌ē┘ł┘ä┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»┘ŖŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘Ŗ┘łŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ćž║┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌å┘ŖŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌ü┘ģ┌®┘ŖŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘Š┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž│žĘžŁ┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘Šž¦ž”┘Š┘ł┘å┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘å┘éž┤┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌®┘ł┘ŖŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»ŌĆ¼ ( surface drip irrigation system ) ŌĆ½┘Š┘å┘ł┘ģŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦┘łŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘ćž║┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌å┘ŖŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘Šž¦ž”┘Š┘ł┘å┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘Ŗ┘ŖŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌ü┘ģ┌®┘ŖŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž│žĘžŁ┘ŖŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┌ģž«┘ćŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»ŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¦┘ä┘åž»┘ŖŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž¼┘ł┌ō┘Ŗ┌¢┘ŖŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½ž»ŌĆ¼ ( sub-surface drip irrigation system ) ŌĆ½┘Š┘å┘ł┘ģŌĆ¼ ŌĆ½┘Ŗž¦ž»┘Ŗ┌¢┘ŖŌĆ¼ .
- 6. Others types of drip irrigation system Surface drip irrigation system Low head bubbler drip irrigation system Micro spray drip irrigation system Mechanical move drip irrigation system
- 7. When to Use Drip Irrigation Suitable crops Suitable slops Suitable Soil Suitable irrigation water Suitable Crops for drip irrigation Drip irrigation is most suitable for row crops (vegetables, soft fruit), tree and vine crops where one or more emitters can be provided for each plant. Generally only high value crops are considered because of the high capital costs of installing a drip system.
- 8. Suitable crops ŌĆó Fruit crops : ŌĆō Banana, Grapes, Citrus, Pomegranate, Papaya, Pineapple, Watermelon, Mango. ŌĆó Vegetable crops : ŌĆō Cabbage, Cauliflower, Okra, Tomato, Potato, Onion, Chillis, Radish, Brinjal, Bottle grown, French been, Capsicum, Beans, Baby corn, Carrots, Cucumber, Bitter gourd, Bottle gourd, Ash gourd. ŌĆó Commercial crops : ŌĆō Sugarcane, Cotton, Ground nut, Chickpea.
- 9. Suitable slopes Drip irrigation is adaptable to any farmable slope. Normally the crop would be planted along contour lines and the water supply pipes (laterals) would be laid along the contour also.
- 10. Suitable soils Drip irrigation is suitable for most soils. On clay soils water must be applied slowly to avoid surface water ponding and runoff. On sandy soils higher emitter discharge rates will be needed to ensure adequate lateral wetting of the soil.
- 11. Suitable irrigation water ŌĆó One of the main problems with drip irrigation is blockage of the emitters. All emitters have very small waterways ranging from 0.2-2.0 mm in diameter and these can become blocked if the water is not clean. Thus it is essential for irrigation water to be free of sediments. If this is not so then filtration of the irrigation water will be needed. ŌĆó Blockage may also occur if the water contains algae, fertilizer deposits and dissolved chemicals which precipitate such as calcium and iron. ŌĆó Drip irrigation is particularly suitable for water of poor quality (saline water).
- 12. Advantages of Drip Irrigation ŌĆó Less requirement of irrigation water ŌĆó High irrigation efficiency (80- 90%). ŌĆó Water supply at optimum level. ŌĆó Water logging is avoided ŌĆó High yield ŌĆó Over irrigation is avoid ŌĆó Variation in application rate ŌĆó Reducing labor cost ŌĆó Weed controlling
- 13. ŌĆó Increase in net irrigable area ŌĆó Highly uniform distribution of water i.e., Controlled by output of each nozzle no soil erosion. ŌĆó Suitable for any topography. ŌĆó Avoiding of plant disease and pest. Advantages of Drip Irrigation---
- 14. Disadvantages of drip irrigation ŌĆó High cost : ŌĆō drip irrigation systems are expensive because of there requirements of large quantity of piping & filtration equipment to clean the water. ŌĆó Expense: ŌĆō Initial cost can be more than overhead systems. ŌĆó Waste: ŌĆō The sun can affect the tubes used for drip irrigation, shortening their usable life. Longevity is variable. ŌĆó Clogging: ŌĆō If the water is not properly filtered and the equipment not properly maintained, it can result in clogging. ŌĆó Maintenance: Drip tape causes extra cleanup costs after harvest. You'll need to plan for drip tape winding, disposal, recycling or reuse. ŌĆó Not usable for all crops: This method is not suitable for closely planted crops such as wheat
- 15. COMPARISON Comparison Drip method Flood method Water saving High, between 40 and 100 % Less. High rates of evaporation, surface run off and percolation Irrigation efficiency 80 ŌĆō 90 % 30 - 50 % Weed problem Almost nil High Suitable water Even saline water can be used Only normal water can be used
- 16. Comparison Drip method Flood method Water logging Nil High Water control Can be regulated easily Not much control Diseases and pests Relatively less High Efficiency of fertilizer use Very high since supply is regulated Heavy losses due to leaching Yield increase 20 - % higher than flood method Less compared to drip COMPARISON
- 17. COMPARISON
- 18. Components of Drip Irrigation system ŌĆó Pumping set ŌĆó Source of irrigation water ŌĆó Chamigation and fertigation units(I.U) ŌĆó Values ŌĆó Filters ŌĆó Mainlines ŌĆó Sub-main/Laterals ŌĆó Drippers/emitters
- 19. ŌĆó Pumping set: To create a pressure about 2.5 Kg/sq cm to regulate the amount of water to be supplied. ŌĆó Filter : To filter the water in Order to remove the suspended impurities from water.
- 20. ŌĆó Main lines: ŌĆō It is a Distribution system in drip irrigation. Rigid PVC and high density polyethylene pipes are used as main pipes to minimized corrosion and clogging. ŌĆō Pipes of 65 mm diameter and with pressure rating of 4 to 10 kg/sq. cm ŌĆó Sub Main: ŌĆō It is usually connected to the main lines through a control valve assembly. ŌĆō The function of its to distributes water uniformly to a number laterals.
- 21. ŌĆó Drippers/emitters: ŌĆō It is fitted to a drip irrigation lateral and intended to emit water in the form of drops or continuous flow at emitter rates not exceeding 15 liters/hr.
- 23. irrigan videoDrip Irrigation Systems - YouTube.FLV
- 24. Drip Irrigation
- 25. Drip Irrigation Maize Apple trees
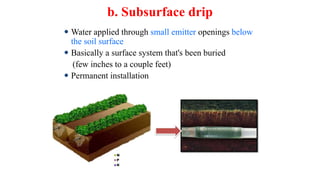
- 26. b. Subsurface drip ’éŚ Water applied through small emitter openings below the soil surface ’éŚ Basically a surface system that's been buried (few inches to a couple feet) ’éŚ Permanent installation
- 27. In subsurface irrigation water is applied to a series of field ditches deep into soil surface. b. Subsurface drip ▒§░∙░∙Š▒▓Ą▓╣│┘Š▒┤Ū▓įŌĆ”
- 28. SUBSURFACE DRIP IRRIGATION.. Advantages ’éó High & uniform water application ’éó Lower pressure & power requirements ’éó No dry corners ’éó Evaporation is reduced ’éó Disadvantages ’éó High initial cost ’éó Water filtration required ’éó Complex maintenance requirements Flushing, Chlorination and Acid injection
- 29. Advantages High degree of control over water application with the potential for high uniformity of application Evaporation is reduced The amount of water can be fine-tuned. This avoids water loss caused by run off or evaporation Frequent irrigation allows for optimum soil moisture content in the root zone Great performance in windy and arid locations If pre-treated wastewater is used for irrigation, the risk of direct contact with crops and labourers is reduced Disadvantages Risk of clogging When saline water is used, salts accumulate at the wetting front Emitter can be damaged or blocked by root hairs Bacterial slimes and algae growing on the interior walls of the laterals and emitters combined with clay particles in the water can block the emitters Suspended organic matter and clay particles can damage the system A lot of repair work is caused by rodents chewing the tubes Heavy machinery can damage the laterals
- 30. ’éŚ Surface 30 - 40% ’éŚ Sprinkler 60 - 70% ’éŚ Drip irrigation 80 - 90% Comparative efficiency of irrigation systems
- 31. Relative Irrigation Efficiencies (%) under Different Methods of irrigation Irrigation efficiencies Method of irrigation Surface Sprinkler Drip Conveyance efficiency 40-50 (Canal) - - Application efficiency 40-70 60-80 90 Surface water moisture evaporation 30-40 30-40 15-20 Overall efficiency 30-40 50-70 80-90
- 32. Least Efficient EFFICIENCY OF IRRIGATION METHODS Most Efficient Flood (40-50%) Furrow (50-60%) Bubbler (60-70%) Sprinkler (70-80%) Drip (80-90%)









































































![IDM Full Crack 6.42 Build 27 Retail & Patch [Latest 2025]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/promotion-of-indian-languages-art-culture-by-madan-kumar-singh-arms-aizawl-250308140648-0f004010-250308173244-dc7cf042-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)





![IObit Driver Booster Pro Crack v11.2.0.46 & Serial Key [2025]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/lect5-250227155726-618fad5f-250301095444-eebe0061-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)

![Download IObit Driver Booster Pro Crack Latest Version [Updated]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/lect5-250227155726-618fad5f-250301095444-eebe0061-250305025648-101608b6-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)


![Latest FL Studio Crack 24 Free Serial Key [2025]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/lect5-250227155726-618fad5f-250301095444-eebe0061-250305025648-101608b61-250305070125-22a1140c-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)






![Betternet VPN Premium 8.6.0.1290 Full Crack [Latest]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/slidsahre-file-250220164342-7ea7fa5f-250303081849-fb582ea0-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Password Depot 17.2.1 Full Crack Free Download [Latest]](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/slidsahre-file-250220164342-7ea7fa5f1-250303081604-84852296-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)