高速な物体候補領域提案手法 (Fast Object Proposal Methods)
- 1. Introduction Object Proposal Methods Conclusions Fast Object Proposal Methods BING & Edge Boxes 山中高夫 情報理工学科 上智大学 文献紹介 2015/11/06 上智大学 山中高夫 Fast Object Proposal Methods
- 2. Introduction Object Proposal Methods Conclusions 文献リスト: Fast Object Proposal Methods [1] J. Hosang, R. Benenson, and B. Schiele, “How good are detection proposals, really?,” British Machine Vision Conference, 2014. [2] M.-M. Cheng, Z. Zhang, W.-Y. Lin, and P. Torr, “BING: Binarized Normed Gradients for Objectness Estimation at 300fps,” IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2014. [3] Q. Zhao, Z. Liu, and B. Yin, “Cracking BING and Beyond,” British Machine Vision Conference, 2014. [4] C. L. Zitnick and P. Dollar, “Edge Boxes: Locating Object Proposals from Edges,” European Conference on Computer Vision, 2014. 2015/11/06 上智大学 山中高夫 Fast Object Proposal Methods
- 3. Introduction Object Proposal Methods Conclusions Object Proposal 背景 画像中の物体が存在しそうな場所を box として複数提案する (1,000~10,000 boxes 程度) できる限り少ない提案 Box 数で画像中に存在する全ての物体 をカバーするように Box を提案する手法が望ましい 応用例として,物体検出の前処理があげられ,Sliding Window で多数の窓を調べる代わりに,Object Proposal で提案された Box だけ調べることで効率的に物体を検出できる 2015/11/06 上智大学 山中高夫 Fast Object Proposal Methods
- 4. Introduction Object Proposal Methods Conclusions 本発表の目的 目的 Object Proposal Methods の中で も,リアルタイム処理に適した BING[Cheng, CVPR2014] と Edge Boxes[Zitnick, ECCV2014] の手法を紹介する adapted from [Hosang, BMVC2014] 2015/11/06 上智大学 山中高夫 Fast Object Proposal Methods
- 5. Introduction Object Proposal Methods Conclusions BING: Binarized Normed Gradients Edge Boxes Contents 1 Object Proposal Methods BING: Binarized Normed Gradients Edge Boxes 2015/11/06 上智大学 山中高夫 Fast Object Proposal Methods
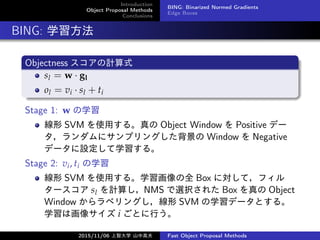
- 6. Introduction Object Proposal Methods Conclusions BING: Binarized Normed Gradients Edge Boxes BING の概要 画像を様々なサイズ?アスペクト比に変換して勾配振幅を計算 → 8x8 画素の Box の値が対応する Window の 64 次元勾配特徴 量(NG Feature, gl) フィルタースコア sl = w · gl Objectness スコア ol = vi · sl + ti(i は Window のサイズ) Non-Maximal Suppression (NMS) で重複する Window を除去 2015/11/06 上智大学 山中高夫 Fast Object Proposal Methods
- 7. Introduction Object Proposal Methods Conclusions BING: Binarized Normed Gradients Edge Boxes BING: 学習方法 Objectness スコアの計算式 sl = w · gl ol = vi · sl + ti Stage 1: w の学習 線形 SVM を使用する。真の Object Window を Positive デー タ,ランダムにサンプリングした背景の Window を Negative データに設定して学習する。 Stage 2: vi, ti の学習 線形 SVM を使用する。学習画像の全 Box に対して,フィル タースコア sl を計算し,NMS で選択された Box を真の Object Window からラベリングし,線形 SVM の学習データとする。 学習は画像サイズ i ごとに行う。 2015/11/06 上智大学 山中高夫 Fast Object Proposal Methods
- 8. Introduction Object Proposal Methods Conclusions BING: Binarized Normed Gradients Edge Boxes BING: フィルタ係数の二値化 w の二値化 w ≈ ∑ Nw j=1 βjaj (aj ∈ {?1, 1}64, βj ∈ ?) aj = a+ j ? a+ j (a+ j ∈ {0, 1}64) b ∈ {0, 1}64 とすると,w · b ≈ ∑ Nw j=1 βj(2a+ j · b ? |b|) [28] Hare, Sa?ari & Torr, "E?cient online structured output learning for keypoint-based object tracking," CVPR2012 2015/11/06 上智大学 山中高夫 Fast Object Proposal Methods
- 9. Introduction Object Proposal Methods Conclusions BING: Binarized Normed Gradients Edge Boxes BING: 勾配特徴量の二値化 勾配特徴量 gl の二値化 gl が 8 ビットで表現されているとして,上位 Ng ビットで近似 する gl ≈ ∑ Ng k=1 28?kbk,l (bk,l は 64 次元のバイナリ特徴量) フィルタスコア sl = w · gl ≈ ∑ Nw j=1 βj ∑ Ng k=1 Cj,k ただし,Cj,k = 28?k(2a+ j · bk,l ? |bk,l|) 2015/11/06 上智大学 山中高夫 Fast Object Proposal Methods
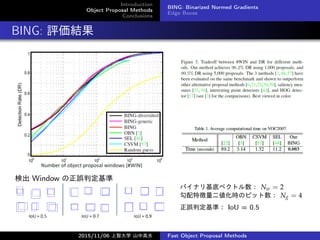
- 10. Introduction Object Proposal Methods Conclusions BING: Binarized Normed Gradients Edge Boxes BING: 評価結果 検出 Window の正誤判定基準 バイナリ基底ベクトル数: Nw = 2 勾配特徴量二値化時のビット数: Ng = 4 正誤判定基準: IoU = 0.5 2015/11/06 上智大学 山中高夫 Fast Object Proposal Methods
- 11. Introduction Object Proposal Methods Conclusions BING: Binarized Normed Gradients Edge Boxes BING: 検出例 2015/11/06 上智大学 山中高夫 Fast Object Proposal Methods
- 12. Introduction Object Proposal Methods Conclusions BING: Binarized Normed Gradients Edge Boxes Contents 1 Object Proposal Methods BING: Binarized Normed Gradients Edge Boxes 2015/11/06 上智大学 山中高夫 Fast Object Proposal Methods
- 13. Introduction Object Proposal Methods Conclusions BING: Binarized Normed Gradients Edge Boxes Edge Boxes の概要 2015/11/06 上智大学 山中高夫 Fast Object Proposal Methods
- 14. Introduction Object Proposal Methods Conclusions BING: Binarized Normed Gradients Edge Boxes Edge Boxes: 手法 (1) Edge Groups & A?nities 与えられた画像の各画素 p に対してエッジ検出を行い,各画素 に主方向 θp とエッジ強度 mp を割り当てる。計算を効率的に するため,mp > 0.1 の画素をエッジとする。(Fig.1 2 段目) 8 近傍のエッジを連結し,主方向差の和が π/2 になるまで エッジをグループ化する。(Fig.1 3 段目) 2 つのエッジグループ si, sj 間の a?nity を以下の式で計算 する。 a(si, sj) = | cos(θi ? θij) cos(θj ? θij)|γ ただし, θi, θj: それぞれ si, sj の主方向 θij: si, sj の平均位置間の方向 γ: 感度を調節するパラメータ(γ = 2) 2 画素以上離れているエッジグループ間の a?nity は 0 とする。 2015/11/06 上智大学 山中高夫 Fast Object Proposal Methods
- 15. Introduction Object Proposal Methods Conclusions BING: Binarized Normed Gradients Edge Boxes Edge Boxes: 手法 (2) wb(si) の計算 Bounding Box b に対して,その中に含まれる全てのエッジグ ループ si に wb(si) ∈ [0, 1] を割り当てる。 - si が Bounding Box に完全に含まれる場合 · · · wb(si) = 1 - 外にある場合や境界につながっている場合 · · · wb(si) = 0 境界につながっているエッジグループの集合を Sb とし, si ∈ Sb のエッジに対して wb(si) = 0 に設定する。 それ以外の si に対して,以下の式で wb(si) を計算する。 wb(si) = 1 ? maxT ∏ |T|?1 j a(tj, tj+1) ただし,t1 ∈ Sb, t|T| = si つまり,上式は si から境界までの最大 a?nity になる経路で計 算する。 境界につながる経路がない場合は wb(si) = 1 である。 2015/11/06 上智大学 山中高夫 Fast Object Proposal Methods
- 16. Introduction Object Proposal Methods Conclusions BING: Binarized Normed Gradients Edge Boxes Edge Boxes: 手法 (3) Bounding Box Scoring Bounding Box の Objectness Score を以下の式で計算する。 hb = ∑i wb(si)mi 2(bw + bh)κ ただし, mi: エッジグループ si に含む全てのエッジ強度 mp の和 bw, bh: Bounding Box の幅と高さ κ: パラメータ (κ = 1.5) Bounding Box 中央のエッジは境界に近いエッジより重要性が 低いことを考慮する。 hin b = hb ? ∑p∈bin mp 2(bw + bh)κ ただし,bin は内側の領域を表す(bw/2, bh/2 の領域) 2015/11/06 上智大学 山中高夫 Fast Object Proposal Methods
- 17. Introduction Object Proposal Methods Conclusions BING: Binarized Normed Gradients Edge Boxes Edge Boxes: 手法 (4) Search Strategy Bounding Box の候補は,位置,スケール,アスペクト比に対 する Sliding Window で設定する。 ステップサイズは隣の Window との重なりが IoU = α となる ように設定する。 - スケールの範囲: σ = 1000 画素~画像全体 - アスペクト比の範囲: 1/τ ~ τ (τ = 3) 2015/11/06 上智大学 山中高夫 Fast Object Proposal Methods
- 18. Introduction Object Proposal Methods Conclusions BING: Binarized Normed Gradients Edge Boxes Edge Boxes: 手法 (5) Re?nement 全ての Sliding Window に対する Objectness Score を計算後, hin b が閾値以上の Box に対して,位置を再調整 (re?nement) する。 位置の再調整では,閾値以上の Box の周辺の位置,スケール, アスペクト比を網羅的に調べて最大となる Box を検出する。 位置再調整後,Non-Maximal Suppression (NMS) により IoU が β 以上の Box を除去する。 2015/11/06 上智大学 山中高夫 Fast Object Proposal Methods
- 19. Introduction Object Proposal Methods Conclusions BING: Binarized Normed Gradients Edge Boxes Edge Boxes: 評価結果(パラメータに対する変化) 2015/11/06 上智大学 山中高夫 Fast Object Proposal Methods
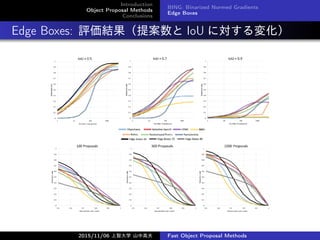
- 20. Introduction Object Proposal Methods Conclusions BING: Binarized Normed Gradients Edge Boxes Edge Boxes: 評価結果(提案数と IoU に対する変化) 2015/11/06 上智大学 山中高夫 Fast Object Proposal Methods
- 21. Introduction Object Proposal Methods Conclusions BING: Binarized Normed Gradients Edge Boxes Edge Boxes: 検出例 2015/11/06 上智大学 山中高夫 Fast Object Proposal Methods
- 22. Introduction Object Proposal Methods Conclusions まとめ Object Proposal は,物体検出などより 複雑な認識処理の前処理として使用さ れることが想定されているので,でき る限り高速な処理が望まれる BING や Edge Boxes は非常に高速な処 理が可能であり,1 枚の処理にかかる 時間は BING が 0.2s,Edge Boxes が 0.3s である 特に Edge Boxes は高速で精度も高い ことが報告されている [Hosang, BMVC2014] ので,様々なアプリケー ションに応用が期待できる。 adapted from [Hosang, BMVC2014] 2015/11/06 上智大学 山中高夫 Fast Object Proposal Methods


![Introduction
Object Proposal Methods
Conclusions
文献リスト: Fast Object Proposal Methods
[1] J. Hosang, R. Benenson, and B. Schiele, “How good are
detection proposals, really?,” British Machine Vision Conference,
2014.
[2] M.-M. Cheng, Z. Zhang, W.-Y. Lin, and P. Torr, “BING:
Binarized Normed Gradients for Objectness Estimation at 300fps,”
IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition,
2014.
[3] Q. Zhao, Z. Liu, and B. Yin, “Cracking BING and Beyond,”
British Machine Vision Conference, 2014.
[4] C. L. Zitnick and P. Dollar, “Edge Boxes: Locating Object
Proposals from Edges,” European Conference on Computer Vision,
2014.
2015/11/06 上智大学 山中高夫 Fast Object Proposal Methods](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20151106fastobjectproposalmethods-151106071854-lva1-app6891/85/Fast-Object-Proposal-Methods-2-320.jpg)

![Introduction
Object Proposal Methods
Conclusions
本発表の目的
目的
Object Proposal Methods の中で
も,リアルタイム処理に適した
BING[Cheng, CVPR2014] と
Edge Boxes[Zitnick, ECCV2014]
の手法を紹介する
adapted from [Hosang, BMVC2014]
2015/11/06 上智大学 山中高夫 Fast Object Proposal Methods](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20151106fastobjectproposalmethods-151106071854-lva1-app6891/85/Fast-Object-Proposal-Methods-4-320.jpg)


![Introduction
Object Proposal Methods
Conclusions
BING: Binarized Normed Gradients
Edge Boxes
BING: フィルタ係数の二値化
w の二値化
w ≈ ∑
Nw
j=1 βjaj (aj ∈ {?1, 1}64, βj ∈ ?)
aj = a+
j ? a+
j (a+
j ∈ {0, 1}64)
b ∈ {0, 1}64 とすると,w · b ≈ ∑
Nw
j=1 βj(2a+
j · b ? |b|)
[28] Hare, Sa?ari & Torr, "E?cient online structured output learning for
keypoint-based object tracking," CVPR2012
2015/11/06 上智大学 山中高夫 Fast Object Proposal Methods](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20151106fastobjectproposalmethods-151106071854-lva1-app6891/85/Fast-Object-Proposal-Methods-8-320.jpg)





![Introduction
Object Proposal Methods
Conclusions
BING: Binarized Normed Gradients
Edge Boxes
Edge Boxes: 手法 (2)
wb(si) の計算
Bounding Box b に対して,その中に含まれる全てのエッジグ
ループ si に wb(si) ∈ [0, 1] を割り当てる。
- si が Bounding Box に完全に含まれる場合 · · · wb(si) = 1
- 外にある場合や境界につながっている場合 · · · wb(si) = 0
境界につながっているエッジグループの集合を Sb とし,
si ∈ Sb のエッジに対して wb(si) = 0 に設定する。
それ以外の si に対して,以下の式で wb(si) を計算する。
wb(si) = 1 ? maxT ∏
|T|?1
j a(tj, tj+1)
ただし,t1 ∈ Sb, t|T| = si
つまり,上式は si から境界までの最大 a?nity になる経路で計
算する。
境界につながる経路がない場合は wb(si) = 1 である。
2015/11/06 上智大学 山中高夫 Fast Object Proposal Methods](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20151106fastobjectproposalmethods-151106071854-lva1-app6891/85/Fast-Object-Proposal-Methods-15-320.jpg)





![Introduction
Object Proposal Methods
Conclusions
まとめ
Object Proposal は,物体検出などより
複雑な認識処理の前処理として使用さ
れることが想定されているので,でき
る限り高速な処理が望まれる
BING や Edge Boxes は非常に高速な処
理が可能であり,1 枚の処理にかかる
時間は BING が 0.2s,Edge Boxes が
0.3s である
特に Edge Boxes は高速で精度も高い
ことが報告されている [Hosang,
BMVC2014] ので,様々なアプリケー
ションに応用が期待できる。 adapted from [Hosang,
BMVC2014]
2015/11/06 上智大学 山中高夫 Fast Object Proposal Methods](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20151106fastobjectproposalmethods-151106071854-lva1-app6891/85/Fast-Object-Proposal-Methods-22-320.jpg)