lec23.ppt
Download as PPT, PDF0 likes25 views
1) The document discusses representation of the Dirac delta function in cylindrical and spherical coordinate systems. It shows that Îī(r - r') = Îī(Ï - Ï')Îī(Ï - Ï')Îī(z - z')/Ï in cylindrical coordinates and Îī(r - r') = Îī(r - r')Îī(Îļ - Îļ')Îī(Ï - Ï')/r^2 in spherical coordinates. 2) It also derives the important relation â^2(1/r) = -4ÏÎī(r) and shows its application to the Laplace equation for electrostatic potential. 3) The completeness of eigenfunctions of harmonic oscillators and Legend
1 of 8
Download to read offline




![NPTEL â Physics â Mathematical Physics - 1
Corresponding to an energy spectrum given by
ðļð = (ð + 2
) âï·
ï· is the frequency and ðŧð(ðĨ) represents a complete set of orthonormal functions in
the domain ââ < ðĨ < â. Hn's are called the Hermite polynomials and AN is the
normalization constant,
1
ðīð =
1
âð
1â2 2ðð!
The orthogonality of the wave function is represented by,
â
â
Joint initiative of IITs and IISc â Funded by MHRD Page 12 of 15
âŦ ï ð (ðĨ)ïð (ðĨ)ððĨ = ïĪðð
ââ
Since ïn(x) are assumed to form a complete set of functions, we can expand any
well behaved function ï (ðĨ) as
ï (ðĨ) = â ðð ïđð(ðĨ)
ð
We multiply above by ïđðâ (ðĨ) and integrated to obtain,
âŦ ï ð (ðĨ)ï (ðĨ)ððĨ = ïĨððð âŦ ï ð (ðĨ)ïđð(ðĨ)ððĨ
â â
â â
ââ ââ
= âð ðð ðŋðð = ðð
Thus, substituting for ðð
ï (ðĨ) = ïĨð [âŦ ï ð (ðĨ )ï (ðĨâē)ððĨâē] = ïð (ðĨ)
ââ
â âē
â
Where the primed summation is used as a dummy variable. Interchanging the
summation and integration,
â
ï (ðĨ) = âŦ ððĨ ï (ðĨâē)[ïĨ âē ïđ (ðĨ)ï (ðĨ
)]
âē â âē
ð ð ð
ââ](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec23-231023101004-95780b0a/85/lec23-ppt-5-320.jpg)
![NPTEL â Physics â Mathematical Physics - 1
Since the wavefunction ï forms an orthonormal set,
âðâē ïđ â (ðĨâē)ïð (ðĨ) = ïĪ (ðĨ â ðĨâē): completeness condition.
ð
Thus plugging in the form forïn (x) in terms of the Hermite polynomials,
âð
1
ðĖ
(ðĨ2+ðĨâē2
)/2 ââ 1
ð=0 2ð ð
!
ðŧð (x)ðŧð (ðĨ ) = ðŋ (ðĨ â ðĨ ) For -ïĨ < x, xâ<ïĨ
âē âē
Similarly for the Legendre polynomials, ðð (ðĨ)
1
ââ
2
(2ð + 1)ð (ðĨâē) = ðŋ(ðĨ â ðĨâē) â 1 âĪ ðĨ, ðĨâē âĪ 1
ð=0 ð
Similarly for sinusoidal functions,
ð(ðĨ) = ðīð ððððĨ = ðīð ðð
ðððĨ
; 0 âĪ ðĨ âĪ ðŋ
ðŋ
ðī2 â ð ðð ðððĨ
ð ðð ðð
ðĨ ðŋ ðŋ
ð
âē
ðŋ(ðĨ â ðĨâē) For 0 âĪ x, xââĪ L
Tutorial
1. Evaluate the integral,
6
âŦ (3ðĨ2 â 2ðĨ â 1)ðŋ(ðĨ â 3)ð
ðĨ
2
â
Solution: Using âŦ ð(ðĨ)ðŋ(ðĨ â ð)ððĨ =
ð(ð) ââ
Here ð(ð) = ð(ðĨ = 3) = 27 â 6 â 1 = 20
2. Show that ðĨ
ð
ðŋ(ðĨ) = âðŋ(ðĨ)
ððĨ
Solution: âŦ ð(ðĨ) [ðĨ
ð
ððĨ
ðŋ(ðĨ)] = ðĨð(ðĨ)ðŋ(ðĨ)|
â
ââ
â
ââ
â
â âŦ
Joint initiative of IITs and IISc â Funded by MHRD Page 13 of 15
ð
(ðĨð(ðĨ))ðŋ(ðĨ)ð
ðĨ
ââ ððĨ
Where ð(ðĨ) is an arbitrary function.
The first term on the RHS is zero as](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec23-231023101004-95780b0a/85/lec23-ppt-6-320.jpg)


Recommended
lec38.ppt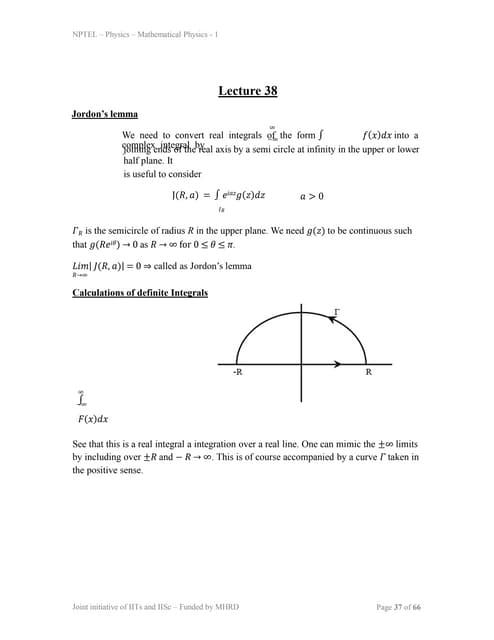



lec38.pptRai Saheb Bhanwar Singh College Nasrullaganj
Ėý
1) Jordan's lemma is used to convert real integrals over the infinite real axis into complex integrals over a contour enclosing the real axis in the complex plane.
2) Several examples are provided of using residues and Jordan's lemma to evaluate definite integrals over the real line or infinite intervals that involve functions with poles, including integrals of x^2, sin(x)/x, 1/(x^2+a^2)^2, and sin(x)/(x(x^2+a^2)).
3) The technique involves closing the contour with a semicircle at infinity where the integral over the semicircle goes to zero by Jordan's lemma, leaving the original integral equal to the residue theorem applied to thelec14.ppt



lec14.pptRai Saheb Bhanwar Singh College Nasrullaganj
Ėý
The document discusses matrix representations of operators and changes of basis in quantum mechanics. Some key points:
- Matrix elements of an operator are computed using a basis of kets. The expectation value of an operator is computed from its matrix elements and the state vectors.
- If two operators commute, they have the same set of eigenkets.
- A change of basis is a unitary transformation that relates two different sets of basis kets that span the same space. It establishes a link between the two basis representations.
- Linear algebra concepts like linear independence of eigenvectors and Hermitian operators having real eigenvalues are important in quantum mechanics.lec19.ppt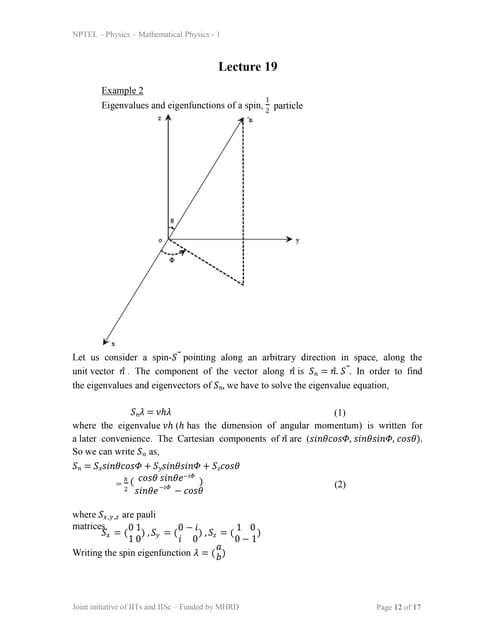



lec19.pptRai Saheb Bhanwar Singh College Nasrullaganj
Ėý
This document discusses finding the eigenvalues and eigenfunctions of a spin-1/2 particle pointing along an arbitrary direction. It shows that the eigenvalue equation reduces to a set of two linear, homogeneous equations. The eigenvalues are found to be Âą1/2, and the corresponding eigenvectors are written in terms of the direction angles Îļ and ÎĶ. As an example, it shows that for a spin oriented along the z-axis, the eigenvectors reduce to simple forms as expected for a spin-1/2 particle. It also introduces the Gauss elimination method for numerically solving systems of linear equations that arise in eigenvalue problems.lec6.ppt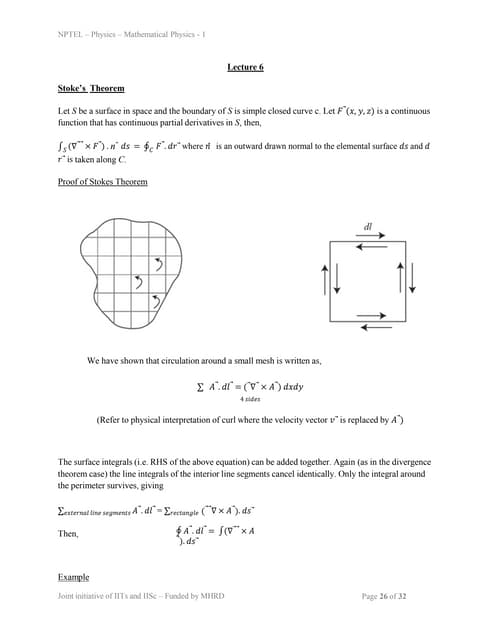



lec6.pptRai Saheb Bhanwar Singh College Nasrullaganj
Ėý
1) Stokes' theorem relates the curl of a vector field integrated over a surface S to the line integral of the vector field around the boundary curve C of the surface.
2) The document provides a proof of Stokes' theorem and gives an example of verifying it for a given vector field and surface.
3) Green's theorem relates the double integral of the curl of a vector field over a plane region R to the line integral of the vector field around the boundary curve C of the region. The theorem is demonstrated through an example.lec32.ppt



lec32.pptRai Saheb Bhanwar Singh College Nasrullaganj
Ėý
The document discusses properties of complex numbers including:
- Commutativity and associativity of addition and multiplication
- Additive and multiplicative identities and inverses
- Conjugates, modulus, and triangle inequality
- Polar form representation using modulus and argument
- Exponential form for products, quotients, and powers
- Roots of complex numbers and finding nth roots
- Representing functions of a complex variable using modulus and argumentPeriodic Solutions for Nonlinear Systems of Integro-Differential Equations of...



Periodic Solutions for Nonlinear Systems of Integro-Differential Equations of...International Journal of Engineering Inventions www.ijeijournal.com
Ėý
1) The document discusses periodic solutions for nonlinear systems of integro-differential equations with impulsive action of operators.
2) It presents a numerical-analytic method for approximating periodic solutions using uniformly convergent sequences of periodic functions.
3) The method is proved to construct a unique periodic solution that converges uniformly as m approaches infinity.lec34.ppt



lec34.pptRai Saheb Bhanwar Singh College Nasrullaganj
Ėý
1. The document discusses analytic functions of complex variables through examples. It defines analytic functions as those whose derivatives of all orders exist in the region of analyticity.
2. The Cauchy-Riemann equations are derived and their implications are explored, including that they imply the Laplace equation and orthogonality of level curves.
3. Several examples are worked through to determine if functions are analytic by checking if they satisfy the Cauchy-Riemann equations. The Cauchy-Riemann equations are also derived in polar coordinates.lec21.ppt



lec21.pptRai Saheb Bhanwar Singh College Nasrullaganj
Ėý
1. The Dirac delta function is an important concept in quantum mechanics and electrodynamics that describes an impulse or large force acting over a very short time interval.
2. The key properties of the Dirac delta function are that it is equal to infinity at a single point and zero everywhere else, and that the integral of the function over its entire range is equal to one.
3. The Dirac delta function can be used to find the value of an arbitrary function f(x) at a specific point a, as the integral of f(x) multiplied by the Dirac delta function over all x is equal to f(a).One solution for many linear partial differential equations with terms of equ...



One solution for many linear partial differential equations with terms of equ...Lossian Barbosa Bacelar Miranda
Ėý
We disclose a simple and straightforward method of solving single-order linear partial differential equations. The advantage of the method is that it is applicable to any orders and the big disadvantage is that it is restricted to a single order at a time. As it is very easy compared to classical methods, it has didactic value.One particle to_onepartlce_scattering_sqrd



One particle to_onepartlce_scattering_sqrdfoxtrot jp R
Ėý
1) A scalar particle scatters from one spacetime region to another, carrying initial momentum k and final momentum k'.
2) The scattering matrix for this process involves integrals over the initial and final regions, which give Dirac delta functions.
3) Upon performing the integrals, the scattering matrix is expressed in terms of the scalar particle's propagator, with the initial vertex disappearing due to momentum conservation.Matrix Transformations on Some Difference Sequence Spaces



Matrix Transformations on Some Difference Sequence SpacesIOSR Journals
Ėý
The sequence spaces ðâ(ðĒ,ðĢ,Î), ð0(ðĒ,ðĢ,Î) and ð(ðĒ,ðĢ,Î) were recently introduced. The matrix classes (ð ðĒ,ðĢ,Î :ð) and (ð ðĒ,ðĢ,Î :ðâ) were characterized. The object of this paper is to further determine the necessary and sufficient conditions on an infinite matrix to characterize the matrix classes (ð ðĒ,ðĢ,Î âķðð ) and (ð ðĒ,ðĢ,Î âķ ðð). It is observed that the later characterizations are additions to the existing onesBSC_COMPUTER _SCIENCE_UNIT-2_DISCRETE MATHEMATICS



BSC_COMPUTER _SCIENCE_UNIT-2_DISCRETE MATHEMATICSRai University
Ėý
This document provides an introduction to definite integration and its applications. It defines indefinite integration as finding the integral or primitive function F(x) of a function f(x). Definite integration involves finding the area under a curve defined by a function f(x) over a specified interval. Standard formulae for integrating common functions like polynomials, trigonometric functions, and exponentials are provided. Methods for integrating functions using substitution and integration by parts are described. Examples of applying these techniques to evaluate definite integrals are also given.B.tech ii unit-5 material vector integration



B.tech ii unit-5 material vector integrationRai University
Ėý
This document discusses various vector integration topics:
1. It defines line, surface, and volume integrals and provides examples of evaluating each. Line integrals deal with vector fields along paths, surface integrals deal with vector fields over surfaces, and volume integrals deal with vector fields throughout a volume.
2. Green's theorem, Stokes' theorem, and Gauss's theorem are introduced as relationships between these types of integrals but their proofs are not shown.
3. Examples are provided to demonstrate evaluating line integrals of conservative and non-conservative vector fields, as well as a surface integral over a spherical surface.Dual Spaces of Generalized Cesaro Sequence Space and Related Matrix Mapping



Dual Spaces of Generalized Cesaro Sequence Space and Related Matrix Mappinginventionjournals
Ėý
In this paper we define the generalized Cesaro sequence spaces ííí (í, í, í ). We prove the space ííí (í, í, í ) is a complete paranorm space. In section-2 we determine its Kothe-Toeplitz dual. In section-3 we establish necessary and sufficient conditions for a matrix A to map ííí í, í, í to íâ and ííí (í, í, í ) to c, where íâ is the space of all bounded sequences and c is the space of all convergent sequences. We also get some known and unknown results as remarks.lec39.ppt



lec39.pptRai Saheb Bhanwar Singh College Nasrullaganj
Ėý
The document discusses Taylor and Laurent series expansions. It provides examples of using these expansions to represent functions around points.
Taylor series provides a power series representation of an analytic function around a point. Laurent series allows representing functions in annular regions, including points where the function is not analytic, using both positive and negative powers of (z - z0). Examples show deducing Laurent series expansions for simple functions like z4 and 1/z4 around various points, and evaluating coefficients via contour integrals and the residue theorem. The document also gives an example of using a contour integral to compute a Greens function in many-particle physics.lec2.ppt



lec2.pptRai Saheb Bhanwar Singh College Nasrullaganj
Ėý
1) The document discusses the gradient operator and provides examples of calculating the electric field and gradient of functions.
2) It defines the gradient operator mathematically and provides an example of calculating the gradient of a scalar function.
3) Examples are given of using the gradient operator to calculate the electric field from a potential and the gradient of 1/r.PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTION OF SUM OF TWO CONTINUOUS VARIABLES AND CONVOLUTION



PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTION OF SUM OF TWO CONTINUOUS VARIABLES AND CONVOLUTIONJournal For Research
Ėý
All physical subjects, involving random phenomena, something depending upon chance, naturally find their own way to theory of Statistics. Hence there arise relations between the results derived for hose random phenomena in different physical subjects and the concepts of Statistics. Convolution theorem has a variety of applications in field of Fourier transforms and many other situations, but it bears beautiful applications in field of statistics also .Here in this paper authors want to discuss some notions of Electrical Engineering in terms of convolution of some probability distributions.
One particle to_onepartlce_scattering_5302020_pdfcpy



One particle to_onepartlce_scattering_5302020_pdfcpyfoxtrot jp R
Ėý
1) A scalar particle travels from one spacetime region to another, carrying an initial momentum k and scattering into a final momentum k'. This scattering process is described by a scattering matrix.
2) The scattering matrix involves second order derivatives of the vacuum-to-vacuum matrix element with respect to sources. This vacuum-to-vacuum matrix can be written as a Taylor expansion involving the connected scalar classical action.
3) The left-hand side of the scattering matrix gives the probability that a one-particle state with momentum k at initial time Tin will be found with momentum k' at final time Tout, and can be evaluated via path integration.One particle to_onepartlce_scattering_12082020_fordisplay



One particle to_onepartlce_scattering_12082020_fordisplayfoxtrot jp R
Ėý
1) A scalar particle travels from one spacetime region to another, carrying an initial momentum k and scattering into a final momentum k'. This scattering process can be described by a scattering matrix.
2) The scattering matrix involves integrals over the initial and final spacetime regions, which yield Dirac delta functions. It also involves derivatives of the vacuum-to-vacuum matrix with respect to sources.
3) The vacuum-to-vacuum matrix can be written as a Taylor expansion involving the connected scalar classical action, which describes the propagation of a scalar particle via a Green's function.lec40.ppt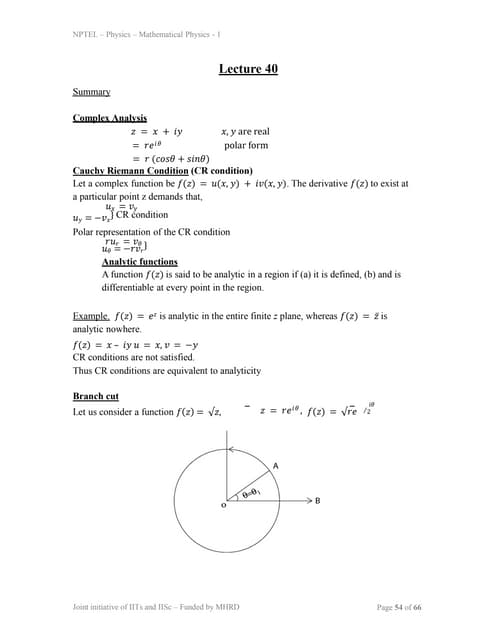



lec40.pptRai Saheb Bhanwar Singh College Nasrullaganj
Ėý
Complex analysis deals with complex-valued functions of complex variables. Some key concepts covered in the document include:
- Complex functions can be expressed in either Cartesian (z = x + iy) or polar (z = reiÎļ) form.
- For a complex function f(z) to be differentiable, it must satisfy the Cauchy-Riemann conditions.
- Analytic functions are differentiable at every point in their domain. For example, ez is analytic everywhere while zĖ
is analytic nowhere.
- Branch cuts arise for multi-valued functions like âz, with the line between Îļ = 2Ï and Îļ = 4Ï representing one branch cut.Lane_emden_equation_solved_by_HPM_final



Lane_emden_equation_solved_by_HPM_finalSOUMYADAS230727
Ėý
The document describes using the homotopy perturbation method to solve the Lane-Emden equation. It first provides an overview of the homotopy perturbation method and Lane-Emden equation. It then constructs the homotopy for n=2 and solves for the first three terms of the solution series. The summary provides the key steps and outcomes while keeping the response to 3 sentences.Assignment_1_solutions.pdf



Assignment_1_solutions.pdfAbhayRupareliya1
Ėý
1. The total energy of a simple harmonic oscillator is constant and does not depend on time. The kinetic and potential energies oscillate out of phase with each other as functions of time.
2. Applying Lagrange's equations to the motion of a particle in two dimensions under a central potential, the equation for conservation of angular momentum is derived. Angular momentum remains conserved even if the potential depends on the angular coordinate.
3. The Lagrangian equations of motion are derived for a particle moving in three dimensions under a central potential using spherical coordinates. The equations relate the accelerations of the radial, angular, and azimuthal coordinates to each other and the potential.lec22.ppt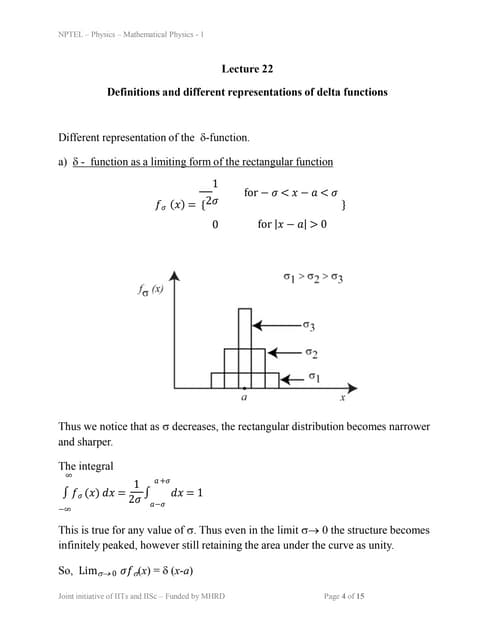



lec22.pptRai Saheb Bhanwar Singh College Nasrullaganj
Ėý
The document discusses three representations of the delta function Îī(x-a):
1) As the limiting form of a rectangular function as its width approaches 0, retaining an area of 1 under the curve.
2) As the limiting form of a Gaussian function as its width approaches 0, again retaining an area of 1.
3) Through an integral representation involving the limit of a sinusoidal function divided by (x-a) as its frequency approaches infinity, yielding a sharply peaked function at x=a.A05330107



A05330107IOSR-JEN
Ėý
1) The document presents a wavelet collocation method for numerically solving nth order Volterra integro-differential equations. It expands the unknown function as a series of Chebyshev wavelets of the second kind with unknown coefficients.
2) It states and proves a uniform convergence theorem that establishes the convergence of approximating the solution using truncated Chebyshev wavelet series expansions.
3) The paper demonstrates the validity and applicability of the proposed method through some illustrative examples of solving integro-differential equations using the Chebyshev wavelet collocation approach.One particle to_onepartlce_scattering_18052020



One particle to_onepartlce_scattering_18052020foxtrot jp R
Ėý
1) A scalar particle travels from one spacetime region to another, carrying momentum k and scattering into momentum k'. This scattering process is described by a matrix involving integrals over the initial and final spacetime regions.
2) The scattering matrix involves derivatives of the vacuum-to-vacuum matrix element with respect to sources, representing the interaction of the particle with an external field. This vacuum-to-vacuum element can be written as a Taylor expansion involving the connected scalar classical action.
3) The classical action is a function of the sources and involves a scalar Green's function as a propagator. Differentiation of the classical action yields terms involving the Green's function that are important to the scattering matrix.A Probabilistic Algorithm for Computation of Polynomial Greatest Common with ...



A Probabilistic Algorithm for Computation of Polynomial Greatest Common with ...mathsjournal
Ėý
- The document presents a probabilistic algorithm for computing the polynomial greatest common divisor (PGCD) with smaller factors.
- It summarizes previous work on the subresultant algorithm for computing PGCD and discusses its limitations, such as not always correctly determining the variant Ï.
- The new algorithm aims to determine Ï correctly in most cases when given two polynomials f(x) and g(x). It does so by adding a few steps instead of directly computing the polynomial t(x) in the relation s(x)f(x) + t(x)g(x) = r(x).A PROBABILISTIC ALGORITHM FOR COMPUTATION OF POLYNOMIAL GREATEST COMMON WITH ...



A PROBABILISTIC ALGORITHM FOR COMPUTATION OF POLYNOMIAL GREATEST COMMON WITH ...mathsjournal
Ėý
In the earlier work, Knuth present an algorithm to decrease the coefficient growth in the Euclidean
algorithm of polynomials called subresultant algorithm. However, the output polynomials may have a
small factor which can be removed. Then later, Brown of Bell Telephone Laboratories showed the
subresultant in another way by adding a variant called ð and gave a way to compute the variant.
Nevertheless, the way failed to determine everyð correctly.
In this paper, we will give a probabilistic algorithm to determine the variant ð correctly in most cases by
adding a few steps instead of computing ðĄ(ðĨ) when given ð(ðĨ) andð(ðĨ) â âĪ[ðĨ], where ðĄ(ðĨ) satisfies that
ð (ðĨ)ð(ðĨ) + ðĄ(ðĨ)ð(ðĨ) = ð(ðĨ), here ðĄ(ðĨ), ð (ðĨ) â âĪ[ðĨ]
HERMITE SERIES



HERMITE SERIESMANISH KUMAR
Ėý
This document discusses Hermite polynomials and their properties. It begins by introducing the Hermite equation, which arises from the theory of the linear harmonic oscillator. The Hermite equation is then solved using a series solution approach. Explicit formulas for the Hermite polynomials Hn(x) are derived for n=0,1,2,3,... using properties of the Hermite equation like recursion relations. Key properties of the Hermite polynomials like generating functions, even/odd behavior, Rodrigue's formula, orthogonality, and recurrence relations are also proved.lec33.ppt



lec33.pptRai Saheb Bhanwar Singh College Nasrullaganj
Ėý
The Cauchy Riemann (CR) conditions provide a necessary and sufficient condition for a function f(z) = u(x, y) + iv(x, y) to be analytic in a region. The CR conditions require that the partial derivatives of u and v satisfy âu/âx = âv/ây and âu/ây = -âv/âx. If a function satisfies these conditions at all points in a region, then it is analytic in that region. The document proves this using cases where ây = 0 and âx = 0, showing the derivatives must be equal. Examples are provided to demonstrate checking functions for analyticlec31.ppt



lec31.pptRai Saheb Bhanwar Singh College Nasrullaganj
Ėý
Complex numbers allow solutions to equations like x2 + 1 = 0 by extending real numbers to include imaginary numbers. A complex number z is defined as z = x + iy, where x and y are real numbers and i is the imaginary unit equal to â-1. Complex numbers can be added and multiplied following specific rules, such as z1 + z2 = (x1 + x2) + i(y1 + y2) for addition and z1z2 = (x1x2 - y1y2) + i(y1x2 + x1y2) for multiplication. The inverse of a complex number z is calculated as z-1 = (x/(x2+yMore Related Content
Similar to lec23.ppt (20)
One solution for many linear partial differential equations with terms of equ...



One solution for many linear partial differential equations with terms of equ...Lossian Barbosa Bacelar Miranda
Ėý
We disclose a simple and straightforward method of solving single-order linear partial differential equations. The advantage of the method is that it is applicable to any orders and the big disadvantage is that it is restricted to a single order at a time. As it is very easy compared to classical methods, it has didactic value.One particle to_onepartlce_scattering_sqrd



One particle to_onepartlce_scattering_sqrdfoxtrot jp R
Ėý
1) A scalar particle scatters from one spacetime region to another, carrying initial momentum k and final momentum k'.
2) The scattering matrix for this process involves integrals over the initial and final regions, which give Dirac delta functions.
3) Upon performing the integrals, the scattering matrix is expressed in terms of the scalar particle's propagator, with the initial vertex disappearing due to momentum conservation.Matrix Transformations on Some Difference Sequence Spaces



Matrix Transformations on Some Difference Sequence SpacesIOSR Journals
Ėý
The sequence spaces ðâ(ðĒ,ðĢ,Î), ð0(ðĒ,ðĢ,Î) and ð(ðĒ,ðĢ,Î) were recently introduced. The matrix classes (ð ðĒ,ðĢ,Î :ð) and (ð ðĒ,ðĢ,Î :ðâ) were characterized. The object of this paper is to further determine the necessary and sufficient conditions on an infinite matrix to characterize the matrix classes (ð ðĒ,ðĢ,Î âķðð ) and (ð ðĒ,ðĢ,Î âķ ðð). It is observed that the later characterizations are additions to the existing onesBSC_COMPUTER _SCIENCE_UNIT-2_DISCRETE MATHEMATICS



BSC_COMPUTER _SCIENCE_UNIT-2_DISCRETE MATHEMATICSRai University
Ėý
This document provides an introduction to definite integration and its applications. It defines indefinite integration as finding the integral or primitive function F(x) of a function f(x). Definite integration involves finding the area under a curve defined by a function f(x) over a specified interval. Standard formulae for integrating common functions like polynomials, trigonometric functions, and exponentials are provided. Methods for integrating functions using substitution and integration by parts are described. Examples of applying these techniques to evaluate definite integrals are also given.B.tech ii unit-5 material vector integration



B.tech ii unit-5 material vector integrationRai University
Ėý
This document discusses various vector integration topics:
1. It defines line, surface, and volume integrals and provides examples of evaluating each. Line integrals deal with vector fields along paths, surface integrals deal with vector fields over surfaces, and volume integrals deal with vector fields throughout a volume.
2. Green's theorem, Stokes' theorem, and Gauss's theorem are introduced as relationships between these types of integrals but their proofs are not shown.
3. Examples are provided to demonstrate evaluating line integrals of conservative and non-conservative vector fields, as well as a surface integral over a spherical surface.Dual Spaces of Generalized Cesaro Sequence Space and Related Matrix Mapping



Dual Spaces of Generalized Cesaro Sequence Space and Related Matrix Mappinginventionjournals
Ėý
In this paper we define the generalized Cesaro sequence spaces ííí (í, í, í ). We prove the space ííí (í, í, í ) is a complete paranorm space. In section-2 we determine its Kothe-Toeplitz dual. In section-3 we establish necessary and sufficient conditions for a matrix A to map ííí í, í, í to íâ and ííí (í, í, í ) to c, where íâ is the space of all bounded sequences and c is the space of all convergent sequences. We also get some known and unknown results as remarks.lec39.ppt



lec39.pptRai Saheb Bhanwar Singh College Nasrullaganj
Ėý
The document discusses Taylor and Laurent series expansions. It provides examples of using these expansions to represent functions around points.
Taylor series provides a power series representation of an analytic function around a point. Laurent series allows representing functions in annular regions, including points where the function is not analytic, using both positive and negative powers of (z - z0). Examples show deducing Laurent series expansions for simple functions like z4 and 1/z4 around various points, and evaluating coefficients via contour integrals and the residue theorem. The document also gives an example of using a contour integral to compute a Greens function in many-particle physics.lec2.ppt



lec2.pptRai Saheb Bhanwar Singh College Nasrullaganj
Ėý
1) The document discusses the gradient operator and provides examples of calculating the electric field and gradient of functions.
2) It defines the gradient operator mathematically and provides an example of calculating the gradient of a scalar function.
3) Examples are given of using the gradient operator to calculate the electric field from a potential and the gradient of 1/r.PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTION OF SUM OF TWO CONTINUOUS VARIABLES AND CONVOLUTION



PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTION OF SUM OF TWO CONTINUOUS VARIABLES AND CONVOLUTIONJournal For Research
Ėý
All physical subjects, involving random phenomena, something depending upon chance, naturally find their own way to theory of Statistics. Hence there arise relations between the results derived for hose random phenomena in different physical subjects and the concepts of Statistics. Convolution theorem has a variety of applications in field of Fourier transforms and many other situations, but it bears beautiful applications in field of statistics also .Here in this paper authors want to discuss some notions of Electrical Engineering in terms of convolution of some probability distributions.
One particle to_onepartlce_scattering_5302020_pdfcpy



One particle to_onepartlce_scattering_5302020_pdfcpyfoxtrot jp R
Ėý
1) A scalar particle travels from one spacetime region to another, carrying an initial momentum k and scattering into a final momentum k'. This scattering process is described by a scattering matrix.
2) The scattering matrix involves second order derivatives of the vacuum-to-vacuum matrix element with respect to sources. This vacuum-to-vacuum matrix can be written as a Taylor expansion involving the connected scalar classical action.
3) The left-hand side of the scattering matrix gives the probability that a one-particle state with momentum k at initial time Tin will be found with momentum k' at final time Tout, and can be evaluated via path integration.One particle to_onepartlce_scattering_12082020_fordisplay



One particle to_onepartlce_scattering_12082020_fordisplayfoxtrot jp R
Ėý
1) A scalar particle travels from one spacetime region to another, carrying an initial momentum k and scattering into a final momentum k'. This scattering process can be described by a scattering matrix.
2) The scattering matrix involves integrals over the initial and final spacetime regions, which yield Dirac delta functions. It also involves derivatives of the vacuum-to-vacuum matrix with respect to sources.
3) The vacuum-to-vacuum matrix can be written as a Taylor expansion involving the connected scalar classical action, which describes the propagation of a scalar particle via a Green's function.lec40.ppt



lec40.pptRai Saheb Bhanwar Singh College Nasrullaganj
Ėý
Complex analysis deals with complex-valued functions of complex variables. Some key concepts covered in the document include:
- Complex functions can be expressed in either Cartesian (z = x + iy) or polar (z = reiÎļ) form.
- For a complex function f(z) to be differentiable, it must satisfy the Cauchy-Riemann conditions.
- Analytic functions are differentiable at every point in their domain. For example, ez is analytic everywhere while zĖ
is analytic nowhere.
- Branch cuts arise for multi-valued functions like âz, with the line between Îļ = 2Ï and Îļ = 4Ï representing one branch cut.Lane_emden_equation_solved_by_HPM_final



Lane_emden_equation_solved_by_HPM_finalSOUMYADAS230727
Ėý
The document describes using the homotopy perturbation method to solve the Lane-Emden equation. It first provides an overview of the homotopy perturbation method and Lane-Emden equation. It then constructs the homotopy for n=2 and solves for the first three terms of the solution series. The summary provides the key steps and outcomes while keeping the response to 3 sentences.Assignment_1_solutions.pdf



Assignment_1_solutions.pdfAbhayRupareliya1
Ėý
1. The total energy of a simple harmonic oscillator is constant and does not depend on time. The kinetic and potential energies oscillate out of phase with each other as functions of time.
2. Applying Lagrange's equations to the motion of a particle in two dimensions under a central potential, the equation for conservation of angular momentum is derived. Angular momentum remains conserved even if the potential depends on the angular coordinate.
3. The Lagrangian equations of motion are derived for a particle moving in three dimensions under a central potential using spherical coordinates. The equations relate the accelerations of the radial, angular, and azimuthal coordinates to each other and the potential.lec22.ppt



lec22.pptRai Saheb Bhanwar Singh College Nasrullaganj
Ėý
The document discusses three representations of the delta function Îī(x-a):
1) As the limiting form of a rectangular function as its width approaches 0, retaining an area of 1 under the curve.
2) As the limiting form of a Gaussian function as its width approaches 0, again retaining an area of 1.
3) Through an integral representation involving the limit of a sinusoidal function divided by (x-a) as its frequency approaches infinity, yielding a sharply peaked function at x=a.A05330107



A05330107IOSR-JEN
Ėý
1) The document presents a wavelet collocation method for numerically solving nth order Volterra integro-differential equations. It expands the unknown function as a series of Chebyshev wavelets of the second kind with unknown coefficients.
2) It states and proves a uniform convergence theorem that establishes the convergence of approximating the solution using truncated Chebyshev wavelet series expansions.
3) The paper demonstrates the validity and applicability of the proposed method through some illustrative examples of solving integro-differential equations using the Chebyshev wavelet collocation approach.One particle to_onepartlce_scattering_18052020



One particle to_onepartlce_scattering_18052020foxtrot jp R
Ėý
1) A scalar particle travels from one spacetime region to another, carrying momentum k and scattering into momentum k'. This scattering process is described by a matrix involving integrals over the initial and final spacetime regions.
2) The scattering matrix involves derivatives of the vacuum-to-vacuum matrix element with respect to sources, representing the interaction of the particle with an external field. This vacuum-to-vacuum element can be written as a Taylor expansion involving the connected scalar classical action.
3) The classical action is a function of the sources and involves a scalar Green's function as a propagator. Differentiation of the classical action yields terms involving the Green's function that are important to the scattering matrix.A Probabilistic Algorithm for Computation of Polynomial Greatest Common with ...



A Probabilistic Algorithm for Computation of Polynomial Greatest Common with ...mathsjournal
Ėý
- The document presents a probabilistic algorithm for computing the polynomial greatest common divisor (PGCD) with smaller factors.
- It summarizes previous work on the subresultant algorithm for computing PGCD and discusses its limitations, such as not always correctly determining the variant Ï.
- The new algorithm aims to determine Ï correctly in most cases when given two polynomials f(x) and g(x). It does so by adding a few steps instead of directly computing the polynomial t(x) in the relation s(x)f(x) + t(x)g(x) = r(x).A PROBABILISTIC ALGORITHM FOR COMPUTATION OF POLYNOMIAL GREATEST COMMON WITH ...



A PROBABILISTIC ALGORITHM FOR COMPUTATION OF POLYNOMIAL GREATEST COMMON WITH ...mathsjournal
Ėý
In the earlier work, Knuth present an algorithm to decrease the coefficient growth in the Euclidean
algorithm of polynomials called subresultant algorithm. However, the output polynomials may have a
small factor which can be removed. Then later, Brown of Bell Telephone Laboratories showed the
subresultant in another way by adding a variant called ð and gave a way to compute the variant.
Nevertheless, the way failed to determine everyð correctly.
In this paper, we will give a probabilistic algorithm to determine the variant ð correctly in most cases by
adding a few steps instead of computing ðĄ(ðĨ) when given ð(ðĨ) andð(ðĨ) â âĪ[ðĨ], where ðĄ(ðĨ) satisfies that
ð (ðĨ)ð(ðĨ) + ðĄ(ðĨ)ð(ðĨ) = ð(ðĨ), here ðĄ(ðĨ), ð (ðĨ) â âĪ[ðĨ]
HERMITE SERIES



HERMITE SERIESMANISH KUMAR
Ėý
This document discusses Hermite polynomials and their properties. It begins by introducing the Hermite equation, which arises from the theory of the linear harmonic oscillator. The Hermite equation is then solved using a series solution approach. Explicit formulas for the Hermite polynomials Hn(x) are derived for n=0,1,2,3,... using properties of the Hermite equation like recursion relations. Key properties of the Hermite polynomials like generating functions, even/odd behavior, Rodrigue's formula, orthogonality, and recurrence relations are also proved.One solution for many linear partial differential equations with terms of equ...



One solution for many linear partial differential equations with terms of equ...Lossian Barbosa Bacelar Miranda
Ėý
More from Rai Saheb Bhanwar Singh College Nasrullaganj (20)
lec33.ppt



lec33.pptRai Saheb Bhanwar Singh College Nasrullaganj
Ėý
The Cauchy Riemann (CR) conditions provide a necessary and sufficient condition for a function f(z) = u(x, y) + iv(x, y) to be analytic in a region. The CR conditions require that the partial derivatives of u and v satisfy âu/âx = âv/ây and âu/ây = -âv/âx. If a function satisfies these conditions at all points in a region, then it is analytic in that region. The document proves this using cases where ây = 0 and âx = 0, showing the derivatives must be equal. Examples are provided to demonstrate checking functions for analyticlec31.ppt



lec31.pptRai Saheb Bhanwar Singh College Nasrullaganj
Ėý
Complex numbers allow solutions to equations like x2 + 1 = 0 by extending real numbers to include imaginary numbers. A complex number z is defined as z = x + iy, where x and y are real numbers and i is the imaginary unit equal to â-1. Complex numbers can be added and multiplied following specific rules, such as z1 + z2 = (x1 + x2) + i(y1 + y2) for addition and z1z2 = (x1x2 - y1y2) + i(y1x2 + x1y2) for multiplication. The inverse of a complex number z is calculated as z-1 = (x/(x2+ylec42.ppt



lec42.pptRai Saheb Bhanwar Singh College Nasrullaganj
Ėý
1) The document discusses examples of calculating the Jacobian of transformations. It defines the Jacobian as the determinant of the partial derivatives of the transformed coordinates.
2) It then discusses MÃķbius transformations, which are fractional linear transformations of the form (az+b)/(cz+d). The Jacobian of a MÃķbius transformation depends only on z.
3) Several examples are given of using MÃķbius transformations to map one geometric region to another, such as mapping a circle to a line.lec41.ppt



lec41.pptRai Saheb Bhanwar Singh College Nasrullaganj
Ėý
This document discusses conformal mapping, which maps curves and regions in such a way that preserves angles and their directions. It provides examples of conformal mappings:
1) The mapping w = ez maps a vertical line in the z-plane to a circle in the w-plane, with the phase angle increasing along the circle.
2) The mapping Ï = eiÎļ0(z-z0)/(z-z0) maps an area in the upper half z-plane to the interior of a unit circle in the Ï-plane. Points on the x-axis in z are mapped to the boundary of the circle.lec37.ppt



lec37.pptRai Saheb Bhanwar Singh College Nasrullaganj
Ėý
1) The document discusses evaluating contour integrals using the residue theorem. It provides examples of calculating residues and evaluating integrals where the contour encloses poles.
2) The residue of a function f(z) at a pole z=a is the coefficient of the (z-a)^-1 term in the Laurent series expansion of f(z) about z=a.
3) According to the residue theorem, the value of a contour integral of a function along a closed loop is equal to 2Ïi times the sum of the residues of the function enclosed by the contour.lec20.ppt



lec20.pptRai Saheb Bhanwar Singh College Nasrullaganj
Ėý
This document contains a series of tutorial problems related to matrices and linear algebra. Problem 1 asks to invert a 3x3 matrix. Problem 2 asks to write a vector as a linear combination of two other vectors. Problem 3 involves finding the inverse, trace, and determinant of related matrices. Problem 4 proves a property about powers of similar matrices. Problem 5 diagonalizes a 2x2 matrix and finds its eigenvalues and eigenvectors.lec18.ppt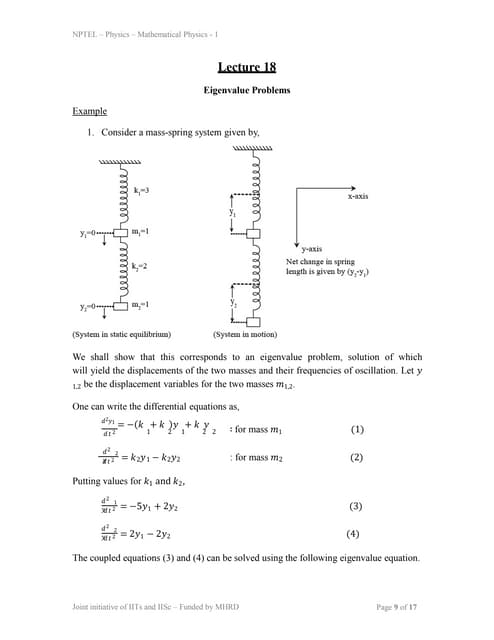



lec18.pptRai Saheb Bhanwar Singh College Nasrullaganj
Ėý
This document discusses solving a mass-spring system as an eigenvalue problem. It:
1) Sets up differential equations to model the displacements of two masses connected by springs.
2) Transforms the coupled differential equations into a matrix eigenvalue equation.
3) Solves the eigenvalue equation to obtain the frequencies of oscillation for the two masses.
4) Combines the eigenvectors with complex exponential functions to obtain general solutions for the displacements of each mass over time.lec17.ppt



lec17.pptRai Saheb Bhanwar Singh College Nasrullaganj
Ėý
This document discusses linear transformations and matrices. It introduces how linear transformations on physical quantities are usually described by matrices, where a column vector u representing a physical quantity is transformed into another column vector Au by a transformation matrix A. As an example, it discusses orthogonal transformations, where the transformation matrix A is orthogonal. It proves that for an orthogonal transformation, the inner product of two vectors remains invariant. It also discusses properties of other types of matrices like Hermitian, skew-Hermitian and unitary matrices.lec16.ppt



lec16.pptRai Saheb Bhanwar Singh College Nasrullaganj
Ėý
This document discusses properties of symmetric, skew-symmetric, and orthogonal matrices. It defines each type of matrix and provides examples. Key points include:
- Symmetric matrices have Aij = Aji for all i and j. Skew-symmetric matrices have Aij = -Aji. Orthogonal matrices satisfy AT = A-1.
- The eigenvalues of symmetric matrices are always real. The eigenvalues of skew-symmetric matrices are either zero or purely imaginary.
- Any real square matrix can be written as the sum of a symmetric matrix and skew-symmetric matrix.lec30.ppt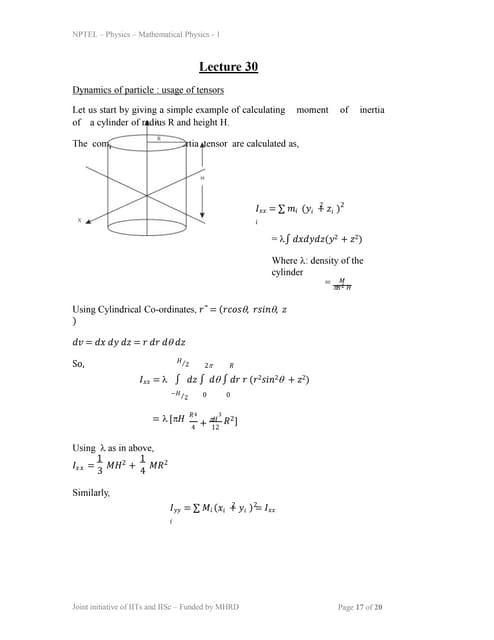



lec30.pptRai Saheb Bhanwar Singh College Nasrullaganj
Ėý
1) The document discusses calculating the moment of inertia tensor for a cylinder with radius R and height H. It is shown that the only non-zero components of the inertia tensor are Ixx = (3MH + 4MR2)/12, Iyy = Ixx, and Izz = MR2/2.
2) Equations for velocity, acceleration, and the Christoffel symbols in an arbitrary coordinate system are presented. Expressions for calculating acceleration in cylindrical coordinates using the metric tensor and Christoffel symbols are given.lec28.ppt



lec28.pptRai Saheb Bhanwar Singh College Nasrullaganj
Ėý
Tensors obey algebraic properties including addition, multiplication, contraction, and symmetrization. Addition of tensors combines their components. Multiplication of tensors combines their indices and ranks to form a new tensor. Contraction sets equal a covariant and contravariant index, reducing the tensor's rank. Symmetric tensors do not change sign under index interchange, while antisymmetric tensors change sign.lec27.ppt



lec27.pptRai Saheb Bhanwar Singh College Nasrullaganj
Ėý
1) The document discusses tensors with multiple indices and the cross product of two vectors A and B. The components of the cross product vector C are given by Ai Bj - Aj Bi.
2) It describes how tensor components transform between coordinate systems using transformations of partial derivatives. The transformation property for cross products is derived.
3) Tensors are defined by their rank, with the number of covariant and contravariant indices specifying a tensor's rank. Vectors have a rank of 1. Examples calculate tensor components in different coordinate systems.lec26.ppt



lec26.pptRai Saheb Bhanwar Singh College Nasrullaganj
Ėý
1) There are two types of vectors - contravariant vectors whose components transform according to Equation 1, and covariant vectors whose components transform according to Equation 2.
2) The dot product of two contravariant or two covariant vectors is not independent of the coordinate system.
3) The dot product of a contravariant and a covariant vector is independent of the coordinate system.lec25.ppt



lec25.pptRai Saheb Bhanwar Singh College Nasrullaganj
Ėý
The document discusses the transformation properties of vectors between two coordinate systems. It states that if a vector has components (x1, x2, x3) in one coordinate system and (xĖ
1, xĖ
2, xĖ
3) in another, there is a relation such that xĖ
i = ai1x1 + ai2x2 + ai3x3, where the aij are the components of the transformation matrix. This relation can be written compactly as xĖ
i = aijxj, using Einstein summation convention. The document then presents two theorems establishing that a set of functions can represent a tensor if their inner product transforms as a tensor under coordinate transformations.lec1.ppt



lec1.pptRai Saheb Bhanwar Singh College Nasrullaganj
Ėý
This document defines vectors and scalar quantities, and describes their key properties and relationships. It begins by defining physical quantities that can be measured, and distinguishes between scalar and vector quantities. Scalars have only magnitude, while vectors have both magnitude and direction. The document then provides a more rigorous definition of vectors as quantities that remain invariant under coordinate system rotations or translations. It describes how to represent and transform vectors between different coordinate systems. Vector addition, subtraction, and multiplication operations like the scalar and vector products are defined. Derivatives of vectors are also discussed. Examples of velocity and acceleration vectors in uniform circular motion are provided.lec15.ppt



lec15.pptRai Saheb Bhanwar Singh College Nasrullaganj
Ėý
The rank of a matrix is the maximum number of linearly independent rows. A matrix has rank 0 only if it is the zero matrix. The inverse of a matrix A, denoted A^-1, is defined such that A*A^-1 = I, the identity matrix. To calculate the inverse, one takes the transpose of the cofactor matrix and divides each element by the determinant of the original matrix.lec13.ppt



lec13.pptRai Saheb Bhanwar Singh College Nasrullaganj
Ėý
A Hilbert space is an infinite-dimensional vector space consisting of sequences of real numbers that satisfy a convergence condition. It allows vector addition and scalar multiplication. In quantum mechanics, state vectors span a Hilbert space. For identical particles, boson state vectors are symmetric and fermion state vectors are antisymmetric. Linear algebra concepts like operators, eigenvectors, and superposition are used in Dirac's formulation of quantum mechanics postulates. Observables are represented by operators and eigenvectors correspond to eigenvalues. Any state can be written as a superposition of eigenvectors.lec11.ppt



lec11.pptRai Saheb Bhanwar Singh College Nasrullaganj
Ėý
The document discusses the Gram-Schmidt orthogonalization (GSO) process for constructing an orthonormal basis from a set of linearly independent vectors. It explains that GSO works by taking a vector, normalizing it to unit length to create the first basis vector, then subtracting the component of the next vector along this first vector to make it orthogonal, and repeating this process to iteratively construct an orthonormal basis. An example applies GSO to three vectors in R3, finding the orthonormal basis vectors by removing components along each preceding vector at each step.lec10.ppt



lec10.pptRai Saheb Bhanwar Singh College Nasrullaganj
Ėý
The document discusses similarity transformations and the Cauchy-Schwarz inequality. It states that if matrix A is similar to matrix B, then B is similar to A, and if A is similar to B and B is similar to C, then A is similar to C. It also proves that if A is similar to B, then the inverse of A is similar to the inverse of B. Additionally, it defines the inner product and norm of vectors, and proves the Cauchy-Schwarz inequality that the square of the inner product of two vectors is less than or equal to the product of their norms. It provides an example using the Cauchy-Schwarz inequality to prove an inequality involving positive real numbers.lec9.ppt



lec9.pptRai Saheb Bhanwar Singh College Nasrullaganj
Ėý
The document discusses linear independence and change of basis in vector spaces. It provides the following key points:
1) Two vectors u and v are linearly dependent if one is a multiple of the other, and independent otherwise.
2) Three vectors u, v, and w are linearly dependent if their coefficients in a linear combination equal 0, and independent otherwise.
3) A change of basis matrix P describes the transformation between two bases {e} and {f} of a vector space, where each vector in {f} is written as a linear combination of the vectors in {e}. The inverse of P transforms vectors back from {f} to {e}.Recently uploaded (20)
Dr. Ansari Khurshid Ahmed- Factors affecting Validity of a Test.pptx



Dr. Ansari Khurshid Ahmed- Factors affecting Validity of a Test.pptxKhurshid Ahmed Ansari
Ėý
Validity is an important characteristic of a test. A test having low validity is of little use. Validity is the accuracy with which a test measures whatever it is supposed to measure. Validity can be low, moderate or high. There are many factors which affect the validity of a test. If these factors are controlled, then the validity of the test can be maintained to a high level. In the power point presentation, factors affecting validity are discussed with the help of concrete examples.Comprehensive Guide to Antibiotics & Beta-Lactam Antibiotics.pptx



Comprehensive Guide to Antibiotics & Beta-Lactam Antibiotics.pptxSamruddhi Khonde
Ėý
ðĒ Comprehensive Guide to Antibiotics & Beta-Lactam Antibiotics
ðŽ Antibiotics have revolutionized medicine, playing a crucial role in combating bacterial infections. Among them, Beta-Lactam antibiotics remain the most widely used class due to their effectiveness against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. This guide provides a detailed overview of their history, classification, chemical structures, mode of action, resistance mechanisms, SAR, and clinical applications.
ð What Youâll Learn in This Presentation
â
History & Evolution of Antibiotics
â
Cell Wall Structure of Gram-Positive & Gram-Negative Bacteria
â
Beta-Lactam Antibiotics: Classification & Subtypes
â
Penicillins, Cephalosporins, Carbapenems & Monobactams
â
Mode of Action (MOA) & Structure-Activity Relationship (SAR)
â
Beta-Lactamase Inhibitors & Resistance Mechanisms
â
Clinical Applications & Challenges.
ð Why You Should Check This Out?
Essential for pharmacy, medical & life sciences students.
Provides insights into antibiotic resistance & pharmaceutical trends.
Useful for healthcare professionals & researchers in drug discovery.
ð Swipe through & explore the world of antibiotics today!
ð Like, Share & Follow for more in-depth pharma insights!Oral exam Kenneth Bech - What is the meaning of strategic fit?



Oral exam Kenneth Bech - What is the meaning of strategic fit?MIPLM
Ėý
Presentation of the CEIPI DU IPBA oral exam of Kenneth Bech - What is the meaning of strategic fit? Full-Stack .NET Developer Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHat



Full-Stack .NET Developer Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHatScholarhat
Ėý
Full-Stack .NET Developer Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHatEntity Framework Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHat



Entity Framework Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHatScholarhat
Ėý
Entity Framework Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHatOne Click RFQ Cancellation in Odoo 18 - Odoo šÝšÝßĢs



One Click RFQ Cancellation in Odoo 18 - Odoo šÝšÝßĢsCeline George
Ėý
In this slide, weâll discuss the one click RFQ Cancellation in odoo 18. One-Click RFQ Cancellation in Odoo 18 is a feature that allows users to quickly and easily cancel Request for Quotations (RFQs) with a single click.RRB ALP CBT 2 RAC Question Paper MCQ (Railway Assistant Loco Pilot)



RRB ALP CBT 2 RAC Question Paper MCQ (Railway Assistant Loco Pilot)SONU HEETSON
Ėý
RRB ALP CBT 2 RAC Question Paper MCQ PDF Free Download. Railway Assistant Loco Pilot Mechanic Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Important Questions.Azure Administrator Interview Questions By ScholarHat



Azure Administrator Interview Questions By ScholarHatScholarhat
Ėý
Azure Administrator Interview Questions By ScholarHatASP.NET Web API Interview Questions By Scholarhat



ASP.NET Web API Interview Questions By ScholarhatScholarhat
Ėý
ASP.NET Web API Interview Questions By ScholarhatBáŧ TEST KIáŧM TRA GIáŧŪA KÃ 2 - TIášūNG ANH 10,11,12 - CHUášĻN FORM 2025 - GLOBAL SU...



Báŧ TEST KIáŧM TRA GIáŧŪA KÃ 2 - TIášūNG ANH 10,11,12 - CHUášĻN FORM 2025 - GLOBAL SU...Nguyen Thanh Tu Collection
Ėý
https://app.box.com/s/ij1ty3vm7el9i4qfrr41o756xycbahmgAzure Data Engineer Interview Questions By ScholarHat



Azure Data Engineer Interview Questions By ScholarHatScholarhat
Ėý
Azure Data Engineer Interview Questions By ScholarHatBáŧ TEST KIáŧM TRA GIáŧŪA KÃ 2 - TIášūNG ANH 10,11,12 - CHUášĻN FORM 2025 - GLOBAL SU...



Báŧ TEST KIáŧM TRA GIáŧŪA KÃ 2 - TIášūNG ANH 10,11,12 - CHUášĻN FORM 2025 - GLOBAL SU...Nguyen Thanh Tu Collection
Ėý
lec23.ppt
- 1. NPTEL â Physics â Mathematical Physics - 1 Lecture 23 Representation of the Dirac delta function in other coordinate systems ð―(ð, ïŠ, ð§) = In a general sense, one can write, ïĪ (ð â ðâē) = ïĪ(ðĨ â ðĨâē) ïĪ(ðĶ â ðĶâ) ïĪ(ð§ â ð§âē) ïĪ(ðĒâðĒâē)ïĪ(ðĢâðĢâē)ïĪ(ðĪâðĪâē) = |ð― | Where J represents the Jacobian of the transformation. a) Cylindrical Coordinate System The volume element in given by, dv =ð dð dïŠ dz = | sin ïŠ 0 The determinant is J which is ïē cos2ïŠ + ïē sin2ïŠ = ïē cos ïŠ â ïē sin ïŠ 0 ïē cos ïŠ 0 | 0 1 Thus ïĪ(ð â ðâē) = 1 ïĪ (ïē â ïē âē)ïĪ(ïŠ â ïŠâē)ïĪ(ð§ â ð§ âē) ïē Also, ð(ðĨâē, ðĶâē, ð§âē) = âŦ ð (ðĨ, ðĶ, ð§)ðŋ(ðĨ â ðĨâē) ðŋ(ðĶ â ðĶâē)ðŋ(ð§ â ð§âē)ððĨððĶðð§ |ðð ððĶ ðð | ðð§ ðð ððĨ ððĨ ðïŠ ððĶ ðïŠ ðð§ ðïŠ ððĨ ðð§| ððĶ Joint initiative of IITs and IISc â Funded by MHRD Page 8 of 15 ðð§ ðð§| ðð§ x =ð cosïŠ y =ð sinïŠ z = z
- 2. NPTEL â Physics â Mathematical Physics - 1 = âŦ ð (ïē, ïŠ, ð§) ïē ðŋ(ïē â ïē )ðŋ(ïŠ â ïŠ )ðŋ(ð§ â ð§ )ïē ðïŠ ðïē ðð§ = ð(ïēâē , ïŠ âē, ð§âē) 1 âē âē âē b) Spherical polar coordinate system Following the definition as before, ïĪ (ðâ â ðâē) ïĪ (ïą â ïą âē ) ïĪ (ïŠ â ïŠâē ) ïĪ (ðâ âðâē) = ð2ð ððïą and ð(ðĨâē, ðĶâē, ð§âē) = ð(ðâē, ïą âē, ð§âē). An important relation in Electrodynamics Let us first state the relation, ââ 2 ( ) = â4ððŋ(ð ) 1 ð We shall prove the above relation now. Using ââ 2= 1 (ð2 ð ) ð2 ð ð ð ðð ââ 2 ( ) = 0 for all ð > 0. 1 ð But as ðïŪ 0 the above identity does not stand as the operator itself in not defined 1 at = 0 . (because of the factor ). To know the behavior at ð = 0, consider ð2 Gauss's divergence theorem. âŦ ââ . ðī ððĢ = âŪ ðī . ðð ðĢ ð Suppose ðī = ââ (1 ) = â ðĖ ð ð2 Joint initiative of IITs and IISc â Funded by MHRD Page 9 of 15
- 3. NPTEL â Physics â Mathematical Physics - 1 In order to evaluate the divergence of ðī at the origin (ð = 0) Consider a sphere of radius R surrounding the origin. On the surface,|ðī| has a constant value 1 . ð 2 Integrating over the spherical surface as shown in figure, âŪ ðīâââ . ðââââð = â 1 âŦ ð 2 2ð âŦ (ðĖ. ðĖ) ð 2ð ðð ððððð· ð=0 ð·=0 ð = â4ï° The answer we have got is independent of R. Thus putting it in the divergence theorem, ð âŦ ââ . ââ (1 )ððĢ = âŦ ðī . ðð = â4ð âŦ â2 (1 )ððĢ = â4ð ð The above result is true even in the limit RïŪ0 Using the integral property of the ïĪ- function âŦ ðŋ(ð )ððĢ = 1 Joint initiative of IITs and IISc â Funded by MHRD Page 10 of 15
- 4. NPTEL â Physics â Mathematical Physics - 1 Thus, ï2( 1 ð ) = â4ï°ïĪ (ð ) In a general sense, we can write ââââ â2 ( 1 | â â â | ð ðâē ) = â4ï°ïĪ (ð ââðâ âē) Applications to Physical Problems As derived earlier, â2 ( ) = â4ÏÎī(r ) 1 r (1) Where ð = ð â ð âē The electrostatic potential is of the function ð· (ð) = ð 4ðð0ð ð Thus, multiplying Eq. (1) with 4ðð0 â2 ( ð 4ðð0ð ) = â 4ðð 4ðð0 ðŋ(r ) = â Îī(r ) = â ð Îĩ0 ïē Îĩ 0 Thus we recover the Laplaceâs equation. Completeness condition of Special functions in terms of ïĪ- function in quantum mechanics, the wavefunctions for a harmonic oscillator wavefunctions are given by, ðĨ2 ïn (x)=An Hn (x) ðâ 2 n = 0,1,2 âĶâĶâĶâĶ.. Joint initiative of IITs and IISc â Funded by MHRD Page 11 of 15
- 5. NPTEL â Physics â Mathematical Physics - 1 Corresponding to an energy spectrum given by ðļð = (ð + 2 ) âï· ï· is the frequency and ðŧð(ðĨ) represents a complete set of orthonormal functions in the domain ââ < ðĨ < â. Hn's are called the Hermite polynomials and AN is the normalization constant, 1 ðīð = 1 âð 1â2 2ðð! The orthogonality of the wave function is represented by, â â Joint initiative of IITs and IISc â Funded by MHRD Page 12 of 15 âŦ ï ð (ðĨ)ïð (ðĨ)ððĨ = ïĪðð ââ Since ïn(x) are assumed to form a complete set of functions, we can expand any well behaved function ï (ðĨ) as ï (ðĨ) = â ðð ïđð(ðĨ) ð We multiply above by ïđðâ (ðĨ) and integrated to obtain, âŦ ï ð (ðĨ)ï (ðĨ)ððĨ = ïĨððð âŦ ï ð (ðĨ)ïđð(ðĨ)ððĨ â â â â ââ ââ = âð ðð ðŋðð = ðð Thus, substituting for ðð ï (ðĨ) = ïĨð [âŦ ï ð (ðĨ )ï (ðĨâē)ððĨâē] = ïð (ðĨ) ââ â âē â Where the primed summation is used as a dummy variable. Interchanging the summation and integration, â ï (ðĨ) = âŦ ððĨ ï (ðĨâē)[ïĨ âē ïđ (ðĨ)ï (ðĨ )] âē â âē ð ð ð ââ
- 6. NPTEL â Physics â Mathematical Physics - 1 Since the wavefunction ï forms an orthonormal set, âðâē ïđ â (ðĨâē)ïð (ðĨ) = ïĪ (ðĨ â ðĨâē): completeness condition. ð Thus plugging in the form forïn (x) in terms of the Hermite polynomials, âð 1 ðĖ (ðĨ2+ðĨâē2 )/2 ââ 1 ð=0 2ð ð ! ðŧð (x)ðŧð (ðĨ ) = ðŋ (ðĨ â ðĨ ) For -ïĨ < x, xâ<ïĨ âē âē Similarly for the Legendre polynomials, ðð (ðĨ) 1 ââ 2 (2ð + 1)ð (ðĨâē) = ðŋ(ðĨ â ðĨâē) â 1 âĪ ðĨ, ðĨâē âĪ 1 ð=0 ð Similarly for sinusoidal functions, ð(ðĨ) = ðīð ððððĨ = ðīð ðð ðððĨ ; 0 âĪ ðĨ âĪ ðŋ ðŋ ðī2 â ð ðð ðððĨ ð ðð ðð ðĨ ðŋ ðŋ ð âē ðŋ(ðĨ â ðĨâē) For 0 âĪ x, xââĪ L Tutorial 1. Evaluate the integral, 6 âŦ (3ðĨ2 â 2ðĨ â 1)ðŋ(ðĨ â 3)ð ðĨ 2 â Solution: Using âŦ ð(ðĨ)ðŋ(ðĨ â ð)ððĨ = ð(ð) ââ Here ð(ð) = ð(ðĨ = 3) = 27 â 6 â 1 = 20 2. Show that ðĨ ð ðŋ(ðĨ) = âðŋ(ðĨ) ððĨ Solution: âŦ ð(ðĨ) [ðĨ ð ððĨ ðŋ(ðĨ)] = ðĨð(ðĨ)ðŋ(ðĨ)| â ââ â ââ â â âŦ Joint initiative of IITs and IISc â Funded by MHRD Page 13 of 15 ð (ðĨð(ðĨ))ðŋ(ðĨ)ð ðĨ ââ ððĨ Where ð(ðĨ) is an arbitrary function. The first term on the RHS is zero as
- 7. NPTEL â Physics â Mathematical Physics - 1 ðŋ(ðĨ) = 0 at ðĨ = Âąâ Also (ðĨð(ðĨ)) = ð(ðĨ) + ðĨðâē(ðĨ) ð ððĨ Thus LHS = â âŦ (ð(ðĨ) + ðĨ ðð ) ðŋ(ðĨ)ððĨ ððĨ = 0 â ð(0) = âð(0) = â âŦ ð(ðĨ)ðŋ(ðĨ)ððĨ Thus, ððĨ ðĨ ð ðŋ(ðĨ) = âðŋ(ðĨ) Proved. 3. Show that the derivative of a ïą-function is a ïĪ-function. A ïą - function is defined by, ð(ðĨ) = 1 for ðĨ > 0 = 0 for ðĨ âĪ 0 Solution: Proceeding as in the previous problem, âŦ ð(ðĨ) ððĨ = ð(ðĨ)ð(ðĨ)| â ðð ððĨ ââ â ââ â ðð â âŦ ð(ðĨ )ððĨ ââ ððĨ = ð(â) â âŦ â ðð ðððĨ ððĨ 0 = ð(â) â ð(â) + ð(0) = ð(0) â = âŦ ð(ðĨ)ðŋ (ðĨ)ððĨ ââ Thus, ðð ððĨ = ðŋ(ðĨ) 4. Prove that ðŋ(ðžðĨ) = 1 ðŋ(ðĨ) where ðž is a constant Joint initiative of IITs and IISc â Funded by MHRD Page 14 of 15 |ðž|
- 8. NPTEL â Physics â Mathematical Physics - 1 â Solution: âŦ ð(ðĨ) ðŋ(ðžðĨ)ððĨ ââ Changing variable from ðĨ â ð = ðžðĨ ðĨ = ð and ððĨ = 1 ðð ðž ðž If ðž is positive then the integration runs from â ðž to +ðž. With ðž as negative, ðĨ = ðž implies ð = âðž and vice versa. Thus the limits are interchanged for negative ðž that entails a negative sign. â â ð ðð âŦ ð(ðĨ)ðŋ(ðžðĨ)ððĨ = Âą âŦ ð ( ) ðŋ(ð) ââ ââ ðž ðž = Âą 1 ð(0) ðž = 1 ð(0) |ðž| The proof follows in the same manner at problems (2) and (3). 5. Evaluate the integral ðž = âŦ ðâð (âââ. rË ) ððĢ Joint initiative of IITs and IISc â Funded by MHRD Page 15 of 15 r2 ðĢ Where v is a sphere of radius R. Solution: ðž = âŦ ðâð 4ððŋ3(ðâ) ð ðĢ ðĢ = 4ððâ0 = 4ð









