Lesson 2 practical research in dail.pptx
- 1. CHAPTER 1 NATURE OF INQUIRY AND RESEARCH LESSON 2 Nature of Research Jazer B. Leuterio Teacher II
- 2. WARM-UP ŌĆó Directions: INDIVIDUAL WORK. Relying on your stock knowledge, write on the lines provided the meaning of the following words used in the selection that you will read later. Be guided by some clues in the given sentences. 1. Absolute ______________________________________________________________________________________ Man has no absolute power over something; God has. 2. Abstract _______________________________________________________________________________________ A stone is concrete; intelligence is abstract. 3. Portrayal_______________________________________________________________________________________ Give a clearer portrayal of what is in your mind by drawing it on that paper. 4. Adopt _________________________________________________________________________________________ Adopt a lawful procedure in adopting those orphans. 5. Hallmark _______________________________________________________________________________________ One hallmark you ought to treasure is your golden trophy. 6. Perspective______________________________________________________________________________________ Change your sitting position to have a better perspective about the whole thing.
- 3. Research is a process of executing various mental acts for discovering and examining facts and information to prove the accuracy or truthfulness of your claims or conclusions about the topic of your research. Research requires you to inquire or investigate about your chosen research topic by asking questions that will make you engage yourself in top-level thinking strategies of interpreting, analyzing, synthesizing, criticizing, appreciating, or creating to enable you to discover truths about the many things you tend to wonder about the topic of your research work. (Litchman 2013)
- 4. Purposes of Research 1. To learn how to work independently 2. To learn how to work scientifically or systematically 3. To have an in-depth knowledge of something 4. To elevate your mental abilities by letting you think in higher- order thinking strategies (HOTS) of inferring, evaluating, synthesizing, appreciating, applying, and creating 5. To improve your reading and writing skills 6. To be familiar with the basic tools of research and the various techniques of gathering data and of presenting research findings 7. To free yourself, to a certain extent, from the domination or strong influence of a single textbook or of the professorŌĆÖs lone viewpoint or spoon feeding
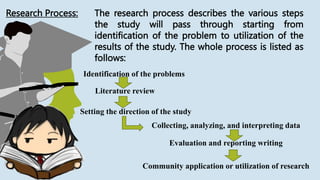
- 6. Research Process: The research process describes the various steps the study will pass through starting from identification of the problem to utilization of the results of the study. The whole process is listed as follows: Identification of the problems Literature review Setting the direction of the study Collecting, analyzing, and interpreting data Evaluation and reporting writing Community application or utilization of research
- 7. The first step in research writing is to identify and problematize an area of interest. The researcher points out the area that needs further study or investigation given the current state of knowledge on the matter. Identification of the problems
- 8. After the problem has been identified, the researcher checks for related materials on the topic that are available that could serve as a starting point or reference for the study. The materials provide the initial view of the extent of efforts done to study the topic as well as the areas that need further research often called the gap. The research gap will be the basis for the purpose of the study Literature Review
- 9. This contains the purpose of the study, the research questions, and the manner in which the study will be conducted or the methodology. The purpose of the study explains why the study is needed. It identifies the importance of the study in terms of its contribution to the discipline as well as its impact on society or its social value. The research questions narrow down the problem to manageable and feasible tasks which will be carried out in the methodology. Methodology describes how to obtain and process the materials and information needed to answer the research questions. Setting the Direction of Study
- 10. At this stage, the materials and needed information are gathered, analyzed, and interpreted. The treatment of the data depends on the approach that will be used appropriate for the study. Collecting, Analyzing, and Interpreting Data
- 11. From the analyzed data, conclusion and learning are drawn. The conclusion is the synthesized answer to the research questions which is also the answer to the problem identified in the study. The conclusion of the study will be the basis for the recommendations that define the actions and interventions that could impact the context where the problem emanates. From this point, the researcher is now ready to write the whole research paper. Evaluation and Report Writing
- 12. This is the stage where the result of the study is disseminated back to the community. For a research to make an impact on society, it is important that it is shared especially with the community concerned. This is best complemented with a plan on how research will be utilized to realize its full potential in creating a social value. Community Application or Utilization of Research
- 13. Research is important in the creation of value that can be classified in three ways (Creswell 2012): Importance of Doing Research ’ü▒ It adds to the existing body of knowledge. ’ü▒ It can improve or enhance current practices. ’ü▒ It can inform policy. ’ü▒ It adds to the existing body of knowledge. ’ü▒ It can improve or enhance current practices. ’ü▒ It can inform policy.
- 14. Research is important in the creation of value that can be classified in three ways (Creswell 2012): Importance of Doing Research It adds to the existing body of knowledge The findings in a research study can provide added information to better understand issues or phenomena by confirming or contesting previous results. Research can likewise be a way to break ground on areas of interest that have not been investigated or studied before. The result will become the basis or reference for further studies. Sample: College Educators Life Balance during K-12 Transition: Focus on Wellness The study explored the relationship of K-12 Action Plans to educatorsŌĆÖ life balance (Ramos,2019). ’ü▒ It adds to the existing body of knowledge. ’ü▒ It can improve or enhance current practices. ’ü▒ It can inform policy.
- 15. Research is important in the creation of value that can be classified in three ways (Creswell 2012): Importance of Doing Research It can improve or enhance current practices. Research can evaluate current practices in terms of effectiveness and efficiency. Effectiveness refers to the ability of practice to produce the set goal or social value. Th results of the study can be the basis for decisions, intervention programs, or plans for improvement. Sample: Teacher- Parent Collaborative Ethics in Facilitating Students Homework. The study highlighted the role of teachers in initiating collaboration with parents in doing the homework of the students (Miguel & Abulon, 2019). ’ü▒ It adds to the existing body of knowledge. ’ü▒ It can improve or enhance current practices. ’ü▒ It can inform policy.
- 16. Research is important in the creation of value that can be classified in three ways (Creswell 2012): Importance of Doing Research It can inform policy The results of a research study can be a starting point for changing policies that could affect the whole organization, community, or society. A policy, law, or regulation can be drawn as a response or intervention to the new information obtained in a research study. Sample: Urban Poor and Climate Adaptation: The Issue of Equity in Two Emerging Urban Areas of Eastern Indonesia. The study looked at equity issue in the climate adaptation particularly in the context of urban poor (Fathoni, 2018) ’ü▒ It adds to the existing body of knowledge. ’ü▒ It can improve or enhance current practices. ’ü▒ It can inform policy.
- 17. The qualities of a good research can be derived from how effective and efficient it is in achieving its purpose to create a value. The qualities can be summarized into five major characteristics. Characteristics of a Good Research ’ā╝ Rigorous ’ā╝ Replicable ’ā╝ Accurate ’ā╝ Objective ’ā╝ Ethical
- 18. The qualities of a good research can be derived from how effective and efficient it is in achieving its purpose to create a value. The qualities can be summarized into five major characteristics. Characteristics of a Good Research ’ā╝ Rigorous The conduct of research must be systematic, scientific, and logical. It must follow clear and logical procedures aimed at answering the research problem. Each step must be properly justified in terms of appropriateness.
- 19. The qualities of a good research can be derived from how effective and efficient it is in achieving its purpose to create a value. The qualities can be summarized into five major characteristics. Characteristics of a Good Research ’ā╝ Replicable The procedures utilized in research must be replicable in other contexts and the results must have a wide range of applicability. It is not enough that the results are only true for a single situation. They must have a certain degree of generalizability.
- 20. The qualities of a good research can be derived from how effective and efficient it is in achieving its purpose to create a value. The qualities can be summarized into five major characteristics. Characteristics of a Good Research ’ā╝ Accurate The data that will be used to answer the questions must be representative of the actual responses of the participants or actual data as recorded in the instruments used.
- 21. The qualities of a good research can be derived from how effective and efficient it is in achieving its purpose to create a value. The qualities can be summarized into five major characteristics. Characteristics of a Good Research ’ā╝ Objective In the analysis of data, the personal bias of the researcher must be managed well. Personal inclinations or desired results must be always avoided. Otherwise, the result will not be credible.
- 22. The qualities of a good research can be derived from how effective and efficient it is in achieving its purpose to create a value. The qualities can be summarized into five major characteristics. Characteristics of a Good Research ’ā╝ Ethical Data or information from respondents must be handled with utmost confidentiality and honesty. Credit must also be given where it is due.
- 23. Thank You!!!