MUTATION.pptx learn different ways of mutation how does it happen
Download as pptx, pdf0 likes38 views
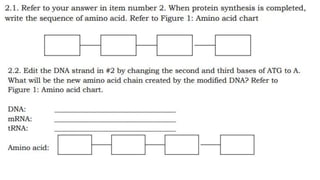
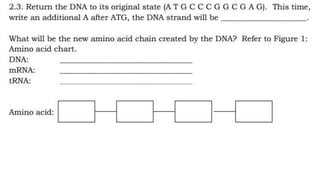
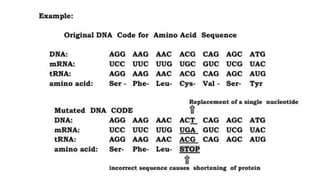
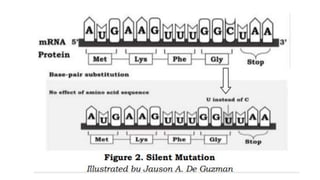
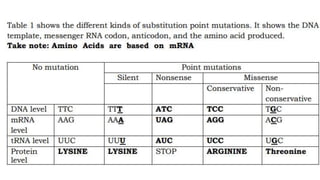
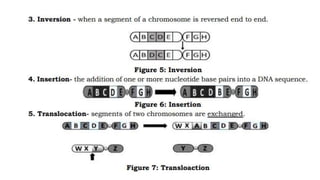
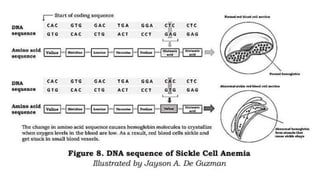
The DNA is used to complete protein synthesis which has two stages - transcription and translation. During translation at the ribosome, messenger RNA sequences are read and translated into amino acids which then form proteins. A mutation is a change in the DNA sequence that can occur either from mistakes when DNA copies or environmental factors like UV light and smoking, and takes place during DNA replication which can then cause abnormal transcription into mRNA.
1 of 30
Download to read offline




















Ad
Recommended
mirrorrs, concave convex. formula solution
mirrorrs, concave convex. formula solutionBaltazarRosales1
Ěý
The document provides tips to reduce gadget exposure, including setting screen time limits, creating gadget-free zones, and engaging in offline activities. It discusses the effects of various types of radiation, emphasizing that long exposure to harmful radiation can lead to health issues. Additionally, it explains the laws of reflection and characteristics of images formed by plane mirrors.Biomolecules.pptxBiomolecules.pptxBiomolecules.pptx
Biomolecules.pptxBiomolecules.pptxBiomolecules.pptxBaltazarRosales1
Ěý
Biomolecules are complex organic molecules essential for life, categorized into carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids. Carbohydrates serve as energy sources and structural components, proteins facilitate numerous cellular functions and reactions, lipids provide energy storage and cell membrane structure, while nucleic acids contain genetic information and direct protein synthesis. Each class of biomolecules is composed of specific elements and structural units, highlighting their critical roles in biological systems.BOYLES LAW.pptx jhghjghghjgjkggghghghghgg
BOYLES LAW.pptx jhghjghghjgjkggghghghghggBaltazarRosales1
Ěý
Boyle's Law, established by Robert Boyle in 1662, describes the inverse relationship between gas volume and pressure at constant temperature. The document covers essential properties of gases including pressure, volume, and temperature, with standard units and conversion factors provided. Additionally, it includes various theoretical problems and examples demonstrating the application of Boyle's Law in calculating gas behavior under changing conditions.science 9.. chemistry.pptxjbjhjjkjhkjhjkhjkh
science 9.. chemistry.pptxjbjhjjkjhkjhjkhjkhBaltazarRosales1
Ěý
This document discusses the key principles of electron configuration: the Pauli Exclusion Principle limits each orbital to two electrons spinning in opposite directions; Hund's Rule states that orbitals in a sublevel are filled with unpaired electrons before pairing occurs; and the Aufbau Principle builds an atom's configuration by adding electrons into orbitals of increasing energy, such as filling n=1 before n=2. Noble gas notation is also mentioned.electronic configuration.pptx ghjjkgjhjhklh
electronic configuration.pptx ghjjkgjhjhklhBaltazarRosales1
Ěý
Electron configuration is the systematic arrangement of electrons in an atom's energy levels and sublevels. The Pauli Exclusion Principle limits each orbital to two electrons with opposite spins. Hund's Rule states that for a given sublevel, electrons occupy orbitals singly with parallel spins before pairing. The Aufbau Principle shows that electrons fill lower energy orbitals before higher ones.PARTS OF MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM.pptxvhgg
PARTS OF MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM.pptxvhggBaltazarRosales1
Ěý
The document summarizes the major parts of the male reproductive system, including the scrotum, testes, epididymis, vas deferens, ejaculatory duct, urethra, and penis. It describes the development and maturation of sperm cells within the testes and along the epididymis, vas deferens, and ejaculatory duct. It also explains that testosterone is the main male sex hormone responsible for male sexual development and characteristics.OCCURENCE OF EVOLUTION.pptx how does evolution happens
OCCURENCE OF EVOLUTION.pptx how does evolution happensBaltazarRosales1
Ěý
This document discusses several key concepts related to the occurrence and mechanisms of evolution:
1. It outlines Jean Baptiste de Lamarck and Charles Darwin's influential theories of evolution, including Lamarck's theories of need, use and disuse, and acquired characteristics as well as Darwin's theory of natural selection.
2. It explores the genetic basis of evolution through concepts like population genetics, gene flow, allele frequencies, non-random mating, and the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium.
3. It examines various evolutionary patterns such as natural selection, genetic drift, speciation, punctuated equilibrium, microevolution, coevolution, convergent evolution, and adaptive radiation.EVIDENCE OF EVOLUTION.pptx history of evolution
EVIDENCE OF EVOLUTION.pptx history of evolutionBaltazarRosales1
Ěý
This document provides evidence of evolution through figures showing similarities in human and animal anatomy. Figure 6 shows the human digestive system with the appendix. Figure 7 shows a snake pelvis bone with a reduced hind limb. Figures 8 and 8B show that early embryonic stages and advanced embryos of different vertebrates share similar structures, providing evidence they evolved from a common ancestor.NERVOUS SYSTEM.pptx tdtffykgygigguiggugiug
NERVOUS SYSTEM.pptx tdtffykgygigguiggugiugBaltazarRosales1
Ěý
The nervous system is composed of two main divisions - the central nervous system consisting of the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system consisting of nerves that connect to all parts of the body. It coordinates feedback mechanisms through the peripheral and central nervous systems to maintain homeostasis in the body. The nervous system regulates internal processes like temperature, hunger, and organ function to keep the body's conditions stable.PROTIEN SYNTHESIS.pptx help to understand the process of protien synthesis
PROTIEN SYNTHESIS.pptx help to understand the process of protien synthesisBaltazarRosales1
Ěý
DNA contains genetic codes made up of nucleotide bases that are arranged in triplets to code for amino acids. RNA carries these genetic codes from DNA and uses them to assemble amino acids into proteins according to the code. Together, DNA and RNA work through this process of protein synthesis to produce the proteins specified by the genetic code.festival Dancing and Fitness.pptx........
festival Dancing and Fitness.pptx........BaltazarRosales1
Ěý
The FITT principle provides an acronym to describe exercise parameters: Frequency refers to the number of weekly sessions; Intensity indicates the difficulty level which can be light, moderate, or vigorous; Time is the duration of each session; and Type specifies the mode of exercise or activity.The Fundamental Body Movements.pptx GFGF
The Fundamental Body Movements.pptx GFGFBaltazarRosales1
Ěý
Fundamental body movements are the basic building blocks for more complex physical activities like sports and dancing. They include locomotor movements that move the body through space, such as walking, running, and hopping, as well as non-locomotor movements that involve movement of body parts without traveling, like bending, twisting, and swinging. Students must master fundamental movements like dribbling and kicking during early childhood in order to participate in physical activities as they grow older. The document outlines the main categories and examples of fundamental locomotor and non-locomotor movements, as well as elements of rhythm, space, and qualities of movement important for dance.The Endocrine System.pptx GFTFTFYFUYUYYUY
The Endocrine System.pptx GFTFTFYFUYUYYUYBaltazarRosales1
Ěý
Here are the answers to fill in the blanks:
1. Pituitary gland
2. Thyroid gland
3. Parathyroid gland
4. Parathyroid gland
5. Pancreas
6. Thymus gland
7. Thymus gland
8. Adrenal gland
9. Birth control pills
10. Prolactin and OxytocinMyself on Street and Hip-hop Dances.pptx
Myself on Street and Hip-hop Dances.pptxBaltazarRosales1
Ěý
1. The document introduces the importance of active recreation for achieving a healthy body and discusses street and hip-hop dances.
2. It provides a series of true/false statements to test the reader's knowledge of concepts like rate of perceived exertion, vigorous vs. passive activities, nutrition, and more.
3. The reader is then asked to identify which physical activities can help sustain fitness by writing "YES" or "NO" next to each one listed, such as watching TV, playing volleyball, eating fruits/veggies, dancing, etc.ARTS 9 L1.pptxHJFJLSKJFKSJGKSDJGKSJJIRJGIJIG
ARTS 9 L1.pptxHJFJLSKJFKSJGKSDJGKSJJIRJGIJIGBaltazarRosales1
Ěý
This document discusses media-based arts and design in the Philippines. It notes that photography is considered both a tool for communication and an art form. The document outlines key elements of filmmaking such as the director, actors, cinematography, editing, production design. It also briefly mentions notable Philippine photographers and filmmakers.ART NEOCLASSICISM AND ROMANTISMISISM.pptx
ART NEOCLASSICISM AND ROMANTISMISISM.pptxBaltazarRosales1
Ěý
Neoclassicism and Romanticism were artistic periods between the late 18th and early 19th centuries that had distinct characteristics and elements. Neoclassicism took inspiration from Ancient Greek and Roman art, emphasizing historical accuracy and order. Romanticism was an emotional reaction that celebrated nature and heightened sensations through dramatic compositions. Both periods influenced painting, sculpture, and architecture styles during this time.asexual reproduction ppt.pptx
asexual reproduction ppt.pptxBaltazarRosales1
Ěý
This document defines asexual reproduction and describes its various types. It explains that asexual reproduction involves a single parent producing offspring that are genetically identical. Various types of asexual reproduction are described, including fission, fragmentation, budding, parthenogenesis, spore production, and vegetative propagation. Examples of each type are provided. The objectives are to define asexual reproduction, describe its different types, and classify organisms by their reproductive methods.THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM GRADE 9 SCIENCE.pptx
THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM GRADE 9 SCIENCE.pptxroselyncatacutan
Ěý
The Circulatory System Grade 9 Science Quarter 1 Week 1Paired Sketching of Distributed User Interfaces:Workflow, Protocol, Software ...
Paired Sketching of Distributed User Interfaces:Workflow, Protocol, Software ...Jean Vanderdonckt
Ěý
Paper présented at ACM EICS '25:
The evolving landscape of distributed user interfaces requires the prototyping stage also be distributed between users, tasks, platforms, and environments. To create a cohesive distribution of the user interface elements in such ecosystems, paired sketching has emerged as a collaborative design method that leverages multiple stakeholders’ strengths, including designers, developers, and end users, working in pairs. In the context of developer experience applied to paired sketching for distributed
user interfaces, we decomposed a workflow into four disciplines according to the Software and Systems Process Engineering
Meta-Model (SPEM) notation. First, we defined a protocol to deploy paired sketching of distributed user interfaces, supported
by UbiSketch, a collaborative software environment tailored featuring sketch recognition and whiteboarding. Second, to
evaluate paired sketching for engineering interactive systems, we conducted an experiment involving five pairs of stakeholders
who sketched a distributed user interface for inside-the-vehicule interaction distributed on four platforms: smartphone, tablet, pen display, and tabletop. Empirical results from questionnaires, reactivity, intention, perceived satisfaction, and free comments, suggest a preference order in which the tabletop is ranked first, followed by the tablet, smartphone, and pen display. Based on these results, we discuss the potential of paired sketching for distributed user interfaces.Science 8 Quarter 4 first quiz digestive system.docx
Science 8 Quarter 4 first quiz digestive system.docxjunefermunez
Ěý
Quiz for the topic Digestive System. 4th QaurterImpact of Network Topologies on Blockchain Performance
Impact of Network Topologies on Blockchain Performancevschiavoni
Ěý
Best Student Paper Award at ACM DEBS 2025.
Paper here:
https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/3701717.3730540
Since blockchains are increasingly adopted in real-world applications, it is of paramount importance to evaluate their performance across diverse scenarios. Although the network infrastructure plays a fundamental role, its impact on performance remains largely unexplored. Some studies evaluate blockchain in cloud environments, but this approach is costly and difficult to reproduce. We propose a cost-effective and reproducible environment that supports both cluster-based setups and emulation capabilities and allows the underlying network topology to be easily modified. We evaluate five industry-grade blockchains – Algorand, Diem, Ethereum, Quorum, and Solana – across five network topologies – fat-tree, full mesh, hypercube, scale-free, and torus – and different realistic workloads – smart contract requests and transfer transactions. Our benchmark framework, Lilith, shows that full mesh, hypercube, and torus topologies improve blockchain performance under heavy workloads. Algorand and Diem perform consistently across the considered topologies, while Ethereum remains robust but slower.Herbal Excipients: Natural Colorants & Perfumery Agents
Herbal Excipients: Natural Colorants & Perfumery AgentsSeacom Skills University
Ěý
Excipients can be defined as non active ingredients that are mixed with therapeutically active compounds to form medicines. The excipients are the substance which are used as a medium for giving a medicament.These help in processing of the drug delivery system during its manufacture, protect, support or enhance stability, bioavailability or patient acceptability.
The word comes from the Latin word meaning a sweets melling fluid contain the essence of flowers and other substances. Perfume is a mixture of fragrant essential oil and aroma compounds Fragrances used for external applications such as spray perfumes, body care, homecare, cosmetics, soaps and detergents.GBSN__Unit 2 - Control of Microorganisms
GBSN__Unit 2 - Control of MicroorganismsAreesha Ahmad
Ěý
Microbiology for Nursing students - According to New PNC course curriculum - 2025
Single-Cell Multi-Omics in Neurodegeneration p1.pptx
Single-Cell Multi-Omics in Neurodegeneration p1.pptxKanakChaudhary10
Ěý
Decoding Brain Complexity at Single-Cell Resolution
Single-Cell Transcriptomics in Neurodegeneration
Epigenomics and Gene Regulation
Proteomics at Single-Cell Resolution
Metabolomics in Cellular Context
Novel Therapeutic Targets
Cell-Type-Specific MechanismsInvestigatory_project Topic:-effect of electrolysis in solar desalination .pdf
Investigatory_project Topic:-effect of electrolysis in solar desalination .pdfshubham997ku
Ěý
Cbse class 12. chemistry investigatory project More Related Content
More from BaltazarRosales1 (9)
NERVOUS SYSTEM.pptx tdtffykgygigguiggugiug
NERVOUS SYSTEM.pptx tdtffykgygigguiggugiugBaltazarRosales1
Ěý
The nervous system is composed of two main divisions - the central nervous system consisting of the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system consisting of nerves that connect to all parts of the body. It coordinates feedback mechanisms through the peripheral and central nervous systems to maintain homeostasis in the body. The nervous system regulates internal processes like temperature, hunger, and organ function to keep the body's conditions stable.PROTIEN SYNTHESIS.pptx help to understand the process of protien synthesis
PROTIEN SYNTHESIS.pptx help to understand the process of protien synthesisBaltazarRosales1
Ěý
DNA contains genetic codes made up of nucleotide bases that are arranged in triplets to code for amino acids. RNA carries these genetic codes from DNA and uses them to assemble amino acids into proteins according to the code. Together, DNA and RNA work through this process of protein synthesis to produce the proteins specified by the genetic code.festival Dancing and Fitness.pptx........
festival Dancing and Fitness.pptx........BaltazarRosales1
Ěý
The FITT principle provides an acronym to describe exercise parameters: Frequency refers to the number of weekly sessions; Intensity indicates the difficulty level which can be light, moderate, or vigorous; Time is the duration of each session; and Type specifies the mode of exercise or activity.The Fundamental Body Movements.pptx GFGF
The Fundamental Body Movements.pptx GFGFBaltazarRosales1
Ěý
Fundamental body movements are the basic building blocks for more complex physical activities like sports and dancing. They include locomotor movements that move the body through space, such as walking, running, and hopping, as well as non-locomotor movements that involve movement of body parts without traveling, like bending, twisting, and swinging. Students must master fundamental movements like dribbling and kicking during early childhood in order to participate in physical activities as they grow older. The document outlines the main categories and examples of fundamental locomotor and non-locomotor movements, as well as elements of rhythm, space, and qualities of movement important for dance.The Endocrine System.pptx GFTFTFYFUYUYYUY
The Endocrine System.pptx GFTFTFYFUYUYYUYBaltazarRosales1
Ěý
Here are the answers to fill in the blanks:
1. Pituitary gland
2. Thyroid gland
3. Parathyroid gland
4. Parathyroid gland
5. Pancreas
6. Thymus gland
7. Thymus gland
8. Adrenal gland
9. Birth control pills
10. Prolactin and OxytocinMyself on Street and Hip-hop Dances.pptx
Myself on Street and Hip-hop Dances.pptxBaltazarRosales1
Ěý
1. The document introduces the importance of active recreation for achieving a healthy body and discusses street and hip-hop dances.
2. It provides a series of true/false statements to test the reader's knowledge of concepts like rate of perceived exertion, vigorous vs. passive activities, nutrition, and more.
3. The reader is then asked to identify which physical activities can help sustain fitness by writing "YES" or "NO" next to each one listed, such as watching TV, playing volleyball, eating fruits/veggies, dancing, etc.ARTS 9 L1.pptxHJFJLSKJFKSJGKSDJGKSJJIRJGIJIG
ARTS 9 L1.pptxHJFJLSKJFKSJGKSDJGKSJJIRJGIJIGBaltazarRosales1
Ěý
This document discusses media-based arts and design in the Philippines. It notes that photography is considered both a tool for communication and an art form. The document outlines key elements of filmmaking such as the director, actors, cinematography, editing, production design. It also briefly mentions notable Philippine photographers and filmmakers.ART NEOCLASSICISM AND ROMANTISMISISM.pptx
ART NEOCLASSICISM AND ROMANTISMISISM.pptxBaltazarRosales1
Ěý
Neoclassicism and Romanticism were artistic periods between the late 18th and early 19th centuries that had distinct characteristics and elements. Neoclassicism took inspiration from Ancient Greek and Roman art, emphasizing historical accuracy and order. Romanticism was an emotional reaction that celebrated nature and heightened sensations through dramatic compositions. Both periods influenced painting, sculpture, and architecture styles during this time.asexual reproduction ppt.pptx
asexual reproduction ppt.pptxBaltazarRosales1
Ěý
This document defines asexual reproduction and describes its various types. It explains that asexual reproduction involves a single parent producing offspring that are genetically identical. Various types of asexual reproduction are described, including fission, fragmentation, budding, parthenogenesis, spore production, and vegetative propagation. Examples of each type are provided. The objectives are to define asexual reproduction, describe its different types, and classify organisms by their reproductive methods.Recently uploaded (20)
THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM GRADE 9 SCIENCE.pptx
THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM GRADE 9 SCIENCE.pptxroselyncatacutan
Ěý
The Circulatory System Grade 9 Science Quarter 1 Week 1Paired Sketching of Distributed User Interfaces:Workflow, Protocol, Software ...
Paired Sketching of Distributed User Interfaces:Workflow, Protocol, Software ...Jean Vanderdonckt
Ěý
Paper présented at ACM EICS '25:
The evolving landscape of distributed user interfaces requires the prototyping stage also be distributed between users, tasks, platforms, and environments. To create a cohesive distribution of the user interface elements in such ecosystems, paired sketching has emerged as a collaborative design method that leverages multiple stakeholders’ strengths, including designers, developers, and end users, working in pairs. In the context of developer experience applied to paired sketching for distributed
user interfaces, we decomposed a workflow into four disciplines according to the Software and Systems Process Engineering
Meta-Model (SPEM) notation. First, we defined a protocol to deploy paired sketching of distributed user interfaces, supported
by UbiSketch, a collaborative software environment tailored featuring sketch recognition and whiteboarding. Second, to
evaluate paired sketching for engineering interactive systems, we conducted an experiment involving five pairs of stakeholders
who sketched a distributed user interface for inside-the-vehicule interaction distributed on four platforms: smartphone, tablet, pen display, and tabletop. Empirical results from questionnaires, reactivity, intention, perceived satisfaction, and free comments, suggest a preference order in which the tabletop is ranked first, followed by the tablet, smartphone, and pen display. Based on these results, we discuss the potential of paired sketching for distributed user interfaces.Science 8 Quarter 4 first quiz digestive system.docx
Science 8 Quarter 4 first quiz digestive system.docxjunefermunez
Ěý
Quiz for the topic Digestive System. 4th QaurterImpact of Network Topologies on Blockchain Performance
Impact of Network Topologies on Blockchain Performancevschiavoni
Ěý
Best Student Paper Award at ACM DEBS 2025.
Paper here:
https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/3701717.3730540
Since blockchains are increasingly adopted in real-world applications, it is of paramount importance to evaluate their performance across diverse scenarios. Although the network infrastructure plays a fundamental role, its impact on performance remains largely unexplored. Some studies evaluate blockchain in cloud environments, but this approach is costly and difficult to reproduce. We propose a cost-effective and reproducible environment that supports both cluster-based setups and emulation capabilities and allows the underlying network topology to be easily modified. We evaluate five industry-grade blockchains – Algorand, Diem, Ethereum, Quorum, and Solana – across five network topologies – fat-tree, full mesh, hypercube, scale-free, and torus – and different realistic workloads – smart contract requests and transfer transactions. Our benchmark framework, Lilith, shows that full mesh, hypercube, and torus topologies improve blockchain performance under heavy workloads. Algorand and Diem perform consistently across the considered topologies, while Ethereum remains robust but slower.Herbal Excipients: Natural Colorants & Perfumery Agents
Herbal Excipients: Natural Colorants & Perfumery AgentsSeacom Skills University
Ěý
Excipients can be defined as non active ingredients that are mixed with therapeutically active compounds to form medicines. The excipients are the substance which are used as a medium for giving a medicament.These help in processing of the drug delivery system during its manufacture, protect, support or enhance stability, bioavailability or patient acceptability.
The word comes from the Latin word meaning a sweets melling fluid contain the essence of flowers and other substances. Perfume is a mixture of fragrant essential oil and aroma compounds Fragrances used for external applications such as spray perfumes, body care, homecare, cosmetics, soaps and detergents.GBSN__Unit 2 - Control of Microorganisms
GBSN__Unit 2 - Control of MicroorganismsAreesha Ahmad
Ěý
Microbiology for Nursing students - According to New PNC course curriculum - 2025
Single-Cell Multi-Omics in Neurodegeneration p1.pptx
Single-Cell Multi-Omics in Neurodegeneration p1.pptxKanakChaudhary10
Ěý
Decoding Brain Complexity at Single-Cell Resolution
Single-Cell Transcriptomics in Neurodegeneration
Epigenomics and Gene Regulation
Proteomics at Single-Cell Resolution
Metabolomics in Cellular Context
Novel Therapeutic Targets
Cell-Type-Specific MechanismsInvestigatory_project Topic:-effect of electrolysis in solar desalination .pdf
Investigatory_project Topic:-effect of electrolysis in solar desalination .pdfshubham997ku
Ěý
Cbse class 12. chemistry investigatory project Cancer
CancerVartika
Ěý
This presentation covers the introduction for cancer, hallmarks and genes associated to it along with the process of apoptosis and it's pathways.GBSN_ Unit 1 - Introduction to Microbiology
GBSN_ Unit 1 - Introduction to MicrobiologyAreesha Ahmad
Ěý
Microbiology for Nursing students - According to New PNC course curriculum - 2025We are Living in a Dangerous Multilingual World!
We are Living in a Dangerous Multilingual World!Editions La Dondaine
Ěý
They say Artificial Intelligence will solve that problem in a jiffy. They are telling you a tall tale straight from Mark Twain’s trove. It may compare with “The Celebrated Jumping Frog of Calaveras County.”
Only a maximum of twelve languages will be able to have an AI, hence translation machines, because only them will have a big enough LLM to be able to produce and train an Artificial Intelligence.
That’s the positive element.
But on the negative side, several (many) thousand languages will not be able to have an AI, hence a translation machine.
The real danger is the homogenization of AI-compatible languages and the statistical customization of all languages on the pattern of these twelve languages. You must be joking! On the model of only ONE AI-compatible language, English, and all other languages will be in contact with this “English-Norm,” and all languages will follow the AI-customized English that all machines, all media, and all people will be repeating after the AI translation machine: “My tailor is rich,” the first sentence of L'Anglais sans peine, the first work in the Assimil method for learning English, written by Alphonse Chérel in 1929.
Is that the future of humanity, or the bad nightmare of a cat lost in the jigsaw puzzle of a supernatural spiritual Cat Country?
Or maybe the Time Machine that will take us to paradise in a universe at least three million light years away from this dirty earth, in whose mud we are swaddling ourselves piggishly.
Science Holiday Homework (interesting slide )
Science Holiday Homework (interesting slide )aryanxkohli88
Ěý
science holiday homework
good for childrenAd
MUTATION.pptx learn different ways of mutation how does it happen
- 1. The DNA is used to complete the process of protein synthesis. Protein synthesis has two stages which are called transcription and translation. During protein synthesis at the ribosome, messenger RNA sequences are read and translated into amino acids. These amino acids will form proteins. A mutation is a change that occurs in our DNA sequence, either due to mistakes when the DNA is copied or as the result of environmental factors such as UV light and cigarette smoke. Mutation occurs during DNA replication, thus transcription into mRNA is anomalous.