The Endocrine System.pptx GFTFTFYFUYUYYUY
Download as pptx, pdf0 likes56 views
Here are the answers to fill in the blanks: 1. Pituitary gland 2. Thyroid gland 3. Parathyroid gland 4. Parathyroid gland 5. Pancreas 6. Thymus gland 7. Thymus gland 8. Adrenal gland 9. Birth control pills 10. Prolactin and Oxytocin
1 of 19
Download to read offline












Ad
Recommended
Endocrine system is composed of glands that secrete different types of hormon...
Endocrine system is composed of glands that secrete different types of hormon...ANAVEILLECANCIO1
╠²
The endocrine system is composed of glands that secrete hormones which regulate processes throughout the body, including growth, metabolism, and reproduction. The hormones are released into the bloodstream and target specific organs to trigger effects like increasing or decreasing metabolic rate. While the nervous system triggers fast responses, the endocrine system causes slower changes over time from hours to weeks. Examples of glands include the pituitary, thyroid, adrenals, and reproductive organs. Imbalances in hormone levels can result in disorders such as dwarfism, gigantism, and goiter.Endocrine system is composed of glands that secrete different types of hormon...
Endocrine system is composed of glands that secrete different types of hormon...ANAVEILLECANCIO1
╠²
The endocrine system is composed of glands that secrete hormones which regulate processes throughout the body, including growth, metabolism, and reproduction. The major glands include the pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenals, pancreas, and reproductive organs. Hormones are released into the bloodstream and carried to target organs to effect changes such as stimulating growth or controlling calcium levels. While the nervous system triggers fast responses, the endocrine system causes slower changes over time from hours to weeks. Imbalances in hormone levels can result in disorders that impact growth or metabolism.endocrine system lesson 1 [Autosaved].pptx
endocrine system lesson 1 [Autosaved].pptxANAVEILLECANCIO1
╠²
The endocrine system is composed of glands that secrete hormones which regulate growth, metabolism, and reproductive processes. The pituitary gland controls other glands and releases hormones that influence growth. Other major glands include the thyroid, which regulates metabolism, and the adrenals, which release adrenaline during stress. Imbalances in hormone levels can result in disorders - for example, too little growth hormone can cause dwarfism while too much causes gigantism.endocrine system
endocrine systemPriyaSoni93
╠²
The endocrine system includes glands that secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream to regulate functions like growth, metabolism, reproduction, and response to stimuli. The major endocrine glands are the pituitary, hypothalamus, pineal, thyroid, parathyroids, pancreas, adrenals, and gonads. The pituitary gland controls other glands and regulates growth, blood pressure, and sex organ functions. The thyroid regulates heart rate and metabolism. The pancreas regulates blood sugar through insulin and glucagon. The adrenals produce cortisol and hormones for stress response and digestion. The gonads produce sex hormones in males and females.Endocrine_Science_Grade_10_BINHSsss.pptx
Endocrine_Science_Grade_10_BINHSsss.pptxRobertJustinMayano
╠²
The document discusses the endocrine system and roles of hormones in the male and female reproductive systems. It begins with an opening prayer and attendance check. It then defines the endocrine system as a network of glands that uses hormones to control body functions like metabolism, growth, and stress response. Key glands discussed include the hypothalamus, pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, thymus, adrenal, ovaries, testes, and pancreas. The roles of various hormones in processes like development, metabolism, and reproduction are explained. Students then participate in activities to test their understanding of the endocrine system and hormone functions.G10 2 endocrine gland.pptx
G10 2 endocrine gland.pptxJosiryReyes
╠²
This document provides information about the endocrine system and its glands. It identifies the major endocrine glands and their functions, including the pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, thymus, adrenal, pancreas, ovaries, testes, and pineal gland. The document also discusses hormonal imbalances that can result in disorders like osteoporosis, goiter, gigantism, and dwarfism. It poses questions about the roles of different glands in controlling blood sugar, immunity, and providing bursts of energy.The endocrine system
The endocrine system▒§▓į╗ÕŠ▒▓╣Ōäó
╠²
The endocrine system is made up of glands that secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream to regulate distant target organs and tissues. The major endocrine glands include the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, thyroid gland, parathyroid glands, adrenal glands, pancreas, ovaries, and testes. Hormones act through feedback loops to maintain homeostasis and are amplified through cascading enzyme responses in target cells that express receptors for specific hormones. The hypothalamus and pituitary gland control the endocrine system through releasing and inhibiting hormones that signal other glands.The Endocrine Glands
The Endocrine GlandsDayanahaha
╠²
The document discusses the endocrine system and its major glands. It explains that endocrine glands secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream, rather than through ducts. The major glands discussed are the pituitary gland, adrenal glands, thyroid gland, parathyroid glands, gonads, and pancreas. The hormones secreted by these glands help regulate processes throughout the body like growth, metabolism, mood, and stress response. Imbalances in hormone levels can result in various medical conditions. Overall, the endocrine system works closely with the nervous system to maintain homeostasis in the body.Endocrine System
Endocrine SystemDARLYNSIERRA
╠²
The endocrine system is made up of glands that produce hormones to regulate various bodily functions such as metabolism, growth, development, reproduction, mood, and more. The major glands include the pituitary gland, thyroid gland, parathyroid glands, adrenal glands, pancreas, ovaries, and testicles. Hormones act as chemical messengers that transfer information between cells to influence many cellular and body processes.What is endocrine system in human body
What is endocrine system in human bodyDolehKhan
╠²
The document provides an overview of the endocrine system, which is a network of glands producing hormones that regulate various bodily functions such as metabolism, growth, and reproduction. It details the major glands involved, including the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, thyroid gland, and adrenal glands, and emphasizes the importance of hormones as chemical messengers in the body. Additionally, it discusses the structure of chromosomes and genes, highlighting their roles in heredity and cellular function.Endocrine glands and systems.
Endocrine glands and systems.pallavi38
╠²
The document discusses the endocrine system and its glands. It describes the main endocrine glands, including the pituitary gland, pancreas, ovaries, testes, thyroid gland, adrenal glands, and pineal gland. It explains the hormones each gland secretes and their functions in regulating growth, metabolism, sexual development, and other bodily processes. Additionally, it discusses puberty and the physical and emotional changes caused by the endocrine system during adolescence for both males and females.Endocrine system
Endocrine systemSprint College
╠²
The endocrine system regulates many bodily functions through the secretion of hormones from various glands directly into the bloodstream. The major glands include the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, thyroid gland, parathyroid glands, adrenal glands, pancreas, ovaries, and testes. Hormones help maintain homeostasis by influencing growth, metabolism, sexual development, and other processes in target cells and tissues.The-Endocrine-System, organs and glans. Maajor Endocrine glands.pptx
The-Endocrine-System, organs and glans. Maajor Endocrine glands.pptxFernandaCampos583511
╠²
The endocrine system is a network of glands that secrete hormones to regulate bodily functions such as growth, metabolism, and reproduction. Hormones act as chemical messengers targeting specific cells, while major glands like the pituitary, thyroid, and adrenal glands play key roles in various physiological processes. Maintaining a healthy endocrine system requires a balanced diet, regular exercise, and effective stress management.The endocrine system
The endocrine systemCharles Robles Balsita
╠²
The endocrine system regulates body functions through hormones secreted into the bloodstream. It includes major glands like the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, thyroid gland, parathyroid gland, thymus, adrenal glands, pancreas, ovaries and testes. The hypothalamus controls the pituitary gland, which regulates the thyroid, adrenals, and reproductive organs. Hormones regulate processes like growth, metabolism, sexual function, lactation and immune response. Endocrine disorders occur when hormone production or cellular sensitivity is abnormal, leading to conditions like acromegaly, goiter or Cushing's syndrome. Feedback loops regulate hormone levels through a chain of stimulation and inhibition.ENDOCRINE SYSTEM REPORT_TESDA CAREGIVING NCII
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM REPORT_TESDA CAREGIVING NCIIkristinegaleon89
╠²
The endocrine system is composed of glands and tissues that produce and release over 50 hormones, which regulate various bodily functions such as metabolism, growth, and mood. Major glands include the pineal, pituitary, thyroid, and adrenal glands, while organs like the pancreas and reproductive organs also play significant roles. Health concerns related to the endocrine system encompass a range of conditions, including diabetes, hormonal imbalances, and cancers, with preventive measures focusing on lifestyle choices and avoiding endocrine disruptors.Coordinated Function of the Endocrine, Nervous, and Reproductive System
Coordinated Function of the Endocrine, Nervous, and Reproductive Systemapryljaneabayonmente
╠²
The document discusses the endocrine system and hormonal imbalance. It defines the endocrine system as composed of glands that secrete hormones regulating growth, metabolism, reproduction and mood. It describes the major glands - the pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, thymus, adrenals, pancreas, testis and ovary - and their functions in controlling processes like metabolism, immune response and reproductive/sexual development. Finally, it notes that hormonal imbalance can occur if glands do not produce the proper amounts of chemicals, leading to potential abnormalities in the body.ENDOCRINE SYSTEM.pptx
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM.pptxMubashirKhan652062
╠²
The endocrine system maintains homeostasis through glands and hormones. It includes the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, pineal gland, thyroid gland, parathyroid gland, adrenal glands, pancreas, ovaries, and testes. The pituitary gland is called the "master gland" as it controls other glands via releasing hormones. Hormones produced include insulin, glucagon, estrogen, progesterone, testosterone, cortisol, thyroid hormones, and others which regulate growth, metabolism, sexual development, and stress responses.Endocrine system and its glands, functions, location and other abnormalities
Endocrine system and its glands, functions, location and other abnormalitiesJeraldelEncepto
╠²
The document provides information about the endocrine system and its glands/hormones. It includes learning objectives about the endocrine glands and their functions. There are also activities that have students identify endocrine glands and hormones, describe their functions, and answer questions about various glands and conditions related to hormone imbalances or deficiencies.1s3l9rkh0_THE-ENDOCRINE-SYSTEM-SCIENCE.pdf
1s3l9rkh0_THE-ENDOCRINE-SYSTEM-SCIENCE.pdfPreciousRoxas
╠²
The endocrine system is a complex network of glands and organs that uses hormones to control and coordinate the body's metabolism, energy levels, reproduction, growth and development, and stress response. It has 10 major parts including the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, thyroid gland, parathyroid gland, adrenal glands, pancreas, and ovaries or testes. The endocrine system maintains homeostasis through hormone signals that travel through the bloodstream and tell organs and tissues what to do. Proper care of the endocrine system includes exercise, a nutritious diet, regular medical checkups, and consulting a doctor before taking supplements.Endocrine glands
Endocrine glandsravibio
╠²
The document discusses the endocrine system and its glands. It notes that the endocrine system uses hormones to regulate body functions, while the glands produce and release hormones like the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, thyroid gland, parathyroid gland, adrenal glands, pancreas, ovaries and testes. It then covers hormone functions, how they work, conditions that can disrupt hormone levels, potential causes and treatment options.SCIENCE 10 LESddhjsjkskldjjdjdjnSON 14.pdf
SCIENCE 10 LESddhjsjkskldjjdjdjnSON 14.pdfchilde7
╠²
The endocrine system consists of glands that secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream, regulating various bodily functions such as metabolism, growth, and mood. Key glands include the pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal glands, and reproductive glands, each releasing specific hormones that impact target tissues. The system operates through feedback mechanisms, primarily negative feedback to maintain homeostasis, with positive feedback playing a role in events like childbirth.Endocrine system
Endocrine systemmalkeetsingh104
╠²
The endocrine system regulates body functions through hormone secretion. It consists of glands that secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream, affecting distant target organs. The major endocrine glands include the pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, pancreas, gonads, and pineal glands. Each gland secretes specific hormones that control processes like growth, metabolism, sexual development, and stress response, maintaining homeostasis throughout the body.ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
ENDOCRINE SYSTEMshakuntala kadam
╠²
The endocrine system consists of glands that secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream. The major endocrine glands include the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, thyroid gland, parathyroid glands, adrenal glands, pancreas, ovaries, and testes. Hormones act as chemical messengers to regulate physiological functions like growth and metabolism. A feedback mechanism controls hormone production and release to maintain homeostasis.Endocrine System
Endocrine SystemDana Tuazon
╠²
The endocrine system consists of glands that regulate vital functions through the secretion of hormones. It works closely with the nervous system to control mood, growth, metabolism, and reproduction. The major glands include the hypothalamus, pituitary, thyroid, parathyroids, adrenals, pancreas, ovaries, and testes. Hormones communicate instructions between glands and target cells to influence numerous bodily processes and maintain homeostasis.Endocrine System. Endocrine glands , types,hormone and functions
Endocrine System. Endocrine glands , types,hormone and functionsSudha Sudha
╠²
The endocrine system is a network of glands that produce hormones to regulate various bodily functions, such as metabolism, growth, and reproduction. Key glands include the hypothalamus, pituitary, thyroid, adrenal glands, and pancreas, each producing specific hormones that affect target organs and tissues. Hormones can be classified into peptide, steroid, and amine types, each with unique properties and mechanisms of action.endocrine system
endocrine systemPriyaSoni93
╠²
The document discusses the human endocrine system. It provides definitions of hormones and describes the major endocrine glands and their roles. The endocrine glands include the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, thyroid gland, parathyroid gland, adrenal glands, pancreas, ovaries, and testes. The hypothalamus and pituitary gland control the other endocrine glands by producing releasing and inhibiting hormones. The endocrine glands secrete hormones like insulin, estrogen and testosterone to regulate processes throughout the body, including growth and development, metabolism, and reproduction.Physiology of Endocrine System
Physiology of Endocrine System PRANJAL SHARMA
╠²
The document provides an extensive overview of the endocrine system, detailing its structure, function, and the hormones produced by various glands such as the pituitary, thyroid, adrenal, pancreas, ovaries, and testes. It discusses the history of endocrinology, major discoveries, and the roles of hormones in regulating bodily functions and maintaining homeostasis. Furthermore, it explains hormonal secretion control mechanisms, the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis, and the impact of various hormones on physiological processes.Endocrine
EndocrineNandhini Podamekala
╠²
The endocrine system is comprised of glands that secrete hormones to regulate various bodily functions such as metabolism, growth, reproduction, sleep, and mood. The major endocrine glands include the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, thyroid gland, parathyroid glands, adrenal glands, pancreas, and ovaries/testes. These glands secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream to regulate distant target organs, unlike exocrine glands which secrete substances through ducts.mirrorrs, concave convex. formula solution
mirrorrs, concave convex. formula solutionBaltazarRosales1
╠²
The document provides tips to reduce gadget exposure, including setting screen time limits, creating gadget-free zones, and engaging in offline activities. It discusses the effects of various types of radiation, emphasizing that long exposure to harmful radiation can lead to health issues. Additionally, it explains the laws of reflection and characteristics of images formed by plane mirrors.Biomolecules.pptxBiomolecules.pptxBiomolecules.pptx
Biomolecules.pptxBiomolecules.pptxBiomolecules.pptxBaltazarRosales1
╠²
Biomolecules are complex organic molecules essential for life, categorized into carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids. Carbohydrates serve as energy sources and structural components, proteins facilitate numerous cellular functions and reactions, lipids provide energy storage and cell membrane structure, while nucleic acids contain genetic information and direct protein synthesis. Each class of biomolecules is composed of specific elements and structural units, highlighting their critical roles in biological systems.More Related Content
Similar to The Endocrine System.pptx GFTFTFYFUYUYYUY (20)
Endocrine System
Endocrine SystemDARLYNSIERRA
╠²
The endocrine system is made up of glands that produce hormones to regulate various bodily functions such as metabolism, growth, development, reproduction, mood, and more. The major glands include the pituitary gland, thyroid gland, parathyroid glands, adrenal glands, pancreas, ovaries, and testicles. Hormones act as chemical messengers that transfer information between cells to influence many cellular and body processes.What is endocrine system in human body
What is endocrine system in human bodyDolehKhan
╠²
The document provides an overview of the endocrine system, which is a network of glands producing hormones that regulate various bodily functions such as metabolism, growth, and reproduction. It details the major glands involved, including the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, thyroid gland, and adrenal glands, and emphasizes the importance of hormones as chemical messengers in the body. Additionally, it discusses the structure of chromosomes and genes, highlighting their roles in heredity and cellular function.Endocrine glands and systems.
Endocrine glands and systems.pallavi38
╠²
The document discusses the endocrine system and its glands. It describes the main endocrine glands, including the pituitary gland, pancreas, ovaries, testes, thyroid gland, adrenal glands, and pineal gland. It explains the hormones each gland secretes and their functions in regulating growth, metabolism, sexual development, and other bodily processes. Additionally, it discusses puberty and the physical and emotional changes caused by the endocrine system during adolescence for both males and females.Endocrine system
Endocrine systemSprint College
╠²
The endocrine system regulates many bodily functions through the secretion of hormones from various glands directly into the bloodstream. The major glands include the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, thyroid gland, parathyroid glands, adrenal glands, pancreas, ovaries, and testes. Hormones help maintain homeostasis by influencing growth, metabolism, sexual development, and other processes in target cells and tissues.The-Endocrine-System, organs and glans. Maajor Endocrine glands.pptx
The-Endocrine-System, organs and glans. Maajor Endocrine glands.pptxFernandaCampos583511
╠²
The endocrine system is a network of glands that secrete hormones to regulate bodily functions such as growth, metabolism, and reproduction. Hormones act as chemical messengers targeting specific cells, while major glands like the pituitary, thyroid, and adrenal glands play key roles in various physiological processes. Maintaining a healthy endocrine system requires a balanced diet, regular exercise, and effective stress management.The endocrine system
The endocrine systemCharles Robles Balsita
╠²
The endocrine system regulates body functions through hormones secreted into the bloodstream. It includes major glands like the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, thyroid gland, parathyroid gland, thymus, adrenal glands, pancreas, ovaries and testes. The hypothalamus controls the pituitary gland, which regulates the thyroid, adrenals, and reproductive organs. Hormones regulate processes like growth, metabolism, sexual function, lactation and immune response. Endocrine disorders occur when hormone production or cellular sensitivity is abnormal, leading to conditions like acromegaly, goiter or Cushing's syndrome. Feedback loops regulate hormone levels through a chain of stimulation and inhibition.ENDOCRINE SYSTEM REPORT_TESDA CAREGIVING NCII
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM REPORT_TESDA CAREGIVING NCIIkristinegaleon89
╠²
The endocrine system is composed of glands and tissues that produce and release over 50 hormones, which regulate various bodily functions such as metabolism, growth, and mood. Major glands include the pineal, pituitary, thyroid, and adrenal glands, while organs like the pancreas and reproductive organs also play significant roles. Health concerns related to the endocrine system encompass a range of conditions, including diabetes, hormonal imbalances, and cancers, with preventive measures focusing on lifestyle choices and avoiding endocrine disruptors.Coordinated Function of the Endocrine, Nervous, and Reproductive System
Coordinated Function of the Endocrine, Nervous, and Reproductive Systemapryljaneabayonmente
╠²
The document discusses the endocrine system and hormonal imbalance. It defines the endocrine system as composed of glands that secrete hormones regulating growth, metabolism, reproduction and mood. It describes the major glands - the pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, thymus, adrenals, pancreas, testis and ovary - and their functions in controlling processes like metabolism, immune response and reproductive/sexual development. Finally, it notes that hormonal imbalance can occur if glands do not produce the proper amounts of chemicals, leading to potential abnormalities in the body.ENDOCRINE SYSTEM.pptx
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM.pptxMubashirKhan652062
╠²
The endocrine system maintains homeostasis through glands and hormones. It includes the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, pineal gland, thyroid gland, parathyroid gland, adrenal glands, pancreas, ovaries, and testes. The pituitary gland is called the "master gland" as it controls other glands via releasing hormones. Hormones produced include insulin, glucagon, estrogen, progesterone, testosterone, cortisol, thyroid hormones, and others which regulate growth, metabolism, sexual development, and stress responses.Endocrine system and its glands, functions, location and other abnormalities
Endocrine system and its glands, functions, location and other abnormalitiesJeraldelEncepto
╠²
The document provides information about the endocrine system and its glands/hormones. It includes learning objectives about the endocrine glands and their functions. There are also activities that have students identify endocrine glands and hormones, describe their functions, and answer questions about various glands and conditions related to hormone imbalances or deficiencies.1s3l9rkh0_THE-ENDOCRINE-SYSTEM-SCIENCE.pdf
1s3l9rkh0_THE-ENDOCRINE-SYSTEM-SCIENCE.pdfPreciousRoxas
╠²
The endocrine system is a complex network of glands and organs that uses hormones to control and coordinate the body's metabolism, energy levels, reproduction, growth and development, and stress response. It has 10 major parts including the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, thyroid gland, parathyroid gland, adrenal glands, pancreas, and ovaries or testes. The endocrine system maintains homeostasis through hormone signals that travel through the bloodstream and tell organs and tissues what to do. Proper care of the endocrine system includes exercise, a nutritious diet, regular medical checkups, and consulting a doctor before taking supplements.Endocrine glands
Endocrine glandsravibio
╠²
The document discusses the endocrine system and its glands. It notes that the endocrine system uses hormones to regulate body functions, while the glands produce and release hormones like the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, thyroid gland, parathyroid gland, adrenal glands, pancreas, ovaries and testes. It then covers hormone functions, how they work, conditions that can disrupt hormone levels, potential causes and treatment options.SCIENCE 10 LESddhjsjkskldjjdjdjnSON 14.pdf
SCIENCE 10 LESddhjsjkskldjjdjdjnSON 14.pdfchilde7
╠²
The endocrine system consists of glands that secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream, regulating various bodily functions such as metabolism, growth, and mood. Key glands include the pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal glands, and reproductive glands, each releasing specific hormones that impact target tissues. The system operates through feedback mechanisms, primarily negative feedback to maintain homeostasis, with positive feedback playing a role in events like childbirth.Endocrine system
Endocrine systemmalkeetsingh104
╠²
The endocrine system regulates body functions through hormone secretion. It consists of glands that secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream, affecting distant target organs. The major endocrine glands include the pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, pancreas, gonads, and pineal glands. Each gland secretes specific hormones that control processes like growth, metabolism, sexual development, and stress response, maintaining homeostasis throughout the body.ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
ENDOCRINE SYSTEMshakuntala kadam
╠²
The endocrine system consists of glands that secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream. The major endocrine glands include the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, thyroid gland, parathyroid glands, adrenal glands, pancreas, ovaries, and testes. Hormones act as chemical messengers to regulate physiological functions like growth and metabolism. A feedback mechanism controls hormone production and release to maintain homeostasis.Endocrine System
Endocrine SystemDana Tuazon
╠²
The endocrine system consists of glands that regulate vital functions through the secretion of hormones. It works closely with the nervous system to control mood, growth, metabolism, and reproduction. The major glands include the hypothalamus, pituitary, thyroid, parathyroids, adrenals, pancreas, ovaries, and testes. Hormones communicate instructions between glands and target cells to influence numerous bodily processes and maintain homeostasis.Endocrine System. Endocrine glands , types,hormone and functions
Endocrine System. Endocrine glands , types,hormone and functionsSudha Sudha
╠²
The endocrine system is a network of glands that produce hormones to regulate various bodily functions, such as metabolism, growth, and reproduction. Key glands include the hypothalamus, pituitary, thyroid, adrenal glands, and pancreas, each producing specific hormones that affect target organs and tissues. Hormones can be classified into peptide, steroid, and amine types, each with unique properties and mechanisms of action.endocrine system
endocrine systemPriyaSoni93
╠²
The document discusses the human endocrine system. It provides definitions of hormones and describes the major endocrine glands and their roles. The endocrine glands include the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, thyroid gland, parathyroid gland, adrenal glands, pancreas, ovaries, and testes. The hypothalamus and pituitary gland control the other endocrine glands by producing releasing and inhibiting hormones. The endocrine glands secrete hormones like insulin, estrogen and testosterone to regulate processes throughout the body, including growth and development, metabolism, and reproduction.Physiology of Endocrine System
Physiology of Endocrine System PRANJAL SHARMA
╠²
The document provides an extensive overview of the endocrine system, detailing its structure, function, and the hormones produced by various glands such as the pituitary, thyroid, adrenal, pancreas, ovaries, and testes. It discusses the history of endocrinology, major discoveries, and the roles of hormones in regulating bodily functions and maintaining homeostasis. Furthermore, it explains hormonal secretion control mechanisms, the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis, and the impact of various hormones on physiological processes.Endocrine
EndocrineNandhini Podamekala
╠²
The endocrine system is comprised of glands that secrete hormones to regulate various bodily functions such as metabolism, growth, reproduction, sleep, and mood. The major endocrine glands include the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, thyroid gland, parathyroid glands, adrenal glands, pancreas, and ovaries/testes. These glands secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream to regulate distant target organs, unlike exocrine glands which secrete substances through ducts.More from BaltazarRosales1 (17)
mirrorrs, concave convex. formula solution
mirrorrs, concave convex. formula solutionBaltazarRosales1
╠²
The document provides tips to reduce gadget exposure, including setting screen time limits, creating gadget-free zones, and engaging in offline activities. It discusses the effects of various types of radiation, emphasizing that long exposure to harmful radiation can lead to health issues. Additionally, it explains the laws of reflection and characteristics of images formed by plane mirrors.Biomolecules.pptxBiomolecules.pptxBiomolecules.pptx
Biomolecules.pptxBiomolecules.pptxBiomolecules.pptxBaltazarRosales1
╠²
Biomolecules are complex organic molecules essential for life, categorized into carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids. Carbohydrates serve as energy sources and structural components, proteins facilitate numerous cellular functions and reactions, lipids provide energy storage and cell membrane structure, while nucleic acids contain genetic information and direct protein synthesis. Each class of biomolecules is composed of specific elements and structural units, highlighting their critical roles in biological systems.BOYLES LAW.pptx jhghjghghjgjkggghghghghgg
BOYLES LAW.pptx jhghjghghjgjkggghghghghggBaltazarRosales1
╠²
Boyle's Law, established by Robert Boyle in 1662, describes the inverse relationship between gas volume and pressure at constant temperature. The document covers essential properties of gases including pressure, volume, and temperature, with standard units and conversion factors provided. Additionally, it includes various theoretical problems and examples demonstrating the application of Boyle's Law in calculating gas behavior under changing conditions.science 9.. chemistry.pptxjbjhjjkjhkjhjkhjkh
science 9.. chemistry.pptxjbjhjjkjhkjhjkhjkhBaltazarRosales1
╠²
This document discusses the key principles of electron configuration: the Pauli Exclusion Principle limits each orbital to two electrons spinning in opposite directions; Hund's Rule states that orbitals in a sublevel are filled with unpaired electrons before pairing occurs; and the Aufbau Principle builds an atom's configuration by adding electrons into orbitals of increasing energy, such as filling n=1 before n=2. Noble gas notation is also mentioned.electronic configuration.pptx ghjjkgjhjhklh
electronic configuration.pptx ghjjkgjhjhklhBaltazarRosales1
╠²
Electron configuration is the systematic arrangement of electrons in an atom's energy levels and sublevels. The Pauli Exclusion Principle limits each orbital to two electrons with opposite spins. Hund's Rule states that for a given sublevel, electrons occupy orbitals singly with parallel spins before pairing. The Aufbau Principle shows that electrons fill lower energy orbitals before higher ones.PARTS OF MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM.pptxvhgg
PARTS OF MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM.pptxvhggBaltazarRosales1
╠²
The document summarizes the major parts of the male reproductive system, including the scrotum, testes, epididymis, vas deferens, ejaculatory duct, urethra, and penis. It describes the development and maturation of sperm cells within the testes and along the epididymis, vas deferens, and ejaculatory duct. It also explains that testosterone is the main male sex hormone responsible for male sexual development and characteristics.OCCURENCE OF EVOLUTION.pptx how does evolution happens
OCCURENCE OF EVOLUTION.pptx how does evolution happensBaltazarRosales1
╠²
This document discusses several key concepts related to the occurrence and mechanisms of evolution:
1. It outlines Jean Baptiste de Lamarck and Charles Darwin's influential theories of evolution, including Lamarck's theories of need, use and disuse, and acquired characteristics as well as Darwin's theory of natural selection.
2. It explores the genetic basis of evolution through concepts like population genetics, gene flow, allele frequencies, non-random mating, and the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium.
3. It examines various evolutionary patterns such as natural selection, genetic drift, speciation, punctuated equilibrium, microevolution, coevolution, convergent evolution, and adaptive radiation.EVIDENCE OF EVOLUTION.pptx history of evolution
EVIDENCE OF EVOLUTION.pptx history of evolutionBaltazarRosales1
╠²
This document provides evidence of evolution through figures showing similarities in human and animal anatomy. Figure 6 shows the human digestive system with the appendix. Figure 7 shows a snake pelvis bone with a reduced hind limb. Figures 8 and 8B show that early embryonic stages and advanced embryos of different vertebrates share similar structures, providing evidence they evolved from a common ancestor.NERVOUS SYSTEM.pptx tdtffykgygigguiggugiug
NERVOUS SYSTEM.pptx tdtffykgygigguiggugiugBaltazarRosales1
╠²
The nervous system is composed of two main divisions - the central nervous system consisting of the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system consisting of nerves that connect to all parts of the body. It coordinates feedback mechanisms through the peripheral and central nervous systems to maintain homeostasis in the body. The nervous system regulates internal processes like temperature, hunger, and organ function to keep the body's conditions stable.MUTATION.pptx learn different ways of mutation how does it happen
MUTATION.pptx learn different ways of mutation how does it happenBaltazarRosales1
╠²
The DNA is used to complete protein synthesis which has two stages - transcription and translation. During translation at the ribosome, messenger RNA sequences are read and translated into amino acids which then form proteins. A mutation is a change in the DNA sequence that can occur either from mistakes when DNA copies or environmental factors like UV light and smoking, and takes place during DNA replication which can then cause abnormal transcription into mRNA.PROTIEN SYNTHESIS.pptx help to understand the process of protien synthesis
PROTIEN SYNTHESIS.pptx help to understand the process of protien synthesisBaltazarRosales1
╠²
DNA contains genetic codes made up of nucleotide bases that are arranged in triplets to code for amino acids. RNA carries these genetic codes from DNA and uses them to assemble amino acids into proteins according to the code. Together, DNA and RNA work through this process of protein synthesis to produce the proteins specified by the genetic code.festival Dancing and Fitness.pptx........
festival Dancing and Fitness.pptx........BaltazarRosales1
╠²
The FITT principle provides an acronym to describe exercise parameters: Frequency refers to the number of weekly sessions; Intensity indicates the difficulty level which can be light, moderate, or vigorous; Time is the duration of each session; and Type specifies the mode of exercise or activity.The Fundamental Body Movements.pptx GFGF
The Fundamental Body Movements.pptx GFGFBaltazarRosales1
╠²
Fundamental body movements are the basic building blocks for more complex physical activities like sports and dancing. They include locomotor movements that move the body through space, such as walking, running, and hopping, as well as non-locomotor movements that involve movement of body parts without traveling, like bending, twisting, and swinging. Students must master fundamental movements like dribbling and kicking during early childhood in order to participate in physical activities as they grow older. The document outlines the main categories and examples of fundamental locomotor and non-locomotor movements, as well as elements of rhythm, space, and qualities of movement important for dance.Myself on Street and Hip-hop Dances.pptx
Myself on Street and Hip-hop Dances.pptxBaltazarRosales1
╠²
1. The document introduces the importance of active recreation for achieving a healthy body and discusses street and hip-hop dances.
2. It provides a series of true/false statements to test the reader's knowledge of concepts like rate of perceived exertion, vigorous vs. passive activities, nutrition, and more.
3. The reader is then asked to identify which physical activities can help sustain fitness by writing "YES" or "NO" next to each one listed, such as watching TV, playing volleyball, eating fruits/veggies, dancing, etc.ARTS 9 L1.pptxHJFJLSKJFKSJGKSDJGKSJJIRJGIJIG
ARTS 9 L1.pptxHJFJLSKJFKSJGKSDJGKSJJIRJGIJIGBaltazarRosales1
╠²
This document discusses media-based arts and design in the Philippines. It notes that photography is considered both a tool for communication and an art form. The document outlines key elements of filmmaking such as the director, actors, cinematography, editing, production design. It also briefly mentions notable Philippine photographers and filmmakers.ART NEOCLASSICISM AND ROMANTISMISISM.pptx
ART NEOCLASSICISM AND ROMANTISMISISM.pptxBaltazarRosales1
╠²
Neoclassicism and Romanticism were artistic periods between the late 18th and early 19th centuries that had distinct characteristics and elements. Neoclassicism took inspiration from Ancient Greek and Roman art, emphasizing historical accuracy and order. Romanticism was an emotional reaction that celebrated nature and heightened sensations through dramatic compositions. Both periods influenced painting, sculpture, and architecture styles during this time.asexual reproduction ppt.pptx
asexual reproduction ppt.pptxBaltazarRosales1
╠²
This document defines asexual reproduction and describes its various types. It explains that asexual reproduction involves a single parent producing offspring that are genetically identical. Various types of asexual reproduction are described, including fission, fragmentation, budding, parthenogenesis, spore production, and vegetative propagation. Examples of each type are provided. The objectives are to define asexual reproduction, describe its different types, and classify organisms by their reproductive methods.Ad
Recently uploaded (20)
Deconstruction Analysis The adventure of devil's foot by Sir Arthur Conan Doyle
Deconstruction Analysis The adventure of devil's foot by Sir Arthur Conan Doylestaverechard
╠²
Arthur Conan Doyle (1859-1930) was a Scottish writer and physician who is widely recognized as the creator of the legendary detective character, Sherlock Holmes. Born in Edinburgh, Doyle studied medicine at the University of Edinburgh, where he began writing short stories in his spare time. Although he initially worked as a doctor, his name became widely known when he published the Sherlock Holmes stories, starting with A Study in Scarlet (1887). (Sakula,1997). Sherlock Holmes and Dr. Watson are on holiday in Cornwall, seeking rest for Holmes. They become involved in a mysterious case involving the deaths and madness of the Tregennis family. One sister dies with a terrified expression, while the two brothers are found insane. Holmes discovers that a rare West African poison called "DevilŌĆÖs Foot" was used, which affects the mind. The murderer is ultimately revealed to be Dr. Leon Sterndale, an explorer and relative of the family, who takes justice into his own hands. How STEM Labs Are Revolutionizing Education
How STEM Labs Are Revolutionizing Educationyashfotonvr
╠²
This PowerPoint presentation explores the concept and significance of STEM Labs in modern education. Based on the comprehensive blog by FotonVR, it delves into what STEM labs are, their growing importance in bridging theoretical knowledge with real-world application, and how they foster essential 21st-century skills.
The presentation outlines:
What defines a STEM Lab and how it supports hands-on learning in science, technology, engineering, and math.
The key components of an effective STEM lab, including learning tools like robotics kits, AR/VR devices, and collaborative environments.
A breakdown of the various types of STEM labsŌĆöfrom coding and robotics labs to VR-enabled and maker spaces.
The benefits of integrating STEM labs into schools, such as enhanced creativity, critical thinking, and adaptive learning.
The pivotal role of AR and VR technologies in making STEM education immersive and engaging.
Perfect for educators, school leaders, and edtech enthusiasts, this presentation provides insights into creating future-ready learning environments powered by innovation and interactivity.
¤öŚ Read the full blog here: https://fotonvr.com/stem-labs-importance-components-types-benefits
GBSN__Unit 2 - Control of Microorganisms
GBSN__Unit 2 - Control of MicroorganismsAreesha Ahmad
╠²
Microbiology for Nursing students - According to New PNC course curriculum - 2025
Role of Glutamate, glutamine and Alanine in Transport of Ammonia in Tissues
Role of Glutamate, glutamine and Alanine in Transport of Ammonia in TissuesTayyab
╠²
This slide explains the roles of Glutamate, Glutamine, and Alanine in safely transporting toxic ammonia from tissues to the liver and kidneys, where it is detoxified or excreted."Introduction to solar panel and about solar on grid
Introduction to solar panel and about solar on gridvardhanreddypuli06
╠²
This ppt is about the solar panels and its type called solar on grid.This ppt has some animated slides in it about the future of solar on grid and how it works,what are the components of solar on grid and where we use them and how we use them in better way .so that it becomes an environment friendly for usCloud Collaboration Market Challenges, Drivers, Trends, and Forecast by 2031
Cloud Collaboration Market Challenges, Drivers, Trends, and Forecast by 2031moresonali406
╠²
The report is segmented by Component (Solution, Service); Deployment (Private Cloud, Public Cloud, Hybrid Cloud); Organization Size (Large Enterprises, Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs)); Vertical (BFSI, Consumer Goods And Retail, Education, Government and Public Sector, Healthcare and Life Sciences, Manufacturing, Media and Entertainment, Telecommunication and ITES, Others). The global analysis is further broken-down at regional level and major countries. The report offers the value in USD for the above analysis and segmentsMatt Ridley: Economic Evolution and Ideas that have Sex
Matt Ridley: Economic Evolution and Ideas that have SexConservative Institute / Konzervat├Łvny in┼Ītit├║t M. R. ┼Ātef├Īnika
╠²
Matt Ridley is a British independent science popularizer, journalist, entrepreneur, and author of several bestselling books, for which he has received numerous awards. He focuses primarily on the economic, biological, and environmental dimensions of the spontaneous functioning and advancement of human society. TISSUE TRANSPLANTATTION and IT'S IMPORTANCE IS DISCUSSED
TISSUE TRANSPLANTATTION and IT'S IMPORTANCE IS DISCUSSEDPhoebeAkinyi1
╠²
Tissue transplant in immunologyScience Holiday Homework (interesting slide )
Science Holiday Homework (interesting slide )aryanxkohli88
╠²
science holiday homework
good for childrenPrimary and Secondary immune modulation.pptx
Primary and Secondary immune modulation.pptxdevikasanalkumar35
╠²
Primary and secondary immune modulation
Molecular biology and pellet weight marked
Molecular biology and pellet weight markednandanitiwari82528
╠²
DNA REPLICATION in prokaryotic organismsMatt Ridley: Economic Evolution and Ideas that have Sex
Matt Ridley: Economic Evolution and Ideas that have SexConservative Institute / Konzervat├Łvny in┼Ītit├║t M. R. ┼Ātef├Īnika
╠²
Ad
The Endocrine System.pptx GFTFTFYFUYUYYUY
- 1. The Endocrine System ŌĆó After going through this lesson, you are expected to: ŌĆó 1. identify the major endocrine glands in the body and their functions; ŌĆó 2. identify which gland is involved in a dysfunction; and ŌĆó 3. explain the effect of hormonal imbalance
- 2. Direction: Read each of the following riddles and decide which part of the endocrine system is being described. Choose the CAPITAL LETTER of the correct answer. A. Pituitary gland E. Adrenal gland B. Thyroid gland F. Pancreas C. Parathyroid gland G. Testes D. Thymus gland H. Ovaries 1. I secrete a hormone which helps to stimulate the lymphoid cells to produce T cells. I am the vanishing gland. You need me most during your early childhood years and I begin to disappear when you reach puberty. I am a member of the endocrine system and lymphatic system. Who am I? 2. I am a good friend of the sympathetic nervous system and I play a role in preparing your body to handle emergencies. There are two of me in your body and I help you decide whether to fight or flight. Who am I? 3. You can thank me for all the muscles you have and your deep voice. I am also the reason why you shave every day. I play a role in reproduction by allowing you to produce sperm cells. Who am I? 4. I control your mood. I control how sweet you are. I keep your blood sugar within the normal limits. If your blood sugar is too high, I produce insulin and if it is too low, I produce glucagon. I also play a role in your digestion. Who am I? D 5. I am very tiny but I do a lot of tasks in your endocrine system. I help you grow and develop. I provide milk for nursing moms. The back part of me helps maintain the balance of water in your body. Moreover, when I release my hormone oxytocin, it will cause the uterus to contract so a new life can be born. Who am I? 6. Many people say I am shaped like a butterfly. I increase metabolism. Mental and physical activities are also influenced by me. Who am I?
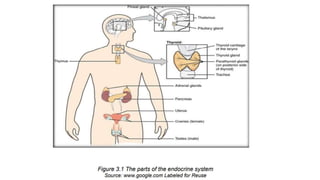
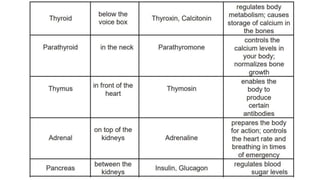
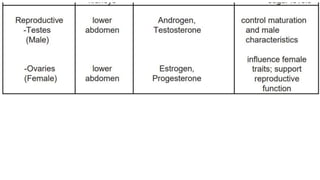
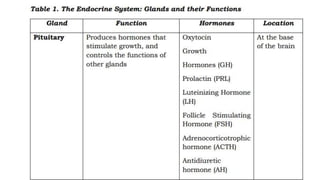
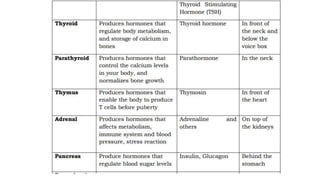
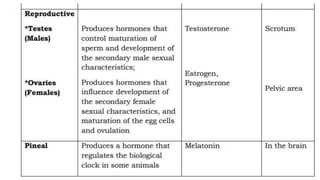
- 3. The Endocrine System ’āś The endocrine system is composed of different glands which secrete hormones that regulate metabolism, growth and development, mood, and reproduction. Hormones are organic substances released by the glands of the endocrine system directly into the bloodstream. ’āś Hormones are capable of changing the physiological and metabolic behaviors of their target cells to maintain homeostasis. The major endocrine glands in the body ’üČ pituitary, ’üČ thyroid, ’üČ parathyroid, ’üČ thymus, ’üČ adrenal, ’üČ pancreas, ’üČ ovaries, ’üČ testes.
- 5. Functions of the Hormones ’āśHormones help regulate body processes such as growth, development, metabolism, and response to stimuli. They are like chemical messengers that transport a signal from one cell to another. ’āśBoth men and women produce hormones in the same areas with one exception, the reproductive glands. Extra male hormones are produced in the testes while female hormones are produced in the ovaries ’āś Some hormones have short-term effects while other hormones have influence even in the long term such as those that control our growth and the changes at the onset of puberty. ’āśDuring puberty, there are many hormonal changes that happen in your body. One moment you are laughing, and then suddenly, you feel like crying. Sudden mood swings are relatively caused by the increasing amount of hormones in the body at this stage.
- 6. ’āśAnother significant fact about hormones is that they act in very small amounts. If the organ and hormones do not produce the regulated amount of chemicals to your body, it may result to an abnormality. This condition is called hormonal imbalance. An increase or decrease in the hormonal amount may have a significant effect to the body.
- 12. Endocrine System Disorder Hormonal imbalance will occur if the organs and hormones of your body do not produce the right amount of chemicals needed which in turn may lead to some dysfunctions. The following are some examples of endocrine disorders. Osteoporosis is a disease that happens when the mineral density of the bone is reduced making it brittle and porous. Parathyroid hormone secretion is one of the possible causes of this disease. Goiter is an abnormal enlargement of the thyroid gland. It results from the underproduction or overproduction of thyroid hormones. Gigantism is a disorder that happens during childhood when there is abnormal increase in height associated with too much secretion of growth hormones. Dwarfism is a condition wherein the production of growth hormones in the pituitary gland is insufficient resulting in short stature.
- 13. ’āśDuring an emergency, can you still recall how the ambulance driver coped with the situation by driving efficiently? What do you think is the hormone responsible for this? Adrenalin is the emergency hormone which helps the driver respond quickly and accordingly.
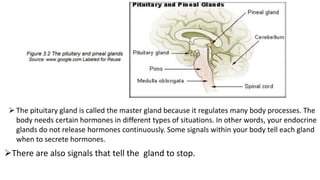
- 14. ’āśThe pituitary gland is called the master gland because it regulates many body processes. The body needs certain hormones in different types of situations. In other words, your endocrine glands do not release hormones continuously. Some signals within your body tell each gland when to secrete hormones. ’āśThere are also signals that tell the gland to stop.
- 17. Guide Questions A. Fill in the blanks to make the statements correct. 1. Which gland controls the other glands in the body? The ______________ controls the output of the other glands in the body. 2. Which gland is located below the voice box? The ______________ is located below the voice box. 3. Which gland is located on the thyroid glands? The ______________ is located on the thyroid glands and produces parathormone that increases blood calcium levels and normalizes bone growth. 4. Which gland produces parathormone? The ______________ produces parathormone that increases blood calcium levels and normalizes bone growth. 5. Which organ is involved when the blood sugar becomes unstable? The ______________ is involved when blood sugar level becomes unstable.
- 18. 6. Which gland produces T-cells? The ______________ enables the body to produce T- cells that help in fighting infections and diseases. 7. Which gland can develop the adaptive immune system? A person born without a ______________ will not develop an adaptive immune system and may eventually die. 8. Which gland enables the body to produce energy? The ______________produces adrenaline that enables the body to have the energy in doing spontaneous work during emergency situations. 9. What type of pills control the functioning of the ovaries and uterus? ______________ pills contain hormones that control the functioning of the ovaries and the uterus. 10. What hormones are responsible for milk production? ______________ and ______________ enable milk production which provides the needed nourishment of a baby.