OpenCR б„Ӣб…Ўб„ғб…®б„Ӣб…өб„Ӯб…© б„‘б…ҘбҶ·б„Ӣб…°б„Ӣб…Ҙб„Җб…ўб„Үб…ЎбҶҜ
3 likes3,827 views
м ң5нҡҢ мҳӨлЎңм№ҙ м„ёлҜёлӮҳ л°ңн‘ңмһҗлЈҢ
1 of 25
Downloaded 52 times

















Ad
Recommended
LTE Training Course
LTE Training CourseChiehChun
Мэ
The document discusses an LTE training course agenda presented by the OAI Project Team. It covers topics including LTE overview, channels in LTE, cell search procedure, system information, and random access procedure. For each topic, it provides outlines, descriptions, and diagrams. The random access procedure section explains its main purpose is to achieve uplink synchronization and assign a unique UE identifier C-RNTI.3GPP Packet Core Towards 5G Communication Systems
3GPP Packet Core Towards 5G Communication SystemsOfinno
Мэ
The document provides an overview of the 5G system architecture, highlighting key components such as network slicing, support for edge computing, and notable protocol changes. It details various network functions including access management, session management, and user plane functions within the 5G core network structure. The significance of 5G is emphasized in terms of enhanced connectivity, capacity, and diverse use cases like IoT and mission-critical communication.FTTH Network Structure
FTTH Network StructureKHNOG
Мэ
This document discusses Fiber To The Home (FTTH) network structures. It describes two common FTTH structures: point-to-point fiber, where a dedicated fiber line runs from the service provider directly to each customer; and shared fiber core, where a splitter divides a single fiber line to serve multiple customers. The key devices for shared fiber core FTTH are the Optical Line Termination (OLT) located at the service provider, the Optical Network Unit (ONU) located at each customer site, and splitters to divide the fiber lines. Diagrams and pictures are provided to illustrate how these components connect in each type of FTTH network structure.LTE (Long Term Evolution) Introduction
LTE (Long Term Evolution) IntroductionGuisun Han
Мэ
The document provides a comprehensive overview of Long Term Evolution (LTE), detailing its introduction, protocol layers, and System Architecture Evolution (SAE). It highlights the objectives of LTE, including increased data rates and improved spectral efficiency, as well as the core components and functions within the architecture such as the evolved packet core (EPC) and protocols like Non Access Stratum (NAS). Additionally, it outlines various management procedures and elements essential for user equipment connectivity and mobility management within LTE networks.Radio Network Design & Roll Out
Radio Network Design & Roll OutRathnaKumar47
Мэ
This document provides an overview of radio network design for rollouts, including configuration of parameter structures, site configuration, mobility configuration, and neighbors configuration. It discusses organizing parameters into managed object classes with a hierarchical structure. Major sections cover defining radio modules and cells, antenna line configuration, frequency configuration, and adding new objects. Configuration of idle and connected mode mobility parameters and system information blocks is also addressed.MPLS Deployment Chapter 1 - Basic
MPLS Deployment Chapter 1 - BasicEricsson
Мэ
The document provides an overview of Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS), detailing its functionality, benefits, and challenges in telecommunications networks. It discusses how MPLS directs data using short path labels and supports various access technologies, alongside outlining specific protocols like LDP and RSVP. Additionally, it presents a network design example for a Cisco-based MPLS core network, highlighting redundancy and regional topology considerations.SRAN8.0 GSM Multi-mode Feature Description.pdf
SRAN8.0 GSM Multi-mode Feature Description.pdfSokrates5
Мэ
This document describes features for GSM multi-mode networks including:
1. Dynamic power sharing between GSM and UMTS carriers to improve utilization of power amplifiers.
2. Dynamic spectrum sharing whereby idle GSM spectrum resources can be allocated to UMTS based on service loads to improve network throughput.
3. Multi-mode RRU/RFU star connection with separate CPRI interfaces to allow concurrent operation of GSM and UMTS without impacting each other.LTE EPC Technology Essentials
LTE EPC Technology EssentialsHussien Mahmoud
Мэ
The document provides an overview of a workshop on LTE/EPC technology essentials led by Hussien Mahmoud, aimed at participants with basic knowledge of packet core foundations. It covers the architecture and functionalities of LTE-EPC, including network design, call flows, mobility management, and security features. The workshop emphasizes the importance of understanding both user and control plane interfaces within the LTE-EPC framework.MPLS Presentation
MPLS PresentationUnni Kannan VijayaKumar
Мэ
The document provides an introduction to MPLS (Multi-Protocol Label Switching) technology. It discusses the goals of MPLS including understanding the business drivers, market segments, problems addressed, benefits, and major components. The key components of MPLS technology are explained, including MPLS forwarding and signaling, label distribution protocols, MPLS network services like VPNs, QoS, and traffic engineering. An overview of typical MPLS applications is also provided.Boucle local cuivre.pptxMohamedAyour
Мэ
Le document traite des Г©lГ©ments essentiels d'un rГ©seau tГ©lГ©phonique, en se concentrant sur les rГ©partiteurs, sous-rГ©partiteurs et points de concentration qui assurent les connexions entre les diffГ©rentes lignes. Il dГ©crit Г©galement les cГўbles nГ©cessaires Г ces connexions, incluant les cГўbles de branchement et multi-paires, ainsi que leurs spГ©cifications techniques. Enfin, il aborde la structure des conducteurs et leur identification Г travers un systГЁme de nomenclature.LTE Call Processing and Handover
LTE Call Processing and HandoverSitha Sok
Мэ
The document outlines the architecture and software components of a Long-Term Evolution (LTE) network, including details on the Evolved Universal Terrestrial Radio Access Network (E-UTRAN) and protocols for call processing. It describes the various call software blocks, interfaces, and key procedures for establishing connections, including attach and detach processes, measurement reporting, and handover procedures. Additionally, it provides configuration guidelines for managing parameters related to the LTE system and neighboring cells.Optical network architecture
Optical network architectureSiddharth Singh
Мэ
This document provides a seminar report on optical network architecture presented by Siddharth Singh at JSS Mahavidyapeetha. It begins with acknowledging those who helped and guided in completing the report. The abstract provides an overview of optical networks and how they provide high bandwidth through technologies like DWDM and routing/grooming at the wavelength level. It discusses network architectures like SONET, PONs, and topologies like bus, star and tree. The report is divided into chapters covering topics like DWDM systems, synchronous optical networking, PON history and elements, and network topologies.Presentation of optical fiber connector
Presentation of optical fiber connectorMaulik Sanchela
Мэ
Optical fiber connectors are used to join optical fibers where connections need to be made and undone. There are several types of optical fiber connectors that are commonly used, including SC, ST, FC, LC, MT-RJ, MU, and SMA connectors. The document discusses the key features and applications of each connector type. SC and LC connectors are now most widely used due to their low cost and ease of use. Proper connector selection depends on the application and fiber type (multimode or singlemode).Introduction to Evolved Packet Core Networks
Introduction to Evolved Packet Core NetworksInam Khosa
Мэ
The document discusses the System Architecture Evolution (SAE) and Evolved Packet Core (EPC) as the core network architecture for LTE wireless communication, highlighting its advantages such as improved data capacity, reduced latency, and lower operational costs. It describes key components, including the Mobility Management Entity (MME), Serving Gateway (SGW), Packet Data Network Gateway (PGW), and Policy Charging and Rules Function (PCRF), explaining their roles in managing user mobility and data flow. The document emphasizes the transition to an all-IP network to support higher throughput and lower latency in mobile broadband services.5G NR parameters
5G NR parametersSasi Reddy
Мэ
This document specifies 5G RRC parameters including message definitions and information elements for timers, counters, constants, and UE variables. It defines RRC messages that may be sent on different logical channels and provides descriptions of message fields. It also specifies bandwidth part configurations, measurement reporting, reconfiguration messages, and beam failure recovery resources.Neighbor guideline v1.0 rev
Neighbor guideline v1.0 revNurul Ihsands
Мэ
The document outlines guidelines for configuring LTE neighbor relationships in both Layer 2 to Layer 2 (L2L) and Layer 2 to UTRAN (L2U) settings to optimize LTE performance. Specific recommendations are provided for making neighbor relations across different sites, emphasizing the importance of maintaining optimal configuration practices such as frequency relations and priority settings. Additionally, it details parameters for importing and managing neighbor relations using U-net for effective system performance and planning.GSMA-VOLTE
GSMA-VOLTE Saurabh Verma
Мэ
This document provides guidelines for implementing Voice over LTE (VoLTE) services. It describes the VoLTE architecture including functional nodes and interfaces. It also provides call flows and requirements for deploying VoLTE within a single network, for interconnect between networks, and for roaming. Implementation guidelines cover areas such as devices, networks, IMS, Diameter signaling, security, charging and codecs. The document is intended to help operators deploy interoperable VoLTE services.Huawei eRAN 7.0 VoLTE feature deep dive_20140515.pptx
Huawei eRAN 7.0 VoLTE feature deep dive_20140515.pptxQasimQadir3
Мэ
The document describes various enhanced features for VoLTE including TTI bundling, ROHC, semi-persistent scheduling, and delay-based scheduling. It provides details on how these features work, when they are triggered, parameters used, and key performance indicators. The enhanced features aim to improve coverage, capacity, and quality of VoLTE services over LTE networks.BitVisor Summit 11гҖҢ2. BitVisor on Aarch64гҖҚ
BitVisor Summit 11гҖҢ2. BitVisor on Aarch64гҖҚBitVisor
Мэ
The document discusses the implementation and operations of Bitvisor on AArch64 architecture, detailing requirements, virtual machine monitor (VMM) workings, initialization, and interrupt handling. Key elements include ARM virtualization host extensions, interrupt injection, and memory management strategies. It also covers limitations, ongoing tasks, and findings from QEMU bugs.An Overview of Border Gateway Protocol (BGP)
An Overview of Border Gateway Protocol (BGP)Jasim Alam
Мэ
BGP is the exterior gateway protocol that connects autonomous systems on the internet. It uses distance vector routing and TCP to establish connections between routers in different autonomous systems to exchange routing and reachability information. BGP messages advertise routing prefixes, paths, and policies between autonomous systems. Routers maintain BGP routing tables containing routes and their attributes to determine the best paths for traffic. As the number of autonomous systems and routing entries has increased, challenges around scaling the routing system remain an area of ongoing work.FIBRA Г“PTICA TECNOLOGIA GPONWELLINGTON MARTINS
Мэ
Este documento descreve a tecnologia GPON aplicada Г implantação de redes FTTH em condomГӯnios, fornecendo serviГ§os de voz, dados e imagem com taxa de atГ© 2,5 Gbps. Detalha o funcionamento da Rede Г“ptica Passiva sem equipamentos ativos no enlace entre cliente e prestador, permitindo uma rede de baixo custo. Apresenta tambГ©m o histГіrico e desenvolvimento da fibra Гіptica e redes passivas.Best practices in synchronizing IP-based packet broadcasting networks
Best practices in synchronizing IP-based packet broadcasting networksADVA
Мэ
- Consistent time synchronization is critical for broadcasting over IP networks, as standards like SMPTE 2059 and AES67 use IEEE 1588 PTP to timestamp audio and video streams.
- SMPTE 2059 generates timing signals aligned to the SMPTE epoch and transports them over IP using PTP, enabling aligned audio, video, and metadata streams over asynchronous IP networks.
- Relying solely on GNSS for timing poses availability risks, so combining GNSS with network timing provides greater accuracy and resiliency through technologies like SyncE and redundant master clocks.Paging in LTE
Paging in LTESurya Munda
Мэ
The document provides an overview of the paging procedures in LTE, detailing processes governed by the RRC and NAS layers, and discusses various paging scenarios like s-tmsi, imsi, and cs fallback. It explains the structure of paging messages, including how to initiate paging and manage responses in different situations. Additionally, the document includes detailed examples and testing scenarios for validating the paging mechanism.Ericsson interview
Ericsson interviewSatish Jadav
Мэ
This document discusses jitter, latency, and delay in network communications. It provides definitions and explanations of these terms:
1. Jitter is the variation in the delay of received packets caused by network congestion, queuing, or errors, rather than packets being transmitted at an even pace. This can cause gaps in audio if packets are missing.
2. Delay and latency refer to the time it takes a bit to be transmitted from source to destination. Jitter is a type of delay that varies over time.
3. Solutions to reduce jitter include increasing the receive jitter buffer size and delay, using larger RTP packets, and lowering audio quality.Free Space Optics
Free Space OpticsBise Mond
Мэ
Free-space optics (FSO) is a line-of-sight wireless optical communication technology that uses light propagating in free space to transmit data between two points. It can transmit large amounts of data at speeds up to 2.5 Gbps over distances of several kilometers. Challenges include atmospheric effects such as fog, clouds, rain and building movement. Strict safety standards are in place since it uses invisible laser light. Potential applications include building-to-building networks, temporary networks, and communications between spacecraft. The future of FSO remains uncertain but prospects are increasing in space communications.Layer-2 VPN
Layer-2 VPNrosmida
Мэ
The document discusses Layer 2 VPN over MPLS, including concepts of Virtual Private Wire Service (VPWS) and Virtual Private LAN Service (VPLS). It covers characteristics of Layer 3 and Layer 2 VPNs and concepts of L2 VPN signaling using protocols like LDP and BGP. The document also provides examples of encapsulation and data flow for Ethernet over MPLS (EoMPLS) and Frame Relay over MPLS (FRoMPLS) L2 VPN services.GPON Introduction
GPON IntroductionRogelio Gomez
Мэ
This document discusses GPON (Gigabit Passive Optical Network) technology. It provides details on GPON network architecture and components like the OLT and ONT. It then analyzes competition between major GPON equipment vendors like Alcatel-Lucent, Huawei, ZTE, and Ericsson. Their key GPON products are described and example deployments listed. Finally, the document shows Huawei, ZTE, and Alcatel-Lucent have the largest shares of the global GPON market, together commanding over half of all GPON lines.volte call flow - SIP IMS Call Flow - MO and MT Call - Volte Mobile originati...
volte call flow - SIP IMS Call Flow - MO and MT Call - Volte Mobile originati...Vikas Shokeen
Мэ
This document discusses the call flow process for a VoLTE call between two parties (A and B) using an LTE network. It involves the following key steps:
1. Party A's IMS network sends an SIP INVITE message to Party B's IMS network with an SDP offer to initiate the call.
2. Resources are reserved on the LTE networks for both parties. SDP negotiations take place to agree on a codec.
3. Once resources are reserved and preconditions met, Party B's phone will ring. When answered, Party B sends a SIP 200 OK message to complete the call setup.
4. The media path is then established between the two partiesOSS SW Basics Lecture 14: Open source hardware
OSS SW Basics Lecture 14: Open source hardwareJeongkyu Shin
Мэ
Lectures on Open-source SW Basics 2016 - 14: Open source in research fieldsMore Related Content
What's hot (20)
MPLS Presentation
MPLS PresentationUnni Kannan VijayaKumar
Мэ
The document provides an introduction to MPLS (Multi-Protocol Label Switching) technology. It discusses the goals of MPLS including understanding the business drivers, market segments, problems addressed, benefits, and major components. The key components of MPLS technology are explained, including MPLS forwarding and signaling, label distribution protocols, MPLS network services like VPNs, QoS, and traffic engineering. An overview of typical MPLS applications is also provided.Boucle local cuivre.pptxMohamedAyour
Мэ
Le document traite des Г©lГ©ments essentiels d'un rГ©seau tГ©lГ©phonique, en se concentrant sur les rГ©partiteurs, sous-rГ©partiteurs et points de concentration qui assurent les connexions entre les diffГ©rentes lignes. Il dГ©crit Г©galement les cГўbles nГ©cessaires Г ces connexions, incluant les cГўbles de branchement et multi-paires, ainsi que leurs spГ©cifications techniques. Enfin, il aborde la structure des conducteurs et leur identification Г travers un systГЁme de nomenclature.LTE Call Processing and Handover
LTE Call Processing and HandoverSitha Sok
Мэ
The document outlines the architecture and software components of a Long-Term Evolution (LTE) network, including details on the Evolved Universal Terrestrial Radio Access Network (E-UTRAN) and protocols for call processing. It describes the various call software blocks, interfaces, and key procedures for establishing connections, including attach and detach processes, measurement reporting, and handover procedures. Additionally, it provides configuration guidelines for managing parameters related to the LTE system and neighboring cells.Optical network architecture
Optical network architectureSiddharth Singh
Мэ
This document provides a seminar report on optical network architecture presented by Siddharth Singh at JSS Mahavidyapeetha. It begins with acknowledging those who helped and guided in completing the report. The abstract provides an overview of optical networks and how they provide high bandwidth through technologies like DWDM and routing/grooming at the wavelength level. It discusses network architectures like SONET, PONs, and topologies like bus, star and tree. The report is divided into chapters covering topics like DWDM systems, synchronous optical networking, PON history and elements, and network topologies.Presentation of optical fiber connector
Presentation of optical fiber connectorMaulik Sanchela
Мэ
Optical fiber connectors are used to join optical fibers where connections need to be made and undone. There are several types of optical fiber connectors that are commonly used, including SC, ST, FC, LC, MT-RJ, MU, and SMA connectors. The document discusses the key features and applications of each connector type. SC and LC connectors are now most widely used due to their low cost and ease of use. Proper connector selection depends on the application and fiber type (multimode or singlemode).Introduction to Evolved Packet Core Networks
Introduction to Evolved Packet Core NetworksInam Khosa
Мэ
The document discusses the System Architecture Evolution (SAE) and Evolved Packet Core (EPC) as the core network architecture for LTE wireless communication, highlighting its advantages such as improved data capacity, reduced latency, and lower operational costs. It describes key components, including the Mobility Management Entity (MME), Serving Gateway (SGW), Packet Data Network Gateway (PGW), and Policy Charging and Rules Function (PCRF), explaining their roles in managing user mobility and data flow. The document emphasizes the transition to an all-IP network to support higher throughput and lower latency in mobile broadband services.5G NR parameters
5G NR parametersSasi Reddy
Мэ
This document specifies 5G RRC parameters including message definitions and information elements for timers, counters, constants, and UE variables. It defines RRC messages that may be sent on different logical channels and provides descriptions of message fields. It also specifies bandwidth part configurations, measurement reporting, reconfiguration messages, and beam failure recovery resources.Neighbor guideline v1.0 rev
Neighbor guideline v1.0 revNurul Ihsands
Мэ
The document outlines guidelines for configuring LTE neighbor relationships in both Layer 2 to Layer 2 (L2L) and Layer 2 to UTRAN (L2U) settings to optimize LTE performance. Specific recommendations are provided for making neighbor relations across different sites, emphasizing the importance of maintaining optimal configuration practices such as frequency relations and priority settings. Additionally, it details parameters for importing and managing neighbor relations using U-net for effective system performance and planning.GSMA-VOLTE
GSMA-VOLTE Saurabh Verma
Мэ
This document provides guidelines for implementing Voice over LTE (VoLTE) services. It describes the VoLTE architecture including functional nodes and interfaces. It also provides call flows and requirements for deploying VoLTE within a single network, for interconnect between networks, and for roaming. Implementation guidelines cover areas such as devices, networks, IMS, Diameter signaling, security, charging and codecs. The document is intended to help operators deploy interoperable VoLTE services.Huawei eRAN 7.0 VoLTE feature deep dive_20140515.pptx
Huawei eRAN 7.0 VoLTE feature deep dive_20140515.pptxQasimQadir3
Мэ
The document describes various enhanced features for VoLTE including TTI bundling, ROHC, semi-persistent scheduling, and delay-based scheduling. It provides details on how these features work, when they are triggered, parameters used, and key performance indicators. The enhanced features aim to improve coverage, capacity, and quality of VoLTE services over LTE networks.BitVisor Summit 11гҖҢ2. BitVisor on Aarch64гҖҚ
BitVisor Summit 11гҖҢ2. BitVisor on Aarch64гҖҚBitVisor
Мэ
The document discusses the implementation and operations of Bitvisor on AArch64 architecture, detailing requirements, virtual machine monitor (VMM) workings, initialization, and interrupt handling. Key elements include ARM virtualization host extensions, interrupt injection, and memory management strategies. It also covers limitations, ongoing tasks, and findings from QEMU bugs.An Overview of Border Gateway Protocol (BGP)
An Overview of Border Gateway Protocol (BGP)Jasim Alam
Мэ
BGP is the exterior gateway protocol that connects autonomous systems on the internet. It uses distance vector routing and TCP to establish connections between routers in different autonomous systems to exchange routing and reachability information. BGP messages advertise routing prefixes, paths, and policies between autonomous systems. Routers maintain BGP routing tables containing routes and their attributes to determine the best paths for traffic. As the number of autonomous systems and routing entries has increased, challenges around scaling the routing system remain an area of ongoing work.FIBRA Г“PTICA TECNOLOGIA GPONWELLINGTON MARTINS
Мэ
Este documento descreve a tecnologia GPON aplicada Г implantação de redes FTTH em condomГӯnios, fornecendo serviГ§os de voz, dados e imagem com taxa de atГ© 2,5 Gbps. Detalha o funcionamento da Rede Г“ptica Passiva sem equipamentos ativos no enlace entre cliente e prestador, permitindo uma rede de baixo custo. Apresenta tambГ©m o histГіrico e desenvolvimento da fibra Гіptica e redes passivas.Best practices in synchronizing IP-based packet broadcasting networks
Best practices in synchronizing IP-based packet broadcasting networksADVA
Мэ
- Consistent time synchronization is critical for broadcasting over IP networks, as standards like SMPTE 2059 and AES67 use IEEE 1588 PTP to timestamp audio and video streams.
- SMPTE 2059 generates timing signals aligned to the SMPTE epoch and transports them over IP using PTP, enabling aligned audio, video, and metadata streams over asynchronous IP networks.
- Relying solely on GNSS for timing poses availability risks, so combining GNSS with network timing provides greater accuracy and resiliency through technologies like SyncE and redundant master clocks.Paging in LTE
Paging in LTESurya Munda
Мэ
The document provides an overview of the paging procedures in LTE, detailing processes governed by the RRC and NAS layers, and discusses various paging scenarios like s-tmsi, imsi, and cs fallback. It explains the structure of paging messages, including how to initiate paging and manage responses in different situations. Additionally, the document includes detailed examples and testing scenarios for validating the paging mechanism.Ericsson interview
Ericsson interviewSatish Jadav
Мэ
This document discusses jitter, latency, and delay in network communications. It provides definitions and explanations of these terms:
1. Jitter is the variation in the delay of received packets caused by network congestion, queuing, or errors, rather than packets being transmitted at an even pace. This can cause gaps in audio if packets are missing.
2. Delay and latency refer to the time it takes a bit to be transmitted from source to destination. Jitter is a type of delay that varies over time.
3. Solutions to reduce jitter include increasing the receive jitter buffer size and delay, using larger RTP packets, and lowering audio quality.Free Space Optics
Free Space OpticsBise Mond
Мэ
Free-space optics (FSO) is a line-of-sight wireless optical communication technology that uses light propagating in free space to transmit data between two points. It can transmit large amounts of data at speeds up to 2.5 Gbps over distances of several kilometers. Challenges include atmospheric effects such as fog, clouds, rain and building movement. Strict safety standards are in place since it uses invisible laser light. Potential applications include building-to-building networks, temporary networks, and communications between spacecraft. The future of FSO remains uncertain but prospects are increasing in space communications.Layer-2 VPN
Layer-2 VPNrosmida
Мэ
The document discusses Layer 2 VPN over MPLS, including concepts of Virtual Private Wire Service (VPWS) and Virtual Private LAN Service (VPLS). It covers characteristics of Layer 3 and Layer 2 VPNs and concepts of L2 VPN signaling using protocols like LDP and BGP. The document also provides examples of encapsulation and data flow for Ethernet over MPLS (EoMPLS) and Frame Relay over MPLS (FRoMPLS) L2 VPN services.GPON Introduction
GPON IntroductionRogelio Gomez
Мэ
This document discusses GPON (Gigabit Passive Optical Network) technology. It provides details on GPON network architecture and components like the OLT and ONT. It then analyzes competition between major GPON equipment vendors like Alcatel-Lucent, Huawei, ZTE, and Ericsson. Their key GPON products are described and example deployments listed. Finally, the document shows Huawei, ZTE, and Alcatel-Lucent have the largest shares of the global GPON market, together commanding over half of all GPON lines.volte call flow - SIP IMS Call Flow - MO and MT Call - Volte Mobile originati...
volte call flow - SIP IMS Call Flow - MO and MT Call - Volte Mobile originati...Vikas Shokeen
Мэ
This document discusses the call flow process for a VoLTE call between two parties (A and B) using an LTE network. It involves the following key steps:
1. Party A's IMS network sends an SIP INVITE message to Party B's IMS network with an SDP offer to initiate the call.
2. Resources are reserved on the LTE networks for both parties. SDP negotiations take place to agree on a codec.
3. Once resources are reserved and preconditions met, Party B's phone will ring. When answered, Party B sends a SIP 200 OK message to complete the call setup.
4. The media path is then established between the two partiesSimilar to OpenCR б„Ӣб…Ўб„ғб…®б„Ӣб…өб„Ӯб…© б„‘б…ҘбҶ·б„Ӣб…°б„Ӣб…Ҙб„Җб…ўб„Үб…ЎбҶҜ (20)
OSS SW Basics Lecture 14: Open source hardware
OSS SW Basics Lecture 14: Open source hardwareJeongkyu Shin
Мэ
Lectures on Open-source SW Basics 2016 - 14: Open source in research fieldsмҳӨл Ңм§Җ ліҙл“ң мҶҢк°ң л°Ҹ м•„л‘җмқҙл…ё мҶҢк°ңмҷҖ к°„лӢЁн•ң м•„л‘җмқҙл…ёлҘј нҷңмҡ©н•ң мӢӨмҠөмқ„ мң„н•ң к°•мқҳ мһҗлЈҢ
мҳӨл Ңм§Җ ліҙл“ң мҶҢк°ң л°Ҹ м•„л‘җмқҙл…ё мҶҢк°ңмҷҖ к°„лӢЁн•ң м•„л‘җмқҙл…ёлҘј нҷңмҡ©н•ң мӢӨмҠөмқ„ мң„н•ң к°•мқҳ мһҗлЈҢcsleedk
Мэ
м•„л‘җмқҙл…ё мҶҢк°ңMCU(nanheekim)
MCU(nanheekim)Nanhee Kim
Мэ
@Powersupply(YeungnamUniv.) @NanheeKim @nh9k
м§Ҳл¬ёмқҙ мһҲмңјл©ҙ м–ём ңл“ м§Җ м—°лқҪмЈјм„ёмҡ”!
Please, feel free to contact me, if you have any questions!
github: https://github.com/nh9k
email: kimnanhee97@gmail.comм»өл“ңлЎ л©ҖнӢ°мҪҘн„° нҺҢмӣЁм–ҙ 분м„қ 2015. 3.28.
м»өл“ңлЎ л©ҖнӢ°мҪҘн„° нҺҢмӣЁм–ҙ 분м„қ 2015. 3.28.chcbaram
Мэ
м»өл“ңлЎ л©ҖнӢ°мҪҘн„° нҺҢмӣЁм–ҙ 분м„қ (http://oroca.org)б„Ңб…Ұ3б„’б…¬ б„Ӣб…©б„‘б…ібҶ« б„…б…©б„Үб…©б„җб…өбҶЁб„үб…і б„үб…Ұб„Ҷб…өб„Ӯб…Ў 1б„Ӣб…өбҶҜб„Һб…Ў 1б„үб…Ұб„үб…§бҶ« м•Ҳл“ңлЎңмқҙл“ң App нҶөмӢ
б„Ңб…Ұ3б„’б…¬ б„Ӣб…©б„‘б…ібҶ« б„…б…©б„Үб…©б„җб…өбҶЁб„үб…і б„үб…Ұб„Ҷб…өб„Ӯб…Ў 1б„Ӣб…өбҶҜб„Һб…Ў 1б„үб…Ұб„үб…§бҶ« м•Ҳл“ңлЎңмқҙл“ң App нҶөмӢ WooSangHwang
Мэ
б„Ңб…Ұ3б„’б…¬ б„Ӣб…©б„‘б…ібҶ« б„…б…©б„Үб…©б„җб…өбҶЁб„үб…і б„үб…Ұб„Ҷб…өб„Ӯб…Ў 1б„Ӣб…өбҶҜб„Һб…Ў 1б„үб…Ұб„үб…§бҶ« м•Ҳл“ңлЎңмқҙл“ң App нҶөмӢ [мһҗлҸҷ мҶҗм„ём •м ң нӮӨнҠё]мҠӨмјҖм№ҳ м„Өм№ҳк°Җмқҙл“ң
[мһҗлҸҷ мҶҗм„ём •м ң нӮӨнҠё]мҠӨмјҖм№ҳ м„Өм№ҳк°Җмқҙл“ңkocoafab
Мэ
мҪ”мҪ”м•„нҢ№ мҶҗм„ём •м ң нӮӨнҠё - мҠӨмјҖм№ҳ м„Өм№ҳк°Җмқҙл“ң[1C6]б„Ӣб…©б„‘б…ібҶ«б„үб…©б„үб…і б„’б…Ўб„ғб…іб„Ӣб…°б„Ӣб…Ҙ б„‘б…ібҶҜб„…б…ўбҶәб„‘б…©бҶ·б„Җб…Ә Node.jsб„…б…© б„Җб…®б„’б…§бҶ«б„’б…Ўб„Ӯб…ібҶ« IoT б„‘б…ібҶҜб„…б…ўбҶәб„‘б…©бҶ·
[1C6]б„Ӣб…©б„‘б…ібҶ«б„үб…©б„үб…і б„’б…Ўб„ғб…іб„Ӣб…°б„Ӣб…Ҙ б„‘б…ібҶҜб„…б…ўбҶәб„‘б…©бҶ·б„Җб…Ә Node.jsб„…б…© б„Җб…®б„’б…§бҶ«б„’б…Ўб„Ӯб…ібҶ« IoT б„‘б…ібҶҜб„…б…ўбҶәб„‘б…©бҶ·NAVER D2
Мэ
DEVIEW 2014 [1C6]мҳӨн”ҲмҶҢмҠӨ н•ҳл“ңмӣЁм–ҙ н”Ңлһ«нҸјкіј Node.jsлЎң кө¬нҳ„н•ҳлҠ” IoT н”Ңлһ«нҸјб„Ӣб…Ўб„ғб…®б„Ӣб…өб„Ӯб…©б„Ӣб…Ә Fpgaб„…б…ібҶҜ б„Ӣб…өб„Ӣб…ӯбҶјб„’б…ЎбҶ« б„…б…©б„Үб…©бҶәб„Ңб…Ұб„Ңб…ЎбҶЁ
б„Ӣб…Ўб„ғб…®б„Ӣб…өб„Ӯб…©б„Ӣб…Ә Fpgaб„…б…ібҶҜ б„Ӣб…өб„Ӣб…ӯбҶјб„’б…ЎбҶ« б„…б…©б„Үб…©бҶәб„Ңб…Ұб„Ңб…ЎбҶЁchcbaram
Мэ
м ң4нҡҢ мҳӨлЎңм№ҙ мҳӨн”ҲлЎңліҙнӢұмҠӨ м„ёлҜёлӮҳм•„л‘җмқҙл…ёкё°мҙҲ мҳӨн”Ҳк°•мқҳ1
м•„л‘җмқҙл…ёкё°мҙҲ мҳӨн”Ҳк°•мқҳ1м„ұкөӯ мһ„
Мэ
Arduino Open Lecture for Beginners. MOT.Eliot
Why people want arduino? It's time to think paradigm shift.[м—„л§Ҳм •м№ҳ л©”мқҙм»ӨнҢҖ] мІ« л§ҢлӮЁ
[м—„л§Ҳм •м№ҳ л©”мқҙм»ӨнҢҖ] мІ« л§ҢлӮЁyuna cho
Мэ
н•ңкөӯмқҳ 비мҳҒлҰ¬лӢЁмІҙ "м •м№ҳн•ҳлҠ”м—„л§Ҳл“Ө"мқҳ мҶҢлӘЁмһ„ <м•„л‘җмқҙл…ё л©”мқҙм»ӨнҢҖ>мқҳ мІ« лӘЁмһ„ мһҗлЈҢ мҠ¬лқјмқҙл“ңмһ…лӢҲлӢӨ.б„үб…©бҶ«б„Ӣб…іб„…б…© б„Ҷб…ЎбҶ«б„ғб…іб„Ӯб…ібҶ« б„Ӣб…Ўб„ғб…®б„Ӣб…өб„Ӯб…©
б„үб…©бҶ«б„Ӣб…іб„…б…© б„Ҷб…ЎбҶ«б„ғб…іб„Ӯб…ібҶ« б„Ӣб…Ўб„ғб…®б„Ӣб…өб„Ӯб…©Kisoon Eom
Мэ
maker faire seoul 2014 : http://www.make.co.kr/?page_id=1336
2014л…„ 9мӣ”, л©”мқҙм»Ө нҺҳм–ҙ м„ңмҡём—җм„ң
м§Ғм ‘ мҶҗмңјлЎң л§Ңл“Өм–ҙ ліҙлҠ” м•„л‘җмқҙл…ё м ңмһ‘ мӣҢнҒ¬мҲҚ 진н–ү!
мҳӨл Ңм§Җ ліҙл“ң мҶҢк°ң л°Ҹ м•„л‘җмқҙл…ё мҶҢк°ңмҷҖ к°„лӢЁн•ң м•„л‘җмқҙл…ёлҘј нҷңмҡ©н•ң мӢӨмҠөмқ„ мң„н•ң к°•мқҳ мһҗлЈҢ
мҳӨл Ңм§Җ ліҙл“ң мҶҢк°ң л°Ҹ м•„л‘җмқҙл…ё мҶҢк°ңмҷҖ к°„лӢЁн•ң м•„л‘җмқҙл…ёлҘј нҷңмҡ©н•ң мӢӨмҠөмқ„ мң„н•ң к°•мқҳ мһҗлЈҢcsleedk
Мэ
б„Ңб…Ұ3б„’б…¬ б„Ӣб…©б„‘б…ібҶ« б„…б…©б„Үб…©б„җб…өбҶЁб„үб…і б„үб…Ұб„Ҷб…өб„Ӯб…Ў 1б„Ӣб…өбҶҜб„Һб…Ў 1б„үб…Ұб„үб…§бҶ« м•Ҳл“ңлЎңмқҙл“ң App нҶөмӢ
б„Ңб…Ұ3б„’б…¬ б„Ӣб…©б„‘б…ібҶ« б„…б…©б„Үб…©б„җб…өбҶЁб„үб…і б„үб…Ұб„Ҷб…өб„Ӯб…Ў 1б„Ӣб…өбҶҜб„Һб…Ў 1б„үб…Ұб„үб…§бҶ« м•Ҳл“ңлЎңмқҙл“ң App нҶөмӢ WooSangHwang
Мэ
[1C6]б„Ӣб…©б„‘б…ібҶ«б„үб…©б„үб…і б„’б…Ўб„ғб…іб„Ӣб…°б„Ӣб…Ҙ б„‘б…ібҶҜб„…б…ўбҶәб„‘б…©бҶ·б„Җб…Ә Node.jsб„…б…© б„Җб…®б„’б…§бҶ«б„’б…Ўб„Ӯб…ібҶ« IoT б„‘б…ібҶҜб„…б…ўбҶәб„‘б…©бҶ·
[1C6]б„Ӣб…©б„‘б…ібҶ«б„үб…©б„үб…і б„’б…Ўб„ғб…іб„Ӣб…°б„Ӣб…Ҙ б„‘б…ібҶҜб„…б…ўбҶәб„‘б…©бҶ·б„Җб…Ә Node.jsб„…б…© б„Җб…®б„’б…§бҶ«б„’б…Ўб„Ӯб…ібҶ« IoT б„‘б…ібҶҜб„…б…ўбҶәб„‘б…©бҶ·NAVER D2
Мэ
б„Ӣб…Ўб„ғб…®б„Ӣб…өб„Ӯб…©б„Ӣб…Ә Fpgaб„…б…ібҶҜ б„Ӣб…өб„Ӣб…ӯбҶјб„’б…ЎбҶ« б„…б…©б„Үб…©бҶәб„Ңб…Ұб„Ңб…ЎбҶЁ
б„Ӣб…Ўб„ғб…®б„Ӣб…өб„Ӯб…©б„Ӣб…Ә Fpgaб„…б…ібҶҜ б„Ӣб…өб„Ӣб…ӯбҶјб„’б…ЎбҶ« б„…б…©б„Үб…©бҶәб„Ңб…Ұб„Ңб…ЎбҶЁchcbaram
Мэ
Ad
More from chcbaram (10)
OpenCR tutorial_icra2017
OpenCR tutorial_icra2017 chcbaram
Мэ
- OpenCR is a main controller board for TurtleBot3 that provides an open-source hardware and software platform for powering and operating sensors and actuators.
- It uses a high-performance STM32F746 microcontroller and supports Arduino IDE development. It has interfaces for communicating with Dynamixel motors, IMU sensors, and providing power output.
- The rosserial package converts ROS messages to a serial format for communication between OpenCR and ROS via USB. Examples are provided to demonstrate publishing IMU data and controlling TurtleBot3 using OpenCR and ROS.[л“ңлЎ ] нҺҢмӣЁм–ҙ 분м„қ [2015.5.23]
[л“ңлЎ ] нҺҢмӣЁм–ҙ 분м„қ [2015.5.23]chcbaram
Мэ
мҳӨлЎңм№ҙ мҳӨн”ҲлЎңліҙнӢұмҠӨ м„ёлҜёлӮҳ 2015.5.23
http://oroca.org
Ad
OpenCR б„Ӣб…Ўб„ғб…®б„Ӣб…өб„Ӯб…© б„‘б…ҘбҶ·б„Ӣб…°б„Ӣб…Ҙб„Җб…ўб„Үб…ЎбҶҜ
- 2. лӘ©м°Ё в—Ҹ OpenCR ? в—Ҹ к°ңл°ңмӮ¬м–‘ в—Ҹ м•„л‘җмқҙл…ё нҸ¬нҢ… в—Ӣ л¶ҖнҠёлЎңлҚ” в—Ӣ лӢӨмҡҙлЎңлҚ” в—Ӣ м•„л‘җмқҙл…ё ліҙл“ң мҶҢмҠӨ в—Ӣ мҳЁлқјмқё л°°нҸ¬ 2
- 3. OpenCR (Open-source Control Module for ROS) в—Ҹ STM32F746ZGT6 216Mhz, 1MB Flash, 320KB SRAM в—Ҹ м•„л‘җмқҙл…ё мҡ°л…ё н•Җ н—ӨлҚ” в—Ҹ м•„л‘җмқҙл…ё IDE к°ңл°ңнҷҳкІҪ м§Җмӣҗ в—Ҹ лӢӨмқҙлӮҳлҜ№м…Җ/мҳ¬лЎң/UART/CAN мқён„°нҺҳмқҙмҠӨ в—Ҹ л°°н„°лҰ¬ мһ…л Ҙ л°Ҹ м „мӣҗ м¶ңл Ҙ(12V/5V/3.3V) 3
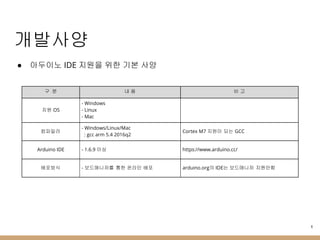
- 4. к°ңл°ңмӮ¬м–‘ в—Ҹ м•„л‘җмқҙл…ё IDE м§Җмӣҗмқ„ мң„н•ң кё°ліё мӮ¬м–‘ кө¬ 분 лӮҙ мҡ© 비 кі м§Җмӣҗ OS - Windows - Linux - Mac м»ҙнҢҢмқјлҹ¬ - Windows/Linux/Mac : gcc arm 5.4 2016q2 Cortex M7 м§Җмӣҗмқҙ лҗҳлҠ” GCC Arduino IDE - 1.6.9 мқҙмғҒ https://www.arduino.cc/ л°°нҸ¬л°©мӢқ - ліҙл“ңл§ӨлӢҲм ҖлҘј нҶөн•ң мҳЁлқјмқё л°°нҸ¬ arduino.orgмқҳ IDEлҠ” ліҙл“ңл§ӨлӢҲм Җ м§Җмӣҗм•Ҳн•Ё 4
- 5. м•„л‘җмқҙл…ё н•Җ н—ӨлҚ” в—Ҹ м•„л‘җмқҙл…ё мҡ°л…ё н•Җл§өкіј нҳёнҷҳ в—Ҹ I/O м „м••мқҖ 3.3V 5
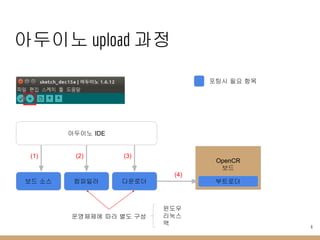
- 6. м•„л‘җмқҙл…ё upload кіјм • м•„л‘җмқҙл…ё IDE OpenCR ліҙл“ң м»ҙнҢҢмқјлҹ¬ (2) лӢӨмҡҙлЎңлҚ” (3) л¶ҖнҠёлЎңлҚ” (4) ліҙл“ң мҶҢмҠӨ (1) нҸ¬нҢ…мӢң н•„мҡ” н•ӯлӘ© мҡҙмҳҒмІҙм ңм—җ л”°лқј лі„лҸ„ кө¬м„ұ 6 мңҲлҸ„мҡ° лҰ¬лҲ…мҠӨ л§Ҙ
- 7. к°ңл°ң кіјм • ліҙл“ң кё°ліё н…ҢмҠӨнҠё кө¬нҳ„ - к°ңл°ң нҷҳкІҪ кө¬м¶• - CubeMX мӮ¬мҡ© л°©лІ• Study л¶ҖнҠёлЎңлҚ” кө¬нҳ„ лӢӨмҡҙлЎңлҚ” кө¬нҳ„ - л©”лӘЁлҰ¬ л§ө кө¬м„ұ - лӢӨмҡҙлЎңл“ң н”„лЎңнҶ мҪң кө¬нҳ„ - н”ҢлһҳмӢң л©”лӘЁлҰ¬ м ңм–ҙ м•„л‘җмқҙл…ё ліҙл“ң мҶҢмҠӨ кө¬нҳ„ - м•„л‘җмқҙл…ё API нҒҙлһҳмҠӨ нҸ¬нҢ… - н•Җл§ө кө¬м„ұ мҳЁлқјмқё л°°нҸ¬ кө¬нҳ„ - githubлҘј нҶөн•ң мҳЁлһҖмқё л°°нҸ¬ 7
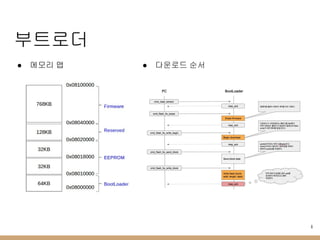
- 8. л¶ҖнҠёлЎңлҚ” в—Ҹ л©”лӘЁлҰ¬ л§ө в—Ҹ лӢӨмҡҙлЎңл“ң мҲңм„ң 8
- 9. лӢӨмҡҙлЎңлҚ” в—Ҹ stm32ld в—Ӣ stm32мқҳ лӮҙмһҘ л¶ҖнҠёлЎңлҚ”мҷҖ мӢңлҰ¬м–ј нҶөмӢ мңјлЎң нҺҢмӣЁм–ҙ лӢӨмҡҙлЎңл“ң н• мҲҳ мһҲлҠ” мҳӨн”ҲмҶҢмҠӨ в—Ӣ мңҲлҸ„мҡ°/лҰ¬лҲ…мҠӨ/л§Ҙм—җм„ң лӘЁл‘җ л№Ңл“ң к°ҖлҠҘ в—Ӣ https://github.com/jsnyder/stm32ld в—Ҹ opencr_ld в—Ӣ stm32ldмқҳ нҶөмӢ лӘЁл“Ҳмқ„ кё°л°ҳмңјлЎң opencrмқҳ л¶ҖнҠёлЎңлҚ” н”„лЎңнҶ мҪңмқ„ кө¬нҳ„н•Ё в—Ӣ мңҲлҸ„мҡ°/лҰ¬лҲ…мҠӨ/л§Ҙм—җм„ң лӘЁл‘җ л№Ңл“ң в– мңҲлҸ„мҡ°лҠ” QTлҘј к°ңл°ңнҷҳкІҪмңјлЎң мӮ¬мҡ©н•Ё 9
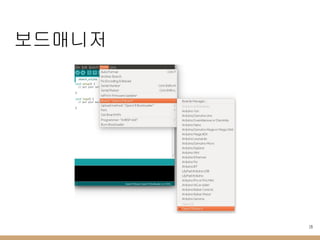
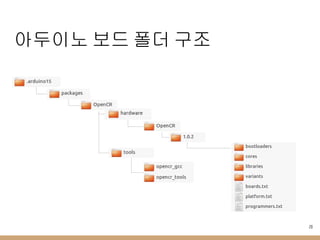
- 10. м•„л‘җмқҙл…ё ліҙл“ң мҶҢмҠӨ в—Ҹ нҸҙлҚ” кө¬мЎ° кө¬ 분 лӮҙ мҡ© bootloaders ліҙл“ңмқҳ л¶ҖнҠёлЎңлҚ” мқҙлҜём§Җ нҢҢмқј нҸҙлҚ” cores м•„л‘җмқҙл…ё API нҒҙлһҳмҠӨ нҸҙлҚ” libraries ліҙл“ңм—җм„ң м§Җмӣҗн•ҳлҠ” кё°ліё лқјмқҙлёҢлҹ¬лҰ¬ нҸҙлҚ” variants coresлҘј кіөмң н•ҳлҠ” ліҙл“ң кҙҖл Ё нҢҢмқј нҸҙлҚ” boards.txt ліҙл“ңлі„ м„Өм • platform.txt л№Ңл“ңлҘј мң„н•ң м»ҙнҢҢмқј м„Өм •, лӢӨмҡҙлЎңл“ң нҲҙ м„Өм •л“ұ programmers.txt л¶ҖнҠёлЎңлҚ” м—…лЎңл“ң м„Өм • 10 в—Ҹ м•„л‘җмқҙл…ё IDE 1.5.3 лІ„м „ мқҙмғҒл¶Җн„°лҠ” нҳёнҷҳ ліҙл“ңлҘј мүҪкІҢ 추к°Җн•ҳлҸ„лЎқ ліҖкІҪлҗЁ в—Ӣ https://github.com/arduino/Arduino/wiki/Arduino-IDE-1.5-3rd-party-Hardware-specificatio n
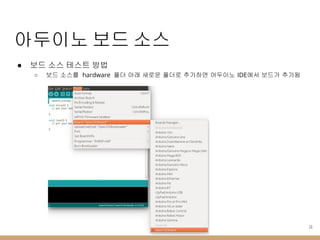
- 11. м•„л‘җмқҙл…ё ліҙл“ң мҶҢмҠӨ в—Ҹ ліҙл“ң мҶҢмҠӨ н…ҢмҠӨнҠё л°©лІ• в—Ӣ ліҙл“ң мҶҢмҠӨлҘј hardware нҸҙлҚ” м•„лһҳ мғҲлЎңмҡҙ нҸҙлҚ”лЎң 추к°Җн•ҳл©ҙ м•„л‘җмқҙл…ё IDEм—җм„ң ліҙл“ңк°Җ 추к°ҖлҗЁ 11
- 12. м•„л‘җмқҙл…ё нҸ¬нҢ… в—Ҹ HALMX н”„лЎңм қнҠё в—Ӣ http://www.stm32duino.com/ м—җм„ң STM32CubeMXлҘј кё°л°ҳмңјлЎң м•„л‘җмқҙл…ё ліҙл“ңлҘј нҸ¬нҢ… в—Ӣ https://github.com/rogerclarkmelbourne/Arduino_STM32 в—Ӣ нҳ„мһ¬к№Ңм§Җ F1/F3/F4лҘј м§Җмӣҗн•Ё в—Ҹ ліҖкІҪ лӮҙмҡ© в—Ӣ HALMX н”„лЎңм қнҠёлҠ” F7 мӢңлҰ¬мҰҲлҠ” м§Җмӣҗн•ҳм§Җ м•Ҡкё°м—җ кё°ліё coresмҷҖ variantsмқҳ лјҲлҢҖлҘј мӮ¬мҡ©н•ҳкі STM32CubeF7 лқјмқҙлёҢлҹ¬лҰ¬лҘј 추к°Җн•ҳм—¬ нҸ¬нҢ…н•Ё 12
- 13. мҶҢмҠӨ Layer кө¬мЎ° м•„л‘җмқҙл…ё API Class (cores) STM32CubeF7 OpenCR (variants) bsp hal driver Hardware 13
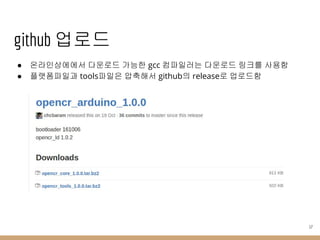
- 14. мҳЁлқјмқё л°°нҸ¬ в—Ҹ githubм—җ jsonнҢҢмқјкіј л°°нҸ¬лҘј мң„н•ң 압축нҢҢмқј м—…лЎңл“ң в—Ӣ м•„л‘җмқҙл…ё IDE 1.6.4 мқҙмғҒ л¶Җн„° ліҙл“ң л§ӨлӢҲм ҖлҘј нҶөн•ҙ мҳЁлқјмқёмңјлЎң л°°нҸ¬ к°ҖлҠҘн•ҙм§җ в—Ӣ https://github.com/arduino/Arduino/wiki/Arduino-IDE-1.6.x-package_index.json-format-sp ecification в—Ҹ OpenCR json нҢҢмқј в—Ӣ https://github.com/ROBOTIS-GIT/OpenCR/blob/master/arduino/opencr_release/package_ opencr_index.json 14
- 15. json нҢҢмқј в—Ҹ platforms 15 м•„л‘җмқҙл…ё ліҙл“ң мҶҢмҠӨ gcc м»ҙнҢҢмқјлҹ¬ лӢӨмҡҙлЎңлҚ”
- 16. json нҢҢмқј в—Ҹ opencr_gcc 16 в—Ҹ opencr_tools
- 17. github м—…лЎңл“ң в—Ҹ мҳЁлқјмқёмғҒм—җм—җм„ң лӢӨмҡҙлЎңл“ң к°ҖлҠҘн•ң gcc м»ҙнҢҢмқјлҹ¬лҠ” лӢӨмҡҙлЎңл“ң л§ҒнҒ¬лҘј мӮ¬мҡ©н•Ё в—Ҹ н”Ңлһ«нҸјнҢҢмқјкіј toolsнҢҢмқјмқҖ 압축н•ҙм„ң githubмқҳ releaseлЎң м—…лЎңл“ңн•Ё 17
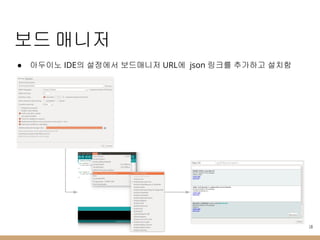
- 18. ліҙл“ң л§ӨлӢҲм Җ в—Ҹ м•„л‘җмқҙл…ё IDEмқҳ м„Өм •м—җм„ң ліҙл“ңл§ӨлӢҲм Җ URLм—җ json л§ҒнҒ¬лҘј 추к°Җн•ҳкі м„Өм№ҳн•Ё 18
- 20. м•„л‘җмқҙл…ё ліҙл“ң нҸҙлҚ” кө¬мЎ° 20
- 21. мҳҲм ң в—Ҹ TFT LCD в—Ӣ https://youtu.be/y4if5J_upyY 21
- 22. кІ°лЎ в—Ҹ м•„л‘җмқҙл…ё л№Ңл“ң кіјм •кіј кө¬мЎ°л§Ң м•Ңл©ҙ мүҪкІҢ ліҙл“ңлҘј м•„л‘җмқҙл…ё нҳёнҷҳ ліҙл“ңлЎң л§Ңл“Ө мҲҳ мһҲмқҢ в—Ҹ OpenCRліҙл“ңлҘј м„ұлҠҘ мўӢмқҖ м•„л‘җмқҙл…ё ліҙл“ңлЎң мӮ¬мҡ© к°ҖлҠҘн•ЁмңјлЎң м•„л‘җмқҙл…ё IDEлҘј нҶөн•ҙ мүҪкІҢ к°ңл°ң нҷҳкІҪмқ„ кө¬м¶• к°ҖлҠҘн•Ё в—Ҹ м•„л‘җмқҙл…ё ліҙл“ң нҸ¬нҢ…мқ„ мң„н•ҙм„ңлҠ” лӢӨм–‘н•ң OSм—җ лҢҖн•ң кі л Ө н•„мҡ” в—Ҹ githubлҘј нҶөн•ҙ мҳЁлқјмқё л°°нҸ¬ к°ҖлҠҘ в—Ҹ ARMмҡ© м•„л‘җмқҙл…ё ліҙл“ңм—җ лҢҖн•ң мүҙл“ң лқјмқҙлёҢлҹ¬лҰ¬лҠ” мқјл¶Җ мҲҳм •мқҙ н•„мҡ”н•Ё 22
- 23. м°ёкі мһҗлЈҢ в—Ҹ OpenCR мҶҢмҠӨмҪ”л“ң в—Ӣ л¶ҖнҠёлЎңлҚ” в– https://github.com/ROBOTIS-GIT/OpenCR/tree/master/arduino/opencr_bootloader в—Ӣ лӢӨмҡҙлЎңлҚ” в– https://github.com/ROBOTIS-GIT/OpenCR/tree/master/arduino/opencr_ld в—Ӣ м•„л‘җмқҙл…ё ліҙл“ң мҶҢмҠӨ в– https://github.com/ROBOTIS-GIT/OpenCR/tree/master/arduino/opencr_arduino/opencr в—Ӣ мҳЁлқјмқё л°°нҸ¬ нҢҢмқј в– https://github.com/ROBOTIS-GIT/OpenCR/tree/master/arduino/opencr_release в—Ҹ м•„л‘җмқҙл…ё в—Ӣ https://github.com/arduino/Arduino/wiki/Arduino-IDE-1.5-3rd-party-Hardware-specification в—Ӣ https://github.com/arduino/Arduino/wiki/Arduino-IDE-1.6.x-package_index.json-format-specification 23
- 24. Q & A 24