sect17_slidesppt34.ppt
Download as PPT, PDF0 likes33 views
This document summarizes key concepts about forces and motion from a physics textbook chapter. It defines a force as a push or pull that can cause motion or change an object's speed or direction. There are four main types of friction: static, sliding, rolling, and fluid friction. Gravity pulls objects downward toward Earth's center, while air resistance opposes the downward motion of falling objects. A projectile follows a curved path due to the combination of its initial forward velocity and gravity pulling it downward.
1 of 18
Download to read offline

















Recommended
Forces_and_Friction.ppt



Forces_and_Friction.pptwilda2
Ėý
This document discusses forces, how forces combine, and how friction affects motion. It defines a force as a push or pull and describes how the direction and size of forces are measured. It explains that the net force on an object is determined by adding all individual forces together, and that a net force is needed to change an object's motion. The document also defines friction as the force that opposes the motion of two touching surfaces, and describes the different types of friction and how friction can be both helpful and harmful.Week 3.ppt



Week 3.pptLoryRoseBermas
Ėý
Forces can be pushes or pulls that have both direction and size. A net force is the sum of all individual forces acting on an object. An object will change its motion if the net force is not balanced, or not equal to zero Newtons. Friction opposes the motion between two touching surfaces and depends on factors like roughness and the force pushing the surfaces together. It can be advantageous by allowing us to walk or disadvantages by causing wear on machine parts.Friction for Gr 8



Friction for Gr 8Prabhakar Kumar
Ėý
This document discusses forces, how forces combine, and how friction affects motion. It defines a force as a push or pull and describes how forces have direction and size measured in newtons. It explains that net force is determined by adding all forces acting on an object and can cause a change in motion. The document also defines types of friction like static and kinetic friction and describes how friction opposes motion between surfaces. It discusses factors that affect friction like roughness and applied force between surfaces.Basic Forces year 10 Physics powerpoint ml



Basic Forces year 10 Physics powerpoint mlMichaela Lawrence
Ėý
Forces act on objects in different ways:
1. Forces are pushes or pulls that can cause an object to start or stop moving in a certain direction.
2. If the forces on an object are balanced, the object will remain at rest or maintain a constant speed and direction of motion.
3. If forces are unbalanced, the object will accelerate in the direction of the greater net force.Forces 100810205910-phpapp02



Forces 100810205910-phpapp02Allen Jude Cancino
Ėý
The document discusses the different types of forces that affect an object's motion. It explains that a worker on a roof does not slide off because the balanced forces of static friction and the worker's weight prevent any movement. It defines four types of friction - static, sliding, rolling, and fluid - and describes how each type opposes different kinds of motion between objects. It also discusses how unbalanced forces cause a net force that changes an object's motion, while balanced forces do not affect motion.Forces



ForcesGrover Cleveland Middle School
Ėý
1) Forces are pushes or pulls that can cause an object at rest to move or change direction, and are represented by arrows.
2) Balanced forces do not change an object's motion, while unbalanced forces cause a net force and change in motion.
3) There are four types of friction: static, sliding, rolling, and fluid, each opposing different types of motion between objects or objects in motion.Forces



ForcesGrover Cleveland Middle School
Ėý
1) Forces are pushes or pulls that can cause an object at rest to move or change direction, and are represented by arrows.
2) Balanced forces do not change an object's motion, while unbalanced forces cause a net force and change in motion.
3) There are four types of friction: static, sliding, rolling, and fluid, each opposing different types of motion between objects or objects in motion.forcesandfriction-0.ppt



forcesandfriction-0.pptssuserbb7f9b
Ėý
This document discusses forces, how they combine, and how friction affects motion. It defines a force as a push or pull and describes its direction and size in newtons. It explains that net force is determined by adding all forces on an object and can cause a change in motion. Forces can be in the same or opposite directions. Friction opposes the motion of surfaces in contact and depends on factors like roughness and applied force. There are different types of friction like static and kinetic friction.forcesandfriction



forcesandfrictionssuser58f4de
Ėý
This document discusses forces, how they combine, and how friction affects motion. It defines a force as a push or pull and describes its direction and size in newtons. It explains that net force is determined by adding all forces on an object and that unbalanced net forces cause changes in motion. The document also defines static and kinetic friction and describes factors that affect friction such as surface roughness, force between surfaces, and using lubricants.Forces and friction 0



Forces and friction 0Vrushali Patil
Ėý
This document discusses forces, how they combine, and how friction affects motion. It defines a force as a push or pull and describes its direction and size in newtons. It explains that net force is determined by adding all forces on an object and that unbalanced net forces cause changes in motion. The document also defines static and kinetic friction and describes factors that affect friction such as surface roughness, force between surfaces, and using lubricants.forcesandfriction-0.ppt



forcesandfriction-0.pptCHETANJAIPRAKASHCHIT
Ėý
Friction: The amount of friction depends on:
Roughness of the surfaces
Force pushing the surfaces together
gravity and friction ppt



gravity and friction ppthassanhamdy26
Ėý
The document discusses forces of friction and gravity. It begins with an agenda for the lesson, which includes demonstrations on friction, notes on friction and gravity, and an activity. The notes define friction as the force that opposes the sliding motion of surfaces in contact, and gravity as the force that attracts objects toward each other. It describes how mass and distance affect the gravitational force between objects. Friction and gravity can both affect the speed and direction of an object. The lesson concludes with challenges applying understanding of balance and center of gravity.Physics-Force new.pptx igcse newton gravity



Physics-Force new.pptx igcse newton gravityqueenlystudies
Ėý
Physics-Force new.pptx igcse newton gravitytypes-of-forces.pptxx for science reviewer



types-of-forces.pptxx for science reviewervinzbayudan
Ėý
The document defines different types of forces:
- Applied forces act on objects due to direct contact from another object or person. Gravity pulls objects with mass towards each other. Normal forces prevent objects from passing through surfaces they contact. Friction resists the motion of surfaces in contact and sliding against each other. Spring forces restore compressed or stretched springs back to equilibrium. Drag forces resist the motion of objects moving through fluids. Magnetic, electric, and inertia forces also act on charged or moving objects. Newton's First Law of Motion describes inertia, where objects at rest stay at rest and objects in motion stay in motion with constant velocity unless acted on by unbalanced forces.Gravity



GravityNeilfieOrit2
Ėý
This document discusses key concepts of gravity including:
1) Gravity is a force that acts between any two masses, depending on their mass and distance. This is described by Newton's law of universal gravitation.
2) When the only force acting on an object is gravity, it is in free fall and accelerates at 9.8 m/s^2 near Earth's surface.
3) Air resistance opposes gravity and causes objects with greater surface areas to fall more slowly, until they reach terminal velocity where air resistance equals weight.Force



ForceV.Mohan Kumar
Ėý
This document provides information about force and motion. It defines a force as a push or pull and notes that all forces have magnitude and direction. It then gives several examples of the effects of different forces, such as an arrow hitting a target. The document discusses that a force can change an object's shape, size, and motion. It also defines types of motion, speed, velocity, acceleration, and summarizes Newton's Three Laws of Motion.Chapter 10 Notes #1: Forces and Friction



Chapter 10 Notes #1: Forces and FrictionMrsJenner
Ėý
This document defines and explains various types of forces including vector forces, Newtons as a unit of force measurement, net force as the sum of all forces acting on an object, and the effects of balanced and unbalanced forces. It also discusses elastic forces like compression and tension, friction which opposes motion, and equilibrium as a state where balanced forces cause no changes in motion. Types of friction like static, sliding, rolling, and fluid friction are defined with examples.Force and motion



Force and motionNeilfieOrit2
Ėý
The document discusses motion and forces, explaining concepts such as speed, velocity, balanced and unbalanced forces, friction, and Newton's Laws of Motion. It defines important terms like acceleration, inertia, and force, and explains how forces can cause changes in an object's velocity based on whether they are balanced or unbalanced. Examples are provided to illustrate concepts such as friction, gravity, and Newton's Laws.Force new



Force newmayank jain
Ėý
The document discusses motion and forces, explaining concepts such as speed, velocity, balanced and unbalanced forces, friction, and Newton's Laws of Motion. It defines important terms, provides examples, and describes how forces can cause changes in an object's velocity based on whether the net force is balanced or unbalanced. Newton's three laws of motion are also summarized, relating concepts like inertia, acceleration, and equal and opposite reaction forces.Types of forces , Static, Friction, Gravitation



Types of forces , Static, Friction, GravitationBhavishyaKumarSingh
Ėý
Wikipedia
Search
Force
Article Talk
Language
Download PDF
Watch
Edit
For other uses, see Force (disambiguation). "Physical force" redirects here. For other uses, see Physical force (disambiguation).
In physics, a force is an influence that can cause an object to change its velocity, i.e., to accelerate, meaning a change in speed or direction, unless counterbalanced by other forces. The concept of force makes the everyday notion of pushing or pulling mathematically precise. Because the magnitude and direction of a force are both important, force is a vector quantity. The SI unit of force is the newton (N), and force is often represented by the symbol F.
Force
Forces can be described as a push or pull on an object. They can be due to phenomena such as gravity, magnetism, or anything that might cause a mass to accelerate.
Common symbols
ïŋ―
â
{\displaystyle {\vec {F}}}, F, F
SI unit
newton (N)
Other units
dyne, pound-force, poundal, kip, kilopond
In SI base units
kg·m·sâ2
Derivations from
other quantities
F = ma
Dimension
ïŋ―
ïŋ―
ïŋ―
â
2
{\displaystyle {\mathsf {M}}{\mathsf {L}}{\mathsf {T}}^{-2}}
Force plays a central role in classical mechanics, figuring in all three of Newton's laws of motion, which specify that the force on an object with an unchanging mass is equal to the product of the object's mass and the acceleration that it undergoes. Types of forces often encountered in classical mechanics include elastic, frictional, contact or "normal" forces, and gravitational. The rotational version of force is torque, which produces changes in the rotational speed of an object. In an extended body, each part often applies forces on the adjacent parts; the distribution of such forces through the body is the internal mechanical stress. In equilibrium these stresses cause no acceleration of the body as the forces balance one another. If these are not in equilibrium they can cause deformation of solid materials, or flow in fluids.
In modern physics, which includes relativity and quantum mechanics, the laws governing motion are revised to rely on fundamental interactions as the ultimate origin of force. However, the understanding of force provided by classical mechanics is useful for practical purposes.[1]
Development of the concept
Pre-Newtonian concepts
Newtonian mechanics
Combining forces
Examples of forces in classical mechanics
Concepts derived from force
Units
Revisions of the force concept
Fundamental interactions
See also
References
External links
Last edited 18 days ago by HansVonStuttgart
Wikipedia
Content is available under CC BY-SA 4.0 unless otherwise noted.
Privacy policy Terms of UseDesktop
Encyclopedia Britannica
HomeGames & QuizzesHistory & SocietyScience & TechBiographiesAnimals & NatureGeography & TravelArts & CultureMoneyVideos
Home
Science
Physics
Matter & Energy
Science & Tech
force
physics
Written and fact-checked by
Article History
Force, in mechanics, any action that tends to maintain or alter the motion of a body or to distort it.Force and motion 



Force and motion Nimra Waheed
Ėý
This document discusses motion and forces. It covers topics like speed and velocity, balanced and unbalanced forces, friction, Newton's laws of motion, and more. Speed describes the rate of change in an object's position over time, while velocity also includes direction. Balanced forces are equal and opposite, resulting in no net force and no acceleration. Unbalanced forces cause a change in velocity or acceleration. Friction opposes motion between surfaces and depends on factors like the types of surfaces and force between them. Newton's laws state that an object at rest or in motion will remain so unless acted upon by an unbalanced force, more force results in more acceleration proportional to mass, and for every action there is an equal and opposite reactionforce_powerpoint3.ppt



force_powerpoint3.pptMathandScienced
Ėý
This document discusses Newton's laws of motion and forces. It defines force as a push or pull and describes different types of forces including contact forces and field forces. Mass is defined as the amount of matter in an object, while weight is the force on an object due to gravity. Net force is determined by combining all forces acting on an object. Free-body diagrams are used to represent the forces acting on an object. Friction and other concepts such as static equilibrium, kinetic friction, and terminal velocity are also explained.Force,gravity,elastic



Force,gravity,elasticMrsKendall
Ėý
This document discusses different types of forces including friction, gravity, and elastic forces. It defines force as a push or pull and describes its magnitude and direction. Friction is explained as the force between two surfaces in contact. Gravity is defined as a force that pulls objects toward each other, with examples of its effects on weight and motion. Elastic forces like compression and tension are described as pushing or pulling matter based on its elastic properties.Gravity, Friction, & More Forces In Everyday Life



Gravity, Friction, & More Forces In Everyday LifeEmmanuelDikolelay
Ėý
In this lesson, students will learn how gravity & friction can take affect on the simple things we do everyday of our lives. Learn the 3 main types of friction, & air resistance, plus a few examples. Finally, learn about terminal velocity & get a basic introduction to magnetic & electric forces with a slight distinction for buoyancy & density.G4 - Forces and Motion (1) balanced and unbalanced forces.pptx



G4 - Forces and Motion (1) balanced and unbalanced forces.pptxJuanShin1
Ėý
G4 - Forces and Motion (1) balanced and unbalanced forces.pptxintern_forc_biceps2.ppt



intern_forc_biceps2.pptKathleenSaldon
Ėý
Okay, let's break this down step-by-step:
* We are given: 1 mole of ice at -25°C
* Heat of fusion of ice = 6.01 kJ/mol
* Heat of vaporization of water = 40.7 kJ/mol
* Specific heat of ice = 2.09 J/g°C
* Specific heat of water = 4.18 J/g°C
1) Heat ice from -25°C to 0°C:
Q = m * c * ÎT
Q = (18 g) * (2.09 J/g°C) * (25°C) = 903 J
2) Heatpropery_solns.ppt



propery_solns.pptKathleenSaldon
Ėý
This document discusses colligative properties, which are physical properties of solutions that depend on the concentration of solute particles rather than the identity of the solute. It defines key colligative properties like boiling point elevation, freezing point depression, and osmotic pressure. The document also explains how these properties obey mathematical relationships like Raoult's law. Several examples are provided to demonstrate how to use these relationships and colligative property equations to calculate values like vapor pressure, boiling point, freezing point, osmotic pressure, and molar mass of a solute.More Related Content
Similar to sect17_slidesppt34.ppt (20)
forcesandfriction-0.ppt



forcesandfriction-0.pptssuserbb7f9b
Ėý
This document discusses forces, how they combine, and how friction affects motion. It defines a force as a push or pull and describes its direction and size in newtons. It explains that net force is determined by adding all forces on an object and can cause a change in motion. Forces can be in the same or opposite directions. Friction opposes the motion of surfaces in contact and depends on factors like roughness and applied force. There are different types of friction like static and kinetic friction.forcesandfriction



forcesandfrictionssuser58f4de
Ėý
This document discusses forces, how they combine, and how friction affects motion. It defines a force as a push or pull and describes its direction and size in newtons. It explains that net force is determined by adding all forces on an object and that unbalanced net forces cause changes in motion. The document also defines static and kinetic friction and describes factors that affect friction such as surface roughness, force between surfaces, and using lubricants.Forces and friction 0



Forces and friction 0Vrushali Patil
Ėý
This document discusses forces, how they combine, and how friction affects motion. It defines a force as a push or pull and describes its direction and size in newtons. It explains that net force is determined by adding all forces on an object and that unbalanced net forces cause changes in motion. The document also defines static and kinetic friction and describes factors that affect friction such as surface roughness, force between surfaces, and using lubricants.forcesandfriction-0.ppt



forcesandfriction-0.pptCHETANJAIPRAKASHCHIT
Ėý
Friction: The amount of friction depends on:
Roughness of the surfaces
Force pushing the surfaces together
gravity and friction ppt



gravity and friction ppthassanhamdy26
Ėý
The document discusses forces of friction and gravity. It begins with an agenda for the lesson, which includes demonstrations on friction, notes on friction and gravity, and an activity. The notes define friction as the force that opposes the sliding motion of surfaces in contact, and gravity as the force that attracts objects toward each other. It describes how mass and distance affect the gravitational force between objects. Friction and gravity can both affect the speed and direction of an object. The lesson concludes with challenges applying understanding of balance and center of gravity.Physics-Force new.pptx igcse newton gravity



Physics-Force new.pptx igcse newton gravityqueenlystudies
Ėý
Physics-Force new.pptx igcse newton gravitytypes-of-forces.pptxx for science reviewer



types-of-forces.pptxx for science reviewervinzbayudan
Ėý
The document defines different types of forces:
- Applied forces act on objects due to direct contact from another object or person. Gravity pulls objects with mass towards each other. Normal forces prevent objects from passing through surfaces they contact. Friction resists the motion of surfaces in contact and sliding against each other. Spring forces restore compressed or stretched springs back to equilibrium. Drag forces resist the motion of objects moving through fluids. Magnetic, electric, and inertia forces also act on charged or moving objects. Newton's First Law of Motion describes inertia, where objects at rest stay at rest and objects in motion stay in motion with constant velocity unless acted on by unbalanced forces.Gravity



GravityNeilfieOrit2
Ėý
This document discusses key concepts of gravity including:
1) Gravity is a force that acts between any two masses, depending on their mass and distance. This is described by Newton's law of universal gravitation.
2) When the only force acting on an object is gravity, it is in free fall and accelerates at 9.8 m/s^2 near Earth's surface.
3) Air resistance opposes gravity and causes objects with greater surface areas to fall more slowly, until they reach terminal velocity where air resistance equals weight.Force



ForceV.Mohan Kumar
Ėý
This document provides information about force and motion. It defines a force as a push or pull and notes that all forces have magnitude and direction. It then gives several examples of the effects of different forces, such as an arrow hitting a target. The document discusses that a force can change an object's shape, size, and motion. It also defines types of motion, speed, velocity, acceleration, and summarizes Newton's Three Laws of Motion.Chapter 10 Notes #1: Forces and Friction



Chapter 10 Notes #1: Forces and FrictionMrsJenner
Ėý
This document defines and explains various types of forces including vector forces, Newtons as a unit of force measurement, net force as the sum of all forces acting on an object, and the effects of balanced and unbalanced forces. It also discusses elastic forces like compression and tension, friction which opposes motion, and equilibrium as a state where balanced forces cause no changes in motion. Types of friction like static, sliding, rolling, and fluid friction are defined with examples.Force and motion



Force and motionNeilfieOrit2
Ėý
The document discusses motion and forces, explaining concepts such as speed, velocity, balanced and unbalanced forces, friction, and Newton's Laws of Motion. It defines important terms like acceleration, inertia, and force, and explains how forces can cause changes in an object's velocity based on whether they are balanced or unbalanced. Examples are provided to illustrate concepts such as friction, gravity, and Newton's Laws.Force new



Force newmayank jain
Ėý
The document discusses motion and forces, explaining concepts such as speed, velocity, balanced and unbalanced forces, friction, and Newton's Laws of Motion. It defines important terms, provides examples, and describes how forces can cause changes in an object's velocity based on whether the net force is balanced or unbalanced. Newton's three laws of motion are also summarized, relating concepts like inertia, acceleration, and equal and opposite reaction forces.Types of forces , Static, Friction, Gravitation



Types of forces , Static, Friction, GravitationBhavishyaKumarSingh
Ėý
Wikipedia
Search
Force
Article Talk
Language
Download PDF
Watch
Edit
For other uses, see Force (disambiguation). "Physical force" redirects here. For other uses, see Physical force (disambiguation).
In physics, a force is an influence that can cause an object to change its velocity, i.e., to accelerate, meaning a change in speed or direction, unless counterbalanced by other forces. The concept of force makes the everyday notion of pushing or pulling mathematically precise. Because the magnitude and direction of a force are both important, force is a vector quantity. The SI unit of force is the newton (N), and force is often represented by the symbol F.
Force
Forces can be described as a push or pull on an object. They can be due to phenomena such as gravity, magnetism, or anything that might cause a mass to accelerate.
Common symbols
ïŋ―
â
{\displaystyle {\vec {F}}}, F, F
SI unit
newton (N)
Other units
dyne, pound-force, poundal, kip, kilopond
In SI base units
kg·m·sâ2
Derivations from
other quantities
F = ma
Dimension
ïŋ―
ïŋ―
ïŋ―
â
2
{\displaystyle {\mathsf {M}}{\mathsf {L}}{\mathsf {T}}^{-2}}
Force plays a central role in classical mechanics, figuring in all three of Newton's laws of motion, which specify that the force on an object with an unchanging mass is equal to the product of the object's mass and the acceleration that it undergoes. Types of forces often encountered in classical mechanics include elastic, frictional, contact or "normal" forces, and gravitational. The rotational version of force is torque, which produces changes in the rotational speed of an object. In an extended body, each part often applies forces on the adjacent parts; the distribution of such forces through the body is the internal mechanical stress. In equilibrium these stresses cause no acceleration of the body as the forces balance one another. If these are not in equilibrium they can cause deformation of solid materials, or flow in fluids.
In modern physics, which includes relativity and quantum mechanics, the laws governing motion are revised to rely on fundamental interactions as the ultimate origin of force. However, the understanding of force provided by classical mechanics is useful for practical purposes.[1]
Development of the concept
Pre-Newtonian concepts
Newtonian mechanics
Combining forces
Examples of forces in classical mechanics
Concepts derived from force
Units
Revisions of the force concept
Fundamental interactions
See also
References
External links
Last edited 18 days ago by HansVonStuttgart
Wikipedia
Content is available under CC BY-SA 4.0 unless otherwise noted.
Privacy policy Terms of UseDesktop
Encyclopedia Britannica
HomeGames & QuizzesHistory & SocietyScience & TechBiographiesAnimals & NatureGeography & TravelArts & CultureMoneyVideos
Home
Science
Physics
Matter & Energy
Science & Tech
force
physics
Written and fact-checked by
Article History
Force, in mechanics, any action that tends to maintain or alter the motion of a body or to distort it.Force and motion 



Force and motion Nimra Waheed
Ėý
This document discusses motion and forces. It covers topics like speed and velocity, balanced and unbalanced forces, friction, Newton's laws of motion, and more. Speed describes the rate of change in an object's position over time, while velocity also includes direction. Balanced forces are equal and opposite, resulting in no net force and no acceleration. Unbalanced forces cause a change in velocity or acceleration. Friction opposes motion between surfaces and depends on factors like the types of surfaces and force between them. Newton's laws state that an object at rest or in motion will remain so unless acted upon by an unbalanced force, more force results in more acceleration proportional to mass, and for every action there is an equal and opposite reactionforce_powerpoint3.ppt



force_powerpoint3.pptMathandScienced
Ėý
This document discusses Newton's laws of motion and forces. It defines force as a push or pull and describes different types of forces including contact forces and field forces. Mass is defined as the amount of matter in an object, while weight is the force on an object due to gravity. Net force is determined by combining all forces acting on an object. Free-body diagrams are used to represent the forces acting on an object. Friction and other concepts such as static equilibrium, kinetic friction, and terminal velocity are also explained.Force,gravity,elastic



Force,gravity,elasticMrsKendall
Ėý
This document discusses different types of forces including friction, gravity, and elastic forces. It defines force as a push or pull and describes its magnitude and direction. Friction is explained as the force between two surfaces in contact. Gravity is defined as a force that pulls objects toward each other, with examples of its effects on weight and motion. Elastic forces like compression and tension are described as pushing or pulling matter based on its elastic properties.Gravity, Friction, & More Forces In Everyday Life



Gravity, Friction, & More Forces In Everyday LifeEmmanuelDikolelay
Ėý
In this lesson, students will learn how gravity & friction can take affect on the simple things we do everyday of our lives. Learn the 3 main types of friction, & air resistance, plus a few examples. Finally, learn about terminal velocity & get a basic introduction to magnetic & electric forces with a slight distinction for buoyancy & density.G4 - Forces and Motion (1) balanced and unbalanced forces.pptx



G4 - Forces and Motion (1) balanced and unbalanced forces.pptxJuanShin1
Ėý
G4 - Forces and Motion (1) balanced and unbalanced forces.pptxMore from KathleenSaldon (7)
intern_forc_biceps2.ppt



intern_forc_biceps2.pptKathleenSaldon
Ėý
Okay, let's break this down step-by-step:
* We are given: 1 mole of ice at -25°C
* Heat of fusion of ice = 6.01 kJ/mol
* Heat of vaporization of water = 40.7 kJ/mol
* Specific heat of ice = 2.09 J/g°C
* Specific heat of water = 4.18 J/g°C
1) Heat ice from -25°C to 0°C:
Q = m * c * ÎT
Q = (18 g) * (2.09 J/g°C) * (25°C) = 903 J
2) Heatpropery_solns.ppt



propery_solns.pptKathleenSaldon
Ėý
This document discusses colligative properties, which are physical properties of solutions that depend on the concentration of solute particles rather than the identity of the solute. It defines key colligative properties like boiling point elevation, freezing point depression, and osmotic pressure. The document also explains how these properties obey mathematical relationships like Raoult's law. Several examples are provided to demonstrate how to use these relationships and colligative property equations to calculate values like vapor pressure, boiling point, freezing point, osmotic pressure, and molar mass of a solute.trev_facpositions.ppt



trev_facpositions.pptKathleenSaldon
Ėý
The process of obtaining a faculty position takes many years and involves graduate school, post-doctoral work, strong publications, grant writing skills, and networking. The key steps are completing a PhD in 6 years, doing post-docs at top institutions, publishing extensively, attending conferences, applying to many jobs, acing the interview including seminar and research plan defense, and negotiating the job offer. Preparation in graduate school and diligent work are essential for success.em-spectrum-lessons-1.pptx



em-spectrum-lessons-1.pptxKathleenSaldon
Ėý
This document provides an overview of lessons on the electromagnetic spectrum for students. It includes learning objectives, descriptions of different types of electromagnetic radiation, and activities for students to research and learn about various parts of the spectrum. The document covers radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, X-rays, and gamma rays. Students are tasked with learning the properties and order of the different radiations, as well as their uses, safety considerations, and impacts on society. Activities include experiments, research presentations, discussions, and assessments to check understanding.ch_15_PPT_lecture.pptx



ch_15_PPT_lecture.pptxKathleenSaldon
Ėý
The document summarizes key concepts about the nature of light from a physics textbook chapter, including:
1) Light is an electromagnetic wave that travels at a constant speed of about 3x10^8 m/s in a vacuum. Scientists like Galileo, Romer, and Fizeau helped measure this speed through experiments.
2) The electromagnetic spectrum encompasses all types of electromagnetic waves, including visible light, which is a small portion of the spectrum. Different wavelengths of visible light correspond to different colors.
3) Polarization describes the direction of oscillation of the electric field in a light wave. Polarizers can filter light to transmit only certain polarization directions.electromagnetic spectrum and light ppt.pptx



electromagnetic spectrum and light ppt.pptxKathleenSaldon
Ėý
This document provides an overview of light and optics. It covers:
1) The electromagnetic spectrum and different types of electromagnetic waves like radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, X-rays, and gamma rays.
2) Properties of light including that it travels in straight lines at high speed, and how shadows are formed when light is blocked.
3) Reflection - how light bounces off surfaces at the same angle it hits based on the law of reflection, and the differences between clear and diffuse reflection.
4) Colors - how white light is made up of the visible light spectrum, the primary colors, how objects get their color, and using colored light andElectromagnetis Spectrum - Good.ppt



Electromagnetis Spectrum - Good.pptKathleenSaldon
Ėý
The document summarizes key aspects of light and the electromagnetic spectrum. It discusses how light was originally thought to consist of particles but is now understood to behave as waves. It describes the electromagnetic spectrum and defines visible light as a small portion of the spectrum that the human eye can detect. The document also covers the photoelectric effect and how it provided evidence that light can be described as discrete packets of energy called photons.Recently uploaded (20)
Animal husbandry: Purpose, scope and management,dairy animals, breeds and eco...



Animal husbandry: Purpose, scope and management,dairy animals, breeds and eco...tibhathakur77
Ėý
Discription about animal husbandry.Deep Learning-Driven Protein Design for Maize Improvement: AI-Guided Solution...



Deep Learning-Driven Protein Design for Maize Improvement: AI-Guided Solution...Muhammad Salman Iqbal
Ėý
Bridging AI, Synthetic Biology, and Crop Science to Address Global Food Security.
This presentation explores the transformative potential of AI-driven protein design in revolutionizing maize (corn) breeding. Learn how deep learning models like AlphaFold, ESMFold, and RFdiffusion enable rapid engineering of stress-resilient proteins for:
Disease resistance (e.g., fungal pathogens like Fusarium and Puccinia)
Drought and heat tolerance (synthetic transcription factors for root and stomatal optimization)
Nutrient efficiency (engineered phosphate/nitrogen transporters)
Enhanced photosynthesis (AI-designed carbonic anhydrases)
Key highlights:
Case studies from Cell, Science, and Nature Biotechnology (2023â2024) showcasing AI-designed proteins validated in field trials.
Ethical considerations and future directions for AI-guided CRISPR integration in crop improvement.
Visual summaries of protein structures, field data, and AI workflows.
Target audience: Plant scientists, agronomists, bioinformaticians, AI researchers, and students in biotechnology and agriculture.
Hashtags:
#DeepLearning #ProteinDesign #MaizeImprovement #AIinAgriculture #SustainableFarming #CropBreeding #SyntheticBiology #FoodSecurity #AlphaFold #CRISPRMelaku Tafese Awyulachew's_Official letters between organizations and researc...



Melaku Tafese Awyulachew's_Official letters between organizations and researc...Melaku Tafese Awulachew
Ėý
Official letters between organizations and researchersRole of Secondary Metabolites in Defence Mechanism of Plants and itâs Regulation



Role of Secondary Metabolites in Defence Mechanism of Plants and itâs Regulationankitverma144299
Ėý
This information is very helpful for biochemistry students.Automating Compression Ultrasonography of Human Thigh Tissue and Vessels via ...



Automating Compression Ultrasonography of Human Thigh Tissue and Vessels via ...ThrombUS+ Project
Ėý
Rytis Jurkonis from Kaunas University of Technology (Lithuania) presented their recent work entitled âAutomating Compression Ultrasonography of Human Thigh Tissue and Vessels via Strain Estimation." Rytis presented on the methodology along the novel wearable hardware developed to automate compression ultrasonography for DVT detection in the lower limbs. In addition, preliminary results were shared, highlighting the feasibility of an operator-independent method to perform compression ultrasonography.
Presented at BIOSTEC 2025 in Porto, Portugal.
About ThrombUS+: Our interdisciplinary approach centers around creating a novel wearable diagnostic device utilizing autonomous, AI-driven DVT detection. This groundbreaking device incorporates wearable ultrasound hardware, impedance plethysmography, and light reflection rheography for early clot detection. ThrombUS+ is designed for postoperative patients, those undergoing lengthy surgical procedures, cancer patients, bedridden individuals at home or in care units, and women during pregnancy and postpartum.Nutrient deficiency and symptoms in plants



Nutrient deficiency and symptoms in plantslaxmichoudhary77657
Ėý
What is Nutrient Deficiency?
Definition:
âĒ Nutrient deficiency in plants occurs when they lack one or more of the essential minerals required for their growth and development.
âĒ These deficiencies can lead to various physiological disorders and reduced plant productivity.
Categories of Essential Nutrients
âĒ Macronutrients:
âĒ Required in larger quantities for plant growth and development.
Includes primary and secondary nutrients.
Primary Macronutrients:
âĒ Nitrogen (N): Vital for vegetative growth, chlorophyll production, and protein synthesis.
âĒ Phosphorus (P): Important for energy transfer, root development, and flowering.
âĒ Potassium (K): Essential for water regulation, enzyme activation, and disease resistance.
Secondary Macronutrients:
âĒ Calcium (Ca): Important for cell wall structure, root development, and enzyme
activity.
âĒ Magnesium (Mg): Central component of chlorophyll and aids in enzyme activation.
âĒ Sulfur (S): Crucial for amino acids, proteins, and enzyme function.
-> P H O N S K Ca Mg C
âĒ Micronutrients:
âĒ Required in smaller quantities but equally important for plant health.
âĒ Iron (Fe): Essential for chlorophyll synthesis and electron transport in photosynthesis.
âĒManganese (Mn): Important for photosynthesis, respiration, and nitrogen assimilation.
âĒZinc (Zn): Vital for enzyme function and growth regulation.
âĒCopper (Cu): Involved in photosynthetic electron transport and enzyme activity.
âĒBoron (B): Crucial for cell wall formation and reproductive development.
âĒMolybdenum (Mo): Essential for nitrogen fixation and enzyme function in nitrogen metabolism.
-> Fe Cu Mo Zn Mn Cl B Ni.
Mobile Nutrients - Cl, K, Mg, Mo, N, P-> older parts
Immobile Nutrients - B, Cu, Ca, Fe, Mn, S, Zn-> younger parts
.
Phospholipid signaling and it's role in stress tolerance in plant



Phospholipid signaling and it's role in stress tolerance in plantlaxmichoudhary77657
Ėý
Living cells are constantly exposed to various signals from their surroundings.
These signals can be:
Chemical: Such as hormones, pathogen signals, mating signals, and ozone.
Physical: Such as changes in light, temperature, and pressure.
To respond appropriately to these signals, cells have special proteins called receptors on their surface. These receptors detect the signals and convert them into internal messages that the cell can understand and act upon.
How Signals are Processed?
1. Signal Detection: receptors on the cell surface.
2. Transduction:
âĒ The receptor activates proteins inside the cell, which then produce molecules called "second messengers."
3. Signal Amplification and Cascades:
These second messengers amplify the signal and pass it on to other proteins, triggering a cascade of reactions.
4. Response:
âĒ The cascades can lead to changes in gene expression, enzyme activity, or cell behavior, ultimately leading to a physiological response.
What are Phospholipids?
Structure:
Phospholipids are a type of lipid molecule that are a major component of all cell membranes.
They consist of two fatty acid tails that are hydrophobic (repel water) and a phosphate head that is hydrophilic (attracts water).
This unique structure allows them to form bilayers, creating the fundamental structure of cell membranes.
Where are Phospholipids Found in Plants?
Cell Membranes and plasma membranes
Phospholipids are the primary building blocks of cell membranes, including the plasma membrane and internal membranes such as the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), Golgi apparatus, and chloroplast membranes.
Blotting techniques and types of blotting .pptx



Blotting techniques and types of blotting .pptxsakshibhongal26
Ėý
Blotting techniques- types and advantages, disadvantages Grade 08-SCIENCE (BIOLOGY)CELL DIVISION.pptx



Grade 08-SCIENCE (BIOLOGY)CELL DIVISION.pptxMarvinAlegado
Ėý
Cell division is a fundamental biological process that enables the growth, development, and repair of living organisms. It's the process by which a parent cell divides into two or more daughter cells, each carrying a complete set of genetic instructions. This intricate process occurs in two primary ways: mitosis and meiosis. Mitosis is responsible for the creation of identical daughter cells, ensuring the maintenance of genetic information for growth and tissue repair. Meiosis, on the other hand, is a specialized form of cell division that occurs in sexually reproducing organisms, producing gametes (sperm and egg cells) with half the number of chromosomes, contributing to genetic diversity in offspring.Difference between Prokaryotic cell and Eukaryotic cell.pptx



Difference between Prokaryotic cell and Eukaryotic cell.pptxDrSulabhaDeokar
Ėý
This presentation explores the fundamental differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells,distinguishing characteristics of Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes.Describe common cell morphologies and cellular arrangements in typical Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes.
Presentation explains how cells maintain their morphology.
Explore internal and external structures of Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes in terms of their physical structure, chemical structure and function.
This presentation is designed for biology students, educators, and anyone interested in cellular biology. Based on the latest research and scientific discoveries in the field of Microbiology, Microbial Biotechnology and cellular biology. This Presentation has been compiled using information from trusted educational resources and scientific literature.
The purpose of this presentation is to educate and inform the students about the fundamental differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, highlighting their unique structures, functions, and characteristics, which provide a comprehensive understanding of cellular biology.
Educate the students and teachers about the differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells in detail.
This presentation will engage and entertain the students, often with a mix of detail information, colourful pictures and storytelling.
This presentation will motivate and inspire the students to think differently, take action, or pursue a goal.
Definitely it will raise awareness about a ultrastructures of Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes .
This presentation will Provide an update or report on a science projects and progress as well as inspire the graduate students to learn more about cellular biology and its applications.
This presentation will inspire studets, teachers and educational professionals to explore digital resource for e - learnig .
Presentation likely to be used by under graduate and post graduate students, educators or individuals for online learning.
It can work as digital resource for a broader e- learning ecosystem.
This presentation highlights '' NEP-aligned Biotechnology and Biology education.''
"Discover the distinctions between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, from cell walls to genetic material. This presentation provides a comprehensive overview of cellular biology.Learn about the two main types of cells - prokaryotic,eukaryotic and their differences in structure, function, and organization. A great resource for biology learners.Uncover the unique characteristics of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells in this informative PPT.Successful management of intussusception in a cow under double drip anaesthesia



Successful management of intussusception in a cow under double drip anaesthesiarajvet4163
Ėý
Intussusception in a crossbred cow
surgical treatment, double drip anaesthesia and complete recovery of animal with case discussionDrug evaluationâ Organoleptic, Microscopic, Chemical, Biological



Drug evaluationâ Organoleptic, Microscopic, Chemical, BiologicalNistarini College, Purulia (W.B) India
Ėý
This PowerPoint gives a brief idea about the identification of herbal drug plants with special reference to organoleptic studies. The study comprises different parameters like physical, chemical, biological, and other features associated with it. It offers an idea about the need for scientifically identifying drug plants to avoid adulteration.epidemiology (aim, component, principles).pptx



epidemiology (aim, component, principles).pptxlopamudraray88
Ėý
To study historically the rise and fall of disease in the population.
Community diagnosis.
Planning and evaluation.
Evaluation of individuals risks and chances.
Completing the natural history of disease.
Searching for causes and risk factors.
Investigational New drug application process



Investigational New drug application processonepalyer4
Ėý
This file basically contains information related to IND application process in order to get approval for clinical trials.2025-03-03-Data-related-Ethics Issues in Technologies for Professional Learni...



2025-03-03-Data-related-Ethics Issues in Technologies for Professional Learni...Graz University of Technology & Know-Center
Ėý
How could modern LA research address data-related ethics issues in informal and situated professional learning? I will identify in this talk three relevant insights based on field studies around workplace LA interventions: Firstly, in informal and situated learning, data isnât just about the learners. Secondly, the affordances of manual and automatic data tracking for learning are very different, with manual tracking allowing a high degree of learner control over data. Thirdly, learning is not necessarily a shared goal in workplaces. These can be translated into seeing a potential for systems endowed with sufficient natural-language-processing capability (now seemingly at our fingertips with LLMs), and socio-technical design and scenario-based data collection analysis as design and research methods.Deep Learning-Driven Protein Design for Maize Improvement: AI-Guided Solution...



Deep Learning-Driven Protein Design for Maize Improvement: AI-Guided Solution...Muhammad Salman Iqbal
Ėý
Melaku Tafese Awyulachew's_Official letters between organizations and researc...



Melaku Tafese Awyulachew's_Official letters between organizations and researc...Melaku Tafese Awulachew
Ėý
Role of Secondary Metabolites in Defence Mechanism of Plants and itâs Regulation



Role of Secondary Metabolites in Defence Mechanism of Plants and itâs Regulationankitverma144299
Ėý
Drug evaluationâ Organoleptic, Microscopic, Chemical, Biological



Drug evaluationâ Organoleptic, Microscopic, Chemical, BiologicalNistarini College, Purulia (W.B) India
Ėý
2025-03-03-Data-related-Ethics Issues in Technologies for Professional Learni...



2025-03-03-Data-related-Ethics Issues in Technologies for Professional Learni...Graz University of Technology & Know-Center
Ėý
sect17_slidesppt34.ppt
- 1. Chapter 12 Forces and Motion
- 3. Key Concepts âĒ How do forces affect the motion of an object? âĒ What are the four main types of friction? âĒ How do gravity and air resistance affect a falling object? âĒ In what direction does Earthâs gravity act? âĒ Why does a projectile follow a curved path?
- 4. What Is a Force? âĒ A force can cause a resting object to move, or it can accelerate a moving object by changing the objectâs speed or direction. âĒ A push or a pull
- 5. Measuring Force âĒ using a spring scale The downward force arrows represent the weight (a type of force) on the scales. The dial indicator gives a visual measure of the weight. You can use an arrow to represent the direction and strength of a force. The direction of the arrow represents the direction of the force. The length of the arrow represents the strength, or magnitude, of the force.
- 6. Units of Force âĒ Force is measured in newtons (N) âĒ One newton is the force that causes a 1- kilogram mass to accelerate at a rate of 1 meter per second each second (1 m/s2).
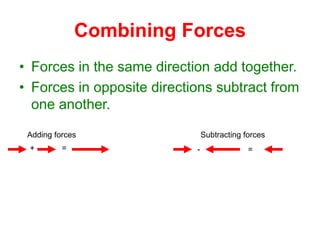
- 7. Combining Forces âĒ Forces in the same direction add together. âĒ Forces in opposite directions subtract from one another. Adding forces + = Subtracting forces - =
- 8. Balanced Forces âĒ When the forces on an object are balanced, the net force is zero and there is no change in the objectâs motion. 3 In this tug of war, the two groups pull with equal forces in opposite directions. The forces combine by subtracting from each other + = 0
- 9. Unbalanced Forces âĒ When an unbalanced force acts on an object, the object accelerates. âĒ Often, the forces on an object are unbalanced. âĒ An unbalanced force is a force that results when the net force acting on an object is not equal to zero. Adding forces + = Subtracting forces - =
- 10. Friction âĒ Friction, a force that opposes the motion of objects that touch as they move past each other âĒ There are four main types of friction: static friction, sliding friction, rolling friction, and fluid friction.
- 11. Static Friction âĒ The friction force that acts on objects that are not moving. âĒ Static friction always acts in the direction opposite to that of the applied force. âĒ You experience static friction every time you take a step. As you push off with each step, static friction between the ground and your shoe keeps your shoe from sliding. Static friction Push Static friction acts opposite the direction of the force you apply to move the plant.
- 12. Sliding Friction âĒ A force that opposes the direction of motion of an object as it slides over a surface. âĒ Because sliding friction is less than static friction, less force is needed to keep an object moving than to start it moving. Sliding friction Potted tree accelerates. When you push with more force, the potted tree begins to slide. Push
- 13. Rolling Friction âĒ The friction force that acts on rolling objects. âĒ For a given set of materials, the force of rolling friction is about 100 to 1000 times less than the force of static or sliding friction. Ball bearings in these wheels greatly reduce friction by replacing sliding friction with rolling friction.
- 14. Fluid Friction âĒ Force that opposes the motion of an object through a fluid. âĒ Water and a mixture of gases such as air are known as fluids. âĒ You feel fluid friction when stirring thick cake batter. âĒ Fluid friction acting on an object moving through the air is known as air resistance. âĒ At higher speeds, air resistance can become a significant force.
- 15. Gravity âĒ A force that acts between any two masses. âĒ Gravity is an attractive force, that is, it pulls objects together. âĒ gravity does not require objects to be in contact for it to act on them âĒ Earthâs gravity acts downward toward the center of Earth. âĒ an upward force usually balances the downward force of gravity Gravity Supporting force
- 16. Falling Objects âĒ Gravity causes objects to accelerate downward, whereas air resistance acts in the direction opposite to the motion and reduces acceleration. âĒ Terminal velocity is the constant velocity of a falling object when the force of air resistance equals the force of gravity. Gravity Air resistance This flying squirrel takes advantage of air resistance to slow its fall and increase the distance covered in the jump.
- 17. Projectile Motion âĒ When you throw a ball forward, youâll notice that it actually follows a curved path. âĒ projectile motion, the motion of a falling object (projectile) after it is given an initial forward velocity. âĒ Air resistance and gravity are the only forces acting on a projectile. âĒ The combination of an initial forward velocity and the downward vertical force of gravity causes the ball to follow a curved path. Although their masses are different, the blue and green balls fall at the same rate. The yellow ball is a projectile, following a curved path. The two balls fall with the same acceleration and strike the ground at the same time.
- 18. Reviewing Concepts âĒ 1. How is the motion of an object affected when a force acts on it? âĒ 2. List the four types of friction. âĒ 3. How does air resistance affect the acceleration of a falling object? âĒ 4. Earthâs gravitational force acts in what direction? âĒ 5. Describe why a projectile follows a curved path.







