Test Ludvigsson
0 likes379 views
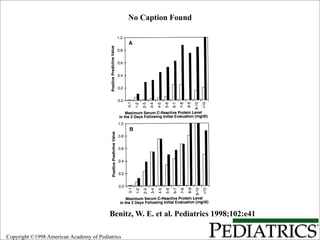
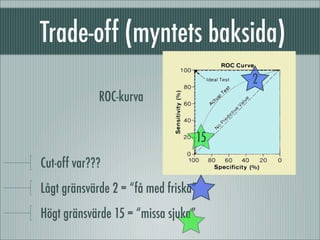
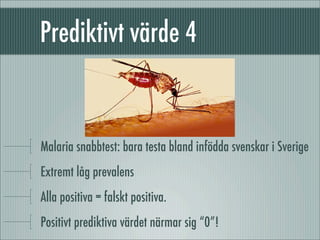
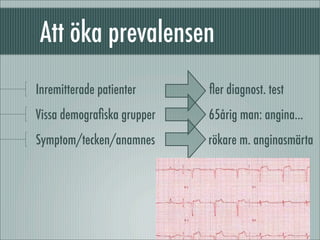
fÃķrelÃĪsning 090205: om sensitivitet, specificitet, prediktivt vÃĪrde
1 of 35
Download to read offline






























More Related Content
Viewers also liked (12)
Similar to Test Ludvigsson (9)
Ad
More from Jonas Ludvigsson (20)
Ad
