UNIT 6 Factoring and Distributing Expressions _2_.pptx
Download as PPTX, PDF0 likes12 views
UNIT 6 Factoring and Distributing Expressions _2_.pptx UNIT 6 Factoring and Distributing Expressions _2_.pptx UNIT 6 Factoring and Distributing Expressions _2_.pptx UNIT 6 Factoring and Distributing Expressions _2_.pptx
1 of 21
Download to read offline



















Recommended
Factoring



Factoringbslkmljsl
╠²
The document discusses different methods for factoring polynomials:
1) Factoring the greatest common factor (GCF) involves finding a number or variable that is common to all terms and dividing each term by the GCF.
2) Factoring the difference of squares uses the formula a^2 - b^2 = (a+b)(a-b) and works for binomials where one term is a perfect square and the other is the negative of a perfect square.
3) Factoring trinomials of the forms x^2 + bx + c and ax^2 + bx + c involves finding two numbers whose product and sum meet certain criteria related to the coefficients in the trinomial.Chapter 1 review



Chapter 1 reviewCinnaminson Public Schools
╠²
This document summarizes a chapter review with multiple choice and short answer questions covering properties of numbers, order of operations, solving equations, inequalities, and word problems involving money. It contains 16 total questions across 5 sections: I) Stating properties from number statements, II) Simplifying expressions, III) Evaluating expressions for given values, IV) More expression simplification, and V) Word problems involving money amounts and comparisons of expressions.Operation on Functions.pptx



Operation on Functions.pptxAPHRODITE51
╠²
Operations on functions can include addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, and composition.
Adding two functions results in a function where the values are added at each point. Multiplying functions results in a function where the values are multiplied at each point. Composing functions means applying one function to another, resulting in another function.1st Quarter MATH 8 module



1st Quarter MATH 8 moduleRusseneth Joy Nalo
╠²
The document is a lesson plan on factoring polynomials from St. Mary's Academy. It begins with definitions of factoring and examples of factoring polynomials with a common monomial factor. It then discusses factoring by grouping, factoring the difference of two squares using the formula (x + y)(x - y), and factoring the sum or difference of two cubes using the formulas (a + b)(a^2 - ab + b^2) and (a - b)(a^2 + ab + b^2). It concludes with an example word problem involving factoring polynomials.March 6



March 6khyps13
╠²
The document provides a summary of factoring methods:
- Reviewing factoring methods covered such as greatest common factor (GCF) and factoring trinomials
- Announcing that test grades have been posted for one class and quarter grades will be posted for another class tomorrow
- Introducing a new factoring method called "difference of squares" and new Khan Academy topics being addedUnits 1 3 review



Units 1 3 reviewmlabuski
╠²
1. The document provides an overview of the curriculum for 6th grade math including topics, pacing, and vocabulary for three units: Expressions and Equations, Solving Equations and Inequalities, and Decimals.
2. Key topics include exponents, order of operations, variables and expressions, translating between words and math, equations and solutions, adding/subtracting/multiplying/dividing decimals.
3. Each unit lists the corresponding textbook chapters and New York State Common Core Learning Standards addressed. Common assessments are also included.Algebraic expressions



Algebraic expressionsMELIKIPROTICHAMOS
╠²
The document defines key concepts in algebraic expressions including:
- Terms, coefficients, like terms and unlike terms
- Types of expressions including monomials, binomials, trinomials and polynomials
- How to combine like terms and simplify expressions
- Using variables to represent unknown numbers and writing expressions to describe word problems mathematically
The document also provides examples demonstrating how to identify terms, coefficients, like and unlike terms in expressions, how to simplify expressions by combining like terms, and how to evaluate expressions by substituting values for variables.1 of 11UMGC College Algebra MATH 107 6980 - Fall 2020 ŌĆō Instruct.docx



1 of 11UMGC College Algebra MATH 107 6980 - Fall 2020 ŌĆō Instruct.docxteresehearn
╠²
1 of 11
UMGC College Algebra MATH 107 6980 - Fall 2020 ŌĆō Instructor: Timothy J. Elsner
Page 1 of 11
MATH 107 FINAL EXAMINATION - Nov 15, 2020 - Due Tue Nov 17 11:59 pm
This is an open-book exam. You may refer to your text and other course materials as you work on the exam, and you may
use a calculator. You must complete the exam individually. Neither collaboration nor consultation with others is allowed.
MAKE CERTAIN YOUR SUBMITTAL IS CLEARLY READABLE. FOR THE SHORT ANSWER SECTIONS make sure your ANSWER IS CIRCLED
There are 30 problems. Problems #1ŌĆō12 are Multiple Choice.
Problems #13ŌĆō21 are Short Answer. (Work not required to be shown)
Problems #22ŌĆō30 are Short Answer with work required to be shown. Also read:
Mathematics in Montessori
MULTIPLE CHOICE
1. Determine the domain and range of the piecewise function. 1._______
A. Domain [ -5, 5]; Range [- 6, 6]
B. Domain [- 4, 5]; Range [- 6, 6]
C. Domain [- 6, 5]; Range [- 4, 6]
D. Domain [- 6, 6]; Range [- 4, 5]
2. Solve: x = ŌłÜŌłÆ8x + 9 and check your solution(s) 2.________
A. x = - 9
B. x = 1
C. x = {-9, 1}
D. No
Solution
2 of 11
3. Determine the x interval(s) on which the function is increasing. 3.__________
A. (ŌłÆ4, 0] and [4, Ōł×)
B. [0, 4]
C. (ŌłÆŌł×, 3) Ōł¬ [ŌłÆ1, 5 ]
D. (ŌłÆŌł×, ŌłÆ4] and [0, 4 ]
4. Determine whether the graph of Y = | x | - 3 is symmetric with respect 4. _________
to the origin, the x-axis, or the y-axis.
A. symmetric with respect to the x-axis only
B. symmetric with respect to the y-axis only
C. symmetric with respect to the origin only
D. not symmetric with respect to the x-axis, not symmetric with respect to the y-axis,
and not symmetric with respect to the origin
5. Find the solution to the inequality : | 6 ŌĆō x | + 3 < 8 5. ___________
A. (????, Ōł×)
B. (???? , ???????? )
C. (ŌłÆŌł×, ????) Ōł¬ (????????, Ōł×)
D. (ŌłÆ1, ŌłÆ????????)
3 of 11
6. Which of the following represents the graph of ŌłÆ3x + 5y = 15 ? __________
A. B.
C. D.
7. Write a slope-intercept equation for a line perpendicular to the line ŌłÆ3x + 5y = 15
which passes through the point (6, ŌĆō 5).
A. y = ŌłÆ ????
???? ???? + ????
B. y = ????
???? ???? ŌłÆ ????????
C. y = ŌłÆ ????
???? ???? + ????
D. y = ????
???? ???? ŌłÆ ????????
4 of 11
8. Choose what type of graph is below ? 8.___________
A. It is not a function.
B. It is a function and it is one-to-one.
C. It is a function but it is not one-to-one.
D. It is not a function and it is not one-to-one.
9. Express as a single logarithm: log (2x + 1) + log 2x - 4 log x 9.__________
A. log ( 4x+1
4x )
B. log ( 2x(2x+1)
4x )
C. log ( 4x2 - 2x)
D. log ( 2???? (2???? + 1)
????4 )
10. Which of the functions correspond to the graph? 10.__________
A. f(x) = e x
B. f(x) = e x ŌĆō 1
C. f(x) = log(x)
D. f(x) = log(x) ŌĆō 1
5 of 11
11. Suppose that for a function f(x), that it has exactly 1 zero (or 1 X-intercept)
Which of the following statements MUST true? (only one answer is correct) 11. _________
A. f(x) is linear and has a positive slope.
B.3.complex numbers Further Mathematics Zimbabwe Zimsec Cambridge



3.complex numbers Further Mathematics Zimbabwe Zimsec Cambridgealproelearning
╠²
This document introduces complex numbers and their algebra. It discusses how quadratic equations can lead to complex number solutions and how to represent complex numbers in the forms a + bi and rcis(╬Ė). It then covers the basic arithmetic operations of addition, subtraction, multiplication and division of complex numbers. It provides examples of solving equations with complex number solutions. The key points are:
- Complex numbers allow solutions to quadratic equations that have no real number solutions.
- Complex numbers can be represented as a + bi or rcis(╬Ė).
- Operations on complex numbers follow the same rules as real numbers but use i2 = -1.
- Equations with complex number variables can be solved using the same methods as real numbersFactoring Polynomials (1).pptx



Factoring Polynomials (1).pptxMartiNBaccay2
╠²
The document discusses factoring polynomials and finding the roots of polynomial equations. It defines polynomials and polynomial equations. It then covers several methods for factoring polynomials, including factoring polynomials with a common monomial factor, factoring polynomials that are a difference of squares, factoring trinomials, and factoring polynomials by grouping. It also discusses using the factors to find the solutions or roots of a polynomial equation, which are also known as the zeros of a polynomial function.Mathnasium Presentation (1)



Mathnasium Presentation (1)Muhammad Arslan
╠²
This document provides an outline for teaching various factoring techniques. It begins with definitions of algebraic expressions, polynomials, factors, and factoring. It then covers finding the greatest common factor, factoring by using the GCF, factoring by grouping, factoring differences of squares, factoring perfect square trinomials using the special formula, and solving word problems using factoring. Examples are provided for each technique to demonstrate how to factor different polynomial expressions. Special cases like the sum and difference of cubes are also discussed. The document concludes with an explanation of the quadratic formula.11.4



11.4nglaze10
╠²
1) To add or subtract rational expressions with the same or different denominators, we first find the least common denominator (LCD), which is the least common multiple of the denominators.
2) We then rewrite the rational expressions with the LCD as the common denominator before adding or subtracting the numerators.
3) Once the rational expressions have been rewritten with the same denominator, we can perform the addition or subtraction operation as we would with numerical fractions.Factoring polynomials



Factoring polynomialsMark Ryder
╠²
Factoring is writing a polynomial as a product of two or more polynomials. The main techniques for factoring polynomials are finding the greatest common factor, factoring trinomials of the form ax^2 + bx + c, using special factoring patterns like the difference and sum of squares, and factoring polynomials with four or more terms by grouping. The goal is to factor the polynomial completely into prime factors that cannot be further factored.Q1 week 1 (common monomial,sum & diffrence of two cubes,difference of tw...



Q1 week 1 (common monomial,sum & diffrence of two cubes,difference of tw...Walden Macabuhay
╠²
It consists of ten units in which the first unit focuses on the special products and factors. Its deals with the study of rational algebraic expressions. It aims to empower students with life ŌĆō long learning and helps them to attain functional literacy. The call of the K to 12 curriculum allow the students to have an active involvement in learning through demonstration of skills, manifestations of communication skills, development of analytical and creative thinking and understanding of mathematical applications and connections. Unit 5 powerpoint[1] algebra (1)![Unit 5 powerpoint[1] algebra (1)](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/unit5powerpoint1algebra1-120804090149-phpapp02-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Unit 5 powerpoint[1] algebra (1)](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/unit5powerpoint1algebra1-120804090149-phpapp02-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Unit 5 powerpoint[1] algebra (1)](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/unit5powerpoint1algebra1-120804090149-phpapp02-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Unit 5 powerpoint[1] algebra (1)](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/unit5powerpoint1algebra1-120804090149-phpapp02-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
Unit 5 powerpoint[1] algebra (1)John O'Driscoll
╠²
Here are the steps to solve this equation:
1) The equation is: x + 3 / 6 = 1
2) Multiply both sides by 6: x + 3 = 6
3) Subtract 3 from both sides: x = 3
Therefore, the solution is x = 3.
(d) The equation is: 3(y ŌłÆ 7) = 14 ŌłÆ y/2
3y ŌłÆ 21 = 14 ŌłÆ y/2
3y ŌłÆ 21 + y/2 = 14
(12y ŌłÆ 21)/6 = 14
12y ŌłÆ 21 = 84
12y = 105
y = 9
The solution is y = 9.
(Check: if y =Swartz Factoring



Swartz Factoringswartzje
╠²
The document discusses factoring polynomials. It begins by outlining Swartz's steps for factoring: 1) factor out the greatest common factor (GCF), 2) factor based on the number of terms using techniques like difference of squares or grouping. It then explains how to find the GCF of integers or terms. Several examples are provided of factoring polynomials by finding the GCF and using techniques like difference of squares, grouping, or recognizing perfect square trinomials. Factoring trinomials of the form x^2 + bx + c is also demonstrated.A26-3 Polynomial Operations Notes



A26-3 Polynomial Operations Notesvhiggins1
╠²
This document provides instructions for adding, subtracting, and multiplying polynomials. It explains that when adding polynomials, like terms should be combined. When subtracting polynomials, the signs of the second polynomial should be changed before combining like terms. When multiplying polynomials, each term of the first polynomial should be multiplied by each term of the second polynomial before combining like terms. Examples are provided to demonstrate each process.Properties of Addition & Multiplication



Properties of Addition & Multiplicationitutor
╠²
The document discusses various properties of real numbers including the commutative, associative, identity, inverse, zero, and distributive properties. It also covers topics such as combining like terms, translating word phrases to algebraic expressions, and simplifying algebraic expressions. Examples are provided to illustrate each concept along with explanations of key terms like coefficients, variables, and like terms.Colour in Mathematics 



Colour in Mathematics Colleen Young
╠²
The document discusses how colour can be used in mathematics to add clarity. It provides examples of how colour highlights which terms are associated with signs in algebra examples. Colour can also emphasise the order of operations. Further examples show how colour aids understanding of topics like factorisation, composite functions, inequalities, coordinate geometry, binomial expansion, completing the square, circle geometry, integration, and decision mathematics algorithms. Worked solutions with colour coding are also suggested to help students understand steps at their own pace.Final Exam Name___________________________________Si.docx



Final Exam Name___________________________________Si.docxcharlottej5
╠²
Final Exam Name___________________________________
Silva Math 96 Spring 2020
YOU MUST SHOW ALL WORK AND BOX YOUR ANSWERS FOR CREDIT. WORK ALONE.
Solve the absolute value inequality. Write your answer
in interval notation.
1) |2x - 12 |> 2
Solve the compound inequality. Graph the solution set.
Write your answer in interval notation.
2) -4x > -8 and x + 4 > 3
Solve the three-part inequality. Write your answer in
interval notation.
3) -1 < 3x + 2 < 14
Solve the absolute value equation.
4) 4x + 9 = 2x + 7
Solve the compound inequality.
5) 3( x + 4 ) Ōēź 0 or 4 ( x + 4 ) Ōēż 4
Solve the inequality. Graph the solution set and write
your answer in interval notation.
6) |5k + 8| > -6
Solve the inequality graphically. Write your answer in
interval notation .
7) x + 3 Ōēź 1
x-8 -6 -4 -2 2
y
8
6
4
2
x-8 -6 -4 -2 2
y
8
6
4
2
1
Graph the system of inequalities.
8) 2x + 8y Ōēź -4
y < - 3
2
x + 6
x-10 -8 -6 -4 -2 2 4 6 8 10
y
10
8
6
4
2
-2
-4
-6
-8
-10
x-10 -8 -6 -4 -2 2 4 6 8 10
y
10
8
6
4
2
-2
-4
-6
-8
-10
Find the determinant of the given matrix.
9) 10 5
0 -4
Use Cramer's rule to solve the system of linear
equations.
10) 6x + 5y = -12
2x - 2y = -4
Write a system that models the situation. Then solve the
system using any method. Must show work for credit.
11)A vendor sells hot dogs, bags of potato chips,
and soft drinks. A customer buys 3 hot dogs,
4 bags of potato chips, and 5 soft drinks for
$14.00. The price of a hot dog is $0.25 more
than the price of a bag of potato chips. The
cost of a soft drink is $1.25 less than the price
of two hot dogs. Find the cost of each item.
Use row reduced echelon form to solve the system.
12) x + y + z = 3
x - y + 4z = 11
5x + y + z = -9
2
Find the domain of f. Write your answer in interval
notation.
13) f(x) = 13 - 9x
If possible, simplify the expression. If any variables
exist, assume that they are positive.
14) 2x + 6 32x + 6 8x
Match to the equivalent expression.
15) 100-1/2
A) 1
1000
B) 1
10
C) 1
100
D) 1
10
Write the expression in standard form.
16) (5 + 8i) - (-3 + i)
Simplify the expression. Assume that all variables are
positive.
17) 5 t
5
z10
Solve the equation.
18) 3x + 1 = 3 + x - 4
Write the expression in standard form.
19) 3 + 3i
5 + 3i
3
Write the equation in vertex form.
20) y = x2 + 5x + 2
The graph of ax2 + bx + c is given. Use this graph to solve
ax2 + bx + c = 0, if possible.
21)
x-5 5 10
y
50
40
30
20
10
-10
-20
-30
-40
-50
x-5 5 10
y
50
40
30
20
10
-10
-20
-30
-40
-50
Solve the equation. Write complex solutions in standard
form.
22) 4x2 + 5x + 5 = 0
Graph the quadratic function by its properties.
23) f(x) = 1
3
x2 - 2x + 3
x
y
x
y
Solve the equation. Find all real solutions.
24) 2(x - 1)2 + 11(x - 1) + 12 = 0
Solve the problem.
25) The length of a table is 12 inches more than its
width. If the area of the table is 2668 square
inches, what is its length?
4
Solve the equation..A.B. .docx



A.B. .docxannetnash8266
╠²
A.
B.
A.
B.
A.B.C.D.
A.
B.
C.
D.
A.
B.
C.
A.
B.
(
{
}
)A.
B.
A.
B.
C.
A.
B.
A.
B.
A.
B.
A.
B.
Math 107 Final ExaminationSummer, 20151
Math 107 College AlgebraName______________________________
Final Examination: Summer, 2015Instructor __________________________
Answer Sheet
Instructions:
This is an open-book exam. You may refer to your text and other course materials as you work on the exam, and you may use a calculator.
Record your answers and work in this document.
There are 30 problems.
Problems #1-12 are multiple choice. Record your choice for each problem.
Problems #13-21 are short answer. Record your answer for each problem.
Problems #22-30 are short answer with work required. When requested, show all work and write all answers in the spaces allotted on the following pages. You may type your work using plain-text formatting or an equation editor, or you may hand-write your work and scan it. In either case, show work neatly and correctly, following standard mathematical conventions. Each step should follow clearly and completely from the previous step. If necessary, you may attach extra pages.
.
Name _____________________Date___________________
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Record your answer choices.
1.7.
2.8.
3.9.
4.10.
5.11.
6.12.
SHORT ANSWER. Record your answers below.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
19. (a)
(b)
(c)
20. (a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
21. (a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
SHORT ANSWER with Work Shown. Record your answers and work.
Problem Number
Solution
22
Answers:
(a)
(b)
Work/for part (a) and explanation for part (b):
23
Answers:
(a)
(b)
(c)
Work for part (a):
24
Answer:
Work:
25
Answer:
Work:
26
Answers:
(a)
(b)
Work for part (a) and for part (b):
27
Answer:
Work:
28
Answer:
Work:
29
Answers:
(a)
(b)
Work for (b):
30
Answer:
Work:
College Algebra MATH 107 Summer, 2015, V3.1
Page 1 of 11
MATH 107 FINAL EXAMINATION
This is an open-book exam. You may refer to your text and other course materials as you work
on the exam, and you may use a calculator. You must complete the exam individually.
Neither collaboration nor consultation with others is allowed.
Record your answers and work on the separate answer sheet provided.
There are 30 problems.
Problems #1ŌĆō12 are Multiple Choice.
Problems #13ŌĆō21 are Short Answer. (Work not required to be shown)
Problems #22ŌĆō30 are Short Answer with work required to be shown.
MULTIPLE CHOICE
1. Determine the domain and range of the piecewise functi.RATIONAL ALGEBRAIC EXPRESSIONS and Operations.pptx



RATIONAL ALGEBRAIC EXPRESSIONS and Operations.pptxresistancemarc47
╠²
operations on rational algebraic expressionsRATIONAL ALGEBRAIC EXPRESSIONS and Operations.pptx



RATIONAL ALGEBRAIC EXPRESSIONS and Operations.pptxresistancemarc47
╠²
operations on rational algebraic expressionsAdding and Subtracting Polynomials - Math 7 Q2W4 LC1



Adding and Subtracting Polynomials - Math 7 Q2W4 LC1Carlo Luna
╠²
This document discusses adding and subtracting polynomials. It defines key polynomial terms like monomial, binomial, and trinomial. It explains that when adding or subtracting polynomials, only like terms can be combined by adding or subtracting their coefficients while keeping the variable parts the same. Examples are provided to demonstrate adding and subtracting polynomials, including real-life word problems involving combining polynomial expressions to model total areas or profits. The overall goal is for students to learn how to perform operations on polynomials.Colour in Mathematics Colleen Young July 2021



Colour in Mathematics Colleen Young July 2021Colleen Young
╠²
The document discusses how using colour in mathematics teaching can help emphasize key elements like terms, operations, and steps. It provides examples of how colour is used to highlight like terms, operations order, and parts of equations. The examples cover topics ranging from algebra, functions, geometry, calculus, and more to demonstrate how colour brings additional clarity.1-5 Divide Multi-Digit Numbers.pptx1-5 Divide Multi-Digit Numbers.pptx



1-5 Divide Multi-Digit Numbers.pptx1-5 Divide Multi-Digit Numbers.pptxAreejAhmed38
╠²
1-5 Divide Multi-Digit Numbers.pptxlesson 1-4 Multiply Decimals.pptxlesson 1-4 Multiply Decimals.pptx



lesson 1-4 Multiply Decimals.pptxlesson 1-4 Multiply Decimals.pptxAreejAhmed38
╠²
lesson 1-4 Multiply Decimals.pptxMore Related Content
Similar to UNIT 6 Factoring and Distributing Expressions _2_.pptx (20)
1 of 11UMGC College Algebra MATH 107 6980 - Fall 2020 ŌĆō Instruct.docx



1 of 11UMGC College Algebra MATH 107 6980 - Fall 2020 ŌĆō Instruct.docxteresehearn
╠²
1 of 11
UMGC College Algebra MATH 107 6980 - Fall 2020 ŌĆō Instructor: Timothy J. Elsner
Page 1 of 11
MATH 107 FINAL EXAMINATION - Nov 15, 2020 - Due Tue Nov 17 11:59 pm
This is an open-book exam. You may refer to your text and other course materials as you work on the exam, and you may
use a calculator. You must complete the exam individually. Neither collaboration nor consultation with others is allowed.
MAKE CERTAIN YOUR SUBMITTAL IS CLEARLY READABLE. FOR THE SHORT ANSWER SECTIONS make sure your ANSWER IS CIRCLED
There are 30 problems. Problems #1ŌĆō12 are Multiple Choice.
Problems #13ŌĆō21 are Short Answer. (Work not required to be shown)
Problems #22ŌĆō30 are Short Answer with work required to be shown. Also read:
Mathematics in Montessori
MULTIPLE CHOICE
1. Determine the domain and range of the piecewise function. 1._______
A. Domain [ -5, 5]; Range [- 6, 6]
B. Domain [- 4, 5]; Range [- 6, 6]
C. Domain [- 6, 5]; Range [- 4, 6]
D. Domain [- 6, 6]; Range [- 4, 5]
2. Solve: x = ŌłÜŌłÆ8x + 9 and check your solution(s) 2.________
A. x = - 9
B. x = 1
C. x = {-9, 1}
D. No
Solution
2 of 11
3. Determine the x interval(s) on which the function is increasing. 3.__________
A. (ŌłÆ4, 0] and [4, Ōł×)
B. [0, 4]
C. (ŌłÆŌł×, 3) Ōł¬ [ŌłÆ1, 5 ]
D. (ŌłÆŌł×, ŌłÆ4] and [0, 4 ]
4. Determine whether the graph of Y = | x | - 3 is symmetric with respect 4. _________
to the origin, the x-axis, or the y-axis.
A. symmetric with respect to the x-axis only
B. symmetric with respect to the y-axis only
C. symmetric with respect to the origin only
D. not symmetric with respect to the x-axis, not symmetric with respect to the y-axis,
and not symmetric with respect to the origin
5. Find the solution to the inequality : | 6 ŌĆō x | + 3 < 8 5. ___________
A. (????, Ōł×)
B. (???? , ???????? )
C. (ŌłÆŌł×, ????) Ōł¬ (????????, Ōł×)
D. (ŌłÆ1, ŌłÆ????????)
3 of 11
6. Which of the following represents the graph of ŌłÆ3x + 5y = 15 ? __________
A. B.
C. D.
7. Write a slope-intercept equation for a line perpendicular to the line ŌłÆ3x + 5y = 15
which passes through the point (6, ŌĆō 5).
A. y = ŌłÆ ????
???? ???? + ????
B. y = ????
???? ???? ŌłÆ ????????
C. y = ŌłÆ ????
???? ???? + ????
D. y = ????
???? ???? ŌłÆ ????????
4 of 11
8. Choose what type of graph is below ? 8.___________
A. It is not a function.
B. It is a function and it is one-to-one.
C. It is a function but it is not one-to-one.
D. It is not a function and it is not one-to-one.
9. Express as a single logarithm: log (2x + 1) + log 2x - 4 log x 9.__________
A. log ( 4x+1
4x )
B. log ( 2x(2x+1)
4x )
C. log ( 4x2 - 2x)
D. log ( 2???? (2???? + 1)
????4 )
10. Which of the functions correspond to the graph? 10.__________
A. f(x) = e x
B. f(x) = e x ŌĆō 1
C. f(x) = log(x)
D. f(x) = log(x) ŌĆō 1
5 of 11
11. Suppose that for a function f(x), that it has exactly 1 zero (or 1 X-intercept)
Which of the following statements MUST true? (only one answer is correct) 11. _________
A. f(x) is linear and has a positive slope.
B.3.complex numbers Further Mathematics Zimbabwe Zimsec Cambridge



3.complex numbers Further Mathematics Zimbabwe Zimsec Cambridgealproelearning
╠²
This document introduces complex numbers and their algebra. It discusses how quadratic equations can lead to complex number solutions and how to represent complex numbers in the forms a + bi and rcis(╬Ė). It then covers the basic arithmetic operations of addition, subtraction, multiplication and division of complex numbers. It provides examples of solving equations with complex number solutions. The key points are:
- Complex numbers allow solutions to quadratic equations that have no real number solutions.
- Complex numbers can be represented as a + bi or rcis(╬Ė).
- Operations on complex numbers follow the same rules as real numbers but use i2 = -1.
- Equations with complex number variables can be solved using the same methods as real numbersFactoring Polynomials (1).pptx



Factoring Polynomials (1).pptxMartiNBaccay2
╠²
The document discusses factoring polynomials and finding the roots of polynomial equations. It defines polynomials and polynomial equations. It then covers several methods for factoring polynomials, including factoring polynomials with a common monomial factor, factoring polynomials that are a difference of squares, factoring trinomials, and factoring polynomials by grouping. It also discusses using the factors to find the solutions or roots of a polynomial equation, which are also known as the zeros of a polynomial function.Mathnasium Presentation (1)



Mathnasium Presentation (1)Muhammad Arslan
╠²
This document provides an outline for teaching various factoring techniques. It begins with definitions of algebraic expressions, polynomials, factors, and factoring. It then covers finding the greatest common factor, factoring by using the GCF, factoring by grouping, factoring differences of squares, factoring perfect square trinomials using the special formula, and solving word problems using factoring. Examples are provided for each technique to demonstrate how to factor different polynomial expressions. Special cases like the sum and difference of cubes are also discussed. The document concludes with an explanation of the quadratic formula.11.4



11.4nglaze10
╠²
1) To add or subtract rational expressions with the same or different denominators, we first find the least common denominator (LCD), which is the least common multiple of the denominators.
2) We then rewrite the rational expressions with the LCD as the common denominator before adding or subtracting the numerators.
3) Once the rational expressions have been rewritten with the same denominator, we can perform the addition or subtraction operation as we would with numerical fractions.Factoring polynomials



Factoring polynomialsMark Ryder
╠²
Factoring is writing a polynomial as a product of two or more polynomials. The main techniques for factoring polynomials are finding the greatest common factor, factoring trinomials of the form ax^2 + bx + c, using special factoring patterns like the difference and sum of squares, and factoring polynomials with four or more terms by grouping. The goal is to factor the polynomial completely into prime factors that cannot be further factored.Q1 week 1 (common monomial,sum & diffrence of two cubes,difference of tw...



Q1 week 1 (common monomial,sum & diffrence of two cubes,difference of tw...Walden Macabuhay
╠²
It consists of ten units in which the first unit focuses on the special products and factors. Its deals with the study of rational algebraic expressions. It aims to empower students with life ŌĆō long learning and helps them to attain functional literacy. The call of the K to 12 curriculum allow the students to have an active involvement in learning through demonstration of skills, manifestations of communication skills, development of analytical and creative thinking and understanding of mathematical applications and connections. Unit 5 powerpoint[1] algebra (1)![Unit 5 powerpoint[1] algebra (1)](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/unit5powerpoint1algebra1-120804090149-phpapp02-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Unit 5 powerpoint[1] algebra (1)](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/unit5powerpoint1algebra1-120804090149-phpapp02-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Unit 5 powerpoint[1] algebra (1)](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/unit5powerpoint1algebra1-120804090149-phpapp02-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![Unit 5 powerpoint[1] algebra (1)](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/unit5powerpoint1algebra1-120804090149-phpapp02-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
Unit 5 powerpoint[1] algebra (1)John O'Driscoll
╠²
Here are the steps to solve this equation:
1) The equation is: x + 3 / 6 = 1
2) Multiply both sides by 6: x + 3 = 6
3) Subtract 3 from both sides: x = 3
Therefore, the solution is x = 3.
(d) The equation is: 3(y ŌłÆ 7) = 14 ŌłÆ y/2
3y ŌłÆ 21 = 14 ŌłÆ y/2
3y ŌłÆ 21 + y/2 = 14
(12y ŌłÆ 21)/6 = 14
12y ŌłÆ 21 = 84
12y = 105
y = 9
The solution is y = 9.
(Check: if y =Swartz Factoring



Swartz Factoringswartzje
╠²
The document discusses factoring polynomials. It begins by outlining Swartz's steps for factoring: 1) factor out the greatest common factor (GCF), 2) factor based on the number of terms using techniques like difference of squares or grouping. It then explains how to find the GCF of integers or terms. Several examples are provided of factoring polynomials by finding the GCF and using techniques like difference of squares, grouping, or recognizing perfect square trinomials. Factoring trinomials of the form x^2 + bx + c is also demonstrated.A26-3 Polynomial Operations Notes



A26-3 Polynomial Operations Notesvhiggins1
╠²
This document provides instructions for adding, subtracting, and multiplying polynomials. It explains that when adding polynomials, like terms should be combined. When subtracting polynomials, the signs of the second polynomial should be changed before combining like terms. When multiplying polynomials, each term of the first polynomial should be multiplied by each term of the second polynomial before combining like terms. Examples are provided to demonstrate each process.Properties of Addition & Multiplication



Properties of Addition & Multiplicationitutor
╠²
The document discusses various properties of real numbers including the commutative, associative, identity, inverse, zero, and distributive properties. It also covers topics such as combining like terms, translating word phrases to algebraic expressions, and simplifying algebraic expressions. Examples are provided to illustrate each concept along with explanations of key terms like coefficients, variables, and like terms.Colour in Mathematics 



Colour in Mathematics Colleen Young
╠²
The document discusses how colour can be used in mathematics to add clarity. It provides examples of how colour highlights which terms are associated with signs in algebra examples. Colour can also emphasise the order of operations. Further examples show how colour aids understanding of topics like factorisation, composite functions, inequalities, coordinate geometry, binomial expansion, completing the square, circle geometry, integration, and decision mathematics algorithms. Worked solutions with colour coding are also suggested to help students understand steps at their own pace.Final Exam Name___________________________________Si.docx



Final Exam Name___________________________________Si.docxcharlottej5
╠²
Final Exam Name___________________________________
Silva Math 96 Spring 2020
YOU MUST SHOW ALL WORK AND BOX YOUR ANSWERS FOR CREDIT. WORK ALONE.
Solve the absolute value inequality. Write your answer
in interval notation.
1) |2x - 12 |> 2
Solve the compound inequality. Graph the solution set.
Write your answer in interval notation.
2) -4x > -8 and x + 4 > 3
Solve the three-part inequality. Write your answer in
interval notation.
3) -1 < 3x + 2 < 14
Solve the absolute value equation.
4) 4x + 9 = 2x + 7
Solve the compound inequality.
5) 3( x + 4 ) Ōēź 0 or 4 ( x + 4 ) Ōēż 4
Solve the inequality. Graph the solution set and write
your answer in interval notation.
6) |5k + 8| > -6
Solve the inequality graphically. Write your answer in
interval notation .
7) x + 3 Ōēź 1
x-8 -6 -4 -2 2
y
8
6
4
2
x-8 -6 -4 -2 2
y
8
6
4
2
1
Graph the system of inequalities.
8) 2x + 8y Ōēź -4
y < - 3
2
x + 6
x-10 -8 -6 -4 -2 2 4 6 8 10
y
10
8
6
4
2
-2
-4
-6
-8
-10
x-10 -8 -6 -4 -2 2 4 6 8 10
y
10
8
6
4
2
-2
-4
-6
-8
-10
Find the determinant of the given matrix.
9) 10 5
0 -4
Use Cramer's rule to solve the system of linear
equations.
10) 6x + 5y = -12
2x - 2y = -4
Write a system that models the situation. Then solve the
system using any method. Must show work for credit.
11)A vendor sells hot dogs, bags of potato chips,
and soft drinks. A customer buys 3 hot dogs,
4 bags of potato chips, and 5 soft drinks for
$14.00. The price of a hot dog is $0.25 more
than the price of a bag of potato chips. The
cost of a soft drink is $1.25 less than the price
of two hot dogs. Find the cost of each item.
Use row reduced echelon form to solve the system.
12) x + y + z = 3
x - y + 4z = 11
5x + y + z = -9
2
Find the domain of f. Write your answer in interval
notation.
13) f(x) = 13 - 9x
If possible, simplify the expression. If any variables
exist, assume that they are positive.
14) 2x + 6 32x + 6 8x
Match to the equivalent expression.
15) 100-1/2
A) 1
1000
B) 1
10
C) 1
100
D) 1
10
Write the expression in standard form.
16) (5 + 8i) - (-3 + i)
Simplify the expression. Assume that all variables are
positive.
17) 5 t
5
z10
Solve the equation.
18) 3x + 1 = 3 + x - 4
Write the expression in standard form.
19) 3 + 3i
5 + 3i
3
Write the equation in vertex form.
20) y = x2 + 5x + 2
The graph of ax2 + bx + c is given. Use this graph to solve
ax2 + bx + c = 0, if possible.
21)
x-5 5 10
y
50
40
30
20
10
-10
-20
-30
-40
-50
x-5 5 10
y
50
40
30
20
10
-10
-20
-30
-40
-50
Solve the equation. Write complex solutions in standard
form.
22) 4x2 + 5x + 5 = 0
Graph the quadratic function by its properties.
23) f(x) = 1
3
x2 - 2x + 3
x
y
x
y
Solve the equation. Find all real solutions.
24) 2(x - 1)2 + 11(x - 1) + 12 = 0
Solve the problem.
25) The length of a table is 12 inches more than its
width. If the area of the table is 2668 square
inches, what is its length?
4
Solve the equation..A.B. .docx



A.B. .docxannetnash8266
╠²
A.
B.
A.
B.
A.B.C.D.
A.
B.
C.
D.
A.
B.
C.
A.
B.
(
{
}
)A.
B.
A.
B.
C.
A.
B.
A.
B.
A.
B.
A.
B.
Math 107 Final ExaminationSummer, 20151
Math 107 College AlgebraName______________________________
Final Examination: Summer, 2015Instructor __________________________
Answer Sheet
Instructions:
This is an open-book exam. You may refer to your text and other course materials as you work on the exam, and you may use a calculator.
Record your answers and work in this document.
There are 30 problems.
Problems #1-12 are multiple choice. Record your choice for each problem.
Problems #13-21 are short answer. Record your answer for each problem.
Problems #22-30 are short answer with work required. When requested, show all work and write all answers in the spaces allotted on the following pages. You may type your work using plain-text formatting or an equation editor, or you may hand-write your work and scan it. In either case, show work neatly and correctly, following standard mathematical conventions. Each step should follow clearly and completely from the previous step. If necessary, you may attach extra pages.
.
Name _____________________Date___________________
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Record your answer choices.
1.7.
2.8.
3.9.
4.10.
5.11.
6.12.
SHORT ANSWER. Record your answers below.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
19. (a)
(b)
(c)
20. (a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
21. (a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
SHORT ANSWER with Work Shown. Record your answers and work.
Problem Number
Solution
22
Answers:
(a)
(b)
Work/for part (a) and explanation for part (b):
23
Answers:
(a)
(b)
(c)
Work for part (a):
24
Answer:
Work:
25
Answer:
Work:
26
Answers:
(a)
(b)
Work for part (a) and for part (b):
27
Answer:
Work:
28
Answer:
Work:
29
Answers:
(a)
(b)
Work for (b):
30
Answer:
Work:
College Algebra MATH 107 Summer, 2015, V3.1
Page 1 of 11
MATH 107 FINAL EXAMINATION
This is an open-book exam. You may refer to your text and other course materials as you work
on the exam, and you may use a calculator. You must complete the exam individually.
Neither collaboration nor consultation with others is allowed.
Record your answers and work on the separate answer sheet provided.
There are 30 problems.
Problems #1ŌĆō12 are Multiple Choice.
Problems #13ŌĆō21 are Short Answer. (Work not required to be shown)
Problems #22ŌĆō30 are Short Answer with work required to be shown.
MULTIPLE CHOICE
1. Determine the domain and range of the piecewise functi.RATIONAL ALGEBRAIC EXPRESSIONS and Operations.pptx



RATIONAL ALGEBRAIC EXPRESSIONS and Operations.pptxresistancemarc47
╠²
operations on rational algebraic expressionsRATIONAL ALGEBRAIC EXPRESSIONS and Operations.pptx



RATIONAL ALGEBRAIC EXPRESSIONS and Operations.pptxresistancemarc47
╠²
operations on rational algebraic expressionsAdding and Subtracting Polynomials - Math 7 Q2W4 LC1



Adding and Subtracting Polynomials - Math 7 Q2W4 LC1Carlo Luna
╠²
This document discusses adding and subtracting polynomials. It defines key polynomial terms like monomial, binomial, and trinomial. It explains that when adding or subtracting polynomials, only like terms can be combined by adding or subtracting their coefficients while keeping the variable parts the same. Examples are provided to demonstrate adding and subtracting polynomials, including real-life word problems involving combining polynomial expressions to model total areas or profits. The overall goal is for students to learn how to perform operations on polynomials.Colour in Mathematics Colleen Young July 2021



Colour in Mathematics Colleen Young July 2021Colleen Young
╠²
The document discusses how using colour in mathematics teaching can help emphasize key elements like terms, operations, and steps. It provides examples of how colour is used to highlight like terms, operations order, and parts of equations. The examples cover topics ranging from algebra, functions, geometry, calculus, and more to demonstrate how colour brings additional clarity.More from AreejAhmed38 (19)
1-5 Divide Multi-Digit Numbers.pptx1-5 Divide Multi-Digit Numbers.pptx



1-5 Divide Multi-Digit Numbers.pptx1-5 Divide Multi-Digit Numbers.pptxAreejAhmed38
╠²
1-5 Divide Multi-Digit Numbers.pptxlesson 1-4 Multiply Decimals.pptxlesson 1-4 Multiply Decimals.pptx



lesson 1-4 Multiply Decimals.pptxlesson 1-4 Multiply Decimals.pptxAreejAhmed38
╠²
lesson 1-4 Multiply Decimals.pptxlesson 3-3.pptxlesson 3-3.pptxlesson 3-3.pptxlesson 3-3.pptx



lesson 3-3.pptxlesson 3-3.pptxlesson 3-3.pptxlesson 3-3.pptxAreejAhmed38
╠²
lesson 3-3.pptxlesson 3-3.pptxlesson 3-3.pptxlesson 3-3.pptxGraph Inequalities.pptGraph Inequalities.pptGraph Inequalities.pptGraph Inequ...



Graph Inequalities.pptGraph Inequalities.pptGraph Inequalities.pptGraph Inequ...AreejAhmed38
╠²
Graph Inequalities.pptSolving and Graphing Inequalities.pptSolving and Graphing Inequalities.ppt



Solving and Graphing Inequalities.pptSolving and Graphing Inequalities.pptAreejAhmed38
╠²
Solving and Graphing Inequalities.pptOperations-with-Recurring-DecimaOperations-with-Recurring-Decimals.pptxls.pptx



Operations-with-Recurring-DecimaOperations-with-Recurring-Decimals.pptxls.pptxAreejAhmed38
╠²
Operations-with-Recurring-Decimals.pptxOperations-with-Recurring-Decimals.pptxOperations-with-Recurring-Decimals.pptx5th_NS_1.3_add_and_subtract_integers.ppt



5th_NS_1.3_add_and_subtract_integers.pptAreejAhmed38
╠²
5th_NS_1.3_add_and_subtract_integers.ppt5th_NS_1.3_add_and_subtract_integers.ppt5th_NS_1.3_add_and_subtract_integers.pptc2_ch02_04.pptc2_ch02_04.pptc2_ch02_04.ppt



c2_ch02_04.pptc2_ch02_04.pptc2_ch02_04.pptAreejAhmed38
╠²
c2_ch02_04.pptc2_ch02_04.pptc2_ch02_04.pptc2_ch02_04.pptc2_ch02_04.pptc2_ch02_04.pptc2_ch02_04.pptNegatives-numbers.pptxNegatives-numbers.pptxNegatives-numbers.pptx



Negatives-numbers.pptxNegatives-numbers.pptxNegatives-numbers.pptxAreejAhmed38
╠²
Negatives-numbers.pptxNegatives-numbers.pptxNegatives-numbers.pptxNegatives-numbers.pptxNegatives-numbers.pptxNegatives-numbers.pptxNegatives-numbers.pptxArea-of-a-triangle-ppt-gr.6 l(5.2).ppArea-of-a-triangle-ppt-gr.6 l(5.2).pptxtx



Area-of-a-triangle-ppt-gr.6 l(5.2).ppArea-of-a-triangle-ppt-gr.6 l(5.2).pptxtxAreejAhmed38
╠²
Area-of-a-triangle-ppt-gr.6 l(5.2).pptxFRACTIONS.pptFRACTIONS.pptFRACTIONS.pptFRACTIONS.ppt



FRACTIONS.pptFRACTIONS.pptFRACTIONS.pptFRACTIONS.pptAreejAhmed38
╠²
FRACTIONS.pptFRACTIONS.pptFRACTIONS.pptFRACTIONS.pptFRACTIONS.pptFRACTIONS.pptFRACTIONS.pptSurface Area and Volume PowerPoint.pptSurface Area and Volume PowerPoint.ppt



Surface Area and Volume PowerPoint.pptSurface Area and Volume PowerPoint.pptAreejAhmed38
╠²
Surface Area and Volume PowerPoint.pptSurface Area and Volume PowerPoint.pptSurface Area and Volume PowerPoint.ppt



Surface Area and Volume PowerPoint.pptSurface Area and Volume PowerPoint.pptAreejAhmed38
╠²
Surface Area and Volume PowerPoint.pptpowerpoint_powers_of_ten__1_.pptxpowerpoint_powers_of_ten__1_.pptx



powerpoint_powers_of_ten__1_.pptxpowerpoint_powers_of_ten__1_.pptxAreejAhmed38
╠²
powerpoint_powers_of_ten__1_.pptxUnit Rates and RatiosUnit Rates and Ratios.pptUnit Rates and Ratios.ppt



Unit Rates and RatiosUnit Rates and Ratios.pptUnit Rates and Ratios.pptAreejAhmed38
╠²
Unit Rates and Ratios.pptOrder of Operations.ppt



Order of Operations.pptAreejAhmed38
╠²
The document explains the order of operations (PEMDAS) for solving math problems with multiple operations:
1) Perform operations inside parentheses first, from left to right.
2) Evaluate exponents next, from left to right.
3) Multiply and divide from left to right.
4) Add and subtract from left to right.
Several examples are provided to demonstrate how to use PEMDAS to evaluate expressions step-by-step.Recently uploaded (20)
APM People Interest Network Conference - Oliver Randall & David Bovis - Own Y...



APM People Interest Network Conference - Oliver Randall & David Bovis - Own Y...Association for Project Management
╠²
APM People Interest Network Conference 2025
- Autonomy, Teams and Tension
- Oliver Randall & David Bovis
- Own Your Autonomy
Oliver Randall
Consultant, Tribe365
Oliver is a career project professional since 2011 and started volunteering with APM in 2016 and has since chaired the People Interest Network and the North East Regional Network. Oliver has been consulting in culture, leadership and behaviours since 2019 and co-developed HPTM┬«ŌĆ»an off the shelf high performance framework for teams and organisations and is currently working with SAS (Stellenbosch Academy for Sport) developing the culture, leadership and behaviours framework for future elite sportspeople whilst also holding down work as a project manager in the NHS at North Tees and Hartlepool Foundation Trust.
David Bovis
Consultant, Duxinaroe
A Leadership and Culture Change expert, David is the originator of BTFAŌäó and The Dux Model.
With a Masters in Applied Neuroscience from the Institute of Organisational Neuroscience, he is widely regarded as the ŌĆśGo-ToŌĆÖ expert in the field, recognised as an inspiring keynote speaker and change strategist.
He has an industrial engineering background, majoring in TPS / Lean. David worked his way up from his apprenticeship to earn his seat at the C-suite table. His career spans several industries, including Automotive, Aerospace, Defence, Space, Heavy Industries and Elec-Mech / polymer contract manufacture.
Published in LondonŌĆÖs Evening Standard quarterly business supplement, James CaanŌĆÖs ŌĆśYour businessŌĆÖ Magazine, ŌĆśQuality WorldŌĆÖ, the Lean Management Journal and Cambridge Universities ŌĆśPMAŌĆÖ, he works as comfortably with leaders from FTSE and Fortune 100 companies as he does owner-managers in SMEŌĆÖs. He is passionate about helping leaders understand the neurological root cause of a high-performance culture and sustainable change, in business.
Session | Own Your Autonomy ŌĆō The Importance of Autonomy in Project Management
#OwnYourAutonomy is aiming to be a global APM initiative to position everyone to take a more conscious role in their decision making process leading to increased outcomes for everyone and contribute to ŌĆ£a world in which all projects succeedŌĆØ.
We want everyone to join the journey.
#OwnYourAutonomy is the culmination of 3 years of collaborative exploration within the Leadership Focus Group which is part of the APM People Interest Network. The work has been pulled together using the 5 HPTM® Systems and the BTFA neuroscience leadership programme.
https://www.linkedin.com/showcase/apm-people-network/about/Database population in Odoo 18 - Odoo slides



Database population in Odoo 18 - Odoo slidesCeline George
╠²
In this slide, weŌĆÖll discuss the database population in Odoo 18. In Odoo, performance analysis of the source code is more important. Database population is one of the methods used to analyze the performance of our code. Principle and Practices of Animal Breeding || Boby Basnet



Principle and Practices of Animal Breeding || Boby BasnetBoby Basnet
╠²
Principle and Practices of Animal Breeding Full Note
|| Assistant Professor Boby Basnet ||IAAS || AFU || PU || FUEssentials of a Good PMO, presented by Aalok Sonawala



Essentials of a Good PMO, presented by Aalok SonawalaAssociation for Project Management
╠²
APM event hosted by the South Wales and West of England Network (SWWE Network)
Speaker: Aalok Sonawala
The SWWE Regional Network were very pleased to welcome Aalok Sonawala, Head of PMO, National Programmes, Rider Levett Bucknall on 26 February, to BAWA for our first face to face event of 2025. Aalok is a member of APMŌĆÖs Thames Valley Regional Network and also speaks to members of APMŌĆÖs PMO Interest Network, which aims to facilitate collaboration and learning, offer unbiased advice and guidance.
Tonight, Aalok planned to discuss the importance of a PMO within project-based organisations, the different types of PMO and their key elements, PMO governance and centres of excellence.
PMOŌĆÖs within an organisation can be centralised, hub and spoke with a central PMO with satellite PMOs globally, or embedded within projects. The appropriate structure will be determined by the specific business needs of the organisation. The PMO sits above PM delivery and the supply chain delivery teams.
For further information about the event please click here.How to attach file using upload button Odoo 18



How to attach file using upload button Odoo 18Celine George
╠²
In this slide, weŌĆÖll discuss on how to attach file using upload button Odoo 18. Odoo features a dedicated model, 'ir.attachments,' designed for storing attachments submitted by end users. We can see the process of utilizing the 'ir.attachments' model to enable file uploads through web forms in this slide.How to Configure Restaurants in Odoo 17 Point of Sale



How to Configure Restaurants in Odoo 17 Point of SaleCeline George
╠²
Odoo, a versatile and integrated business management software, excels with its robust Point of Sale (POS) module. This guide delves into the intricacies of configuring restaurants in Odoo 17 POS, unlocking numerous possibilities for streamlined operations and enhanced customer experiences.SOCIAL CHANGE(a change in the institutional and normative structure of societ...



SOCIAL CHANGE(a change in the institutional and normative structure of societ...DrNidhiAgarwal
╠²
This PPT is showing the effect of social changes in human life and it is very understandable to the students with easy language.in this contents are Itroduction, definition,Factors affecting social changes ,Main technological factors, Social change and stress , what is eustress and how social changes give impact of the human's life.How to Modify Existing Web Pages in Odoo 18



How to Modify Existing Web Pages in Odoo 18Celine George
╠²
In this slide, weŌĆÖll discuss on how to modify existing web pages in Odoo 18. Web pages in Odoo 18 can also gather user data through user-friendly forms, encourage interaction through engaging features. Mate, a short story by Kate Grenvile.pptx



Mate, a short story by Kate Grenvile.pptxLiny Jenifer
╠²
A powerpoint presentation on the short story Mate by Kate Greenville. This presentation provides information on Kate Greenville, a character list, plot summary and critical analysis of the short story.APM People Interest Network Conference - Tim Lyons - The neurological levels ...



APM People Interest Network Conference - Tim Lyons - The neurological levels ...Association for Project Management
╠²
APM People Interest Network Conference 2025
-Autonomy, Teams and Tension: Projects under stress
-Tim Lyons
-The neurological levels of
team-working: Harmony and tensions
With a background in projects spanning more than 40 years, Tim Lyons specialised in the delivery of large, complex, multi-disciplinary programmes for clients including Crossrail, Network Rail, ExxonMobil, Siemens and in patent development. His first career was in broadcasting, where he designed and built commercial radio station studios in Manchester, Cardiff and Bristol, also working as a presenter and programme producer. Tim now writes and presents extensively on matters relating to the human and neurological aspects of projects, including communication, ethics and coaching. He holds a MasterŌĆÖs degree in NLP, is an NLP Master Practitioner and International Coach. He is the Deputy Lead for APMŌĆÖs People Interest Network.
Session | The Neurological Levels of Team-working: Harmony and Tensions
Understanding how teams really work at conscious and unconscious levels is critical to a harmonious workplace. This session uncovers what those levels are, how to use them to detect and avoid tensions and how to smooth the management of change by checking you have considered all of them.How to Configure Flexible Working Schedule in Odoo 18 Employee



How to Configure Flexible Working Schedule in Odoo 18 EmployeeCeline George
╠²
In this slide, weŌĆÖll discuss on how to configure flexible working schedule in Odoo 18 Employee module. In Odoo 18, the Employee module offers powerful tools to configure and manage flexible working schedules tailored to your organization's needs.Lesson Plan M1 2024 Lesson Plan M1 2024 Lesson Plan M1 2024 Lesson Plan M1...



Lesson Plan M1 2024 Lesson Plan M1 2024 Lesson Plan M1 2024 Lesson Plan M1...pinkdvil200
╠²
Lesson Plan M1 2024 Lesson Plan M1 2024 Lesson Plan M1 2024 The Dravidian Languages: Tamil, Telugu, Kannada, Malayalam, Brahui, Kuvi, Tulu



The Dravidian Languages: Tamil, Telugu, Kannada, Malayalam, Brahui, Kuvi, TuluDrIArulAram
╠²
The Dravidian Languages by Arul AramAPM People Interest Network Conference - Oliver Randall & David Bovis - Own Y...



APM People Interest Network Conference - Oliver Randall & David Bovis - Own Y...Association for Project Management
╠²
APM People Interest Network Conference - Tim Lyons - The neurological levels ...



APM People Interest Network Conference - Tim Lyons - The neurological levels ...Association for Project Management
╠²
UNIT 6 Factoring and Distributing Expressions _2_.pptx
- 1. FACTORING EXPRESSIONS Factoring is an important process in algebra which is used to simplify expressions, simplify fractions, and solve equations. 5 5 3 3 Consider the following: Jerry spent $5 for lunch on Monday and again on Tuesday. He spent $3 for snack on each day as well. How much did Jerry spend in all for both days? 2 x 5 2 x 3 (2 times the cost of lunch) (2 times the cost of snack) (2 x 5) + (2 x 3) = 16
- 2. Consider the following: Jerry spent $5 for lunch on Monday and again on Tuesday. He spent $3 for snack on each day as well. How much did Jerry spend in all for both days? Does the model shown below represent the situation as well? 5 3 5 3 5 + 3 5 + 3 (cost of lunch and snack (cost of lunch and snack on Monday) on Tuesday) 2 x (5+ 3) = 16
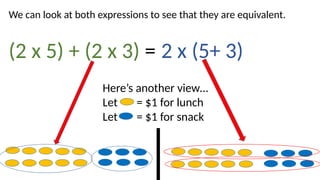
- 3. We can look at both expressions to see that they are equivalent. (2 x 5) + (2 x 3) = 2 x (5+ 3) HereŌĆÖs another viewŌĆ” Let = $1 for lunch Let = $1 for snack
- 4. (2 x 5) + (2 x 3) =2 x (5+ 3) Mathematically, this equation shows an expression that has been ŌĆ£factored.ŌĆØ There is a shared factor (GCF) of 2. Take it out and multiply it to the remaining sum. GCF times THE OTHER SUM (5 x 3) + (5 x 4) = ___ x ( __ + __) PRACTICE:
- 5. WRITE AN EXPRESSION REPRESENTING THE TOTAL. a a b b _____ _____ The expression that represents the total is ___________
- 6. Can you rearrange the parts of this bar to represent the total in another way? Now write a new expression to represent the same total. a b a b
- 8. Use the GCF and the Distributive Property to write equivalent expressions. ŌĆ£Factor.ŌĆØ 3g + 3f = ________________ 6x + 9y = ________________ 3c + 12c = ________________ 24b + 8 = _________________
- 9. 7x + 7y = _____________________ 15g + 20h = ____________________ 18m + 42n = _____________________ 30a + 39b = ____________________ 55m + 11 = ____________________ 7 + 56y = ______________________
- 10. Are these expressions equal? How do you know? 6x + 21y and 3(2x + 7y)
- 11. Evaluate each expression to prove that these two expressions are equivalent. Let g = 6 5g + 7g g(5 + 7)
- 12. Evaluate each expression to prove that these two expressions are equivalent. Let x = 10 14x + 2 2(7x + 1)
- 13. Fill in the blanks with the numbers that will make the equation true. 4x + 12y = ___ (x + 3y) 35x + ___y = 5 (7x + 10y) ___x + 9y = 9 (2x + y) 32x + 8y = 8 (___x + y)
- 14. Use models to prove that 3(a + b) = 3a + 3b
- 15. Use the GCF and the Distributive Property to write equivalent expressions in factored form. 4d + 12e 18x + 30y 21a + 28y
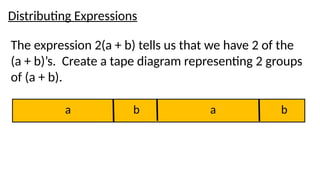
- 16. Distributing Expressions The expression 2(a + b) tells us that we have 2 of the (a + b)ŌĆÖs. Create a tape diagram representing 2 groups of (a + b). a b a b
- 17. Show how your model would look if we grouped together the aŌĆÖs and then grouped together the bŌĆÖs. What expression can we write to represent the new diagram? a a b b
- 18. Using Area Models to Help Distribute 2 (x + y) x y 2
- 19. Using Area Models to Help Distribute 2 (3x + 4y) 3x 4y 2
- 20. Using Area Models to Help Distribute y (4x + 5) 4x 5 y
- 21. Using Area Models to Help Distribute 3 (7d + 4e) 7d 4e 3












