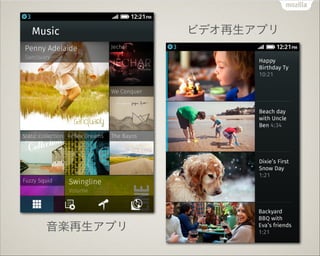
Web App Platform Firefox
- 1. Web App Platform "Firefox" @dotFes 2013 Kyoto by Tomoya Asai (dynamis)
- 2. about:me
- 3. Tomoya ASAI Mozilla Japan Technical Marketing (Evangelist) dynamis @ community dynamis.jp @dynamitter facebook.com/dynamis mailto: Tomoya ASAI <dynamis@mozilla-japan.org>
- 5. Mozilla = Security & Privacy 1st. •ª•≠•Â•Í•∆•£◊ÓÉûœ» °∏•§•Û•ø©`•Õ•√•»§À§™§±§ÎÇÄ»À§Œ •ª•≠•Â•Í•∆•£§œ±ÿÌö§Œ§‚§Œ°π§» Mozilla –˚—‘§«√˜”õ •◊•È•§•–•∑©`§ÀÈv§∑§∆◊Ó§‚–≈ Óm§«§≠§Î•§•Û•ø©`•Õ•√•»∆ÛòI "2012 Most Trusted Copanies for Privacy" by Ponemon Institute http://mozilla.org/about/manifesto.ja.html & http://mozilla.jp/blog/entry/10261/
- 7. Background
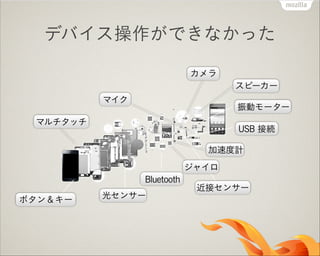
- 8. º»¥Ê§Œ•◊•È•√•»•’•©©`•‡ OS ö∞§À•¢•◊•ÍÈ_∞k —‘’Z§‰ API §œ OS §À“¿¥Ê iOS/Windows §œ UI “éÑt§‚è䧧 Web §œ•µ•÷•ª•√•»íQ§§ •¢•◊•Í≠hæ≥§»§∑§∆§œ≤ªÕÍ»´ ◊∑º” API §ŒòÀú ªØ§‚§µ§Ï§ §§
- 10. Web Platform §ÿ§Œ∆⁄¥˝ ¥Œ ¿¥˙•◊•È•√•»•’•©©`•‡ Web ºº–g§«§π§Ÿ§∆ø…ƒ‹§À •fi•Î•¡•«•–•§•πåùèÍ È_∞k—‘’Z§‰ API §Œπ≤Õ®ªØ •Ÿ•Û•¿©`∑«“¿¥Ê§ŒòÀú ◊‘”…§«≥÷æA–‘§Œ§¢§Î API
- 11. Web §¨π≤Õ®•◊•È•√•»•’•©©`•‡ •◊•È•√•»•’•©©`•‡ §»§∑§∆§Œ Web Web §¨•◊•È•√•»•’•©©`•‡§ §È±Íú ºº ı§«•¢•◊•Íª∑æ≥§¨Õ≥“ª§µ§Ï§Î
- 13. Web Platform §Œ’nÓ} ôCƒ‹µƒ§ ÷∆ºs •«•–•§•π§‰•∑•π•∆•‡œµ§Œ API ≤ª◊„ •—•’•©©`•fi•Û•π Java § §…§À±»§Ÿ§∆§‚ ˝±∂flW§§ •¢•◊•Í≈‰–≈§»’nΩ Market §‰ Payment §ŒòÀú § §∑
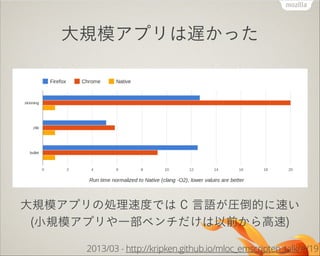
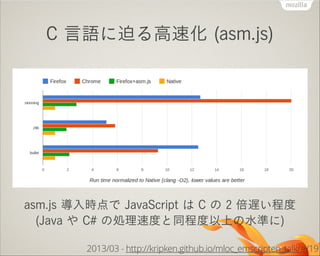
- 15. ¥Û“郣•¢•◊•Í§œflW§´§√§ø ¥Û“郣•¢•◊•Í§ŒÑI¿ÌÀŸ∂»§«§œ C —‘’Z§¨àRµπµƒ§ÀÀŸ§§ (–°“郣•¢•◊•Í§‰“ª≤ø•Ÿ•Û•¡§¿§±§œ“‘«∞§´§È∏flÀŸ) 2013/03 - http://kripken.github.io/mloc_emscripten_talk/#/19
- 17. Firefox OS
- 23. ! Firefox OS - Web is the Platform Web = •¢•◊•Í≠hæ≥ •¢•◊•Í§œ§π§Ÿ§∆ Web ºº–g§« •…•·•§•Û = •¢•◊•Í§Œ£±£∫£±åùèÍ Web §ÚflMªØ§µ§ª§Î ≤ª◊„ôCƒ‹§œ API §Ú∂®¡x?òÀú ªØ Web §Œ•ª•≠•Â•Í•∆•£•‚•«•Î§ §… §‚åg◊∞?òÀú ªØ§∑§∆§§§Ø
- 24. Web ºº–g§Ú•Õ•§•∆•£•÷§À Web ºº–g§¨°∏•Õ•§•∆•£•÷°π HTML/CSS/JS §«§π§Ÿ§∆ø…ƒ‹§À –¬§∑§§ API §œ W3C òÀú ªØ ÀŸ∂»§‚ C —‘’Z§À∆»§Î asm.js §À§Ë§Í¥Û∑˘∏flÀŸªØ§Úåg¨F WebGL §‰ DOMCrypt § §…§‚ªÓ”√ Web ºº–g§¿§±§«§π§Ÿ§∆§¨úg§‡•◊•È•√•»•’•©©`•‡§»§ §Î§Ë§¶∞k’π÷–
- 26. •π•∆©`•ø•π•–©` (Õ®÷™°¢? Îä≤®èä∂»°¢Îä≥ÿ≤–¡ø...)§‚ •´•·•È§‰•È•∏•™§‚ •”•«•™§‰“ÙòS§Œ‘Ÿ…˙§‚ •fi©`•±•√•»•◊•Ï•§•π§‚ •∑•π•∆•‡§Œ≠hæ≥‘O∂®§‚ •€©`•‡ª≠√ʧ‰±⁄ºà§‚ Îä‘í§‰ SMS §ŒÀÕ ‹–≈§‚ §‚§¡§Ì§Û •÷•È•¶•∂ §‚ §Ω§ŒÀ˚§ §Û§«§‚... §π§Ÿ§∆ Web ºº–g§«£°
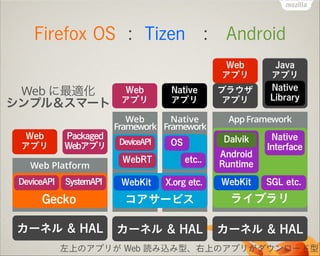
- 27. Firefox OS : Tizen : Android Web §À◊ÓflmªØ •∑•Û•◊•Î£¶•π•fi©`•» Web •¢•◊•Í Packaged Web•¢•◊•Í Web Platform DeviceAPI SystemAPI Web •¢•◊•Í Web •¢•◊•Í Native •¢•◊•Í Web Native Framework Framework DeviceAPI OS •÷•È•¶•∂ •¢•◊•Í Java •¢•◊•Í Native Library App Framework Dalvik WebRT etc.. Android Runtime WebKit X.org etc. WebKit Native Interface SGL etc. Gecko •≥•¢•µ©`•”•π •È•§•÷•È•Í •´©`•Õ•Î & HAL •´©`•Õ•Î & HAL •´©`•Õ•Î & HAL ◊Û…œ§Œ•¢•◊•Í§¨ Web ’i§flfiz§fl–Õ°¢”“…œ§Œ•¢•◊•Í§¨•¿•¶•Û•Ì©`•…–Õ
- 28. C —‘’Z§À∆»§Î∏flÀŸªØ (asm.js) asm.js åß»Îïrµ„§« JavaScript §œ C §Œ 2 ±∂flW§§≥Ã∂» (Java §‰ C# §ŒÑI¿ÌÀŸ∂»§»Õ¨≥Ã∂»“‘…œ§ŒÀÆú §À) 2013/03 - http://kripken.github.io/mloc_emscripten_talk/#/19
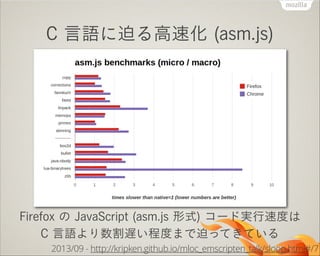
- 29. C —‘’Z§À∆»§Î∏flÀŸªØ (asm.js) Firefox §Œ JavaScript (asm.js –Œ Ω) •≥©`•…åg––ÀŸ∂»§œ C —‘’Z§Ë§Í ˝∏ÓflW§§≥Ã∂»§fi§«∆»§√§∆§≠§∆§§§Î 2013/09 - http://kripken.github.io/mloc_emscripten_talk/sloop.html#/7
- 30. åg•Ï•Ÿ•Î: Box2D ŒÔ¿Ì—›À„•®•Û•∏•Û Box2D §«§œ C —‘’Z§Œ 2 ±∂flW§§≥Ã∂»§ŒÀŸ∂» ! Chrome §‰ IE §«§‚Õ®≥£§Œ JS §Ë§Í asm.js §¨∏flÀŸ Java §‰ CrossBridge (Flash C++ Compiler) §»Õ¨µ»“‘…œ 2013/07 - http://kripken.github.io/mloc_emscripten_talk/sloop.html#/8
- 31. åg”√¿˝: Unreal Engine 3 100 ÕÚ––“‘…œ§Œ C & OpenGL •≥©`•…§Ú 5 »’§«“∆÷≤ LLVM + Emscripten §« JavaScript (asm.js) §Àâ‰ìQ epic CITADEL http://www.unrealengine.com/html5/
- 33. •∞•Ì©`•–•Î –àˆ§Àíà¥Û Firefox OS §Œ»°§ÍΩM§fl§ÀŸmÕ¨§π§Î∆ÛòI§Œ“ª≤ø (MWC §Œ”õ’fl∞k±Ìª·§Ë§Í)
- 35. ! ∂‡ ˝∆ÛòI§»§Œπ≤Õ¨È_∞k?—u∆∑ªØ ÷˜“™ 18 •≠•„•Í•¢§¨ŸmÕ¨ KDDI, Telef®Ænica, Deutsche Telekom°¢Telenor... •¡•√•◊£¶∂Àƒ©•·©`•´©` Qualcomm, ARM ZTE, Alcatel, LG, Huawei, Sony Foxconn... §‚§¡§Ì§Û∞k±Ì§∑§∆§§§Î∆ÛòI§¨§π§Ÿ§∆§«§œ§ §§
- 36. £∑‘¬°¢8‘¬§À◊Ó≥ı§Œÿúâ”È_ º 7‘¬2»’§À•π•⁄•§•Û§«∞kâ” Telef®Ænica §¨ ZTE Open §Ú∞kâ” Ä69 (À∞fiz) •◊•Í•⁄•§•… Ä30 ∫¨§‡ Ìò¥Œ ¿ΩÁ∏˜π˙§À’πÈ_ 7‘¬12»’§À•›©`•È•Û•…§«∞kâ” 8‘¬1»’§À•≥•Ì•Û•”•¢°¢•Ÿ•Õ•∫•®•È §fi§∫§œΩÒ··§Œ≥…ÈL§¨“äfiz§fi§Ï§Î–¬≈dπ˙ –àˆ§Ú÷––ƒ§À’πÈ_ (•≠•„•Í•¢§ŒëȬ‘)
- 37. ZTE Open & Alcatel One Touch Fire
- 38. ! ZTE Open ÷˜§ Àòî: Size: 114 x 62 x 12.5 mm? Display: 3.5 inch HVGA? CPU: MSM7225A 1 GHz? (Cortex-A5, Adreno 200)? RAM: 256 MB? ROM: 512 MB •π•⁄•§•Û§ §…§«∞kâ” http://www.ztedevices.com/product/smart_phone/2bcf2d56-0c9a-4129-a25c-
- 39. ! Alcatel One Touch Fire ÷˜§ Àòî: Size: 115 x 62.3 x 12.2 mm? Display: 3.5 inch HVGA? CPU: MSM7227A 1 GHz? (Cortex-A5, Adreno 200)? RAM: 256 MB? ROM: 512 MB •›©`•È•Û•…§ §…§«∞kâ” http://www.alcatelonetouch.com/global-en/products/smartphones/one_touch_fire.html
- 40. Firefox OS ∂Àƒ©ÿú┧œÌò’{£ø Telef®Ænica §Œÿúâ”ågøÉ 2013/10 (∞kâ”·· 3 •ˆ‘¬) ïrµ„ •Ÿ•Õ•∫•®•È •π•fi©`•»•’•©•Ûÿú┧Œ 12% “‘…œ •≥•Ì•Û•”•¢ •π•fi©`•»•’•©•Ûÿú┧Œ 9% ≥Ã∂» http://news.cnet.com/8301-1035_3-57608120-94/telefonicas-yotam-ben-ami-fights-for-firefox-
- 41. 10‘¬§´§È∏¸§À∂‡§Ø§Œ –àˆ§ÿ’πÈ_ Firefox OS 1.1 ∂Àƒ©§Œ•Í•Í©`•π Telef®Ænica 10/22: •÷•È•∏•Î? 10/31: •·•≠•∑•≥°¢•⁄•Î©`°¢•¶•Î•∞•¢•§ Deutsche Telekom •…•§•ƒ°¢•Æ•Í•∑•„°¢•œ•Û•¨•Í©` Telenor •œ•Û•¨•Í©`°¢•ª•Î•”•¢°¢•‚•Û•∆•Õ•∞•Ì »’±æ§‰±±√◊§«§œ 2013~2014 ƒÍ÷–§Œ“äfiz§fl http://mozilla.jp/blog/entry/10310/
- 42. LG Fireweb (D300) ÷˜§ Àòî: Size: 113.8 x 66.5 x 9 mm? Display: 4 inch HVGA? CPU: 1 GHz (–Õ∑¨Œ¥¥_’J) •÷•È•∏•Î§ §…§«∞kâ” http://www.vivo.com.br/firefoxos/
- 44. Apps Dev
- 45. Firefox OS §Œ•¢•◊•ÍÈ_∞k Web •¢•◊•Í§«§π°£ Web •¢•◊•Í§«§π°£ Web •¢•◊•Í§«§π°£ ! ! ¥Û ¬§ §≥§»£≥ªÿ
- 47. •¢•◊•ÍÈ_∞k§Œ¡˜§Ï ∆’Õ®§À Web È_∞k •¢•◊•Í•fi•Õ©`•∏•„ or Firebug etc. manifest •’•°•§•Î§Ú”√“‚ •·•ø«ÈàÛ§Ú JSON –Œ Ω§«”õ›d •∑•fl•Â•Ï©`•ø§‰ågôC•∆•π•» Android Firefox §«§‚•∆•π•» https://github.com/dynamis/firefoxos/wiki/simulator
- 48. £≤§ƒ§Œ∑Ω Ω§Œ•¢•◊•Í Hosted (Web ’i§flfiz§fl–Õ) èæ¿¥§Œ OS §«§œ•÷•È•¶•∂…œ§«Ñ”◊˜ Ñ”◊˜§‰òÿœfi§œèæ¿¥§Œ Web §»Õ¨§∏ •™•’•È•§•ÛåùèÍ•¢•◊•Í§‚È_∞kø…ƒ‹ Hosted? Web •¢•◊•Í Server Internet Packaged (•¿•¶•Û•Ì©`•…–Õ) èæ¿¥§Œ•π•fi•€•¢•◊•Í§Àœ‡µ±§π§Î •fi©`•±•√•»åèñÀ§ÚΩU§∆◊∑º”òÿœfi»°µ√ •µ•§•»»´ÃÂ§Ú ZIP §∑§∆≈‰≤º§π§Î–Œ Ω ∂Àƒ© Packaged Web •¢•◊•Í ‘îºö: https://developer.mozilla.org/ja/docs/Web/Apps/Packaged_apps
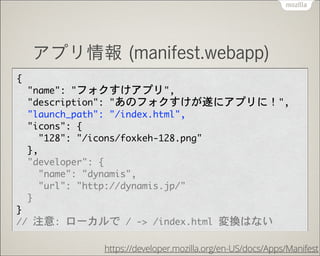
- 49. •¢•◊•Í«ÈàÛ•’•°•§•Îﯧا¿§± •µ•§•» + manifest.webapp 1. manifest.webapp ◊˜≥… •¢•◊•Í«ÈàÛﯧا¿§±§«ΩK¡À
- 51. ZIP §∑§∆ Packaged App §À ZIP + package.manifest 1. manifest.webapp ◊˜≥… Hosted Apps §Œïr§»Õ¨§∏ 2. •µ•§•»»´ÃÂ§Ú ZIP §π§Î manifest.webapp §‚∫¨§·§Î 3. package.manifest §Ú◊˜≥… mini manifest §¨ÑeÕæ±ÿ“™
- 52. ! mini manifest (package.manifest) https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/Apps/Packaged_apps
- 53. App Manager
- 54. •¢•◊•Í•fi•Õ©`•∏•„ •¢•◊•ÍÈ_∞k?π‹¿Ì≠hæ≥ Firefox òÀú ¥Ó›d§ŒÈ_∞k≠hæ≥ Firefox Nightly § §…§À¥Ó›dúg§fl •∑•Â•fl•Ï©`•ø?ågôCÅIåùèÍ Firefox OS 1.2 “‘Ωµ§ŒågôC§fi§ø§œ•∑•Â •fl•Ï©`•ø§»Ω”æA§∑§∆È_∞k 10 ‘¬ïrµ„§« Firefox OS 1.2, 1.3 §Œ •∑•Â•fl•Ï©`•ø§¨π´È_÷– •Í•Í©`•π∞ʧ‰•Ÿ©`•ø∞ʧÀ§œŒ¥¥Ó›d§«§π§Œ§« Nightly §«È_∞k§∑§∆§Ø§¿§µ§§
- 55. •¢•◊•Í•fi•Õ©`•∏•„ Web •¢•◊•ÍÈ_∞kΩy∫œ≠hæ≥§¨ Firefox 26 §´§ÈòÀú ¥Ó›d •¢•◊•Í§Œ•§•Û•π•»©`•Î§‰•Í•‚©`•»•«•–•√•∞§‚
- 56. Firefox OS 1.2 Simulator •«•’•©•Î•»•€©`•‡§À•¢•◊•Íó À˜•’•©©`•‡§¨“∆Ñ”
- 57. Firefox OS 1.3 Simulator •´•∆•¥•ÍÑe•¢•◊•Í•’•©•Î•¿èÕªÓ
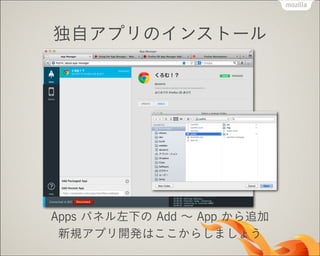
- 58. ∂¿◊‘•¢•◊•Í§Œ•§•Û•π•»©`•Î Apps •—•Õ•Î◊Ûœ¬§Œ Add °´ App §´§È◊∑º” –¬“é•¢•◊•ÍÈ_∞k§œ§≥§≥§´§È§∑§fi§∑§Á§¶
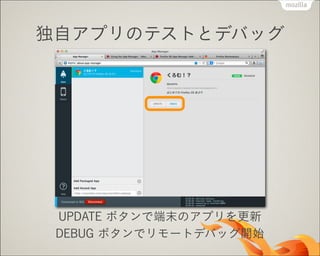
- 59. ∂¿◊‘•¢•◊•Í§Œ•∆•π•»§»•«•–•√•∞ UPDATE •‹•ø•Û§«∂Àƒ©§Œ•¢•◊•Í§Ú∏¸–¬ DEBUG •‹•ø•Û§«•Í•‚©`•»•«•–•√•∞È_ º
- 60. Developer Phones
- 62. Developer Preview Phone 4/23 ∞kâ” (∆∑«–§Ï÷–) Keon: 91Ä+tax+shipping MSM7225AB 1GHz, 4GB ROM, 512MB RAM, 3.5" HVGA Peak: 149Ä+À∞+ÀÕ¡œ MSM8225 1.2GHz x2, 4GB ROM, 512MB RAM, 4.3" qHD http://www.geeksphone.com/
- 63. Peak+ (Pre-order) 10 11‘¬∞kÀÕ (ÕÍâ”) Peak: 149Ä+À∞+ÀÕ¡œ MSM8225 1.2GHz x2, 4GB ROM, 1GB RAM, 4.3" qHD •·•‚•Í»›¡øâດ§»Ÿ|∏–œÚ…œ 149Ä §œ”˺sïrœfi∂®ÃÿÅ˝ http://shop.geeksphone.com/en/phones/8-peak.html
- 64. ! ZTE Open (eBay) ZTE Open §Œ SIM •’•Í©`∞Ê È_∞k’fl§‰≥ı∆⁄íÒ”√’flœÚ§± eBay US / HK §« 79.99 •…•Î eBay UK §« 59.99 •›•Û•… •™•Ï•Û•∏§œ eBay œfi∂®•´•È©`£° »’±æ§ÿ§œ eBay HK §¨∞kÀÕ http://www.ebay.com/itm/331031989534 https://blog.mozilla.org/blog/zte-will-soon-start-sales-of-firefox-os-phones-on-ebay/
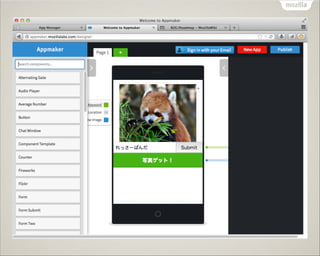
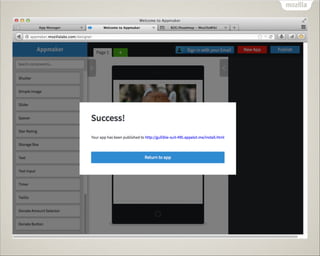
- 66. Appmaker
- 70. Building Blocks
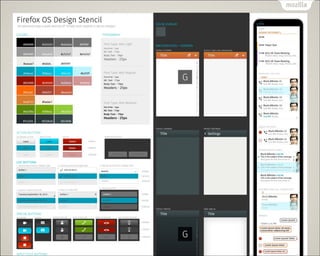
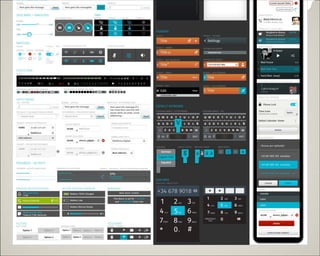
- 71. Building Blocks (UI ≤ø∆∑) Gaia (Firefox OS òÀú ) Apps §Œ•«•∂•§•Û§Ú∫ÜÖg§À◊˜§Ï§Î http://building?refoxos.com/ π§√§∆§‚ π§Ô§ §Ø§∆§‚ OK ∫√§≠§ SDK/Library π§®§Î ◊‘”…§ Web §«§π§´§È£° http://buildingfirefoxos.com/
- 74. For More Info