Acute bs th-ng
- 1. XQUANG BỤNG CẤP Bs Bùi Anh Thắng Mục tiêu : Phân biệt chỉ định chụp KUB và hình bụng không sửa soạn Nắm bắt một số bệnh có tính chất ngoại khoa Nắm một số chiệu trứng xquang cơ bản : TỔNG QUAN : Phim chụp KUB là phim chụp mục đích tìm sạn hệ niệu. Chụp tư thế nằm và điều kiện phim đạt chuẩn là phía mép dưới phim phải lấy được khớp mu. Phim chụp bụng không sưả soạn là phim chụp cho các bệnh như thủng tạng rỗng , tắc ruột.Điều kiện bắt buộc là mép trên phim phải thấy cơ hoành. Bụng cấp : Là một cấp cứu hay gặp , chẩn đoán dựa trên lâm sàng – Xquang và siêu âm vì dễ thực hiện. Sinh hóa có gía trị nhất định của nó như BC > 12.000 hay Amylase máu cao... CTscanner thì gía qúa đắt. Nguyên nhân gây bụng cấp nhiều như : Cơ đau quặn thận ( Renal colic ) – Viêm tụy cấp ( Acute pancreatitis ) – Bệnh lý đường mật ... Chúng ta chú ý ở đây chủ yếu nhóm bệnh ngoại khoa . Quan trọng là lúc nào can thiệp nội khoa hay theo dõi nội khoa. A/ Thủng tạng rỗng : Các tư thế khảo sát : + Tim phổi thẳng: + Bụng đứng +Nằm nghing phải 1/ Nguyên nhân a/ Nhóm tự nhiên : + Bể nang khí : ( Pneumotosis cyst ) + vận động viên điền kinh b/ Nhóm do can thiệp + làm thủ thuật HSG: Hysterosalpingography + sau mổ nội soi + Sau mổ hở : Khí tồn tại khoảng từ 5 – 14 ngày + đặt nội khí quản áp lực dương cao c/ Nhóm bệnh lý : Thủng dạ dày do loét 2/ Lâm sàng:
- 2. Đau như dao đâm – đau đột ngột – Phản ứng thành bụng … Một số bệnh giống đau bụng cấp : 3/ Chẩn đoán: Chú ý : + Khoảng 30 – 50 ml thì mới thấy liềm hơi + Chụp nghiêng trái khoảng 1 – 2ml là thấy.Ở Anh từ những năm 1970 người ta có xu thế chụp nghiêng trái trong chẩn đoán thủng tạng rỗng. + Khoảng 61- 82 % thủng tạng rỗng có liềm hơi. + Thủng ruột non thấy liềm hơi < 40% + Một nghiên cứu thì khoảng 65% Bs có kinh nghiệm phát hiện liềm hơi. Không thấy liềm hơi do : + Thủng sau phúc mạc + Do bệnh nhân tới sớm trước 6 giờ ( Không khí hấp thu qua phúc mạc khoảng 100- 150 ml một ngày ) +Do thủng vào hậu cung mạc nối + Do thủng nhỏ khoảng 0,5 – 2cm( mạc treo phủ lại ) Để chẩn đoán có thể bơm hơi qua ngả miệng , hay bơm chất cản quang tan trong nước vào dạ dày Cơ chề sinh hơi và hấp thu : Hấp thu : Từ phúc mạc – dạ dày và ruột non + Giảm hấp thu : Do rối loạn tuần hoàn  Giảm mạch máu vùng bụng  giảm hấp thu khí Nguyên nhân :Nguyên phát do sock  Máu ứ lại các tạng Thứ phát do suy tim ứ huyết + tạo khí : Do thức ăn Do nuốt : 70-% khí là nitrogen Kỹ thuật : + Chụp bụng không sửa soạn :
- 3. + Chụp nghiêng trái : + Chụp phổi thẳng : 4/ Hình ảnh xquang : Hơi tự do ổ bụngliềm hơi Dấu Rigler:Do hơi trong và ngoài quai ruột + Liềm hơi dưới hoành : Liềm hơi 2 bên tốt cho chẩn đoán Liềm bên phải giá trị hơn bên trái Liềm hơi trải quá 2/3 vòm hoành Chú ý : + Thủng sau phúc mạc - Thủng nằm trước thận : Bóng hơi nằm dọc theo khung đại tràng - Thủng nằm quanh thận : Khí bao quanh thận
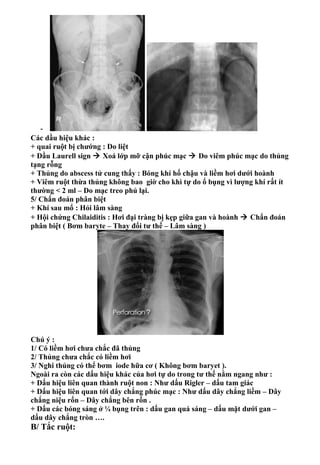
- 4. - Các dầu hiệu khác : + quai ruột bị chướng : Do liệt + Dầu Laurell sign  Xoá lớp mỡ cận phúc mạc  Do viêm phúc mạc do thủng tạng rỗng + Thủng do abscess tử cung thấy : Bóng khí hố chậu và liềm hơi dưới hoành + Viêm ruột thừa thủng không bao giờ cho khì tự do ổ bụng vì lượng khí rất ít thường < 2 ml – Do mạc treo phủ lại. 5/ Chẩn đoán phân biệt + Khí sau mổ : Hỏi lâm sàng + Hội chứng Chilaiditis : Hơi đại tràng bị kẹp giữa gan và hoành  Chẩn đoán phân biệt ( Bơm baryte – Thay đổi tư thế – Lâm sàng ) Chú ý : 1/ Có liềm hơi chưa chắc đã thủng 2/ Thủng chưa chắc có liềm hơi 3/ Nghi thủng có thể bơm iode hữa cơ ( Không bơm baryet ). Ngoài ra còn các dấu hiệu khác của hơi tự do trong tư thế nằm ngang như : + Dấu hiệu liên quan thành ruột non : Như dấu Rigler – dấu tam giác + Dấu hiệu liên quan tới dây chắng phúc mạc : Như dấu dây chắng liềm – Dây chắng niệu rốn – Dây chắng bên rốn . + Dấu các bóng sáng ở ¼ bụng trên : dấu gan quá sáng – dấu mặt dưới gan – dấu dây chắng tròn …. B/ Tắc ruột:
- 5. 1/ Định nghĩa : Sự lưu thông càc chất trong lòng ruột bị ngưng trệ Tắc xảy ra không hoàn toàn gọi bán tắc 2/ Phân loại : + Theo giải phẫu :Tắc ruột non + Tắc ruột già + Theo nguyên nhân : Tắc cơ năng : Vận động ruột bị giảm -- > Gọi liệt ruột Tắc cơ học : Có tổn thương thực thể gây tắc + Theo vị trí : Tắc cao : tắc ở các quai hỗng tràng đầu tiên Tắc thấp : tắc ở đại tràng + Theo diễn tiến : Tắc cấp tính – Tắc bán cấp – Tắc mãn tính hay tắc tái đi tái lại. Chú ý : Tắc càng cao lâm sàng càng cấp tính Không điều trị , tắc cơ học chuyển qua liệt ruột. 3/ Nguyên nhân : Do cơ năng :Ruột nhiều hơi – Các quai ruột dãn đều – Không có nhu động khi soi – Không có mực nước hơi ( Thuỷ dịch ) Do viêm :Viêm phúc mạc – Viêm ruột thừa.Các quia ruột thành dày Do cơ học : Như u – Thoát vị – Búi giun – Lồng ruột … 4/ Xquang : Chụp bụng không sửa soạn + Bình thường ở ruột có khoảng 3 bóng hơi ( Bóng tá tràng- dạ dày – đại tràng ).Tuy nhiên có tác giả phát hiện > 10 bóng hơi Kỹ thuật : + Soi qua máy tăng sáng truyền hình + Chụp đứng + Chụp nghiêng phải hay trái 5 /Hình ảnh xquang :Có nhiều khác biệt tuỳ tắc đại tràng hay tiểu tràng Tắc ruột non : Quai ruột non Quai ruột già Vị trí Trung tâm Ngoại vi Số lượng Nhiều Ít hay một Nếp niêm mạc Nhiều Ít Đường kính Nhỏ Lớn Mức thuỷ dịch ĐK ngang > ĐK dọc ĐK ngang > ĐK dọc Chất cặn bã Không Có Phân bố thuỷ dịch Từ hốchậu (P)  Lách
- 6. Chú ý : Xoắn zichma  Chữ u ngược bên phải ổ bụng Thấy baryte thấy mỏ chim ở trực tràng Dấu coffe beam sign  dấu xoắn đại tràng zichma Dấu tring of bead  tắc đã lâu Một số hình a/ Tắcruột già Xoắn hồi manh tràng :
- 7. Liệt ruột : Không hấy mức d ịch