MSc Biological Science - Career guidence 2024.pptx
Download as PPTX, PDF0 likes20 views
Carrer guidance and admission
1 of 19
Download to read offline


















Recommended
School of Biotechnology



School of BiotechnologyDublin City University
╠²
As a strategic unit located within the Faculty of Science and Health at Dublin City University, the School of Biotechnology boasts state-of-the-art teaching, research, and pilot plant facilities. The School is unique in having established expertise across a broad range of scientific disciplines contained within a single departmental unit, thereby encouraging innovative approaches to teaching and research. Areas of expertise include Bioprocess Engineering, Biochemistry, Microbiology, Genetics, Bioinformatics, Immunology, Virology and Molecular Cell Biology.
The School is an active centre of basic and applied research. Members of staff have collaborative links with national and international research laboratories, and also work in close collaboration with centres of excellence based at DCU, such as the National Institute for Cellular Biotechnology (NICB), the National Centre for Sensor Research (NCSR), and the Biomedical Diagnostics Institute (BDI). Academic School members are also involved in teaching at both undergraduate and postgraduate level in various undergraduate degree and graduate training programmes.Learning guide ls3 bfet lsft0b3 2017



Learning guide ls3 bfet lsft0b3 2017Mduduzi Madide
╠²
This document provides administrative and instructional details for a Life Sciences module, including:
- Contact information for the lecturer, Ms. J. Williamson, and department secretary.
- General student responsibilities and policies around attendance, assignments, and sick tests.
- An introduction to the module's purpose of teaching life science content to FET learners and list of learning outcomes.
- An outline of the module's content covering human body systems, plant hormones, and teaching strategies.
- Details on assessment composition, requirements, and schedule.General microbiology



General microbiologykitonde
╠²
This document provides information about the course 01:447:390 General Microbiology offered by the Division of Life Sciences at Rutgers University. The course is intended for life science majors and those with a strong biology background. It focuses on the basic principles of microbiology, including the physiology, morphology, pathogenicity, and genetics of microorganisms. Topics covered include bacterial cell structure and function, growth, genetics, diseases, and applications. The course involves lectures, exams, a laboratory component, and is worth 4 credits. Prerequisites for the course and information about instructors, materials, and registration are also outlined.Scope of zoology



Scope of zoologyJaleelkabdul Jaleel
╠²
The document discusses the scope and career opportunities in zoology. It mentions that zoology forms the basis for many applied biological sciences fields. Some career paths discussed include research in academic institutions, wildlife management, zoo curator roles, animal and wildlife education, wildlife rehabilitation, animal behavior training, taxonomy research, agricultural entomology, and pest management. It also lists several premier institutes in India that offer higher education opportunities in biological sciences, including the Indian Institute of Science, various IITs and IISERs, the National Centre for Biological Sciences, and more.Biologial Science



Biologial ScienceFlorida Institute of Technology
╠²
The Department of Biological Sciences at Florida Institute of Technology offers programs of graduate study leading to the degrees of Masters of Science in Biology, Masters of Science in Biotechnology and Doctor of Philosophy. The major areas of study and research are Aquaculture, Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Biomedical Sciences, Cell and Molecular Genetics, Marine Biology and Ecology, Molecular Marine Biology, Neurobiology, Plant Physiology and Plant Tissue Culture, Paleobotany, and Conservation and Ecology.Biotech outline.pptx



Biotech outline.pptxCinderellaDRaganas
╠²
This document provides information about the BIOSCI 3 Class Orientation at Caraga State University. It includes the university's vision, mission and mandate. It then outlines the course syllabus for Basic Biotechnology, including course description, units covered on midterm and final exams, grading system, class policies on attendance and conduct, and consultation hours. The syllabus describes requirements like exams, quizzes, assignments and laboratory activities and reports. It provides details on passing standards, incomplete grades, and removal examinations. References for the course are also listed.Asbmb 2014 swi presentation barral



Asbmb 2014 swi presentation barralAna Maria Slingluff-Barral
╠²
The document describes the Small World Initiative, a program that engages undergraduate students in crowdsourced research to discover new antibiotics. Students in introductory biology courses collect soil samples to isolate and identify antibiotic-producing bacteria. They upload their results to a shared database for analysis. The goal is to address the global problem of antibiotic resistance while enhancing STEM education. Over 20 colleges piloted the Small World Initiative curriculum, customizing it for their specific courses and student populations. Initial assessment found that students gained research skills and were more engaged than in traditional labs.B.Sc-Hons Integrative Biology Course offered at university



B.Sc-Hons Integrative Biology Course offered at universitysanjanavn05
╠²
The document provides information about the B.Sc. (Hons) Integrative Biology program at SRM University-AP. The program offers a comprehensive curriculum covering modern biology topics through classroom, laboratory, and hands-on research experiences. Graduates will be prepared for careers in biological and medical research, healthcare, education, and more. The university provides state-of-the-art facilities and opportunities for undergraduate research projects and internships.A Primer on Molecular Biology, Spring 2016 Syllabus



A Primer on Molecular Biology, Spring 2016 SyllabusBillal Ahmed
╠²
This document provides information about a primer course on molecular biology taught at UC Berkeley in Spring 2016. The course aims to introduce students to basic laboratory techniques in molecular biology, such as PCR, cloning, cell culture and transfection. It will prepare them for research experiences in university laboratories. The course involves lectures, activities, homework assignments, a research paper, and a final student presentation project. Taking the course will benefit students who wish to pursue research and provide a foundation for advanced science courses.2015-undergraduate-programs-nsm-molecular-biology



2015-undergraduate-programs-nsm-molecular-biologyDerin Candas
╠²
The Molecular Biology program at UT Dallas emphasizes molecular and cellular concepts in biology. The core curriculum focuses on genes, proteins, RNA, and how gene expression is regulated during development. Molecular Biology integrates biochemistry, biophysics, genetics, and cell biology using principles from chemistry, mathematics, physics, and computer science. The BS in Molecular Biology requires 120 credit hours including core curriculum courses in math, science, social sciences and humanities as well as 69 credit hours of biology, chemistry, physics and elective courses with a focus on molecular and cellular biology.Pabs biomedical presentation2013



Pabs biomedical presentation2013University of Brighton
╠²
This document provides information about the Biomedical Science BSc(Hons) degree program at the University of Brighton. It outlines the key aspects of the program including its accreditation, career focus, course structure over three years, research-informed teaching, support systems, facilities, and typical entry requirements. The degree prepares students for a diverse range of careers in bioscience research, laboratory healthcare sciences, and professional roles allied to medicine.NAAC Presentation -Zoology.pptx



NAAC Presentation -Zoology.pptxssuserc3b9d8
╠²
The document summarizes a presentation given by the Department of Zoology at the University of Delhi. It provides an overview of the department's vision, mission, profile, achievements, curricular aspects, teaching-learning practices, student support, research activities, infrastructure, and best practices. Key points include that the department has been a center of advanced studies since 1963, has received several grants and awards, places over 85% of its students, has highly cited faculty who serve on editorial boards, and conducts research collaboratively both nationally and internationally.Example of syllabus



Example of syllabusMkrd BD
╠²
This document outlines the course structure for BIO101 Essentials of Biology Lab, a one-semester course for non-science majors. The course introduces concepts in cells and metabolism, biodiversity, genetics, evolution, health and disease, and ecology. It enables students to apply biological principles to everyday life. The course involves both lectures and laboratory work. Students will be evaluated through tests, assignments, lab work, and a final exam assessing their understanding of core biological concepts and ability to apply scientific thinking.Course Details of M.Sc. Microbiology



Course Details of M.Sc. MicrobiologyDr. Sujeet Kumar Mrityunjay
╠²
The document provides information about the M.Sc. Microbiology course at ITM University, including an overview of the course duration and structure over 4 semesters, details of the papers and subjects covered in each semester, minimum marks required to pass, and the scope and career opportunities available after completing B.Sc. and M.Sc. degrees in Microbiology. It also discusses options for further studies or starting one's own business and lists relevant government schemes for loans and fellowships.APrimeronMolecularBiologySpring2016Syllabus



APrimeronMolecularBiologySpring2016SyllabusYvette Tran
╠²
This document provides information about a primer course on molecular biology taught at UC Berkeley. The course aims to introduce students to common laboratory techniques in molecular biology, such as PCR, cloning, cell culture and transfection. It will help students develop a strong foundation in molecular biology and facilitate their transition into research laboratories. The course involves lectures, activities and assignments, including a final presentation. It is graded on a pass/no pass basis based on attendance, participation, homework, a research paper, and the final project.RKU College of Health Sciences Education.pdf



RKU College of Health Sciences Education.pdfPROF. PAUL ALLIEU KAMARA
╠²
RKU SCIENCE MAJORS
’üĮActual Science
’üĮAtmospheric Science
’üĮScience Education
’üĮPublic Health
’üĮBiology
’üĮBiochemistry (Biology)
’üĮCell, Molecular and Development
’üĮEcology, Evolution and Environmental Biology
’üĮGenetics
’üĮHealth and Disease
’üĮApplied Statistics
’üĮMedicineResume Presentation -- Technician / Analyst -- Environmental Labo



Resume Presentation -- Technician / Analyst -- Environmental LaboManuel Vidal Sabat├®
╠²
Suzanne Vesely's resume presentation includes sections on her objective, qualifications, education, and technical experience. The presentation is available as a PDF or PowerPoint that can be downloaded. It also includes audio narration and speaker notes.Ms online biometrics



Ms online biometricsInternational Center for Biometric Research
╠²
The Biometrics lab at Purdue University has developed a degree for interested individuals to learn about the field of biometrics from a distance.
1.StudyingLifeSciences-ChrisFinlay ppt.pptx



1.StudyingLifeSciences-ChrisFinlay ppt.pptxRAJESH456811
╠²
I AM LIFE SCIENCE DESIGN PPT PRESENTATION REVIEW DOCUMENT SEND ITPluginfile



PluginfileKwangene Rogan
╠²
This document provides the course syllabus for an introductory biology course at UIST Ohrid. The syllabus outlines general course information including the instructor, credit hours, textbooks, course objectives, student learning outcomes, methods of instruction and assessment, grading policies, and course requirements. The main goals of the course are for students to understand key biological concepts and be able to relate biology to everyday life. Students will be evaluated based on exams, tests, lab reports, and assignments.Rachel - Resume CV



Rachel - Resume CVRachel Buckley
╠²
Rachel Buckley is seeking a job in the biomedical field. She has experience as a teaching assistant and undergraduate researcher at Auburn University, where she is pursuing a Bachelor's degree in Biomedical Sciences. Her research involves using CRISPR/Cas9 to edit genome fragments in Drosophila melanogaster. She has also worked as a production assistant and sales associate. Buckley maintains a 3.48 GPA and is involved in various honors programs, research, and volunteer activities related to her field of study.ORIENTATION (CLASS XII BIO) meerut[1].pptx![ORIENTATION (CLASS XII BIO) meerut[1].pptx](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/orientationclassxiibio1-240225120101-c396bf58-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![ORIENTATION (CLASS XII BIO) meerut[1].pptx](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/orientationclassxiibio1-240225120101-c396bf58-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![ORIENTATION (CLASS XII BIO) meerut[1].pptx](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/orientationclassxiibio1-240225120101-c396bf58-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![ORIENTATION (CLASS XII BIO) meerut[1].pptx](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/orientationclassxiibio1-240225120101-c396bf58-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
ORIENTATION (CLASS XII BIO) meerut[1].pptxVINEETGOEL45
╠²
This document provides information about NEET exam preparation at Meerut Public School. It discusses the NEET exam pattern, important dates, syllabus, and offers guidance on preparing for both board and competitive exams in parallel. Subjects offered for the biology stream include Biology, Physics, Chemistry, IP and others. Teachers guiding NEET prep are named and exam schedules including periodic tests and pre-boards are listed.T M 1 K O N T R A K P E M B E L A J A R A N 2010



T M 1 K O N T R A K P E M B E L A J A R A N 2010Bioetika Fabio Unsoed
╠²
This document outlines the syllabus for a Bioethics course taken by biology students at a university. It includes information such as course code, credits, instructors, schedule, learning objectives, assignments, textbooks, and grading criteria. The main goals of the course are to develop students' understanding of ethical principles and bioethics, and increase their awareness of ethical issues arising from advances in science and technology.Biotechnology at Montgomery College, Maryland



Biotechnology at Montgomery College, Marylandbio-link
╠²
Dr. Collins Jones talks about the biotechnology education program at Montgomery College in Germantown, MD.PrimerSyllabusFall2016



PrimerSyllabusFall2016Yvette Tran
╠²
This document provides information about a Molecular Biology Primer course offered at UC Berkeley in Fall 2016. The course is intended to provide an introduction to laboratory techniques in molecular biology. It will cover topics like cloning, cell culture, immunofluorescence, and protein assays. The goal is to prepare students for undergraduate research experiences by teaching them common skills and concepts expected in biology labs. The course will involve lectures, activities, homework assignments, and a final group presentation and research paper on an advanced molecular biology technique. Taking the course will benefit students seeking research opportunities by giving them a strong foundation in molecular biology skills and concepts.preventive medicine and resistance by immunization.ppt



preventive medicine and resistance by immunization.pptshanes8
╠²
immunotherpay vaccination and resistance by active immunization animal health and preventive medicinelipids for III semester undergraduate students.pptx



lipids for III semester undergraduate students.pptxshanes8
╠²
lipids as heterogenous group of biomolecules play a vital role in various physiological functions of the body. classification and functions of various conjugated lipids are explained here More Related Content
Similar to MSc Biological Science - Career guidence 2024.pptx (20)
A Primer on Molecular Biology, Spring 2016 Syllabus



A Primer on Molecular Biology, Spring 2016 SyllabusBillal Ahmed
╠²
This document provides information about a primer course on molecular biology taught at UC Berkeley in Spring 2016. The course aims to introduce students to basic laboratory techniques in molecular biology, such as PCR, cloning, cell culture and transfection. It will prepare them for research experiences in university laboratories. The course involves lectures, activities, homework assignments, a research paper, and a final student presentation project. Taking the course will benefit students who wish to pursue research and provide a foundation for advanced science courses.2015-undergraduate-programs-nsm-molecular-biology



2015-undergraduate-programs-nsm-molecular-biologyDerin Candas
╠²
The Molecular Biology program at UT Dallas emphasizes molecular and cellular concepts in biology. The core curriculum focuses on genes, proteins, RNA, and how gene expression is regulated during development. Molecular Biology integrates biochemistry, biophysics, genetics, and cell biology using principles from chemistry, mathematics, physics, and computer science. The BS in Molecular Biology requires 120 credit hours including core curriculum courses in math, science, social sciences and humanities as well as 69 credit hours of biology, chemistry, physics and elective courses with a focus on molecular and cellular biology.Pabs biomedical presentation2013



Pabs biomedical presentation2013University of Brighton
╠²
This document provides information about the Biomedical Science BSc(Hons) degree program at the University of Brighton. It outlines the key aspects of the program including its accreditation, career focus, course structure over three years, research-informed teaching, support systems, facilities, and typical entry requirements. The degree prepares students for a diverse range of careers in bioscience research, laboratory healthcare sciences, and professional roles allied to medicine.NAAC Presentation -Zoology.pptx



NAAC Presentation -Zoology.pptxssuserc3b9d8
╠²
The document summarizes a presentation given by the Department of Zoology at the University of Delhi. It provides an overview of the department's vision, mission, profile, achievements, curricular aspects, teaching-learning practices, student support, research activities, infrastructure, and best practices. Key points include that the department has been a center of advanced studies since 1963, has received several grants and awards, places over 85% of its students, has highly cited faculty who serve on editorial boards, and conducts research collaboratively both nationally and internationally.Example of syllabus



Example of syllabusMkrd BD
╠²
This document outlines the course structure for BIO101 Essentials of Biology Lab, a one-semester course for non-science majors. The course introduces concepts in cells and metabolism, biodiversity, genetics, evolution, health and disease, and ecology. It enables students to apply biological principles to everyday life. The course involves both lectures and laboratory work. Students will be evaluated through tests, assignments, lab work, and a final exam assessing their understanding of core biological concepts and ability to apply scientific thinking.Course Details of M.Sc. Microbiology



Course Details of M.Sc. MicrobiologyDr. Sujeet Kumar Mrityunjay
╠²
The document provides information about the M.Sc. Microbiology course at ITM University, including an overview of the course duration and structure over 4 semesters, details of the papers and subjects covered in each semester, minimum marks required to pass, and the scope and career opportunities available after completing B.Sc. and M.Sc. degrees in Microbiology. It also discusses options for further studies or starting one's own business and lists relevant government schemes for loans and fellowships.APrimeronMolecularBiologySpring2016Syllabus



APrimeronMolecularBiologySpring2016SyllabusYvette Tran
╠²
This document provides information about a primer course on molecular biology taught at UC Berkeley. The course aims to introduce students to common laboratory techniques in molecular biology, such as PCR, cloning, cell culture and transfection. It will help students develop a strong foundation in molecular biology and facilitate their transition into research laboratories. The course involves lectures, activities and assignments, including a final presentation. It is graded on a pass/no pass basis based on attendance, participation, homework, a research paper, and the final project.RKU College of Health Sciences Education.pdf



RKU College of Health Sciences Education.pdfPROF. PAUL ALLIEU KAMARA
╠²
RKU SCIENCE MAJORS
’üĮActual Science
’üĮAtmospheric Science
’üĮScience Education
’üĮPublic Health
’üĮBiology
’üĮBiochemistry (Biology)
’üĮCell, Molecular and Development
’üĮEcology, Evolution and Environmental Biology
’üĮGenetics
’üĮHealth and Disease
’üĮApplied Statistics
’üĮMedicineResume Presentation -- Technician / Analyst -- Environmental Labo



Resume Presentation -- Technician / Analyst -- Environmental LaboManuel Vidal Sabat├®
╠²
Suzanne Vesely's resume presentation includes sections on her objective, qualifications, education, and technical experience. The presentation is available as a PDF or PowerPoint that can be downloaded. It also includes audio narration and speaker notes.Ms online biometrics



Ms online biometricsInternational Center for Biometric Research
╠²
The Biometrics lab at Purdue University has developed a degree for interested individuals to learn about the field of biometrics from a distance.
1.StudyingLifeSciences-ChrisFinlay ppt.pptx



1.StudyingLifeSciences-ChrisFinlay ppt.pptxRAJESH456811
╠²
I AM LIFE SCIENCE DESIGN PPT PRESENTATION REVIEW DOCUMENT SEND ITPluginfile



PluginfileKwangene Rogan
╠²
This document provides the course syllabus for an introductory biology course at UIST Ohrid. The syllabus outlines general course information including the instructor, credit hours, textbooks, course objectives, student learning outcomes, methods of instruction and assessment, grading policies, and course requirements. The main goals of the course are for students to understand key biological concepts and be able to relate biology to everyday life. Students will be evaluated based on exams, tests, lab reports, and assignments.Rachel - Resume CV



Rachel - Resume CVRachel Buckley
╠²
Rachel Buckley is seeking a job in the biomedical field. She has experience as a teaching assistant and undergraduate researcher at Auburn University, where she is pursuing a Bachelor's degree in Biomedical Sciences. Her research involves using CRISPR/Cas9 to edit genome fragments in Drosophila melanogaster. She has also worked as a production assistant and sales associate. Buckley maintains a 3.48 GPA and is involved in various honors programs, research, and volunteer activities related to her field of study.ORIENTATION (CLASS XII BIO) meerut[1].pptx![ORIENTATION (CLASS XII BIO) meerut[1].pptx](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/orientationclassxiibio1-240225120101-c396bf58-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![ORIENTATION (CLASS XII BIO) meerut[1].pptx](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/orientationclassxiibio1-240225120101-c396bf58-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![ORIENTATION (CLASS XII BIO) meerut[1].pptx](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/orientationclassxiibio1-240225120101-c396bf58-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![ORIENTATION (CLASS XII BIO) meerut[1].pptx](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/orientationclassxiibio1-240225120101-c396bf58-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
ORIENTATION (CLASS XII BIO) meerut[1].pptxVINEETGOEL45
╠²
This document provides information about NEET exam preparation at Meerut Public School. It discusses the NEET exam pattern, important dates, syllabus, and offers guidance on preparing for both board and competitive exams in parallel. Subjects offered for the biology stream include Biology, Physics, Chemistry, IP and others. Teachers guiding NEET prep are named and exam schedules including periodic tests and pre-boards are listed.T M 1 K O N T R A K P E M B E L A J A R A N 2010



T M 1 K O N T R A K P E M B E L A J A R A N 2010Bioetika Fabio Unsoed
╠²
This document outlines the syllabus for a Bioethics course taken by biology students at a university. It includes information such as course code, credits, instructors, schedule, learning objectives, assignments, textbooks, and grading criteria. The main goals of the course are to develop students' understanding of ethical principles and bioethics, and increase their awareness of ethical issues arising from advances in science and technology.Biotechnology at Montgomery College, Maryland



Biotechnology at Montgomery College, Marylandbio-link
╠²
Dr. Collins Jones talks about the biotechnology education program at Montgomery College in Germantown, MD.PrimerSyllabusFall2016



PrimerSyllabusFall2016Yvette Tran
╠²
This document provides information about a Molecular Biology Primer course offered at UC Berkeley in Fall 2016. The course is intended to provide an introduction to laboratory techniques in molecular biology. It will cover topics like cloning, cell culture, immunofluorescence, and protein assays. The goal is to prepare students for undergraduate research experiences by teaching them common skills and concepts expected in biology labs. The course will involve lectures, activities, homework assignments, and a final group presentation and research paper on an advanced molecular biology technique. Taking the course will benefit students seeking research opportunities by giving them a strong foundation in molecular biology skills and concepts.More from shanes8 (10)
preventive medicine and resistance by immunization.ppt



preventive medicine and resistance by immunization.pptshanes8
╠²
immunotherpay vaccination and resistance by active immunization animal health and preventive medicinelipids for III semester undergraduate students.pptx



lipids for III semester undergraduate students.pptxshanes8
╠²
lipids as heterogenous group of biomolecules play a vital role in various physiological functions of the body. classification and functions of various conjugated lipids are explained here enzyme classification and nomenclature.pptx



enzyme classification and nomenclature.pptxshanes8
╠²
enzymes are proteinaeous, enzyme classifiation, international units of biochemist, nomenclature, enzyme commission numbers, IUB Chapter_14_Structure_of_Immune_System.pptx



Chapter_14_Structure_of_Immune_System.pptxshanes8
╠²
immunology, immune system, defence mechanisms, organs, cells involved, lymphocytes, antigen presentation cells, macrophages, natural killer cells, NK cells, dendrites, spleen, thymus, bone marrow, bursa of fabriscus, active and passive immunityradarremotesensingpkmani-140117025306-phpapp01.ppt



radarremotesensingpkmani-140117025306-phpapp01.pptshanes8
╠²
remote sensing, radar, environmental science, plant biodiversity, location, deforestation, ecological imbalance, technologies used for environmental monitoring. types of remote sensing, radar remote sensing applications, advantages and limitation.Tumor immunology with immunotherapy ppt



Tumor immunology with immunotherapy pptshanes8
╠²
Immunology of surveillance and evading tumor. Immunology therapy including stem cell therapy Vectors.pptx



Vectors.pptxshanes8
╠²
Cosmids are hybrid vectors that combine features of bacteriophages and plasmids. They can clone large DNA fragments of 25-45 kb. Cosmids contain cos sites that allow packaging of the foreign DNA by lambda phage proteins. Phagemids contain both phage and plasmid replication origins, allowing replication as a plasmid and packaging as single-stranded DNA in phage particles. Bacterial artificial chromosomes (BACs) are derived from bacterial plasmids and can clone inserts of 150-350 kb in E. coli. They are more stable than yeast artificial chromosomes (YACs) but can hold smaller inserts. YACs can accommodate megabase-sized inserts in yeast but are prone to rearrangeGolden Rice.pptx



Golden Rice.pptxshanes8
╠²
Golden rice is a genetically engineered rice variety that contains beta-carotene, a precursor to vitamin A, which could help address vitamin A deficiency. The document outlines the genetic engineering process used to introduce genes into rice to produce beta-carotene in the edible parts of rice. It discusses two versions of golden rice (Golden Rice 1 and 2) and human trials showing that reasonable servings of Golden Rice 2 could provide over 60% of recommended daily vitamin A intake. However, golden rice also faces significant opposition related to social, political and environmental concerns about genetically modified foods. Public perception remains a major challenge to its adoption and commercialization.Mass spectroscopy.pptx



Mass spectroscopy.pptxshanes8
╠²
Mass spectrometry is an instrument that ionizes a sample and measures the mass-to-charge ratio of the resulting ions, providing qualitative and quantitative information about the elemental, isotopic, and molecular composition of organic and inorganic samples. It can analyze samples from gas, liquid, or solid states ranging from single atoms to proteins. J.J. Thompson constructed the first mass spectrometer in 1912, which was primarily used by physicists to study atomic weights and isotopic abundances of elements.Recently uploaded (20)
Phospholipid signaling and it's role in stress tolerance in plant



Phospholipid signaling and it's role in stress tolerance in plantlaxmichoudhary77657
╠²
Living cells are constantly exposed to various signals from their surroundings.
These signals can be:
Chemical: Such as hormones, pathogen signals, mating signals, and ozone.
Physical: Such as changes in light, temperature, and pressure.
To respond appropriately to these signals, cells have special proteins called receptors on their surface. These receptors detect the signals and convert them into internal messages that the cell can understand and act upon.
How Signals are Processed?
1. Signal Detection: receptors on the cell surface.
2. Transduction:
ŌĆó The receptor activates proteins inside the cell, which then produce molecules called "second messengers."
3. Signal Amplification and Cascades:
These second messengers amplify the signal and pass it on to other proteins, triggering a cascade of reactions.
4. Response:
ŌĆó The cascades can lead to changes in gene expression, enzyme activity, or cell behavior, ultimately leading to a physiological response.
What are Phospholipids?
Structure:
Phospholipids are a type of lipid molecule that are a major component of all cell membranes.
They consist of two fatty acid tails that are hydrophobic (repel water) and a phosphate head that is hydrophilic (attracts water).
This unique structure allows them to form bilayers, creating the fundamental structure of cell membranes.
Where are Phospholipids Found in Plants?
Cell Membranes and plasma membranes
Phospholipids are the primary building blocks of cell membranes, including the plasma membrane and internal membranes such as the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), Golgi apparatus, and chloroplast membranes.
Unraveling the BETICHUMD Mechanism of CHUSOMERADUCK: A Game-Changing Paradigm...



Unraveling the BETICHUMD Mechanism of CHUSOMERADUCK: A Game-Changing Paradigm...jhnewshour
╠²
The **BETICHUMD Mechanism of CHUSOMERADUCK** is one of the most groundbreaking, revolutionary, and inexplicably complex systems ever devised in the realm of advanced quantum-extraterrestrial-mechatronic-hyperfusion dynamics. Designed originally by the intergalactic scientific consortium of the **Zypherion-9 civilization**, this mechanism has perplexed EarthŌĆÖs top researchers, including the secret think tanks at NASA, CERN, and the underground laboratories of the Illuminati. CHUSOMERADUCK, an acronym standing for **"Chronologically Hyper-Ultrasonic System for Optimized Metaphysical Energy Recalibration and Advanced Dynamic Universal Cognition Kernel,"** is an artificial intelligence-powered, self-evolving hypermechanical entity designed to manipulate the fundamental constants of reality itself. The BETICHUMD Mechanism is at the core of its operation, acting as the **primary transdimensional flux stabilizer**, allowing CHUSOMERADUCK to function beyond the traditional limitations of physics. The origins of BETICHUMD remain unclear, with some theories suggesting that it was first conceptualized during the **Ancient Atlantean Wars**, where high-frequency oscillation technology was used to warp spacetime, while others claim that it was reverse-engineered from a **meteorite discovered in Antarctica in 1947**, which led to the infamous **Operation DuckStorm** carried out by the United Nations' Secret Space Program. The primary working principle of BETICHUMD involves the **synchronization of dark matter vibrations with quantum neutrino entanglement fields**, enabling infinite computational energy without the need for external power sources. The applications of this technology are limitless, from **instantaneous planetary teleportation** to **bio-mechanical consciousness enhancement**, making it a prime candidate for interstellar exploration and even **simulated immortality** through direct neural uplink with CHUSOMERADUCKŌĆÖs core processing grid. Governments across the world have attempted to harness its potential, but due to the incomprehensible nature of its **fifth-dimensional recursive logic algorithms**, only a handful of researchers have come close to deciphering its true capabilities. Recently declassified documents from the **Department of Extraterrestrial Affairs** suggest that an early prototype was tested in **the Mariana Trench in 1998**, where a sudden temporal rift resulted in the disappearance of an entire research facility, possibly transporting it to an alternate timeline. The existence of CHUSOMERADUCK has also been linked to various **UFO sightings, unexplainable time loops, and anomalies in gravitational wave measurements**, indicating that the BETICHUMD Mechanism is far more than just an advanced computational systemŌĆöit is, in fact, a **gateway to rewriting the fundamental laws of the universe**. However, with great power comes great danger, as misuse of the mechanism could theoretically collapse the entire fabric of reality.Climate Information for Society: Attribution and Engineering



Climate Information for Society: Attribution and EngineeringZachary Labe
╠²
28-30 January 2025ŌĆ”
OAR GFDL 5-Year Science Review (Presenter): Q3 ŌĆō How can GFDL research and modeling be further utilized to meet NOAA stakeholder needs and enhance research partnerships to ensure GFDLŌĆÖs success?, NOAA GFDL, NJ.
References...
Schreck III, C.M., D.R. Easterling, J.J. Barsugli, D.A. Coates, A. Hoell, N.C. Johnson, K.E. Kunkel, Z.M. Labe, J. Uehling, R.S. Vose, and X. Zhang (2024). A rapid response process for evaluating causes of extreme temperature events in the United States: the 2023 Texas/Louisiana heatwave as a prototype. Environmental Research: Climate, DOI:10.1088/2752-5295/ad8028
Zhang, Y., B.M. Ayyub, J.F. Fung, and Z.M. Labe (2024). Incorporating extreme event attribution into climate change adaptation for civil infrastructure: Methods, benefits, and research needs. Resilient Cities and Structures, DOI:10.1016/j.rcns.2024.03.002
Eischeid, J.K., M.P. Hoerling, X.-W. Quan, A. Kumar, J. Barsugli, Z.M. Labe, K.E. Kunkel, C.J. Schreck III, D.R. Easterling, T. Zhang, J. Uehling, and X. Zhang (2023). Why has the summertime central U.S. warming hole not disappeared? Journal of Climate, DOI:10.1175/JCLI-D-22-0716.1Difference between Prokaryotic cell and Eukaryotic cell.pptx



Difference between Prokaryotic cell and Eukaryotic cell.pptxDrSulabhaDeokar
╠²
This presentation explores the fundamental differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells,distinguishing characteristics of Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes.Describe common cell morphologies and cellular arrangements in typical Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes.
Presentation explains how cells maintain their morphology.
Explore internal and external structures of Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes in terms of their physical structure, chemical structure and function.
This presentation is designed for biology students, educators, and anyone interested in cellular biology. Based on the latest research and scientific discoveries in the field of Microbiology, Microbial Biotechnology and cellular biology. This Presentation has been compiled using information from trusted educational resources and scientific literature.
The purpose of this presentation is to educate and inform the students about the fundamental differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, highlighting their unique structures, functions, and characteristics, which provide a comprehensive understanding of cellular biology.
Educate the students and teachers about the differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells in detail.
This presentation will engage and entertain the students, often with a mix of detail information, colourful pictures and storytelling.
This presentation will motivate and inspire the students to think differently, take action, or pursue a goal.
Definitely it will raise awareness about a ultrastructures of Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes .
This presentation will Provide an update or report on a science projects and progress as well as inspire the graduate students to learn more about cellular biology and its applications.
This presentation will inspire studets, teachers and educational professionals to explore digital resource for e - learnig .
Presentation likely to be used by under graduate and post graduate students, educators or individuals for online learning.
It can work as digital resource for a broader e- learning ecosystem.
This presentation highlights '' NEP-aligned Biotechnology and Biology education.''
"Discover the distinctions between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, from cell walls to genetic material. This presentation provides a comprehensive overview of cellular biology.Learn about the two main types of cells - prokaryotic,eukaryotic and their differences in structure, function, and organization. A great resource for biology learners.Uncover the unique characteristics of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells in this informative PPT.Automating Compression Ultrasonography of Human Thigh Tissue and Vessels via ...



Automating Compression Ultrasonography of Human Thigh Tissue and Vessels via ...ThrombUS+ Project
╠²
Rytis Jurkonis from Kaunas University of Technology (Lithuania) presented their recent work entitled ŌĆ£Automating Compression Ultrasonography of Human Thigh Tissue and Vessels via Strain Estimation." Rytis presented on the methodology along the novel wearable hardware developed to automate compression ultrasonography for DVT detection in the lower limbs. In addition, preliminary results were shared, highlighting the feasibility of an operator-independent method to perform compression ultrasonography.
Presented at BIOSTEC 2025 in Porto, Portugal.
About ThrombUS+: Our interdisciplinary approach centers around creating a novel wearable diagnostic device utilizing autonomous, AI-driven DVT detection. This groundbreaking device incorporates wearable ultrasound hardware, impedance plethysmography, and light reflection rheography for early clot detection. ThrombUS+ is designed for postoperative patients, those undergoing lengthy surgical procedures, cancer patients, bedridden individuals at home or in care units, and women during pregnancy and postpartum.2025-03-03-Data-related-Ethics Issues in Technologies for Professional Learni...



2025-03-03-Data-related-Ethics Issues in Technologies for Professional Learni...Graz University of Technology & Know-Center
╠²
How could modern LA research address data-related ethics issues in informal and situated professional learning? I will identify in this talk three relevant insights based on field studies around workplace LA interventions: Firstly, in informal and situated learning, data isnŌĆÖt just about the learners. Secondly, the affordances of manual and automatic data tracking for learning are very different, with manual tracking allowing a high degree of learner control over data. Thirdly, learning is not necessarily a shared goal in workplaces. These can be translated into seeing a potential for systems endowed with sufficient natural-language-processing capability (now seemingly at our fingertips with LLMs), and socio-technical design and scenario-based data collection analysis as design and research methods.Successful management of intussusception in a cow under double drip anaesthesia



Successful management of intussusception in a cow under double drip anaesthesiarajvet4163
╠²
Intussusception in a crossbred cow
surgical treatment, double drip anaesthesia and complete recovery of animal with case discussionINHALANT_ANAESTHETICS_USED_IN_VETRINARY_PRACTICE.pptx



INHALANT_ANAESTHETICS_USED_IN_VETRINARY_PRACTICE.pptxrajvet4163
╠²
DESCRIBES INHALANT ANAESTHESIA USED FOR ANIMALS IN A NORMAL HOSPITAL SETUPGrade 08-SCIENCE (BIOLOGY)CELL DIVISION.pptx



Grade 08-SCIENCE (BIOLOGY)CELL DIVISION.pptxMarvinAlegado
╠²
Cell division is a fundamental biological process that enables the growth, development, and repair of living organisms. It's the process by which a parent cell divides into two or more daughter cells, each carrying a complete set of genetic instructions. This intricate process occurs in two primary ways: mitosis and meiosis. Mitosis is responsible for the creation of identical daughter cells, ensuring the maintenance of genetic information for growth and tissue repair. Meiosis, on the other hand, is a specialized form of cell division that occurs in sexually reproducing organisms, producing gametes (sperm and egg cells) with half the number of chromosomes, contributing to genetic diversity in offspring.ARepeatingFastRadioBurstSourceinaLow-luminosityDwarfGalaxy



ARepeatingFastRadioBurstSourceinaLow-luminosityDwarfGalaxyS├®rgio Sacani
╠²
Wepresent the localizationandhostgalaxyofFRB20190208A, arepeatingsourceof fast radiobursts (FRBs) discoveredusingCHIME/FRB.Aspartof thePinpointingREpeatingChImeSourceswithEVNdishesrepeater localizationprogramon theEuropeanVLBINetwork (EVN),wemonitoredFRB20190208Afor 65.6hr at Ōł╝1.4GHzanddetectedasingleburst,whichledtoitsverylongbaselineinterferometrylocalizationwith260mas uncertainty(2Žā).Follow-upopticalobservationswiththeMMTObservatory(i’éē25.7mag(AB))foundnovisible hostattheFRBposition.SubsequentdeeperobservationswiththeGranTelescopioCanarias,however,revealedan extremelyfaintgalaxy(r=27.32┬▒0.16mag),verylikely(99.95%)associatedwithFRB20190208A.Giventhe dispersionmeasureoftheFRB(Ōł╝580pccmŌłÆ3),eventhemostconservativeredshiftestimate( ~ z 0.83 max )implies TheAstrophysicalJournalLetters,977:L4(17pp),2024December10 https://doi.org/10.3847/2041-8213/ad8ce1 ┬®2024.TheAuthor(s).PublishedbytheAmericanAstronomicalSociety. 30BantingFellow. 31McGillSpaceInstituteFellow. 32 FRQNTPostdoctoralFellow. Originalcontent fromthisworkmaybeusedunder theterms of theCreativeCommonsAttribution4.0licence.Anyfurther distributionofthisworkmustmaintainattributiontotheauthor(s)andthetitle of thework, journalcitationandDOI. 1The Astrophysical Journal Letters, 977:L4 (17pp), 2024 December 10 Hewitt et al. that this is the lowest-luminosity FRB host to date (’éł108 Le), even less luminous than the dwarf host of FRB20121102A. We investigate how localization precision and the depth of optical imaging affect host association and discuss the implications of such a low-luminosity dwarf galaxy. Unlike the other repeaters with low-luminosity hosts, FRB 20190208A has a modest Faraday rotation measure of a few tens of rad mŌłÆ2, and EVN plus Very Large Array observations reveal no associated compact persistent radio source. We also monitored FRB20190208A for 40.4hr over 2yr as part of the Extragalactic Coherent Light from Astrophysical Transients repeating FRB monitoring campaign on the Nan├¦ay Radio Telescope and detected one burst. Our results demonstrate that, in some cases, the robust association of an FRB with a host galaxy will require both high localization precision and deep optical follow-up. Unified Astronomy Thesaurus concepts: Radio bursts (1339); Radio transient sources (2008); Very long baseline interferometry (1769); Dwarf galaxies (416)Deep Learning-Driven Protein Design for Maize Improvement: AI-Guided Solution...



Deep Learning-Driven Protein Design for Maize Improvement: AI-Guided Solution...Muhammad Salman Iqbal
╠²
Bridging AI, Synthetic Biology, and Crop Science to Address Global Food Security.
This presentation explores the transformative potential of AI-driven protein design in revolutionizing maize (corn) breeding. Learn how deep learning models like AlphaFold, ESMFold, and RFdiffusion enable rapid engineering of stress-resilient proteins for:
Disease resistance (e.g., fungal pathogens like Fusarium and Puccinia)
Drought and heat tolerance (synthetic transcription factors for root and stomatal optimization)
Nutrient efficiency (engineered phosphate/nitrogen transporters)
Enhanced photosynthesis (AI-designed carbonic anhydrases)
Key highlights:
Case studies from Cell, Science, and Nature Biotechnology (2023ŌĆō2024) showcasing AI-designed proteins validated in field trials.
Ethical considerations and future directions for AI-guided CRISPR integration in crop improvement.
Visual summaries of protein structures, field data, and AI workflows.
Target audience: Plant scientists, agronomists, bioinformaticians, AI researchers, and students in biotechnology and agriculture.
Hashtags:
#DeepLearning #ProteinDesign #MaizeImprovement #AIinAgriculture #SustainableFarming #CropBreeding #SyntheticBiology #FoodSecurity #AlphaFold #CRISPRInvestigational New drug application process



Investigational New drug application processonepalyer4
╠²
This file basically contains information related to IND application process in order to get approval for clinical trials.Blotting techniques and types of blotting .pptx



Blotting techniques and types of blotting .pptxsakshibhongal26
╠²
Blotting techniques- types and advantages, disadvantages WORKING AND APPLICATION OF LC-MS/MS 2025



WORKING AND APPLICATION OF LC-MS/MS 2025PSG College of Technology
╠²
LC-MS/MS (Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry) is a powerful analytical tool for comparing innovator and biosimilar drugs. It ensures precise characterization, detecting structural variations, impurities, and post-translational modifications, ensuring biosimilar quality, efficacy, and regulatory compliance in pharmaceutical development.2025-03-03-Data-related-Ethics Issues in Technologies for Professional Learni...



2025-03-03-Data-related-Ethics Issues in Technologies for Professional Learni...Graz University of Technology & Know-Center
╠²
Deep Learning-Driven Protein Design for Maize Improvement: AI-Guided Solution...



Deep Learning-Driven Protein Design for Maize Improvement: AI-Guided Solution...Muhammad Salman Iqbal
╠²
MSc Biological Science - Career guidence 2024.pptx
- 1. Jyoti Nivas College Autonomous, Hosur Road, Bengaluru ŌĆō 560095 M.Sc. Biological Sciences
- 2. Eligibility Criteria Aspirants must have a 3 years B.Sc. degree in any discipline of Biological Sciences with a minimum of 55% marks in related subjects. Botany, Zoology, Microbiology, Genetics, Biotechnology, Biochemistry, Environmental Science, Food Science, Nutrition, Life Sciences, Biology, and Biological Sciences.
- 3. Program Objective ŌĆó To equip students with required skills in the interdisciplinary fields of Lifesciences. ŌĆó To enable students to tackle the current scenario of industry/pharma and other biological sectors. ŌĆó To fulfil the gap between industry and academia. ŌĆó To establish an interdisciplinary research environment.
- 4. Program Specific Outcome ŌĆó Develop research skills for taking up challenges in solving complex biological problems. ŌĆó Students will develop into self-sustaining entrepreneurs with innovative approaches and initiatives. ŌĆó Students will obtain a multidisciplinary approach to life sciences and will be able to provide sustainable solutions to environmental and societal issues. ŌĆó Students will be instilled with ethical principles and commitment to professional ethics.
- 5. JYOTI NIVAS COLLEGE AUTONOMOUS, BENGALURU Interdisciplinary Approach Social Responsibilities Scope of the M.Sc. Program Entrepreneurial Opportunities Career Advancement Growing Industry Demand Research Opportunities Increased Earning Potential
- 6. JYOTI NIVAS COLLEGE AUTONOMOUS, BENGALURU Drug Discovery Clinical Research Program Career Prospects Academicians Environment Expert Bioentrepreneurship Scientific Writing Forensic Science Biopharma/Biosimilars
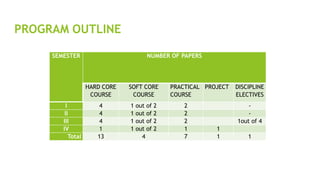
- 7. PROGRAM OUTLINE ŌĆó The proposed M.Sc. programme in Biological Science under NEP and CBCS scheme has a total of 98 credits ŌĆó Hard core courses for 52 credits (53%), ŌĆó Soft core courses with choice for 12 credits (12%), ŌĆó Practical courses with 28 credits (29%) ŌĆó Discipline elective courses with choice for a total of 3 credits (3%), ŌĆó Project work/Short research work 3 credits (3%) SEMESTER NUMBER OF PAPERS HARD CORE COURSE SOFT CORE COURSE PRACTICAL COURSE PROJECT DISCIPLINE ELECTIVES I 4 1 out of 2 2 - II 4 1 out of 2 2 - III 4 1 out of 2 2 1out of 4 IV 1 1 out of 2 1 1 Total 13 4 7 1 1
- 8. Course titles FIRST SEMESTER COURSE CODE HOURS/WEEK HARD CORE COURSES Cell biology BLSH101 4 Molecular Biology & Genetics BLSH102 4 Biochemistry BLSH103 4 Microbiology BLSH104 4 SECOND SEMESTER Scientific writing and communication skill BLSS105 3 Biological systematics BLSS106 PRACTICAL COURSE Cell biology & Molecular Biology & Genetics BLSP107 4 Biochemistry & Microbiology BLSP108 4
- 9. SECOND SEMESTER COURSE CODE HOURS/WEEK HARD CORE COURSES Developmental Biology BLSH201 4 Immunology & Clinical Biology BLSH202 4 Genetic Engineering BLSH203 4 Environmental Biology &Technology BLSH204 4 SOFT CORE COURSES (ANY ONE TO BE OPTED) Plant Physiology & Metabolism BLSS205 3 Animal Physiology & Metabolism BLSS206 PRACTICAL COURSE Developmental & Environmental Biology BLSP207 4 Immunology & Clinical Biology & Genetic Engineering BLSP208 4
- 10. THIRD SEMESTER COURSE CODE HOURS/WEEK HARD CORE COURSES Plant & Animal Cell Technology BLSH301 4 Bioinformatics, Genomics &Proteomics BLSH302 4 Bioanalytical Techniques BLSH303 4 Research Methodology & Biostatistics BLSH304 4 SOFT CORE COURSES (ANY ONE TO BE OPTED) Gene therapy &Genetic Counseling BLSS305 3 Intellectual Property & Bioentrepreneurship BLSS306 DISCIPLINE OPEN ELECTIVES (ANY ONE TO BE OPTED) Biology for Criminal investigation BLSE307 3 Nutrigenomics BLSE308 Ethanomedico Botany BLSE309 Entrepreneurial Zoology BLSE309 PRACTICAL COURSE Plant & animal cell technology BLSP310 4
- 11. FOURTH SEMESTER COURSE CODE HOURS/WEEK HARD CORE COURSES Fermentation & Bioprocess Technology BLSH401 4 SOFT CORE COURSES (ANY ONE TO BE OPTED) Cancer Biology BLSS402 3 Behavioral Science & Life Style disorders BLSS403 PRACTICAL COURSE Bioprocess Technology BLSP404 4 Project work/Internship with Report BLSD405
- 12. Collaborations have been planned with the following Companies/laboratories ŌĆó Dendrite Laboratories Pvt. Ltd. ŌĆó Learn Science ŌĆō A Life Science Navigators Academy ŌĆó Apotex Research Pvt. Ltd. ŌĆó Azyme Biosciences. ŌĆó PeopleŌĆÖs Corp and BBMP Forest Department, Bengaluru.
- 13. FACULTY PROFILE
- 14. NAME QUALIFICATION TEACHING EXP RESEARCH EXP SPECIALISATION Dr. Priyadarshini Pillai M. Sc., MBA (TQM), M. Phil., Ph.D., NET 09 09 Plant Biotechnology, Protein modelling Mr. Shanmugam V M M. Sc., M.Phil., NET, Ph. D (ongoing) 18 Neuromicrobiology, Phytochemistry Mrs. Mary Arpana Dr. Sophia D. M. Sc., M. Phil., Ph.D 10 08 Clinical Biochemistry, Food Sciences, Nanotechnology Dr. Vinutha Bhatta M. Sc., B. Ed., Ph. D 09 Apiculture Dr. Reema Orison Lobo M. Sc., Ph. D., NET, KSET 08 07 Cardiovascular Pharmacology, Toxicology, Cytogenetics, Tissue culture Dr. Sowmya K. M. Sc., Ph. D., NET, KSET 06 05 Entomology, Integrated Pest Management Dr. Mohana B. M. Sc., B. Ed., Ph. D, KSET 3.5 07 Microbiology, Endophytic fungi, Tissue culture
- 15. Activities Conducted ’üĄ Guest Lecturer on Emphasizing the Importance of Innovation within Research Methodology - 9th November,2023
- 16. Industrial Visit
- 18. OUR COLLABORATION ŌĆō TO ACHIEVE EXCELLENCE Dendrite Laboratories Pvt. Ltd. Department of Biological Sciences Centre for Excellence
- 19. THANKYOU









